Exogenous Gibberellins and Auxins Promote Crown Bud Regeneration and Influence Endogenous Hormone Changes in Alfalfa
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Effects of Exogenous GA3 and IAA Spraying on the Regeneration and Biomass of Alfalfa Crown Buds
2.1.1. Effects of Exogenous GA3 and IAA Spraying on the Regeneration of Alfalfa Crown Buds
2.1.2. The Effect of Exogenous GA3 and IAA Spraying on the Length of Crown Buds in Alfalfa
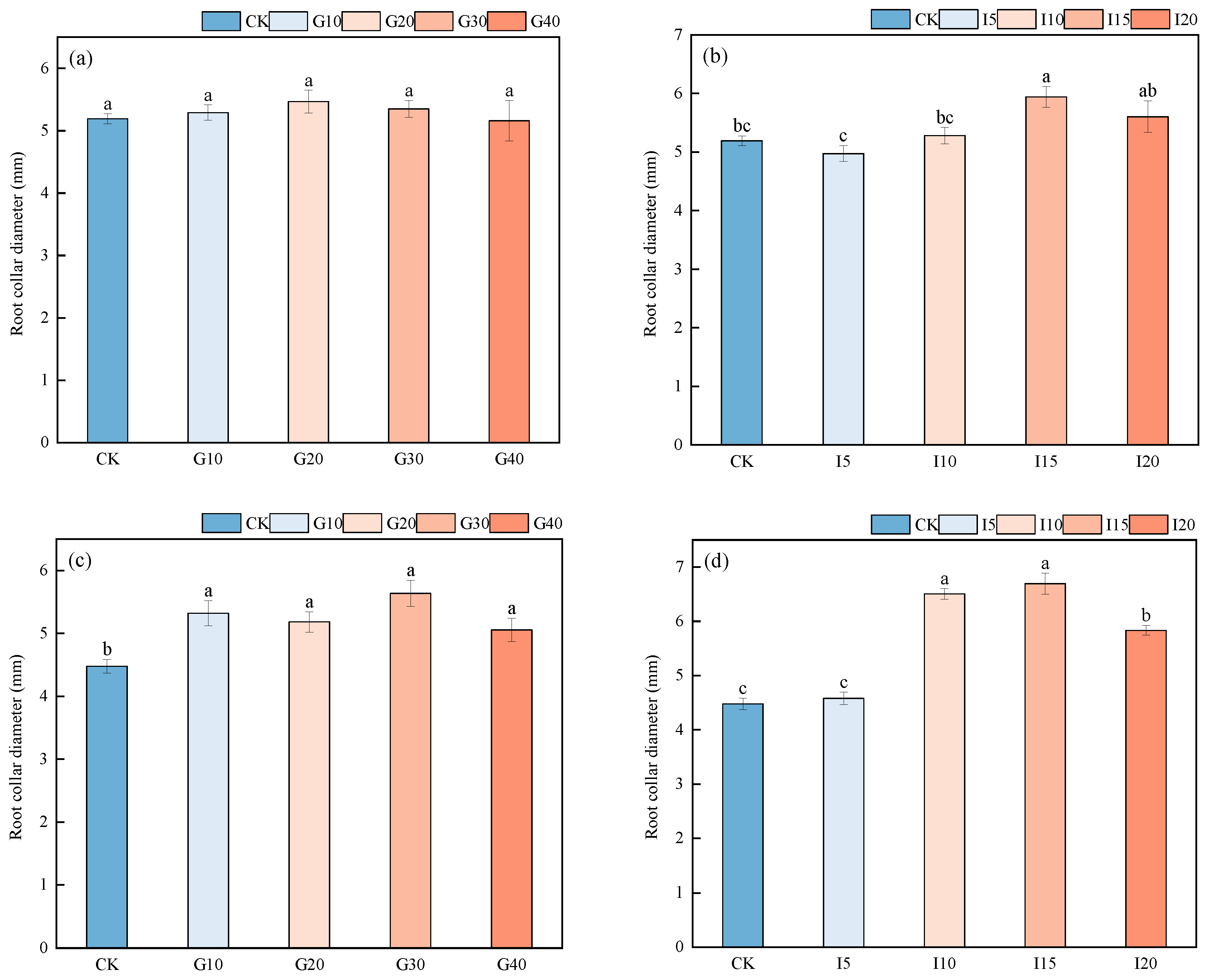
2.1.3. The Effect of Exogenous GA3 and IAA Spraying on the Neck Traits of Alfalfa Roots
2.1.4. Effects of Exogenous GA3 and IAA Spraying on Aboveground Biomass of Alfalfa
2.2. Effects of Exogenous GA3 and IAA on Endogenous GA3, IAA, and ABA Content in Alfalfa Crown Buds
2.2.1. Effects of Exogenous GA3 and IAA on Endogenous GA3 Content in Alfalfa Crown Buds
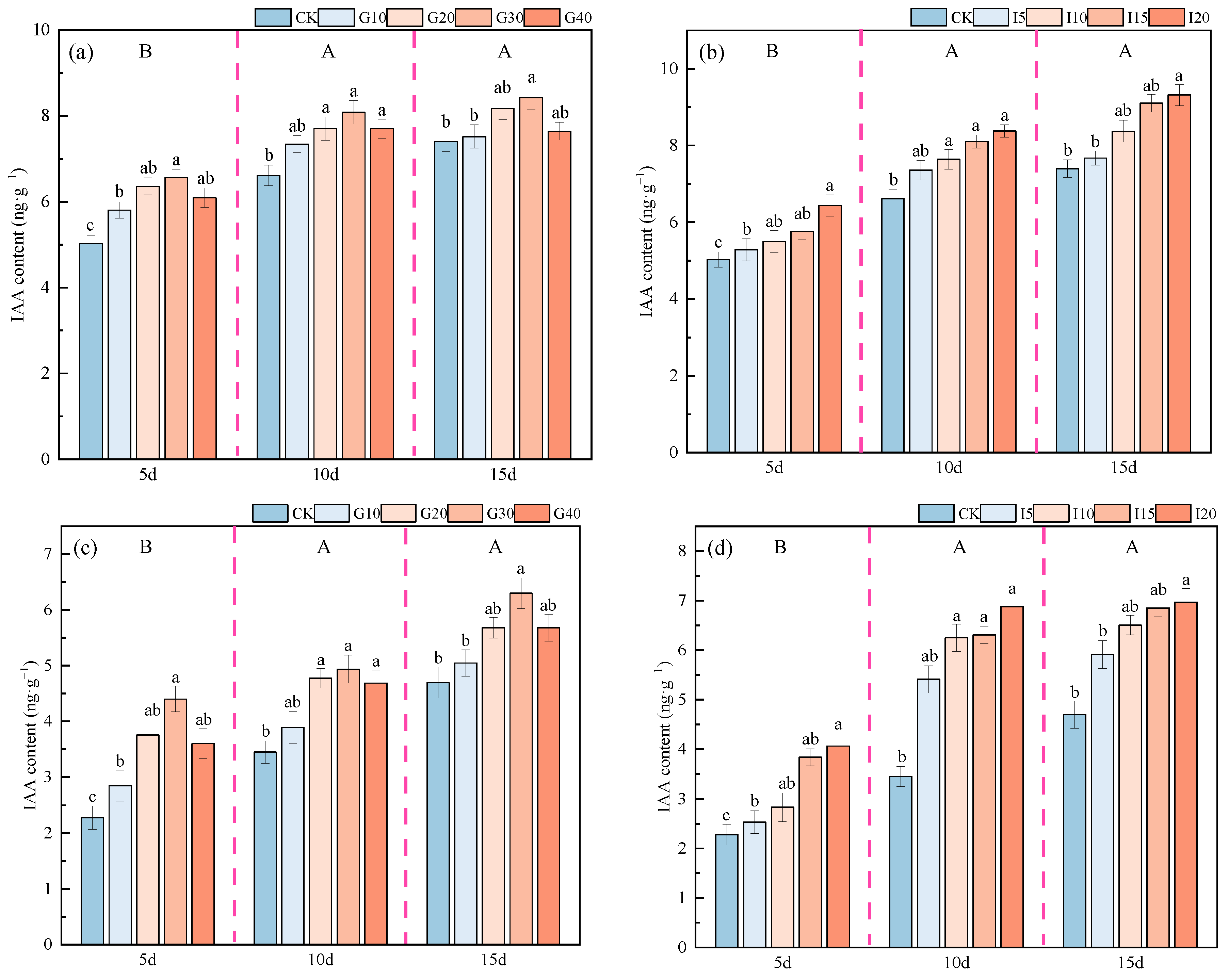
2.2.2. Effects of Exogenous GA3 and IAA on Endogenous IAA Content in Alfalfa Crown Buds
2.2.3. Effects of Exogenous GA3 and IAA on Endogenous ABA Content in Alfalfa Crown Buds
2.2.4. Effects of Exogenous GA3 and IAA on the Ratio of Endogenous GA3 to ABA in Alfalfa Crown Buds
2.2.5. Effects of Exogenous GA3 and IAA on the Ratio of Endogenous IAA to ABA in Alfalfa Crown Buds
2.3. Effects of Exogenous GA3 and IAA on Soluble Sugar, Starch, and NSC Content in Alfalfa Crown Buds
2.3.1. Effects of Exogenous GA3 and IAA on Soluble Sugar Content in Alfalfa Crown Buds
2.3.2. Effects of Exogenous GA3 and IAA on Starch Content in Alfalfa Crown Buds
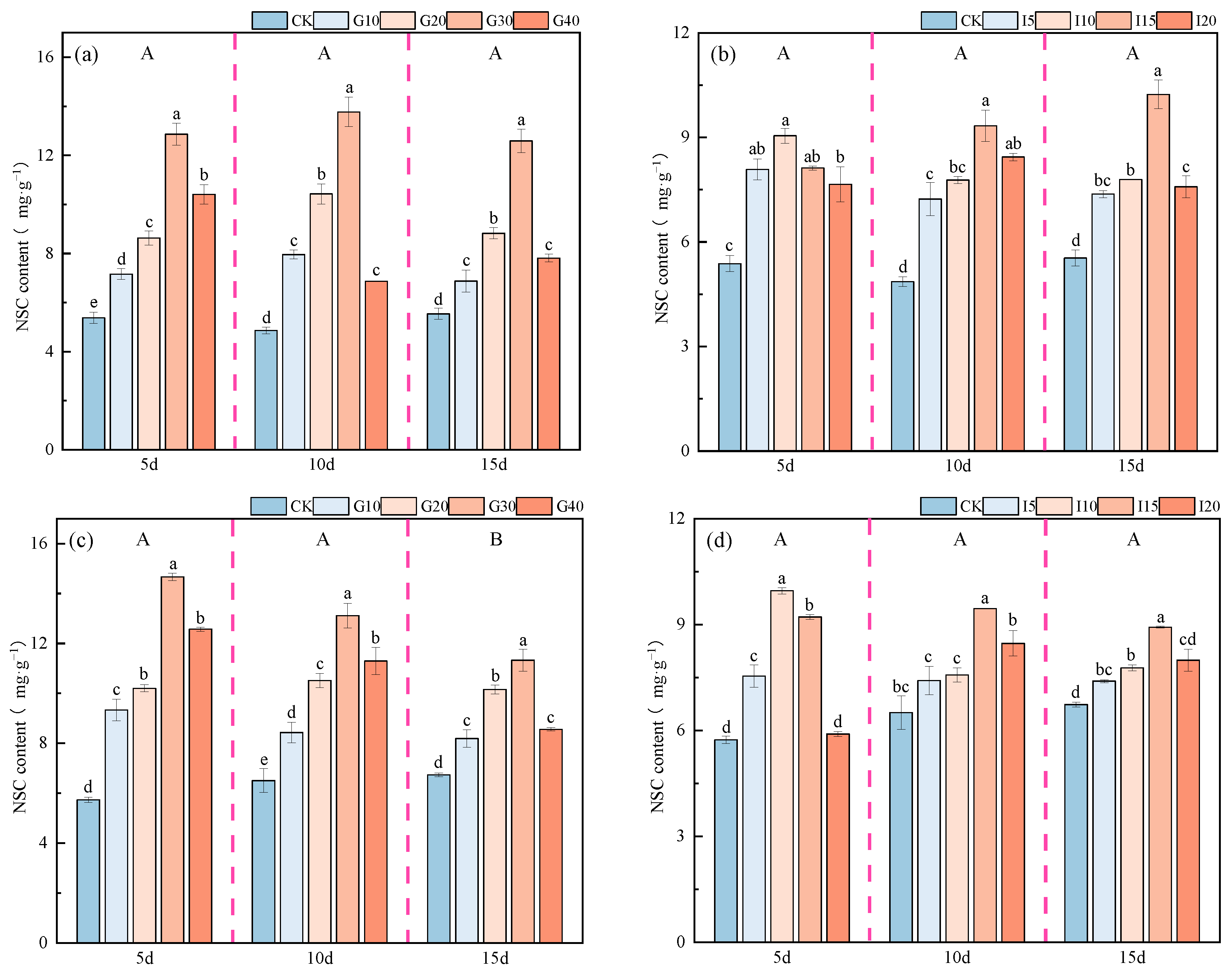
2.3.3. Effects of Exogenous GA3 and IAA on NSC Content in Alfalfa Crown Buds
2.4. Effects of Exogenous GA3 and IAA on Total Nitrogen Content in Alfalfa Crown Buds
2.5. Correlation Analysis Among Aboveground Biomass, Crown Bud Number, and Various Biochemical Parameters in Alfalfa
2.6. Regression Analysis Among Exogenous GA3, IAA Concentrations, and Aboveground Biomass
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Experimental Materials
4.2. Experimental Design
4.3. Measurement Content and Methods
4.4. Data Processing
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, M.; Wang, Z.; Mu, L.; Xu, R.; Yang, H. Effect of regulated deficit irrigation on alfalfa performance under two irrigation systems in the inland arid area of mid western China. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 248, 106764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Nan, L.; Smith, K.F. The Current Status, Problems, and Prospects of Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) Breeding in China. Agronomy 2017, 7, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Tian, Y.; Song, Y.; Li, Q. A Thermal Time Basis for Comparing the Germination Requirements of Alfalfa Cultivars with Different Fall Dormancy Ratings. Agronomy 2023, 13, 2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, H. Dynamic Study of Endogenous Hormone Content in the Roots of Alfalfa with Different Dormancy Types. Ph.D. Thesis, Northwest A&F University, Xianyang, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Djaman, K.; O’neill, M.; Lauriault, L.; Marsalis, M.; Koudahe, K.; Darapuneni, M.K. The Dynamics of Forage Yield of Different Fall Dormancy Rating Alfalfa Cultivars in a Semiarid Climate. Agric. Res. 2021, 10, 378–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallenbach, R.L.; Roberts, C.A.; Teuber, L.R.; Bishop-Hurley, G.J.; Benedict, H.R. Estimation of fall dormancy in alfalfa by Near InfReflectance Spectroscopy. Crop Sci. 2001, 41, 774–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brouwer, D.J.; Duke, S.H.; Osborn, T.C. Mapping genetic factors associated with winter hardiness, fall growth, and freezing injury in autotetraploid alfalfa. Crop Sci. 2000, 40, 1387–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosse, G.; Lemaire, G.; Chartier, M.; Balfourier, F. Structure of a Lucerne Population (Medicago sativa L.) and Dynamics of Stem Competition for Light During Regrowth. J. Appl. Ecol. 1988, 25, 609–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Undersander, D.J.; Vassalotti, P.; Cosgrove, D. Alfalfa Germination and Growth; University of Wisconsin: Madison, WI, USA, 2011; pp. 9–11. [Google Scholar]
- Hanson, C.H.; William, R. Alfalfa Science and Technology; ASA-CSSA-SSSA: Madison, WI, USA, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin, R.J.; Christie, B.R. Genetic variation for temperature response in alfalfa. Can. J. Plant Sci. 1980, 60, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquez-Ortiz, J.J.; Johnson, L.D.; Barnes, D.K.; Basigalup, D.H. Crown Morphology Relationships among Alfalfa Plant Introductions and Cultivars. Crop Sci. 1996, 36, 766–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volenec, J.J. Physiological control of alfalfa growth and yield. In Crop Yield, Physiology and