Change in C, N, and P Characteristics of Hypericum kouytchense Organs in Response to Altitude Gradients in Karst Regions of SW China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Changes in C, N, and P Contents and Ratios
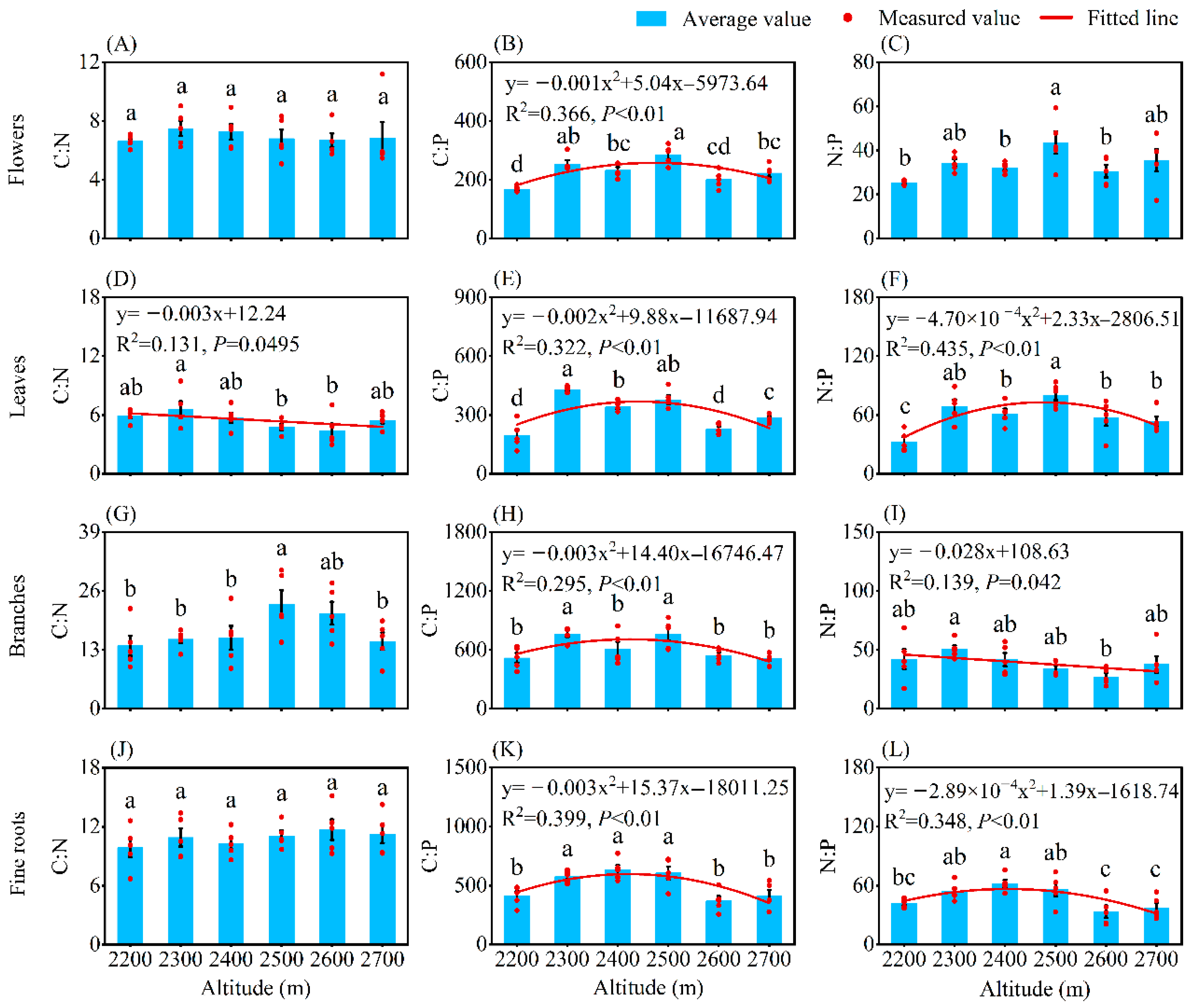
2.2. Altitudinal Patterns of C, N, and P Contents
2.3. Altitudinal Patterns of C, N, and P Ratios
2.4. Ecological Stoichiometric Homeostasis
2.5. Correlation Relationships Among C, N, and P Contents and Ratios
3. Discussion
3.1. Variations in Element Contents and Stoichiometric Ratios of H. kouytchense Shrublands in Karst Regions
3.2. Altitudinal Effects on Element Contents and Stoichiometric Ratios of H. kouytchense Shrublands
3.3. Relationship Between Plant Organs and Soil
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Research Area
4.2. Experimental Design and Sample Collection
4.3. Chemical Element Determination
4.4. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tang, X.G.; Xiao, J.F.; Ma, M.G.; Yang, H.; Li, X.; Ding, Z.; Yu, P.J.; Zhang, Y.G.; Wu, C.Y.; Huang, J.; et al. Satellite evidence for China’s leading role in restoring vegetation productivity over global karst ecosystems. For. Ecol. Manag. 2022, 507, 120000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.H.; Qi, X.K.; Wang, K.L.; Zhang, M.Y.; Yue, Y.M. The application of geospatial techniques in monitoring karst vegetation recovery in southwest China: A review. Prog. Phys. Geog. 2017, 41, 450–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.G.; Wang, X.D.; Wang, Z.Y.; Zhang, X.M.; Chen, C.; Liu, H.F. The challenge of soil loss control and vegetation restoration in the karst area of southwestern China. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2020, 8, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Ettorre, U.S.; Liso, I.S.; Parise, M. Desertification in karst areas: A review. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2024, 253, 104786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.N.; Huang, Y.; Wu, F.; Liu, W.J.; Ning, Y.Q.; Huang, Z.R.; Tang, S.Q.; Liang, Y. Plant adaptability in karst regions. J. Plant Res. 2021, 134, 889–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.H.; Zhao, N.; Liu, C.C.; Yang, H.; Li, M.L.; Yu, G.R.; Wilcox, K.; Yu, Q.; He, N.P. C:N:P stoichiometry in China’s forests: From organs to ecosystems. Funct. Ecol. 2018, 32, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, D.S.; Reich, P.B.; Chen, H.Y.H.; Xiang, Y.Z.; Luo, Y.Q.; Shen, Y.; Meng, C.; Han, W.X.; Niu, S.L. Global changes alter plant multi-element stoichiometric coupling. New Phytol. 2019, 221, 807–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivera-Viciedo, D.; Oliveira, K.S.; Prado, R.D.M.; Habermann, E.; Martínez, C.A.; Zanine, A.D.M. Silicon uptake and utilization on Panicum maximum grass modifies C:N:P stoichiometry under warming and soil water deficit. Soil Tillage Res. 2024, 235, 105884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koerselman, W.; Meuleman, A.F.M. The vegetation N:P ratio: A new tool to detect the nature of nutrient limitation. J. Appl. Ecol. 1996, 33, 1441–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.J.; Huang, J.Y.; Na, X.F.; Huang, S.Y.; Fang, Z.; Zhang, S.X.; Zhou, Z.C.; Wang, B. Variations in plant-microbe-soil C:N:P stoichiometry along a 900-year age gradient in Torreya grandis ‘Merrillii’ plantations in Southeast China. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2024, 8, 1397393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Wilcox, K.; La Pierre, K.; Knapp, A.K.; Han, X.G.; Smith, M.D. Stoichiometric homeostasis predicts plant species dominance, temporal stability, and responses to global change. Ecology 2015, 96, 2328–2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sistla, S.A.; Schimel, J.P. Stoichiometric flexibility as a regulator of carbon and nutrient cycling in terrestrial ecosystems under change. New Phytol. 2012, 196, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, J.; Zhou, J.; Yang, F.G.; Li, Z.; Dong, R.; Horne, D.; Lopez, I.; Zhou, Z.B.; Chen, J.H. Alternations in the element stoichiometry of the grasses drive the aboveground C:N:P ratio of an agriculturally improved pasture on karst in response to differential N and P fertilization. Plant Soil 2024, 504, 271–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.B.; Zhou, C.Y.; Lv, W.Q.; Dai, L.H.; Tang, J.G.; Zhou, S.Q.; Huang, L.H.; Li, A.D.; Zhang, J.L. Comparative study of the stoichiometric characteristics of karst and non-karst forests in Guizhou, China. J. For. Res. 2019, 30, 799–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.J.; Wang, P.; Sheng, M.Y.; Tian, J. Ecological stoichiometry and environmental influencing factors of soil nutrients in the karst rocky desertification ecosystem, Southwest China. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2018, 16, e00449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Huang, X.X.; Chen, S.Y.; Hu, C.; Zhong, C.F.; Xu, C.H.; Zhang, Z.H. Biotic and abiotic factors affecting soil C, N, P and their stoichiometries under different land-use types in a karst agricultural watershed, China. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.; Li, D.J.; Xiao, K.C.; Tang, H.M.; Xiao, X.P.; Li, C. Difference in total N and its aggregate-associated N following cropland restoration in a karst region, Southwest China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 50759–50771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.H.; Zheng, W.; Zhong, X.P.; Ying, B. Stoichiometric characteristics in Zanthoxylum planispinum var. dintanensis plantation of different ages. Agron. J. 2021, 113, 685–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.J.; Sheng, M.Y.; Bai, Y.X.; Jie, Y.; Xiao, H.L. Response of C, N, and P stoichiometry characteristics of Broussonetia papyrifera to altitude gradients and soil nutrients in the karst rocky ecosystem, SW China. Plant Soil 2022, 475, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.B.; Zamanian, K.; Schleuss, P.M.; Zarebanadkouki, M.; Kuzyakov, Y. Degradation of Tibetan grasslands: Consequences for carbon and nutrient cycles. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 252, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Zhang, C.C.; Deng, J.; Zhang, B.W.; Chen, F.S.; Chen, W.; Fang, X.M.; Li, J.J.; Zu, K.L.; Bu, W.S. Response of tree growth to nutrient addition is size dependent in a subtropical forest. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 923, 171501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, A.R.; Doraisami, M.; Thomas, S.C. Global patterns in wood carbon concentration across the world’s trees and forests. Nat. Geosci. 2018, 11, 915–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.X.; Fang, J.Y.; Guo, D.L.; Zhang, Y. Leaf nitrogen and phosphorus stoichiometry across 753 terrestrial plant species in China. New Phytol. 