Characterization of the Mitochondrial Genome of Hippophae rhamnoides subsp. sinensis Rousi Based on High-Throughput Sequencing and Elucidation of Its Evolutionary Mechanisms
Abstract
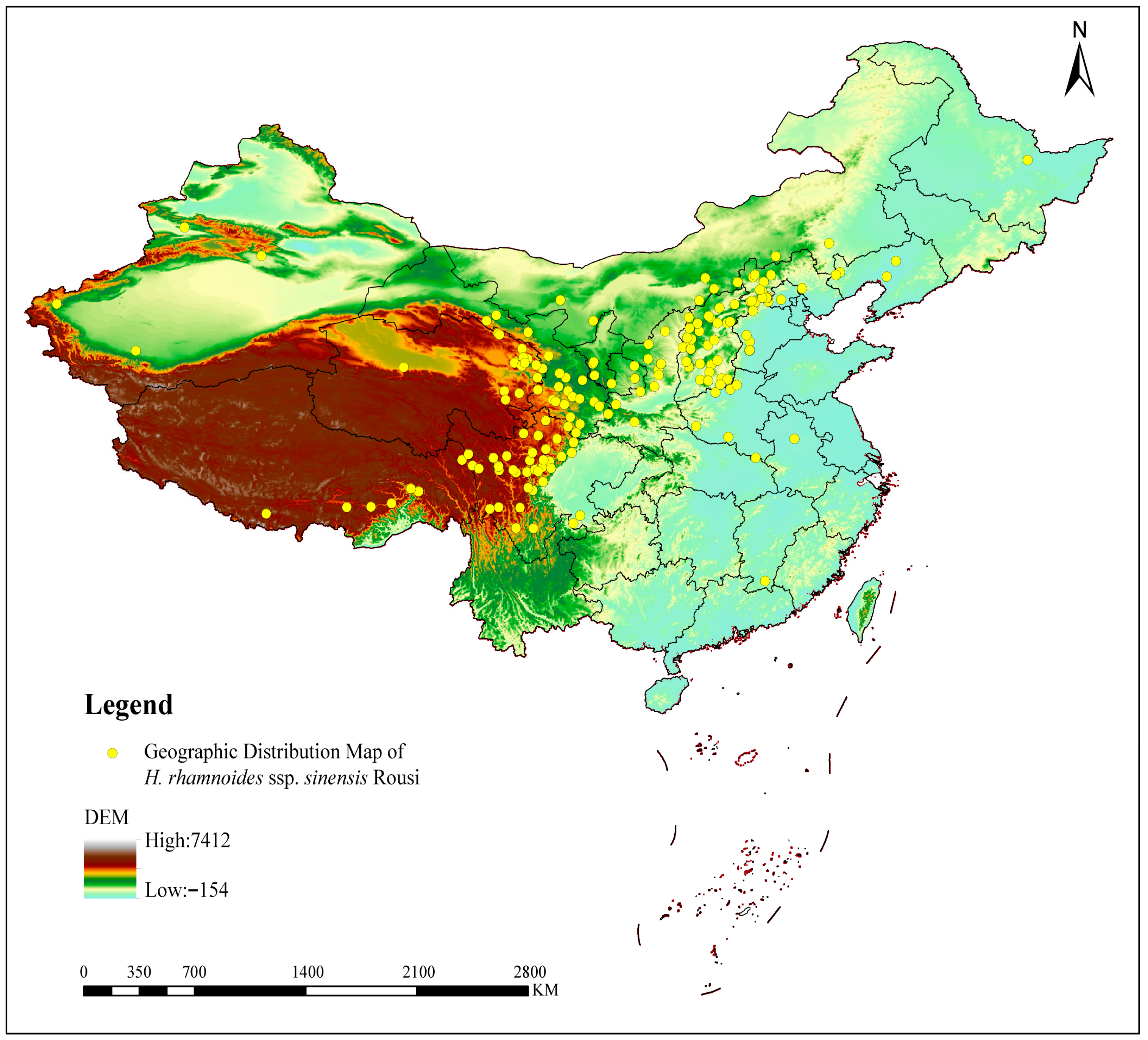
1. Introduction
2. Results
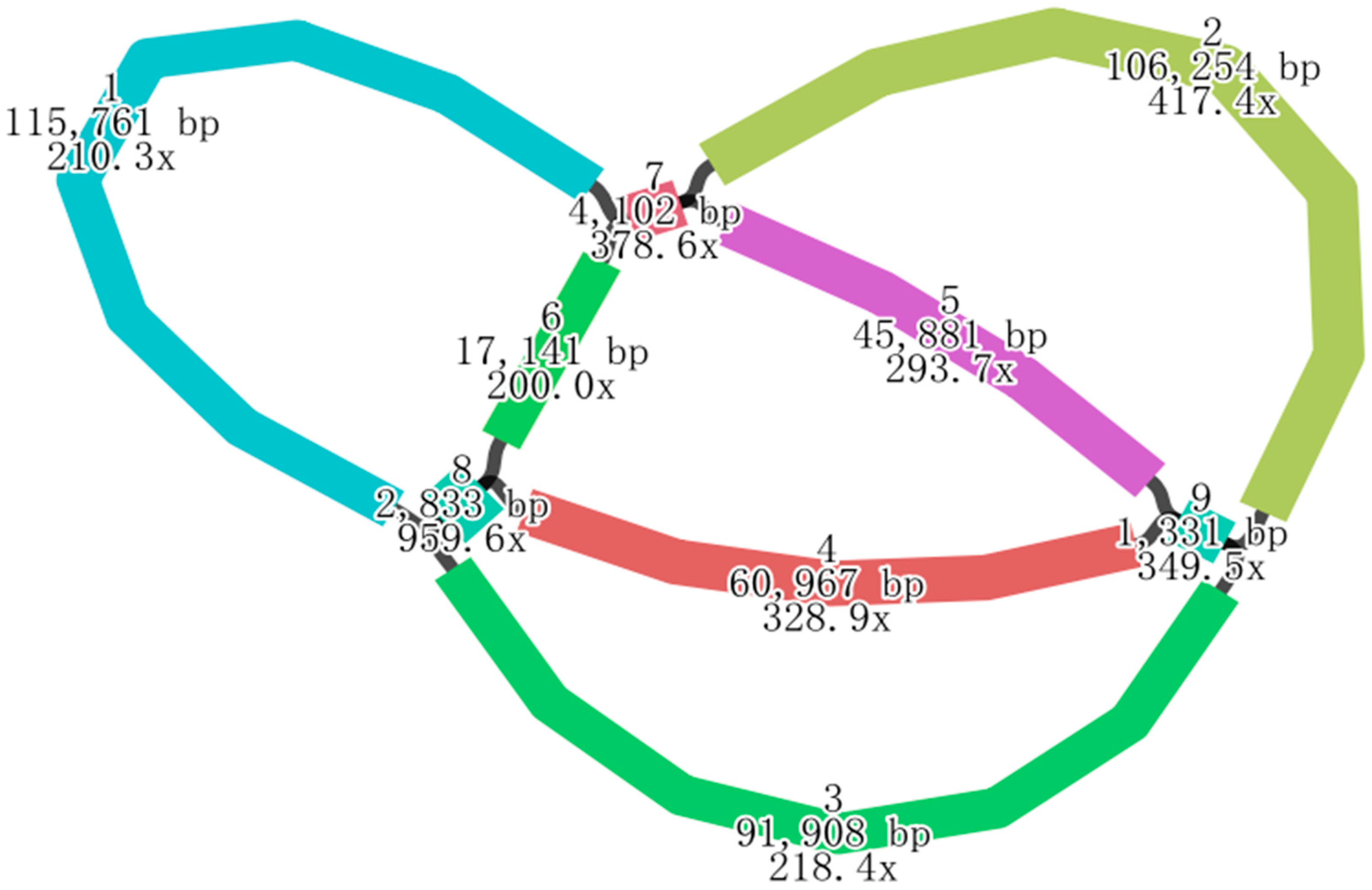
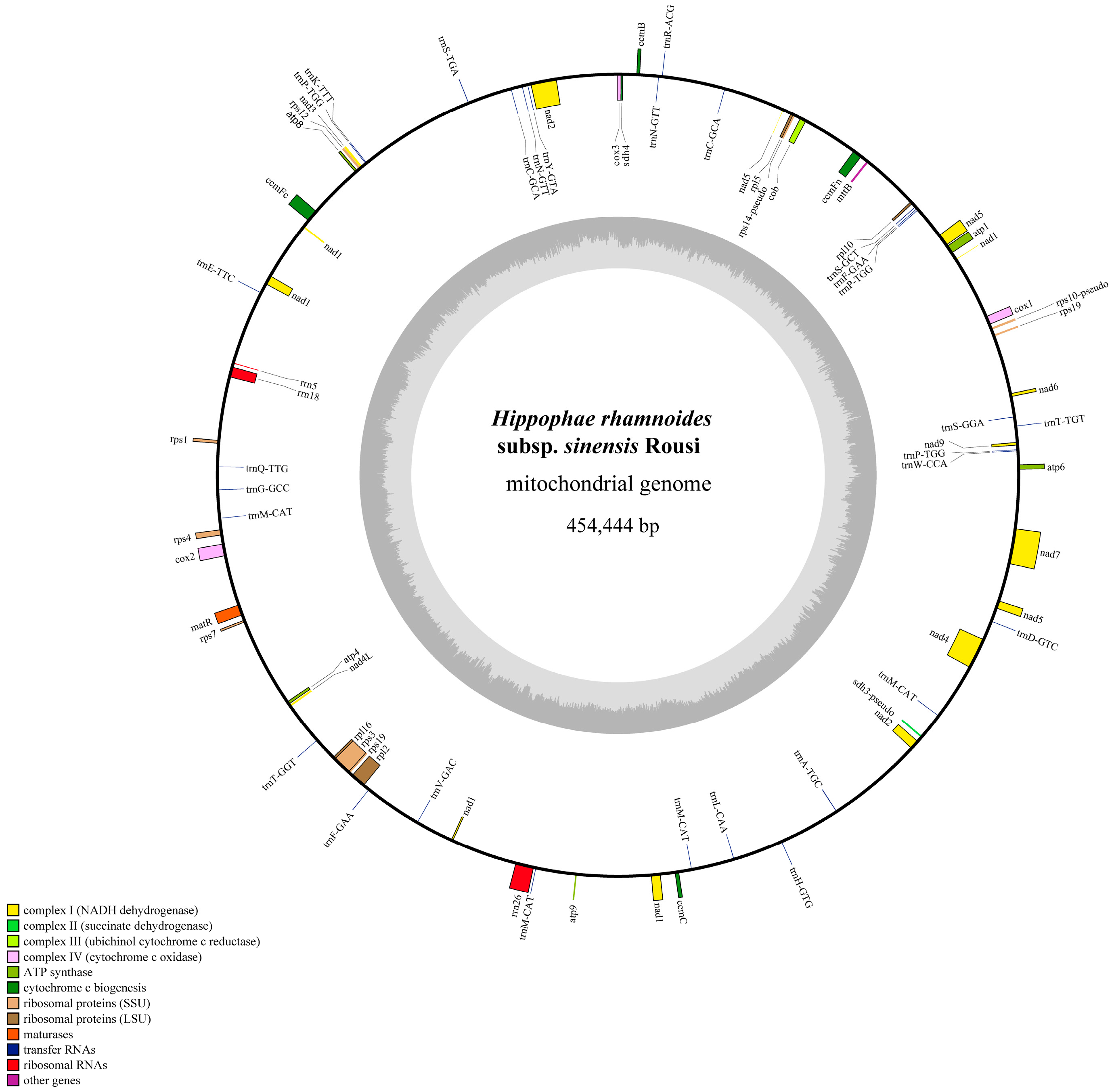
2.1. Sequencing and Genomic Features of the H. rhamnoides ssp. sinensis Mitogenome
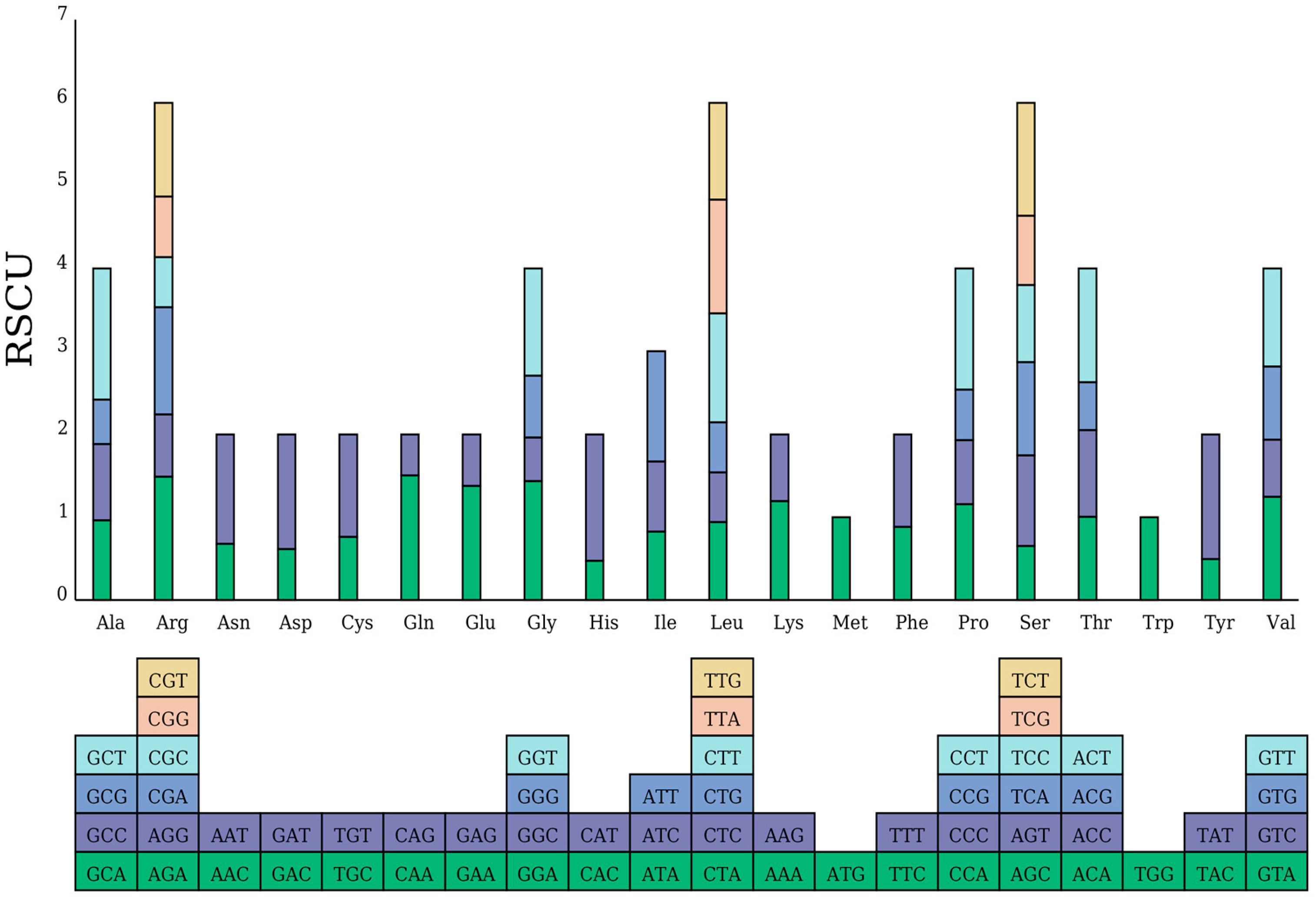
2.2. Codon Usage Bias Analysis
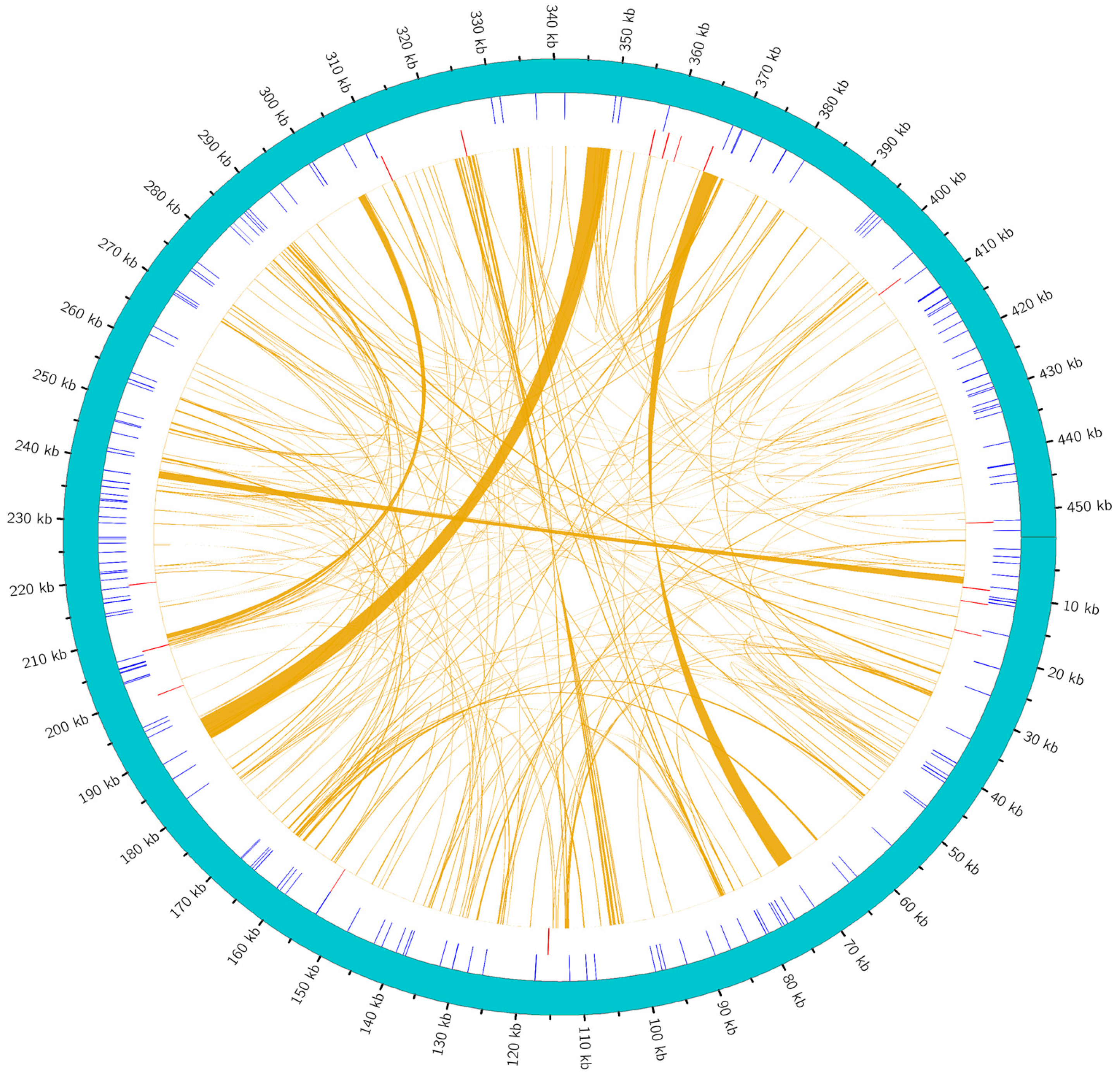
2.3. Repeat Sequence Analysis
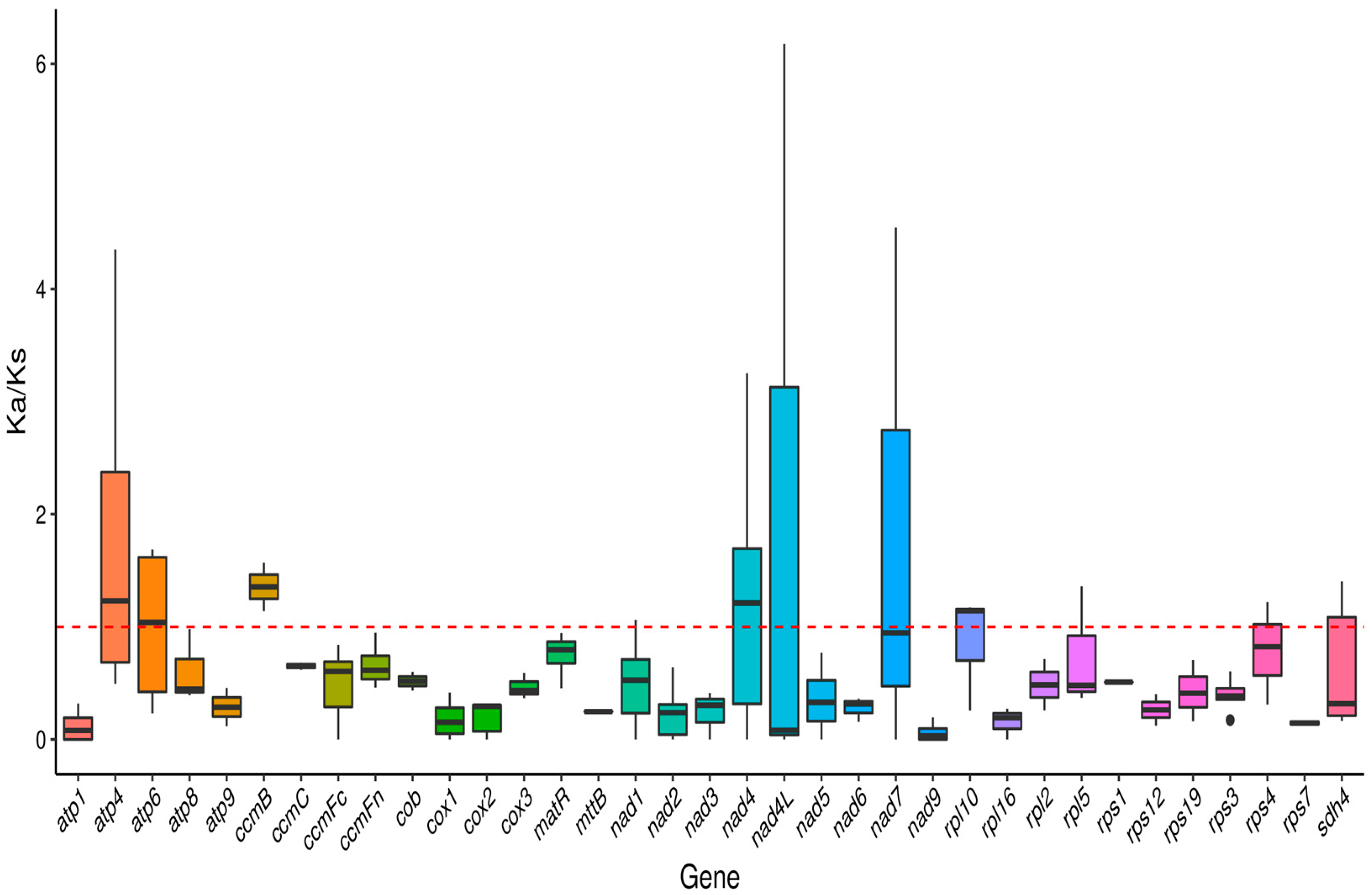
2.4. Analysis of Synonymous and Nonsynonymous Replacement Rates
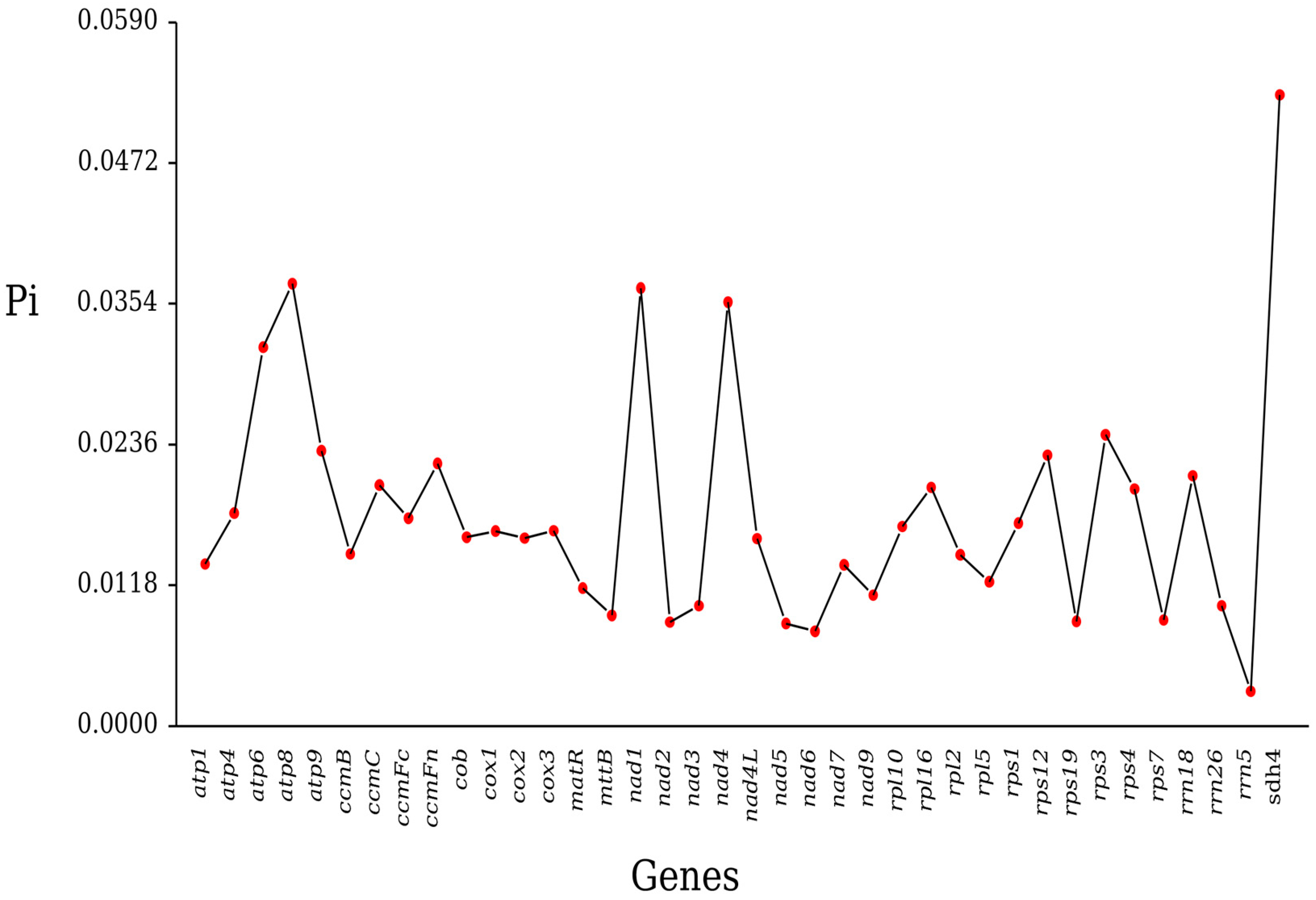
2.5. Nucleotide Diversity
2.6. Phylogenetic Analysis
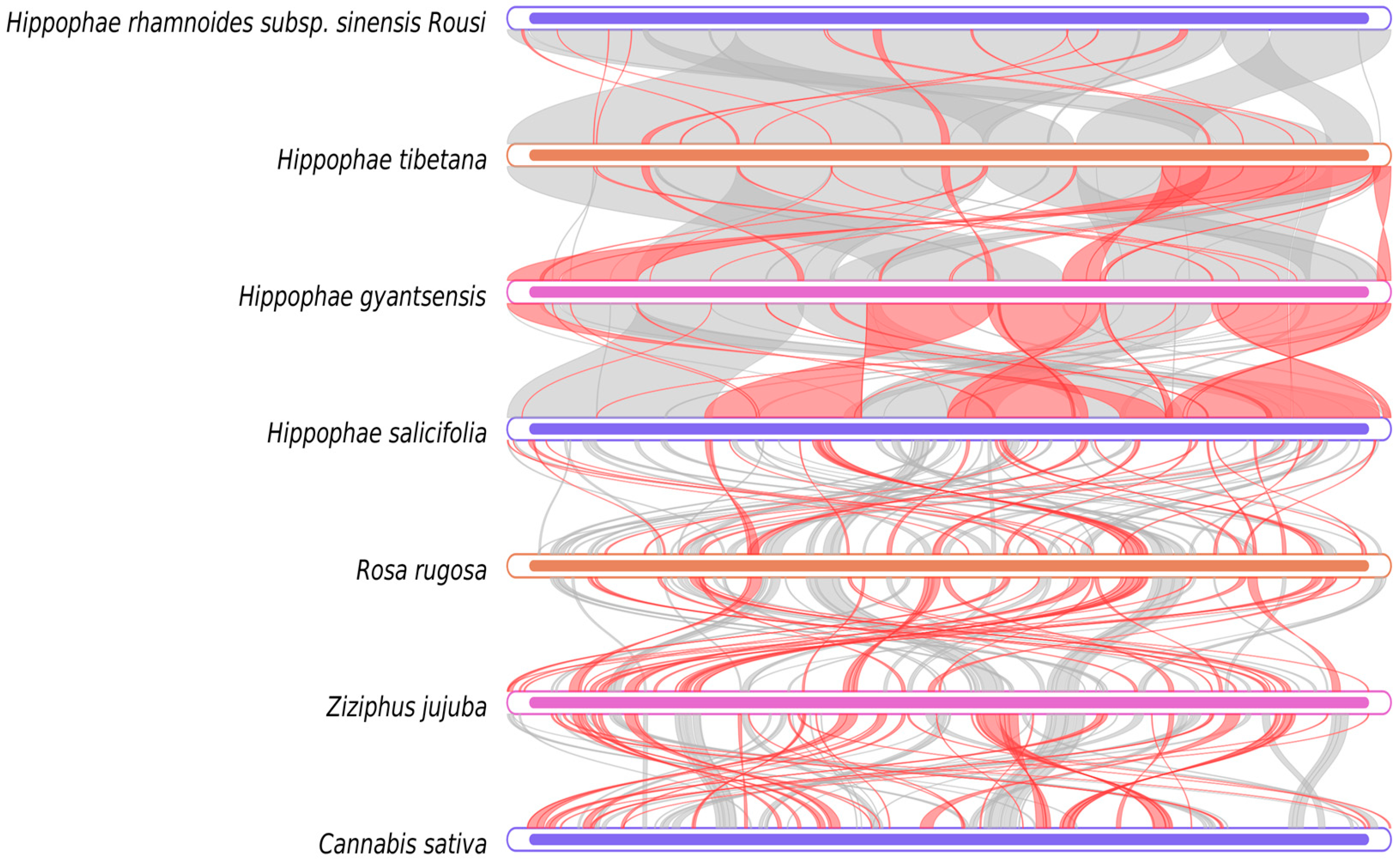
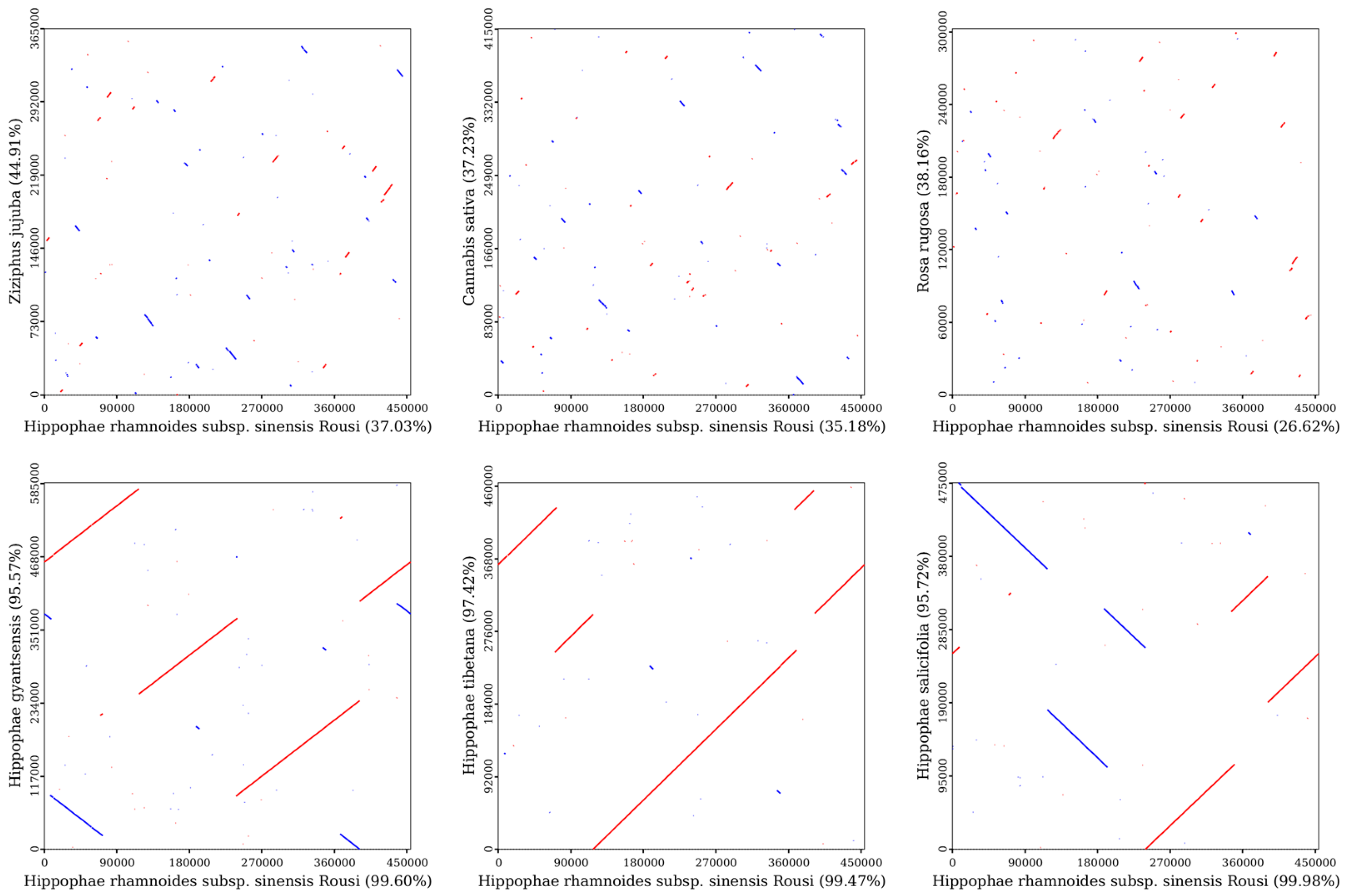
2.7. Synteny Analysis
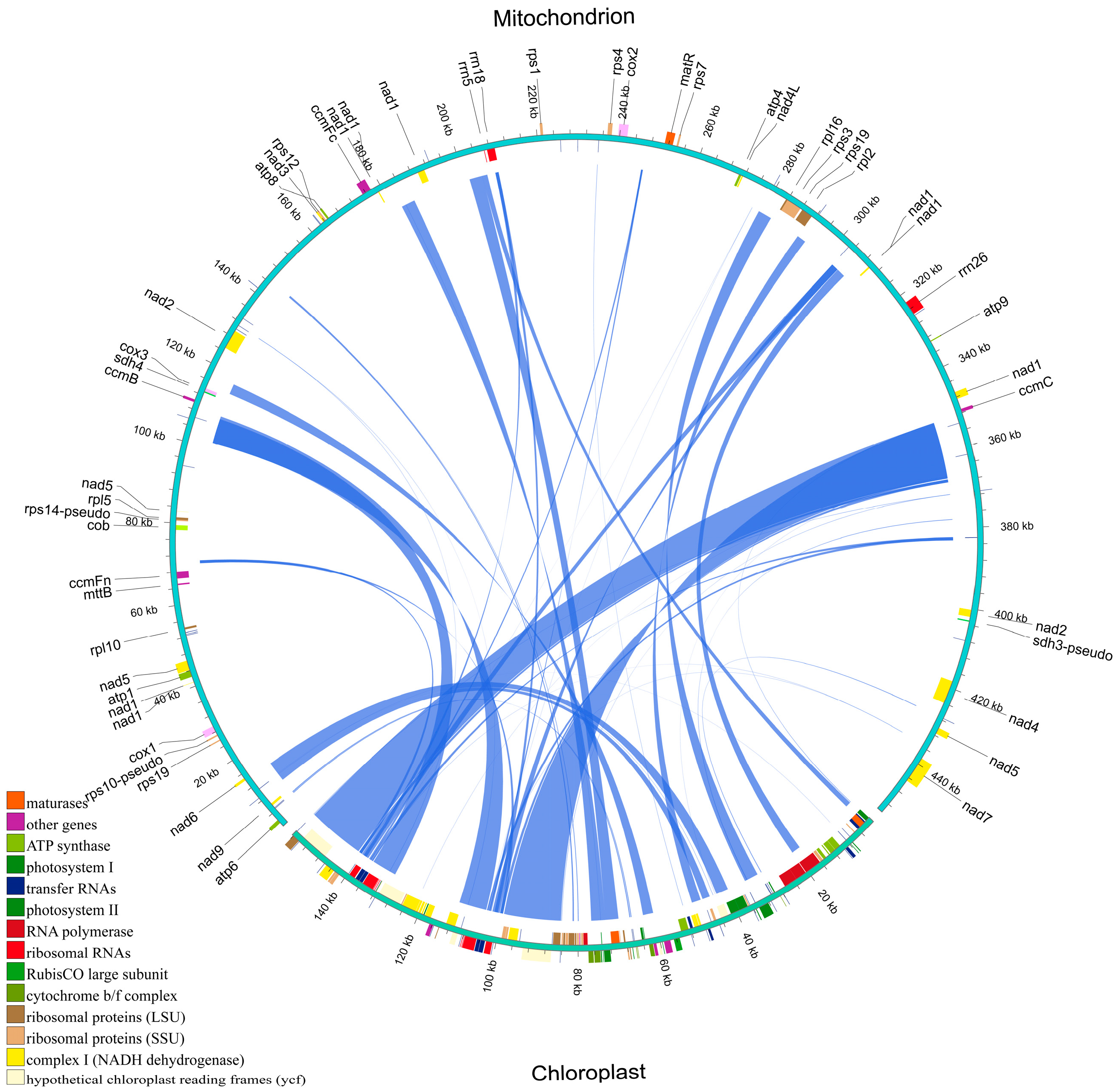
2.8. Homologous Fragments of the Mitochondrial and Chloroplast Genomes of H. rhamnoides ssp. sinensis
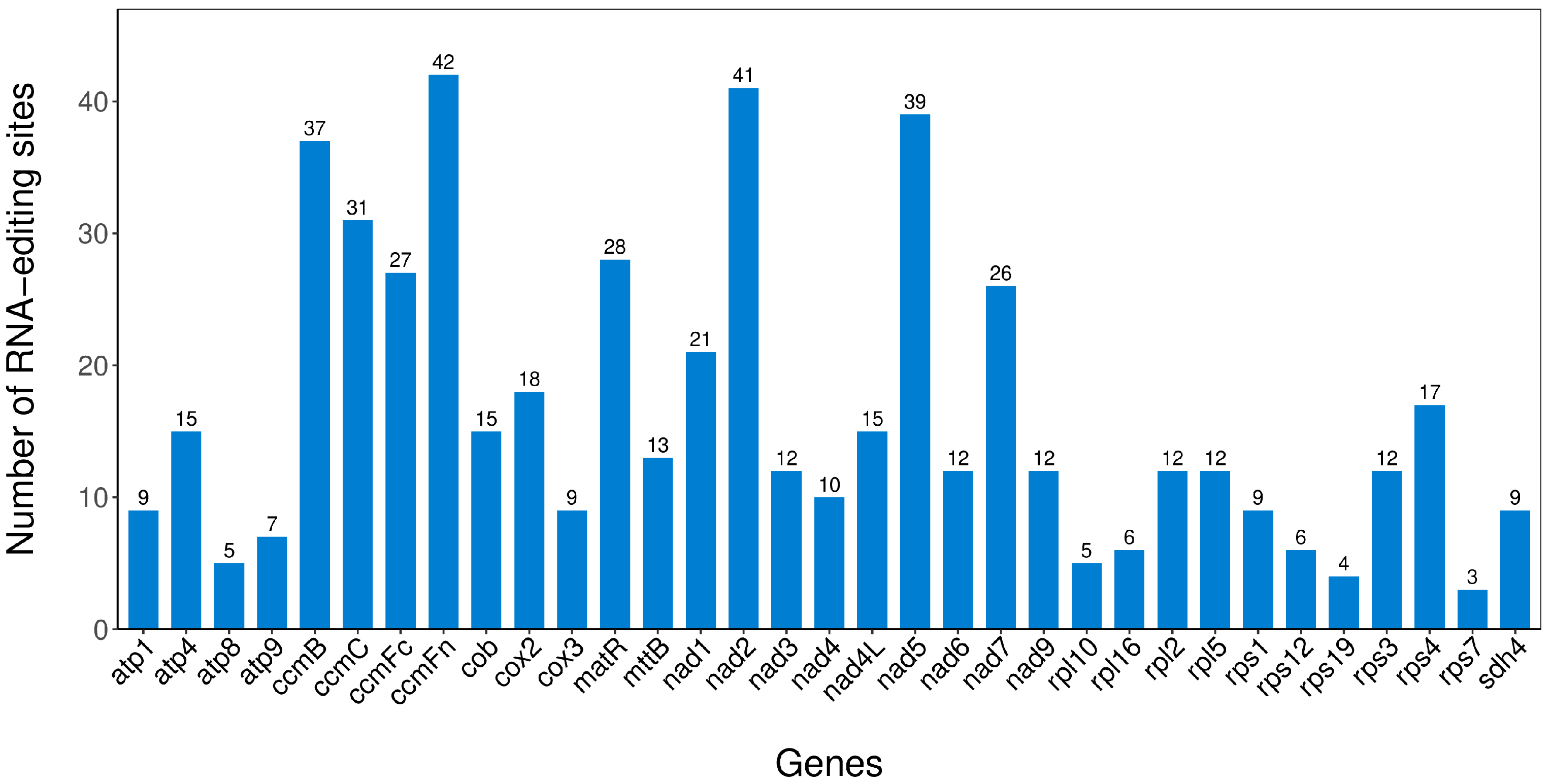
2.9. RNA Editing Events
3. Discussion
3.1. Conservation of Mitochondrial Genome Structure and Function
3.2. Codon Usage Bias and Adaptation
3.3. The Role of Repetitive Sequences in the Structure and Evolution of the Genome
3.4. Ka/Ks Ratio and Nucleotide Diversity Analysis
3.5. Characterization and Function of RNA Editing
3.6. Phylogenetic Analysis and Evolutionary Relationship
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sample Collection and Sequencing Data
4.2. Genome Assembly
4.3. Genome Annotation and Other Analyses
4.4. Codon Preference Analysis
4.5. Repeat Sequence Analysis
4.6. Assessment of ka/ks Ratio
4.7. Nucleotide Diversity (Pi) Analysis
4.8. Evolutionary Tree Analysis
4.9. Mitochondrial Sequence Covariance Analysis
4.10. Chloroplast and Mitochondrial Homologous Sequence Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nass, M.M.; Nass, S. Intramitochondrial Fibers with DNA Characteristics. I. Fixation and Electron Staining Reactions. J. Cell Biol. 1963, 19, 593–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, P.B.; Bu, W.J. Progress on heredity and evolution of mitochondrial genome. Chin. J. Biol. 2005, 40, 5–7. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.Q.; Liao, X.Z.; Zhang, X.N.; Tembrock, L.R.; Broz, A. Genomic architectural variation of plant mitochondria-A review of multichromosomal structuring. J. Syst. Evol. 2022, 60, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, M.W. Mitochondrial evolution. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2012, 4, a011403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gray, M.W.; Burger, G.; Lang, B.F. Mitochondrial evolution. Science 1999, 283, 1476–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sloan, D.B.; Warren, J.M.; Williams, A.M.; Wu, Z.Q.; Abdel-Ghany, S.E.; Chicco, A.J.; Havird, J.C. Cytonuclear integration and co-evolution. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2018, 19, 635–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Putintseva, Y.A.; Bondar, E.I.; Simonov, E.P.; Sharov, V.V.; Oreshkova, N.V.; Kuzmin, D.A.; Konstantinov, Y.M.; Shmakov, V.N.; Belkov, V.I.; Sadovsky, M.G.; et al. Siberian larch (Larix sibirica Ledeb.) mitochondrial genome assembled using both short and long nucleotide sequence reads is currently the largest known mitogenome. BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergthorsson, U.; Richardson, A.O.; Young, G.J.; Goertzen, L.R.; Palmer, J.D. Massive horizontal transfer of mitochondrial genes from diverse land plant donors to the basal angiosperm Amborella. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 17747–17752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mower, J.P.; Stefanovic, S.; Hao, W.; Gummow, J.S.; Jain, K.; Ahmed, D.; Palmer, J.D. Horizontal acquisition of multiple mitochondrial genes from a parasitic plant followed by gene conversion with host mitochondrial genes. BMC Biol. 2010, 8, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, A.O.; Palmer, J.D. Horizontal gene transfer in plants. J. Exp. Bot. 2007, 58, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Zhang, M.; Chen, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, B.; Li, J.; Wang, R.; Zhao, K.; Wu, J. Rearrangement and domestication as drivers of Rosaceae mitogenome plasticity. BMC Biol. 2022, 20, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Ni, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, C. Characterisation of the complete mitochondrial genome of Taraxacum mongolicum revealed five repeat-mediated recombinations. Plant Cell Rep. 2023, 42, 775–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korpelainen, H. The evolutionary processes of mitochondrial and chloroplast genomes differ from those of nuclear genomes. Naturwissenschaften 2004, 91, 505–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, N.; Wang, Y.; Hua, J. The Roles of Mitochondrion in Intergenomic Gene Transfer in Plants: A Source and a Pool. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Fu, X.X.; Li, R.Q.; Zhao, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, M.H.; Zwaenepoel, A.; Ma, H.; Goffinet, B.; Guan, Y.L.; et al. The hornwort genome and early land plant evolution. Nat. Plants 2020, 6, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, H.; Yang, M.; Bao, L.; Ge, J. Phylogeographic study of Chinese seabuckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides subsp. sinensis Rousi) reveals two distinct haplotype groups and multiple microrefugia on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Ecol. Evol. 2014, 4, 4370–4379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, Y.; Chen, X. The Ecogeographical Distribution of Hippophae rhamnoides Subp. sinensis and Its Phytogeographical Significance. Acta Phytotaxon. Sin. 1992, 30, 349–355. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Ma, R.; Sun, K.; Lian, Y. Germplasm resource and habitat types of Seabuckthorn in China. Acta Bot. Boreali-Occident. Sin. 2003, 23, 451–455. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Tian, L.; Zhang, J.; Ma, L.; Li, X.; Tian, C. Rhizospheric fungi and their link with the nitrogen-fixing Frankia harbored in host plant Hippophae rhamnoides L. J. Basic Microbiol. 2017, 57, 1055–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.Y.; Zhang, G.Y.; Zhang, J.G.; Duan, A.G.; Luo, H.M. Physiological, biochemical, and proteome profiling reveals key pathways underlying the drought stress responses of Hippophae rhamnoides. Proteomics 2016, 16, 2688–2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Chen, X.; Li, X.; Lin, X.; Yue, L.; Liu, C.; Li, Y. Growth and physiological response of Yulu Hippophae rhamnoides to drought stress and its omics analysis. Plant Signal. Behav. 2024, 19, 2439256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhyani, D.; Maikhuri, R.K.; Dhyani, S. Seabuckthorn: An underutilized resource for the nutritional security and livelihood improvement of rural communities in Uttarakhand Himalaya. Ecol. Food Nutr. 2011, 50, 168–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suryakumar, G.; Gupta, A. Medicinal and therapeutic potential of Sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.). J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 138, 268–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luntraru, C.M.; Apostol, L.; Oprea, O.B.; Neagu, M.; Popescu, A.F.; Tomescu, J.A.; Mulțescu, M.; Susman, I.E.; Gaceu, L. Reclaim and Valorization of Sea Buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides) By-Product: Antioxidant Activity and Chemical Characterization. Foods 2022, 11, 462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, N.; Tian, H.; Wang, Q.; Gao, M.; Xu, G.; Sun, Y.; Song, D.; Li, W.; Ji, C. Advance in Hippophae rhamnoides polysaccharides: Extraction, structural characteristics, pharmacological activity, structure-activity relationship and application. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 270 Pt 2, 132420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negi, B.; Dey, G. Effects of co-fermentation by Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Issatchenkia orientalis on sea buckthorn juice. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2013, 64, 508–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zosimidou, S.S.; Vouvoudi, E.C.; Tsagkalias, I.S.; Lykidou, S.S.; Nikolaidis, N.F. Preparation of Cosmetic Emulsions Containing Hippophae Oil Isolated by Various Methods: Study of Their Antioxidant, Sun-Blocking and Physicochemical Properties. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Mao, C.; Shang, Z.; Norbu, N.; Bonjor, N.; Jia, X.; Li, W.; Zhang, W.; Wang, J.; Qiong, L. Assembly and Comparative Analysis of the Complete Mitochondrial Genome of Hippophae salicifolia. Biology 2025, 14, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Tso, N.; Zhang, S.; Chen, Y.; Shu, Q.; Li, J.; Liang, Z.; Wang, R.; Wang, J.; et al. Complete mitochondrial genome of Hippophae tibetana: Insights into adaptation to high-altitude environments. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1449606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wynn, E.L.; Christensen, A.C. Repeats of Unusual Size in Plant Mitochondrial Genomes: Identification, Incidence and Evolution. G3-Genes Genomes Genet. 2019, 9, 549–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Fan, K.; Zhen, S.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Fu, J.; Qi, C.; Wei, Q.; Du, Y.; Tatar, W.; et al. Tetratricopeptide-containing SMALL KERNEL 11 is essential for the assembly of cytochrome c oxidase in maize mitochondria. Plant Physiol. 2023, 192, 170–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, S.; Chen, J.; Chen, C.; Lin, X.; Peng, H.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, X. Characterization and phylogenetic analysis of the complete mitochondrial genome sequence of Photinia serratifolia. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantatore, P.; Gadaleta, M.N.; Roberti, M.; Saccone, C.; Wilson, A.C. Duplication and remoulding of tRNA genes during the evolutionary rearrangement of mitochondrial genomes. Nature 1987, 329, 853–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Song, Y.; Chen, N.; Wei, J.; Zhang, J.; He, C. Chromosome-level genome assembly of Hippophae tibetana provides insights into high-altitude adaptation and flavonoid biosynthesis. BMC Biol. 2024, 22, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mower, J.P. Variation in protein gene and intron content among land plant mitogenomes. Mitochondrion 2020, 53, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikemura, T. Correlation between the abundance of Escherichia coli transfer RNAs and the occurrence of the respective codons in its protein genes: A proposal for a synonymous codon choice that is optimal for the E. coli translational system. J. Mol. Biol. 1981, 151, 389–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharp, P.M.; Li, W.H. The codon Adaptation Index—A measure of directional synonymous codon usage bias, and its potential applications. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987, 15, 1281–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Yuan, J.; Liu, J.; Jin, L.; Chen, J.Q. Codon usage bias and determining forces in green plant mitochondrial genomes. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2011, 53, 324–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyim, M.; Jinjin, F.; Gulmira, A. Characterization and phylogenetic analysis of Ramalina sinensis mitogenome. Mycosystema 2023, 42, 1273–1284. [Google Scholar]
- Junlin, L.; Shuhong, G.; Qiang, Z.; Lijun, Z.; Hongling, T.; Qiong, Z. Characteristics and phylogenetic analysis of Astragalus membranaceus var. mongholicus chloroplast whole genome. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2024, 55, 2366–2374. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, W.; Chen, X.; He, J.; Sha, A.; Luo, Y.; Xiao, W.; Xiong, Z.; Li, Q. Intraspecific and interspecific variations in the synonymous codon usage in mitochondrial genomes of 8 pleurotus strains. BMC Genom. 2024, 25, 456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Jin, X.J.; Zhang, C.Y.; Li, P.; Meng, H.H.; Zhang, Y.H. Plastome evolution of Engelhardia facilitates phylogeny of Juglandaceae. BMC Plant Biol. 2024, 24, 634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duret, L.; Mouchiroud, D. Expression pattern and, surprisingly, gene length shape codon usage in Caenorhabditis, Drosophila, and Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 4482–4487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolfe, K.H.; Li, W.H.; Sharp, P.M. Rates of nucleotide substitution vary greatly among plant mitochondrial, chloroplast, and nuclear DNAs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1987, 84, 9054–9058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, H.; Gong, X.; Ou, X.; Guo, Y.; Tang, M. De Novo assembly and phylogenetic analysis of the complete mitochondrial genome of Eleutherococcus senticosus and related araliaceous species. BMC Plant Biol. 2025, 25, 760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alverson, A.J.; Rice, D.W.; Dickinson, S.; Barry, K.; Palmer, J.D. Origins and recombination of the bacterial-sized multichromosomal mitochondrial genome of cucumber. Plant Cell 2011, 23, 2499–2513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forner, J.; Kleinschmidt, D.; Meyer, E.H.; Fischer, A.; Morbitzer, R.; Lahaye, T.; Schöttler, M.A.; Bock, R. Targeted introduction of heritable point mutations into the plant mitochondrial genome. Nat. Plants 2022, 8, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, C.; Cui, T.; Zhang, C.; Zang, S.; Su, Y.; Que, Y. Assembly of the Complete Mitochondrial Genome of Gelsemium elegans Revealed the Existence of Homologous Conformations Generated by a Repeat Mediated Recombination. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 24, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, J.D.; Adams, K.L.; Cho, Y.; Parkinson, C.L.; Qiu, Y.L.; Song, K. Dynamic evolution of plant mitochondrial genomes: Mobile genes and introns and highly variable mutation rates. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 6960–6966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.; Mower, J.P.; Qiu, Y.L.; Palmer, J.D. Mitochondrial substitution rates are extraordinarily elevated and variable in a genus of flowering plants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 17741–17746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, K.L.; Palmer, J.D. Evolution of mitochondrial gene content: Gene loss and transfer to the nucleus. Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2003, 29, 380–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, A.C. Plant mitochondrial genome evolution can be explained by DNA repair mechanisms. Genome Biol. Evol. 2013, 5, 1079–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mower, J.P. The PREP suite: Predictive RNA editors for plant mitochondrial genes, chloroplast genes and user-defined alignments. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, W253–W259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takenaka, M.; Zehrmann, A.; Verbitskiy, D.; Härtel, B.; Brennicke, A. RNA editing in plants and its evolution. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2013, 47, 335–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bentolila, S.; Oh, J.; Hanson, M.R.; Bukowski, R. Comprehensive high-resolution analysis of the role of an Arabidopsis gene family in RNA editing. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giegé, P.; Brennicke, A. RNA editing in Arabidopsis mitochondria effects 441 C to U changes in ORFs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 15324–15329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Dugardeyn, J.; Zhang, C.; Takenaka, M.; Kühn, K.; Craddock, C.; Smalle, J.; Karampelias, M.; Denecke, J.; Peters, J.; et al. SLO2, a mitochondrial pentatricopeptide repeat protein affecting several RNA editing sites, is required for energy metabolism. Plant J. 2012, 71, 836–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, D.R.; Wang, Y.J.; Liu, T.L.; Wu, G.L.; Kou, Y.X.; Cheng, K.; Liu, J.Q. Diploid hybrid origin of Hippophae gyantsensis (Elaeagnaceae) in the western Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 2016, 117, 658–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.D.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.F.; Shrestha, N.; Liu, J.Q. Species divergence with gene flow and hybrid speciation on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. N. Phytol. 