OsMAPKKK69 Negatively Regulates Resistance to Blast and Bacterial Blight Diseases in Rice (Oryza sativa L.)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
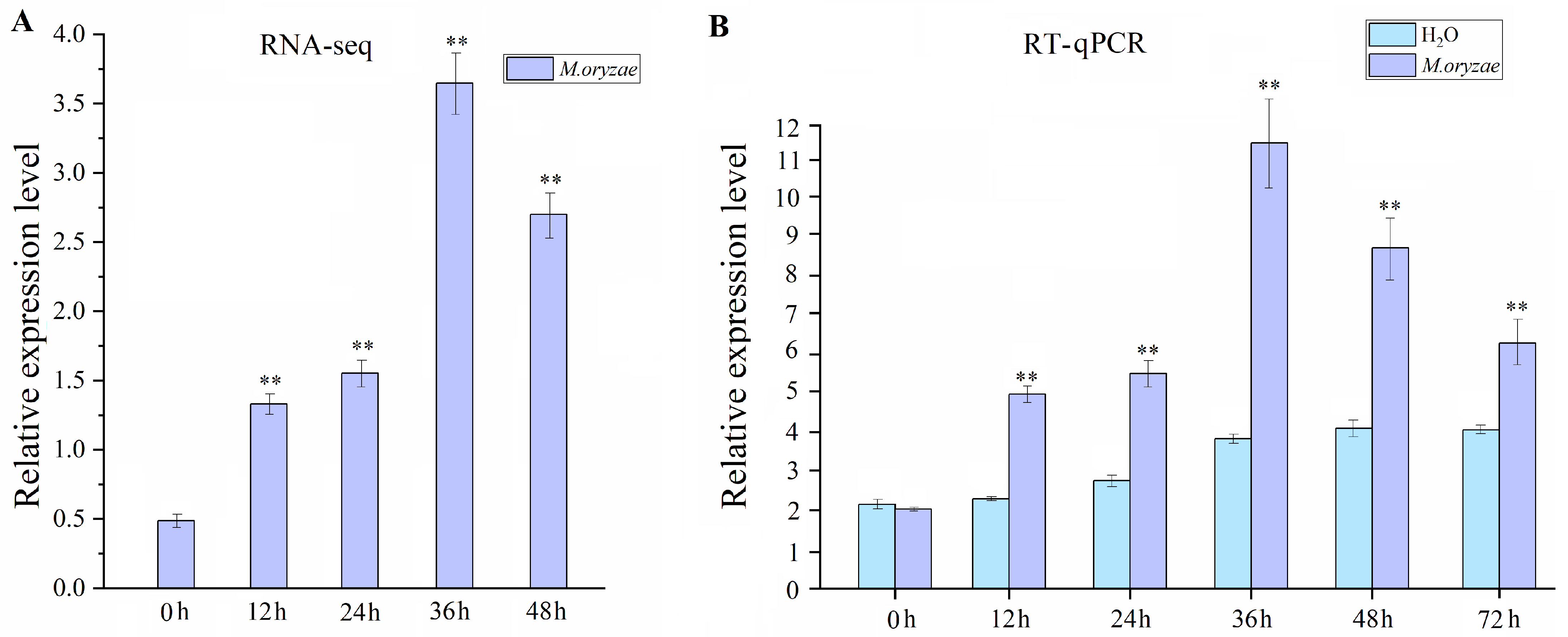
2.1. Transcript Accumulation of OsMAPKKK69 in Response to M. oryzae Infection
2.2. Genetic Characterization of the Osmapkkk69 Mutants
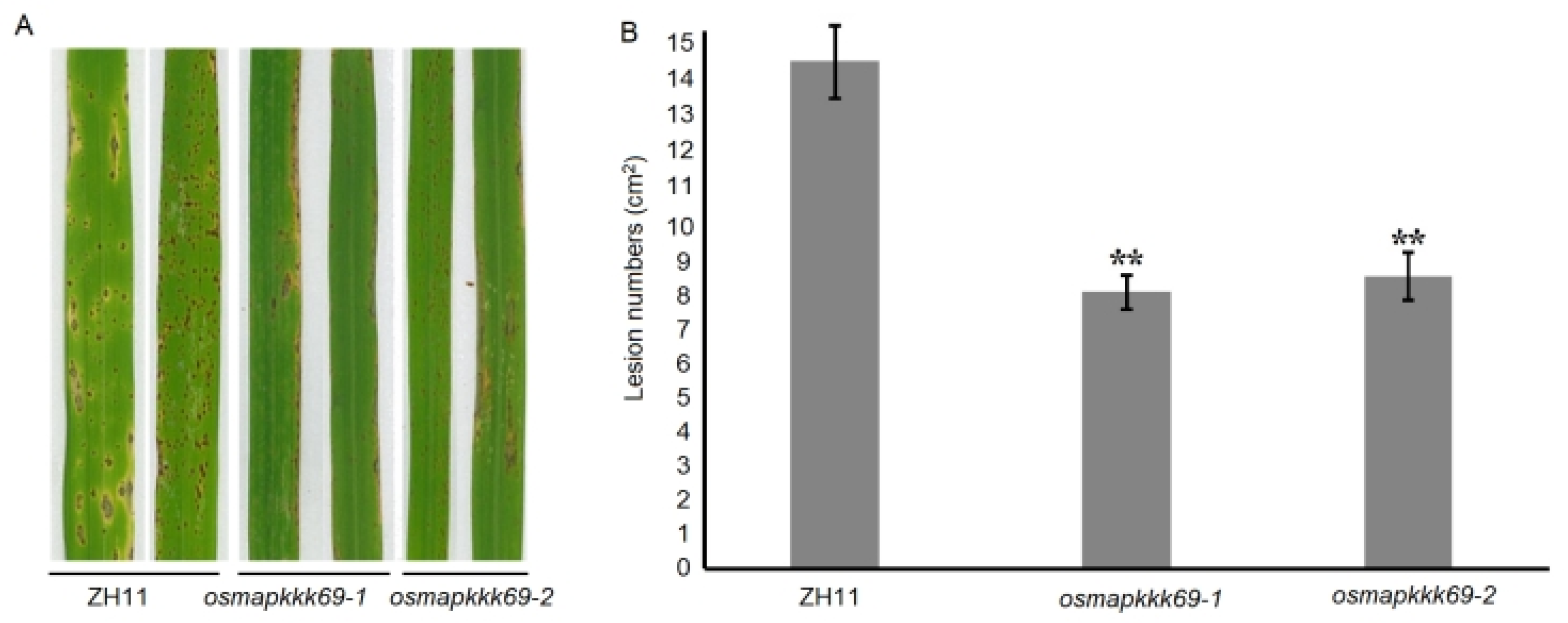
2.3. Osmapkkk69 Mutants Are More Resistant to Blast Disease
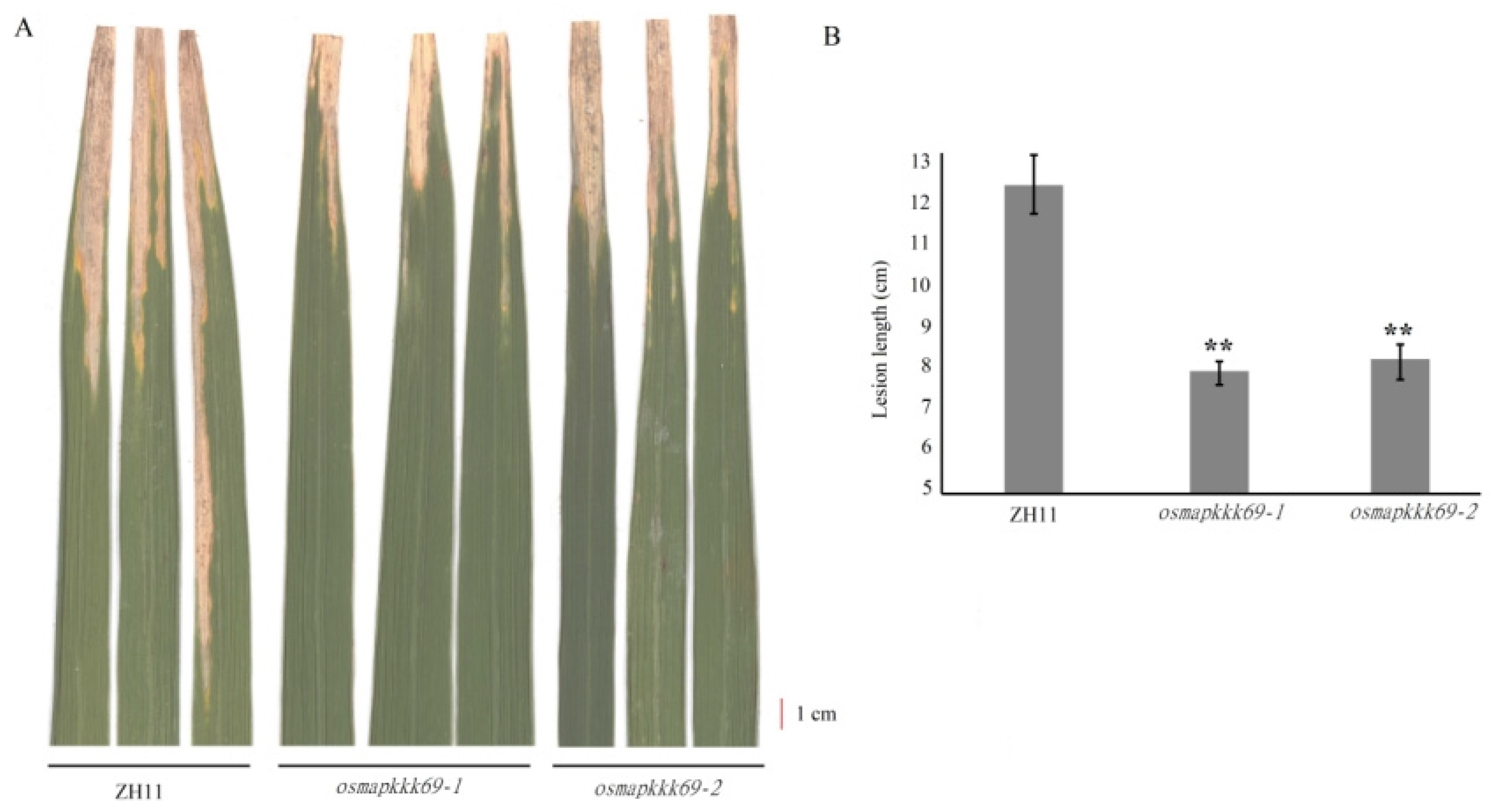
2.4. Osmapkkk69 Mutants Are Also More Resistant to Bacterial Blight
2.5. Analysis of Agronomical Traits of the Osmapkkk69 Mutants and Wild Type ZH11
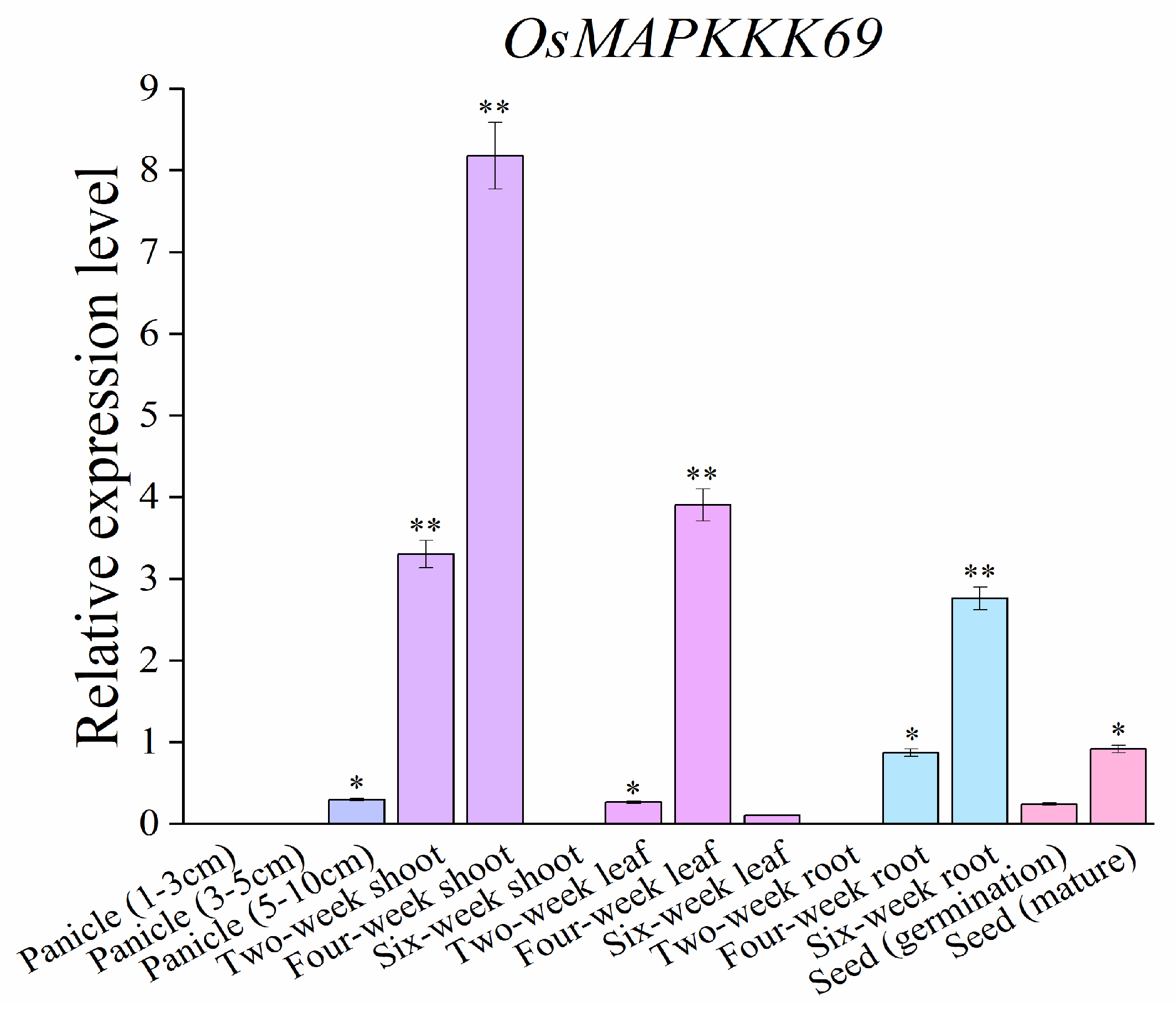
2.6. Temporal and Spatial Transcript Accumulations of OsMAPKKK69
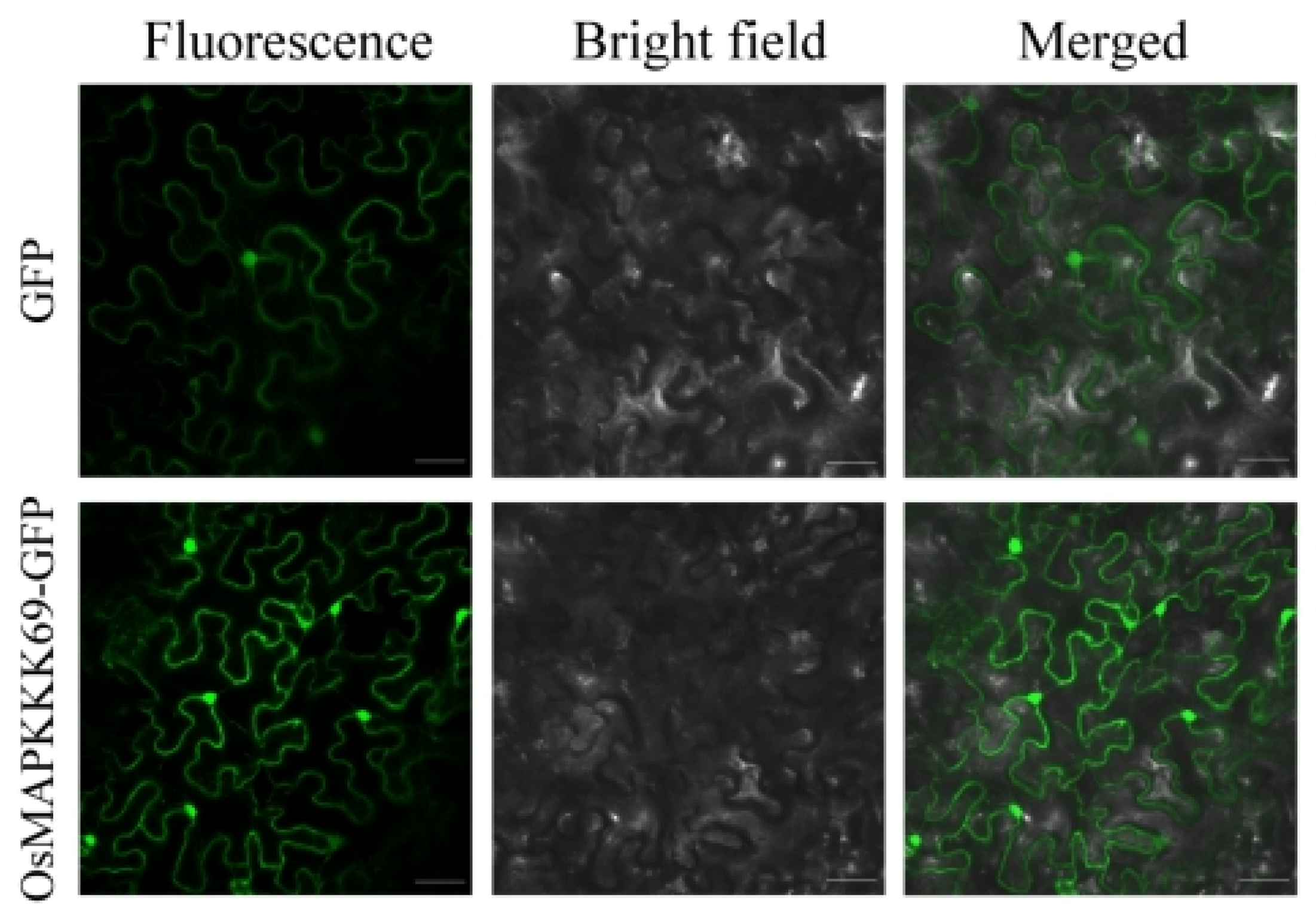
2.7. Subcellular Localization of OsMAPKKK69
2.8. Amino Acid Sequence Analysis of OsMAPKKK69 in Different Rice Varieties
3. Discussion
3.1. OsMAPKKK69 Negatively Regulates the Disease Resistance of Rice
3.2. OsMAPKKK69 Simultaneously Negatively Regulates Agronomic Traits Related to the Growth and Development of Rice
3.3. Application of OsMAPKKK69 in Rice Breeding
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials
4.2. Evaluation of Resistance Between Rice Blast Fungus and Bacterial Blight
4.3. RT-qPCR Analyses
4.4. Subcellular Localization of OsMAPKKK69
