Rhizosphere and Non-Rhizosphere Soil Microbial Communities in Alpine Desertified Grassland Affected by Vegetation Restoration
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Characteristics of Soil Enzyme Activity at Different Restoration Years
2.2. Characteristics of Soil Microbial Diversity at Different Restoration Years
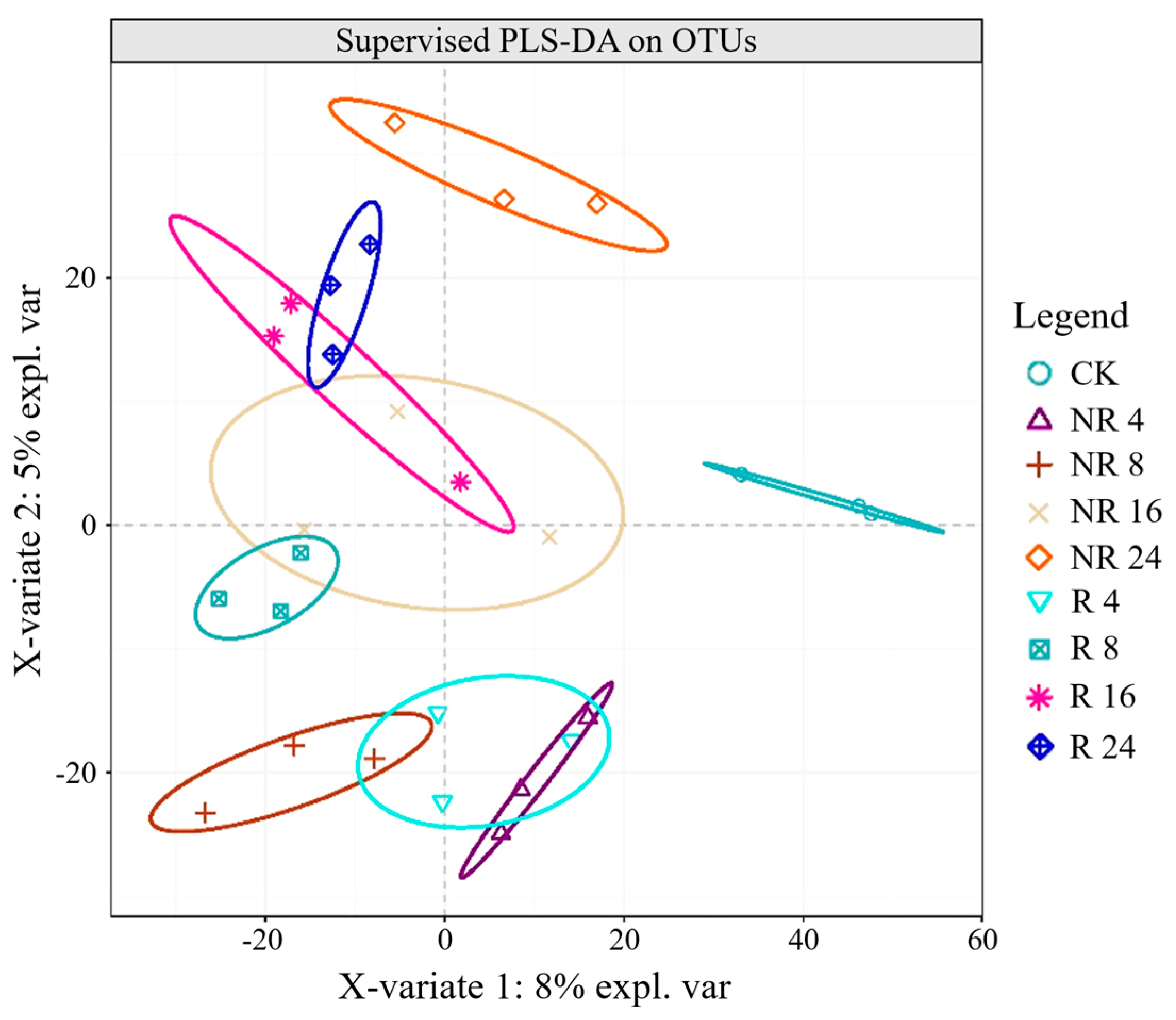
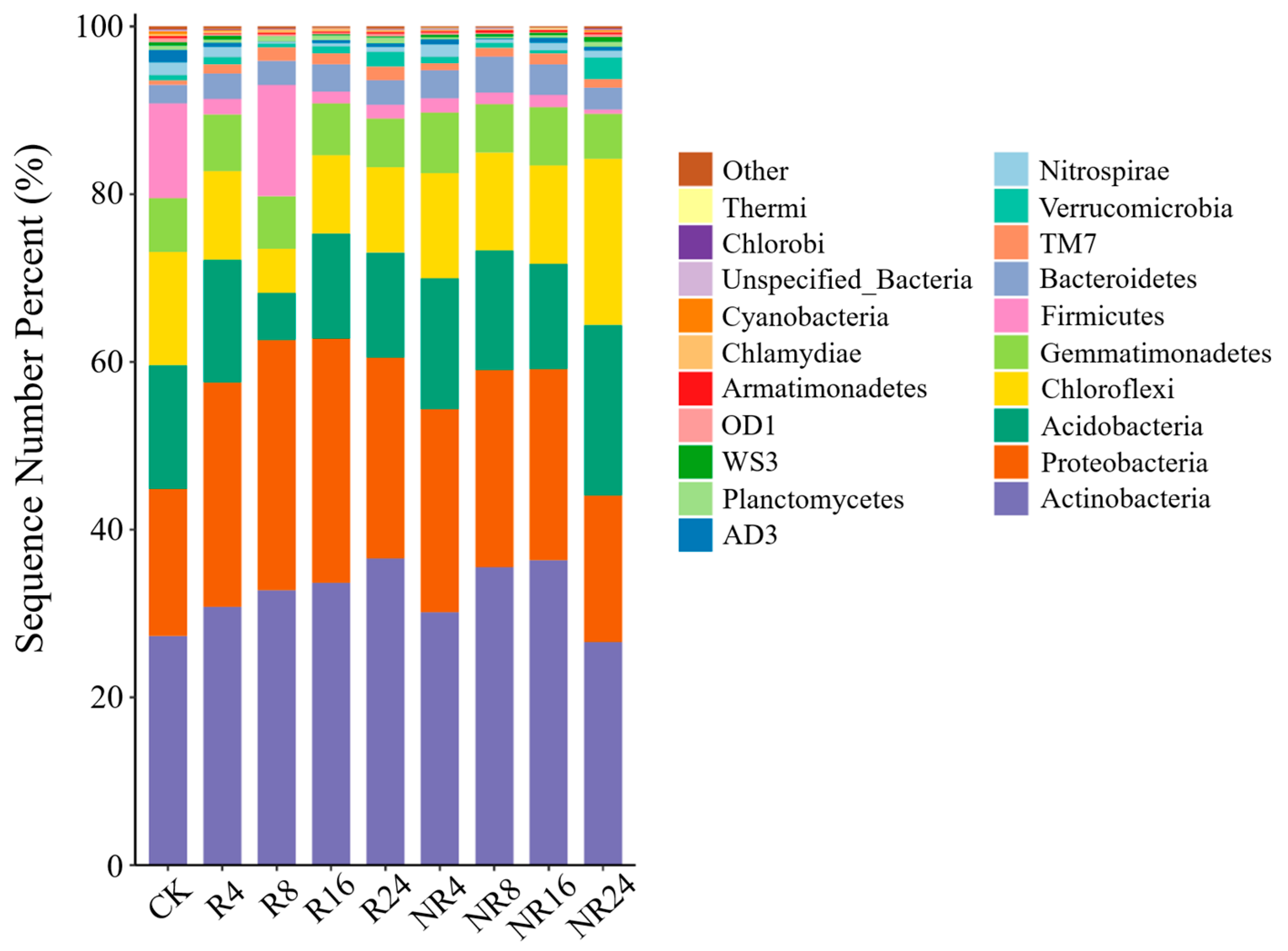
2.3. Characteristics of Soil Microbial Community Structure, Composition and Species Abundance at Different Restoration Years
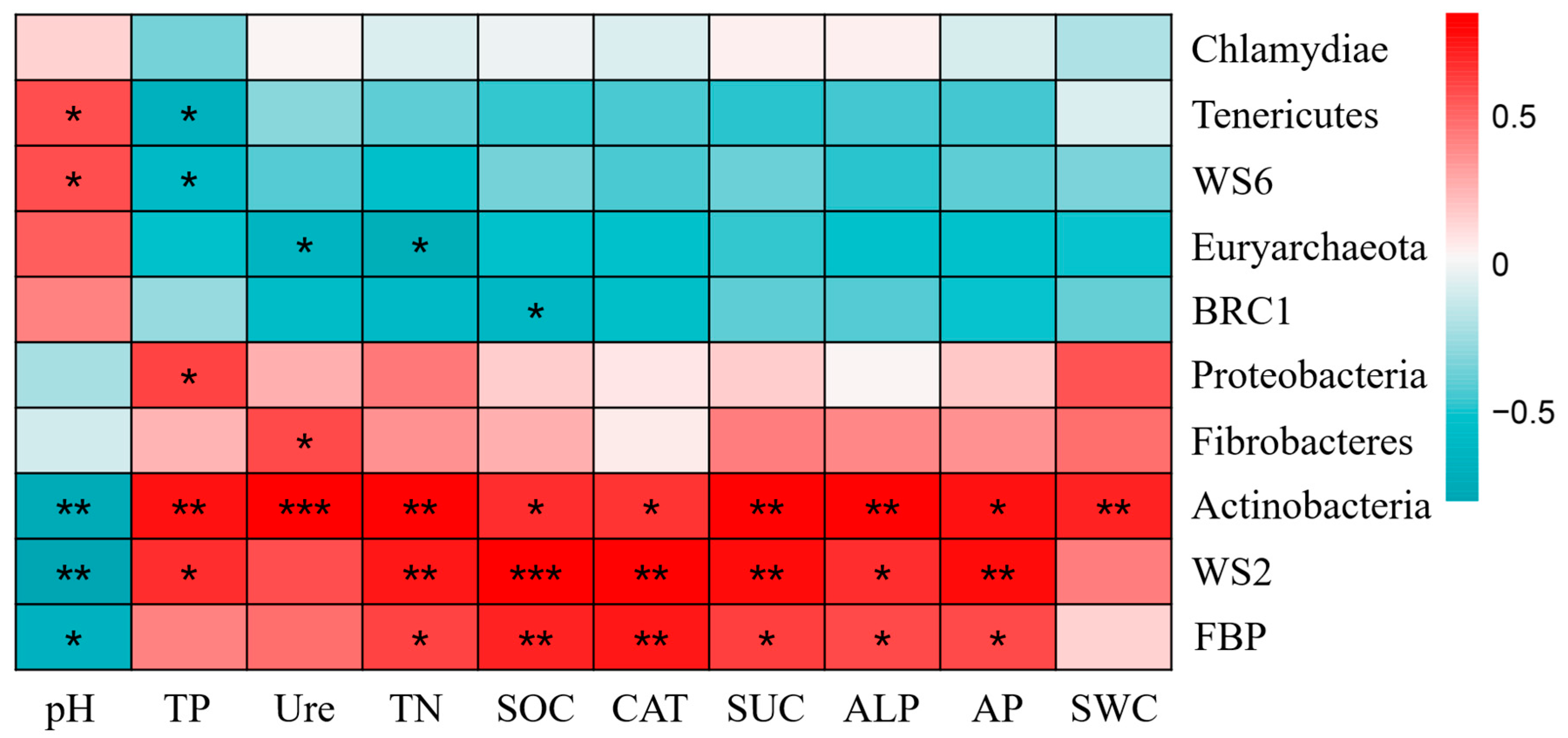
2.4. Correlation Analysis Between Bacterial Communities and Soil Environmental Factors
3. Discussion
3.1. Effects of Ecological Restoration on Soil Enzyme Activity
3.2. Effects of Ecological Restoration on Soil Microbial Communities
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Site Description
4.2. Measurement Parameters
4.3. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Iniesta-Pallarés, M.; Brenes-Álvarez, M.; Lasa, A.V.; Fernández-López, M.; Álvarez, C.; Molina-Heredia, F.P.; Mariscal, V. Changes in rice rhizosphere and bulk soil bacterial communities in the Doñana wetlands at different growth stages. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2023, 190, 105013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Ding, D.; Zhang, X.R.; Gu, H.Y. A comparative analysis of soil physicochemical properties and microbial community structure among four shelterbelt species in the northeast China plain. Microbiol. Spectr. 2024, 12, e0368323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.B.; Li, S.C.; Chen, H.; Wu, J.P. Reseeding promotes plant biomass by improving microbial community stability and soil fertility in a degraded subalpine grassland. Geoderma 2025, 453, 117160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.X.; Zhang, W.H.; Grossart, H.P.; Gadd, G.M.; Liu, W.Z.; Yang, Y.Y. The unique climate shapes distinct life-history traits of abundant bacteria in Tibetan Plateau grassland soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 908, 168353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.L.; Fu, L.C.; Ao, G.; Ji, C.J.; Zeng, H.; Zhu, B. Climate, plant and microorganisms jointly influence soil organic matter fractions in temperate grasslands. Sci. Total Environ. 