Analysis of Cadmium Accumulation Characteristics Affected by Rhizosphere Bacterial Community of Two High-Quality Rice Varieties
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
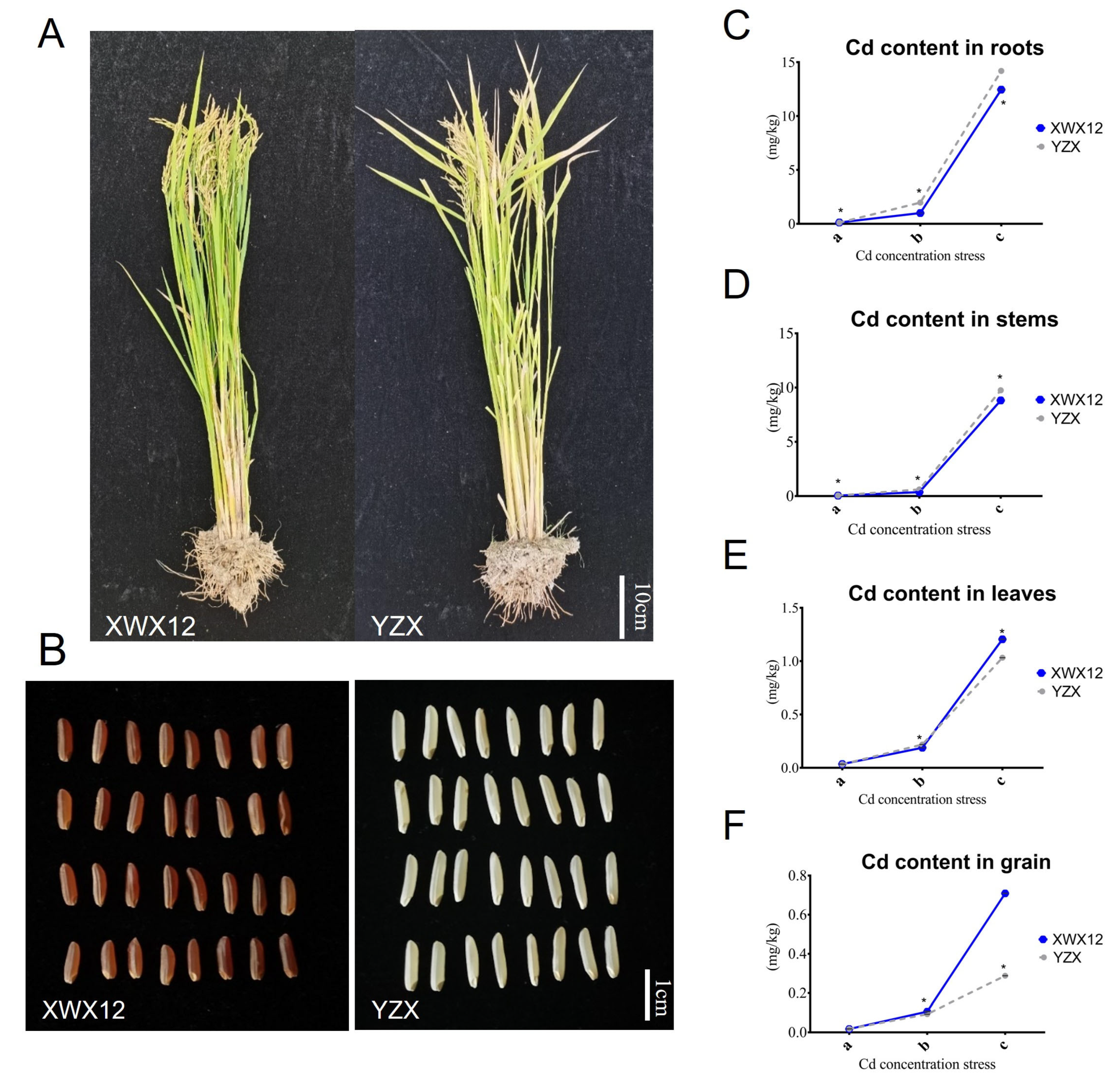
2.1. Differences in Phenotypes and Cd Contents Between YZX and XWX12 Under Different Cd Stress Conditions
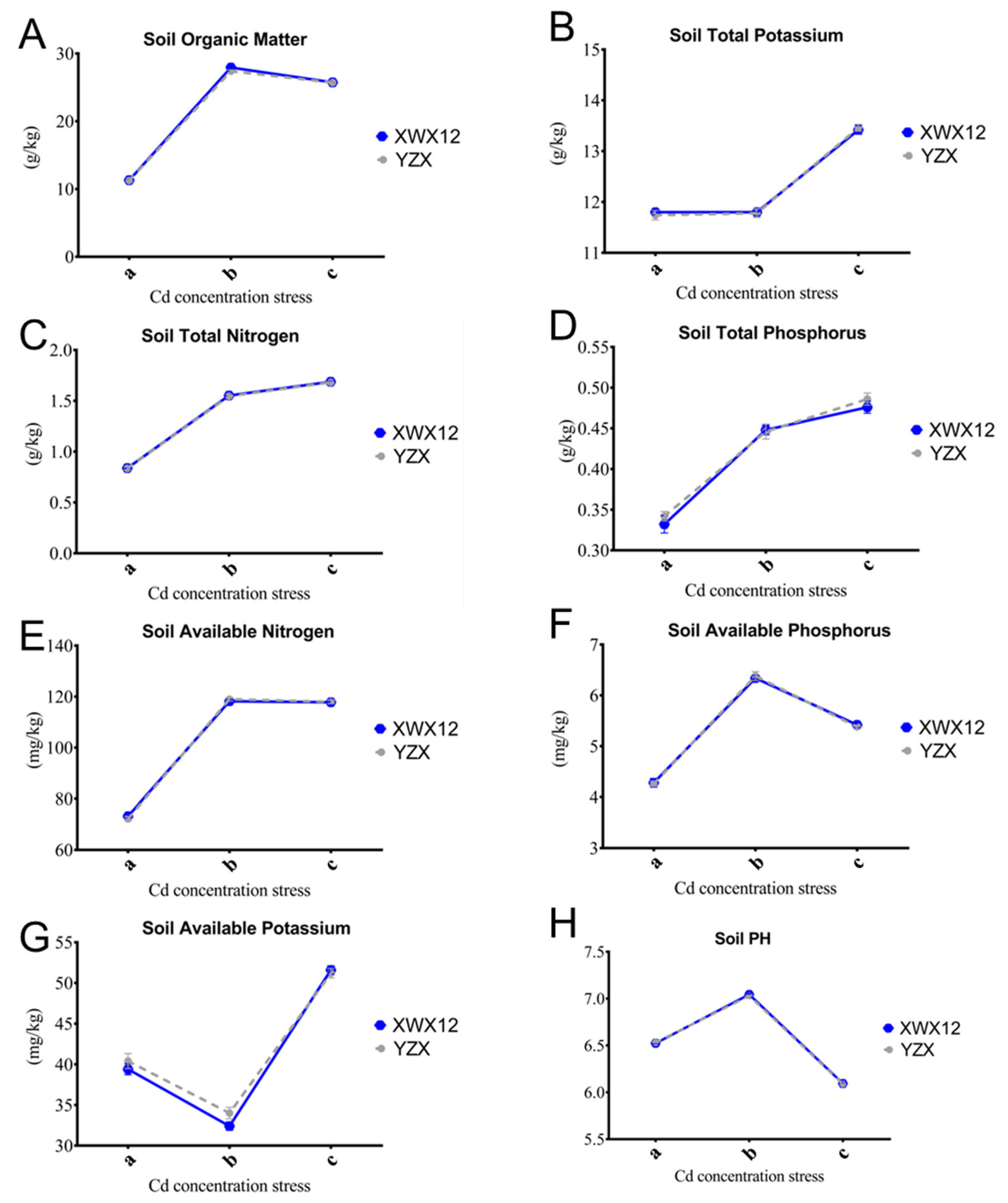
2.2. The Dynamic Changes in Soil Physicochemical Properties Under Different Cd Contents
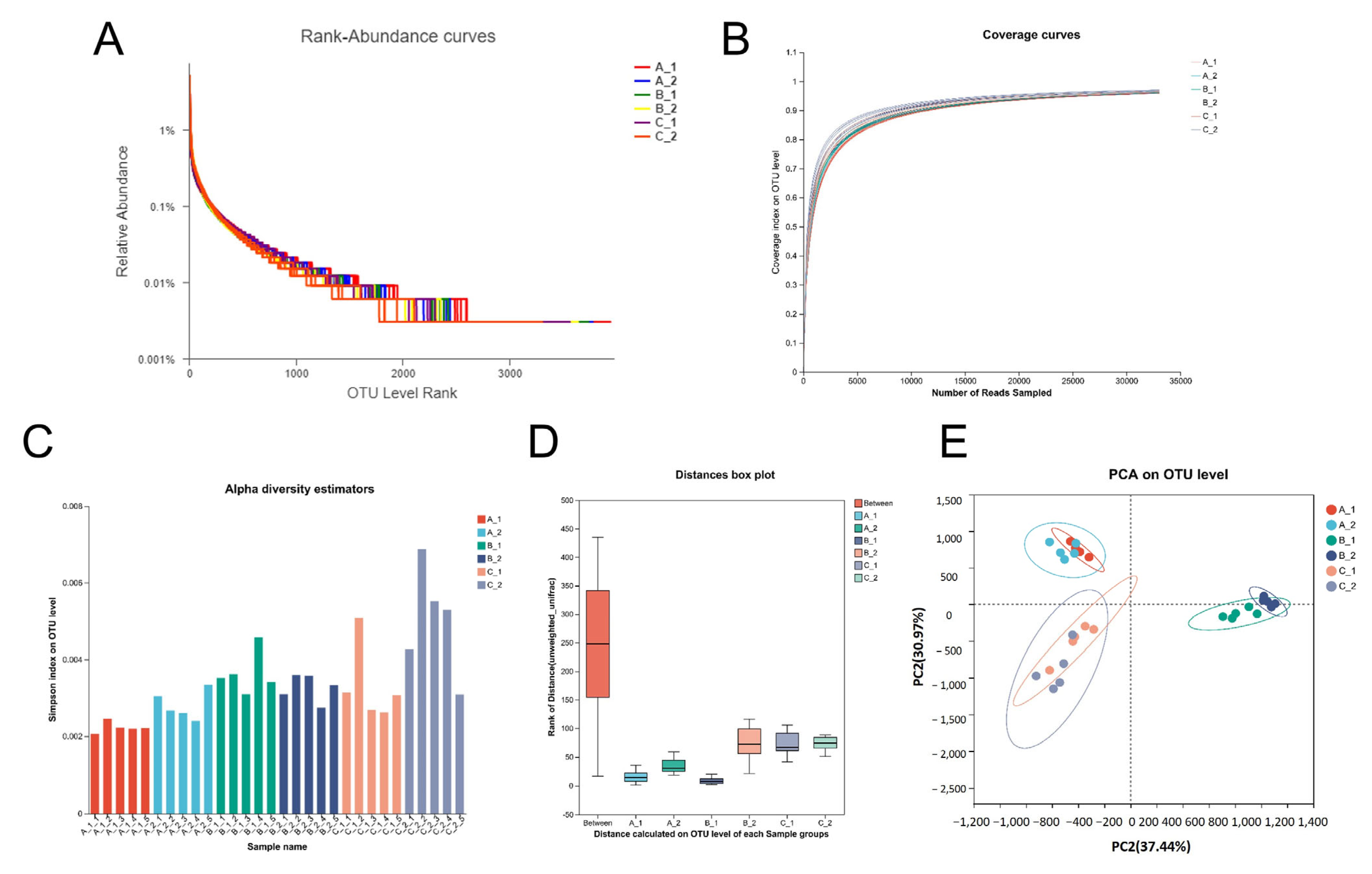
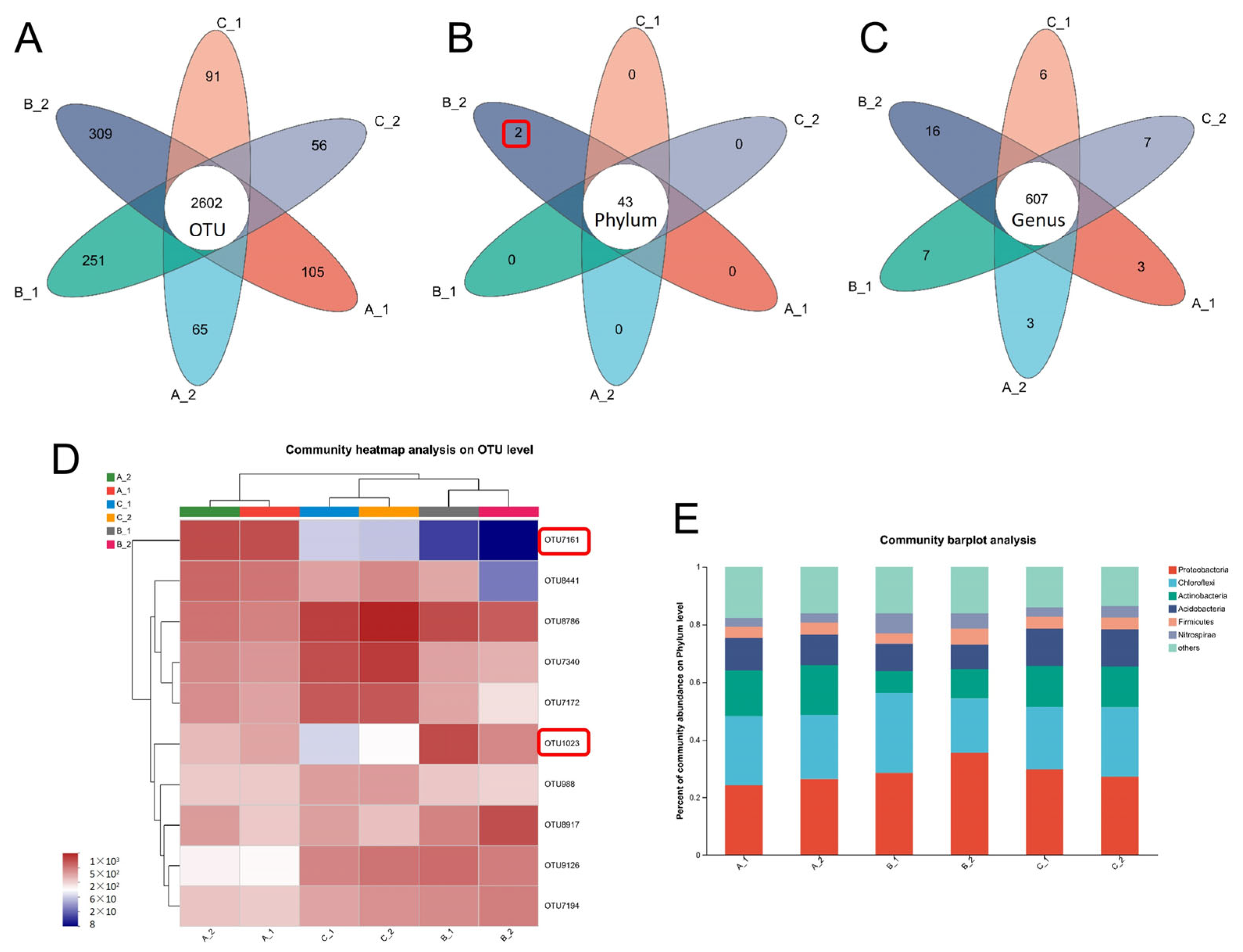
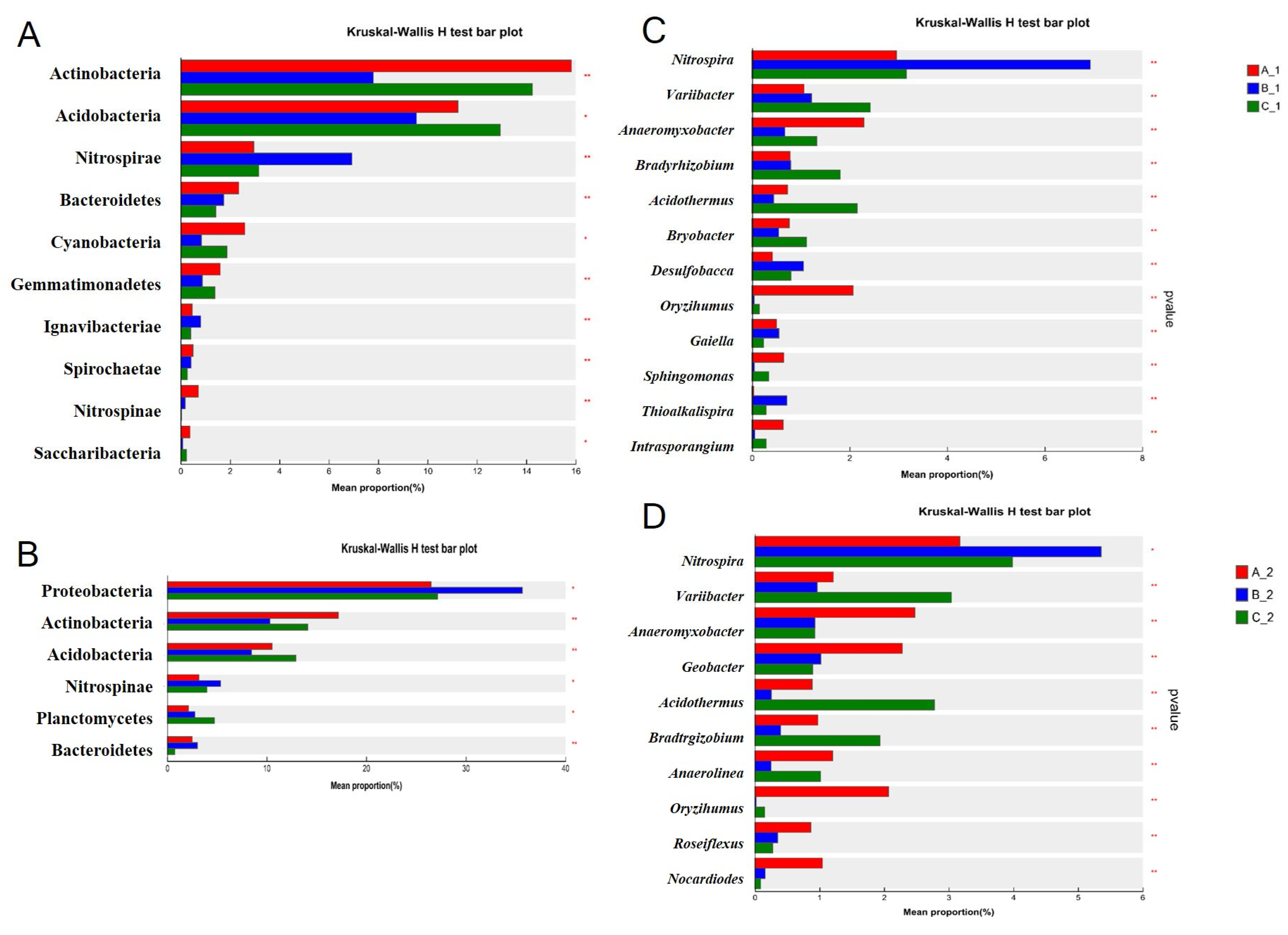
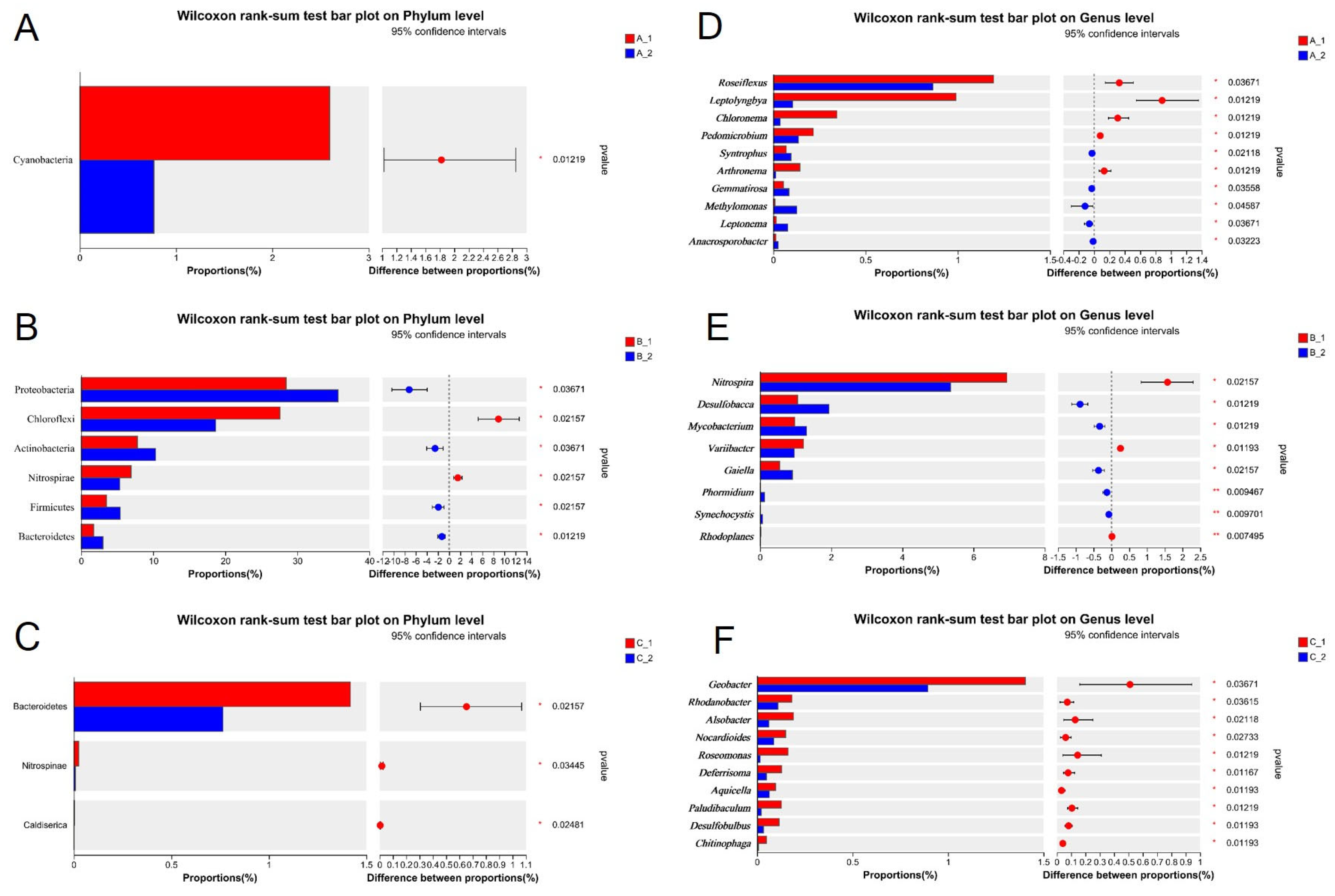
2.3. Altered Rhizosphere Bacterial Community Structure Under Increasing Cd Stress Conditions in YZX and XWX12
3. Discussion
3.1. How Rice Varieties and Different Cd Stress Conditions Influenced the Cd Content
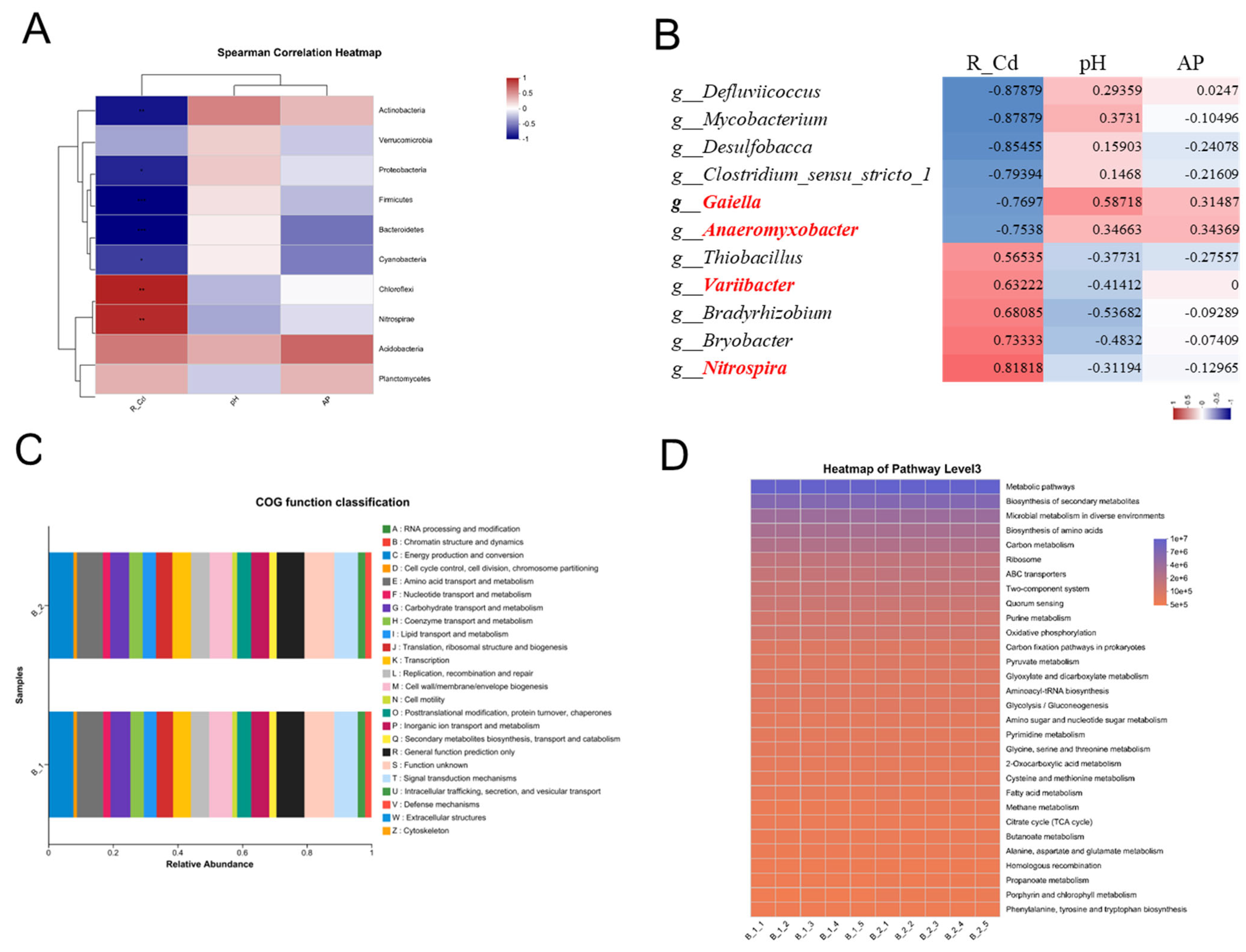
3.2. The Rhizosphere Bacterial Community Has a Relationship to Rice Cd Accumulation
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Experimental Design
4.2. Determination of Cd Content in Plants
4.3. Soil Physicochemical Property Determination
4.4. Soil DNA Extraction and 16S rDNA Sequencing
4.5. Sequencing Data Processing
4.6. Functional Trait Prediction of the Rhizosphere Bacterial Community
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAOSTAT. Available online: https://www.fao.org/faostat/ (accessed on 1 January 2025).
- Yu, S.B.; Ali, J.; Zhou, S.C.; Ren, G.J.; Xie, H.A.; Xu, J.L.; Yu, X.Q.; Zhou, F.S.; Peng, S.B.; Ma, L.Y.; et al. From green super rice to green agriculture: Reaping the promise of functional genomics research. Mol. Plant 2022, 15, 9–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.; Kaur, I.; Nagpal, A.K. Contamination of rice crop with potentially toxic elements and associated human health risks—A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 12282–12299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Chen, H.; Kopittke, P.M.; Zhao, F.J. Cadmium contamination in agricultural soils of China and the impact on food safety. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 249, 1038–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zakaria, Z.; Zulkafflee, N.S.; Mohd Redzuan, N.A.; Selamat, J.; Ismail, M.R.; Praveena, S.M.; Tóth, G.; Abdull Razis, A.F. Understanding Potential Heavy Metal Contamination, Absorption, Translocation and Accumulation in Rice and Human Health Risks. Plants 2021, 10, 1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liang, Y.; Hu, H.; Shaheen, S.M.; Zhong, H.; Tack, F.M.G.; Wu, M.; Li, Y.F.; Gao, Y.; Rinklebe, J. Speciation, transportation, and pathways of cadmium in soil-rice systems: A review on the environmental implications and remediation approaches for food safety. Environ. Int. 2021, 156, 106749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, L.; Pan, Z.; Dai, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhang, L.; Liao, Q.; Yu, X.; Guo, H.; Zhou, G. High-throughput sequencing clarifies the spatial structures of microbial communities in cadmium-polluted rice soils. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 47086–47098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, C.; Fan, M.; Song, C.; Li, N.; Zhang, C.; Fu, S.; Wang, W.; Yang, Z. Unveiling Endophytic Bacterial Community Structures of Different Rice Cultivars Grown in a Cadmium-Contaminated Paddy Field. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 756327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.D.; Luo, Z.L.; Wu, X.; Shi, B.Z.; Jiang, H.D.; Zhou, L.L.; Bai, L.Y. Comparative Transcriptomic Analysis of Root Cadmium Responses in Two Chinese Rice Cultivars Yuzhenxiang and Xiangwanxian 12. J. Chem. 2021, 2021, 