The Impact of Harvest Season on Oolong Tea Aroma Profile and Quality
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Seasonal Variation in Volatile Profiles of Tieguanyin Oolong Tea
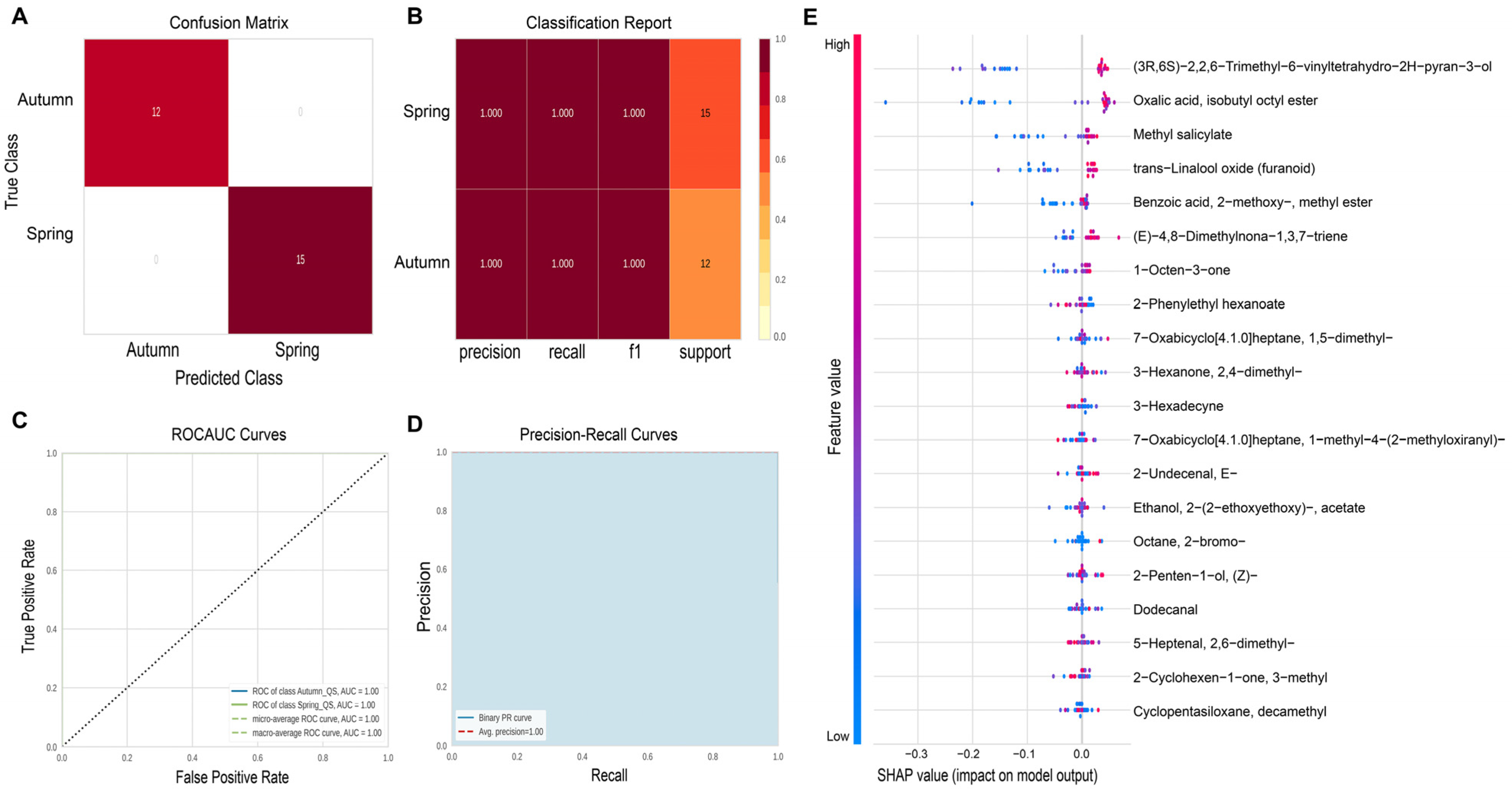
2.2. Machine Learning Algorithms for Distinguishing Seasons
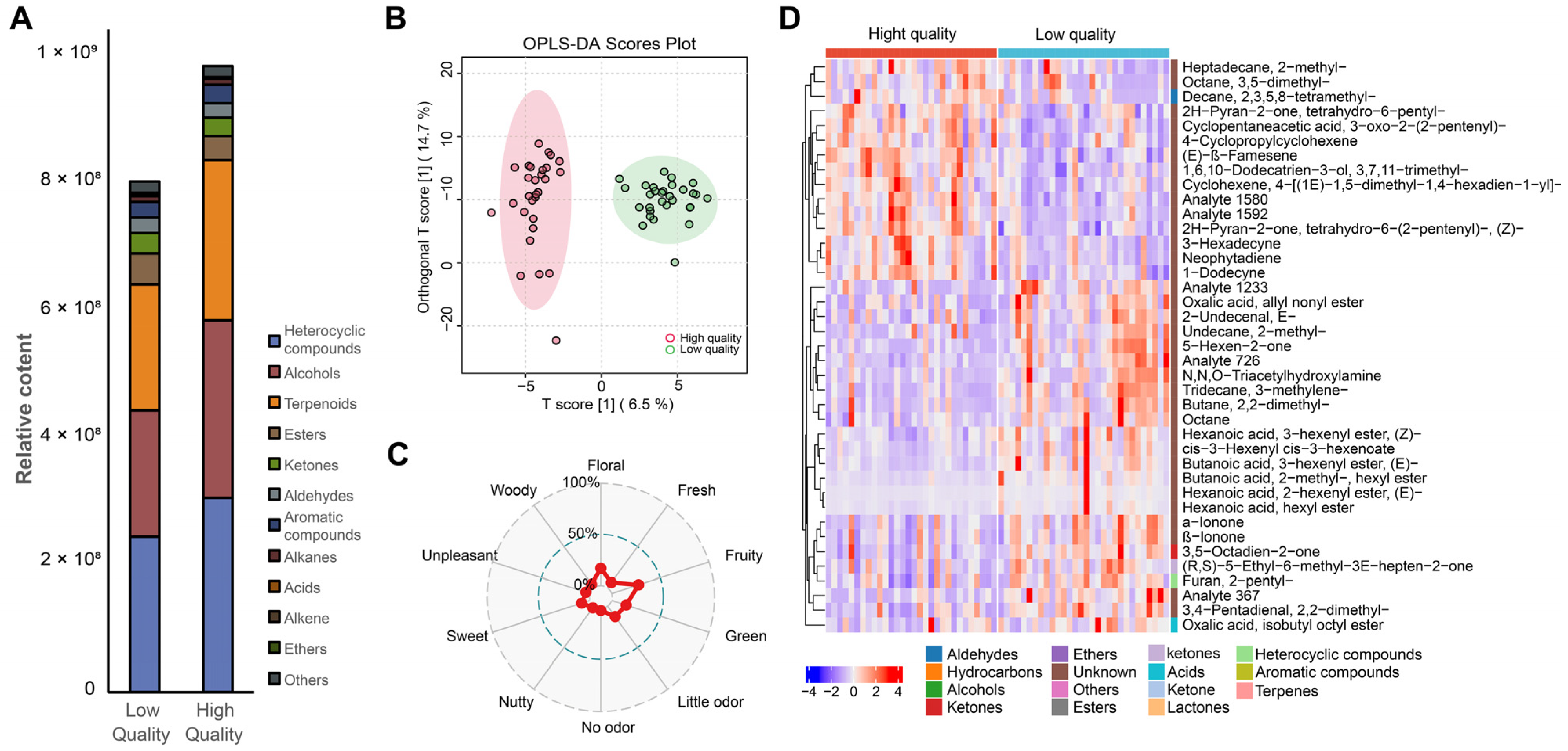
2.3. Relationship Between Volatile Metabolites and Sensory Quality
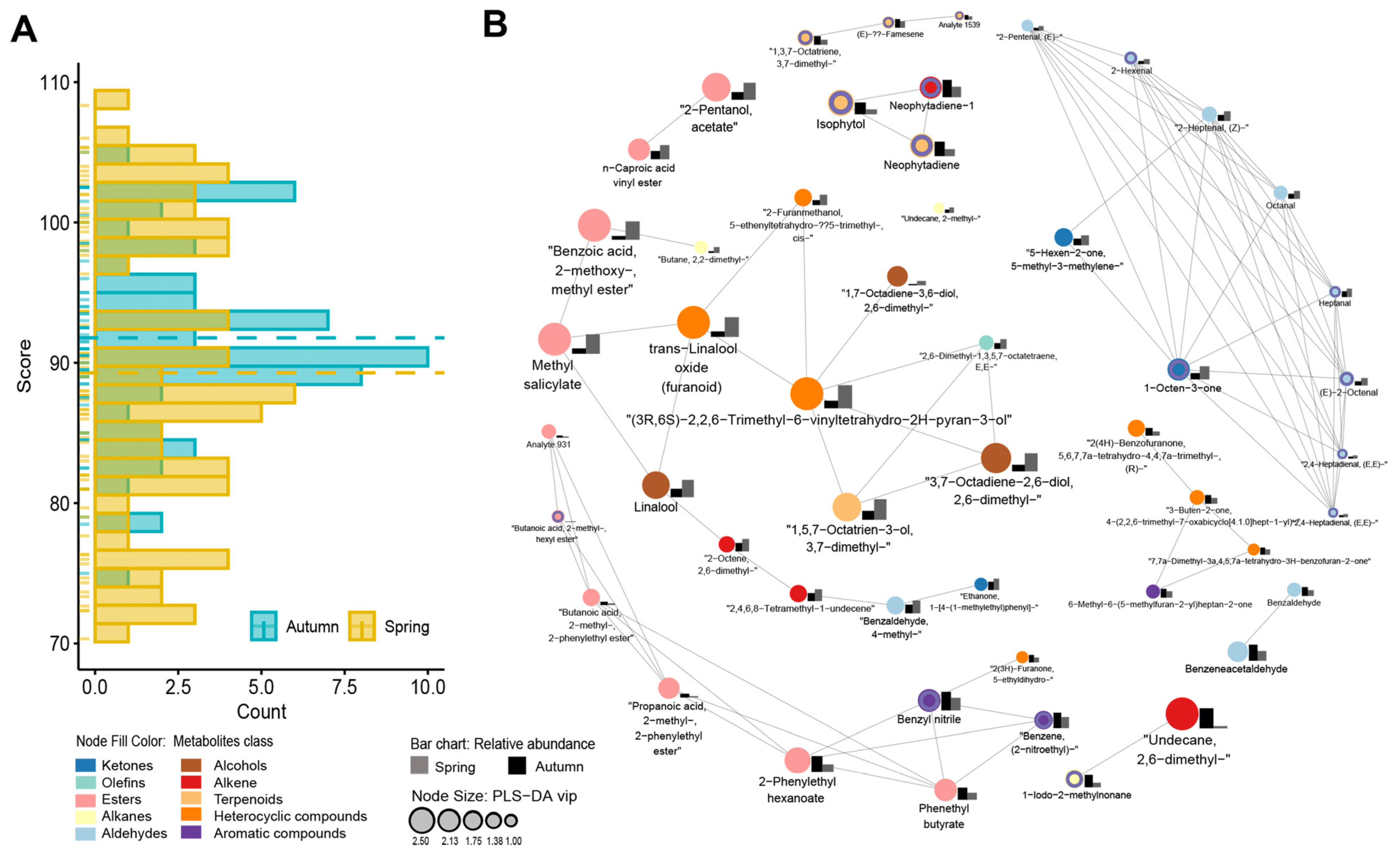
2.4. Combined Aroma, Seasonality, and Sensory Data
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Reagents and Materials
3.2. Sample Collection
3.3. Untargeted Volatile Metabolite Analysis
3.4. Aroma Sensory Evaluation
3.5. Statistical Analysis
3.6. Machine Learning Modeling
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, P.; Li, Z.; Ouyang, L.; Gong, X.; Meng, P.; Dai, M.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y. A multi-element stable isotope approach coupled with chemometrics for the determination of Tieguanyin tea geographical origin and harvest season. Anal. Methods 2019, 11, 346–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Gao, S.; Du, Z.; Jin, S.; Yang, Z.; Xu, T.; Zheng, C.; Liu, Y. Seasonal variations and sensory profiles of oolong tea: Insights from metabolic analysis of Tieguanyin cultivar. Food Chem. 2025, 462, 140977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, X.; Wu, Y.; Qu, F.; Liu, L.; Wang, B.; Wang, P.; Zhang, X. HS−SPME/GC−MS Reveals the Season Effects on Volatile Compounds of Green Tea in High−Latitude Region. Foods 2022, 11, 3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhou, C.; Xu, K.; Tian, C.; Zhang, M.; Lu, L.; Zhu, C.; Lai, Z.; Guo, Y. A Comprehensive Investigation of Macro-Composition and Volatile Compounds in Spring-Picked and Autumn-Picked White Tea. Foods 2022, 11, 3628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, P.; Huang, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhao, X.; Huang, H.; Zhong, N.; Zheng, H.; Chen, Q. Difference in Aroma Components of Black Teas Processed on Different Dates in the Spring Season. Foods 2023, 12, 4368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gianturco, M.A.; Biggers, R.E.; Ridling, B.H. Seasonal variations in the composition of the volatile constituents of black tea. A numerical approach to the correlation between composition and quality of tea aroma. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1974, 22, 758–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Fu, Y.; Huang, J.; Wang, J.; Jin, S.; Yin, J.; Xu, Y. Comparative analysis of volatile vompounds in Tieguanyin with different types based on HS-SPME-GC-MS. Foods 2022, 11, 1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Fu, Y.Q.; Liu, Y.Y.; Huang, J.S.; Chen, J.X.; Yin, J.F.; Jin, S.; Sun, W.J.; Xu, Y.Q. Comparative analysis of different grades of Tieguanyin oolong tea based on metabolomics and sensory evaluation. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 174, 114423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; He, W.; He, Y.; Chen, Q.; Gao, Y.; Geng, J.; Zhu, Z.-R. Formation of 8-hydroxylinalool in tea plant Camellia sinensis var. Assamica ‘Hainan dayezhong’. Food Chem. Mol. Sci. 2023, 6, 100173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, J.; Fu, X.; Zhou, Y.; Katsuno, T.; Mei, X.; Deng, R.; Xu, X.; Zhang, L.; Dong, F.; Watanabe, N.; et al. Does Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Glycosidically Bound Volatile Compounds Really Contribute to the Formation of Volatile Compounds During the Oolong Tea Manufacturing Process? J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 6905–6914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, E.R.; Li, X.; Wei, J.-P.; Kfoury, N.; Morimoto, J.; Guo, M.; Agyei, A.; Robbat, A.; Ahmed, S.; Cash, S.B.; et al. Changes in Tea Plant Secondary Metabolite Profiles as a Function of Leafhopper Density and Damage. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Watanabe, N.; Yang, Z. Understanding the biosyntheses and stress response mechanisms of aroma compounds in tea (Camellia sinensis) to safely and effectively improve tea aroma. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, 2321–2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Li, J.; Liu, X.; Liu, C.; Qian, J.; Yang, J.; Zhou, X.; Jia, Y.; Tang, J.; Zeng, L. Characterization of Key Odorants in Lingtou Dancong Oolong Tea and Their Differences Induced by Environmental Conditions from Different Altitudes. Metabolites 2022, 12, 1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Cai, J.; Zheng, P.; Yuan, Y.; Tsewang, W.; Chen, Y.; Xiao, X.; Liao, J.; Sun, B.; Liu, S. Quantitatively Unravelling the Impact of High Altitude on Oolong Tea Flavor from Camellia sinensis Grown on the Plateaus of Tibet. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouinguené, S.P.; Turlings, T.C.J. The Effects of Abiotic Factors on Induced Volatile Emissions in Corn Plants. Plant Physiol. 2002, 129, 1296–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawat, R.; Gulati, A. Seasonal and clonal variations in some major glycosidic bound volatiles in Kangra tea (Camellia sinensis (L.) O. Kuntze). Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2007, 226, 1241–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; Sun, J.; Lu, B.; Chen, Q.; Xun, W.; Jin, Y. Classification of oolong tea varieties based on hyperspectral imaging technology and BOSS-LightGBM model. J. Food Process Eng. 2019, 42, e13289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Sun, J.; Wu, X.; Lu, B.; Wu, M.; Dai, C. Grade Identification of Tieguanyin Tea Using Fluorescence Hyperspectra and Different Statistical Algorithms. J. Food Sci. 2019, 84, 2234–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Wen, Y.; Huang, J.; Xiong, A.; Wen, J.; Li, H.; Huang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Ai, S.; Wu, R. A novel strategy of near-infrared spectroscopy dimensionality reduction for discrimination of grades, varieties and origins of green tea. Vib. Spectrosc. 2019, 105, 102984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Wang, R.; Wang, M.; Gao, K.; Duc Duy, N.; Wei, G.-W. Boosting Tree-Assisted Multitask Deep Learning for Small Scientific Datasets. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2020, 60, 1235–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Zheng, C.; Guo, S.; Gao, F.; Wang, X.; Du, Z.; Gao, F.; Su, F.; Zhang, W.; Yu, X.; et al. Metabolomics integrated with machine learning to discriminate the geographic origin of Rougui Wuyi rock tea. NPJ Sci. Food 2023, 7, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, J.; Zhao, M.; Jing, T.; Zhang, M.; Lu, M.; Yu, G.; Wang, J.; Guo, D.; Pan, Y.; Hoffmann, T.D.; et al. Volatile compound-mediated plant–plant interactions under stress with the tea plant as a model. Hortic. Res. 2023, 10, uhad143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Xu, Y.; Wu, J.; Wen, J.; Yu, Y.; An, K.; Zou, B. GC-IMS and olfactometry analysis on the tea aroma of Yingde black teas harvested in different seasons. Food Res. Int. 2021, 150, 110784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Chen, F.; Wang, L.; Niu, Y.; Xiao, Z. Evaluation of the synergism among volatile compounds in Oolong tea infusion by odour threshold with sensory analysis and E-nose. Food Chem. 2017, 221, 1484–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, Y.; Kubota, K. Sensory evaluation of the synergism among odorants present in concentrations below their odor threshold in a Chinese jasmine green tea infusion. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2005, 49, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Zhou, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, D.; Ntezimana, B.; Zhu, J.; Wang, X.; Xu, W.; Wen, X.; Chen, Y.; et al. The aroma characteristics of oolong tea are jointly determined by processing mode and tea cultivars. Food Chem. 2023, 18, 100730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Li, Y.; Zhou, J.; Yu, X.; Zhang, D.; Chen, Y.; Ni, D.; Yu, Z. Study on the Suitability of Tea Cultivars for Processing Oolong Tea from the Perspective of Aroma Based on Olfactory Sensory, Electronic Nose, and GC-MS Data Correlation Analysis. Foods 2022, 11, 2880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldermann, S.; Yang, Z.; Katsuno, T.; Tu, V.A.; Mase, N.; Nakamura, Y.; Watanabe, N. Discrimination of Green, Oolong, and Black Teas by GC-MS Analysis of Characteristic Volatile Flavor Compounds. Am. J. Anal. Chem. 2014, 5, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Dai, Y.; Guo, Y.n.; Xu, H.; Wang, X. Volatile profile analysis and quality prediction of Longjing tea (Camellia sinensis) by HS-SPME/GC-MS. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2012, 13, 972–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Xie, P.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, H.; Wang, S.; Han, W.; Wu, R.; Li, X.; Guan, Y.; et al. New Insights into Stress-Induced β-Ocimene Biosynthesis in Tea (Camellia sinensis) Leaves during Oolong Tea Processing. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 11656–11664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Du, Z.; Wang, X.; Wu, R.; Zheng, C.; Han, W.; Liu, L.; Gao, F.; Liu, G.; Liu, B.; et al. From heat to flavor: Unlocking new chemical signatures to discriminate Wuyi rock tea under light and moderate roasting. Food Chem. 2024, 431, 137148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 30357.2-2013; Oolong Tea—Part 2: Tieguanyin. State Administration for Market Regulation: Beijing, China; National Standardization Administration: Beijing, China, 2013. (In Chinese)
- Worley, B.; Powers, R. Multivariate Analysis in Metabolomics. Curr. Metabolomics 2013, 1, 92–107. [Google Scholar]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, C.; Gao, S.; Wang, X.; Yang, Z.; Zhou, J.; Liu, Y. The Impact of Harvest Season on Oolong Tea Aroma Profile and Quality. Plants 2025, 14, 2378. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14152378
Zheng C, Gao S, Wang X, Yang Z, Zhou J, Liu Y. The Impact of Harvest Season on Oolong Tea Aroma Profile and Quality. Plants. 2025; 14(15):2378. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14152378
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Chao, Shuilian Gao, Xiaxia Wang, Zhenbiao Yang, Junling Zhou, and Ying Liu. 2025. "The Impact of Harvest Season on Oolong Tea Aroma Profile and Quality" Plants 14, no. 15: 2378. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14152378
APA StyleZheng, C., Gao, S., Wang, X., Yang, Z., Zhou, J., & Liu, Y. (2025). The Impact of Harvest Season on Oolong Tea Aroma Profile and Quality. Plants, 14(15), 2378. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14152378