2025, 958, 178133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Wang, S.C.; Liu, C.; Yu, Y.D.; Zong, M.M.; Duan, C.Q. Soil microbial communities’ contributions to soil ecosystem multifunctionality in the natural restoration of abandoned metal mines. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 353, 120244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukhat, S.; Imran, A.; Javaid, S.; Shahid, M.; Majeed, A.; Naqqash, T. Communication of plants with microbial world: Exploring the regulatory networks for PGPR mediated defense signaling. Microbiol. Res. 2020, 238, 126486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venturi, V.; Keel, C. Signaling in the rhizosphere. Trends Plant Sci. 2016, 21, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzyakov, Y.; Razavi, B.S. Rhizosphere size and shape: Temporal dynamics and spatial stationarity. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2019, 135, 343–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmann, S.; Turlings, T.C. Root signals that mediate mutualistic interactions in the rhizosphere. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2016, 32, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, W.; Janda, T.; Molnár, Z. Unveiling the significance of rhizosphere: Implications for plant growth, stress response, and sustainable agriculture. Plant Physiol. Bioch. 2024, 206, 108290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korenblum, E.; Dong, Y.; Szymanski, J.; Panda, S.; Jozwiak, A.; Massalha, H.; Meir, S.; Rogachev, I.; Aharoni, A. Rhizosphere microbiome mediates systemic root metabolite exudation by root-to-root signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 3874–3883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhalnina, K.; Louie, K.B.; Hao, Z.; Mansoori, N.; da Rocha, U.N.; Shi, S.; Cho, H.; Karaoz, U.; Loqué, D.; Bowen, B.P.; et al. Dynamic root exudate chemistry and microbial substrate preferences drive patterns in rhizosphere microbial community assembly. Nat. Microbiol. 