Comparative Effects of Clump-Based and Traditional Selective Harvesting on Understory Biodiversity in Sympodial Bamboo Forests
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Experimental Design
2.2. Understory Vegetation Survey and Soil Sample Collection
2.3. Determination of Soil Chemical Properties
2.4. Data Calculation
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Species Composition and Importance Value of Understory Vegetation Under Different Harvesting Intensities
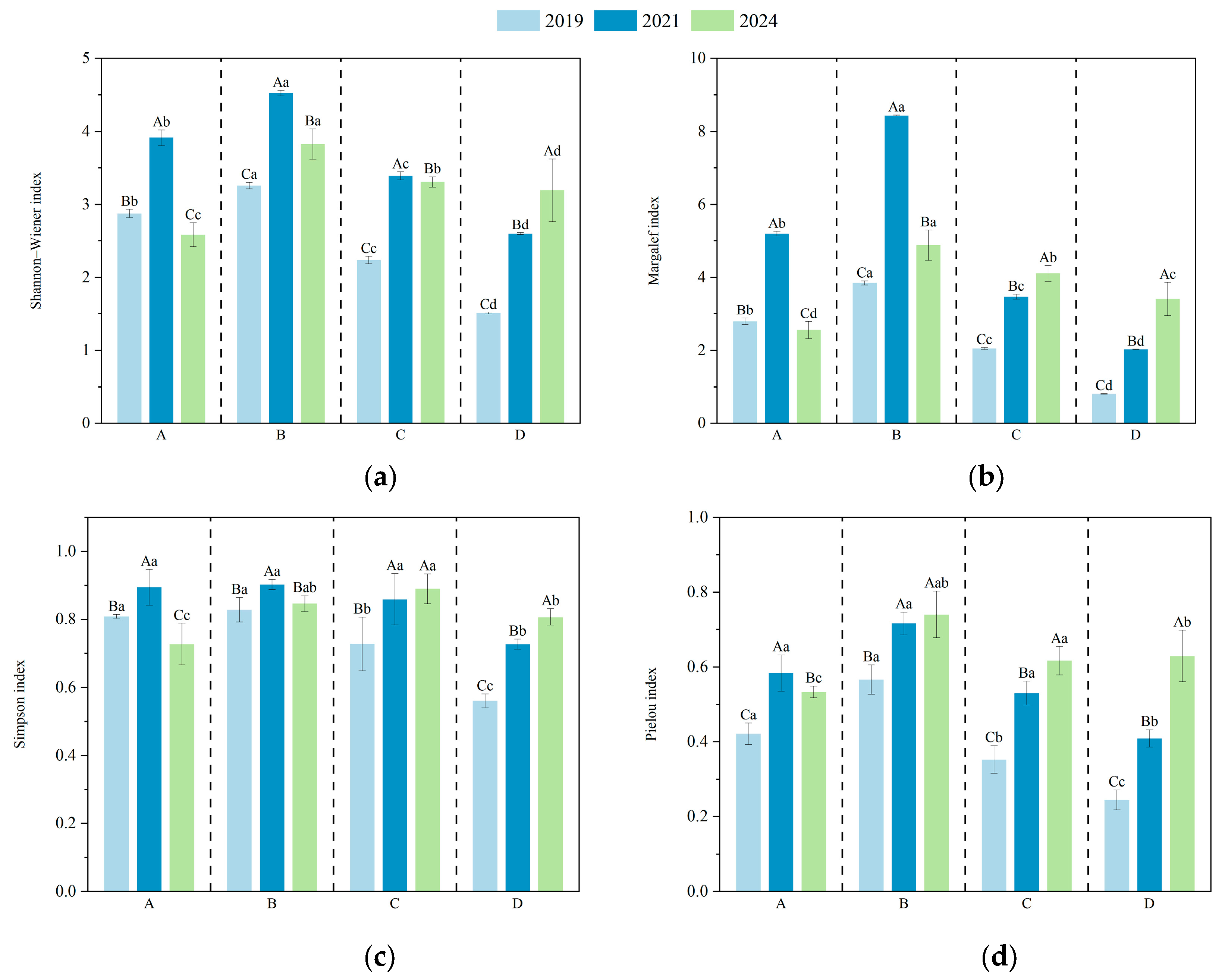
3.2. Changes in Understory Plant Diversity Indices Under Different Harvesting Intensities
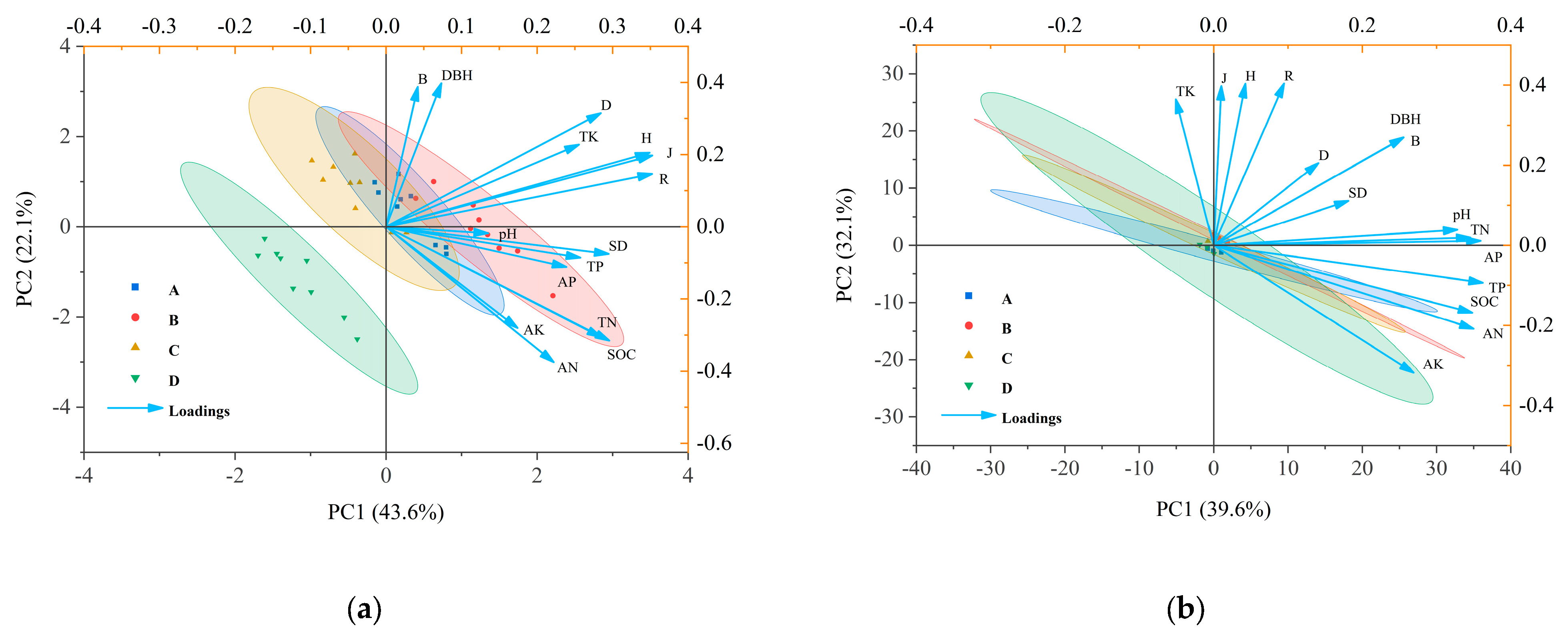
3.3. Principal Component Analysis of Diversity Indices, Stand Structure, and Soil Chemical Properties
3.4. Effects of Harvesting Intensity and Recovery Time on Understory Plant Diversity
3.5. Evaluation of Diversity Indices, Stand Characteristics, and Soil Chemical Properties Based on Fuzzy Membership Function Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Different Clump Harvesting Patterns on the Understory Plant Community Structure of D. giganteus Forests
4.2. Effects of Different Clump Harvesting Patterns on Understory Plant Diversity in D. giganteus Forests
4.3. Relationships Between Soil Chemical Properties, Stand Structure, and Species Diversity
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- de Avila, A.L.; van der Sande, M.T.; Dormann, C.F.; Peña-Claros, M.; Poorter, L.; Mazzei, L.; Ruschel, A.R.; Silva, J.N.M.; de Carvalho, J.O.P.; Bauhus, J. Disturbance Intensity Is a Stronger Driver of Biomass Recovery than Remaining Tree-Community Attributes in a Managed Amazonian Forest. J. Appl. Ecol. 2018, 55, 1647–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.L.; Zhou, X.G.; Wen, Y.G.; Zhou, X.M.; Chen, J.L.; Xu, J.M.; Yang, T.; Chen, Q.H.; Sun, D.J.; Huang, Y.J.; et al. Effects of Cutting Intensity on Understory Plant Diversity in the Mixed Eucalyptus urophylla × E. grandis and Castanopsis hystrix Plantations under Eco-silviculture Regime. Guangxi Sci. 2025, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Q.M.; Geng, Y.; von Gadow, K.; Fan, C.Y.; Zhang, C.Y.; Zhao, X.H. Effects of Neighborhood Interaction on Tree Growth in a Temperate Forest Following Selection Harvesting. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 136, 108663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.X.; Liu, S.; Feng, W.B.; Zhao, S.B.; Wang, S.J.; Sun, Y.; Li, E.P.; Cheng, F.S. Effects of Thinning Intensity on Canopy Structure and Herbaceous Species Diversity of Larix olgensis Plantation. J. Northeast For. Univ. 2022, 50, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.M.; Deng, Z.W.; Li, B.J.; Li, S.K.; Wen, W.Q.; Rong, J.D.; Zheng, Y.S.; Chen, L.G. Effects of Strip-Cutting Width