4.5. Bioinformatics Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, N.; Luo, J.; Rossman, A.Y.; Aoki, T.; Chuma, I.; Crous, P.W.; Dean, R.; de Vries, R.P.; Donofrio, N.; Hyde, K.D.; et al. Generic names in Magnaporthales. IMA Fungus 2016, 7, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.T.; Chern, M.S.; Yin, J.J.; Wang, J.; Chen, X.W. Recent advances in broad-spectrum resistance to the rice blast disease. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2019, 50, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.W.; Zhai, K.R.; Xie, Z.; Yang, D.Y.; Zhu, X.D.; Liu, J.Z.; Wang, X.; Qin, P.; Yang, Y.Z.; Zhang, G.M.; et al. Epigenetic regulation of antagonistic receptors confers rice blast resistance with yield balance. Science 2017, 355, 962–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.C.; Yang, D.W.; Zhong, G.T.; Li, S.P.; Wang, W.; Tang, D.Z. Nucleotide-binding leucine-rich repeat receptor homologs Pib and PibH8 interact and contribute to immunity in rice. Plant Physiol. 2024, 195, 3010–3023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.W.; Li, S.P.; Lu, L.; Fang, J.B.; Wang, W.; Cui, H.T.; Tang, D.Z. Identification and application of the Pigm-1 gene in rice disease-resistance breeding. Plant Biol. 2020, 22, 1022–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Feng, B.M.; Zhou, J.M.; Tang, D.Z. Plant immune signaling: Advancing on two frontiers. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2020, 62, 2–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngou, B.P.M.; Ahn, H.K.; Ding, P.T.; Jones, J.D.G. Mutual potentiation of plant immunity by cell-surface and intracellular receptors. Nature 2021, 592, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, M.Y.; Jiang, Z.Y.; Bi, G.Z.; Nomura, K.; Liu, M.H.; Wang, Y.P.; Cai, B.Y.; Zhou, J.M.; He, S.Y.; Xin, X.F. Pattern-recognition receptors are required for NLR-mediated plant immunity. Nature 2021, 592, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asano, T.; Nguyen, T.H.; Yasuda, M.; Sidiq, Y.; Nishimura, K.; Nakashita, H.; Nishiuchi, T. Arabidopsis MAPKKK δ-1 is required for full immunity against bacterial and fungal infection. J. Exp. Bot. 2020, 71, 2085–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Chen, D.; Ahsan, N.; Jorge, G.L.; Thelen, J.J.; Stacey, G. The Raf-like MAPKKK INTEGRIN-LINKED KINASE 5 regulates purinergic receptor-mediated innate immunity in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2023, 35, 1572–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuoka, D.; Yasufuku, T.; Furuya, T.; Nanmori, T. An abscisic acid inducible Arabidopsis MAPKKK, MAPKKK18 regulates leaf senescence via its kinase activity. Plant Mol. Biol. 2015, 87, 565–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Liu, H.; Yuan, B.; Li, X.; Xu, C.; Wang, S. OsEDR1 negatively regulates rice bacterial resistance via activation of ethylene biosynthesis. Plant Cell Environ. 