2005, 168, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergutz, L.; Manzoni, S.; Porporato, A.; Novais, R.F.; Jackson, R.B. Global resorption efficiencies and concentrations of carbon and nutrients in leaves of terrestrial plants. Ecol. Monogr. 2012, 82, 205–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, D.B.; Wang, G.Z.; Li, G.J.; Sun, Y.L.; Liu, Y.G.; Zhou, J.X. Ecological stoichiometric characteristics of two typical plantations in the karst ecosystem of southwestern China. Forests 2018, 9, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.H.; Xiong, K.N.; Yu, Y.H.; Wang, J.; Wu, Y.W. Ecological stoichiometry and homeostasis characteristics of plant-litter-soil system with vegetation restoration of the karst desertification control. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1224691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Cui, Y.C.; Zhao, W.J.; Hou, Y.J.; Zhu, J.; Ding, F.J.; Yang, W.B. Leaf stoichiometric characteristics of 68 typical plant species in Maolan National Nature Reserve, Guizhou, China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2020, 40, 5063–5080. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.Q.; Yu, K.L.; Lv, S.Q.; Niklas, K.J.; Donko Mipam, T.; Crowther, T.W.; Umaña, M.N.; Zhao, Q.; Huang, H.; Reich, P.B. The scaling of fine root nitrogen versus phosphorus in terrestrial plants: A global synthesis. Funct. Ecol. 2019, 33, 2081–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Zhang, J.B.; Xin, Z.M.; Hang, Y.R.; Han, C.X.; Li, Y.H.; Lu, Q. Ecological stoichiometric characteristics in organs of Ammopiptanthus mongolicus in Different Habitats. Plants 2023, 12, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, G.H.; Hu, T.M.; Liu, J.; Cheng, J.M.; Li, W. Biomass estimation, nutrient accumulation, and stoichiometric characteristics of dominant tree species in the semi-arid region on the Loess Plateau of China. Sustainability 2020, 12, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, D.; Yan, Z.B.; Ma, S.H.; Ding, Y.H.; Luo, Y.K.; Chen, Y.H.; Du, E.Z.; Han, W.X.; Kovacs, E.D.; Shen, H.H.; et al. Family-level leaf nitrogen and phosphorus stoichiometry of global terrestrial plants. Sci. China Life Sci. 2019, 62, 1047–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Yao, Y.F.; Li, Y.Q.; Yu, L.; Ni, L.K.; Fu, B.L.; Huang, J.J.; Li, D.X. Accurately estimating and revealing the patterns of leaf C:N:P stoichiometry with remote sensing and neural network methods in a karst area. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2025, 231, 110006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.H.; Li, M.X.; Xu, L.; Zhu, J.X.; Dai, G.H.; He, N.P. C:N:P stoichiometry in terrestrial ecosystems in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 795, 148849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.L.; Dong, L.W.; Lu, J.L.; Hu, W.G.; Gong, H.Y.; Xie, S.B.; Zhao, D.M.; Zhang, Y.H.; Wang, X.T.; Deng, Y.; et al. Variation in plant carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus contents across the drylands of China. Funct. Ecol. 2022, 36, 174–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.J.; Augusto, L.; Goll, D.S.; Ringeval, B.; Wang, Y.P.; Helfenstein, J.; Huang, Y.Y.; Yu, K.L.; Wang, Z.Q.; Yang, Y.C.; et al. Global patterns and drivers of soil total phosphorus concentration. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 5831–5846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, B.C.; Zhang, C.X.; Wang, G.D.; Xie, Y.G. Global convergence in correlations among soil properties. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2020, 13, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.S.; Wu, B.Y.; Zhang, D.D.; Cheng, X.L. Elevational variation in soil phosphorus pools and controlling factors in alpine areas of Southwest China. Geoderma 2023, 431, 116361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Wang, X.; Tognetti, R.; Lei, J.P.; Pan, H.L.; Liu, X.L.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, X.Y.; He, P.; Yu, F.H.; et al. Elevation alters carbon and nutrient concentrations and stoichiometry in Quercus aquifolioides in southwestern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 622, 1463–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.J.; Jiao, L.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, J.J.; Che, X.C. Elevation affects the ecological stoichiometry of Qinghai spruce in the Qilian Mountains of northwest China. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 917755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bin, H.; Li, Q.; Zhang, P.; Li, W.J.; Xue, X.H.; Zou, S.; Zhang, Q.S. Effects of elevation on ecological stoichiometry of plant leaves, litter, and soils in Pseudotsuga sinensis forest in the karst mountain region, southwest China. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2022, 22, 3582–3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drenovsky, R.E.; Richards, J.H. Critical N:P values: Predicting nutrient deficiencies in desert shrublands. Plant Soil 2004, 259, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.Z.; Zeng, F.P.; Lv, S.W.; Zhang, H.; Zeng, Z.X.; Peng, W.X.; Song, T.Q.; Wang, K.L.; Du, H. Soil C:N:P stoichiometry and its influencing factors in forest ecosystems in southern China. Front. For. Glob. Change 2023, 16, 1142933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, T.; Yi, M.; Chen, F.S.; Lai, M.; Jin, C.F.; Nie, Z.X.; Zhou, L.J.; Xie, J.W.; Zhang, L. Response of c:n:p stoichiometry to phosphorus addition and homeostasis of plant tissues in a subtropical slash pine plantation. Forests 2023, 14, 1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.Q.; Zhao, P.; Peng, S.Z.; Chen, Y.M.; Cao, Y. The coupling of leaf, litter, and soil nutrients in warm temperate forests in northwestern China. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dieckow, J.; Mielniczuk, J.; Knicker, H.; Bayer, C.; Dick, D.P.; Kögel-Knabner, I. Comparison of carbon and nitrogen determination methods for samples of a Paleudult subjected to no-till cropping systems. Sci. Agric. 2007, 64, 532–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, S.R.; Sommers, L.E. Phosphorus. Methods of Soil Analysis. Part 2: Chemical and Microbiological Properties; American Society of Agronomy Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 1982; pp. 403–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heanes, D.L. Determination of total organic-C in soils by an improved chromic acid digestion and spectrophotometric procedure. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 1984, 15, 1191–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, S.D. Soil and Agricultural Chemical Analysis Methods; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Sterner, R.W.; Elser, J.J. Ecological Stoichiometry: The Biology of Elements from Molecules to the Biosphere; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Makino, W.; Cotner, J.B.; Sterner, R.W.; Elser, J.J. Are bacteria more like plants or animals? Growth rate and resource dependence of bacterial C:N:P