on the Structural Characteristics of Underground Bamboo Rhizome in Moso Bamboo Forests. Sci. Silvae Sin. 2023, 59, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.J.; Guan, F.Y.; Zheng, Y.X.; Zhou, X. Effects of Proportioned Fertilization on Understory Vegetation Diversity in Strip-Harvested Phyllostachys edulis Forests. Chin. J. Ecol. 2023, 42, 796–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.X.; Fan, S.H.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, X.; Guan, F.Y. Productivity Dynamics of Moso Bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis) Forest after Strip Clearcutting. Sci. Silvae Sin. 2023, 59, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.X.; Fan, S.H.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, X.; Guan, F.Y. Dynamic Characteristics of Nutrients in Strip-Cutting Moso Bamboo Forests. J. Beijing For. Univ. 2023, 45, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Guan, F.Y.; Wang, S.M. Dynamics of Understory Plant Diversity and Its Relationship with Growth of New Bamboo in Strip-Cutting Bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis) Forest. J. Northeast For. Univ. 2022, 50, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.Y.; Cai, C.J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.J.; Fan, S.H. Regeneration and Restoration Characteristics of Strip-Clear Cutting of Bambusa rigida. J. For. Environ. 2023, 43, 614–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, S.M.; Zheng, Y.X.; Guan, F.Y. Effects of Strip Cutting on Spatial Structure and Stability of New Bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis). J. Nanjing For. Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2023, 47, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.X.; Liu, W.; Wang, J.F.; You, G.B.; Ye, H.J.; Lian, F.L.; He, X.Y. Early Effects of Forest Harvesting Gap on Understory Plant Diversity of Three Different Plantations in Baiyun Mountain, China. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2018, 29, 2121–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, D.D.; Hui, C.M.; Liu, W.Y.; Zhu, L.Y. Biodiversity Recovery of Dendrocalamus giganteus Undergrowth After Clump Logging. J. Southwest For. Univ. 2022, 42, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, D.D.; Hui, C.M.; Liu, W.Y.; Zhu, L.Y.; Zhang, W.J. Impacts of Clump Logging on Growth Dynamics and Economic Benefits of Bamboo (Dendrocalamus giganteus) Forest. J. Bamboo Res. 2021, 40, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.Y. Effects of Fertilization on the Recovery and Growth of Bambusa rigida After Cluster Cutting. Ph.D. Thesis, Chinese Academy of Forestry, Beijing, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, H.; Tu, D.D.; Liu, W.Y.; Hui, C.M.; Wang, Y. Microclimate Characteristics