Cryopreservation and Maturation Media Optimization for Enhanced Somatic Embryogenesis in Masson Pine (Pinus massoniana)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
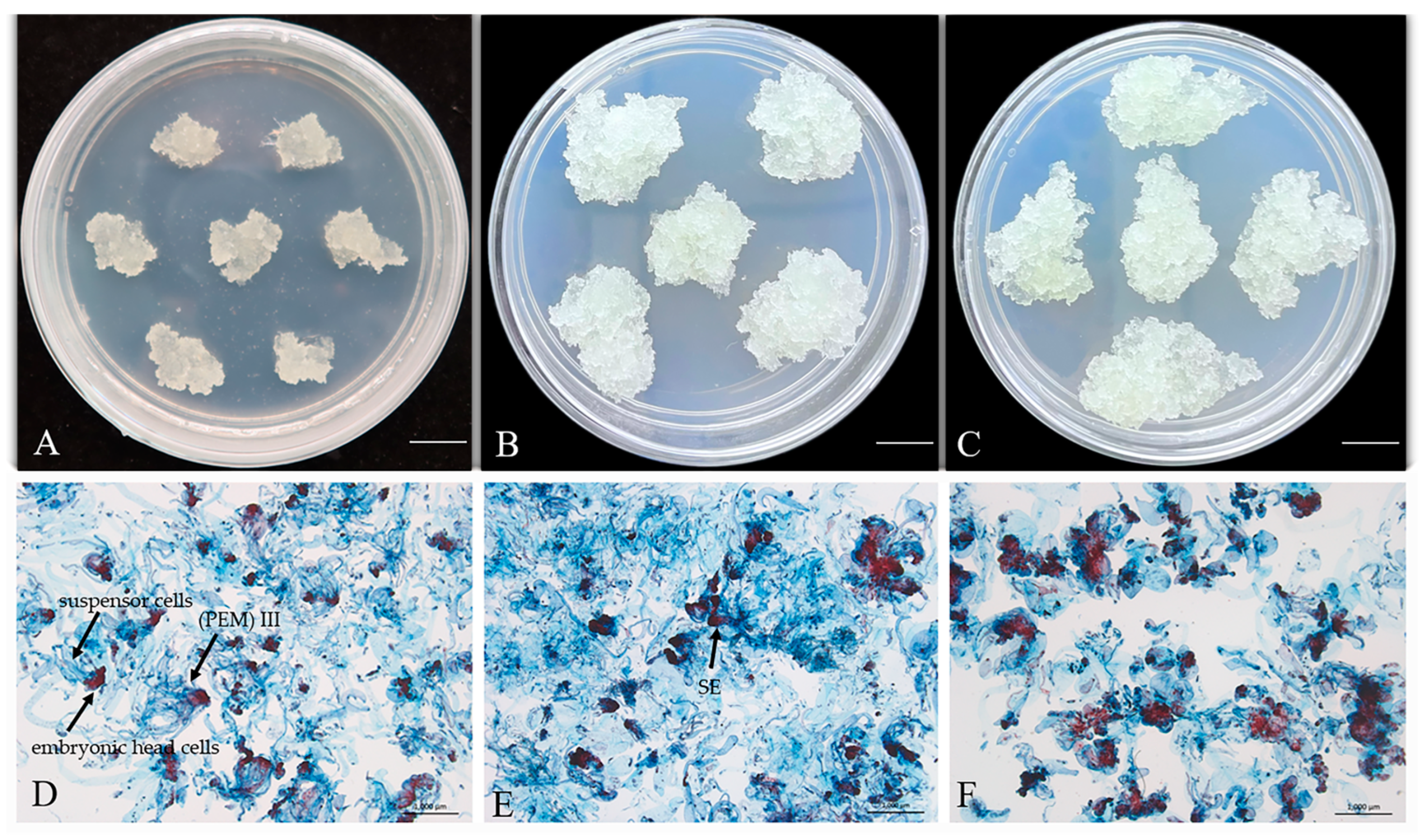
2.1. Cryopreservation of Embryogenic Callus of P. massoniana
2.1.1. Post-Thaw Recovery Rate of Embryogenic Callus in P. massoniana
2.1.2. Microstructure of P. massoniana Embryogenic Callus Before and After Cryopreservation
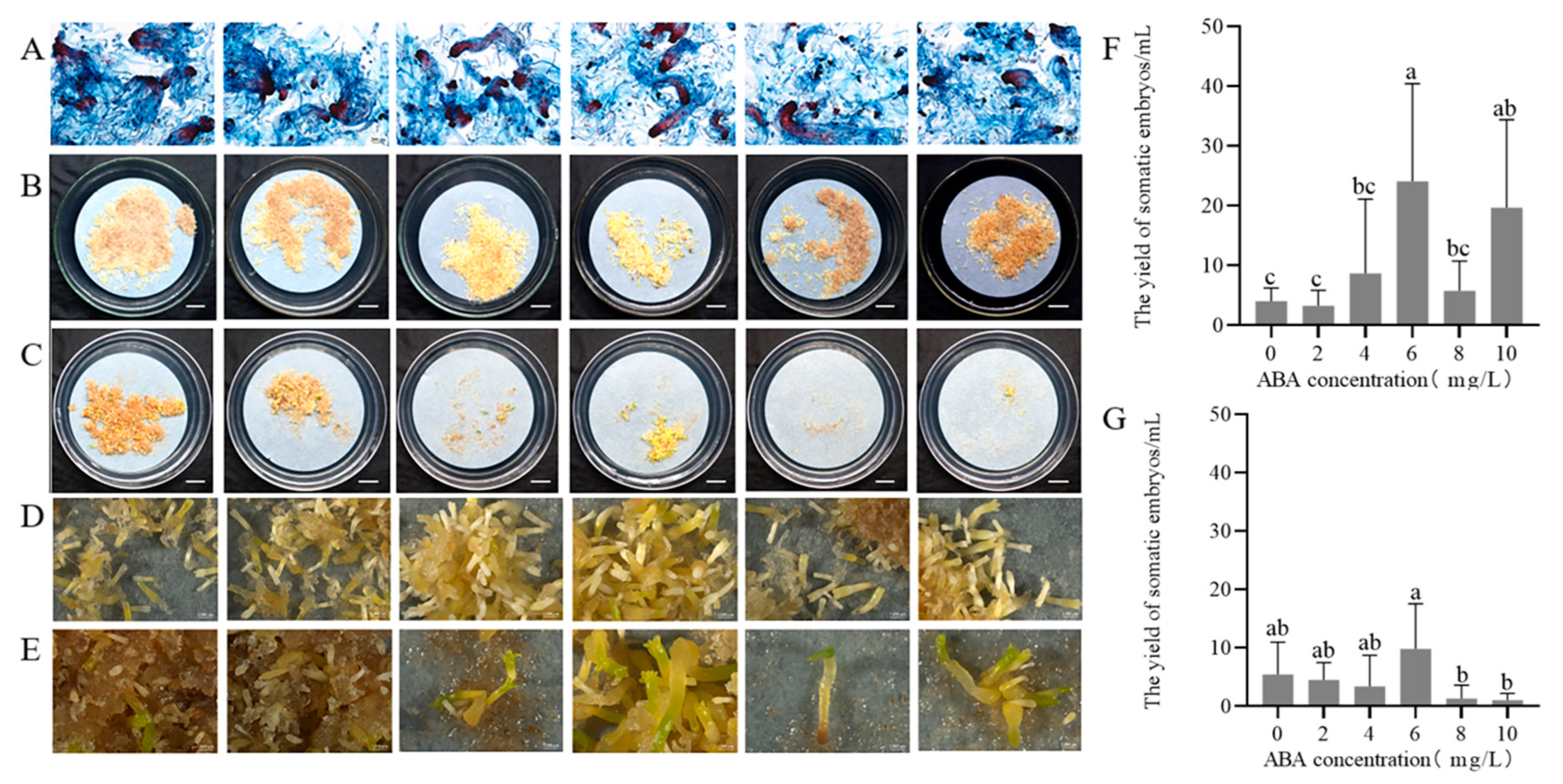
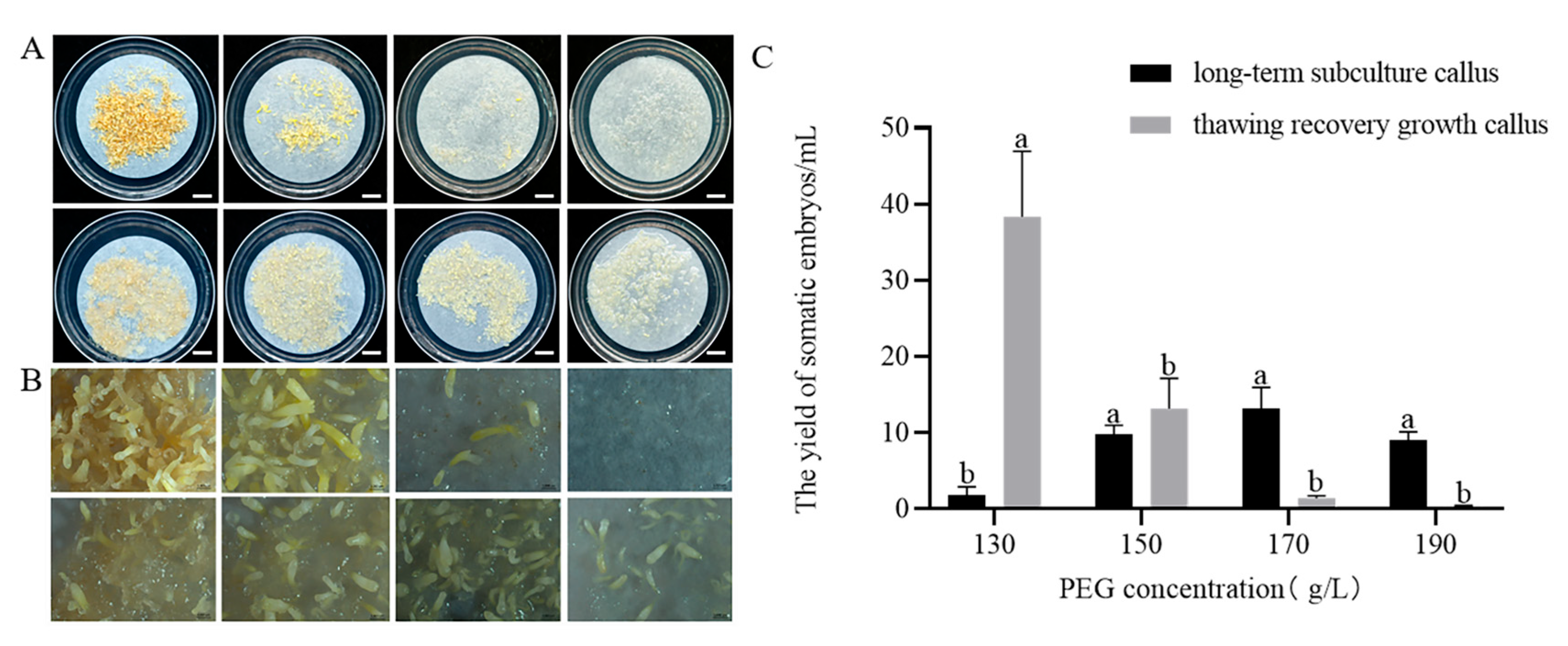
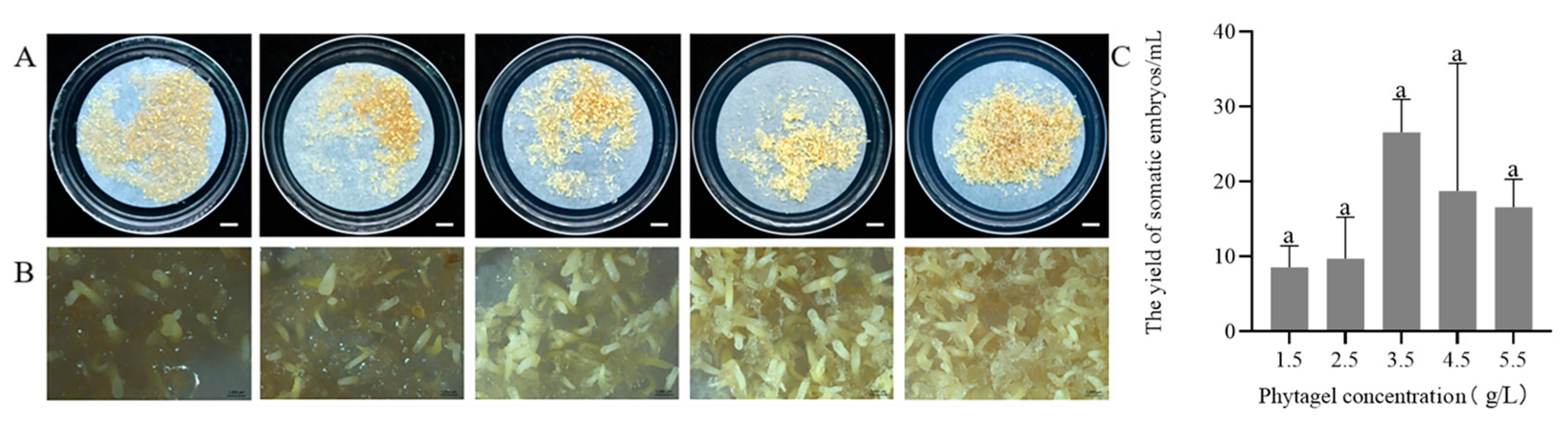
2.2. Maturation of Somatic Embryos of P. massoniana
2.2.1. Effect of ABA Concentrations on Somatic Embryo Maturation
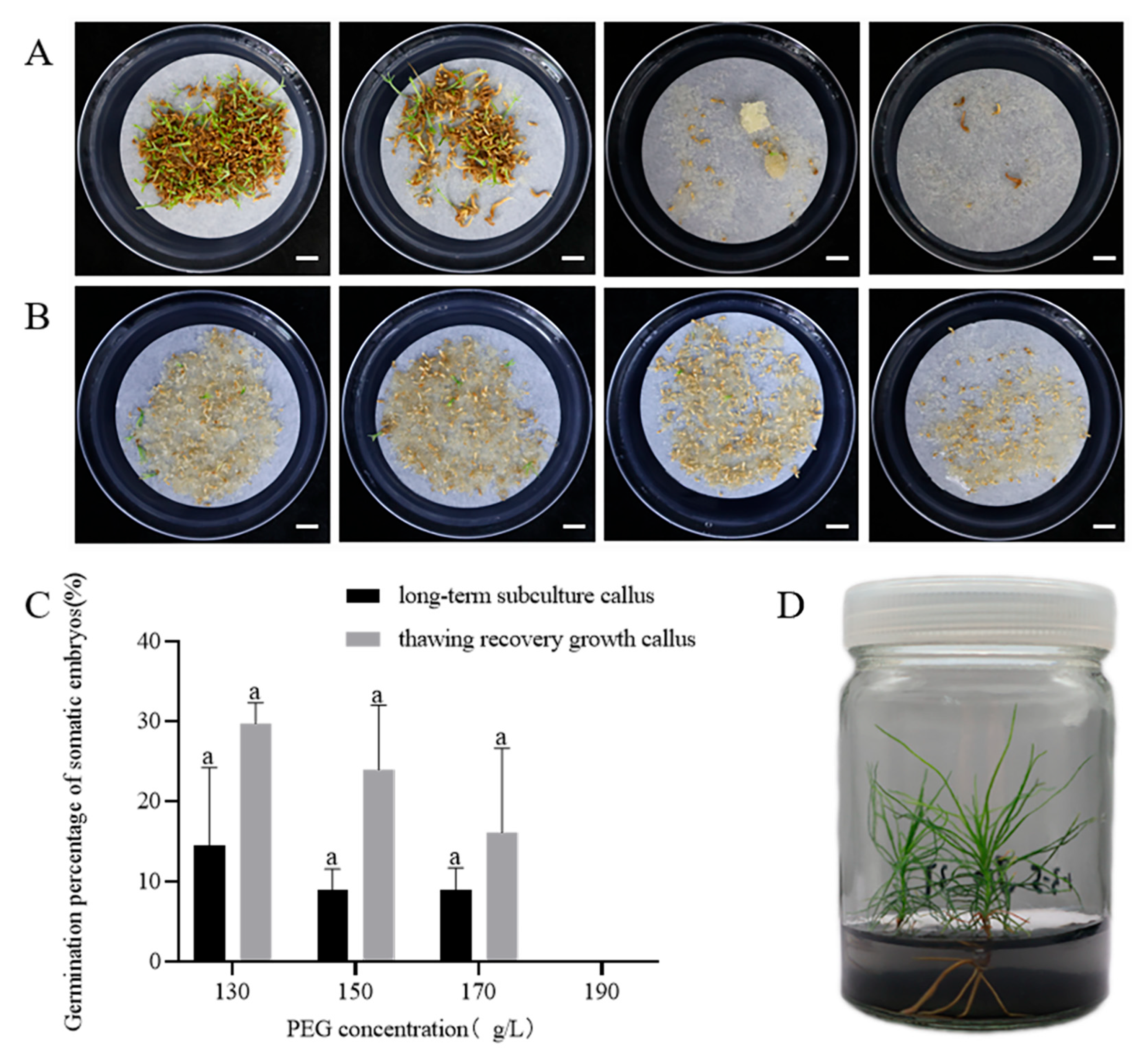
2.2.2. Effect of PEG 8000 Concentrations on Somatic Embryo Maturation
2.2.3. Effect of Phytagel Concentrations on Somatic Embryo Maturation
2.3. Somatic Embryo Germination and Plantlet Regeneration
2.4. Acclimatization and Transplantation of Regenerated Plantlets
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cryopreservation of Embryogenic Callus of P. massoniana
4.2. Microscopic Observation of Embryogenic Callus
4.3. Maturation of Somatic Embryos of P. massoniana
4.3.1. Effect of Pretreatment with Different Concentrations of ABA on Somatic Embryo Maturation
4.3.2. Effect of PEG 8000 Concentrations on the Maturation Capacity of Embryonic Callus After Thaw Recovery and Long-Term Culture
4.3.3. Effect of Phytagel Concentrations on the Maturation of Embryonic Callus After Thaw Recovery
4.4. Somatic Embryo Germination and Plantlet Regeneration
4.4.1. Effect of Different Maturation Treatments on the Germination of Somatic Embryos
4.4.2. Effect of Transplanting Substrate on Growth and Survival of Regeneration Plantlets
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SE | Somatic embryogenesis |
| EC | Embryogenic callus |
| PEM | Pro-embryogenic mass |
| 2,4- D | 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid |
| 6-BA | 6-Benzylaminopurine |
| VC | Vitamin C |
| NAA | 1-Naphthylacetic acid |
| AC | Activated carbon |
| KT | Kinetin |
| GA3 | Gibberellic acid |
| IBA | Indole-3-butyric acid |
References