2166775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toju, H.; Peay, G.K.; Yamamichi, M.; Narisawa, K.; Hiruma, K.; Naito, K.; Fukuda, S.; Ushio, M.; Nakaoka, S.; Onoda, Y.; et al. Core microbiomes for sustainable agroecosystems. Nat. Plants 2018, 4, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Wang, X.; Chi, Y.; Huang, L.; Li, W.C.; Ye, Z. Rhizosphere bacterial community composition affects cadmium and arsenic accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 222, 112474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, B.; Ashraf, M.N.; Shafeeq Ur, R.; Abbas, A.; Li, J.; Farooq, M. Cadmium stress in paddy fields: Effects of soil conditions and remediation strategies. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 754, 142188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, M.; Zhou, S.; Zhou, Y.; Jia, Z.; Guo, T.; Wang, J. Cadmium pollution of soil-rice ecosystems in rice cultivation dominated regions in China: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 280, 116965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Li, J.; Peng, D.; Wang, Z.; Xu, H. Cadmium Exposure Alters Rhizospheric Microbial Community and Transcriptional Expression of Vetiver Grass. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 808844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Cheng, H.; Tao, S. The Challenges and Solutions for Cadmium-contaminated Rice in China: A Critical Review. Environ. Int. 2016, 92–93, 515–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, Z.; Singh, V.P. Bioremediation of toxic heavy metals (THMs) contaminated sites: Concepts, applications and challenges. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 27563–27581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, L.; Tiwari, J.; Bauddh, K.; Ma, Y. Recent Developments in Microbe-Plant-Based Bioremediation for Tackling Heavy Metal-Polluted Soils. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 731723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Treesubsuntorn, C.; Dhurakit, P.; Khaksar, G.; Thiravetyan, P. Effect of microorganisms on reducing cadmium uptake and toxicity in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 25690–25701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Li, P.; Meng, D.; Gu, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Yin, H.; Zhou, Q.; Li, J. Isolation characterization and inoculation of Cd tolerant rice endophytes and their impacts on rice under Cd contaminated environment. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 260, 113990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Xiao, C.; Chi, R. Remediation of soil cadmium pollution by biomineralization using microbial-induced precipitation: A review. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 37, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayangbenro, A.S.; Babalola, O.O. A New Strategy for Heavy Metal Polluted Environments: A Review of Microbial Biosorbents. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.D.; Wu, X.; Peng, J.; Meng, X.F.; Shi, B.Z.; Zhou, L.L.; Bai, L.Y. Study of the Physiological Dynamics of Cadmium Accumulation in Two Varieties of Rice with Different Cadmium-Accumulating Properties. J. Chem. 2021, 2021, 6238893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Schlaeppi, K.; Heijden, M.G.A. Keystone Taxa as Drivers of Microbiome Structure and Functioning. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 567–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finkel, O.M.; Castrillo, G.; Paredes, S.H.; Salas, G.I.; Dangl, J.L. Understanding and Exploiting Plant Beneficial Microbes. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2017, 38, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.X.; Zhang, X.N.; Qin, Y.; Liu, Y.X.