The PIN Gene Family in Cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.): Genome-Wide Identification and Gene Expression Analysis in Phytohormone and Abiotic Stress Response
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Genome-Wide Identification and Phylogenetic Analysis of PIN Proteins in Cucumber
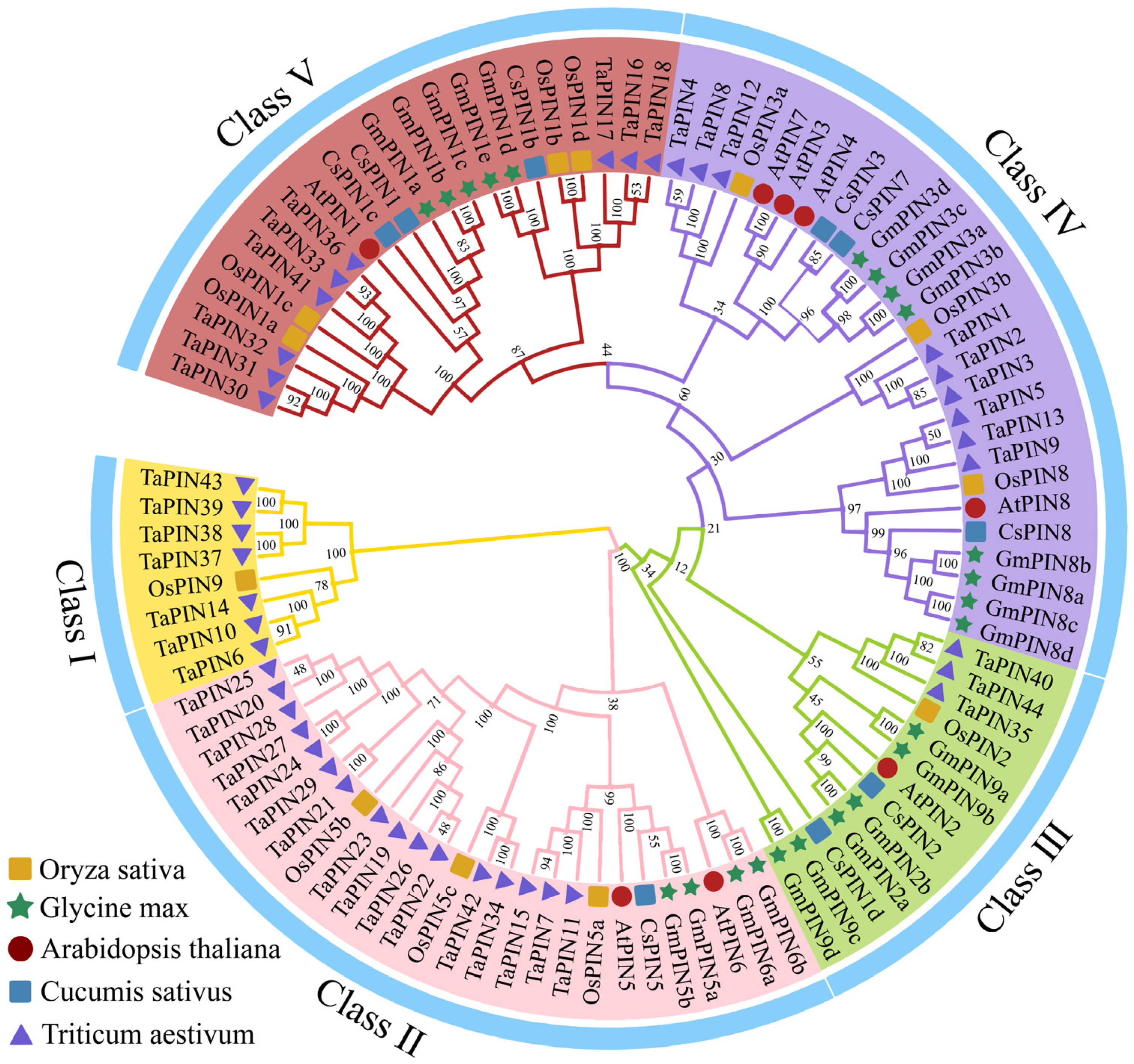
2.2. Phylogenetic Relationship Analysis of Cucumber PINs
2.3. Chromosomal Distribution of Cucumber PIN Genes
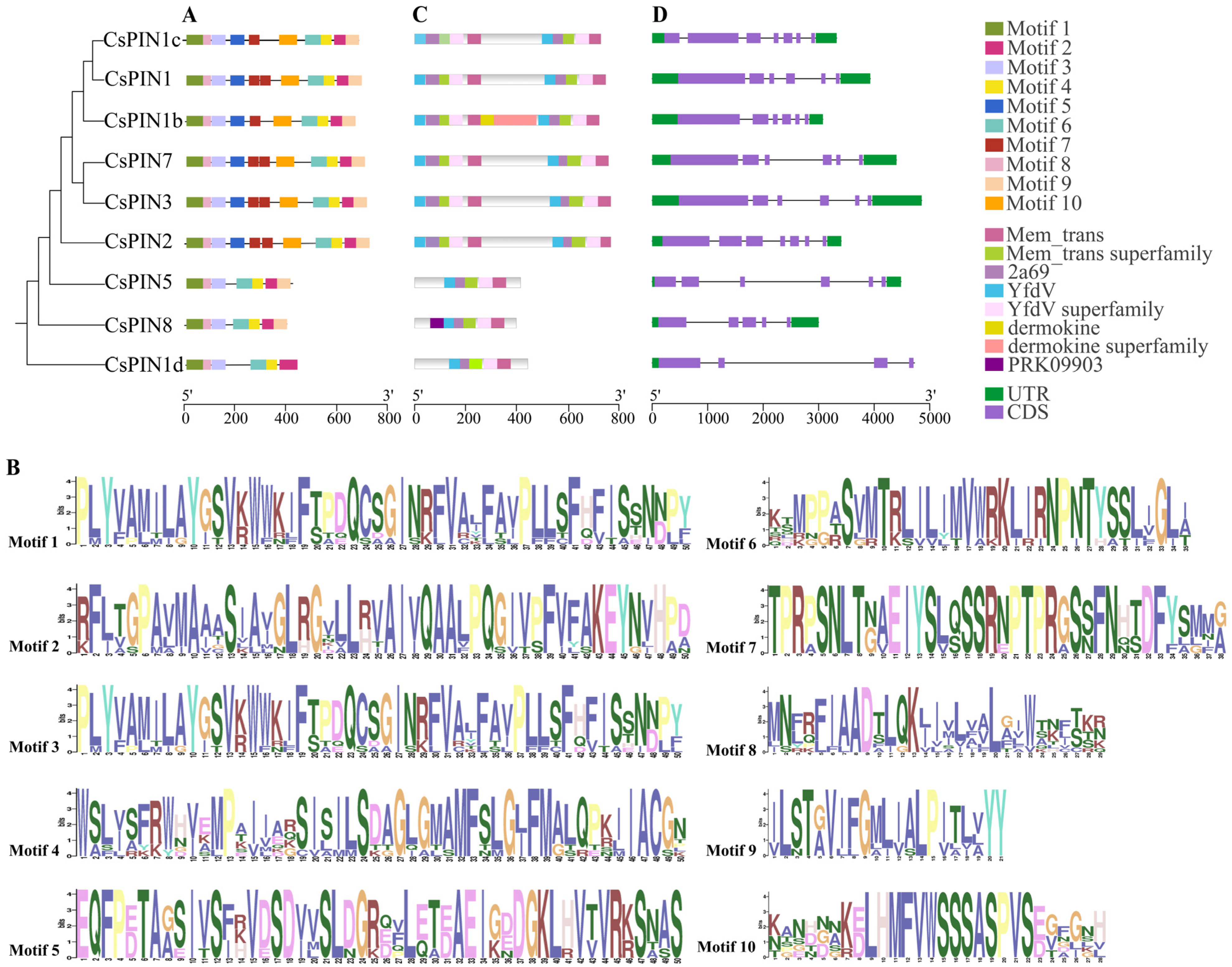
2.4. The Conserved Domains and Gene Structure of Cucumber PIN Genes
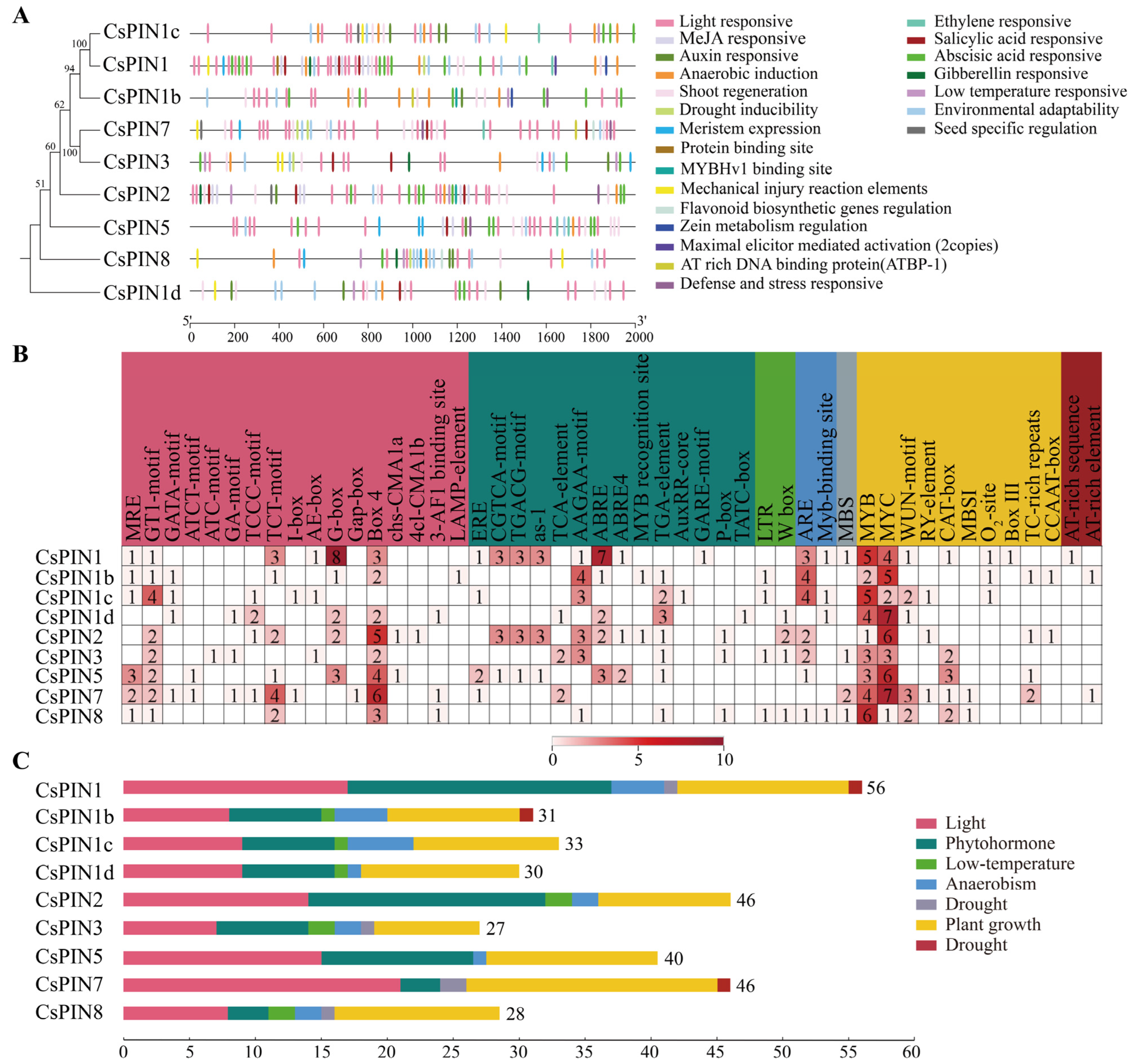
2.5. Analysis of Cis-Acting Elements Prediction in CsPIN Promoters
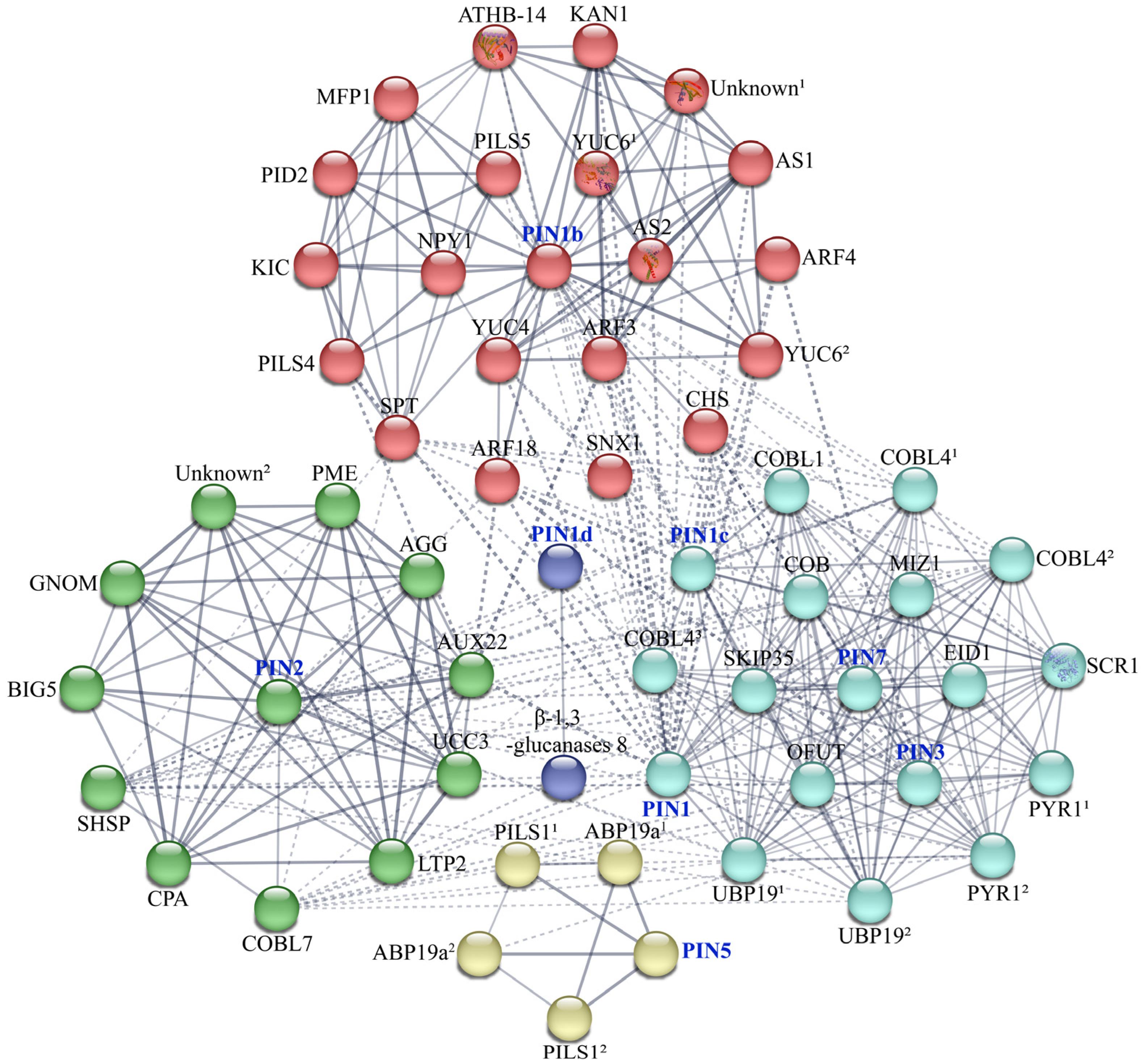
2.6. Interaction Network of CsPIN Proteins
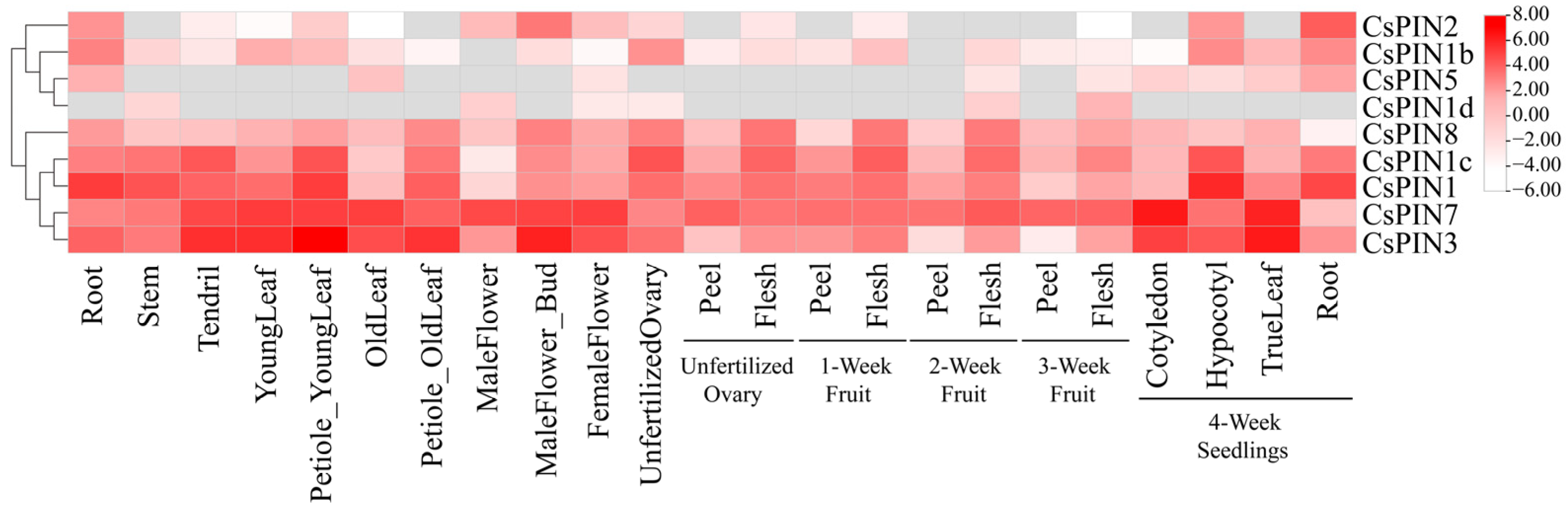
2.7. Expression Profiles of CsPIN Genes in Different Tissues and Organs
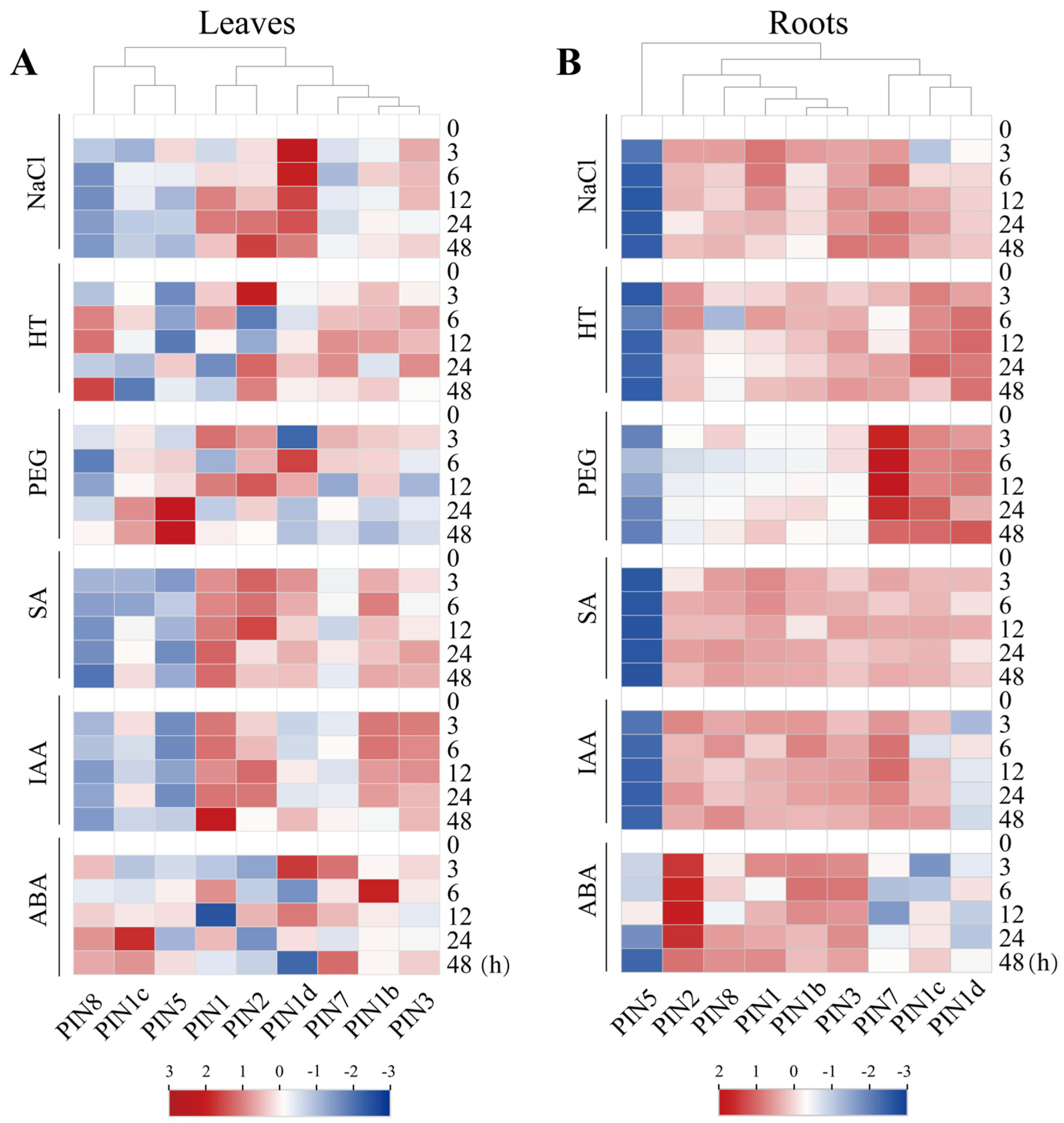
2.8. Expression Analysis of CsPIN Genes Under Different Stress Conditions
3. Discussion
3.1. Identification and Evolution of CsPIN Gene Family in Cucumber
3.2. Protein–Protein Interaction Network of CsPIN
3.3. Role of the CsPIN Genes in Plant Growth and Development
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Identification and Physicochemical Properties of PIN Genes in Cucumber
4.2. Phylogenetic Analysis of Cucumber PIN Gene Family
4.3. Chromosome Localization and Gene Duplication Analysis
4.4. The Conserved Motifs, Gene Structure, Function Domain, Putative Cis-Acting Elements Analysis
4.5. Protein–Protein Interaction Network
4.6. Analysis of Expression Profiles of CsPINs Genes in Different Tissues
4.7. Plant Materials and Treatment
4.8. RNA Extraction and Quantitative qRT-PCR Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABA | Abscisic acid |
| HT | High temperature |
| IAA | Indole-3-acetic acid |
| NaCl | Sodium chloride |
| PEG | Polyethylene glycol |
| SA | Salicylic acid |
| qRT-PCR | Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction |
References
- Vanneste, S.; Friml, J. Auxin: A Trigger for Change in Plant Development. Cell 2009, 136, 1005–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.D. Essential Roles of Local Auxin Biosynthesis in Plant Development and in Adaptation to Environmental Changes. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2018, 69, 417–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, G.L.B.; Scortecci, K.C. Auxin and its role in plant development: Structure, signalling, regulation and response mechanisms. Plant Biol. 2021, 23, 894–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swarup, R.; Kargul, J.; Marchant, A.; Zadik, D.; Rahman, A.; Mills, R.; Yemm, A.; May, S.; Williams, L.; Millner, P.; et al. Structure-function analysis of the presumptive Arabidopsis auxin permease AUX1. Plant Cell 2004, 16, 3069–3083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrásek, J.; Mravec, J.; Bouchard, R.; Blakeslee, J.J.; Abas, M.; Seifertová, D.; Wisniewska, J.; Tadele, Z.; Kubes, M.; Covanová, M.; et