- Chen, D.; Fu, X.Q.; Wang, C.; Liu, X.L.; Li, H.; Shen, J.L.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Wu, J.S. Nitrous oxide emissions from a masson pine forest soil in subtropical central China. Pedosphere 2015, 25, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mota, M.M.; Braasch, H.; Bravo, M.A.; Penas, A.C.; Burgermeister, W.; Metge, K.; Sousa, E. First report of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus in Portugal and in Europe. Nematology 1999, 1, 727–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abelleira, A.; Picoaga, A.; Mansilla, J.P.; Aguin, O. Detection of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus, Causal Agent of Pine Wilt Disease on Pinus pinaster in Northwestern Spain. Plant Dis. 2011, 95, 776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.H.; Chu, X.F.; Sun, T.Y.; Ye, J.R.; Wu, X.Q. Micropropagation of Pinus densiflora and the evaluation of nematode resistance of regenerated microshoots in vitro. J. For. Res. 2018, 30, 519–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbuzova, N.E.; Karagyan, H.G.; Kozyreva, I.N.; Shchukovskaya, A.G.; Ghrejyan, T.L.; Kalashian, M.Y.; Akopyan, K.V. First finding of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus in pine plantations of the Republic of Armenia. J. Nematol. 2025, 57, 20250004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.R. Epidemic Status of Pine Wilt Disease in China and Its Prevention and Control Techniques and Counter Measures. Sci. Silvae Sin. 2019, 55, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Back, M.A.; Bonifácio, L.; Inácio, M.L.; Mota, M.; Boa, E. Pine wilt disease: A global threat to forestry. Plant Pathol. 2024, 73, 1026–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nose, M.; Shiraishi, S. Breeding for resistance to pine wilt disease. In Pine Wilt Disease; Zhao, B.G., Futai, K., Sutherland, J.R., Takeuchi, Y., Eds.; Springer: Tokyo, Japan, 2008; pp. 334–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.B.; Xu, L.Y.; Xi, Q.J.; Gao, J.B.; Toda, T. Resistant breeding technique to pine nematode. J. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2005, 33, 248–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.Y.; Zhang, J.; Gao, J.B.; Hao, Y.P.; Chen, X.L.; Jiang, C.W. Research progress on resistance breeding to pine wood nematodiasis in Anhui province. Anhui For. Sci. Technol. 