Chloroplast-Localized Protein, OsAL7, with Two Elongation Factor Thermostable Domains Is Essential for Normal Chloroplast Development and Seedling Longevity in Oryza sativa
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
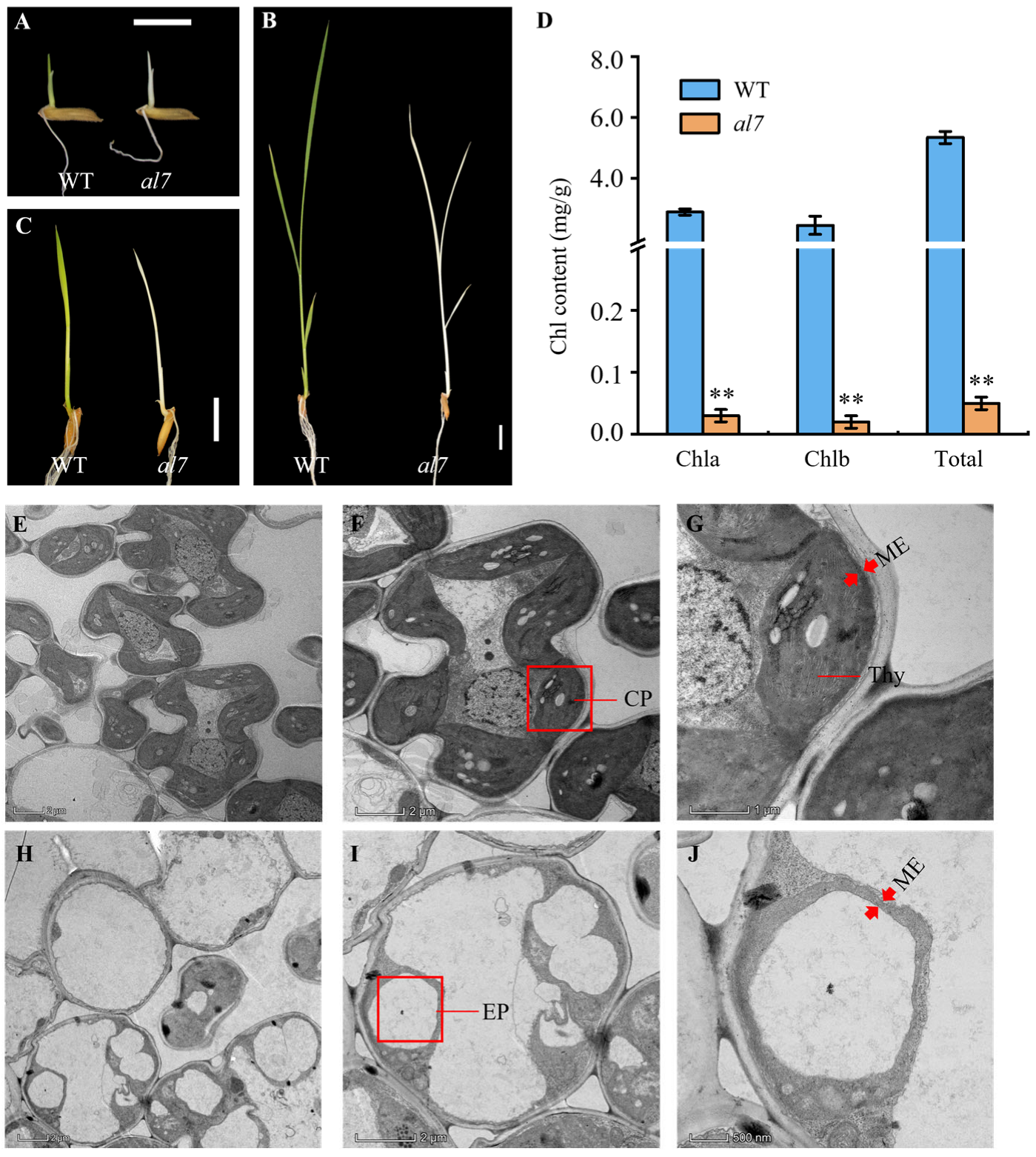
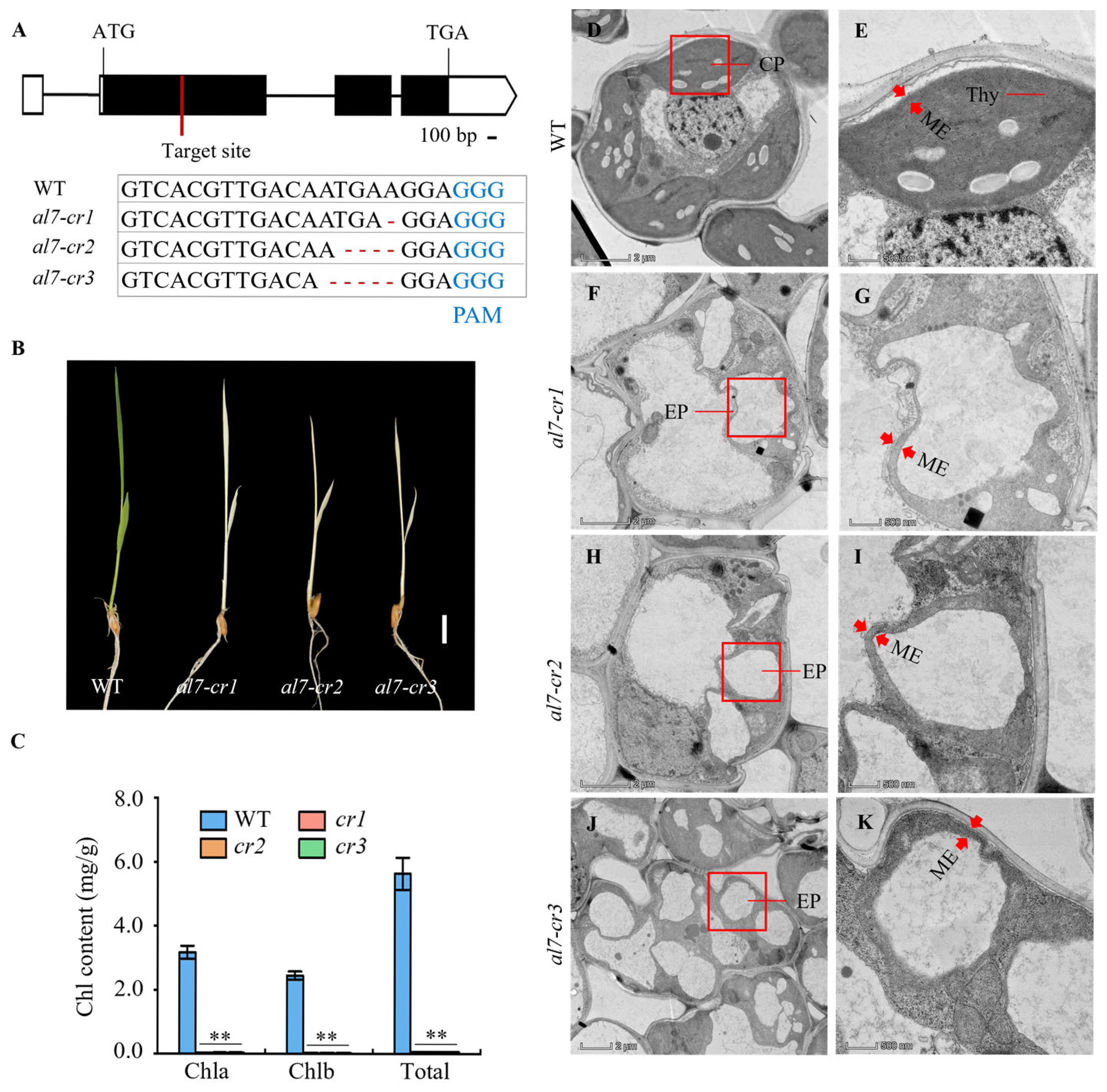
2.1. al7 Mutant Exhibits a Seedling-Lethal Phenotype
2.2. Chloroplast Development Is Impaired in the al7 Mutant
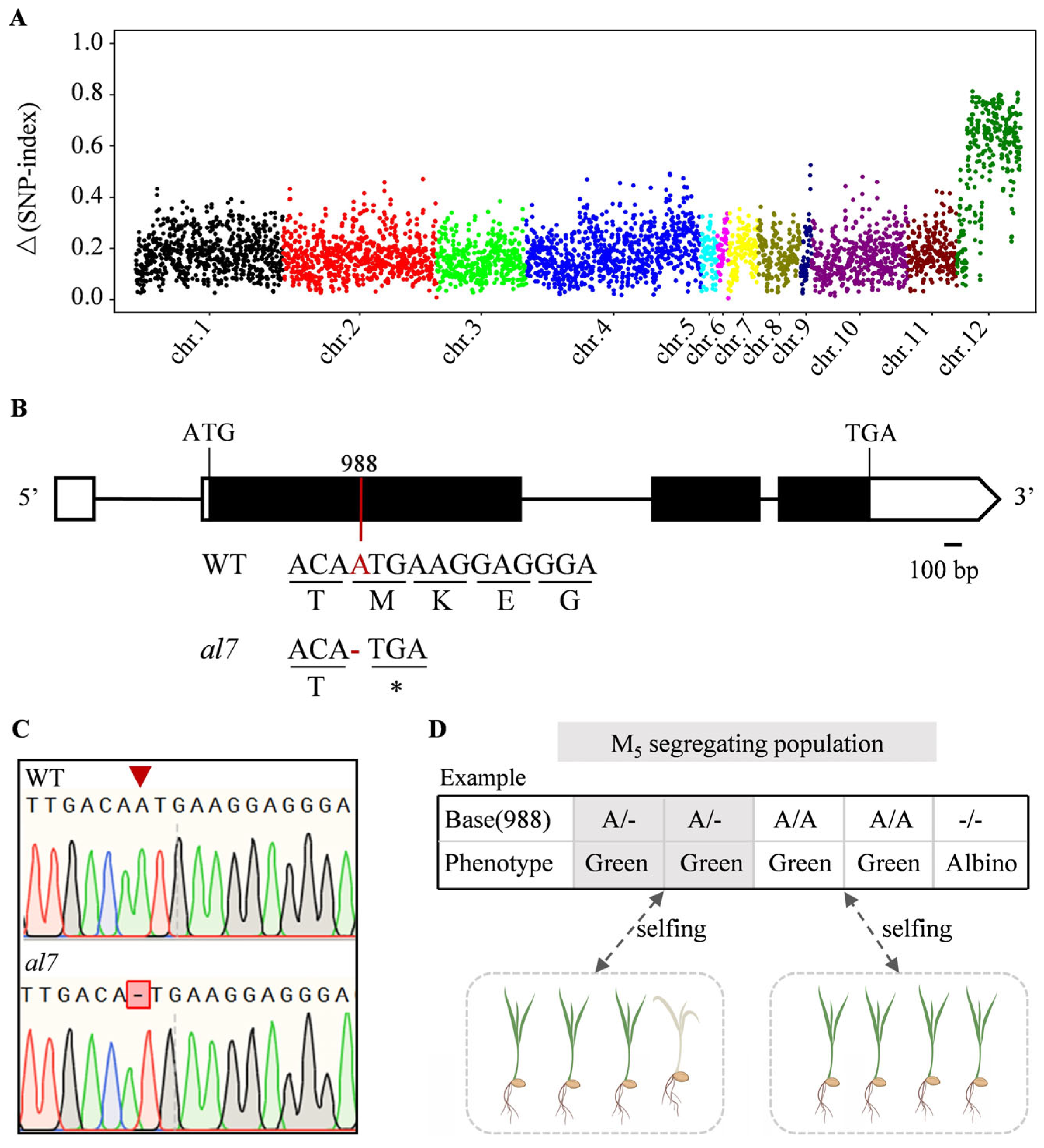
2.3. Molecular Cloning of OsAL7
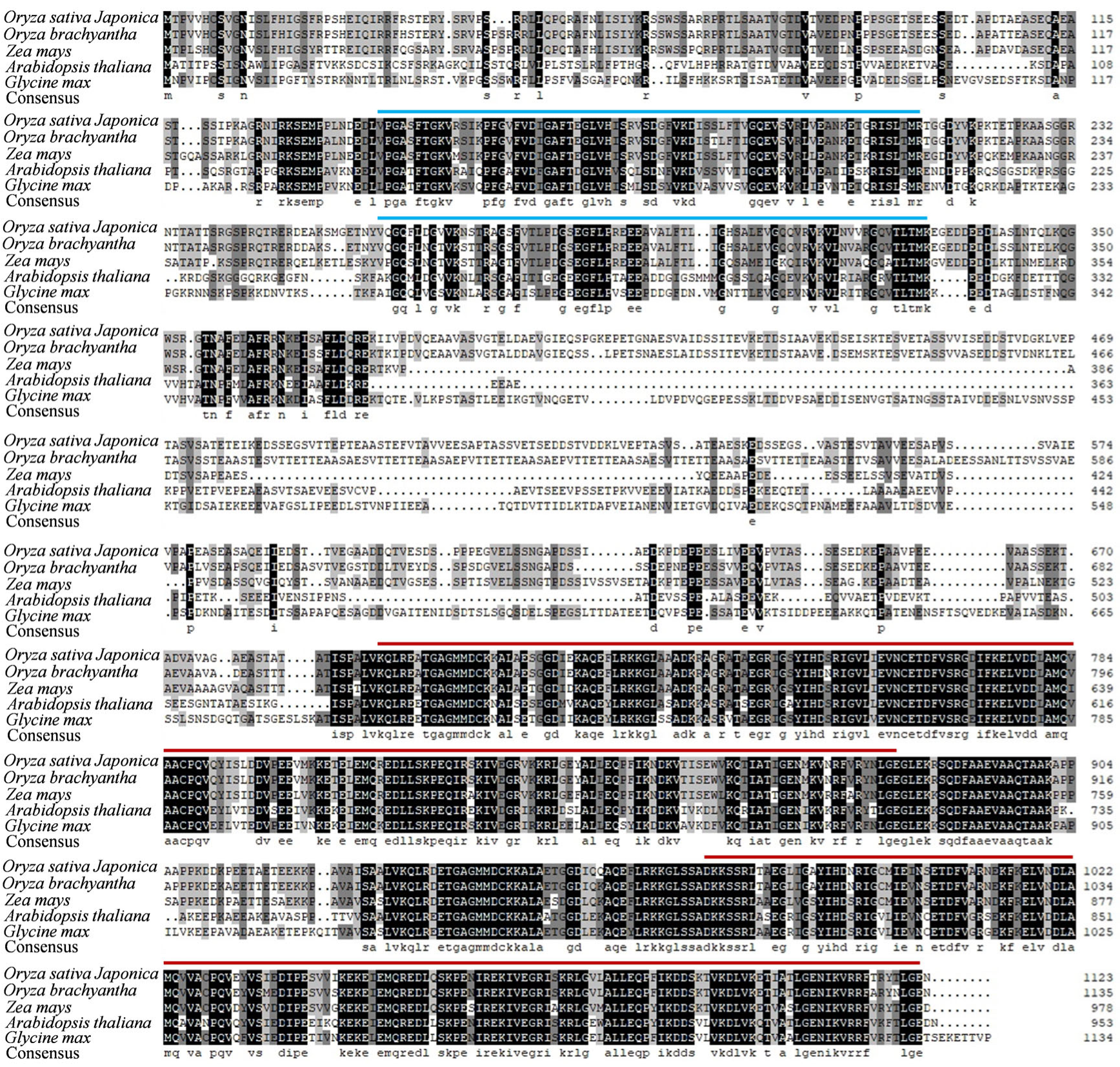
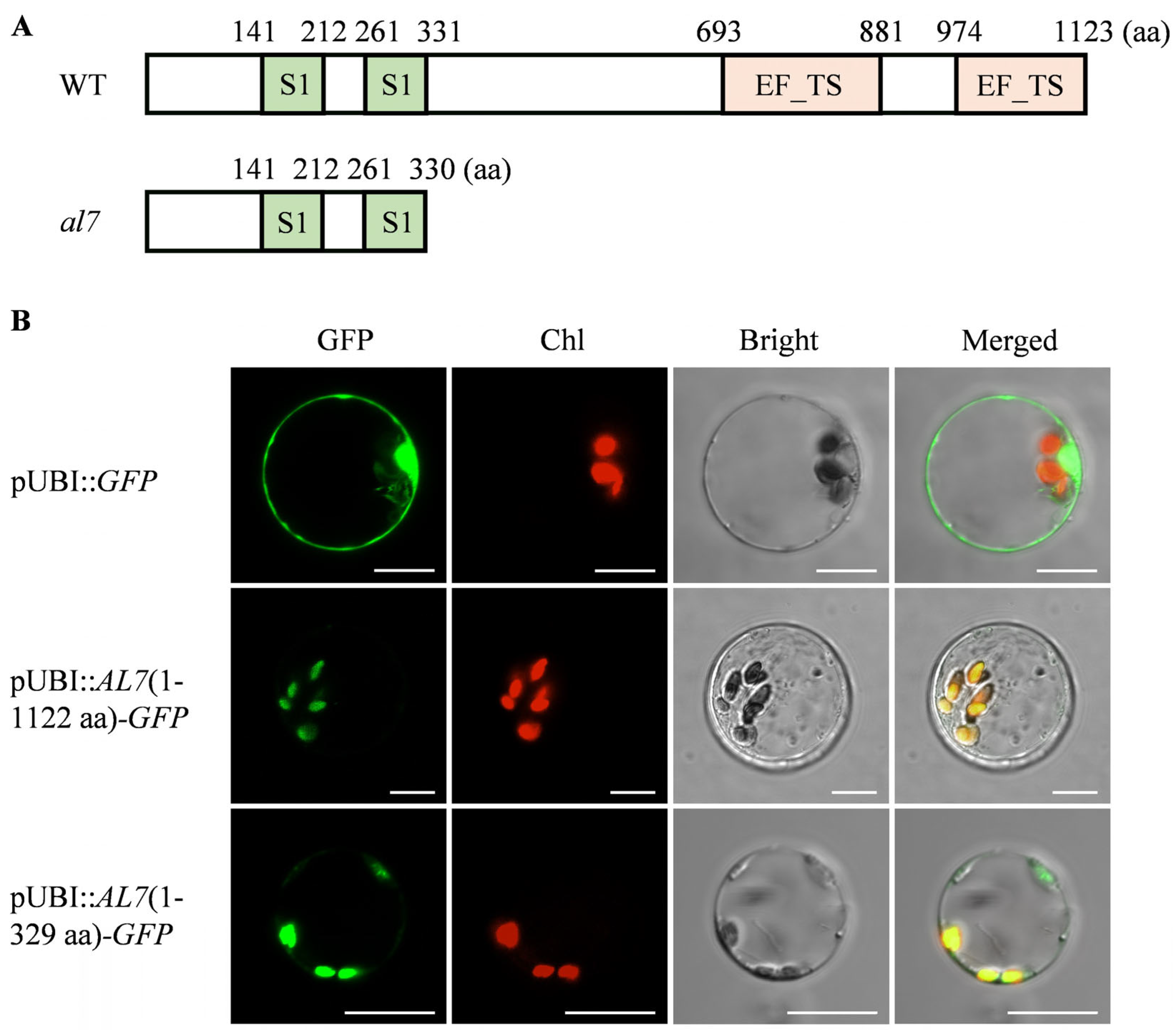
2.4. OsAL7 Is a Chloroplast-Localized Protein Containing Two EF-Ts Domains
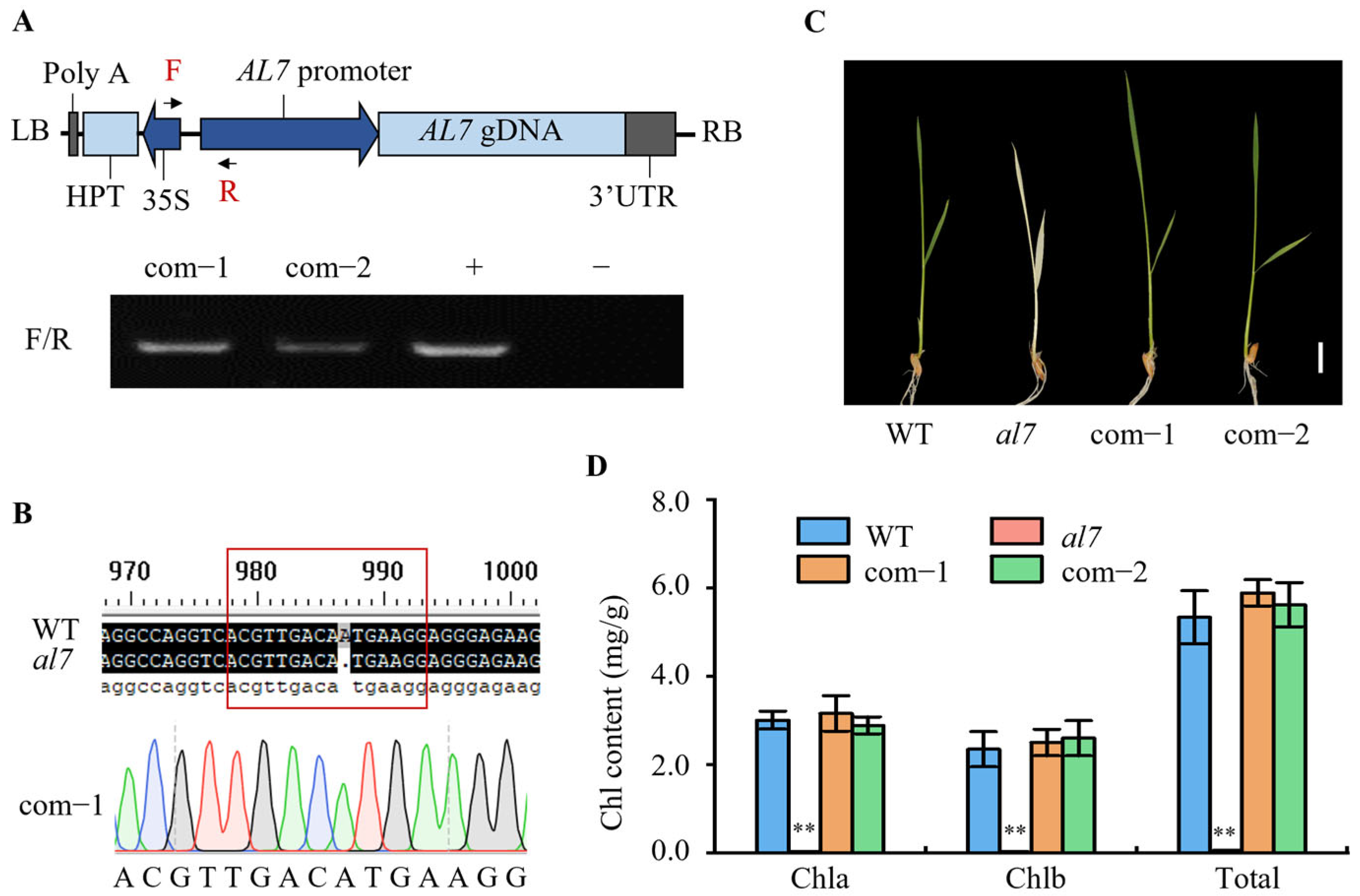
2.5. EF-Ts Domains of OsAL7 Are Critical for Its Function
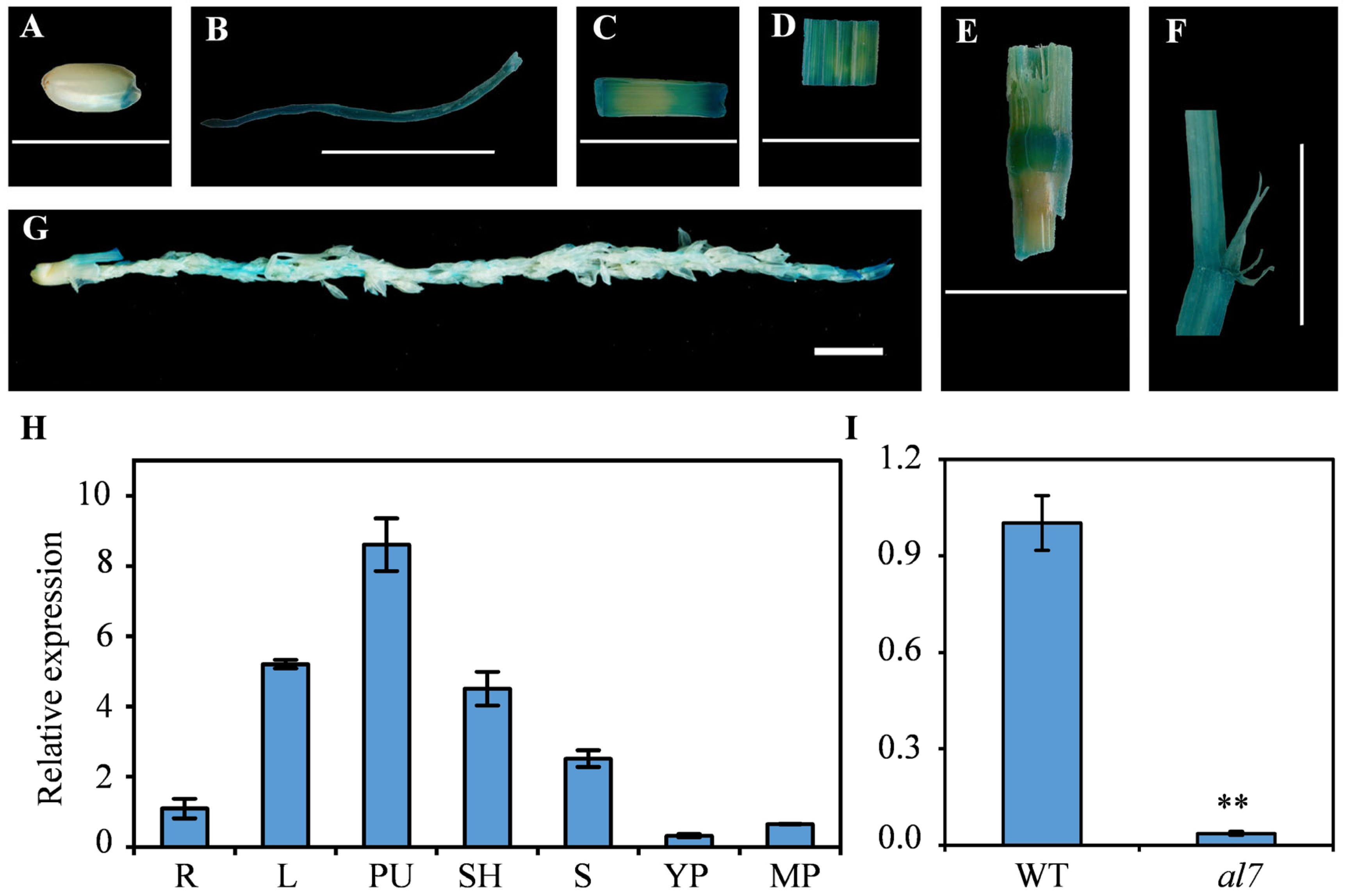
2.6. Expression Pattern of OsAL7
2.7. Mutation in OsAL7 Affects the Transcription of Chloroplast-Associated Genes
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials and Growth Conditions
4.2. Chlorophyll Content Measurement
4.3. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
4.4. MutMap+ Method for Mapping the OsAL7 Gene
4.5. Complementation Test
4.6. CRISPR/Cas9 Knockout of OsAL7
4.7. Sequence Alignment Analyses
4.8. RNA Isolation and qRT-PCR Analysis
4.9. Subcellular Localization
4.10. β-Glucuronidase (GUS) Histochemical Staining
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mullet, J.E. Dynamic regulation of chloroplast transcription. Plant Physiol. 1993, 103, 309–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugimoto, H.; Kusumi, K.; Tozawa, Y.; Yazaki, J.; Kishimoto, N.; Kikuchi, S.; Iba, K. The virescent-2 mutation inhibits translation of plastid transcripts for the plastid genetic system at an early stage of chloroplast differentiation. Plant Cell Physiol. 2004, 45, 985–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ren, Y.; Zhou, K.; Liu, L.; Wang, J.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, L.; Feng, Z.; Wang, L.; et al. WHITE STRIPE LEAF4 encodes a novel P-type PPR protein required for chloroplast biogenesis during early leaf development. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furbank, R.; Kelly, S.; von Caemmerer, S. Photosynthesis and food security: The evolving story of C4 rice. Photosynth. Res. 2023, 158, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.S.; Zhang, Q.; Pan, H.; Huang, C.; Yang, Z.N.; Yu, Q.B. EMB2738, which encodes a putative plastid-targeted GTP-binding protein, is essential for embryogenesis and chloroplast development in higher plants. Physiol. Plant 2017, 161, 414–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Marino, G.; Klingl, A.; Enderle, B.; Monte, E.; Kurth, J.; Hiltbrunner, A.; Leister, D.; Kleine, T. Extrachloroplastic PP7L functions in chloroplast development and abiotic stress tolerance. Plant Physiol. 2019, 180, 323–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, L.; Fang, Q.; Liu, Q.; Gong, C.; Zhang, C.; Zhou, Y.; Mao, C.; Zhu, Y.; et al. Accumulation of the RNA polymerase subunit RpoB depends on RNA editing by OsPPR16 and affects chloroplast development during early leaf development in rice. New Phytol. 2020, 228, 1401–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.L.; Shang, J.X.; Qiu, C.L.; Zhang, B.; Wang, J.; Wang, S.; Sun, Y. Plastid-localized EMB2726 is involved in chloroplast biogenesis and early embryo development in Arabidopsis. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 675838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, C.; Qian, Q.; Guo, L. WAL3 encoding a PLS-type PPR protein regulates chloroplast development in rice. Plant Sci. 2022, 323, 111382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pogson, B.J.; Albrecht, V. Genetic dissection of chloroplast biogenesis and development: An overview. Plant Physiol. 2011, 155, 1545–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.; Phua, S.; Crisp, P.A.; McQuinn, R.; Pogson, B.J. Learning the languages of the chloroplast: Retrograde signaling and beyond. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2016, 67, 25–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusumi, K.; Chono, Y.; Shimada, H.; Gotoh, E.; Tsuyama, M.; Iba, K. Chloroplast biogenesis during the early stage of leaf development in rice. Plant Biotechnol. 2010, 27, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pogson, B.J.; Ganguly, D.; Albrecht-Borth, V. Insights into chloroplast biogenesis and development. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1847, 1017–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, K.; Zhang, C.; Xia, J.; Yun, P.; Wang, Y.; Ma, T.; Li, Z. Albino seedling lethality 4; Chloroplast 30S ribosomal protein S1 is required for chloroplast ribosome biogenesis and early chloroplast development in rice. Rice 2021, 14, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, L.; Hong, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wu, G.Z. Chloroplast proteostasis: A story of birth, life, and death. Plant Commun. 2023, 4, 100424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, J.; Lin, Q.; Zhou, C.; Liu, X.; Miao, R.; Ma, T.F.; Chen, Y.; Mou, C.; Jing, R.; Feng, M.; et al. Young leaf white stripe encodes a p-type PPR protein required for chloroplast development. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2023, 65, 1687–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Santis-MacIossek, G.; Kofer, W.; Bock, A.; Schoch, S.; Maier, R.M.; Wanner, G.; Rüdiger, W.; Koop, H.-U.; Herrmann, R.G. Targeted disruption of the plastid RNA polymerase genes rpoA, B and C1: Molecular biology, biochemistry and ultrastructure. Plant J. 1999, 18, 477–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerbs-Mache, S. Function of plastid sigma factors in higher plants: Regulation of gene expression or just preservation of constitutive transcription? Plant Mol. Biol. 2011, 76, 235–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, X.; Cao, R.; Jiao, G.; Hu, S.; Shao, G.; Sheng, Z.; Xie, L.; Tang, S.; Wei, X.; et al. CDE4 encodes a pentatricopeptide repeat protein involved in chloroplast RNA splicing and affects chloroplast development under low-temperature conditions in rice. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2021, 63, 1724–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courtois, F.; Merendino, L.; Demarsy, E.; Mache, R.; Lerbs-Mache, S. Phagetype RNA polymerase RPOTmp transcribes the rrn operon from the PC promoter at early developmental stages in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2007, 145, 712–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bock, S.; Ortelt, J.; Link, G. AtSIG6 and other members of the sigma gene family jointly but differentially determine plastid target gene expression in Arabidopsis thaliana. Front. Plant Sci. 2014, 