stoichiometry. Funct. Ecol. 2003, 17, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persson, J.; Fink, P.; Goto, A.; Hood, J.M.; Jonas, J.; Kato, S. To be or not to be what you eat: Regulation of stoichiometric homeostasis among autotrophs and heterotrophs. Oikos 2010, 119, 741–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Indicators | Flowers | Leaves | Branches | Fine roots | Soil |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C (g·kg−1) | 539.14 ± 4.5 a | 547.82 ± 5.31 a | 498.77 ± 10.54 b | 437.35 ± 3.41 c | 108.07 ± 7.31 d |
| N (g·kg−1) | 79.74 ± 2.41 b | 105.55 ± 4.48 a | 31.49 ± 1.8 d | 41.42 ± 1.37 c | 4.82 ± 0.49 e |
| P (g·kg−1) | 2.46 ± 0.09 a | 1.97 ± 0.14 b | 0.85 ± 0.04 c | 0.95 ± 0.05 c | 2.01 ± 0.08 b |
| C:N | 6.96 ± 0.24 cd | 5.46 ± 0.24 d | 17.35 ± 1.07 b | 10.87 ± 0.34 c | 27.74 ± 2.93 a |
| C:P | 227.32 ± 8.2 d | 308.91 ± 16.61 c | 618.82 ± 26.9 a | 501.98 ± 25.02 b | 56.5 ± 4.52 e |
| N:P | 33.59 ± 1.58 c | 58.89 ± 3.5 a | 38.85 ± 2.42 c | 47.42 ± 2.66 b | 2.38 ± 0.2 d |
| C:N:P | 219:80:1 | 277:106:1 | 589:31:1 | 462:41:1 | 57:5:1 |
| Organ | Indicator | C | N | P | AN | AP | C:N | C:P | N:P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flowers | H | ∞ | ∞ | ∞ | ∞ | ∞ | ∞ | 4.14 | ∞ |
| p | >0.05 | >0.05 | >0.05 | >0.05 | >0.05 | >0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | |
| Leaves | H | ∞ | ∞ | ∞ | ∞ | ∞ | ∞ | 2.53 | ∞ |
| p | >0.05 | >0.05 | >0.05 | >0.05 | >0.05 | >0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | |
| Branches | H | ∞ | ∞ | ∞ | ∞ | ∞ | ∞ | ∞ | ∞ |
| p | >0.05 | >0.05 | >0.05 | >0.05 | >0.05 | >0.05 | >0.05 | >0.05 | |
| Fine root | H | ∞ | ∞ | 1.98 | ∞ | ∞ | ∞ | 3.80 | ∞ |
| p | >0.05 | >0.05 | <0.05 | >0.05 | >0.05 | >0.05 | <0.05 | >0.05 |
| Sample Site No. | Altitude (m) | Latitude (°N) | Longitude (°E) | Average Plant Height (cm) | Average Crown Width (cm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2200 | 26.9534 | 104.7572 | 97.4 ± 5.2 | 87.3 ± 26.0 |
| 2 | 2300 | 26.9866 | 104.7623 | 90.0 ± 7.0 | 65.7 ± 16.4 |
| 3 | 2400 | 26.9883 | 104.7599 | 66.0 ± 3.1 | 55.7 ± 11.9 |
| 4 | 2500 | 26.9903 | 104.7578 | 53.0 ± 3.8 | 73.3 ± 17.2 |
| 5 | 2600 | 26.9911 | 104.7557 | 54.4 ± 7.4 | 62.0 ± 15.5 |
| 6 | 2700 | 26.9923 | 104.7537 | 38.0 ± 1.8 | 64.5 ± 20.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Zhao, C.; Wu, J.; Ba, S.; Liu, S.; Dai, P. Change in C, N, and P Characteristics of Hypericum kouytchense Organs in Response to Altitude Gradients in Karst Regions of SW China. Plants 2025, 14, 2307. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14152307
Li Y, Zhao C, Wu J, Ba S, Liu S, Dai P. Change in C, N, and P Characteristics of Hypericum kouytchense Organs in Response to Altitude Gradients in Karst Regions of SW China. Plants. 2025; 14(15):2307. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14152307
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yage, Chunyan Zhao, Jiajun Wu, Suyan Ba, Shuo Liu, and Panfeng Dai. 2025. "Change in C, N, and P Characteristics of Hypericum kouytchense Organs in Response to Altitude Gradients in Karst Regions of SW China" Plants 14, no. 15: 2307. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14152307
APA StyleLi, Y., Zhao, C., Wu, J., Ba, S., Liu, S., & Dai, P. (2025). Change in C, N, and P Characteristics of Hypericum kouytchense Organs in Response to Altitude Gradients in Karst Regions of SW China. Plants, 14(15), 2307. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14152307








