Hormonal and Transcriptomic Insights into Inflorescence Stalk Elongation in Oil Palm
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation
2.2. Determination of Endogenous Hormones
2.3. RNA Extraction, Library Construction, and Sequencing
2.4. Differentially Expressed Genes (DEGs) Analysis
2.5. Data Analysis and Visualization
3. Results
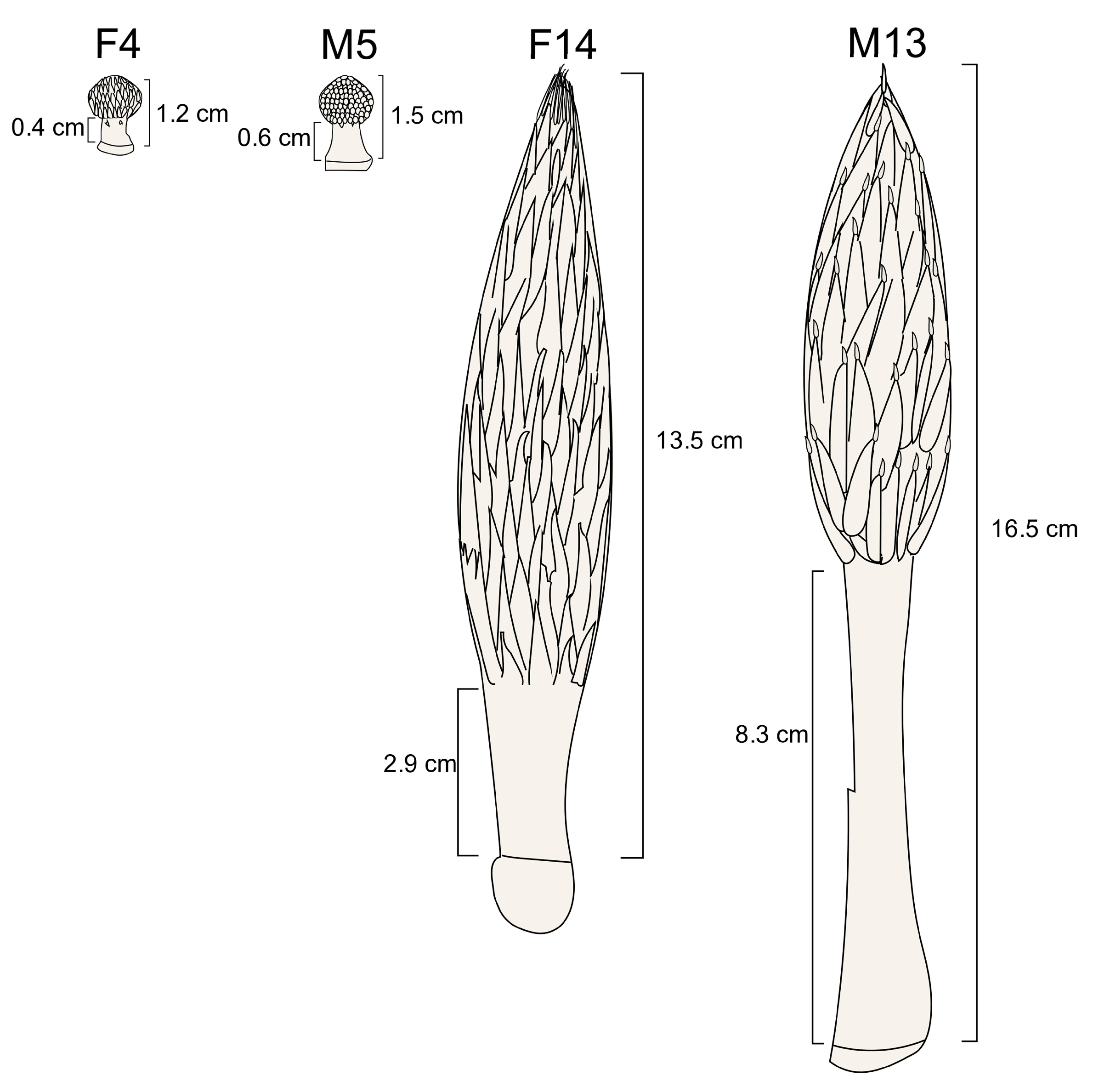
3.1. Differences in Stalk Lengths Between Female and Male Inflorescences
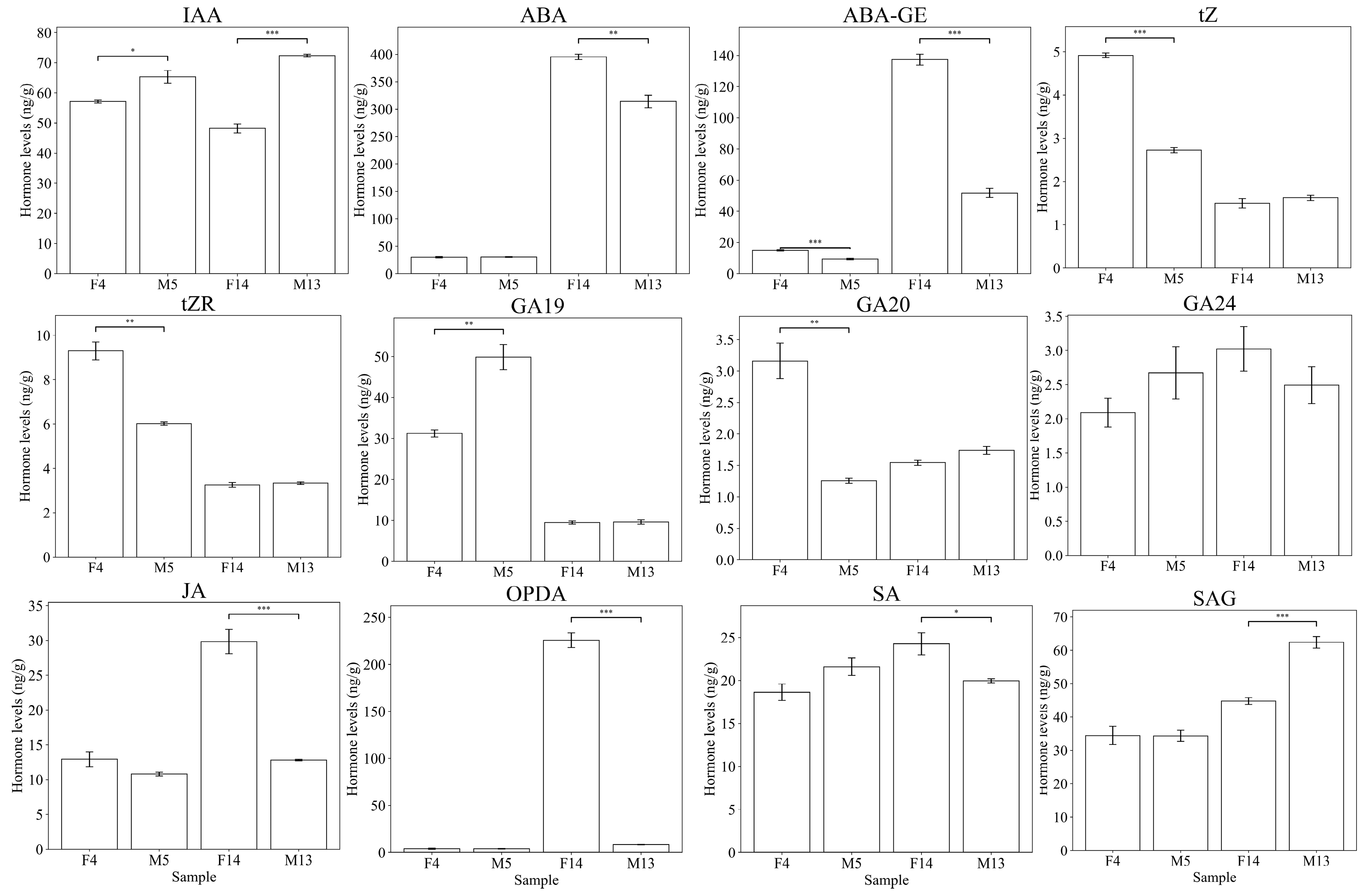
3.2. Quantification of Endogenous Hormones
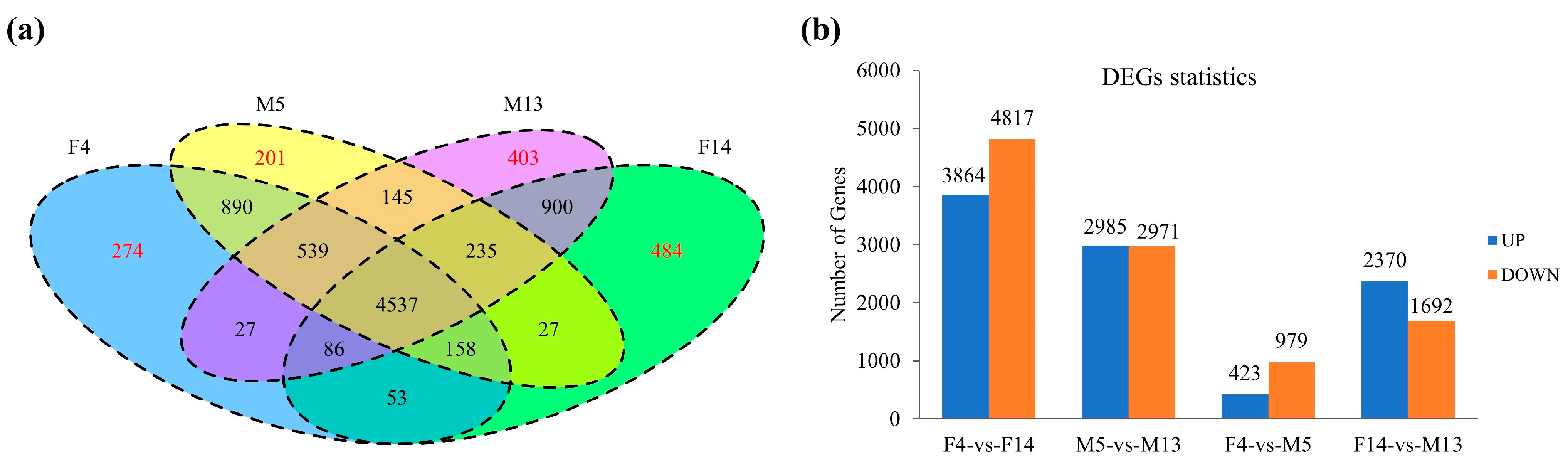
3.3. Transcriptomic Analysis
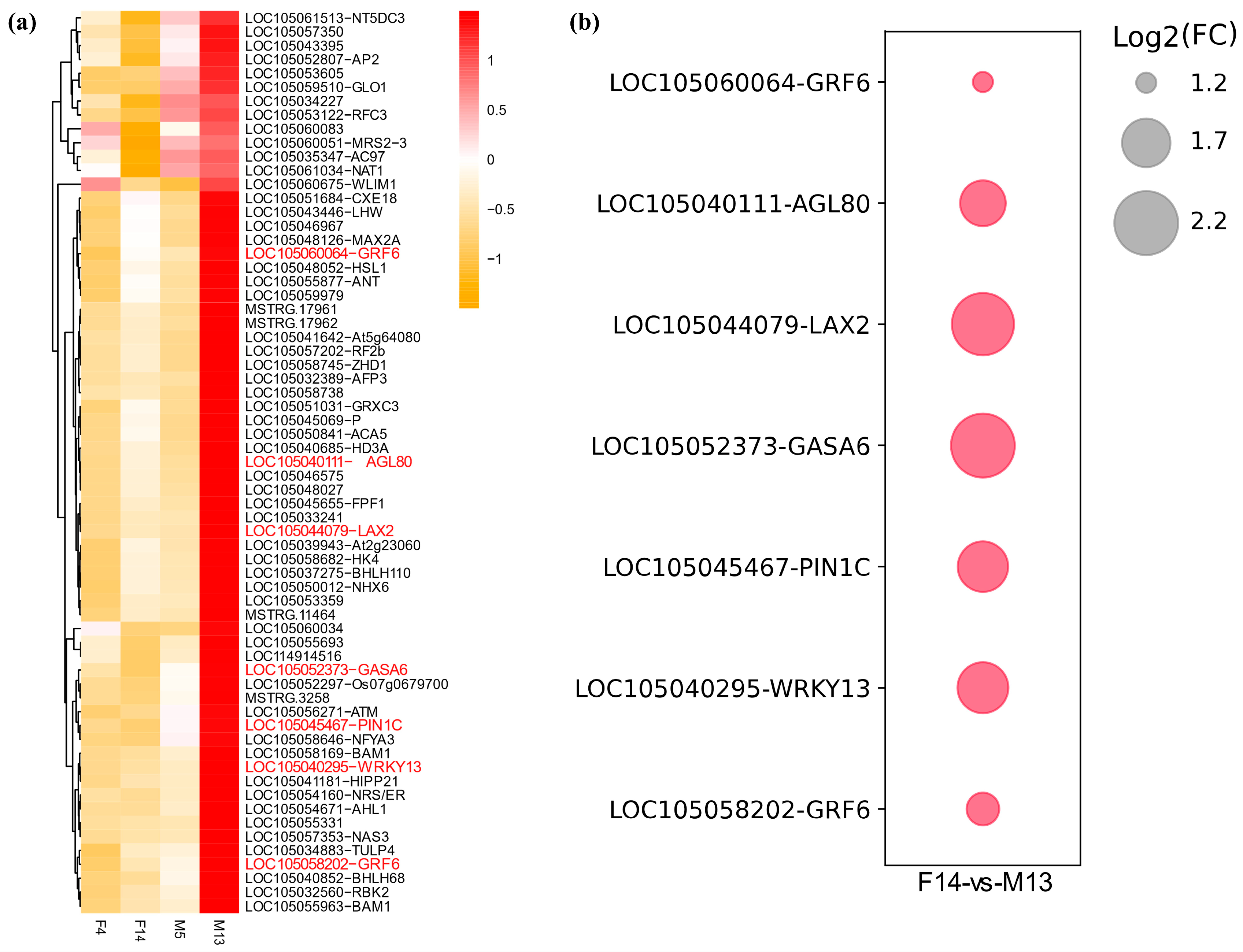
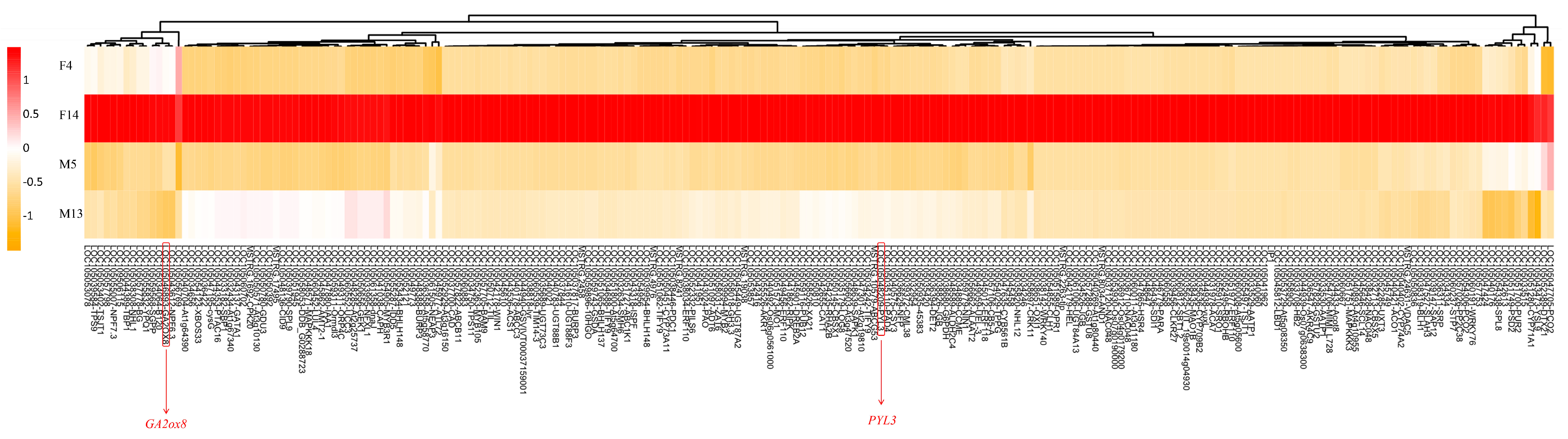
3.4. Expression Analysis of DEGs
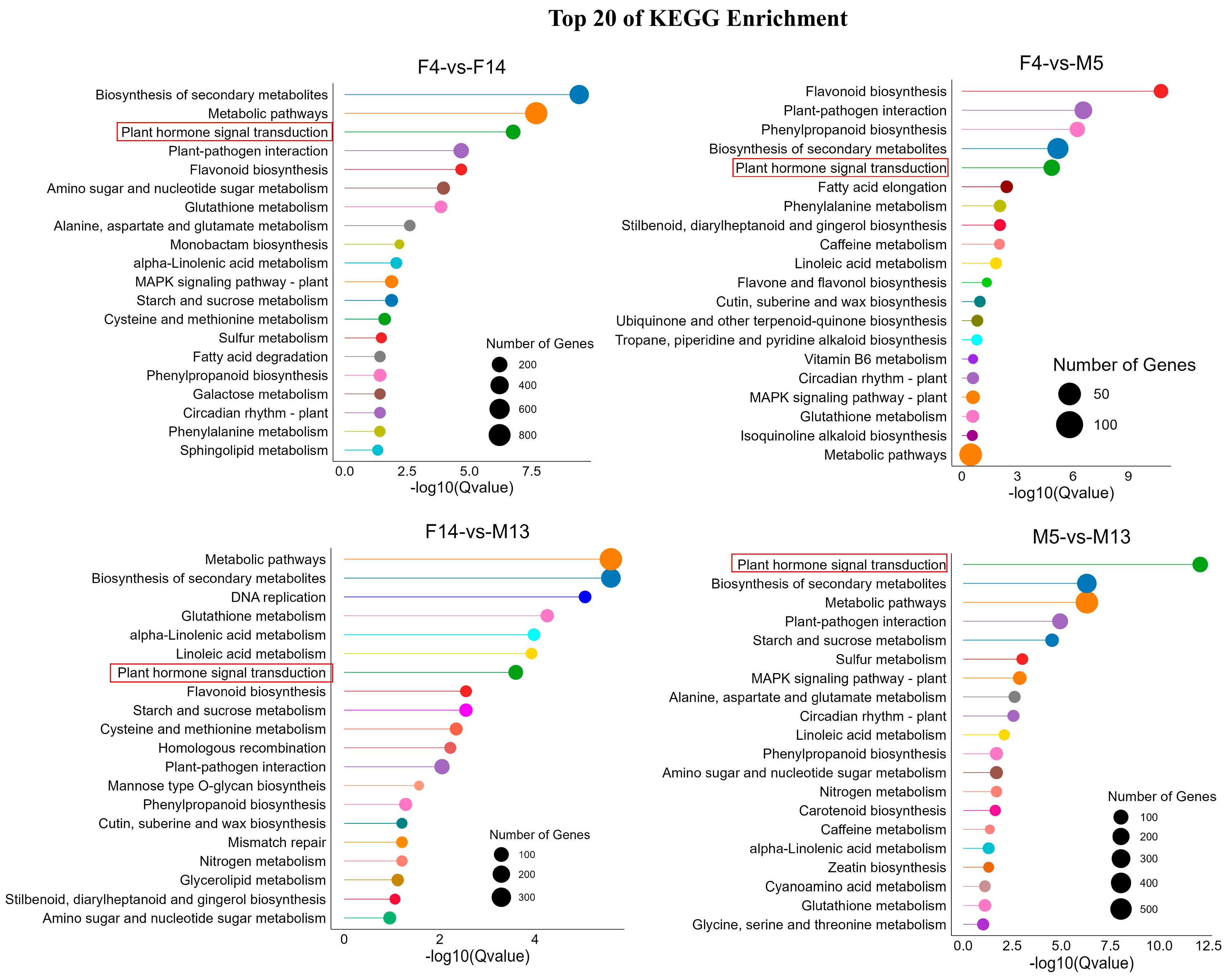
3.5. Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Htwe, Y.M.; Shi, P.; Zhang, D.; Li, Z.; Yu, Q.; Wang, Y. GWAS Determined Genetic Loci Associated with Callus Induction in Oil Palm Tissue Culture. Plant Cell Rep. 2024, 43, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barcelos, E.; De Almeida Rios, S.; Cunha, R.N.V.; Lopes, R.; Motoike, S.Y.; Babiychuk, E.; Skirycz, A.; Kushnir, S. Oil Palm Natural Diversity and the Potential for Yield Improvement. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majda, M.; Robert, S. The Role of Auxin in Cell Wall Expansion. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, E.; Huang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Su, W.; Liu, H.; Sun, G.; Chen, R.; Hao, Y.; Song, S. Crosstalk between Auxin and Gibberellin during Stalk Elongation in Flowering Chinese Cabbage. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 3976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luan, J.; Xin, M.; Qin, Z. Genome-Wide Identification and Functional Analysis of the Roles of SAUR Gene Family Members in the Promotion of Cucumber Root Expansion. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chae, K.; Isaacs, C.G.; Reeves, P.H.; Maloney, G.S.; Muday, G.K.; Nagpal, P.; Reed, J.W. Arabidopsis SMALL AUXIN UP RNA63 Promotes Hypocotyl and Stamen Filament Elongation. Plant J. 2012, 71, 684–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Lei, Y.; Guan, H.; Hao, Y.; Liu, H.; Sun, G.; Chen, R.; Song, S. Transcriptomic Analysis of the Regulation of Stalk Development in Flowering Chinese Cabbage (Brassica Campestris) by RNA Sequencing. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Li, J.; Wang, Q.; Lv, K.; Du, K.; Zhang, W.; Li, Q.; Kang, X.; Wei, H. Growth-Regulating Factor 5 (GRF5)-Mediated Gene Regulatory Network Promotes Leaf Growth and Expansion in Poplar. New Phytol. 