2011, 34, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizobuchi, R.; Sugimoto, K.; Tsushima, S.; Fukuoka, S.; Tsuiki, C.; Endo, M.; Mikami, M.; Saika, H.; Sato, H. A MAPKKK gene from rice, RBG1res, confers resistance to Burkholderia glumae through negative regulation of ABA. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 3947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Wang, L.; Yang, Z.; Liu, H.; Chu, C.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Li, X.; Xiao, J.; Wang, S.; et al. The rice Raf-like MAPKKK OsILA1 confers broad-spectrum resistance to bacterial blight by suppressing the OsMAPKK4-OsMAPK6 cascade. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2021, 63, 1815–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, G.; Zhang, C.; Zhu, P.; Dai, H.; Yu, N.; He, Z.; Xu, L.; Wang, E. OsCERK1-Mediated Chitin Perception and Immune Signaling Requires Receptor-like Cytoplasmic Kinase 185 to Activate an MAPK Cascade in Rice. Mol. Plant 2017, 10, 619–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, K.; Yamaguchi, K.; Yoshimura, S.; Terauchi, A.; Kawasaki, T. Conservation of Chitin-Induced MAPK Signaling Pathways in Rice and Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Physiol. 2017, 58, 993–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.W.; Li, S.P.; Lu, L.; Zheng, Z.C.; Tang, D.Z.; Cui, H.T. Transcriptome analysis of rice response to blast fungus identified core genes involved in immunity. Plant Cell Environ. 