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Zhang, N.; Wu, K.; Qu, B.Y.; He, Z.S.; Wang, X.; et al. Host-associated quantitative abundance profiling reveals the microbial load variation of root microbiome. Plant Commun. 2020, 1, 100003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Yan, L.; Ye, L.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, B.; Peng, W.; Zhang, X.; Li, X. Chinese Black Truffle (Tuber indicum) Alters the Ectomycorrhizosphere and Endoectomycosphere Microbiome and Metabolic Profiles of the Host Tree Quercus aliena. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijayan, A.; Vattiringal, J.R.K.; Pillai, D.; Prasannan, G.P.; Joseph, V.; Isaac, B.S. Nitrospira as versatile nitrifiers: Taxonomy, ecophysiology, genome characteristics, growth, and metabolic diversity. J. Basic Microbiol. 2021, 61, 88–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Ma, J.; Gonzalez-Ollauri, A.; Yang, Y.J.; Chen, F. Soil microbes-mediated enzymes promoted the secondary succession in post-mining plantations on the Loess Plateau, China. Soil Ecol. Lett. 2023, 5, 79–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, G.M.; Maffei, V.J.; Zaneveld, J.R. PICRUSt2 for prediction of metagenome functions. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 685–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Qu, W.; Kadiiska, M.B. Role of oxidative stress in cadmium toxicity and carcinogenesis. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2009, 238, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizwan, M.; Ali, S.; Adrees, M.; Rizvi, H.; Zia-Ur-Rehman, M.; Hannan, F.; Qayyum, M.F.; Hafeez, F.; Ok, Y.S. Cadmium stress in rice: Toxic effects, tolerance mechanisms, and management: A critical review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 17859–17879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.Y.; Chen, A.K.; Wong, M.H.; Qiu, R.L.; Cheng, H.; Ye, Z.H. Cadmium accumulation in and tolerance of rice (Oryza sativa L.) varieties with different rates of radial oxygen loss. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 1730–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, H.; Douillard, F.P.; Korkeala, H.; Lindström, M. Mobile Elements Harboring Heavy Metal and Bacitracin Resistance Genes Are Common among Listeria monocytogenes Strains Persisting on Dairy Farms. mSphere 2021, 6, e0038321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Zhang, H.; Yang, Y.; Fu, G.; Tao, L.; Xiong, J. Effects and oxygen-regulated mechanisms of water management on cadmium (Cd) accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa). Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 846, 157484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Wang, C.; Ow, D.W. Root microbiome changes associated with cadmium exposure and/or overexpression of a transgene that reduces Cd content in rice. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 237, 113530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wassenaar, T.M.; Cabal, A. The mobile dso-gene-sso element in rolling-circle plasmids of staphylococci reflects the evolutionary history of its resistance gene. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2017, 65, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.J.; Pan, J.; Liu, Y.; Duan, C.H.; Li, M. Genomic and transcriptomic insights into methanogenesis potential of novel methanogens from mangrove sediments. Microbiome 2020, 8, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.T.; Liu, J.X.; Jiang, W.Y. Metabolomics and Microbiomics Reveal Impacts of Rhizosphere Metabolites on Alfalfa Continuous Cropping. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 833968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Wang, Y.L.; Li, N.; Zhao, N.; Xu, S.X. Bacteria-Like Gaiella Accelerate Soil Carbon Loss by Decomposing Organic Matter of Grazing Soils in Alpine Meadows on the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. Microb. Ecol. 2024, 87, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, P.; Kang, H.X.; Peng, Q.Z.; Wicaksono, W.A.; Berg, G.; Liu, Z.; Ma, J.; Zhang, D.Y.; Cernava, T.; Liu, Y. Microbiome homeostasis on rice leaves is regulated by a precursor molecule of lignin biosynthesis. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 5009.15-2014; National Food Safety Standard for the Determination of Cadmium in Foods. National Standards of People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2014.
- GB/T 17141-1997; Soil Quality—Determination of Lead, Cadmium-Graphite Furnace Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometry. National Standards of People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 1997.
- GB/T 23739-2009; Soil Quality—Analysis of Available Lead and Cadmium Contents in Soils—Atomic Absorption Spectrometry. National Standards of People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2009.
- LY/T1228-2015; Nitrogen Determination Methods of Forest Soils. People’s Republic of China Forestry Industry Standard: Beijing, China, 2015.
- GB9837-88; Method for Determination of Soil Total Phosphorus. National Standards of People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 1988.
- NY/T 1121.7-2014; Soil Testing-Part 7: Method for Determination of Available Phosphorus in Soil. Ministry of Agriculture of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2014.
- NY/T889-2004; Determination of Exchangeable Potassium and Non-Exchangeable Potassium Content in Soil. Ministry of Agriculture of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2004.