2018, 3, 470–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.Q.; Fan, X.F.; Zhang, M.C.; Zhang, H.; Yue, Y.; Wu, J.Y.; Teng, W.J.; Mu, N.; Teng, K.; Wen, H.F. Insights into the interlinkages between rhizosphere soil extracellular enzymes and microbiome assemblages across soil profiles in grasslands. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2025, 211, 106139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, J.L.; Wang, X.; Liu, X.T.; Li, C.N.; Han, J.R.; Yao, T. Inoculation of cold-adapted microbial consortium screened from alpine meadows promotes the growth of mixed grasses by changing soil properties and enzyme activity. Rhizosphere 2023, 28, 100782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, H.T.; Sun, C.C.; Dong, Q.M.; Yang, X.X.; Liu, W.T.; Wang, X.X.; Wang, X.L.; Zhao, X.Q. Responses of rhizosphere soil and bulk soils microbial activity to livestock assembly. Acta Agrestia Sin. 2025, 33, 813–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.X.; Zhao, L.Y.; Hu, J.P.; Khan, A.; Yang, X.X.; Dong, Q.M.; Rensing, C.; Fang, X.L.; Zhang, J.L. Different grazers and grazing practices alter the growth, soil properties, and rhizosphere soil bacterial communities of Medicago ruthenica in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau grassland. Agr. Ecosyst. Environ. 2023, 352, 108522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, H.Y.; Yang, N.R.; Jiang, H.D.; Li, Y.N.; Shen, A.; Hu, Y.F. Effects of Artificial Vegetation Restoration Pattern on Soil Phosphorus Fractions in Alpine Desertification Grassland. Plants 2025, 14, 1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.J.; Hu, Y.B.; Li, S.; Wu, S.L.; Zhang, Z.T.; Luo, L.; Yin, C.Y.; Zhao, C.Z. Slight degradation significantly alters plant functional groups and biomass accumulation in alpine meadow on the eastern Tibetan Plateau. Agr. Ecosyst. Environ. 