2021, 44, 3103–3121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, K.P.; Richa, T.; Kumar, K.; Raghuram, B.; Sinha, A.K. In silico analysis reveals 75 members of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase gene family in rice. DNA Res. 2010, 17, 139–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuoka, S.; Saka, N.; Koga, H.; Ono, K.; Shimizu, T.; Ebana, K.; Hayashi, N.; Takahashi, A.; Hirochika, H.; Okuno, K.; et al. Loss of function of a proline-containing protein confers durable disease resistance in rice. Science 2009, 325, 998–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Mei, E.; Tian, X.; He, M.; Tang, J.; Xu, M.; Liu, J.; Song, L.; Li, X.; Wang, Z.; et al. OsMKKK70 regulates grain size and leaf angle in rice through the OsMKK4-OsMAPK6-OsWRKY53 signaling pathway. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2021, 63, 2043–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Duan, P.; Yu, H.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, B.; Wang, R.; Li, J.; Zhang, G.; Zhuang, S.; Lyu, J.; et al. Control of Grain Size and Weight by the OsMKKK10-OsMKK4-OsMAPK6 Signaling Pathway in Rice. Mol. Plant 2018, 11, 860–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, R.; Wiesner-Hanks, T.; Wisser, R.; Balint-Kurti, P. Navigating complexity to breed disease-resistant crops. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2018, 19, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, T.; Wei, S.; Fang, K.; Zhang, M.; Li, Y.; Feng, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, S.; Tian, J.; Gao, A.; et al. The atypical Dof transcriptional factor OsDes1 contributes to stay-green, grain yield, and disease resistance in rice. Sci. Adv. 2024, 10, eadp0345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.W.; He, N.Q.; Huang, F.H. Pyramiding Pigm-1 and Xa23 genes by marker-assisted selection in rice (Oryza sativa L.). J. Northwest A F Univ.-Nat. Sci. Ed. 2023, 51, 37–45. [Google Scholar]


| Traits | ZH11 | Osmapkkk69-1 | Osmapkkk69-2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Plant height (cm) | 119.75 ± 2.82 | 78.25 ± 2.73 ** | 79.27 ± 2.67 ** |
| Panicle length (cm) | 23.42 ± 0.80 | 20.41 ± 0.52 * | 20.83 ± 0.62 * |
| Number of effective panicles | 9.75 ± 0.63 | 14.01 ± 1.08 ** | 14.34 ± 1.10 ** |
| Spikelets per panicle | 166.15 ± 5.12 | 148.32 ± 4.15 * | 146.24 ± 4.22 * |
| Seed-setting rate (%) | 86.39 ± 1.84 | 85.62 ± 4.19 | 86.12 ± 3.68 |
| 1000-grain weight (g) | 27.27 ± 1.38 | 25.15 ± 1.80 * | 24.59 ± 1.45 * |
| Grain length (mm) | 7.44 ± 0.04 | 7.41 ± 0.08 | 7.43 ± 0.06 |
| Grain width (mm) | 3.34 ± 0.06 | 3.16 ± 0.08 * | 3.15 ± 0.07 * |