5, e667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.; Zhang, W.; Wen, K.; Chen, G.; Sun, J.; Tian, Y.; Tang, W.; Yu, J.; An, H.; Wu, T.; et al. OsPPR6, a pentatricopeptide repeat protein involved in editing and splicing chloroplast RNA, is required for chloroplast biogenesis in rice. Plant Mol. Biol. 2017, 95, 345–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Wang, C.; Zhu, Q.; Dongchen, W.; Zhang, X.; Li, W. Albino lethal 13, a chloroplast-imported protein required for chloroplast development in rice. Plant Direct 2024, 8, e610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoschke, R.; Bock, R. Chloroplast translation: Structural and functional organization, operational control, and regulation. Plant Cell 2018, 30, 745–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.M.; Chiu, C.C. Protein transport into chloroplasts. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2010, 61, 157–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paila, Y.D.; Richardson, L.G.; Schnell, D.J. New insights into the mechanism of chloroplast protein import and its integration with protein quality control, organelle biogenesis and development. J. Mol. Biol. 2015, 427, 1038–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, C.C.; Li, H.M. Developmental regulation of protein import into plastids. Photosynth. Res. 2018, 138, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, X.; Jiang, Q.; Xu, J.; Zhang, J.; Teng, S.; Lin, D.; Dong, Y. Disruption of the rice plastid ribosomal protein s20 leads to chloroplast developmental defects and seedling lethality. G3 Genes|Genomes|Genetics 2013, 3, 1769–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Wei, X.; Shao, G.; Sheng, Z.; Chen, D.; Liu, C.; Jiao, G.; Xie, L.; Tang, S.; Hu, P. The rice nuclear gene WLP1 encoding a chloroplast ribosome L13 protein is needed for chloroplast development in rice grown under low temperature conditions. Plant Mol. Biol. 2014, 84, 301–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Jiang, Q.; Zheng, K.; Chen, S.; Zhou, H.; Gong, X.; Xu, J.; Teng, S.; Dong, Y. Mutation of the rice ASL2 gene encoding plastid ribosomal protein L21 causes chloroplast developmental defects and seedling death. Plant Biol. 2015, 17, 