2013, 39, 8–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renau-Morata, B.; Ollero, J.; Arrillaga, I.; Segura, J. Factors influencing axillary shoot proliferation and adventitious budding in cedar. Tree Physiol. 2005, 25, 477–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Guo, J.-Y.; Zhu, Z.-H.; Chen, Y.-M.; Zhu, L.-H. Screen of Pinus massoniana for Resistance to Pinewood Nematode: In Vitro Propagation and Evaluation of Regenerated Microshoots. Forests 2023, 14, 1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pullman, G.S.; Zeng, X.Y.; Copeland-Kamp, B.; Crockett, J.; Lucrezi, J.; May, S.W.; Bucalo, K. Conifer somatic embryogenesis: Improvements by supplementation of medium with oxidation-reduction agents. Tree Physiol. 2015, 35, 209–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hakman, I.; Fowke, L.C.; Von Arnold, S.; Eriksson, T. The development of somatic embryos in tissue cultures initiated from immature embryos of Picea abies (Norway Spruce). Plant Sci. 1985, 38, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagmani, R.; Bonga, J.M. Embryogenesis in subcultured callus of Larix decidua. Can. J. For. Res. 1985, 15, 1088–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.Q.; Wei, Z.M.; Xu, Z.H. Somatic embryogenesis and plantlet regeneration from callus of mature zygotic embryos of masson pine. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 1995, 37, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozhkov, P.V.; Ahn, I.S.; Park, Y.G. Two alternative pathways of somatic embryo origin from polyembryonic mature stored seeds of Pinus koraiensis Sieb et Zucc. Can. J. Bot. 1997, 75, 509–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montalbán, I.A.; Moncaleán, P. Rooting of Pinus radiata somatic embryos: Factors involved in the success of the process. J. For. Res. 2018, 30, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, L.; Wu, X.; Ye, J.R. Plant regeneration by somatic embryogenesis in Pinus thunbergii resistant to the pine wood nematode. Can. J. For. Res. 2019, 49, 1604–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Xia, X.-R.; Ke, X.; Ye, J.; Zhu, L.