2021, 230, 612–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.J.; Yan, J.Y.; Li, C.X.; Li, G.X.; Wu, Y.R.; Zheng, S.J. Transcription Factor WRKY46 Modulates the Development of Arabidopsis Lateral Roots in Osmotic/Salt Stress Conditions via Regulation of ABA Signaling and Auxin Homeostasis. Plant J. 2015, 84, 56–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.Q.; Xu, Y.; Lu, Y.; Yu, H.X.; Gu, M.H.; Liu, Q.Q. The WRKY Transcription Factor OsWRKY78 Regulates Stem Elongation and Seed Development in Rice. Planta 2011, 234, 541–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piya, S.; Liu, J.; Burch-Smith, T.; Baum, T.J.; Hewezi, T. A Role for Arabidopsis Growth-Regulating Factors 1 and 3 in Growth-Stress Antagonism. J. Exp. Bot. 2020, 71, 1402–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapia-López, R.; García-Ponce, B.; Dubrovsky, J.G.; Garay-Arroyo, A.; Pérez-Ruíz, R.V.; Kim, S.H.; Acevedo, F.; Pelaz, S.; Alvarez-Buylla, E.R. An AGAMOUS-Related MADS-Box Gene, XAL1 (AGL12), Regulates Root Meristem Cell Proliferation and Flowering Transition in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2008, 146, 1182–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Sun, Y.; Tian, Z.; Fu, G.; Pei, X.; Pan, Z.; Nazir, M.F.; Song, S.; Li, H.; Wang, X.; et al. GhGASA10–1 Promotes the Cell Elongation in Fiber Development through the Phytohormones IAA-Induced. BMC Plant Biol. 2021, 21, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Welti, R.; Wang, X. Quantitative Analysis of Major Plant Hormones in Crude Plant Extracts by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry. Nat. Protoc. 