Efficacy of Transgenic Maize LD05 Against Fall Armyworm (Spodoptera frugiperda)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials
2.2. Bioassay of FAW Susceptibilities to M2CryAb-VIP3A Proteins
- Mortality (%) = (Dead larvae/Total larvae) × 100
- Corrected mortality (%) = [(Treatment mortality − Control mortality)/(1 − Control mortality)] × 100
- Weight inhibition (%) = [(Control weight gain − Treatment weight gain)/Control weight gain] × 100
2.3. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.4. Bioassays Using Plant Tissues
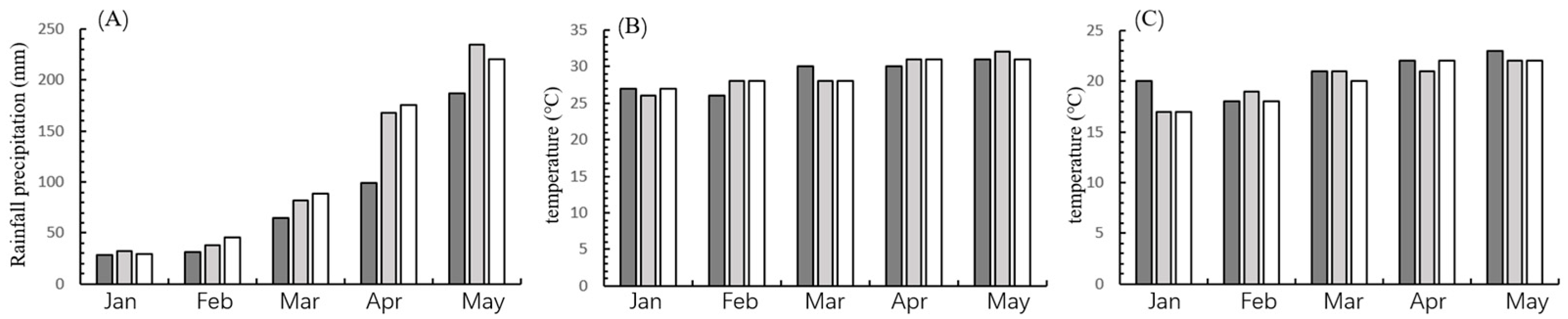
2.5. Field Trials
2.6. The Agronomic Traits Detection
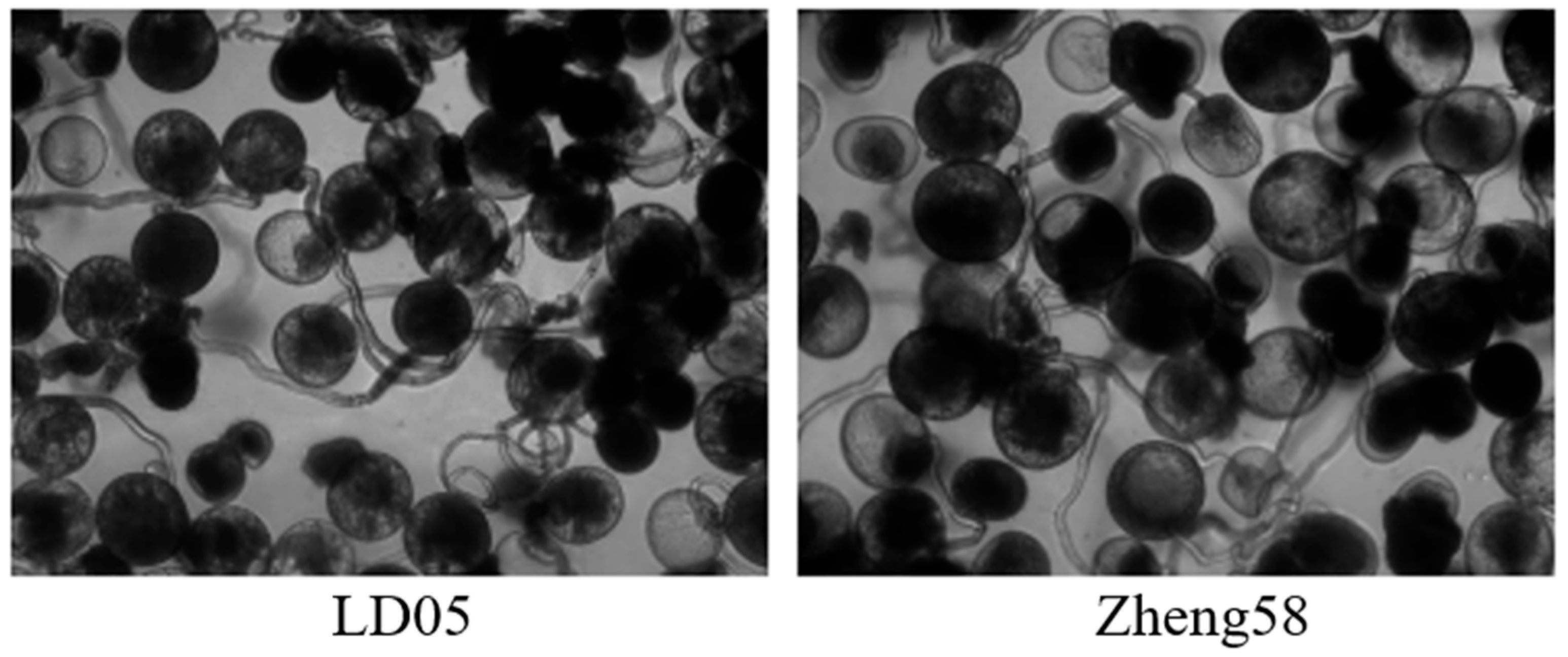
2.7. Pollen Viability Detection
2.8. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Sensitivity of Spodoptera frugiperda Larvae to M2CryAb-VIP3A
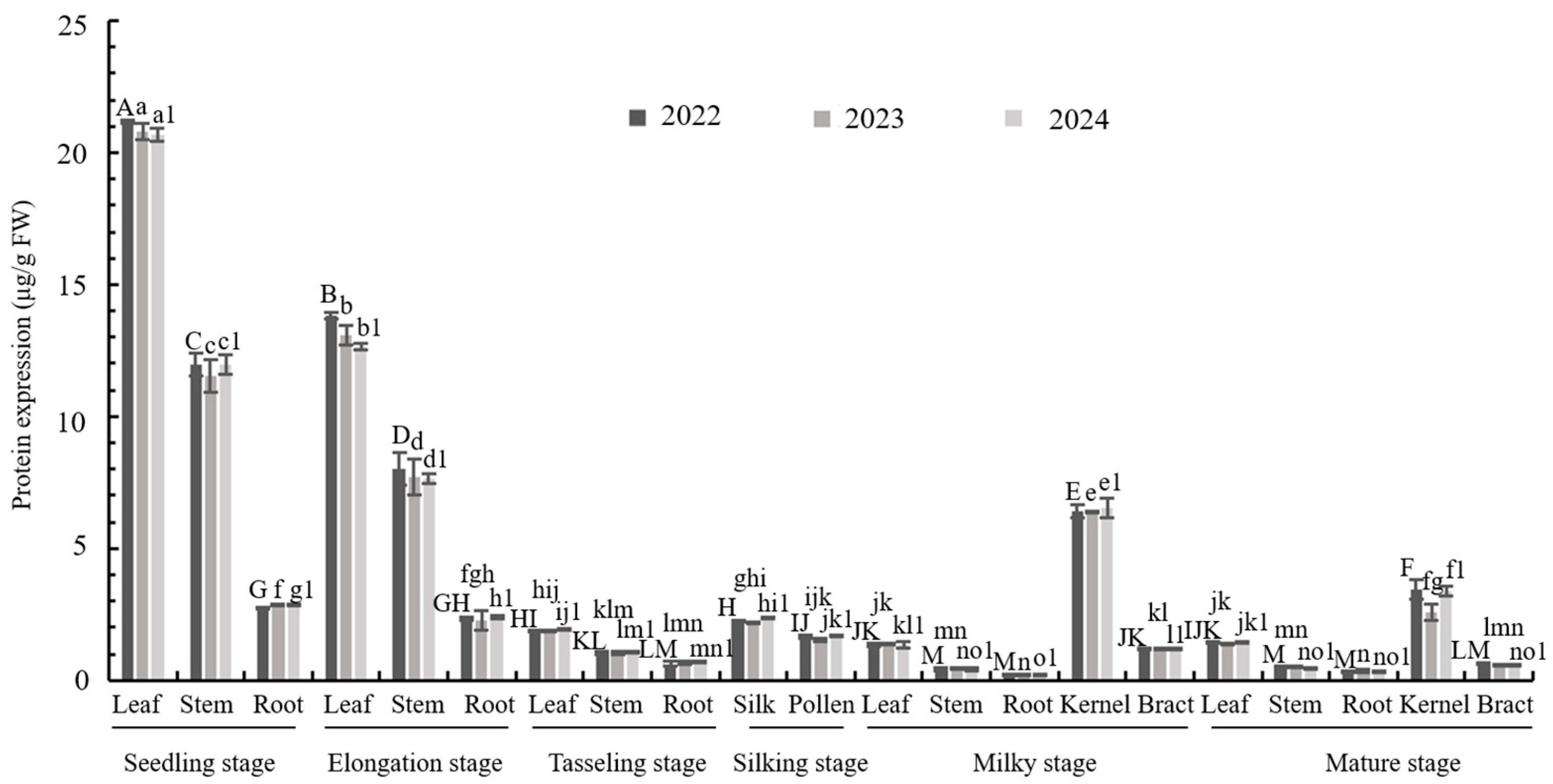
3.2. Expression Analysis of M2CryAb-VIP3A Protein in Transgenic Maize LD05
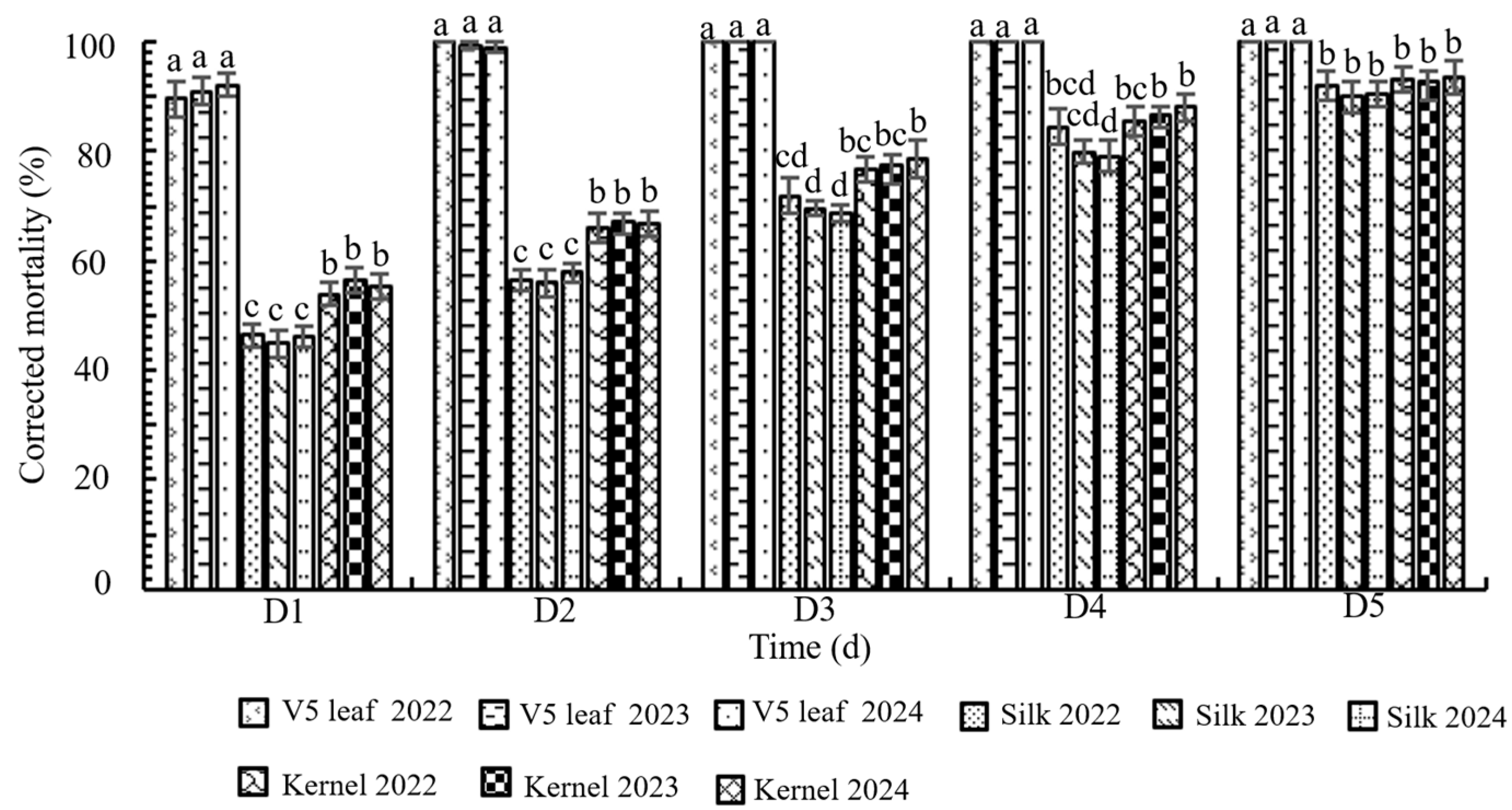
3.3. Bioassay of Transgenic Maize LD05 Tissues Against FAW Neonates
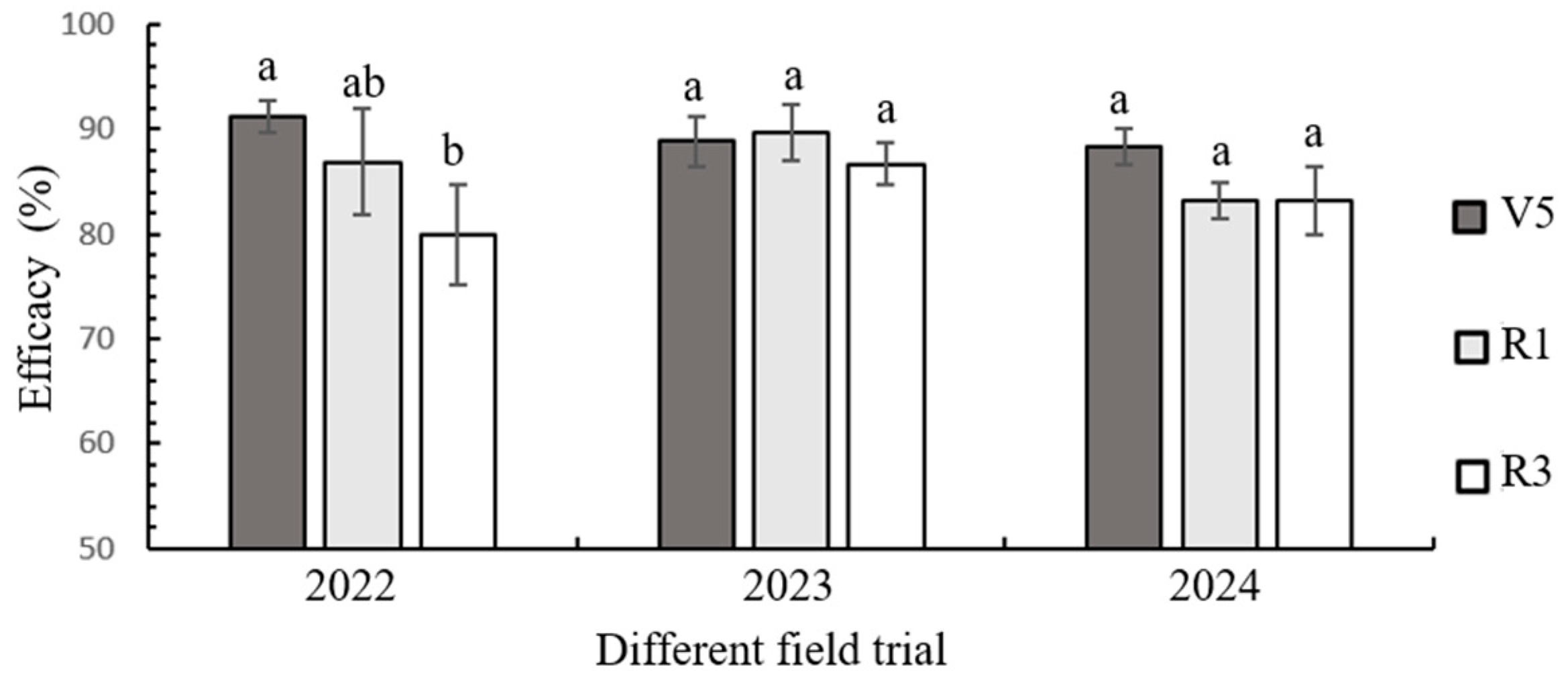
3.4. Field Evaluation of Transgenic Maize LD05 Against FAW During 2022–2024
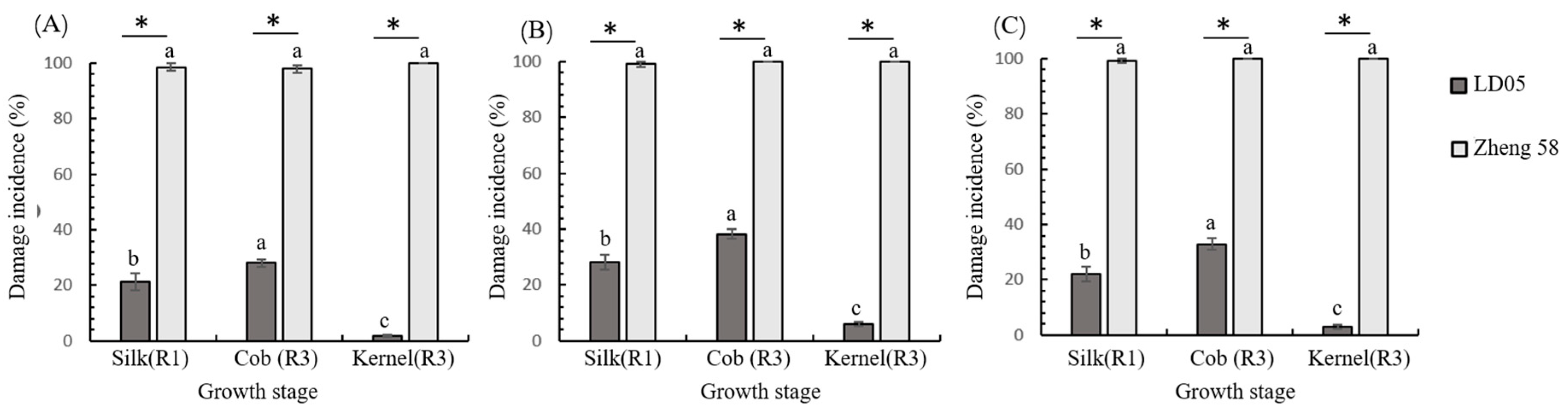
3.5. Field Control of Transgenic Maize LD05 Against FAW During 2022–2024
3.6. Agronomic Traits of Transgenic Maize LD05 During 2022–2024
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ge, S.; He, L.; He, W.; Yan, R.; Wyckhuys, K.A.G.; Wu, K. Laboratory-based flight performance of the fall armyworm, Spodoptera frugiperda. J. Integr. Agric. 2021, 20, 707–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Hu, C.; Jia, H.; Wu, Q.; Shen, X.; Zhao, S.; Jiang, Y.; Wu, K. Case study on the first immigration of fall armyworm, Spodoptera frugiperda invading into China. J. Integr. Agric. 2021, 20, 664–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, D.; He, W.; Wyckhuys, K.; Wu, K. Interference competition and predation between invasive and native herbivores in maize. J. Pest. Sci. 2021, 94, 1053–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, M.; Tai, H.; Gu, R.; Wang, G.; Liu, Z.; Mi, Q.; Zhang, J.; Li, H.; Wang, Z.; Nie, F.; et al. Economic loss assessment of maize production caused by the fall armyworm Spodoptera frugiperda and investigation of control strategies in Dehong prefecture of Yunnan province. Plant Prot. 2022, 48, 220–226. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Huang, L.; Liu, J.; Zhang, H.; Qiu, K.; Lu, F.; Hu, G. Migration Dynamics of Fall Armyworm Spodoptera frugiperda (Smith) in the Yangtze River Delta. Insects 2023, 14, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K. Management strategies of fall amryworm (Spodoptera frugiperda) in China. Plant Prot. 2020, 46, 1–5. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Prasanna, B.M.; Huesing, J.E.; Eddy, R.; Peschke, V.M. (Eds.) Fall Armyworm in Africa: A Guide for Integrated Pest Management, 1st ed.; CIMMYT: Texcoco, Mexico, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Q.; He, L.; Shen, X.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, J.; Hu, G.; Wu, K.-M. Estimation of the potential infestation area of newly-invaded fall armyworm Spodoptera frugiperda in the Yangtze River valley of China. Insects 2019, 10, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wyckhuys, K.; Jia, X.; Nie, F.; Wu, K. Fall armyworm invasion heightens pesticide expenditure among Chinese smallholder farmers. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 282, 111949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitre, H.N. Chemical control of the fall armyworm (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae): An update. Fla. Entomol. 1986, 69, 570–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leibee, G.L.; Capinera, J.L. Pesticide resistance in Florida insects limits management options. Fla. Entomol. 1995, 78, 386–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IRAC. Integrated Pest Management (IPM) & Insect Resistance Management (IRM) for Fall Armyworm in South African Maize. 2018. Available online: https://irac-online.org/documents/ipm-irm-for-fall-armyworm-in-s-african-maize/?ext=pdf (accessed on 1 June 2021).