-H. Somatic embryogenesis in slash pine (Pinus elliottii Engelm): Improving initiation of embryogenic tissues and maturation of somatic embryos. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2020, 143, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.X.; Gao, F.; Wang, H.; Shen, H.L.; Yang, L. Physiological and Biochemical Traits in Korean Pine Somatic Embryogenesis. Forests 2020, 11, 577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelmann, F. Plant cryopreservation: Progress and prospects. Vitr. Cell. Dev. Biol. Plant 2004, 40, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marum, L.; Estêvão, C.; Oliveira, M.M.; Amâncio, S.; Rodrigues, L.; Miguel, C. Recovery of cryopreserved embryogenic cultures of maritime pine—Effect of cryoprotectant and suspension density. CryoLetters 2004, 25, 363–374. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, C.X.; Gao, F.; Wang, H.; Shen, H.L.; Yang, L. Optimization of maturation process for somatic embryo production and cryopreservation of embryogenic tissue in Pinus koraiensis. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2021, 144, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawrot-Chorabik, K.; Sitko, K. The effect of abscisic acid and dimethyl sulfoxide and different temperatures on the cryopreservation process of Abies nordmanniana embryogenic callus. Phyton-Ann REI Bot 2014, 54, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawrot-Chorabik, K.; Grad, B.; Kowalski, T. Interactions between callus cultures of Pinus sylvestris and pine fungi with different trophic properties. For. Pathol. 2015, 46, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazubska-Przybył, T.; Chmielarz, P.; Michalak, M.; Dering, M.; Bojarczuk, K. Survival and genetic stability of Picea abies embryogenic cultures after cryopreservation using a pregrowth-dehydration method. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2012, 113, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salaj, T.; Klubicová, K.; Matusova, R.; Salaj, J. Somatic Embryogenesis in Selected Conifer Trees Pinus nigra Arn. and Abies Hybrids. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-M.; Fei, Q.; Xia, X.-R.; Ke, X.; Ye, J.-R.; Zhu, L.