2010, 5, 986–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. Fastp: An Ultra-Fast All-in-One FASTQ Preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. Fast Gapped-Read Alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. HISAT: A Fast Spliced Aligner with Low Memory Requirements. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated Estimation of Fold Change and Dispersion for RNA-Seq Data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, M.D.; McCarthy, D.J.; Smyth, G.K. EdgeR: A Bioconductor Package for Differential Expression Analysis of Digital Gene Expression Data. Bioinformatics 2009, 26, 139–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the False Discovery Rate: A Practical and Powerful Approach to Multiple Testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R CoreTeam. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Allaire, J.J. RStudio: Integrated Development Environment for R. In Proceedings of the R User Conference, useR!, University of Warwick, Coventry, UK, 16–18 August 2011; Volume 75. [Google Scholar]
- Lorrai, R.; Boccaccini, A.; Ruta, V.; Possenti, M.; Costantino, P.; Vittorioso, P. Abscisic Acid Inhibits Hypocotyl Elongation Acting on Gibberellins, DELLA Proteins and Auxin. AoB Plants 2018, 10, ply061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schomburg, F.M.; Bizzell, C.M.; Lee, D.J.; Zeevaart, J.A.D.; Amasino, R.M. Overexpression of a Novel Class of Gibberellin 2-Oxidases Decreases Gibberellin Levels and Creates Dwarf Plants. Plant Cell 2003, 15, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.; Ma, J.; Zhang, M.; Li, X.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, M.; Ding, Z. Auxin Promotes Hypocotyl Elongation by Enhancing BZR1 Nuclear Accumulation in Arabidopsis. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eade2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.H.; Liu, Y.B.; Zhang, X.S. Auxin-Cytokinin Interaction Regulates Meristem Development. Mol. Plant 2011, 4, 616–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Du, K.; Kang, X.; Wei, H. The Diverse Roles of Cytokinins in Regulating Leaf Development. Hortic. Res. 2021, 8, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swarup, R.; Bhosale, R. Developmental Roles of AUX1/LAX Auxin Influx Carriers in Plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kramer, E.M.; Bennett, M.J. Auxin Transport: A Field in Flux. Trends Plant Sci. 2006, 11, 382–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garay-Arroyo, A.; Ortiz-Moreno, E.; De La Paz Sánchez, M.; Murphy, A.S.; García-Ponce, B.; Marsch-Martínez, N.; De Folter, S.; Corvera-Poiré, A.; Jaimes-Miranda, F.; Pacheco-Escobedo, M.A.; et al. The MADS Transcription Factor XAL2/AGL14 Modulates Auxin Transport during Arabidopsis Root Development by Regulating PIN Expression. EMBO J. 2013, 32, 2884–2895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouteraa, M.T.; Ben Romdhane, W.; Baazaoui, N.; Alfaifi, M.Y.; Chouaibi, Y.; Ben Akacha, B.; Ben Hsouna, A.; Kačániová, M.; Ćavar Zeljković, S.; Garzoli, S.; et al. GASA Proteins: Review of Their Functions in Plant Environmental Stress Tolerance. Plants 2023, 12, 2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Gao, J.; Wang, G.; Wang, S.; Chen, K.; Pu, W.; Wang, Y.; Xia, Q.; Fan, X. Genome-Wide Identification and Characterization of GASA Gene Family in Nicotiana Tabacum. Front. Genet. 2022, 12, 768942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Chen, W.; Xu, Z.; Chen, M.; Yu, D. Functions of WRKYs in Plant Growth and Development. Trends Plant Sci. 2023, 28, 630–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Guo, P.; Wang, J.; Xu, Z.Y. Growth-Regulating Factors: Conserved and Divergent Roles in Plant Growth and Development and Potential Value for Crop Improvement. Plant J. 2023, 113, 1122–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omidbakhshfard, M.A.; Proost, S.; Fujikura, U.; Mueller-Roeber, B. Growth-Regulating Factors (GRFs): A Small Transcription Factor Family with Important Functions in Plant Biology. Mol. Plant 2015, 8, 998–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Portereiko, M.F.; Lloyd, A.; Steffen, J.G.; Punwani, J.A.; Otsuga, D.; Drews, G.N. AGL80 Is Required for Central Cell and Endosperm Development in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2006, 18, 1862–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, L.; Gu, L.; Wang, S.; Cai, H.; Wu, J.; Wang, J.; Yang, M. Progress in the Understanding of WRKY Transcription Factors in Woody Plants. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 242, 124379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schluttenhofer, C.; Yuan, L. Regulation of Specialized Metabolism by WRKY Transcription Factors. Plant Physiol. 2015, 167, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

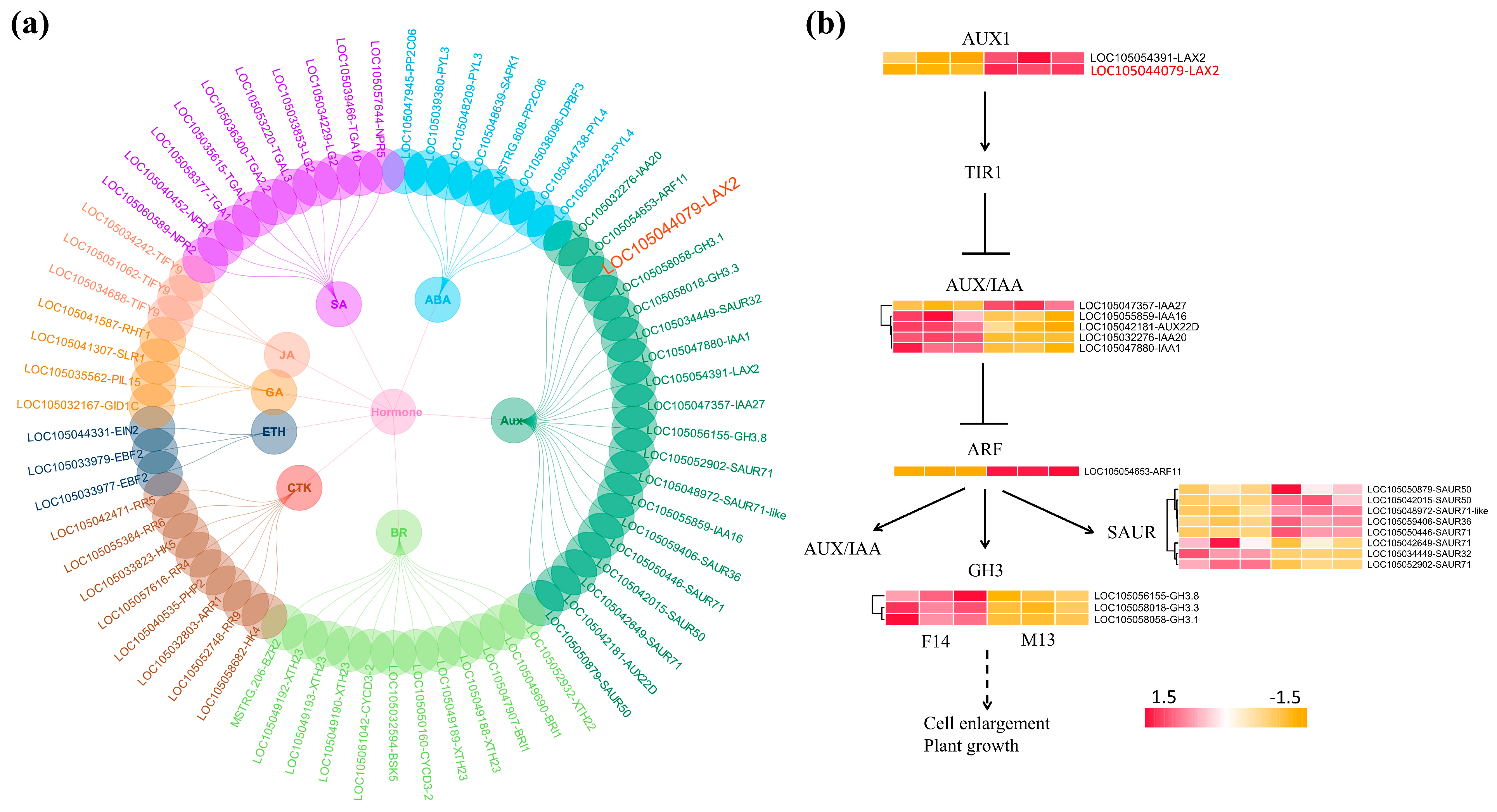
| Gene | Expression Pattern | Hormone Pathway | Inferred Function |
|---|---|---|---|
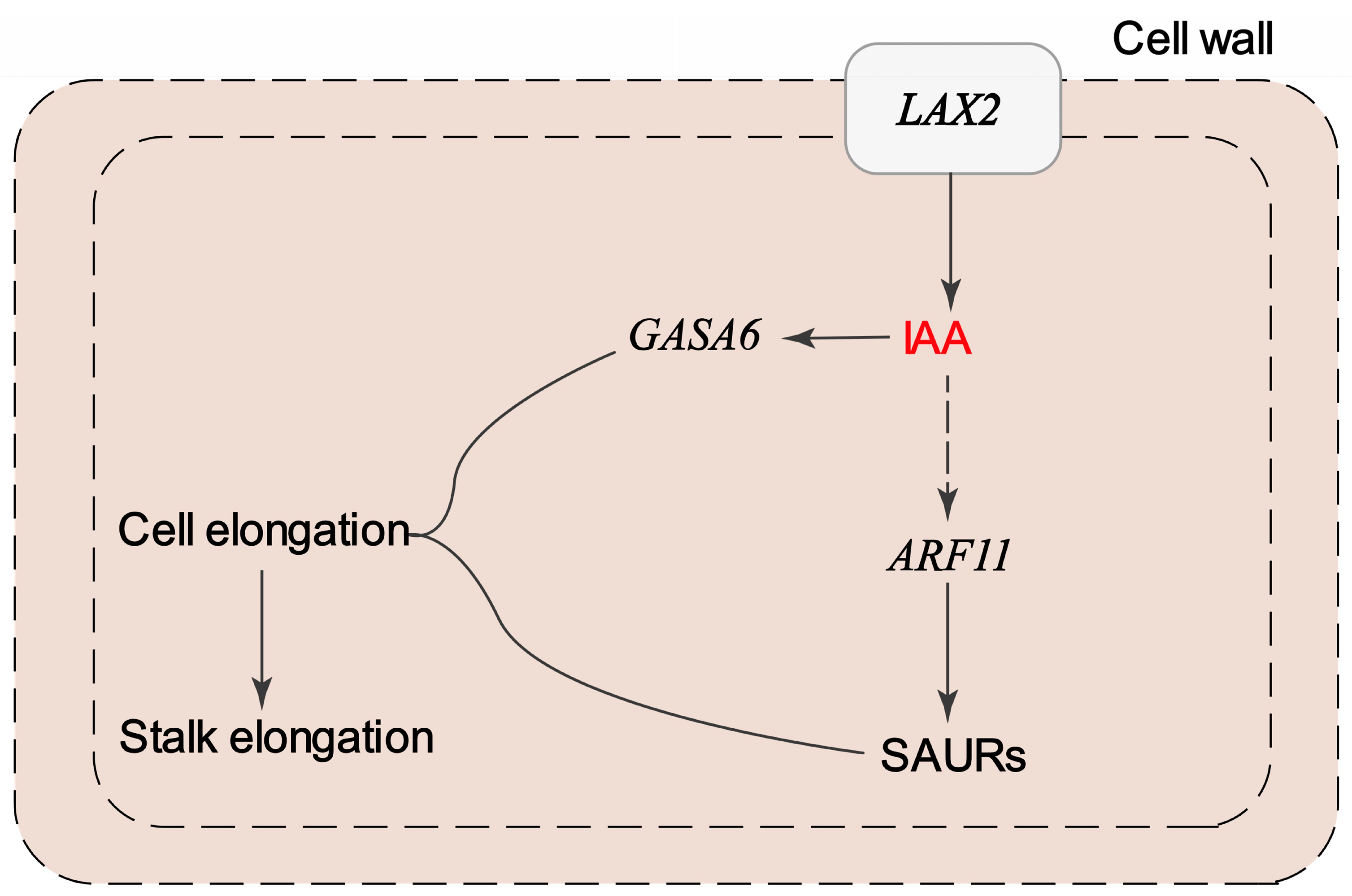
| LAX2 | Upregulated in M13 | Auxin influx carrier | Promotes IAA transport into cells; contributes to auxin accumulation and signaling in elongating stalks |
| ARF11 | Upregulated in M13 | Auxin response factor | Activates downstream auxin-responsive genes involved in cell elongation |
| SAURs | Multiple members upregulated in M13 | Auxin-responsive genes | Promote cell wall loosening and elongation; direct targets of ARFs |
| GASA6 | Upregulated in M13 | Gibberellin associated | May act downstream of auxin–gibberellin crosstalk to promote stalk elongation |