2025, 387, 109640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Shen, X.D.; Huang, Q.; Sun, F.D.; Zhou, J.Q.; Ma, X.; Ran, Z.Y.; Chen, Y.J.; Li, Z.; Yan, Y.H.; et al. Resource islands of Salix cupularis facilitating seedling emergence of the companion herbs in the restoration process of desertified alpine meadow, the Tibetan Plateau. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 289, 112434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.Y.; Qian, H.Y.; Liu, A.Y.; Hu, Y.F.; Wang, W.; Chen, G.; Li, Z. Rhizosphere and non-rhizosphere soil organic carbon and its labile fractions in alpine desertified grassland affected by vegetation restoration. Plant Soil Environ. 2024, 70, 523–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Qu, Y.P.; Zeng, H.Y.; Yang, J.T.; Liu, L.; Deng, D.Z.; Ma, Y.L.; Chen, D.C.; Jian, B.H.; Guan, L.L.; et al. Long-term ecological restoration increased plant diversity and soil total phosphorus content of the alpine flowing sand land in northwest Sichuan, China. Heliyon 2024, 2, e24035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.F.; Shu, X.Y.; He, J.; Zhang, Y.L.; Xiao, H.H.; Tang, X.Y.; Gu, Y.F.; Lan, T.; Xia, J.G.; Ling, J.; et al. Storage of C, N, and P affected by afforestation with Salix cupularis in an alpine semiarid desert ecosystem. Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Wang, Y.; Sun, J.; Zhang, Z.C.; Xu, X.L.; Zhou, H.K.; Wu, G.L. Shift in nurse effect from facilitation to competition with increasing size of Salix cupularis canopy in a desertified alpine meadow on the Tibetan Plateau. Catena 2020, 195, 104757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Zhang, H.J.; Lu, J.Y.; Liang, Y.; Li, Y.D.; Xu, L.Y.; Ye, J.L.; Yang, R.Y.; Li, P.; Jiao, J.G.; et al. Green manuring with balanced fertilization improves soil ecosystem multifunctionality by enhancing soil quality and enzyme activities in a smooth vetch-maize rotation system. Agr. Ecosyst. Environ. 