-H. Pinus massoniana somatic embryo maturation, mycorrhization of regenerated plantlets and its resistance to Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1130471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avila-Victor, C.M.; Arjona-Suárez, E.d.J.; Iracheta-Donjuan, L.; Valdez-Carrasco, J.M.; Gómez-Merino, F.C.; Robledo-Paz, A. Callus Type, Growth Regulators, and Phytagel on Indirect Somatic Embryogenesis of Coffee (Coffea arabica L. var. Colombia). Plants 2023, 12, 3570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, G.H.; Vidaver, W.E. Root production and plantlet development in tissue-cultured conifers. Plant Cell, Tissue Organ Cult. 1988, 14, 137–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tret’yakova, I.; Shuvaev, D.N. Somatic embryogenesis in Pinus pumila and productivity of embryogenic lines during long-term cultivation in vitro. Russ. J. Dev. Biol. 2015, 46, 276–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, C.-H.; Tull, A.R.; Montello, P.M.; Merkle, S.A. A clonal propagation system for Atlantic white cedar (Chamaecyparis thyoides) via somatic embryogenesis without the use of plant growth regulators. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2017, 130, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.F.; Deng, C.; Zhu, T.Q.; Ling, J.J.; Zhang, H.G.; Kong, L.S.; Zhang, S.G.; Wang, J.H.; Chen, X.Y. Dynamics of physiological and miRNA changes after long-term proliferation in somatic embryogenesis of Picea balfouriana. Trees 2019, 33, 469–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Shi, Y.J.; Wang, R.R.; Tretyakova, I.N.; Nosov, A.M.; Shen, H.L.; Yang, L. Optimization of Key Technologies for Induction of Embryogenic Callus and Maturation of Somatic Embryos in Korean Pine (Pinus koraiensis). Forests 2023, 14, 850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lineros, Y.; Balocchi, C.; Muñoz, X.; Sánchez, M.; Ríos, D. Cryopreservation of Pinus radiata embryogenic tissue: Effects of cryoprotective pretreatments on maturation ability. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. (PCTOC) 2018, 135, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.Y.; Wu, X.Q.; Chen, T.T.; Sun, T.Y.; Wang, Y.L. Cryopreservation of Nematode-resistant Pinus massoniana Embryogenic Callus. J. Northeast. For. Univ. 2019, 47, 108–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazubska-Przybył, T.; Wawrzyniak, M.K.; Obarska, A.; Salaj, T. Cryopreservation of Abies alba × A. numidica and Pinus nigra embryogenic tissues by stepwise dehydration method. Plant Methods 2024, 20, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandoval, K.P.; Castander-Olarieta, A.; Moncaleán, P.; Montalbán, I.A. Assessment of alternative freezing methods for preservation at −80 °C of radiata pine embryogenic cultures: A six-year study. Cryobiology 2025, 119, 105217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montalbán, I.A.; De Diego, N.; Moncaleán, P.J.T. Bottlenecks in Pinus radiata somatic embryogenesis: Improving maturation and germination. Trees 2010, 24, 1061–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimaszewska, K.; Hargreaves, C.; Lelu-Walter, M.A.; Trontin, J.F. Advances in conifer somatic embryogenesis since year 2000. In In Vitro Embryogenesis in Higher Plants; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 131–166. [Google Scholar]
- Lelu-Walter, M.-A.; Thompson, D.; Harvengt, L.; Sanchez, L.; Toribio, M.; Pâques, L.E. Somatic embryogenesis in forestry with a focus on Europe: State-of-the-art, benefits, challenges and future direction. Tree Genet. Genomes 2013, 9, 883–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazubska-Przybył, T.; Kalemba, E.M.; Ratajczak, E.; Bojarczuk, K. Effects of abscisic acid and an osmoticum on the maturation, starch accumulation and germination of Picea spp. somatic embryos. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2016, 38, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lelu-Walter, M.-A.; Gautier, F.; Eliášová, K.; Sanchez, L.; Teyssier, C.; Lomenech, A.-M.; Le Metté, C.; Hargreaves, C.; Trontin, J.-F.; Reeves, C. High gellan gum concentration and secondary somatic embryogenesis: Two key factors to improve somatic embryo development in Pseudotsuga menziesii [Mirb.]. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2017, 132, 137–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.P.; Zhang, X.S.; Su, Y.H. Regulation of cell reprogramming by auxin during somatic embryogenesis. aBIOTECH 2020, 1, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneros, E.; Toribio, M.; Celestino, C. Effect of ABA, the auxin antagonist PCIB and partial desiccation on stone pine somatic embryo maturation. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2017, 131, 445–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.-F.; Lan, Q.; Han, S.-Y.; Qi, L.-W. A GH3-like gene, LaGH3, isolated from hybrid larch (Larix leptolepis × Larix olgensis) is regulated by auxin and abscisic acid during somatic embryogenesis. Trees 2019, 33, 1723–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.Q.; Yao, J.B.; Hu, L.F.; Chen, J.H.; Shi, J.S. Multiple Methods Synergistically Promote the Synchronization of Somatic Embryogenesis Through Suspension Culture in the New Hybrid Between Pinus elliottii and Pinus caribaea. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 857972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Arnold, S.; Hakman, I. Regulation of Somatic Embryo Development in Picea abies by Abscisic Acid (ABA). J. Plant Physiol. 1988, 132, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.S.; von Aderkas, P. Genotype effects on ABA consumption and somatic embryo maturation in interior spruce (Picea glauca × engelmanni). J. Exp. Bot. 2007, 58, 1525–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, J.M.; Bueno, N.; Cortizo, M.; Ordás, R.J. Improving plantlet yield in Pinus pinaster somatic embryogenesis. Scand. J. For. Res. 2013, 28, 613–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoji, M.; Sato, H.; Nakagawa, R.; Funada, R.; Kubo, T.; Ogita, S. Influence of osmotic pressure on somatic embryo maturation in Pinus densiflora. J. For. Res. 2006, 11, 449–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, B. Commercial delivery of genetic improvement to conifer plantations using somatic embryogenesis. Ann. For. Sci. 2002, 59, 657–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.T.; Ye, J.R.; Wu, X.Q.; Shen, L.Y.; Zhu, L.H. Somatic embryogenesis and plantlet regeneration of disease-resistant Pinus massoniana Lamb. J. Nanjing For. Univ. 2019, 62, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.J.; Yong, L.; Yan, W.; Shan, L.J.; Lei, L.G. Effects of mushroom residue compost on growth and nutrient uptake of Pinus tabulaeformis container seedlings. Sci. Silvae Sin. 2017, 53, 129–137. [Google Scholar]