599–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Wu, Z.; Shen, W.; Zhou, H.; Li, H.; He, X.; Li, R.; Qin, B. Disruption of the rice ALS1 localized in chloroplast causes seedling-lethal albino phenotype. Plant Sci. 2024, 338, 111925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krab, I.M.; Parmeggiani, A. Mechanisms of EF-Tu, a pioneer GTPase. Prog. Nucleic Acid. Res. Mol. Biol. 2002, 71, 513–551. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cai, L.; Liu, Z.; Cai, L.; Yan, X.; Hu, Y.; Hao, B.; Xu, Z.; Tian, Y.; Liu, X.; Liu, L.; et al. Nuclear encoded elongation factor EF-Tu is required for chloroplast development in rice grown under low-temperature conditions. J. Genet. Genom. 2022, 49, 502–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beligni, M.V.; Yamaguchi, K.; Mayfield, S.P. Chloroplast elongation factor ts pro-protein is an evolutionarily conserved fusion with the s1 domain-containing plastid-specific ribosomal protein-7. Plant Cell 2004, 16, 3357–3369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Liu, S.; Zheng, L.; Jia, J.; Guo, J.; Zheng, M.; Zhao, J.; Shao, J.; Liu, X.; An, L.; Yu, F.; et al. Chloroplast Translation elongation factor EF-Tu/SVR11 is involved in var2-mediated leaf variegation and leaf development in Arabidopsis. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, e295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Tan, J.; Shi, Z.; Xie, Q.; Xing, Y.; Liu, C.; Chen, Q.; Zhu, H.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; et al. Albino Leaf 1 that encodes the sole octotricopeptide repeat protein is responsible for chloroplast development. Plant Physiol. 2016, 171, 1182–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhu, H.; Xing, Y.; Tan, J.; Chen, X.; Zhang, J.; Peng, H.; Xie, Q.; Zhang, Z. Albino Leaf 2 is involved in the splicing of chloroplast group I and II introns in rice. J. Exp. Bot. 2016, 67, 5339–5347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Li, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, M.; Chen, T.; Ding, D.; Wang, W.; et al. Exon skipping in IspE gene is associated with abnormal chloroplast development in rice albino leaf 4 mutant. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 986678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Cao, P.H.; Huang, Q.Q.; Yang, Y.R.; Tao, D.D. Disruption of a rice chloroplast-targeted gene OsHMBPP causes a seedling-lethal albino phenotype. Rice 2020, 13, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Chen, H.; Liang, Y.; Hao, M.; Yin, Y. Molecular mechanisms of chlorophyll deficiency in Ilex × attenuata ‘Sunny Foster’ mutant. Plants 2024, 13, 1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Huang, L.; Dai, L.; Gao, Y.; Zou, W.; Lu, X.; Wang, C.; Zhang, G.; Ren, D.; Hu, J.; et al. PALE-GREEN LEAF12 encodes a novel pentatricopeptide repeat protein required for chloroplast development and 16S rRNA processing in rice. Plant Cell Physiol. 2019, 60, 587–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, D.Z.; Pan, Q.W.; Wang, X.M.; Chen, Y.; Pan, X.B.; Dong, Y.J. Mutation of the rice AN1-type zinc-finger protein gene ASL4 causes chloroplast development defects and seedling lethality. Plant Biol. 2022, 24, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, M.; Ai, P. A chloroplast-localized pentatricopeptide repeat protein involved in RNA editing and splicing and its effects on chloroplast development in rice. BMC Plant Biol. 2022, 22, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shim, K.; Kang, Y.; Song, J.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, J.K.; Kim, C.; Tai, T.H.; Park, I.; Ahn, S.-N. A frameshift mutation in the Mg-chelatase I subunit gene OsCHLI is associated with a lethal chlorophyll-deficient, yellow seedling phenotype in rice. Plants 2023, 12, 2831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swiatecka-Hagenbruch, M.; Emanuel, C.; Hedtke, B.; Liere, K.; Börner, T. Impaired function of the phage-type RNA polymerase RpoTp in transcription of chloroplast genes is compensated by a second phage-type RNA polymerase. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, 785–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajdukiewicz, P.T.J.; Allison, L.A.; Maliga, P. The two RNA polymerases encoded by the nuclear and the plastid compartments transcribe distinct groups of genes in tobacco plastids. EMBO J. 1997, 16, 4041–4048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Shao, G.; Qiu, J.; Jiao, G.; Sheng, Z.; Xie, L.; Wu, Y.; Tang, S.; Wei, X.; Hu, P. White leaf and panicle 