2025, 387, 109632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhou, L.J.; Lin, W.F. Calla lily intercropping in rubber tree plantations changes the nutrient content, microbial abundance, and enzyme activity of both rhizosphere and non-rhizosphere soil and calla lily growth. Ind. Crops Prod. 2019, 132, 344–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.P.; Li, X.; Zhou, S.Y.D.; Liu, X.J.; Lie, Z.Y.; Aguila, L.C.R.; Xu, W.F.; Liu, J.X. Soil organic carbon sources exhibit different patterns with stand age in rhizosphere and non-rhizosphere soils. Catena 2025, 248, 108579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Q.; Li, J.Y.; Wang, J.H.; Wang, H.; Sun, K.; He, Q.; Su, Y.; Pan, X. Microbes, enzyme activities and nutrient characteristics of rhizosphere and non-rhizosphere soils under four shrubs in Xining Nanshan, Prefecture, China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2014, 34, 7411–7420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.L.; Dong, Y.M.; Zhang, Z.; Song, Z.G. Effect of dibutyl phthalate on microbial function diversity and enzyme activity in wheat rhizosphere and non-rhizosphere soils. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265, 114800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, D.J.; Smemo, K.A.; López-Gutiérrez, J.C.; Hewins, C.R. Soil enzyme activity in an old-growth northern hardwood forest: Interactions between soil environment, ectomycorrhizal fungi and plant distribution. Pedobiologia 2012, 55, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Yan, F.; Chen, D.M.; Zhou, J.Q.; Ma, Z.W.; Bai, Y.F.; Hu, X.P.; Ma, C.Y.; Aloufi, A.S.; Sun, F.D.; et al. Root exudates of Salix cupularis orchestrate the accumulation of soil carbon and nitrogen in the rhizosphere during the restoration of a desertified alpine meadow. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2025, 209, 106041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donhauser, J.; Frey, B. Alpine soil microbial ecology in a changing world. Fems Microbiol. Ecol. 2018, 94, fiy099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuai, L.L.; Zhou, Q.P.; Chen, Y.J.; Zhou, R. Soil microorganism dynamics during grassland restoration in sub-humid sandy land. Acta Pratacult. Sin. 2019, 28, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.H.; Song, K.C.; Zhang, H.; Guan, S.Y.; Yong, J.Y.; Hu, H.Y. Structure and