of Dendrocalamus giganteus Stand after Cluster Cutting and Restoration. J. West China For. Sci. 2022, 51, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, F.Q.; Ren, J.J.; Zhang, Y.M. Effect of Slope Aspect and Terrain of Sand Dune on Herbaceous Diversity in Gurbantunggut Desert. Chin. J. Ecol. 2018, 37, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isbell, F.; Calcagno, V.; Hector, A.; Connolly, J.; Harpole, W.S.; Reich, P.B.; Scherer-Lorenzen, M.; Schmid, B.; Tilman, D.; van Ruijven, J.; et al. High Plant Diversity Is Needed to Maintain Ecosystem Services. Nature 2011, 477, 199–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaraja, B.C.; Somashekar, R.K.; Raj, M.B. Tree Species Diversity and Composition in Logged and Unlogged Rainforest of Kudremukh National Park, South India. J. Environ. Biol. 2005, 26, 627–637. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, J.Y.; Qi, J.Q.; Zhang, L.H.; Wang, M.Z.; Li, T.T.; Zhang, X.Y.; Hao, J.F. Effects of Anthropogenic Disturbance on Species Diversity and Soil Physicochemical Properties of Symplocos sumuntia Secondary Forest in Bifengxia. Chin. J. Ecol. 2018, 37, 2942–2950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Döbert, T.F.; Webber, B.L.; Sugau, J.B.; Dickinson, K.J.M.; Didham, R.K. Logging Increases the Functional and Phylogenetic Dispersion of Understorey Plant Communities in Tropical Lowland Rain Forest. J. Ecol. 2017, 105, 1235–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Y.; Yue, Q.M.; Zhang, C.Y.; Zhao, X.H. Dynamics and Drivers of Aboveground Biomass Accumulation during Recovery from Selective Harvesting in an Uneven-Aged Forest. Eur. J. For. Res. 2021, 140, 1163–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, M.C.; Guan, F.Y.; Yan, Y.J.; Zhang, M.M.; Zheng, Y.X. Effects of Strip Harvesting on Species Diversity of Undergrowth in Bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis) Forest. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2020, 40, 4169–4179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.Y.; Hao, J.F.; Zhao, F.; Chen, H.Q.; Bai, Y.S.; Tang, L. Species Diversity and Soil Physicochemical Properties of Different Shrub Communities at Sanxingdui City Wall. J. Cent. South Univ. For. Technol. 2025, 47, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hume, A.M.; Chen, H.Y.H.; Taylor, A.R. Intensive Forest Harvesting Increases Susceptibility of Northern Forest Soils to Carbon, Nitrogen and Phosphorus Loss. J. Appl. Ecol. 2018, 55, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, M.È.; Surget-Groba, Y.; Rivest, D. Long-Term Effects of Different Harvesting Intensities on Soil Microbial Communities in a Hardwood Temperate Forest. For. Ecol. Manag. 