al. PIN proteins perform a rate-limiting function in cellular auxin efflux. Science 2006, 312, 914–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, M.; Lee, S.H.; Cho, H.T. P-glycoprotein4 displays auxin efflux transporter-like action in Arabidopsis root hair cells and tobacco cells. Plant Cell 2007, 19, 3930–3943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbez, E.; Kubes, M.; Rolcík, J.; Béziat, C.; Pencík, A.; Wang, B.J.; Rosquete, M.R.; Zhu, J.S.; Dobrev, P.I.; Lee, Y.; et al. A novel putative auxin carrier family regulates intracellular auxin homeostasis in plants. Nature 2012, 485, 119-U155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, I. A showcase of future plant biology: Moving towards next-generation plant genetics assisted by genome sequencing and systems biology. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krecek, P.; Skupa, P.; Libus, J.; Naramoto, S.; Tejos, R.; Friml, J.; Zazímalová, E. The PIN-FORMED (PIN) protein family of auxin transporters. Genome Biol. 2009, 10, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Dong, W.; Huang, Z.A.; Cho, M.; Yu, Q.; Wu, C.; Yu, C. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the CaLAX and CaPIN gene families in pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) under various abiotic stresses and hormone treatments. Genome 2018, 61, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Wang, D.; Zhang, C.; Kong, N.; Ma, H.; Chen, Q. Comparative Analysis of the PIN Auxin Transporter Gene Family in Different Plant Species: A Focus on Structural and Expression Profiling of PINs in Solanum tuberosum. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forestan, C.; Farinati, S.; Varotto, S. The Maize PIN Gene Family of Auxin Transporters. Front. Plant Sci. 2012, 3, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sańko-Sawczenko, I.; Łotocka, B.; Czarnocka, W. Expression Analysis of PIN Genes in Root Tips and Nodules of Medicago truncatula. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Bai, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhang, S.; Wu, Y.; Chen, M.; Jiang, D.; Qi, Y. Expression profile of PIN, AUX/LAX and PGP auxin transporter gene families in Sorghum bicolor under phytohormone and abiotic stress. FEBS J. 2010, 277, 2954–2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, H.; Nai, G.; Lu, S.; Ma, W.; Chen, B.; Mao, J. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of PIN gene family under phytohormone and abiotic stresses in Vitis vinifera L. Physiol. Mol. Biol. Plants 2022, 28, 1905–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.; Chen, L.; Wang, C.; Zhang, S.; Yang, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, D.; Song, J.; Wang, R. Characterization of the Auxin Efflux Transporter PIN Proteins in Pear. Plants 2020, 9, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Zhang, J.; Wang, L.; Li, J.; Zheng, H.; Chen, J.; Lu, M. A survey of Populus PIN-FORMED family genes reveals their diversified expression patterns. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 2437–2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, P.; Zhao, P.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Xiao, H.; Yu, J.; Xiao, G. The PIN gene family in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum): Genome-wide identification and gene expression analyses during root development and abiotic stress responses. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Qin, G.; Si, P.; Luo, Z.; Gao, J.; Chen, X.; Zhang, J.; Wei, P.; Xia, Q.; Lin, F.; et al. Analysis of Nicotiana tabacum PIN genes identifies NtPIN4 as a key regulator of axillary bud growth. Physiol. Plant 2017, 160, 222–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chai, C.; Valliyodan, B.; Maupin, C.; Annen, B.; Nguyen, H.T. Genome-wide analysis and expression profiling of the PIN auxin transporter gene family in soybean (Glycine max). BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friml, J. Auxin transport—Shaping the plant. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2003, 6, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamowski, M.; Friml, J. PIN-dependent auxin transport: Action, regulation, and evolution. Plant Cell 2015, 27, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Wang, B.; Moreno, I.; Dupláková, N.; Simon, S.; Carraro, N.; Reemmer, J.; Pěnčík, A.; Chen, X.; Tejos, R.; et al. ER-localized auxin transporter PIN8 regulates auxin homeostasis and male gametophyte development in Arabidopsis. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, T.; Brockington, S.F.; Rothfels, C.; Graham, S.W.; Stevenson, D.; Kutchan, T.; Rolf, M.; Thomas, P.; Wong, G.K.; Leyser, O.; et al. Paralogous radiations of PIN proteins with multiple origins of noncanonical PIN structure. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2014, 31, 2042–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mravec, J.; Skůpa, P.; Bailly, A.; Hoyerová, K.; Krecek, P.; Bielach, A.; Petrásek, J.; Zhang, J.; Gaykova, V.; Stierhof, Y.D.; et al. Subcellular homeostasis of phytohormone auxin is mediated by the ER-localized PIN5 transporter. Nature 2009, 459, 1136–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, S.; Skůpa, P.; Viaene, T.; Zwiewka, M.; Tejos, R.; Klíma, P.; Čarná, M.; Rolčík, J.; De Rycke, R.; Moreno, I.; et al. PIN6 auxin transporter at endoplasmic reticulum and plasma membrane mediates auxin homeostasis and organogenesis in Arabidopsis. New Phytol. 2016, 211, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganguly, A.; Lee, S.H.; Cho, M.; Lee, O.R.; Yoo, H.; Cho, H.T. Differential auxin-transporting activities of PIN-FORMED proteins in Arabidopsis root hair cells. Plant Physiol. 