diversity characteristics of the rhizosphere microbial community of dominant plants on the desert steppe under changing precipitation. Acta Pratacult. Sin. 2025, 34, 12–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.X.; Jing, R.Y.; Huang, Y.L.; Chen, B.J.; Ma, F.Y. Bacterial structure and diversity of rhizosphere and bulk soil of Robinia pseudoacacia forests in Yellow River Delta. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2017, 54, 1293–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rui, J.P.; Peng, J.J.; Lu, Y.J. Succession of bacterial populations during plant residue decomposition in rice field soil. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2009, 75, 4879–4886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontaine, S.; Mariotti, A.; Abbadie, L. The priming effect of organic matter: A question of microbial competition? Soil Biol. Biochem. 2003, 35, 837–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Chen, B.; Zhang, H. High throughput sequencing analysis of bacterial communities in soils of a typical Poyang Lake wetland. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2017, 37, 1650–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. Guidelines for Soil Description, 4th ed.; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, A.; Dubey, S.K. Temporal variation in methanogenic community structure and methane production potential of tropical tice ecosystem. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2012, 48, 162–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.K. Soil Agrochemical Analysis Methods; China Agricultural Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, S.Y. Soil Enzymes and Their Research Methods; Agricultural Press: Beijing, China, 1986. [Google Scholar]

| Location | Years | Alpha Diversity | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chao1 | Faith_PD | Shannon | Simpson | ||
| R | CK | 1034.09 ± 44.69 Ab | 96.98 ± 6.96 Aa | 8.74 ± 0.41 Ab | 0.99 ± 0.01 Aa |
| 4 | 1264.67 ± 55.40 Aa | 97.32 ± 4.31 Aa | 9.49 ± 0.11 Aa | 1.00 ± 0.00 Aa | |
| 8 | 1285.72 ± 14.89 Aa | 98.96 ± 3.05 Aa | 9.48 ± 0.23 Aa | 0.99 ± 0.00 Aa | |