Processes; Smith, D.L., Hamel, C., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Petr, J.; Černý, V.; Hruška, L. Yield Formation in the Main Field Crops; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Musgrave, D.J.; Langer, R.H.M. Crown development of two diverse genotypes of lucerne. New Zealand J. Agric. Res. 1977, 20, 453–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukanov, K.A.; Chebotar, V.K.; Meyer, J.J.M.; Bibikova, T.N. Effect of plant growth-promoting Rhizobacteria on plant hormone homeostasis. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2017, 113, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denancé, N.; Sánchez-Vallet, A.; Goffner, D.; Molina, A. Disease resistance or growth: The role of plant hormones in balancing immune responses and fitness costs. Front. Plant Sci. 2013, 4, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, T.; Cheng, L.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, J.; Guo, R.; Cheng, C. The effects of boron and gibberellin on the fruit set rate and fruit quality of ‘Li Guang Apricot’. Acta Bot. Boreali-Occident. Sin. 2020, 40, 319–327. [Google Scholar]
- Jabir, B.M.O. The Effects of Plant Growth Regulators on the Growth and Development of Radish. Ph.D. Thesis, Nanjing Agricultural University, Nanjing, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, C.; Lu, M.Z.; Zhang, J. Exogenous hormones supplementation improve adventitious root formation in woody plants. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 1009531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Lei, Y.; Sun, J.; Ma, M.; Deng, P.; Quan, J.E.; Bi, H. Effects of Different Growth Hormones on Rooting and Endogenous Hormone Content of Two Morus alba L. Cuttings. Horticulturae 2023, 9, 552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillespie, L.M.; Volaire, F.A. Are winter and summer dormancy symmetrical seasonal adaptive strategies? The case of temperate herbaceous perennials. Ann. Bot. 2017, 119, 311–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersson, S.V.; Johansson, A.I.; Kowalczyk, M.; Makoveychuk, A.; Wang, J.Y.; Moritz, T.; Grebe, M.; Benfey, P.N.; Sandberg, G.; Ljung, K. An auxin gradient and maXinmum in the arabidopsis root apex shown by high-resolution cell-specific analysis of IAA distribution and synthesis. Plant Cell 2009, 21, 1659–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teale, W.D.; Paponov, I.A.; Palme, K. Auxin in action: Signaling, transport and the control of plant growth and development. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2006, 7, 847–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Li, R.; Shen, H.; Yang, L. Effect of Exogenous Plant Growth Regulators and Rejuvenation Measures on the Endogenous Hormone and Enzyme Activity Responses of Acer mono Maxim in Cuttage Rooting. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora, V.; Baigorri, R.; Bacaicoa, E.; Zamarreno, A.M.; García-Mina, J.M. The humic acid-induced changes in the root concentration of nitric oxide, IAA and ethylene do not explain the changes in root architecture caused by humic acid in cucumber. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2012, 76, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tailor, A.; Bhatla, S.C. Inhibition of polyamine homeostasis facilitates root extension by modulating IAA and PIN1 distribution in etiolated salt-stressed sunflower seedlings. Theor. Exp. Plant Physiol. 2024, 36, 747–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, D.K.; Rai, P.; Guerriero, G.; Sharma, S.; Corpas, F.J.; Singh, V.P. Silicon induces adventitious root formation in rice under arsenate stress with involvement of nitric oxide and indole-3-acetic acid. J. Exp. Bot. 2021, 72, 4457–4471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez-Corrionero, A.; Sánchez-Vicente, I.; Arteaga, N.; Manrique-Gil, I.; Gómez-Jiménez, S.; Torres-Quezada, I.; Albertos, P.; Lorenzo, O. Fine-tuned nitric oxide and hormone interface in plant root development and regeneration. J. Exp. Bot. 2023, 74, 6104–6118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, A.; Maness, N.; Ferguson, L.; Deng, W.; Zhang, L. Role of plant hormones in flowering and exogenous hormone application in fruit/nut trees: A review of pecans. Fruit Res. 2021, 1, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Li, K.; Zhu, K.; Tian, Y.; Yu, Q.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Z. Effect of exogenous plant hormones on agronomic and physiological performance of a leaf early-senescent rice mutant osled. Plant Growth Regul. 2020, 92, 517–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.-H.; Sun, X.-F.; Zhao, L.-L.; Huang, L.-J.; Wang, P.