2024, 559, 121810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.J.; Lin, D.M.; Mi, X.C.; Ren, H.B.; Ma, K.P. Recovery Dynamics of Secondary Forests with Different Disturbance Intensity in the Gutianshan National Nature Reserve. Biodivers. Sci. 2014, 22, 358–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azadeh, A.; Ghavami, K.; García, J.J. The Influence of Heat on Mechanical Properties of Dendrocalamus giganteus Bamboo. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 43, 102613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, J.Q.; Silva, F.A.; Ghavami, K.; Gomes, O.F.M.; Toledo Filho, R.D. On the Influence of Dendrocalamus giganteus Bamboo Microstructure on Its Mechanical Behavior. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 127, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.X.; Li, D.Z.; Xue, J.R. Flora of Yunnan: Volume 9; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.; Wistara, N.; Febrianto, F.; Lee, M. Evaluation of Sembilang Bamboo (Dendrocalamus giganteus) Charcoal for Potential Utilization. BioResources 2020, 15, 6–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- State Forestry Administration. Forest Soil Analysis Methods; China Standard Press: Beijing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.F.; Chen, Y.N.; Chen, Y.P.; Li, W.H. Species Quantity Change and Ecosystem Dynamics in the Lower Reaches of Tarim River. Chin. J. Ecol. 2004, 4, 21–24. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.Q.; Niu, S.K.; Liu, Y.H. Forest Ecology, 3rd ed.; Higher Education Press: Beijing, China, 2017; pp. 352–358. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.R.; Luo, W.X.; Shu, Q.T.; Luo, H.B.; Lai, H.Y.; Shan, D.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, H.Y. Analysis of Moisture Content and Construction of Aboveground Biomass Regression Model for Dendrocalamus giganteus Plantation. J. Southwest For. Univ. 2021, 41, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Q.; Li, Z.C.; Hou, L.Y.; Song, L.G.; Yang, H.G.; Sun, Q.W. Effects of Stand Density on Understory Species Diversity and Soil Nutrients in Chinese Fir Plantation. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2020, 57, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, Q.; Xu, L.; Li, M.; Chen, Z.; Song, Z.; Hou, J.; He, N. Plant Community Traits Can Explain Variation in Productivity of Selective Logging Forests after Different Restoration Times. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 131, 108181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.J.; He, T.