| 16 | 1198.80 ± 29.93 Aa | 89.58 ± 5.33 Aa | 9.40 ± 0.08 Aa | 1.00 ± 0.00 Aa | |
| 24 | 1191.29 ± 32.37 Aa | 86.38 ± 4.24 Aa | 9.42 ± 0.17 Aa | 0.99 ± 0.00 Aa | |
| NR | CK | 1034.09 ± 44.69 Ac | 96.98 ± 6.96 Aa | 8.74 ± 0.41 Ab | 0.99 ± 0.01 Aa |
| 4 | 1193.46 ± 79.46 Aa | 95.63 ± 5.26 Aa | 9.46 ± 0.06 Aa | 1.00 ± 0.00 Aa | |
| 8 | 1201.40 ± 24.78 Ba | 93.14 ± 7.11 Aa | 9.46 ± 0.13 Aa | 1.00 ± 0.00 Aa | |
| 16 | 1091.40 ± 55.25 Ba | 83.47 ± 2.82 Aa | 9.30 ± 0.04 Aab | 1.00 ± 0.00 Aa | |
| 24 | 1115.85 ± 17.87 Bb | 86.68 ± 4.87 Aa | 9.07 ± 0.18 Bab | 1.00 ± 0.00 Aa | |
| Location | Years | Dominant Bacterial Phyla | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Actinobacteria | Proteobacteria | Acidobacteria | Chloroflexi | Gemmatimonadetes | ||
| R | 0 | 0.27 ± 0.01 Ac | 0.18 ± 0.05 Aa | 0.15 ± 0.02 Aa | 0.14 ± 0.02 Aa | 0.06 ± 0.05 Aa |
| 4 | 0.31 ± 0.00 Ab | 0.27 ± 0.04 Aa | 0.15 ± 0.03 Aa | 0.11 ± 0.02 Aab | 0.07 ± 0.01 Aa | |
| 8 | 0.33 ± 0.02 Ab | 0.30 ± 0.02 Aa | 0.06 ± 0.00 Bb | 0.05 ± 0.01 Bb | 0.06 ± 0.01 Aa | |
| 16 | 0.34 ± 0.01 Ab | 0.29 ± 0.08 Aa | 0.13 ± 0.03 Aab | 0.13 ± 0.02 Aab | 0.06 ± 0.01 Aa | |
| 24 | 0.37 ± 0.01 Aa | 0.24 ± 0.02 Aa | 0.13 ± 0.03 Bab | 0.10 ± 0.01 Bab | 0.06 ± 0.00 Aa | |
| NR | 0 | 0.27 ± 0.01 Ab | 0.18 ± 0.05 Aa | 0.15 ± 0.02 Ab | 0.14 ± 0.02 Ab | 0.06 ± 0.05 Aa |
| 4 | 0.30 ± 0.05 Aab | 0.24 ± 0.04 Aa | 0.16 ± 0.00 Ab | 0.13 ± 0.02 Ab | 0.07 ± 0.02 Aa | |
| 8 | 0.35 ± 0.03 Aa | 0.23 ± 0.04 Ba | 0.14 ± 0.04 Ab | 0.12 ± 0.03 Ab | 0.06 ± 0.00 Aa | |
| 16 | 0.36 ± 0.02 Aa | 0.23 ± 0.02 Aa | 0.13 ± 0.01 Ab | 0.12 ± 0.02 Ab | 0.07 ± 0.01 Aa | |
| 24 | 0.27 ± 0.02 Bb | 0.17 ± 0.03 Ba | 0.20 ± 0.01 Aa | 0.20 ± 0.01 Aa | 0.05 ± 0.01 Aa | |
| Location | Years | SWC (%) | pH | SOC (g/kg) | TN (g/kg) | TP (g/kg) | AP (mg/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R | 0 | 7.68 ± 0.50 c | 7.31 ± 0.04 a | 1.15 ± 0.02 d | 0.21 ± 0.01 d | 146.63 ± 2.79 d | 7.94 ± 0.14 d |
| 4 | 10.63 ± 0.52 b | 6.99 ± 0.04 b | 1.37 ± 0.13 cd | 0.24 ± 0.00 c | 174.94 ± 4.60 c | 8.77 ± 0.18 d | |