2010, 153, 1046–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benková, E.; Michniewicz, M.; Sauer, M.; Teichmann, T.; Seifertová, D.; Jürgens, G.; Friml, J. Local, efflux-dependent auxin gradients as a common module for plant organ formation. Cell 2003, 115, 591–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudgett, M.; Shen, Z.; Dai, X.; Briggs, S.P.; Zhao, Y. Suppression of pinoid mutant phenotypes by mutations in PIN-FORMED 1 and PIN1-GFP fusion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2312918120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Kamiya, T.; Fujiwara, T. Differential Roles of PIN1 and PIN2 in Root Meristem Maintenance Under Low-B Conditions in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Physiol. 2015, 56, 1205–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Liu, Y.; Maere, S.; Lee, E.; Van Isterdael, G.; Xie, Z.; Xuan, W.; Lucas, J.; Vassileva, V.; Kitakura, S.; et al. A coherent transcriptional feed-forward motif model for mediating auxin-sensitive PIN3 expression during lateral root development. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friml, J.; Benková, E.; Blilou, I.; Wisniewska, J.; Hamann, T.; Ljung, K.; Woody, S.; Sandberg, G.; Scheres, B.; Jürgens, G.; et al. AtPIN4 mediates sink-driven auxin gradients and root patterning in Arabidopsis. Cell 2002, 108, 661–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazzonelli, C.I.; Vanstraelen, M.; Simon, S.; Yin, K.; Carron-Arthur, A.; Nisar, N.; Tarle, G.; Cuttriss, A.J.; Searle, I.R.; Benkova, E.; et al. Role of the Arabidopsis PIN6 auxin transporter in auxin homeostasis and auxin-mediated development. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ditengou, F.A.; Gomes, D.; Nziengui, H.; Kochersperger, P.; Lasok, H.; Medeiros, V.; Paponov, I.A.; Nagy, S.K.; Nádai, T.V.; Mészáros, T.; et al. Characterization of auxin transporter PIN6 plasma membrane targeting reveals a function for PIN6 in plant bolting. New Phytol. 2018, 217, 1610–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, F.; Liu, H.H.; Duan, C.Y.; Zhang, B.K.; Wei, G.; Zhang, Y.; Li, S. Arabidopsis JANUS Regulates Embryonic Pattern Formation through Pol II-Mediated Transcription of WOX2 and PIN7. iScience 2019, 19, 1179–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Zhu, L.; Shou, H.; Wu, P. A PIN1 family gene, OsPIN1, involved in auxin-dependent adventitious root emergence and tillering in rice. Plant Cell Physiol. 2005, 46, 1674–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Fan, X.; Song, W.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, G. Over-expression of OsPIN2 leads to increased tiller numbers, angle and shorter plant height through suppression of OsLAZY1. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2012, 10, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.R.; Hu, H.; Wang, G.H.; Li, J.; Chen, J.Y.; Wu, P. Expression of PIN genes in rice (Oryza sativa L.): Tissue specificity and regulation by hormones. Mol. Plant 2009, 2, 823–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carraro, N.; Forestan, C.; Canova, S.; Traas, J.; Varotto, S. ZmPIN1a and ZmPIN1b encode two novel putative candidates for polar auxin transport and plant architecture determination of maize. Plant Physiol. 