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, H.L.; Li, B.W. Effects of Thinning Intensity on Understory Plant of Natural Forest in Altai Mountains, Xinjiang, China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2022, 42, 9761–9768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.N.; Zhang, Y.C.; Du, Y.J.; Ren, H.B. Influences of Disturbances on Successional Dynamics of Species Diversity in Mid-Subtropical Forests. Biodivers. Sci. 2025, 33, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.Z.; Yin, H.F.; Shen, Y.; Kang, W.S.; Luo, Y.; Fan, C.; Li, X.W. Effects of Thinning Intensity on Species Composition and Diversity of Undergrowth Vegetation Community in Pinus massoniana Plantation at Initial Stage of Thinning. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2020, 31, 2866–2874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Chen, B.L.; Lan, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, J.Q.; Zhang, J.F. Changes in Species Diversity and Biomass of Plant Communities in Panzhihua Tailings Pond with Recovery Years. Chin. J. Appl. Environ. Biol. 2025, 31, 797–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Gong, C.W. Effects of Terrain Factors on Vegetation Cover Change in National Park of Qilian Mountains. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2021, 41, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.S.; Wen, Z.M.; Miao, L.P.; Qi, D.H.; Hua, D.W. Responses of Plant Functional Traits to Micro-Topographical Changes in Hilly and Gully Region of the Loess Plateau, China. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2014, 25, 3413–3419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baraloto, C.; Hérault, B.; Paine, C.E.T.; Massot, H.; Blanc, L.; Bonal, D.; Molino, J.-F.; Nicolini, E.A.; Sabatier, D. Contrasting Taxonomic and Functional Responses of a Tropical Tree Community to Selective Logging. J. Appl. Ecol. 2012, 49, 861–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adekunle, V.A.J.; Olagoke, A.O.; Ogundare, L.F. Logging Impacts in Tropical Lowland Humid Forest on Tree Species Diversity and Environmental Conservation. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2013, 11, 491–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connell, J.H. Diversity in Tropical Rain Forests and Coral Reefs: High Diversity of Trees and Corals Is Maintained Only in a Nonequilibrium State. Science 1978, 199, 1302–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.H.; Song, Y.T.; Wu, Y.N.; Huo, G.W.; Zhang, F.J.; Wang, X.G.; Di, Z.L. Effects of Grazing Intensity on Plant Functional Groups of Stipa krylovii Steppe. Pratacult. Sci. 2017, 34, 2033–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Fu, T.; Gao, H.; Li, M.; Liu, J. Climatic and Non-Climatic Drivers of Plant Diversity along an Altitudinal Gradient in the Taihang Mountains of Northern China. Diversity 2023, 15, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.Y.; Li, C.Y.; Wang, X.Q.; Xu, X. Effects of Thinning on the Growth and the Diversity of Undergrowth of Pinus tabulaeformis Plantation in Beijing Mountainous Areas. Sci. Silvae Sin. 2007, 43, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, L.F.; Zhou, X.N. Dynamic Effects of Selective Cutting Intensity on the Species Composition and Diversity of Natural Forest. J. Mount. Sci. 2008, 26, 699–706. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, J.M.; Sun, Y.K.; Feng, J.; Lin, X.P. Influence of Thinning on the Growth and the Diversity of Undergrowth of Larix kaempferi Plantation Forest. J. Cent. South Univ. For. Technol. 2018, 38, 90–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.X.; Ma, H.J.; Min, J.G.; Hao, J.P.; Guan, Q.W. Short-Term and Long-Term Effects of Thinning on the Undergrowth Diversity in the Pinus massoniana Plantation. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2012, 21, 807–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britton, A.J.; Beale, C.M.; Towers, W.; Hewison, R.L. Biodiversity Gains and Losses: Evidence for Homogenisation of Scottish Alpine Vegetation. Biol. Conserv. 2009, 142, 1728–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoorn, C.; Wesselingh, F.P.; ter Steege, H.; Bermudez, M.A.; Mora, A.; Sevink, J.; Sanmartín, I.; Sanchez-Meseguer, A.; Anderson, C.L.; Figueiredo, J.P.; et al. Amazonia Through Time: Andean Uplift, Climate Change, Landscape Evolution, and Biodiversity. Science 2010, 330, 927–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.T.; Xiao, L.; Wang, W.J. Effects of Species Diversity and Spatial Structure on Biomass and Soil Nutrients in Larix gmelinii, Daxing’anling Mts., NE China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2025, 45, 4276–4283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spohn, M.; Bagchi, S.; Biederman, L.A.; Borer, E.T.; Bråthen, K.A.; Bugalho, M.N.; Caldeira, M.C.; Catford, J.A.; Collins, S.L.; Eisenhauer, N.; et al. The Positive Effect of Plant Diversity on Soil Carbon Depends on Climate. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 6624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.Y.; Zhang, W.Q.; Zhao, L.Q.; Chi, M.F.; Luo, G.S.; Zheng, X.M.; Jia, Z.K.; Wang, Q.C. Variation of Understory Plant Diversity and Its Relationship with Soil Moisture in Pinus tabulaeformis Plantation before and after Clearcutting. J. Cent. South Univ. For. Technol. 2020, 40, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, W.W.; Lu, L.H.; Li, H.; Nong, Y.; He, R.M.; Chen, H.; Huang, B. Effects of Stand Density on Understory Vegetation and Soil Properties of Cunninghamia lanceolata Plantation. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2021, 41, 4521–4530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrew, S.M.; Totland, Ø.; Moe, S.R. Spatial Variation in Plant Species Richness and Diversity along Human Disturbance and Environmental Gradients in a Tropical Wetland. Wetl. Ecol. Manag. 