-C. Exogenous hormone application regulates dwarf mutant plant height in Sophora davidii (Franch.) Skeels by changing endogenous hormone levels. Chil. J. Agric. Res. 2023, 83, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J. The Effects of Exogenous 6-BA on the Endogenous Hormones, Photosynthesis, and Seed Setting of Alfalfa Leaves. Ph.D. Thesis, Xinjiang Agricultural University, Urumqi, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Li, B.; Yang, Z. The effects of exogenous ABA on the endogenous hormone content of alfalfa under soda saline-alkali stress. Heilongjiang Anim. Sci. Vet. Med. 2020, 103–106, 111. [Google Scholar]
- Davies, P.J. Plant Hormones, Physiology, Biochemistry, Molecular Biology; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Niimi, Y.; Endo, Y.; Arisaka, E. Effeets of chilling and GAs treatments on breaking dormancy in Lilium rubellabaker bulblets cultured in vitro. J. Jpn. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 1988, 57, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Yang, B.; Shen, Y. Study on the changes in endogenous hormone content in the endosperm of Pinus tabuliformis seeds during the initial stage of germination. J. Beijing For. Univ. 2012, 34, 30–33. [Google Scholar]
- Razerm, F.A.; Baron, K.; Hill, R.D. Turing on Gibberellin and Abscisic Acid Signaling. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2006, 9, 454–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X. The Effects of Exogenous Growth Regulators on the Regulation of Endogenous GA3 Content, Pod Shattering, and Yield Components of Alfalfa. Ph.D. Thesis, Xinjiang Agricultural University, Urumqi, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Weiss, D.; Ori, N. Mechanisms of cross talk between gibberellin and other hormones. Plant Physiol. 2007, 144, 1240–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, X.; Harberd, N.P. Auxin promotes Arabidopsis root growth by modulating gibberellin response. Nature 2003, 421, 740–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapman, E.J.; Estelle, M. Mechanism of auxin-regulated gene expression in plants. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2009, 43, 265–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodgkinson, K.C. Establishment and growth of shoots following low and high cutting of lucerne in relation to the pattern of nutrient uptake. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 1973, 24, 497–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Abibulla, Y.; Halimulati, N.; Wan, J.; Lin, S. Comparison of growth and production performance of alfalfa varieties with different fall dormancy grades in the agricultural area of northern Tianshan Mountain slope. Feed. Res. 2024, 21, 130–137. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, J. Study on Functional Differences of Regeneration-Related Genes in Alfalfa Varieties with Different Fall Dormancy Grades. Ph.D. Thesis, Shihezi University, Shihezi, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, Q. The effects of exogenous plant hormones on the photosynthetic capacity and yield of rice. J. Jiangsu Agric. Coll. 1995, 16, 27–31. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, Q.; Zong, Y.; Qian, M.; Yang, F.; Teng, Y. Simultaneous quantitative determination of major plant hormones in pear flowers and fruit by UPLC/ESI-MS/MS. Anal. Methods 2014, 6, 1766–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.; Peng, X. Comparative study of two starch determination methods: Anthrone colorimetry and enzymatic hydrolysis. J. Hunan Univ. Arts Sci. 2007, 19, 34–36, 38. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Han, Q.; Yang, C.; Wang, Y.; Yang, K. Exploration of method optimization for determining total nitrogen content in soil samples using the Kjeldahl apparatus. Instrum. Stand. Metrol. 2024, 5, 15–17. [Google Scholar]















Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yue, H.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, S.; An, Y.; Peng, X.; Wen, B.; Ge, X.; Wang, Y. Exogenous Gibberellins and Auxins Promote Crown Bud Regeneration and Influence Endogenous Hormone Changes in Alfalfa. Plants 2025, 14, 1699. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14111699
Yue H, Sun Q, Zhang S, An Y, Peng X, Wen B, Ge X, Wang Y. Exogenous Gibberellins and Auxins Promote Crown Bud Regeneration and Influence Endogenous Hormone Changes in Alfalfa. Plants. 2025; 14(11):1699. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14111699
Chicago/Turabian StyleYue, Haiyan, Qunce Sun, Shuzhen Zhang, Youping An, Xianwei Peng, Binghan Wen, Xingyu Ge, and Yuxiang Wang. 2025. "Exogenous Gibberellins and Auxins Promote Crown Bud Regeneration and Influence Endogenous Hormone Changes in Alfalfa" Plants 14, no. 11: 1699. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14111699
APA StyleYue, H., Sun, Q., Zhang, S., An, Y., Peng, X., Wen, B., Ge, X., & Wang, Y. (2025). Exogenous Gibberellins and Auxins Promote Crown Bud Regeneration and Influence Endogenous Hormone Changes in Alfalfa. Plants, 14(11), 1699. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14111699