| PYL3 | Upregulated in F14 | ABA receptor | Suggests a role for ABA signaling modulation in stalk development |
| GA2ox8 | Upregulated in F14 | Gibberellin metabolism | Inactivates bioactive gibberellins; likely contributes to growth suppression and shorter stalk length in female inflorescences |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, P.; Htwe, Y.M.; Zhang, D.; Li, Z.; Yu, Q.; He, X.; Yang, J.; Wang, Y. Hormonal and Transcriptomic Insights into Inflorescence Stalk Elongation in Oil Palm. Plants 2025, 14, 1715. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14111715
Shi P, Htwe YM, Zhang D, Li Z, Yu Q, He X, Yang J, Wang Y. Hormonal and Transcriptomic Insights into Inflorescence Stalk Elongation in Oil Palm. Plants. 2025; 14(11):1715. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14111715
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Peng, Yin Min Htwe, Dapeng Zhang, Zhiying Li, Qun Yu, Xiangman He, Jing Yang, and Yong Wang. 2025. "Hormonal and Transcriptomic Insights into Inflorescence Stalk Elongation in Oil Palm" Plants 14, no. 11: 1715. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14111715
APA StyleShi, P., Htwe, Y. M., Zhang, D., Li, Z., Yu, Q., He, X., Yang, J., & Wang, Y. (2025). Hormonal and Transcriptomic Insights into Inflorescence Stalk Elongation in Oil Palm. Plants, 14(11), 1715. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14111715