2022, 234, 392–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fauré, S.; Noyer, J.L.; Carreel, F.; Horry, J.P.; Bakry, F.; Lanaud, C. Maternal inheritance of chloroplast genome and paternal inheritance of mitochondrial genome in bananas (Musa acuminata). Curr. Genet. 1994, 25, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, D.R.; Bartish, I.V. Climatic Changes and Orogeneses in the Late Miocene of Eurasia: The Main Triggers of an Expansion at a Continental Scale? Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drouin, G.; Daoud, H.; Xia, J. Relative rates of synonymous substitutions in the mitochondrial, chloroplast and nuclear genomes of seed plants. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2008, 49, 827–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.D.; Soltis, D.E.; Yang, Y.; Li, D.Z.; Yi, T.S. Multi-gene analysis provides a well-supported phylogeny of Rosales. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2011, 60, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, J.; He, W.; Kan, S.; Liao, X.; Jordan, D.R.; Mace, E.S.; Tao, Y.; Cruickshank, A.W.; Klein, R.; et al. Variation in mitogenome structural conformation in wild and cultivated lineages of sorghum corresponds with domestication history and plastome evolution. BMC Plant Biol. 2023, 23, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H. Minimap2: Pairwise alignment for nucleotide sequences. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 3094–3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koren, S.; Walenz, B.P.; Berlin, K.; Miller, J.R.; Bergman, N.H.; Phillippy, A.M. Canu: Scalable and accurate long-read assembly via adaptive k-mer weighting and repeat separation. Genome Res. 2017, 27, 722–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wick, R.R.; Schultz, M.B.; Zobel, J.; Holt, K.E. Bandage: Interactive visualization of de novo genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 3350–3352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, P.P.; Lowe, T.M. tRNAscan-SE: Searching for tRNA Genes in Genomic Sequences. In Gene Prediction; Methods in Molecular Biology; Humana: New York, NY, USA, 2019; Volume 1962, pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Beier, S.; Thiel, T.; Münch, T.; Scholz, U.; Mascher, M. MISA-web: A web server for microsatellite prediction. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 2583–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, G. Tandem repeats finder: A program to analyze DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999, 27, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ye, W.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Y. High speed BLASTN: An accelerated MegaBLAST search tool. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 7762–7768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: Improvements in performance and usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, J.; Yu, J. KaKs_Calculator 2.0: A toolkit incorporating gamma-series methods and sliding window strategies. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2010, 8, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Librado, P.; Rozas, J. DnaSP v5: A software for comprehensive analysis of DNA polymorphism data. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1451–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capella-Gutiérrez, S.; Silla-Martínez, J.M.; Gabaldón, T. trimAl: A tool for automated alignment trimming in large-scale phylogenetic analyses. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1972–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darriba, D.; Taboada, G.L.; Doallo, R.; Posada, D. jModelTest 2: More models, new heuristics and parallel computing. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Chen, Y.; Cai, G.; Cai, R.; Hu, Z.; Wang, H. Tree Visualization By One Table (tvBOT): A web application for visualizing, modifying and annotating phylogenetic trees. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, W587–w592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marçais, G.; Delcher, A.L.; Phillippy, A.M.; Coston, R.; Salzberg, S.L.; Zimin, A. MUMmer4: A fast and versatile genome alignment system. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2018, 14, e1005944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, M.; Hu, N.; Sun, J.; Zhou, W. Characterization of the Mitochondrial Genome of Hippophae rhamnoides subsp. sinensis Rousi Based on High-Throughput Sequencing and Elucidation of Its Evolutionary Mechanisms. Plants 2025, 14, 2547. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14162547
Lin M, Hu N, Sun J, Zhou W. Characterization of the Mitochondrial Genome of Hippophae rhamnoides subsp. sinensis Rousi Based on High-Throughput Sequencing and Elucidation of Its Evolutionary Mechanisms. Plants. 2025; 14(16):2547. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14162547
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Mengjiao, Na Hu, Jing Sun, and Wu Zhou. 2025. "Characterization of the Mitochondrial Genome of Hippophae rhamnoides subsp. sinensis Rousi Based on High-Throughput Sequencing and Elucidation of Its Evolutionary Mechanisms" Plants 14, no. 16: 2547. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14162547
APA StyleLin, M., Hu, N., Sun, J., & Zhou, W. (2025). Characterization of the Mitochondrial Genome of Hippophae rhamnoides subsp. sinensis Rousi Based on High-Throughput Sequencing and Elucidation of Its Evolutionary Mechanisms. Plants, 14(16), 2547. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14162547





