Unraveling the Multilayered Regulatory Networks of miRNAs and PhasiRNAs in Ginkgo biloba
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials and Data Sources
2.2. sRNA Library Construction and Alignment Analysis
2.3. miRNA and PHAS Loci Identification
2.4. Screening of Differential Expressed miRNAs and PHAS
2.5. Identification of Target Genes for miRNA and phasiRNA
2.6. Identification of Regulatory Networks
2.7. Degradome Sequencing
3. Results
3.1. Identification of miRNA and PHAS Loci
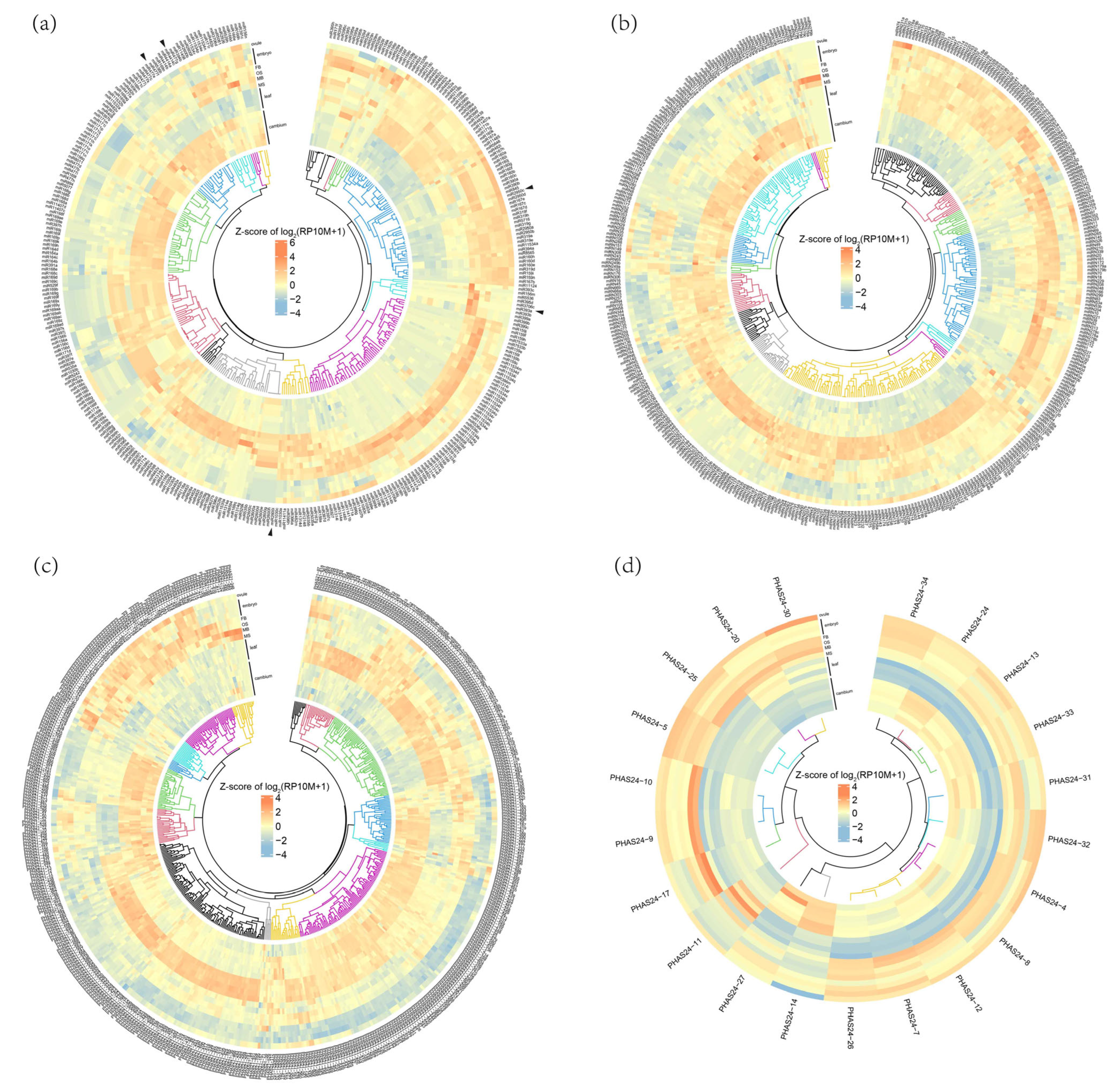
3.2. Expression Patterns of miRNA and PHAS Loci
3.3. Reproductive Tissues Preferentially Expressed miRNAs and PHAS Loci
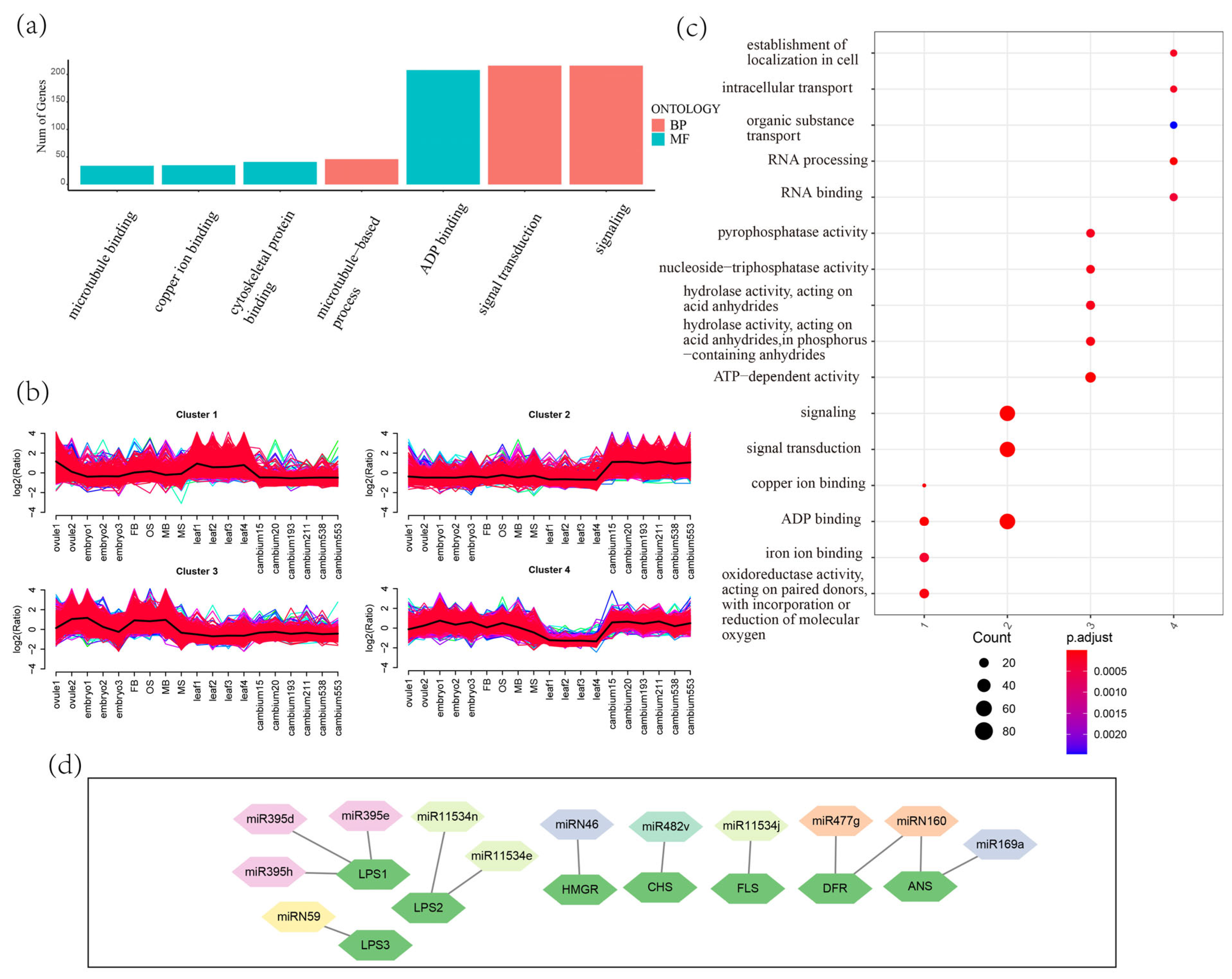
3.4. The Target Genes of miRNAs and phasiRNAs in G. biloba
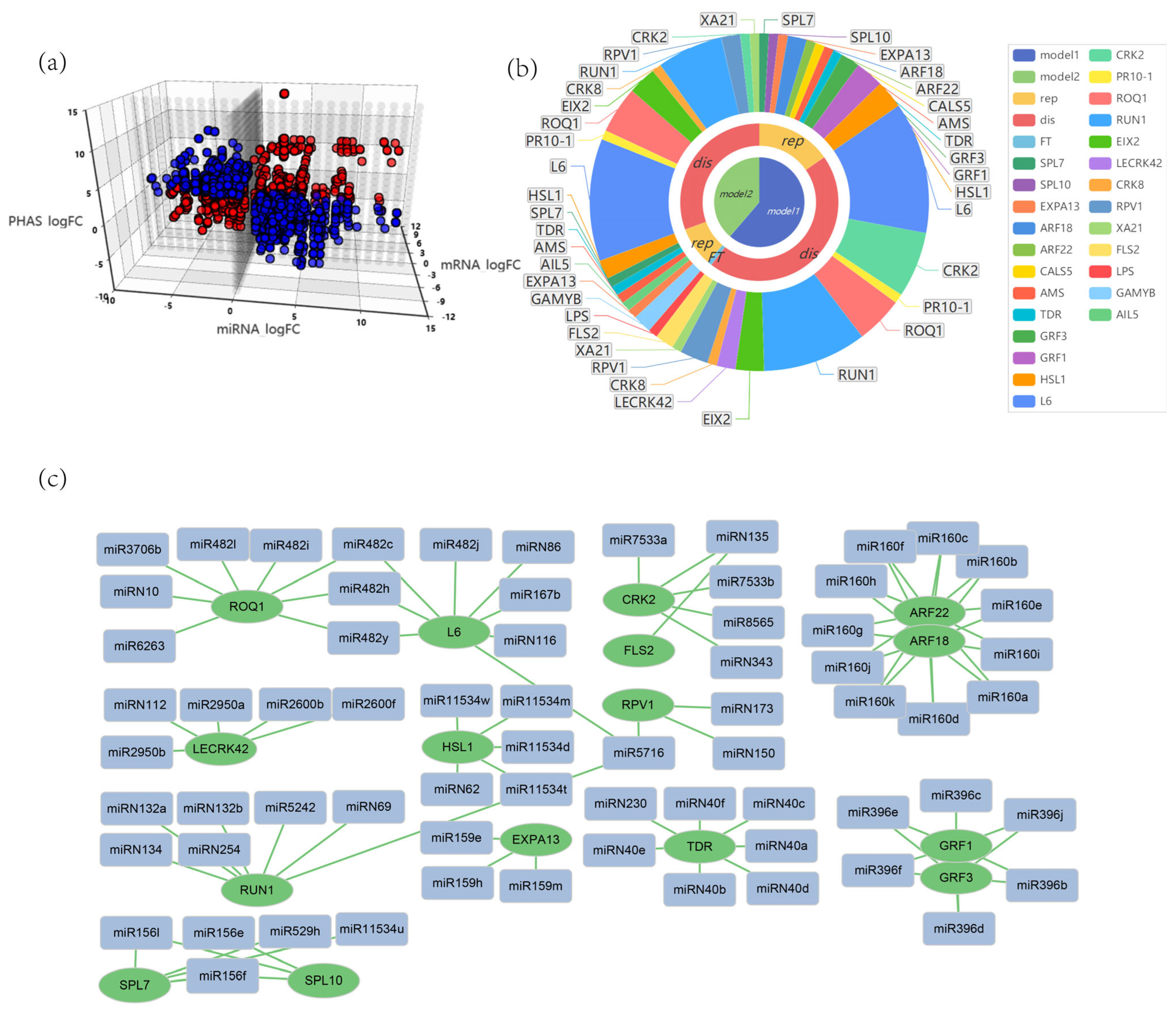
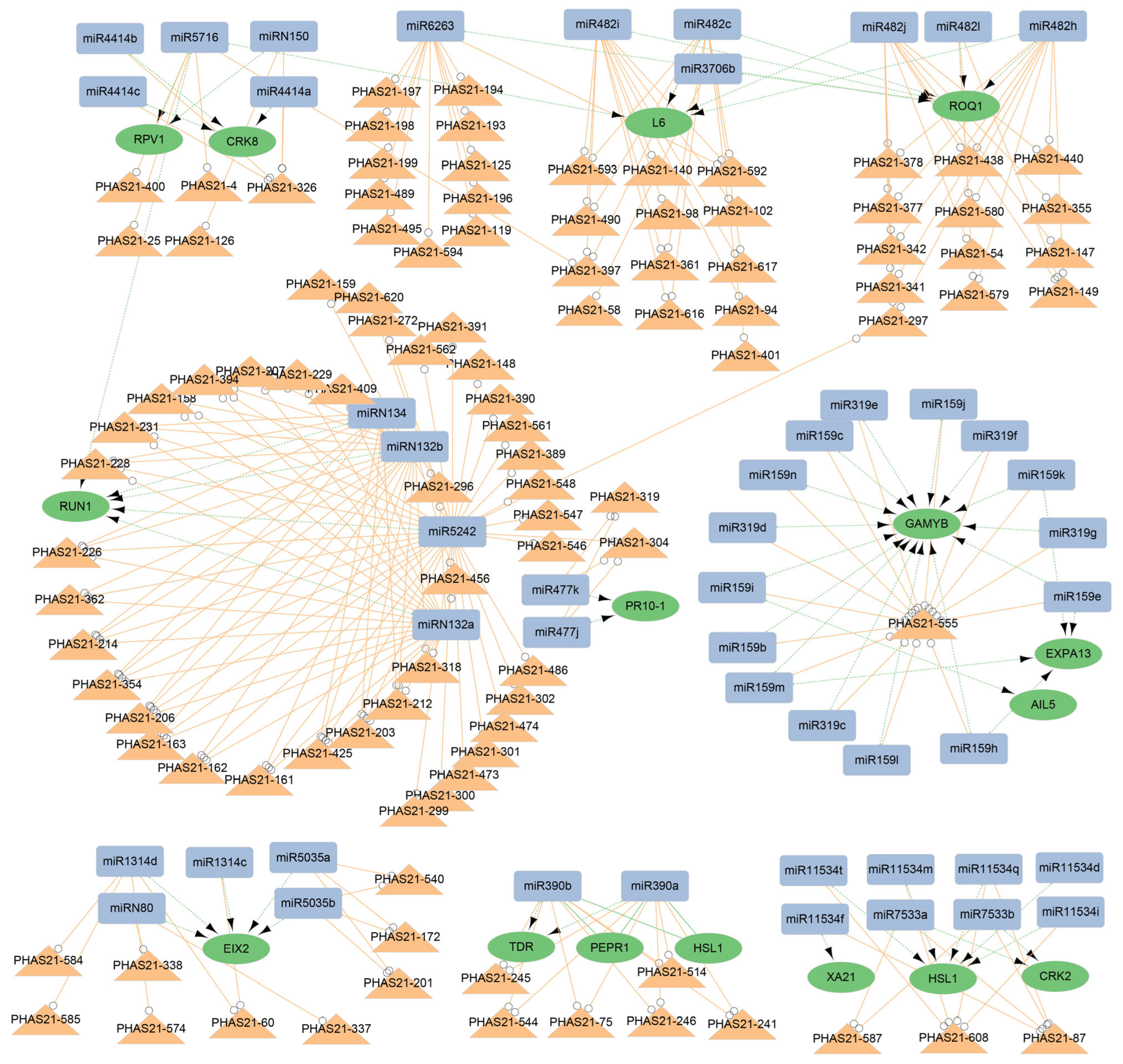
3.5. Multiple Regulatory Networks of miRNAs and phasiRNAs in G. biloba
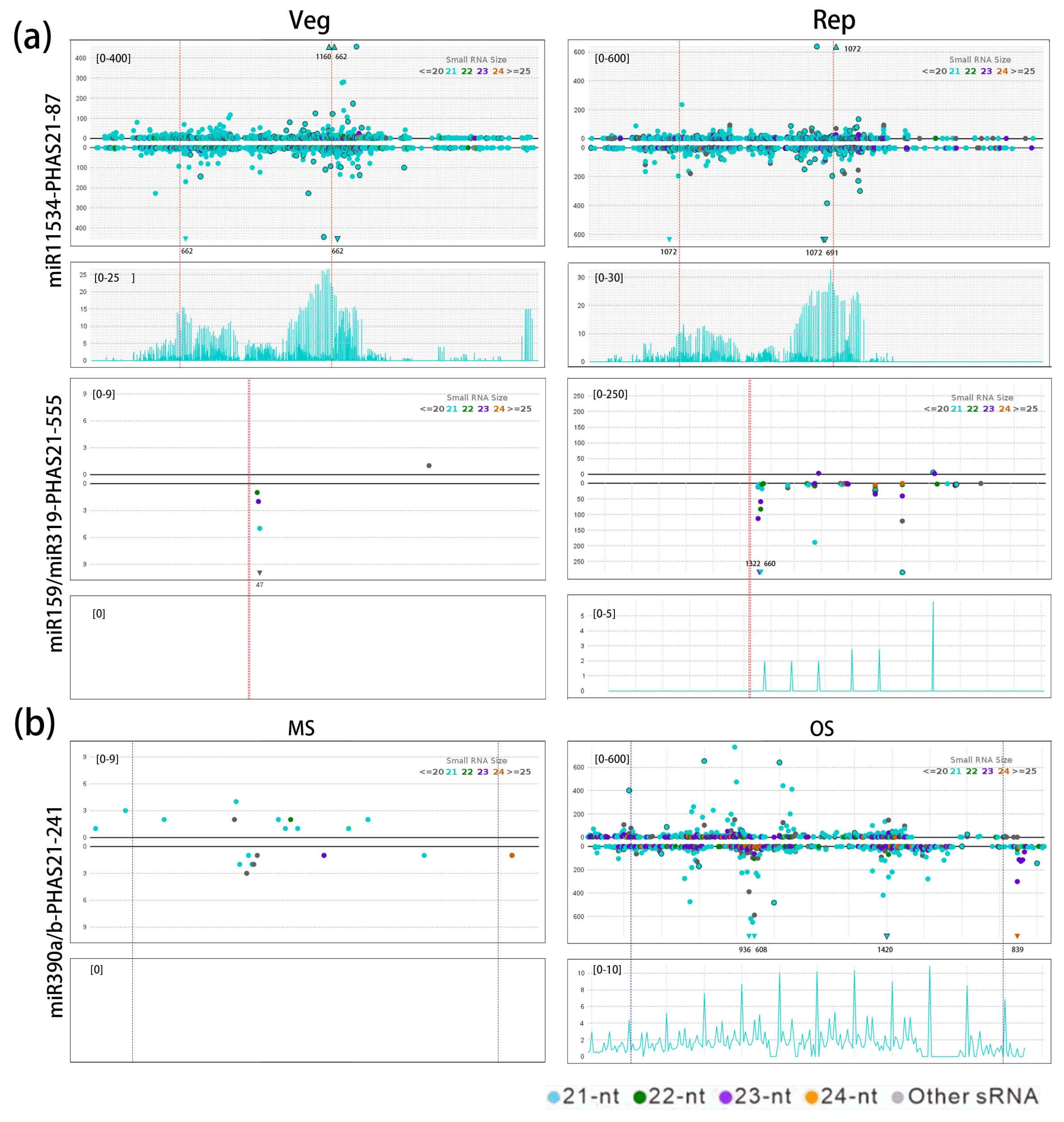
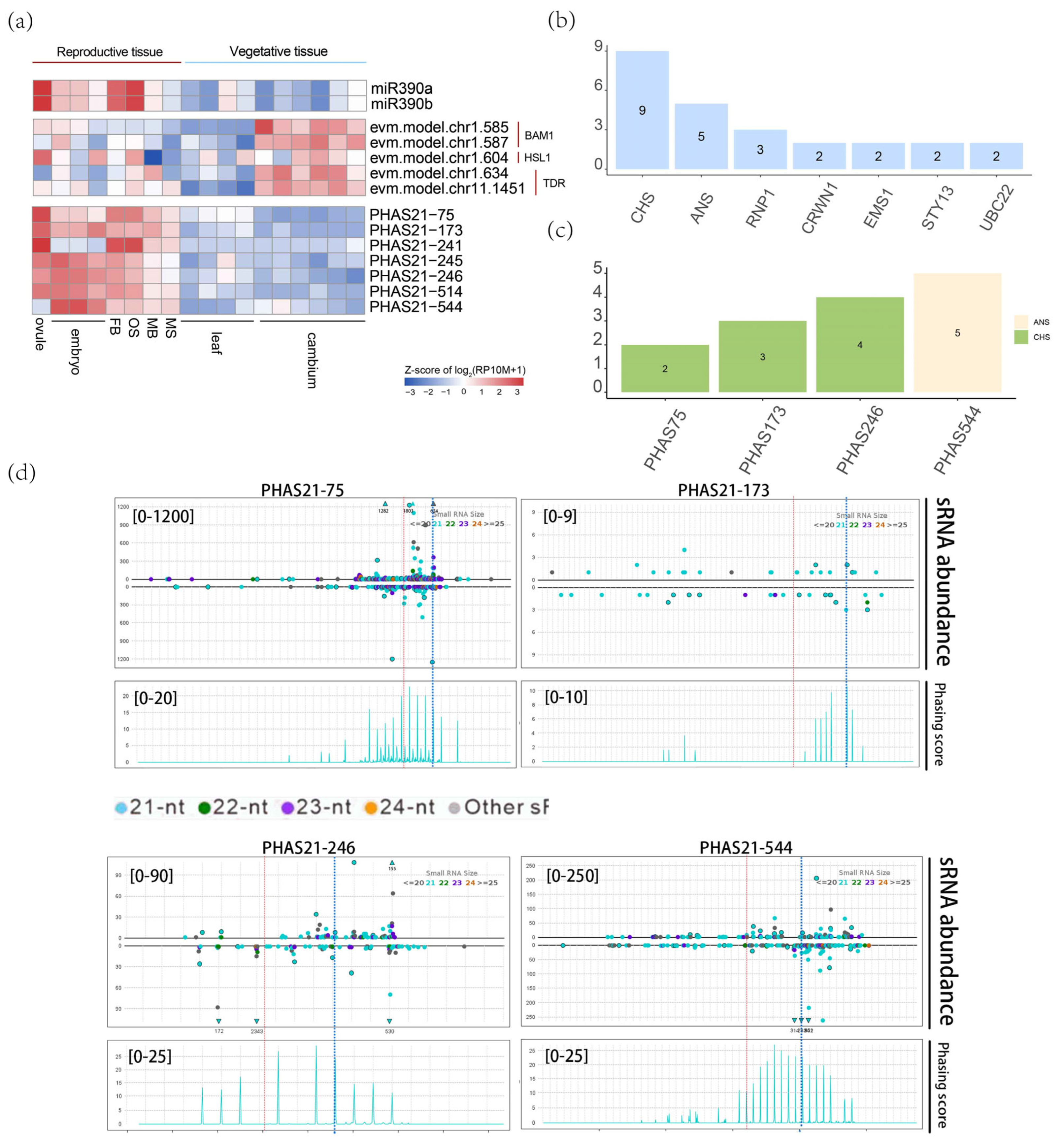
3.6. Function of the miR159/miR319-PHAS Module in the Reproductive Development of G. biloba
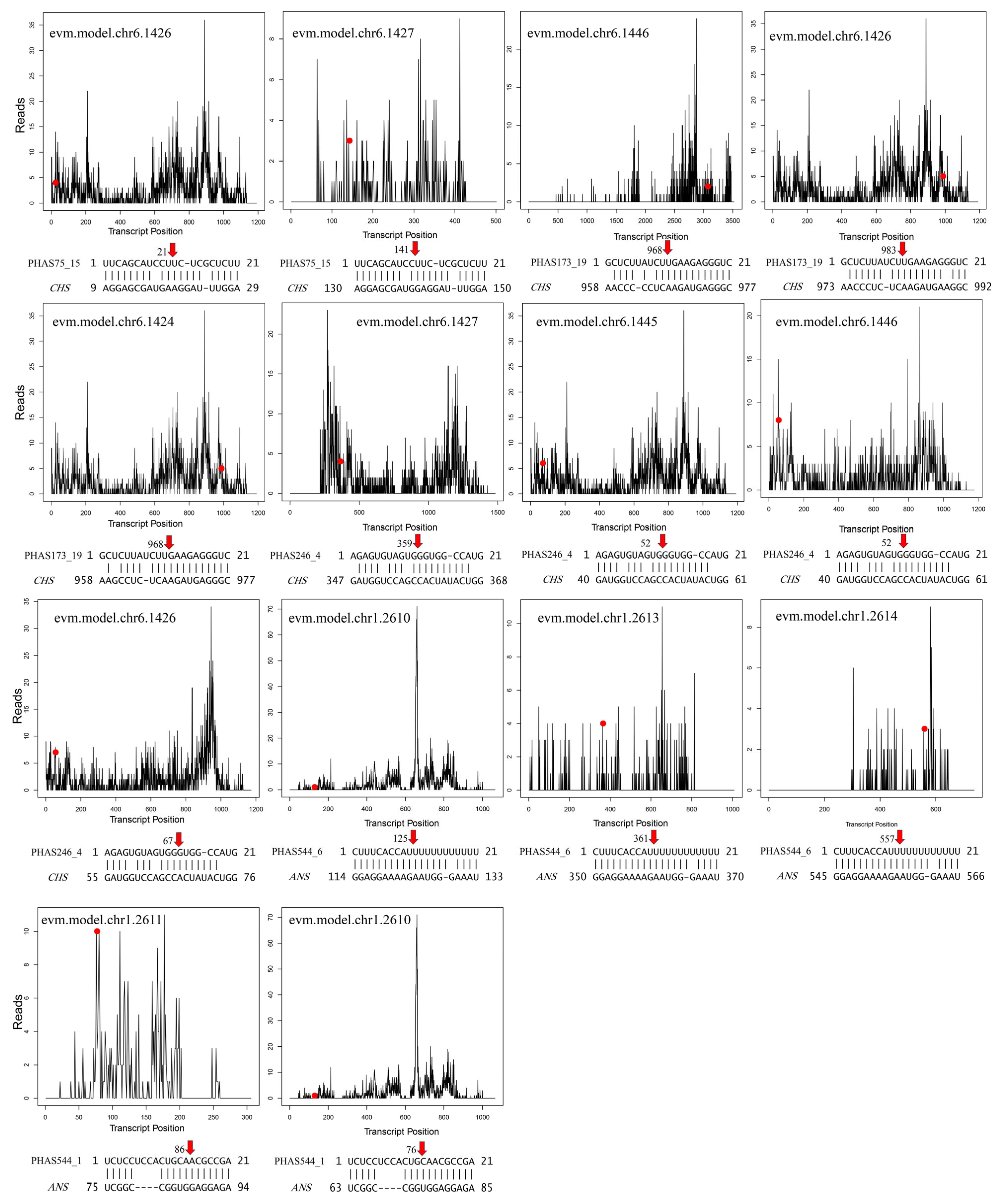
3.7. miR390-PHAS Module Involvement in Flavonoid Biosynthesis
4. Discussion
4.1. miRNAs and miRNAs-phasiRNAs Regulatory Models in Ginkgo biloba
4.2. Typical miRNA-PHAS Modules in G. biloba
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Voinnet, O. Origin, Biogenesis, and Activity of Plant MicroRNAs. Cell 2009, 136, 669–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, J.; Meyers, B.C. Plant Small RNAs: Their Biogenesis, Regulatory Roles, and Functions. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2023, 74, 21–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, G.; Park, M.Y.; Conway, S.R.; Wang, J.-W.; Weigel, D.; Poethig, R.S. The Sequential Action of miR156 and miR172 Regulates Developmental Timing in Arabidopsis. Cell 2009, 138, 750–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-W. Regulation of flowering time by the miR156-mediated age pathway. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 4723–4730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, R.S.; Li, J.; Stahle, M.I.; Dubroué, A.; Gubler, F.; Millar, A.A. Genetic analysis reveals functional redundancy and the major target genes of the Arabidopsis miR159 family. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 16371–16376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, E.; Jouannet, V.; Herz, A.; Lokerse, A.S.; Weijers, D.; Vaucheret, H.; Nussaume, L.; Crespi, M.D.; Maizel, A. miR390, Arabidopsis TAS3 tasiRNAs, and Their AUXIN RESPONSE FACTOR Targets Define an Autoregulatory Network Quantitatively Regulating Lateral Root Growth. Plant Cell 2010, 22, 1104–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas-Asencio, J.A.; Perry, K.L. A Small RNA-Mediated Regulatory Network in Arabidopsis thaliana Demonstrates Connectivity Between phasiRNA Regulatory Modules and Extensive Co-Regulation of Transcription by misRNAs and phasiRNAs. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 10, 1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.-H.; Zhang, S.-G.; Li, S.-G.; Han, S.-Y.; Li, W.-F.; Li, X.-M.; Qi, L.-W. Regulation of synchronism by abscisic-acid-responsive small noncoding RNAs during somatic embryogenesis in larch (Larix leptolepis). Plant Cell Tiss. Organ Cult. 2014, 116, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, Q.; Xia, R.; Meyers, B.C. Phased, secondary, small interfering RNAs in posttranscriptional regulatory networks. Plant Cell 2013, 25, 2400–2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, J.; Zhang, H.; Arikit, S.; Huang, K.; Nan, G.-L.; Walbot, V.; Meyers, B.C. Spatiotemporally dynamic, cell-type–dependent premeiotic and meiotic phasiRNAs in maize anthers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 3146–3151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Li, G.; Chen, C.; Zeng, Z.; Xu, J.; Zhang, J.; Xia, R.; Liu, Y. Species-specific regulatory pathways of small RNAs play sophisticated roles in flower development in Dimocarpus longan Lour. Hortic. Plant J. 2023, 9, 237–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlemeyer, B.; Krieglstein, J. Neuroprotective effects of Ginkgo biloba extract. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. CMLS 2003, 60, 1779–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.-M.; Cheng, S.-Y.; Ye, J.-B.; Chen, Z.-X.; Liao, Y.-L.; Zhang, W.-W.; Kim, S.-U.; Xu, F. Screening and identification of miRNAs related to sexual differentiation of strobili in Ginkgo biloba by integration analysis of small RNA, RNA, and degradome sequencing. BMC Plant Biol. 2020, 20, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Z.; Jiang, B.; Zhao, B.; Mao, X.; Lu, J.; Jin, B.; Wang, L. Liquid profiling in plants: Identification and analysis of extracellular metabolites and miRNAs in pollination drops of Ginkgo biloba. Tree Physiol. 2020, 40, 1420–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, M.; Li, W.; Luo, K.; Lu, Z.; Zhang, C.; Jin, B. Identification and characterization of microRNA expression in Ginkgo biloba L. leaves. Tree Genet. Genomes 2015, 11, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Zhao, B.; Liu, S.; Lu, Z.; Chang, B.; Jiang, H.; Cui, H.; He, Q.; Li, W.; Jin, B.; et al. Embryo transcriptome and miRNA analyses reveal the regulatory network of seed dormancy in Ginkgo biloba. Tree Physiol. 2021, 41, 571–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, J.; Xu, H.; Wang, L.; Jin, B. Cytological and miRNA expression changes during the vascular cambial transition from the dormant stage to the active stage in Ginkgo biloba L. Trees 2016, 30, 2177–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wang, L.; Cao, M.; Pang, S.; Li, W.; Kato-Noguchi, H.; Jin, B.; Wang, L. Identification and characterization of long non-coding RNAs regulating flavonoid biosynthesis in Ginkgo biloba leaves. Ind. Crops Prod. 2020, 158, 112980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Xia, X.; Jiang, H.; Lu, Z.; Cui, J.; Cao, F.; Jin, B. Genome-wide identification and characterization of novel lncRNAs in Ginkgo biloba. Trees 2018, 32, 1429–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Qi, Y.; Feng, Y.; Yang, Y.; Xue, L.; El-Kassaby, Y.A.; Wang, G.; Fu, F. Inferring the Regulatory Network of miRNAs on Terpene Trilactone Biosynthesis Affected by Environmental Conditions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 17002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Jia, Z.; Liu, S.; Zhao, B.; Li, W.; Jin, B.; Wang, L. Identification and characterization of long non-coding RNAs involved in embryo development of Ginkgo biloba. Plant Signal. Behav. 2019, 14, 1674606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Cui, J.; Jin, B.; Zhao, J.; Xu, H.; Lu, Z.; Li, W.; Li, X.; Li, L.; Liang, E.; et al. Multifeature analyses of vascular cambial cells reveal longevity mechanisms in old Ginkgo biloba trees. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 2201–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalvari, I.; Nawrocki, E.P.; Argasinska, J.; Quinones-Olvera, N.; Finn, R.D.; Bateman, A.; Petrov, A.I. Non-coding RNA analysis using the Rfam database. Curr. Protoc. Bioinforma 2018, 62, e51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mano, S.; Nakamura, T.; Kondo, M.; Miwa, T.; Nishikawa, S.; Mimura, T.; Nagatani, A.; Nishimura, M. The Plant Organelles Database 3 (PODB3) update 2014: Integrating electron micrographs and new options for plant organelle research. Plant Cell Physiol. 2014, 55, e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmead, B. Aligning short sequencing reads with Bowtie. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2010, 32, 11.7.1–11.7.14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Chen, C.; Chen, P.; Meyers, B.C.; Xia, R. sRNAminer: A multifunctional toolkit for next-generation sequencing small RNA data mining in plants. Sci. Bull. 2024, 69, 784–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, X.; Wang, G.; Cui, P.; Wu, S.; Ai, C.; Hu, N.; Li, A.; He, B.; Shao, X.; et al. The nearly complete genome of Ginkgo biloba illuminates gymnosperm evolution. Nat. Plants 2021, 7, 748–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, M.D.; McCarthy, D.J.; Smyth, G.K. edgeR: A Bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 139–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UniProt Consortium, T. UniProt: The universal protein knowledgebase. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, 2699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashburner, M.; Ball, C.A.; Blake, J.A.; Botstein, D.; Butler, H.; Cherry, J.M.; Davis, A.P.; Dolinski, K.; Dwight, S.S.; Eppig, J.T.; et al. Gene ontology: Tool for the unification of biology. Nat. Genet. 2000, 25, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehisa, M.; Goto, S.; Kawashima, S.; Okuno, Y.; Hattori, M. The KEGG resource for deciphering the genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, D277–D280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, G.; Wang, L.-G.; Han, Y.; He, Q.-Y. clusterProfiler: An R package for comparing biological themes among gene clusters. Omics J. Integr. Biol. 2012, 16, 284–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, L.; Futschik, M.E. Mfuzz: A software package for soft clustering of microarray data. Bioinformation 2007, 2, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.-W.; Czech, B.; Weigel, D. miR156-regulated SPL transcription factors define an endogenous flowering pathway in Arabidopsis thaliana. Cell 2009, 138, 738–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes, J.L.; Chua, N.-H. ABA induction of miR159 controls transcript levels of two MYB factors during Arabidopsis seed germination. Plant J. 2007, 49, 592–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Li, Z.; Zhao, D. Deregulation of the OsmiR160 Target Gene OsARF18 Causes Growth and Developmental Defects with an Alteration of Auxin Signaling in Rice. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 29938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebsch, D.; Palatnik, J.F. MicroRNA miR396, GRF transcription factors and GIF co-regulators: A conserved plant growth regulatory module with potential for breeding and biotechnology. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2020, 53, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morea, E.G.O.; da Silva, E.M.; e Silva, G.F.F.; Valente, G.T.; Barrera Rojas, C.H.; Vincentz, M.; Nogueira, F.T.S. Functional and evolutionary analyses of the miR156 and miR529 families in land plants. BMC Plant Biol. 2016, 16, 40. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.W.; Song, J.B.; Shu, X.X.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Z.M. miR395 is involved in detoxification of cadmium in Brassica napus. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 250–251, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, L.; Xie, B.; Guan, P.; Jiang, N.; Cui, J. New insight into the molecular mechanism of miR482/2118 during plant resistance to pathogens. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1026762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, G.J.; Finnegan, E.J.; Ayliffe, M.A.; Ellis, J.G. The L6 gene for flax rust resistance is related to the Arabidopsis bacterial resistance gene RPS2 and the tobacco viral resistance gene N. Plant Cell 1995, 7, 1195–1206. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, L.; Yang, L.; Pi, L.; Liu, Q.; Ling, Q.; Wang, H.; Poethig, R.S.; Huang, H. Genetic Interaction between the AS1–AS2 and RDR6–SGS3–AGO7 Pathways for Leaf Morphogenesis. Plant Cell Physiol. 2006, 47, 853–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roman, A.-O.; Jimenez-Sandoval, P.; Augustin, S.; Broyart, C.; Hothorn, L.A.; Santiago, J. HSL1 and BAM1/2 impact epidermal cell development by sensing distinct signaling peptides. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Guo, H.; Chen, S.; Yue, Q.; Wang, P.; Chen, X. Receptor-like kinase HAESA-like 1 positively regulates seed longevity in Arabidopsis. Planta 2022, 256, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Z.; Yu, J.; Cheng, X.; Zong, X.; Xu, J.; Chen, M.; Li, Z.; Zhang, D.; Liang, W. The Rice Basic Helix-Loop-Helix Transcription Factor TDR INTERACTING PROTEIN2 Is a Central Switch in Early Anther Development. Plant Cell 2014, 26, 1512–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Sun, L.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, P.; Liu, L.; Abbas, A.; Xiang, X.; Wu, W.; Zhan, X.; et al. TDR INTERACTION PROTIEN 3, encoding a PHD-finger transcription factor, regulates Ubisch bodies and pollen wall formation in rice. Plant J. 2019, 99, 844–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Mao, X.; Xu, Y.; Liu, S.; Wang, L. MicroRNA Identification and Integrated Network Analyses for Age-Dependent Flavonoid Biosynthesis in Ginkgo biloba. Forests 2023, 14, 1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ražná, K.; Sawinska, Z.; Ivanišová, E.; Vukovic, N.; Terentjeva, M.; Stričík, M.; Kowalczewski, P.Ł.; Hlavačková, L.; Rovná, K.; Žiarovská, J.; et al. Properties of Ginkgo biloba L.: Antioxidant Characterization, Antimicrobial Activities, and Genomic MicroRNA Based Marker Fingerprints. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, T.; Guo, J.; Cao, F.; Wang, G. Ginkgo biloba microRNA profiling reveals new insight into leaf color mutation. Sci. Hortic. 2020, 265, 109189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Zhang, X.; Tan, J.; Xu, F.; Cheng, S.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, W.; Liao, Y. Global identification of Ginkgo biloba microRNAs and insight into their role in metabolism regulatory network of terpene trilactones by high-throughput sequencing and degradome analysis. Ind. Crops Prod. 2020, 148, 112289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; He, X.; Zhou, X.; Liu, X.; Yi, Y.; Su, D.; Zhang, W.; Liao, Y.; Ye, J.; Xu, F. The Ginkgo biloba microRNA160–ERF4 module participates in terpene trilactone biosynthesis. Plant Physiol. 2024, 195, 1446–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wan, P.; Li, W.; Wang, L.; Liu, S. Combined Analysis of Transcriptome and Small RNA Sequencing Reveals the Mechanism of UV-B-promoted Flavonoid Biosynthesis in Ginkgo biloba. Russ. J. Plant Physiol. 2024, 71, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, J.; Sang, Y.; Xing, S.; Wu, Q.; Liu, X. Identification and Characterization of MicroRNAs in Ginkgo biloba var. epiphylla Mak. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0127184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Zhao, J.; Luo, K.; Cui, J.; He, Q.; Xia, X.; Lu, Z.; Li, W.; Jin, B. Deep sequencing discovery and profiling of conserved and novel miRNAs in the ovule of Ginkgo biloba. Trees 2016, 30, 1557–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.-F.; Qi, L.-W.; Yang, W.-H. Age-Related miRNA-Mediated Regulatory Networks Orchestrating Chronological Development of Meristems in Larix Kaempferi. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2022, 41, 2305–2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Huang, X.; Li, W.; Lu, Y.; Dai, X.; Zhou, Z.; Li, Q. MicroRNA comparison between poplar and larch provides insight into the different mechanism of wood formation. Plant Cell Rep. 2020, 39, 1199–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Ma, X.; Wu, X.; Wu, W.; Shen, B.; Li, S.; Tang, Y.; Wang, J.; Shao, C.; Meng, Y.; et al. Genome-wide identification of phasiRNAs in Arabidopsis thaliana, and insights into biogenesis, temperature sensitivity, and organ specificity. Plant Cell Environ. 2024, 47, 3797–3812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, R.; Xu, J.; Arikit, S.; Meyers, B.C. Extensive Families of miRNAs and PHAS Loci in Norway Spruce Demonstrate the Origins of Complex phasiRNA Networks in Seed Plants. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 2905–2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, P.; Mathioni, S.; Kakrana, A.; Shatkay, H.; Meyers, B.C. Reproductive phasiRNAs in grasses are compositionally distinct from other classes of small RNAs. New Phytol. 2018, 220, 851–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, P.; Zhang, X.; Xia, R.; Liu, Y.; Wang, M.; Li, B.; Liu, T.; Shi, J.; Wing, R.A.; Meyers, B.C.; et al. Evolution and diversification of reproductive phased small interfering RNAs in Oryza species. New Phytol. 2021, 229, 2970–2983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilfoyle, T.J.; Hagen, G. Auxin response factors. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2007, 10, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Meng, Y.; Zeng, J.; Luo, Y.; Feng, Z.; Bian, L.; Gao, S. Coordination between GROWTH-REGULATING FACTOR1 and GRF-INTERACTING FACTOR1 plays a key role in regulating leaf growth in rice. BMC Plant Biol. 2020, 20, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.-W.; Wang, L.-J.; Mao, Y.-B.; Cai, W.-J.; Xue, H.-W.; Chen, X.-Y. Control of root cap formation by microRNA-targeted auxin response factors in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2005, 17, 2204–2216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, R.E.; Mecchia, M.A.; Debernardi, J.M.; Schommer, C.; Weigel, D.; Palatnik, J.F. Control of cell proliferation in Arabidopsis thaliana by microRNA miR396. Development 2010, 137, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shivaprasad, P.V.; Chen, H.-M.; Patel, K.; Bond, D.M.; Santos, B.A.C.M.; Baulcombe, D.C. A MicroRNA Superfamily Regulates Nucleotide Binding Site–Leucine-Rich Repeats and Other mRNAs. Plant Cell 2012, 24, 859–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, L.; Dunoyer, P.; Jay, F.; Arnold, B.; Dharmasiri, N.; Estelle, M.; Voinnet, O.; Jones, J.D.G. A Plant miRNA Contributes to Antibacterial Resistance by Repressing Auxin Signaling. Science 2006, 312, 436–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Wu, L.; Qi, Y.; Zhou, J.-M. Identification of MicroRNAs Involved in Pathogen-Associated Molecular Pattern-Triggered Plant Innate Immunity. Plant Physiol. 2010, 152, 2222–2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sunkar, R.; Zhou, X.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, J.-K. Identification of novel and candidate miRNAs in rice by high throughput sequencing. BMC Plant Biol. 2008, 8, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, J.; Zhu, L.; Xue, J.; Hu, H.; Cui, J.; Xu, J. Identification of microRNAs and their target genes related to needle discoloration of evergreen tree Chinese cedar (Cryptomeria fortunei) in cold winters. Planta 2021, 254, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, J.; Jeong, D.-H.; Paoli, E.D.; Park, S.; Rosen, B.D.; Li, Y.; González, A.J.; Yan, Z.; Kitto, S.L.; Grusak, M.A.; et al. MicroRNAs as master regulators of the plant NB-LRR defense gene family via the production of phased, trans-acting siRNAs. Genes. Dev. 2011, 25, 2540–2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Felippes, F.F.; Marchais, A.; Sarazin, A.; Oberlin, S.; Voinnet, O. A single miR390 targeting event is sufficient for triggering TAS3-tasiRNA biogenesis in Arabidopsis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, 5539–5554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montgomery, T.A.; Howell, M.D.; Cuperus, J.T.; Li, D.; Hansen, J.E.; Alexander, A.L.; Chapman, E.J.; Fahlgren, N.; Allen, E.; Carrington, J.C.; et al. Specificity of ARGONAUTE7-miR390 Interaction and Dual Functionality in TAS3 Trans-Acting siRNA Formation. Cell 2008, 133, 128–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, E.; Xie, Z.; Gustafson, A.M.; Carrington, J.C. microRNA-directed phasing during trans-acting siRNA biogenesis in plants. Cell 2005, 121, 207–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Jiang, L.; Long, P.; Wang, C.; Liu, P.; Hou, F.; Zhang, M.; Zou, C.; Huang, Y.; Ma, L.; et al. A phased small interfering RNA-derived pathway mediates lead stress tolerance in maize. Plant Physiol. 2024, 196, 1163–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.; Li, P.; Zhai, J.; Zhou, M.; Ma, L.; Liu, B.; Jeong, D.-H.; Nakano, M.; Cao, S.; Liu, C.; et al. Roles of DCL4 and DCL3b in rice phased small RNA biogenesis. Plant J. 2012, 69, 462–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, E.; Howell, M.D. miRNAs in the biogenesis of trans-acting siRNAs in higher plants. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2010, 21, 798–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, M.; Peragine, A.; Park, M.Y.; Poethig, R.S. A pathway for the biogenesis of trans-acting siRNAs in Arabidopsis. Genes Dev. 2005, 19, 2164–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Zhang, J.; Wu, B.; Jouni, R.; Yu, C.; Meyers, B.C.; Liang, W.; Fei, Q. Temperature-sensitive male sterility in rice determined by the roles of AGO1d in reproductive phasiRNA biogenesis and function. New Phytol. 2022, 236, 1529–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosa-Valencia, G.; Romero-Pérez, P.S.; Palomar, V.M.; Covarrubias, A.A.; Reyes, J.L. Insights into the function of the phasiRNA-triggering miR1514 in response to stress in legumes. Plant Signal. Behav. 2017, 12, e1284724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millar, A.A.; Gubler, F. The Arabidopsis GAMYB-like genes, MYB33 and MYB65, are microRNA-regulated genes that redundantly facilitate anther development. Plant Cell 2005, 17, 705–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millar, A.A.; Lohe, A.; Wong, G. Biology and Function of miR159 in Plants. Plants 2019, 8, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koyama, T.; Sato, F.; Ohme-Takagi, M. Roles of miR319 and TCP Transcription Factors in Leaf Development. Plant Physiol. 2017, 175, 874–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ori, N.; Cohen, A.R.; Etzioni, A.; Brand, A.; Yanai, O.; Shleizer, S.; Menda, N.; Amsellem, Z.; Efroni, I.; Pekker, I.; et al. Regulation of LANCEOLATE by miR319 is required for compound-leaf development in tomato. Nat. Genet. 2007, 39, 787–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Lu, W.; Li, J.; Duan, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y. Roles of miR319-regulated TCPs in plant development and response to abiotic stress. Crop J. 2021, 9, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Shen, X.; Xiang, X.; Cao, J. Evolution of MIR159/319 genes in Brassica campestris and their function in pollen development. Plant Mol. Biol. 2019, 101, 537–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palatnik, J.F.; Wollmann, H.; Schommer, C.; Schwab, R.; Boisbouvier, J.; Rodriguez, R.; Warthmann, N.; Allen, E.; Dezulian, T.; Huson, D.; et al. Sequence and Expression Differences Underlie Functional Specialization of Arabidopsis MicroRNAs miR159 and miR319. Dev. Cell 2007, 13, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Li, C.; Ding, G.; Jin, Y. Evolution of MIR159/319 microRNA genes and their post-transcriptional regulatory link to siRNA pathways. BMC Evol. Biol. 2011, 11, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichel, M.; Millar, A.A. Specificity of plant microRNA target MIMICs: Cross-targeting of miR159 and miR319. J. Plant Physiol. 2015, 180, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Feng, Z.; Liu, X.; Bian, L.; Xie, H.; Zhang, C.; Mysore, K.S.; Liang, J. MiR393 and miR390 synergistically regulate lateral root growth in rice under different conditions. BMC Plant Biol. 2018, 18, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dmitriev, A.A.; Kudryavtseva, A.V.; Bolsheva, N.L.; Zyablitsin, A.V.; Rozhmina, T.A.; Kishlyan, N.V.; Krasnov, G.S.; Speranskaya, A.S.; Krinitsina, A.A.; Sadritdinova, A.F.; et al. miR319, miR390, and miR393 Are Involved in Aluminum Response in Flax (Linum usitatissimum L.). BioMed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 4975146. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.; Liu, Q.; Chen, Y.; He, Y.; Hu, F. miR390 family of Cymbidium goeringii is involved in the development of reproductive organs in transgenic Arabidopsis. BMC Plant Biol. 2022, 22, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahrajabian, M.H.; Sun, W.; Cheng, Q. Ginkgo Biloba: A Famous Living Fossil Tree and an Ancient Herbal Traditional Chinese Medicine. Curr. Nutr. Food Sci. 2022, 18, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, S. Advances in the chemical constituents and chemical analysis of Ginkgo biloba leaf, extract, and phytopharmaceuticals. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2021, 193, 113704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.-G.; Lu, X.; Gao, W.; Li, P.; Yang, H. Structure, synthesis, biosynthesis, and activity of the characteristic compounds from Ginkgo biloba L. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2022, 39, 474–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Sun, D.; Wang, C.; Li, Y.; Guo, T. Expression of flavonoid biosynthesis genes and accumulation of flavonoid in wheat leaves in response to drought stress. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2014, 80, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wei, Q.; Xu, A.; Zhao, A.; Shi, L.; Wang, Q.; Yang, X.; Ming, M.; Xue, L.; Cao, F.; Fu, F. Unraveling the Multilayered Regulatory Networks of miRNAs and PhasiRNAs in Ginkgo biloba. Plants 2025, 14, 1650. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14111650
Wei Q, Xu A, Zhao A, Shi L, Wang Q, Yang X, Ming M, Xue L, Cao F, Fu F. Unraveling the Multilayered Regulatory Networks of miRNAs and PhasiRNAs in Ginkgo biloba. Plants. 2025; 14(11):1650. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14111650
Chicago/Turabian StyleWei, Qixuan, Ang Xu, Anqi Zhao, Lisha Shi, Qi Wang, Xiaoming Yang, Meiling Ming, Liangjiao Xue, Fuliang Cao, and Fangfang Fu. 2025. "Unraveling the Multilayered Regulatory Networks of miRNAs and PhasiRNAs in Ginkgo biloba" Plants 14, no. 11: 1650. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14111650
APA StyleWei, Q., Xu, A., Zhao, A., Shi, L., Wang, Q., Yang, X., Ming, M., Xue, L., Cao, F., & Fu, F. (2025). Unraveling the Multilayered Regulatory Networks of miRNAs and PhasiRNAs in Ginkgo biloba. Plants, 14(11), 1650. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14111650