2015, 23, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.X.; Chen, L.; Pang, D.B.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Li, B.; Chen, Y.L.; Li, X.B. Effects of Shrub Encroachment on Grassland Vegetation Communities in Desert Grasslands of Eastern Ningxia. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2025, 45, 5568–5581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhao, X.Z.; Ding, B.; Ding, G.J.; Wang, H.Y. Seasonal Dynamic Response of Soil Characteristic of Pinus massoniana Plantation to Different Thinning Treatments. J. Northeast For. Univ. 2023, 51, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.T.; Qian, Z.J.; Cao, S.X.; Wang, X.Y.; Luo, Z.; Peng, Z.D.; Wang, Y.X.; Chen, Y.; Lin, M.N.; Deng, C.Y. Species Diversity and Functional Diversity of Acacia confusa Plantation Forest Community and Its Influencing Factors on the Islands in Eastern Fujian. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2025, 45, 5527–5540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

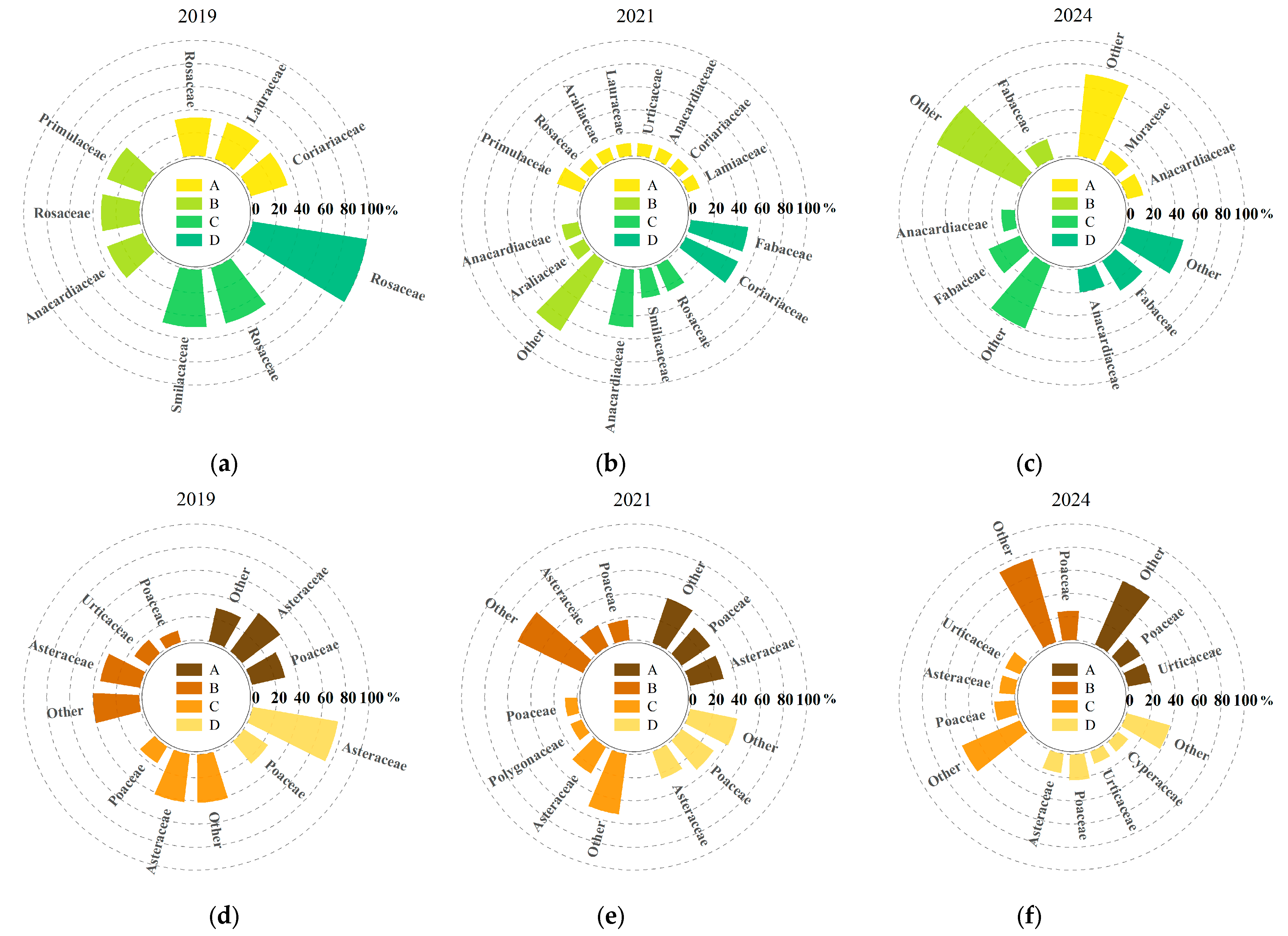
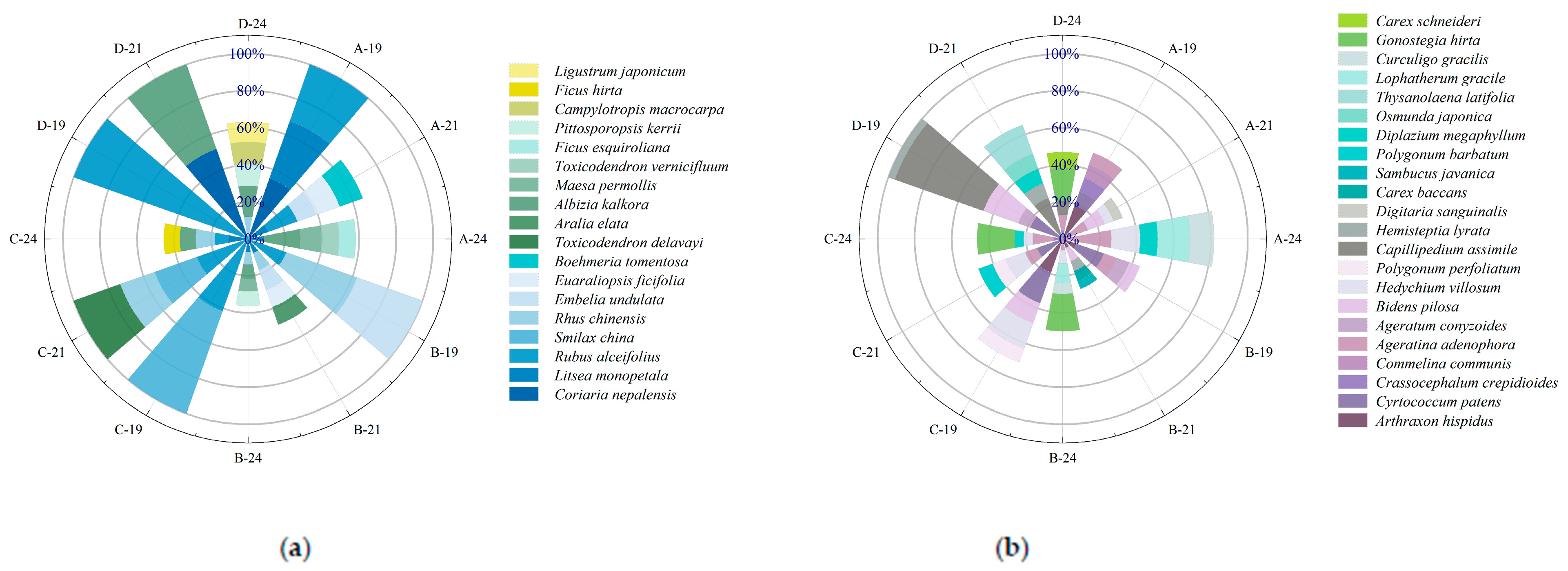
| Treatment | 2018 Before Harvesting | 2018 After Harvesting | 2021 | 2024 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Density (Stems·ha−1) | Mean DBH (cm) | Density (Stems·ha−1) | Mean DBH (cm) | Density (Stems·ha−1) | Mean DBH (cm) | Density (Stems·ha−1) | Mean DBH (cm) | |
| A (Selective cutting) | 2970 | 12.87 | 1782 | 11.92 | 3371 | 12.8 | 3584 | 10.27 |
| B (1/2 clump cutting) | 2939 | 11.80 | 1959 | 10.81 | 3760 | 12.62 | 4025 | 11.36 |
| C (1/3 clump cutting) | 3024 | 12.19 | 1512 | 10.96 | 1766 | 8.49 | 2158 | 10.19 |
| D (Whole clump cutting) | 2904 | 11.46 | - | - | 2279 | 5.93 | 2434 | 8.76 |
| Age Class | Regression Model Ba = a·DBHb | Applicable Age Range |
|---|---|---|
| Class I | Ba = 0.089·DBH2.378 | ≤1 year |
| Class II | Ba = 0.1751·DBH2.4262 | 1–3 years |
| Class III | Ba = 0.2305·DBH2.3255 | >3 years |
| All ages | Ba = 0.1889·DBH2.405 | All age classes |
| Indicator | Recovery Time | Logging Intensity | Logging Intensity × Recovery Time | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| df | F | p | df | F | p | df | F | p | |
| Simpson index | 2.00 | 58.95 | 0.00 | 3.00 | 38.42 | 0.00 | 6.00 | 12.11 | 0.00 |
| Margalef index | 2.00 | 3303.21 | 0.00 | 3.00 | 2376.45 | 0.00 | 6.00 | 591.52 | 0.00 |
| Shannon–Wiener index | 2.00 | 1198.38 | 0.00 | 3.00 | 576.00 | 0.00 | 6.00 | 91.93 | 0.00 |
| Pielou index | 2.00 | 279.32 | 0.00 | 3.00 | 137.50 | 0.00 | 6.00 | 13.56 | 0.00 |
| Treatment | 2019 | 2024 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | D | A | B | C | D | |
| pH | 0.81 | 1.00 | 0.43 | 0.00 | 0.72 | 1.00 | 0.93 | 0.00 |
| SOC | 1.00 | 0.94 | 0.89 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 0.68 | 0.11 | 0.00 |