2006, 142, 254–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallavotti, A.; Yang, Y.; Schmidt, R.J.; Jackson, D. The Relationship between auxin transport and maize branching. Plant Physiol. 2008, 147, 1913–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, R.; Tie, S.; Sun, T.; Zhang, L.; Yang, Y.; Qi, J.; Yan, S.; Han, X.; Wang, H.; Shen, C. Genome-wide identification and expression profiling analysis of ZmPIN, ZmPILS, ZmLAX and ZmABCB auxin transporter gene families in maize (Zea mays L.) under various abiotic stresses. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0118751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roychoudhry, S.; Sageman-Furnas, K.; Wolverton, C.; Grones, P.; Tan, S.; Molnár, G.; De Angelis, M.; Goodman, H.L.; Capstaff, N.; Lloyd, J.P.B.; et al. Antigravitropic PIN polarization maintains non-vertical growth in lateral roots. Nat. Plants 2023, 9, 1500–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibata, A.; Yumoto, G.; Shimizu, H.; Honjo, M.N.; Kudoh, H. Flower movement induced by weather-dependent tropism satisfies attraction and protection. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 4132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ung, K.L.; Winkler, M.; Schulz, L.; Kolb, M.; Janacek, D.P.; Dedic, E.; Stokes, D.L.; Hammes, U.Z.; Pedersen, B.P. Structures and mechanism of the plant PIN-FORMED auxin transporter. Nature 2022, 609, 605–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, M.E.; Barley, R.; Curtis, M.; Arroyo, J.M.; Dunham, M.; Hudson, A.; Martienssen, R.A. Asymmetric leaves1 mediates leaf patterning and stem cell function in Arabidopsis. Nature 2000, 408, 967–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semiarti, E.; Ueno, Y.; Tsukaya, H.; Iwakawa, H.; Machida, C.; Machida, Y. The ASYMMETRIC LEAVES2 gene of Arabidopsis thaliana regulates formation of a symmetric lamina, establishment of venation and repression of meristem-related homeobox genes in leaves. Development 2001, 128, 1771–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Yu, C.W.; Chen, F.F.; Zhao, L.; Tian, G.; Liu, X.; Cui, Y.; Yang, J.Y.; Wu, K. Histone deacetylase HDA6 is functionally associated with AS1 in repression of KNOX genes in arabidopsis. PLoS Genet. 2012, 8, e1003114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumura, Y.; Ohbayashi, I.; Takahashi, H.; Kojima, S.; Ishibashi, N.; Keta, S.; Nakagawa, A.; Hayashi, R.; Saéz-Vásquez, J.; Echeverria, M.; et al. A genetic link between epigenetic repressor AS1-AS2 and a putative small subunit processome in leaf polarity establishment of Arabidopsis. Biol. Open 2016, 5, 942–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, T.J.; Flores-Sandoval, E.; Alvarez, J.P.; Bowman, J.L. PIN-FORMED is required for shoot phototropism/gravitropism and facilitates meristem formation in Marchantia polymorpha. New Phytol. 