2, encoding a PEP-associated protein, is required for chloroplast biogenesis under heat stress in rice. J. Exp. Bot. 2017, 68, 5147–5160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gromadski, K.B.; Wieden, H.J.; Rodnina, M.V. Kinetic mechanism of elongation factor Ts-catalyzed nucleotide exchange in elongation factor Tu. Biochemistry 2002, 41, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishnan, V. Ribosome structure and the mechanism of translation. Cell 2002, 108, 557–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieden, H.J.; Gromadski, K.; Rodnin, D.; Rodnina, M.V. Mechanism of elongation factor (EF)-Ts-catalyzed nucleotide exchange in EF-Tu. Contribution of contacts at the guanine base. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 277, 6032–6036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnett, B.J.; Altman, R.B.; Ferrao, R.; Alejo, J.L.; Kaur, N.; Kanji, J.; Blanchard, S.C. Elongation factor Ts directly facilitates the formation and disassembly of the Escherichia coli elongation factor Tu·GTP·aminoacyl-tRNA ternary complex. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 13917–13928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, B.; Gao, Y.; Gao, W.; Li, Y.; Li, Z.; Qi, Q.; Lan, X.; Shen, H.; Gan, J.; Zhao, G. Structural insights of the elongation factor EF-Tu complexes in protein translation of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Commun. Biol. 2022, 5, 1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Chen, C.; Wang, Y.; He, M.; Li, Z.; Shen, L.; Li, Q.; Zhu, L.; Ren, D.; Hu, J.; et al. OsPPR11 encoding p-type PPR protein that affects group II intron splicing and chloroplast development. Plant Cell Rep. 2023, 42, 421–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, K.; Prieto, S.; Beligni, M.V.; Haynes, P.A.; McDonald, W.H.; Yates, J.R., 3rd; Mayfield, S.P. Proteomic characterization of the small subunit of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii chloroplast ribosome: Identification of a novel S1 domain-containing protein and unusually large orthologs of bacterial S2, S3, and S5. Plant Cell 2002, 14, 2957–2974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Fan, X.; Lin, Y.; Chen, H. Determination of chlorophyll content in rice. Bio-Protocol 2018, e1010147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fekih, R.; Takagi, H.; Tamiru, M.; Abe, A.; Natsume, S.; Yaegashi, H.; Sharma, S.; Sharma, S.; Kanzaki, H.; Matsumura, H.; et al. MutMap+: Genetic mapping and mutant identification without crossing in rice. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Liu, Y.G. CRISPR/Cas9-based multiplex genome editing in monocot and dicot plants. Cur. Protoc. Mol. Biol. 2016, 115, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Su, J.; Duan, S.; Ao, Y.; Dai, J.; Liu, J.; Wang, P.; Li, Y.; Liu, B.; Feng, D.; et al. A highly efficient rice green tissue protoplast system for transient gene expression and studying light/chloroplast-related processes. Plant Methods 2011, 7, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Chen, G.; Guan, G.; Huang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xu, T.; Chen, T.; Zhang, Z. Chloroplast-Localized Protein, OsAL7, with Two Elongation Factor Thermostable Domains Is Essential for Normal Chloroplast Development and Seedling Longevity in Oryza sativa. Plants 2025, 14, 1634. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14111634
Zhang J, Chen G, Guan G, Huang Y, Liu Y, Xu T, Chen T, Zhang Z. Chloroplast-Localized Protein, OsAL7, with Two Elongation Factor Thermostable Domains Is Essential for Normal Chloroplast Development and Seedling Longevity in Oryza sativa. Plants. 2025; 14(11):1634. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14111634
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Jingjing, Gaokun Chen, Guohua Guan, Yicai Huang, Yunlong Liu, Tingting Xu, Tong Chen, and Zemin Zhang. 2025. "Chloroplast-Localized Protein, OsAL7, with Two Elongation Factor Thermostable Domains Is Essential for Normal Chloroplast Development and Seedling Longevity in Oryza sativa" Plants 14, no. 11: 1634. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14111634
APA StyleZhang, J., Chen, G., Guan, G., Huang, Y., Liu, Y., Xu, T., Chen, T., & Zhang, Z. (2025). Chloroplast-Localized Protein, OsAL7, with Two Elongation Factor Thermostable Domains Is Essential for Normal Chloroplast Development and Seedling Longevity in Oryza sativa. Plants, 14(11), 1634. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14111634