- Zhang, D.; Xiao, Y.; Xu, P.; Yang, X.; Wu, Q.; Wu, K. Insecticide resistance monitoring for the invasive populations of fall armyworm, Spodoptera frugiperda in China. J. Integr. Agric. 2021, 20, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Wu, K.; Jiang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Desneux, N. Widespread adoption of Bt cotton and insecticide decrease promotes biocontrol services. Nature 2012, 487, 362–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchison, W.D.; Burkness, E.C.; Mitchell, P.D.; Moon, R.D.; Leslie, T.W.; Fleischer, S.J.; Abrahamson, M.; Hamilton, K.L.; Steffey, K.L.; Gray, M.E.; et al. Areawide suppression of European corn borer with Bt maize reaps savings to non–Bt maize growers. Science 2010, 330, 222–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, F.N.; Leonard, B.R.; Gable, R.H. Comparative susceptibility of European corn borer, Southwestern corn borer, and Sugarcane borer (Lepidoptera: Crambidae) to Cry1Ab protein in a commercial Bacillus thuringiensis corn hybrid. J. Econ. Entomol. 2006, 99, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buntin, G.D. Corn expressing Cry1Ab or Cry1F endotoxin for fall armyworm and corn earworm (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) management in field corn for grain production. Fla. Entomol. 2008, 91, 523–530. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, R.Q. Insect-Resistant Fusion Gene M2CryAb-VIP3A, Its Expression Vector, Product and Application. China ZL 2021 l 1346791.X, 15 November 2021. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Yue, R.; Li, W.; Ding, Z.; Meng, Z. Molecular characteristics and resistance evaluation of transgenic maize LD05 with stacked insect and herbicide resistance traits. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2025, 58, 1269–1283. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, R.; Li, W.; Meng, Z. Acquisition and resistance analysis of transgenic maize inbred line LG11 with insect and herbicide resistance. Acta Agric. Sin. 2024, 50, 89–99. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Prasanna, B.; Huesing, J.E.; Peschke, V.M.; Nagoshi, R.N.; Jia, X.; Wu, K.; Trisyono, Y.A.; Tay, T.; Watson, A.; Day, R.; et al. Fall Armyworm in Asia: Invasion, Impacts, and Strategies for Sustainable Management, in Fall Armyworm in Asia: A Guide for Integrated Pest Management; CIMMYT: Texcoco, Mexico, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, S.; Yang, X.; Liu, D.; Sun, X.; Li, G.; Wu, K. Performance of the domestic Bt corn event expressing pyramided Cry1Ab and Vip3Aa19 against the invasive Spodoptera frugiperda (J. E. Smith) in China. Pest. Manag. Sci. 2023, 79, 1018–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Overton, K.; Maino, J.L.; Day, R.; Umina, P.A.; Bett, B.; Carnovale, D.; Ekesi, S.; Meagher, R.; Reynolds, O.L. Global crop impacts, yield losses and action thresholds for fall armyworm (Spodoptera frugiperda): A review. Crop Prot. 2021, 145, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, W.; Wang, L.; Yang, Q.; Liang, G.; Wu, K. Control efficacy of Bt-Cry1Ab maize (event DBN9936) against Ostrinia furnacalis (Guenée) in Sichuan Province, China. Pest. Manag. Sci. 2025, 81, 1218–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Huang, C.; Chen, Y.; Han, L.; Xie, J.; Chen, X. Sensitivities of fall armyworm (Spodoptera frugiperda) populations in different regions of China to four Bt proteins. Agronomy 2023, 13, 2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sena, J.A.D.; Hernández–Rodríguez, C.S.; Ferré, J. Interaction of Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1 and Vip3A proteins with Spodoptera frugiperda midgut binding sites. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 2236–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares Figueiredo, C.; Nunes Lemes, A.R.; Sebastião, I.; Desidério, J.A. Synergism of the Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1, Cry2, and Vip3 Proteins in Spodoptera frugiperda Control. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2019, 188, 798–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergamasco, V.B.; Mendes, D.R.; Fernandes, O.A.; Desidério, J.A.; Lemos, M.V. Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1Ia10 and Vip3Aa protein interactions and their toxicity in Spodoptera spp. (Lepidoptera). J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2013, 112, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemes, A.R.; Davolos, C.C.; Legori, P.C.B.C.; Fernandes, O.A.; Ferre, J.; Lemos, M.V.F.; Desiderio, J.A. Synergism and antagonism between Bacillus thuringiensis Vip3A and Cry1 proteins in Heliothis virescens, Diatraea saccharalis and Spodoptera frugiperda. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e107196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Martínez, P.; Hernández-Rodríguez, C.S.; Rie, J.V.; Escriche, B.; Ferré, J. Insecticidal activity of Vip3Aa, Vip3Ad, Vip3Ae, and Vip3Af from Bacillus thuringiensis against lepidopteran corn pests. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2013, 113, 78–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Ji, T.; Kong, X.; Wu, K. Evaluation of the sensitivity of invasive Spodoptera frugiperda population in Yunnan Province to five commonly used Bt proteins. Plant Prot. 2019, 45, 15–20. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Liu, S.; Bai, S.; He, K.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, H.; Zhang, T.; Wang, Z. Toxicity of Cry- and Vip3Aa-Class Proteins and Their Interactions against Spodoptera frugiperda (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Toxins 2024, 16, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhang, D.; Zhao, S.; Wu, K. Susceptibilities of the invasive fall armyworm (Spodoptera frugiperda) to the insecticidal proteins of Bt maize in China. Toxins 2022, 14, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Chang, X.; Chang, X.; Wang, Z.; Natalie, F.; Angharad, M.R.G. Genetic and molecular mechanisms of Cry1Ab resistance in Ostrinia furnacalis (Guenée). Plant Prot. 2007, 5, 92–93. [Google Scholar]
- Kurtz, R.W. A review of Vip3A mode of action and effects on Bt cry protein-resistant colonies of Lepidopteran larvae. Southwest. Entomol. 2010, 35, 391–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.K.; Walters, F.S.; Hart, H.; Palekar, N.; Chen, J.S. The mode of action of the Bacillus thuringiensis vegetative insecticidal protein Vip3A differs from that of Cry1Ab delta-endotoxin. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 4648–4657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eghrari, K.; Oliveira, S.C.; Nascimento, A.M.; Queiroz, B.; Fatoretto, J.; De Souza, B.H.S.; Fernandes, O.A.; Môro, G.V. The implications of homozygous Vip3Aa20- and Cry1Ab-maize on Spodoptera frugiperda control. J. Pest. Sci. 2022, 95, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; Guo, J.; Head, G.P.; Price, P.A.; Huang, F. Phenotypic performance of nine genotypes of Cry1A.105/Cry2Ab2 dual-gene resistant fall armyworm on non-Bt and MON89034 maize. Pest. Manag. Sci. 2019, 75, 2124–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Storer, N.P.; Kubiszak, M.E.; King, J.E.; Thompson, G.D.; Santos, A.C. Status of resistance to Bt maize in Spodoptera frugiperda: Lessons from Puerto Rico. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2012, 110, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Qureshi, J.A.; Meagher, R.L., Jr.; Reisig, D.D.; Head, G.P.; Andow, D.A.; Ni, X.Z.; Kerns, D.; Buntin, G.D.; Niu, Y.; et al. Cry1F resistance in fall armyworm Spodoptera frugiperda: Single gene versus pyramided Bt maize. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e112958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omoto, C.; Bernardi, O.; Salmeron, E.; Sorgatto, R.J.; Dourado, P.M.; Crivellari, A.; Carvalho, R.; Willse, A.; Martinelli, S.; Head, G.P. Field-evolved resistance to Cry1Ab maize by Spodoptera frugiperda in Brazil. Pest. Manag. Sci. 2016, 72, 1727–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardi, O.; Bernardi, D.; Horikoshi, R.J.; Okuma, D.M.; Miraldo, L.L.; Fatoretto, J.; Medeiros, F.C.; Burd, T.; Omoto, C. Selection and characterization of resistance to the Vip3Aa20 protein from Bacillus thuringiensis in Spodoptera frugiperda. Pest. Manag. Sci. 2016, 72, 1794–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardi, O.; Bernardi, D.; Amado, D.; Sousa, R.S.; Fatoretto, J.; Medeiros, F.C.; Conville, J.; Burd, T.; Omoto, C. Resistance risk assessment of Spodoptera frugiperda (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) and Diatraea saccharalis (Lepidoptera: Crambidae) to Vip3Aa20 insecticidal protein expressed in corn. J. Econ. Entomol. 2015, 108, 2711–2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, S.A.; Guidolin, A.S.; Salmeron, E.; Kanno, R.H.; Padovez, F.E.O.; Fatorettob, J.C.; Omoto, C. Geographical distribution of Vip3Aa20 resistance allele frequencies in Spodoptera frugiperda (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) populations in Brazil. Pest. Manag. Sci. 2020, 76, 169–178. [Google Scholar]

| Bt Protein | N | Regression Equation | LC50 (95%FL) (μg cm−2) | LC95 (95%FL) (μg cm−2) | GIC50 (95%FL) (μg cm−2) | GIC95 (95%FL) (μg cm−2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M2CryAb-VIP3A | 720 | y = 1.246 + 2.012x | 0.024 (0.001~0.062) | 0.508 (0.217~14.296) | - | - |
| M2CryAb-VIP3A | 720 | y = 1.229 − 1.347x | - | - | 0.142 (0.120~0.162) | 0.556 (0.482~7.146) |
| Agronomic Trait | LD05 (2022) | Zheng58 (2022) | LD05 (2023) | Zheng58 (2023) | LD05 (2024) | Zheng58 (2024) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tasseling stage (d) | 52.4 ± 0.5 a | 52.2 ± 0.4 a | 52.3 ± 0.7 a | 51.9 ± 0.6 a | 52.3 ± 0.5 a | 52.2 ± 0.8 a |
| Silking stage (d) | 56.9 ± 0.6 a | 56.9 ± 0.6 a | 56.8 ± 0.4 a | 57.1 ± 0.3 a | 57.0 ± 0.8 a | 56.7 ± 1.0 a |
| Pollen stage (d) | 57.1 ± 0.3 a | 57.3 ± 0.5 a | 57.4 ± 0.5 a | 57.3 ± 0.7 a | 57.2 ± 0.4 a | 57.3 ± 0.7 a |
| Growth stage (d) | 109.0 ± 0.5 a | 109.1 ± 0.6 a | 109.2 ± 0.4 a | 109.2 ± 0.8 a | 109.3 ± 0.5 a | 108.9 ± 0.6 a |
| Plant height (cm) | 155.9 ± 1.4 a | 155.7 ± 1.3 a | 155.2 ± 1.1 a | 155.5 ± 1.4 a | 155.2 ± 1.1 a | 155.9 ± 1.3 a |
| Ear height (cm) | 54.4 ± 0.6 a | 54.3 ± 0.9 a | 54.3 ± 0.5 a | 54.5 ± 0.9 a | 54.4 ± 0.5 a | 54.5 ± 0.6 a |
| Rows per ear | 12.0 ± 0 a | 12.0 ± 0 a | 12.0 ± 0 a | 12.2 ± 0 a | 12.0 ± 0 a | 12.0 ± 0 a |
| Ear diameter (cm) | 3.84 ± 0.07 a | 3.87 ± 0.5 a | 3.82 ± 0.08 a | 3.86 ± 0.06 a | 3.85 ± 0.05 a | 3.84 ± 0.06 a |
| 100-kernel weight (g) | 34.5 ± 0.3 a | 34.3 ± 0.5 a | 34.4 ± 0.5 a | 34.6 ± 0.4 a | 34.4 ± 0.5 a | 34.5 ± 0.5 a |
| Pollen diameter (µm) | 89.7 ± 2.6 a | 89.9 ± 3.1 a | 89.4 ± 3.7 a | 89.8 ± 3.5 a | 91.6 ± 2.8 a | 90.8 ± 3.3 a |
| Temperature Treatment | Processing Time | Germination Rate of LD05 (%) (2022) | Germination Rate of Zheng58 (%) (2022) | Germination Rate of LD05 (%) (2023) | Germination Rate of Zheng58 (%) (2023) | Germination Rate of LD05 (%) (2024) | Germination Rate of Zheng58 (%) (2024) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| — | 0 min | 74.22 ± 2.04 a | 74.69 ± 2.07 a | 76.43 ± 2.62 a | 76.93 ± 1.73 a | 75.73 ± 3.01 a | 75.92 ± 1.77 a |