2023, 238, 1498–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Kherawat, B.S.; Dey, P.; Saha, D.; Singh, A.; Bhatia, S.K.; Ghodake, G.S.; Kadam, A.A.; Kim, H.U.; Manorama; et al. Genome-Wide Identification and Characterization of PIN-FORMED (PIN) Gene Family Reveals Role in Developmental and Various Stress Conditions in Triticum aestivum L. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyashita, Y.; Takasugi, T.; Ito, Y. Identification and expression analysis of PIN genes in rice. Plant Sci. 2010, 178, 424–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, T. PIN proteins and the evolution of plant development. Trends Plant Sci. 2015, 20, 498–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viaene, T.; Delwiche, C.F.; Rensing, S.A.; Friml, J. Origin and evolution of PIN auxin transporters in the green lineage. Trends Plant Sci. 2013, 18, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michniewicz, M.; Zago, M.K.; Abas, L.; Weijers, D.; Schweighofer, A.; Meskiene, I.; Heisler, M.G.; Ohno, C.; Zhang, J.; Huang, F.; et al. Antagonistic regulation of PIN phosphorylation by PP2A and PINOID directs auxin flux. Cell 2007, 130, 1044–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Liu, X.; Xuan, W.; Mei, H.; Li, J.; Chen, X.; Zhao, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Jeyaraj, A.; Periakaruppan, R.; et al. Genome-wide identification and characterization of PIN-FORMED (PIN) and PIN-LIKES (PILS) gene family reveals their role in adventitious root development in tea nodal cutting (Camellia sinensis). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 229, 791–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Bai, X.; Guo, T.; Xie, Z.; Laimer, M.; Du, D.; Gbokie, T., Jr.; Zhang, Z.; He, C.; Lu, Y.; et al. Genome-Wide Analysis of the PIN Auxin Efflux Carrier Gene Family in Coffee. Plants 2020, 9, 1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brun, C.; Chevenet, F.; Martin, D.; Wojcik, J.; Guénoche, A.; Jacq, B. Functional classification of proteins for the prediction of cellular function from a protein-protein interaction network. Genome Biol. 2003, 5, R6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geldner, N.; Anders, N.; Wolters, H.; Keicher, J.; Kornberger, W.; Muller, P.; Delbarre, A.; Ueda, T.; Nakano, A.; Jürgens, G. The Arabidopsis GNOM ARF-GEF mediates endosomal recycling, auxin transport, and auxin-dependent plant growth. Cell 2003, 112, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinmann, T.; Geldner, N.; Grebe, M.; Mangold, S.; Jackson, C.L.; Paris, S.; Gälweiler, L.; Palme, K.; Jürgens, G. Coordinated polar localization of auxin efflux carrier PIN1 by GNOM ARF GEF. Science 1999, 286, 316–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakusová, H.; Gallego-Bartolomé, J.; Vanstraelen, M.; Robert, H.S.; Alabadí, D.; Blázquez, M.A.; Benková, E.; Friml, J. Polarization of PIN3-dependent auxin transport for hypocotyl gravitropic response in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 2011, 67, 817–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, H.; Kitakura, S.; Rakusová, H.; Uemura, T.; Feraru, M.I.; De Rycke, R.; Robert, S.; Kakimoto, T.; Friml, J. Cell polarity and patterning by PIN trafficking through early endosomal compartments in Arabidopsis thaliana. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baster, P.; Robert, S.; Kleine-Vehn, J.; Vanneste, S.; Kania, U.; Grunewald, W.; De Rybel, B.; Beeckman, T.; Friml, J. SCF(TIR1/AFB)-auxin signalling regulates PIN vacuolar trafficking and auxin fluxes during root gravitropism. Embo J. 2013, 32, 260–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abas, L.; Benjamins, R.; Malenica, N.; Paciorek, T.; Wiśniewska, J.; Moulinier-Anzola, J.C.; Sieberer, T.; Friml, J.; Luschnig, C. Intracellular trafficking and proteolysis of the Arabidopsis auxin-efflux facilitator PIN2 are involved in root gravitropism. Nat. Cell Biol. 2006, 8, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleine-Vehn, J.; Huang, F.; Naramoto, S.; Zhang, J.; Michniewicz, M.; Offringa, R.; Friml, J. PIN auxin efflux carrier polarity is regulated by PINOID kinase-mediated recruitment into GNOM-independent trafficking in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2009, 21, 3839–3849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.J.; Lee, H.J.; Gil, K.E.; Kim, J.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, H.; Cho, H.T.; Vu, L.D.; De Smet, I.; Park, C.M. Developmental Programming of Thermonastic Leaf Movement. Plant Physiol. 2019, 180, 1185–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Shi, X.; Zhong, T.; Jie, W.; Xu, R.; Ding, Y.; Ding, C. PINOID and PIN-FORMED Paralogous Genes Are Required for Leaf Morphogenesis in Rice. Plant Cell Physiol. 2023, 64, 1146–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omelyanchuk, N.A.; Kovrizhnykh, V.V.; Oshchepkova, E.A.; Pasternak, T.; Palme, K.; Mironova, V.V. A detailed expression map of the PIN1 auxin transporter in Arabidopsis thaliana root. BMC Plant Biol. 2016, 16 (Suppl. S1), 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Y.; Chen, Q.; Qu, Y.; Liu, P.; Jiao, Y.; Cai, Y.; Deng, X.; Zheng, K. Identification and functional analysis of PIN family genes in Gossypium barbadense. PeerJ 2022, 10, e14236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, I.C.R.; Hammes, U.Z.; Schwechheimer, C. Activation and Polarity Control of PIN-FORMED Auxin Transporters by Phosphorylation. Trends Plant Sci. 2018, 23, 523–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Wang, P.; Long, X.; Wu, W.; Zhang, J.; Pan, Y.; Cheng, T.; Shi, J.; Chen, J. The PIN gene family in relic plant L. chinense: Genome-wide identification and gene expression profiling in different organizations and abiotic stress responses. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 162, 634–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, W.; Yu, L.; Li, D.; Zhang, H.; Miao, C.; Ding, X.; Jiang, Y. Genome-Wide Analysis and Expression Profiling of Glyoxalase Gene Families Under Abiotic Stresses in Cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 11294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Gene Name | Gene Locus | Chromosome Location | ORF Length (bp) | No. of AA | MW (kDa) | pI | Aliphatic Index | GRAVY | TMHs | Subcellular Localization # |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CsPIN1 | CsaV3_1G007160.1 | chr1:4542181–4546111(−) | 1857 | 618 | 67.44 | 9.13 | 89.61 | 0.077 | 9 | PM |
| CsPIN1b | CsaV3_4G029470.1 | chr4:19012575–19015651(+) | 1791 | 596 | 63.70 | 8.77 | 96.71 | 0.264 | 9 | ER |
| CsPIN1c | CsaV3_1G004350.1 | chr1:2730713–2734038(−) | 1827 | 608 | 66.63 | 9.09 | 90.90 | 0.098 | 8 | PM |
| CsPIN1d | CsaV3_2G009700.1 | chr2:6188991–6193716(+) | 1191 | 396 | 43.04 | 7.57 | 112.75 | 0.494 | 5 | ER |
| CsPIN2 | CsaV3_1G032010.1 | chr1:19030115–19033521(+) | 1938 | 645 | 70.83 | 9.29 | 85.46 | 0.017 | 9 | PM |
| CsPIN3 | CsaV3_5G028620.1 | chr5:23739663–23744519(−) | 1911 | 636 | 69.46 | 7.12 | 91.42 | 0.111 | 9 | PM |
| CsPIN5 | CsaV3_2G009610.1 | chr2:6112103–6116586(+) | 1116 | 371 | 40.37 | 7.04 | 112.24 | 0.675 | 9 | ER |
| CsPIN7 | CsaV3_5G013380.1 | chr5:9982996–9987398(−) | 1890 | 629 | 68.48 | 8.50 | 92.62 | 0.137 | 9 | PM |
| CsPIN8 | CsaV3_3G041710.1 | chr3:34023847–34026847(+) | 1071 | 356 | 38.98 | 9.59 | 129.61 | 0.692 | 8 | ER |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Zhu, K.; Shen, W.; Cui, J.; Miao, C.; Lu, P.; Wu, S.; Zhu, C.; Jin, H.; Zhang, H.; et al. The PIN Gene Family in Cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.): Genome-Wide Identification and Gene Expression Analysis in Phytohormone and Abiotic Stress Response. Plants 2025, 14, 1566. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14111566
Zhang Y, Zhu K, Shen W, Cui J, Miao C, Lu P, Wu S, Zhu C, Jin H, Zhang H, et al. The PIN Gene Family in Cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.): Genome-Wide Identification and Gene Expression Analysis in Phytohormone and Abiotic Stress Response. Plants. 2025; 14(11):1566. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14111566
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yongxue, Kaili Zhu, Weiyao Shen, Jiawei Cui, Chen Miao, Panling Lu, Shaofang Wu, Cuifang Zhu, Haijun Jin, Hongmei Zhang, and et al. 2025. "The PIN Gene Family in Cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.): Genome-Wide Identification and Gene Expression Analysis in Phytohormone and Abiotic Stress Response" Plants 14, no. 11: 1566. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14111566
APA StyleZhang, Y., Zhu, K., Shen, W., Cui, J., Miao, C., Lu, P., Wu, S., Zhu, C., Jin, H., Zhang, H., Chang, L., & Ding, X. (2025). The PIN Gene Family in Cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.): