Differential Effects of Two Herbivore-Induced Plant Volatiles on the Oviposition of Chilo suppressalis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. 2-Heptanol and α-Cedrene Differentially Regulate Oviposition
2.2. Volatile-Induced Changes in Preoviposition Period and Adult Longevity
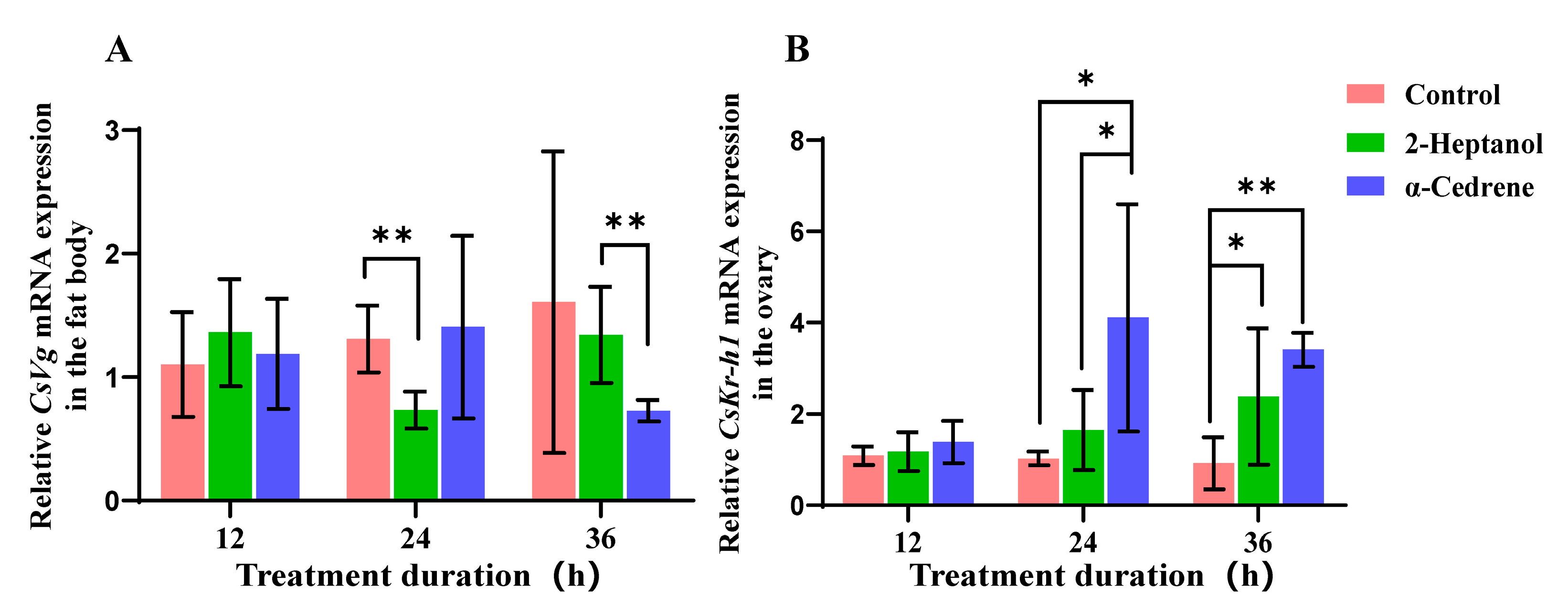
2.3. The Expression Levels of Vitellogenin (Vg) in the Fat Body and Krüppel Homolog 1 (Kr-h1) in the Ovaries
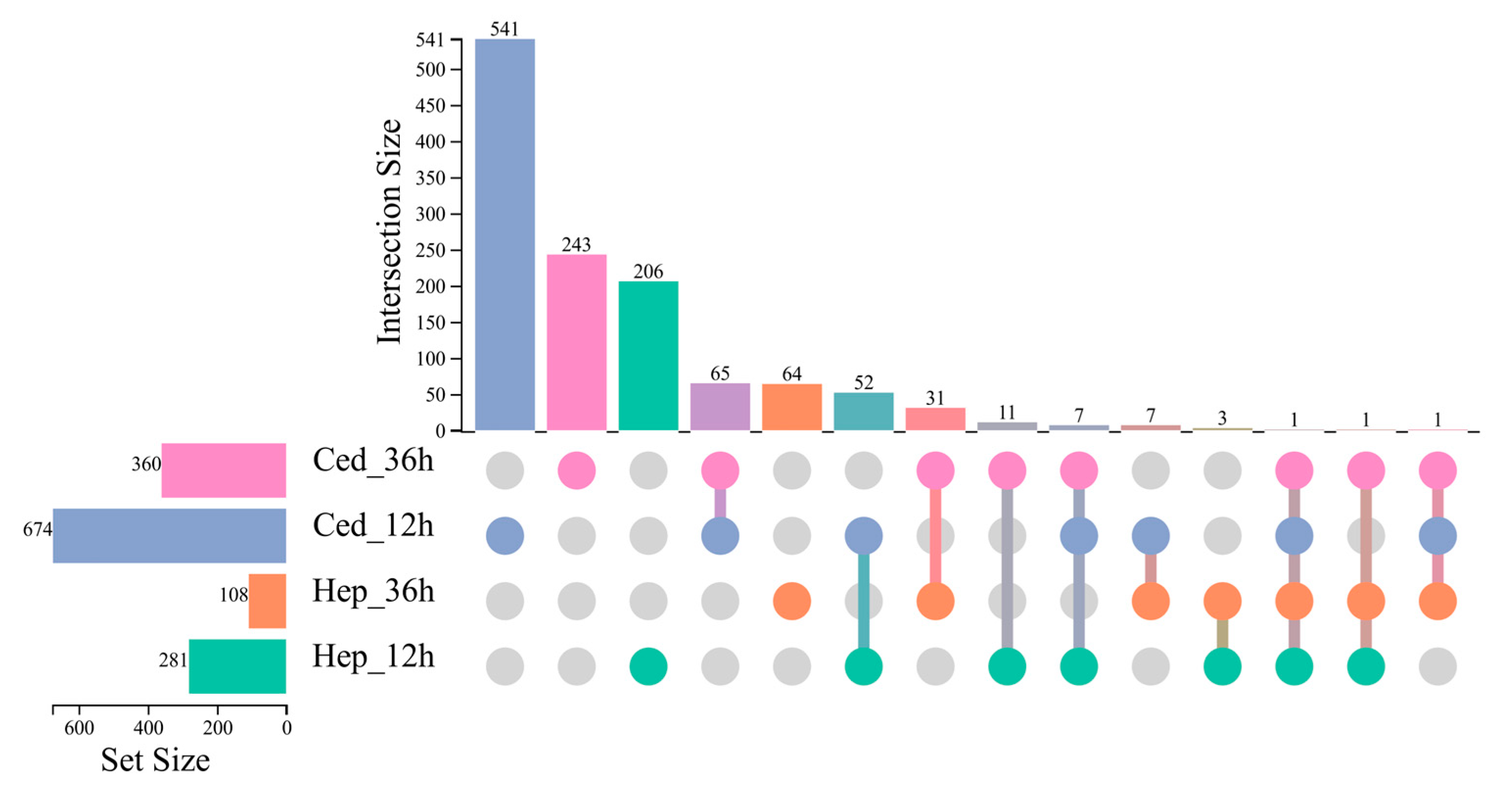
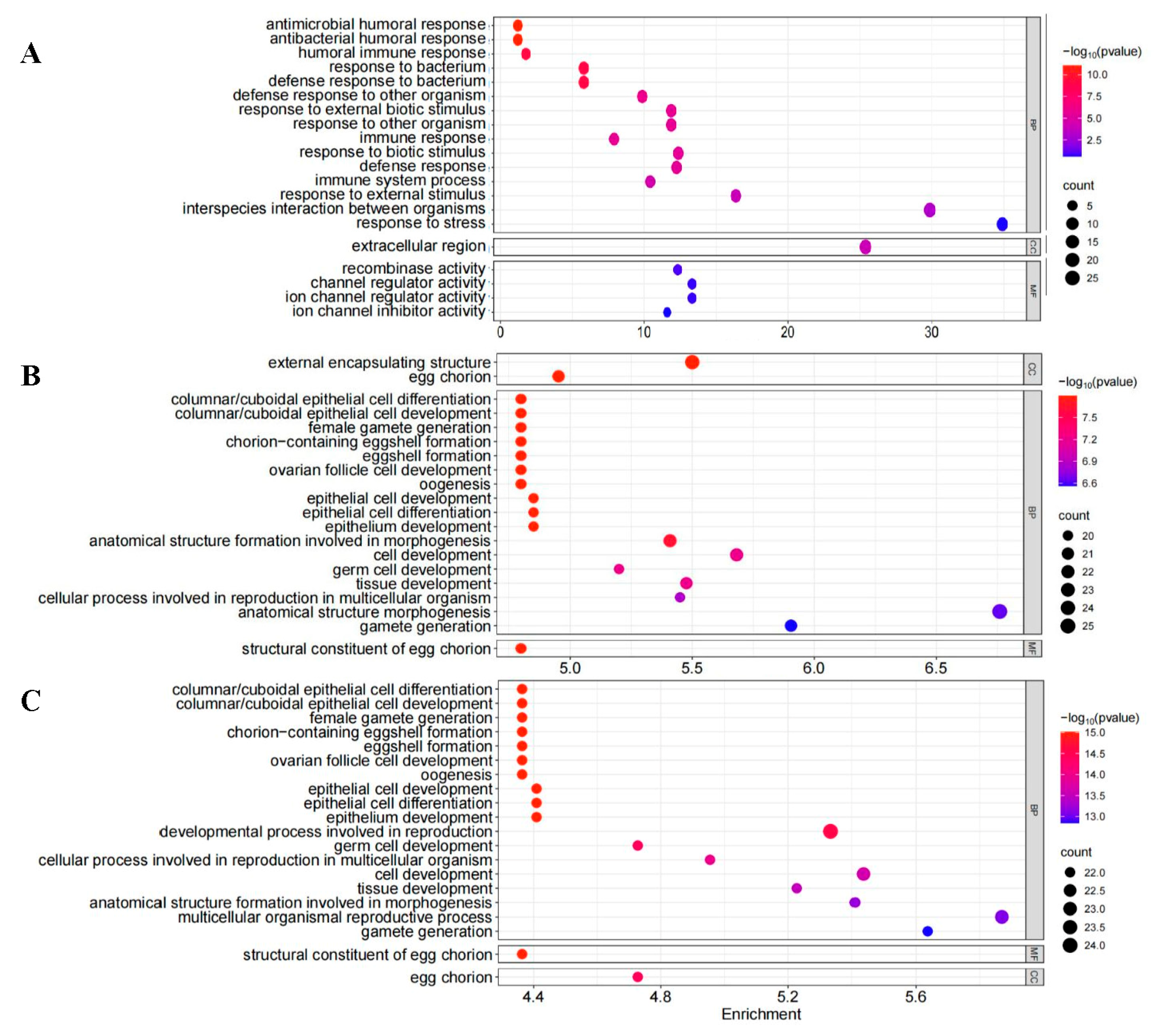
2.4. Transcriptome Analysis of C. suppressalis After Volatile Treatment
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. The Rice Stem Borer Strain
4.2. Decoy Treatment
4.3. Effects of Volatiles on Fecundity and Longevity of Female Adults
4.4. Sample Collection for High-Throughput Sequencing and qPCR
4.5. RNA Extraction and qPCR for Vg and Kr-h1 Gene Expression
4.6. Transcriptome Sequencing and Bioinformatics Analysis
4.7. Data Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HIPV | Herbivore-induced plant volatile |
| GLMM | Generalized linear mixed model |
| DEG | Differentially expressed gene |
References
- Nishida, R. Chemical ecology of insect-plant interactions: Ecological significance of plant secondary metabolites. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2014, 78, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binyameen, M.; Ali, Q.; Roy, A.; Schlyter, F. Plant volatiles and their role in insect olfaction. In Plant-Pest Interactions: From Molecular Mechanisms to Chemical Ecology; Singh, I.K., Singh, A., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2021; pp. 127–156. [Google Scholar]
- Danner, H.; Desurmont, G.A.; Cristescu, S.M.; van Dam, N.M. Herbivore-induced plant volatiles accurately predict history of coexistence, diet breadth, and feeding mode of herbivores. New Phytol. 2017, 220, 726–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.; Du, L.; Liu, Q.; Hu, X.; Ye, W.; Turlings, T.C.J.; Li, Y. Stemborer-induced rice plant volatiles boost direct and indirect resistance in neighboring plants. New Phytol. 2023, 237, 2375–2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turlings, T.C.J.; Erb, M. Tritrophic interactions mediated by herbivore-induced plant volatiles: Mechanisms, ecological relevance, and application potential. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2018, 63, 433–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Moraes, C.M.; Mescher, M.C.; Tumlinson, J.H. Caterpillar-induced nocturnal plant volatiles repel conspecific females. Nature 2001, 410, 577–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatano, E.; Saveer, A.M.; Borrero-Echeverry, F.; Strauch, M.; Zakir, A.; Bengtsson, M.; Ignell, R.; Anderson, P.; Becher, P.G.; Witzgall, P.; et al. A herbivore-induced plant volatile interferes with host plant and mate location in moths through suppression of olfactory signalling pathways. BMC Biol. 2015, 13, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wei, J.; Yi, T.; Li, Y.Y.; Xu, T.; Chen, L.; Xu, H. A green leaf volatile, (Z)-3-hexenyl-acetate, mediates differential oviposition by Spodoptera frugiperda on maize and rice. BMC Biol. 2023, 21, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Saha, T.T.; Zou, Z.; Raikhel, A.S. Regulatory pathways controlling female insect reproduction. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2018, 63, 489–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardoso-Jaime, V.; Broderick, N.A.; Maya-Maldonado, K. Metal ions in insect reproduction: A crosstalk between reproductive physiology and immunity. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2022, 52, 100924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourtzis, K. Wolbachia-based technologies for insect pest population control. In Transgenesis and the Management of Vector-Borne Disease; Aksoy, S., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 104–113. [Google Scholar]
- Tabashnik, B.E.; Liesner, L.R.; Ellsworth, P.C.; Unnithan, G.C.; Fabrick, J.A.; Naranjo, S.E.; Li, X.; Dennehy, T.J.; Antilla, L.; Staten, R.T.; et al. Transgenic cotton and sterile insect releases synergize eradication of pink bollworm a century after it invaded the United States. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2019115118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, C.; Leigh, S.; Alphey, L.; Haerty, W.; Chapman, T. Reproductive interference and Satyrisation: Mechanisms, outcomes and potential use for insect control. J. Pest. Sci. 2022, 95, 1023–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Jiang, J.; Pang, Z.; Ma, W.; Jiang, Y.; Fu, Y.; Liu, Y. Tracking existing factors directly affecting the reproduction of bumblebees: Current knowledge. Insects 2024, 15, 654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anholt, R.R.H.; O’Grady, P.; Wolfner, M.F.; Harbison, S.T. Evolution of reproductive behavior. Genetics 2020, 214, 49–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Koppenhagen, N.; Gourgoulianni, N.; Rohner, P.T.; Roy, J.; Wegmann, A.; Blanckenhorn, W.U. Sublethal effects of the parasiticide ivermectin on male and female reproductive and behavioural traits in the yellow dung fly. Chemosphere 2020, 242, 125240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leith, N.T.; Macchiano, A.; Moore, M.P.; Fowler-Finn, K.D. Temperature impacts all behavioral interactions during insect and arachnid reproduction. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2021, 45, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Jander, G.; Ort, D. Molecular ecology of plant volatiles in interactions with insect herbivores. J. Exp. Bot. 2022, 73, 449–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, R.; Zhao, D.D.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, L.Q.; Wang, X.; Gao, C.F.; Wu, S.F. Monitoring and mechanisms of insecticide resistance in Chilo suppressalis (Lepidoptera: Crambidae), with special reference to diamides. Pest. Manag. Sci. 2016, 73, 1169–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Shelton, A.; Ye, G.Y. Insect-resistant genetically modified rice in China: From research to commercialization. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2011, 56, 81–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.-z.; Klein, M.G. Efficacy of insecticides against the rice stem-borer, Chilo suppressalis (Walker) (Lepidoptera: Crambidae), and use of sex pheromones to time accurately the yearly application. Int. J. Pest. Manag. 2012, 58, 354–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Li, S.; Li, J.; Wang, C.Y.; Yang, L.; Li, J.; Meng, Y.; Tan, X.Y.; Jing, M.F.; Luo, G.H.; et al. Ferritin from striped stem borer (Chilo suppressalis) iral secretion acts as an effector helping to maintain iron homoeostasis and impair defenses in rice. Plant Cell Environ. 2025, 48, 3735–3749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, X.; Liu, S.; Li, H.; Danso Ofori, A.; Yi, X.; Zheng, A. Defense strategies of rice in response to the attack of the herbivorous Insect, Chilo suppressalis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, T.; Bagni, C.; Sutherland, J.D.; Kafatos, F.C. The transcriptional factor CF2 is a mediator of EGF-R-activated dorsoventral patterning in Drosophila oogenesis. Gene Dev. 1996, 10, 1411–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Z.Z.; Zhu, H.X.; Wu, B.; Zhang, A.Z.; Wang, H.X.; Cheng, Y.; Zhao, H.; Li, J.Y.; Liu, M.; Gao, J.A. Cathepsin B plays a role in spermatogenesis and sperm maturation through regulating autophagy and apoptosis in mice. Peerj 2022, 10, e14472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, W.L.; Tsao, S.M.; Hays, A.R.; Walter, R.; Chen, J.S.; Snigirevskaya, E.S.; Raikhel, A.S. Mosquito cathepsin B-like protease involved in embryonic degradation of vitellin is produced as a latent extraovarian precursor. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 13311–13321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.S.; Meng, J.Y.; Yang, L.; Zhang, C.Y. Identification and expression analysis of cathepsin B genes in (Hemiptera: Aphididae) and their response to environmental stresses. Bull. Entomol. Res. 2025, 115, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Li, M.M.; Ma, J.Y.; Wang, X.X.; Liu, J.Z. Effects of temperature on cathepsin B, cathepsin D and acid phosphatase during embryo development of the hard tick. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2023, 89, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.X.; Li, H.; Guo, X.R.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, L.J.; Wang, G.P.; Li, W.Z.; Zhao, M. Functional roles of two novel P450 genes in the adaptability of to three commonly used pesticides. Front. Physiol. 2023, 14, 1186804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.; Dong, Q.Q.; Tang, X.Y.; Zhu, X.H.; Deng, D.; Ding, Y.T.; Ahmad, S.; Zhang, W.; Mao, Z.Y.; Zhao, X.D.; et al. CYP303A1 regulates molting and metamorphosis through 20E signaling in Nilaparvata lugens Stål (Hemiptera: Delphacidae). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 281, 136234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macedo-Silva, A.; Rios, T.; Ramos, I.; Majerowicz, D. Lipophorin receptor knockdown reduces hatchability of kissing bug Rhodnius prolixus eggs. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2025, 176, 104221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, Y.; Hu, X.; Peng, Y.; Wu, K.; Romeis, J.; Li, Y. Bt rice plants may protect neighbouring non-Bt rice plants against the striped stem borer, Chilo suppressalis. Proc. R. Soc. B 2018, 285, 20181283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmo, E.B.S.; Macedo-Rego, R.C.; Penaflor, M. Herbivory by multiple arthropods does not hinder the attraction of natural enemies to plant volatiles: Insights from a meta-analysis. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2025, 69, 101347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paudel Timilsena, B.; Seidl-Adams, I.; Tumlinson, J.H. Herbivore-specific plant volatiles prime neighboring plants for nonspecific defense responses. Plant Cell Environ. 2019, 43, 787–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anastasaki, E.; Drizou, F.; Milonas, P.G. Electrophysiological and oviposition responses of Tuta absoluta females to herbivore-induced volatiles in tomato plants. J. Chem. Ecol. 2018, 44, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakir, A.; Bengtsson, M.; Sadek, M.M.; Hansson, B.S.; Witzgall, P.; Anderson, P. Specific response to herbivore-inducedde novosynthesized plant volatiles provide reliable information for host plant selection in a moth. J. Exp. Biol. 2013, 216, 3257–3263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Yan, L.; Ren, Q.I.N.; Li, C.; Ge, F.; Kang, L.E. Antagonism between herbivore-induced plant volatiles and trichomes affects tritrophic interactions. Plant Cell Environ. 2012, 36, 315–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molnár, B.P.; Tóth, Z.; Fejes-Tóth, A.; Dekker, T.; Kárpáti, Z. Electrophysiologically-active maize volatiles attract gravid female European corn borer, Ostrinia nubilalis. J. Chem. Ecol. 2015, 41, 997–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Zeng, F.; Bedoukian, R.H.; Leal, W.S. DEET and other repellents are inhibitors of mosquito odorant receptors for oviposition attractants. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2019, 113, 103224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, J.; Guo, P.; Li, H.; Wei, C.; Liu, Q.; Gong, Z.; Duan, Y.; Li, T.; Jiang, Y.; Feng, H.; et al. Low barometric pressure enhances tethered-flight performance and reproductive of the oriental armyworm, Mythimna separata (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2021, 114, 620–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettinger, J.C.; Nasiri Moghadam, N.; Holmstrup, M.; Manenti, T.; Brandt Mouridsen, M.; Pertoldi, C.; Loeschcke, V. The role of storage lipids in the relation between fecundity, locomotor activity, and lifespan of Drosophila melanogaster longevity-selected and control lines. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0130334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Yang, L.; He, Q.; Zhou, S. Regulatory mechanisms of vitellogenesis in insects. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 8, 593613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diksha; Singh, S.; Mahajan, E.; Sohal, S.K. Immunomodulatory, cyto-genotoxic, and growth regulatory effects of nerolidol on melon fruit fly, Zeugodacus cucurbitae (Coquillett) (Diptera: Tephritidae). Toxicon 2023, 233, 107248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Zeng, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, X.; Han, Y.; Zeng, R.; Song, Y.; Chen, D.; Lin, Y. Maize herbivore-induced volatiles enhance xenobiotic detoxification in larvae of Spodoptera frugiperda and S. litura. Plants 2025, 14, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, L.; Li, S.; Liu, P.; Peng, Y.; Hou, M. New artificial diet for continuous rearing of Chilo suppressalis (Lepidoptera: Crambidae). Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 2012, 105, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anders, S.; Huber, W. Differential expression analysis for sequence count data. Nat. Prec. 2010, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, M.D.; Wakefield, M.J.; Smyth, G.K.; Oshlack, A. Gene ontology analysis for RNA-seq: Accounting for selection bias. Genome Biol. 2010, 11, R14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, X.; Liu, C.; Jia, X.; Zhang, C.; Han, L.; Cai, W.; Li, Y. Differential Effects of Two Herbivore-Induced Plant Volatiles on the Oviposition of Chilo suppressalis. Plants 2025, 14, 2384. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14152384
Yang X, Liu C, Jia X, Zhang C, Han L, Cai W, Li Y. Differential Effects of Two Herbivore-Induced Plant Volatiles on the Oviposition of Chilo suppressalis. Plants. 2025; 14(15):2384. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14152384
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Xiaowei, Chang Liu, Xixi Jia, Chen Zhang, Lanzhi Han, Wanlun Cai, and Yunhe Li. 2025. "Differential Effects of Two Herbivore-Induced Plant Volatiles on the Oviposition of Chilo suppressalis" Plants 14, no. 15: 2384. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14152384
APA StyleYang, X., Liu, C., Jia, X., Zhang, C., Han, L., Cai, W., & Li, Y. (2025). Differential Effects of Two Herbivore-Induced Plant Volatiles on the Oviposition of Chilo suppressalis. Plants, 14(15), 2384. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14152384