- NY/T 1121.2-2006; Soil Testing Part 2: Method for Determination of Soil PH. Ministry of Agriculture of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2006.
- NY/T 1121.6-2006; Soil Testing Part 2: Method for Determination of Soil Organic Matter. Ministry of Agriculture of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2006.
- Schloss, P.D.; Westcott, S.L.; Ryabin, T. Introducing mothur: Open-Source, Platform-Independent, Community-Supported Software for Describing and Comparing Microbial Communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 7537–7541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, S.; Luo, Z.; Peng, J.; Wu, X.; Meng, X.; Qin, Y.; Zhu, F. Analysis of Cadmium Accumulation Characteristics Affected by Rhizosphere Bacterial Community of Two High-Quality Rice Varieties. Plants 2025, 14, 1790. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14121790
Zhang S, Luo Z, Peng J, Wu X, Meng X, Qin Y, Zhu F. Analysis of Cadmium Accumulation Characteristics Affected by Rhizosphere Bacterial Community of Two High-Quality Rice Varieties. Plants. 2025; 14(12):1790. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14121790
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Shangdu, Zhengliang Luo, Ju Peng, Xiang Wu, Xiufei Meng, Yuanyi Qin, and Feiying Zhu. 2025. "Analysis of Cadmium Accumulation Characteristics Affected by Rhizosphere Bacterial Community of Two High-Quality Rice Varieties" Plants 14, no. 12: 1790. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14121790
APA StyleZhang, S., Luo, Z., Peng, J., Wu, X., Meng, X., Qin, Y., & Zhu, F. (2025). Analysis of Cadmium Accumulation Characteristics Affected by Rhizosphere Bacterial Community of Two High-Quality Rice Varieties. Plants, 14(12), 1790. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14121790