- von Arnold, S.; Eriksson, T. A Revised Medium for Growth of Pea Mesophyll Protoplasts. Physiol. Plant. 1977, 39, 257–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| The Ratio of Nutrient Soil, Perlite, and Mushroom Residue | Plants Height (cm) | Plant Height Increment (cm) | Transplant Survival Rate (%) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 Month | 3 Months | 6 Months | 12 Months | 3 Months | 6 Months | 12 Months | 3 Months | 6 Months | 12 Months | |
| 3:1:0 | 2.4 ± 0.8 a | 4.6 ± 1.6 a | 15.0 ± 4.4 a | 26.9 ± 5.9 a | 2.3 ± 1.6 ab | 12.6 ± 4.4 a | 22.3 ± 5.4 a | 56.5 | 56.5 | 56.5 |
| 3:1:1 | 2.5 ± 0.8 a | 5.1 ± 2.1 a | 7.3 ± 2.8 b | 11.4 ± 3.7 b | 2.6 ± 1.6 a | 4.8 ± 2.8 b | 5.0 ± 2.6 b | 95.7 | 82.6 | 26.1 |
| 3:1:2 | 2.5 ± 0.8 a | 4.7 ± 1.9 a | 5.8 ± 1.9 bc | 6.2 ± 1.5 bc | 2.1 ± 1.4 ab | 3.3 ± 1.9 bc | 1.1 ± 0.6 b | 95.7 | 78.3 | 21.7 |
| 3:1:3 | 2.5 ± 0.6 a | 4.1 ± 1.2 a | 4.8 ± 1.19 c | 5.2 ± 0.9 c | 1.6 ± 0.8 b | 2.3 ± 1.2 c | 1.2 ± 0.5 b | 100 | 79.2 | 21.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Q.; Lin, Y.; Chen, Y.-M.; Fei, Q.; Ye, J.-R.; Zhu, L.-H. Cryopreservation and Maturation Media Optimization for Enhanced Somatic Embryogenesis in Masson Pine (Pinus massoniana). Plants 2025, 14, 1569. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14111569
Yang Q, Lin Y, Chen Y-M, Fei Q, Ye J-R, Zhu L-H. Cryopreservation and Maturation Media Optimization for Enhanced Somatic Embryogenesis in Masson Pine (Pinus massoniana). Plants. 2025; 14(11):1569. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14111569
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Qian, Ying Lin, You-Mei Chen, Qi Fei, Jian-Ren Ye, and Li-Hua Zhu. 2025. "Cryopreservation and Maturation Media Optimization for Enhanced Somatic Embryogenesis in Masson Pine (Pinus massoniana)" Plants 14, no. 11: 1569. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14111569
APA StyleYang, Q., Lin, Y., Chen, Y.-M., Fei, Q., Ye, J.-R., & Zhu, L.-H. (2025). Cryopreservation and Maturation Media Optimization for Enhanced Somatic Embryogenesis in Masson Pine (Pinus massoniana). Plants, 14(11), 1569. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14111569