| 25 °C | 1 h | 76.23 ± 2.61 a | 75.45 ± 3.06 a | 74.96 ± 2.22 a | 74.40 ± 3.00 a | 75.25 ± 3.18 a | 75.93 ± 3.12 a |
| 3 h | 30.65 ± 1.88 a | 30.51 ± 1.63 a | 31.92 ± 2.14 a | 31.70 ± 2.90 a | 29.70 ± 2.01 a | 30.96 ± 2.74 a | |
| 6 h | 3.12 ± 0.28 a | 2.84 ± 0.26 a | 2.83 ± 0.22 a | 2.98 ± 0.30 a | 2.71 ± 0.33 a | 3.18 ± 0.22 a | |
| 30 °C | 1 h | 75.58 ± 2.80 a | 75.41 ± 3.82 a | 74.81 ± 4.31 a | 76.07 ± 3.96 a | 75.71 ± 3.19 a | 78.11 ± 2.56 a |
| 3 h | 24.67 ± 3.75 a | 26.10 ± 5.41 a | 23.63 ± 4.63 a | 26.53 ± 5.82 a | 25.41 ± 5.29 a | 23.28 ± 5.01 a | |
| 6 h | 0.00 ± 0.00 a | 0.00 ± 0.00 a | 0.00 ± 0.00 a | 0.00 ± 0.00 a | 0.00 ± 0.00 a | 0.00 ± 0.00 a | |
| 35 °C | 1 h | 58.35 ± 4.07 a | 59.53 ± 2.77 a | 63.44 ± 5.03 a | 60.91 ± 6.00 a | 61.74 ± 5.17 a | 57.35 ± 4.57 a |
| 3 h | 19.08 ± 3.70 a | 20.97 ± 4.92 a | 19.53 ± 4.26 a | 20.27 ± 3.70 a | 18.65 ± 3.53 a | 17.24 ± 4.01 a | |
| 6 h | 0.00 ± 0.00 a | 0.00 ± 0.00 a | 0.00 ± 0.00 a | 0.00 ± 0.00 a | 0.00 ± 0.00 a | 0.00 ± 0.00 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, W.; Gao, X.; Hou, X.; Ding, Z.; Meng, Z.; Yue, R. Efficacy of Transgenic Maize LD05 Against Fall Armyworm (Spodoptera frugiperda). Plants 2025, 14, 2504. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14162504
Li W, Gao X, Hou X, Ding Z, Meng Z, Yue R. Efficacy of Transgenic Maize LD05 Against Fall Armyworm (Spodoptera frugiperda). Plants. 2025; 14(16):2504. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14162504
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Wenlan, Xiang Gao, Xinwei Hou, Zhaohua Ding, Zhaodong Meng, and Runqing Yue. 2025. "Efficacy of Transgenic Maize LD05 Against Fall Armyworm (Spodoptera frugiperda)" Plants 14, no. 16: 2504. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14162504
APA StyleLi, W., Gao, X., Hou, X., Ding, Z., Meng, Z., & Yue, R. (2025). Efficacy of Transgenic Maize LD05 Against Fall Armyworm (Spodoptera frugiperda). Plants, 14(16), 2504. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14162504