| Average yield per plant (g) | 38.16 ± 0.92 | 44.94 ± 1.13 * | 44.62 ± 1.10 ** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, D.; Jin, Y.; He, N.; Lin, S.; Cheng, Z.; Huang, F.; Zhang, H.; Li, Q.Q.; Yu, W. OsMAPKKK69 Negatively Regulates Resistance to Blast and Bacterial Blight Diseases in Rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plants 2025, 14, 2566. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14162566
Yang D, Jin Y, He N, Lin S, Cheng Z, Huang F, Zhang H, Li QQ, Yu W. OsMAPKKK69 Negatively Regulates Resistance to Blast and Bacterial Blight Diseases in Rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plants. 2025; 14(16):2566. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14162566
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Dewei, Yidan Jin, Niqing He, Shaojun Lin, Zhaoping Cheng, Fenghuang Huang, Haifeng Zhang, Qingshun Q. Li, and Wenquan Yu. 2025. "OsMAPKKK69 Negatively Regulates Resistance to Blast and Bacterial Blight Diseases in Rice (Oryza sativa L.)" Plants 14, no. 16: 2566. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14162566
APA StyleYang, D., Jin, Y., He, N., Lin, S., Cheng, Z., Huang, F., Zhang, H., Li, Q. Q., & Yu, W. (2025). OsMAPKKK69 Negatively Regulates Resistance to Blast and Bacterial Blight Diseases in Rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plants, 14(16), 2566. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14162566