| 8 | 11.60 ± 0.84 b | 6.86 ± 0.08 b | 1.83 ± 0.04 bc | 0.25 ± 0.00 bc | 185.12 ± 11.83 bc | 10.75 ± 0.61 c | |
| 16 | 11.80 ± 0.75 b | 6.64 ± 0.00 c | 2.19 ± 0.08 b | 0.28 ± 0.00 ab | 209.93 ± 11.63 ab | 13.54 ± 0.59 b | |
| 24 | 14.29 ± 0.89 a | 6.46 ± 0.08 c | 2.78 ± 0.37 a | 0.30 ± 0.00 a | 231.27 ± 5.64 a | 16.71 ± 0.76 a | |
| NR | 0 | 7.68 ± 0.50 b | 7.31 ± 0.04 a | 1.15 ± 0.02 b | 0.21 ± 0.01 b | 146.63 ± 2.79 c | 7.94 ± 0.14 c |
| 4 | 9.43 ± 1.56 a | 7.03 ± 0.05 b | 1.21 ± 0.10 b | 0.21 ± 0.01 b | 158.39 ± 4.40 b | 8.12 ± 0.43 c | |
| 8 | 10.91 ± 2.35 a | 6.98 ± 0.02 ab | 1.34 ± 0.14 b | 0.22 ± 0.01 ab | 176.60 ± 15.53 ab | 9.75 ± 1.16 bc | |
| 16 | 11.24 ± 0.52 a | 6.94 ± 0.06 ab | 1.83 ± 0.04 a | 0.24 ± 0.01 ab | 193.25 ± 4.53 a | 11.51 ± 0.39 ab | |
| 24 | 12.21 ± 0.65 a | 6.88 ± 0.03 c | 2.00 ± 0.05 a | 0.24 ± 0.00 a | 190.77 ± 13.65 a | 13.70 ± 0.90 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, X.; Qian, H.; Huang, R.; He, W.; Jiang, H.; Shen, A.; Li, Z.; Hu, Y. Rhizosphere and Non-Rhizosphere Soil Microbial Communities in Alpine Desertified Grassland Affected by Vegetation Restoration. Plants 2025, 14, 1925. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14131925
Gao X, Qian H, Huang R, He W, Jiang H, Shen A, Li Z, Hu Y. Rhizosphere and Non-Rhizosphere Soil Microbial Communities in Alpine Desertified Grassland Affected by Vegetation Restoration. Plants. 2025; 14(13):1925. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14131925
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Xuan, Hongyu Qian, Rui Huang, Wangyi He, Haodong Jiang, Ao Shen, Zhi Li, and Yufu Hu. 2025. "Rhizosphere and Non-Rhizosphere Soil Microbial Communities in Alpine Desertified Grassland Affected by Vegetation Restoration" Plants 14, no. 13: 1925. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14131925
APA StyleGao, X., Qian, H., Huang, R., He, W., Jiang, H., Shen, A., Li, Z., & Hu, Y. (2025). Rhizosphere and Non-Rhizosphere Soil Microbial Communities in Alpine Desertified Grassland Affected by Vegetation Restoration. Plants, 14(13), 1925. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14131925