| AN | 0.62 | 1.00 | 0.43 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 0.60 | 0.58 | 0.00 |
| AP | 0.00 | 0.70 | 1.00 | 0.37 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 0.60 | 0.16 |
| AK | 0.55 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 0.33 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.13 | 0.40 |
| TN | 0.60 | 1.00 | 0.65 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 0.38 | 0.17 |
| TP | 0.60 | 0.81 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 0.85 | 0.90 | 0.00 |
| TK | 0.87 | 1.00 | 0.69 | 0.00 | 0.39 | 0.94 | 1.00 | 0.00 |
| Shannon–Wiener index | 0.78 | 1.00 | 0.42 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 0.58 | 0.49 |
| Simpson index | 0.92 | 1.00 | 0.63 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.73 | 1.00 | 0.49 |
| Pielou index | 0.55 | 1.00 | 0.34 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 0.41 | 0.47 |
| Margalef index | 0.65 | 1.00 | 0.41 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 0.67 | 0.37 |
| Stand density | 0.55 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.30 | 0.76 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.15 |
| Diameter at breast height | 0.61 | 0.40 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.58 | 1.00 | 0.55 | 0.00 |
| Biomass of individual plant | 0.54 | 0.32 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.57 | 1.00 | 0.52 | 0.00 |
| Average | 0.64 | 0.81 | 0.66 | 0.07 | 0.47 | 0.86 | 0.56 | 0.19 |
| Rank | 3 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Z.; Li, H.; Bao, H.; Guan, F.; Hui, C.; Liu, W. Comparative Effects of Clump-Based and Traditional Selective Harvesting on Understory Biodiversity in Sympodial Bamboo Forests. Plants 2025, 14, 2578. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14162578
Zhang Y, Zhang C, Wang Z, Li H, Bao H, Guan F, Hui C, Liu W. Comparative Effects of Clump-Based and Traditional Selective Harvesting on Understory Biodiversity in Sympodial Bamboo Forests. Plants. 2025; 14(16):2578. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14162578
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Ying, Chaohang Zhang, Zuming Wang, Haoting Li, Haofeng Bao, Fengying Guan, Chaomao Hui, and Weiyi Liu. 2025. "Comparative Effects of Clump-Based and Traditional Selective Harvesting on Understory Biodiversity in Sympodial Bamboo Forests" Plants 14, no. 16: 2578. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14162578
APA StyleZhang, Y., Zhang, C., Wang, Z., Li, H., Bao, H., Guan, F., Hui, C., & Liu, W. (2025). Comparative Effects of Clump-Based and Traditional Selective Harvesting on Understory Biodiversity in Sympodial Bamboo Forests. Plants, 14(16), 2578. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14162578






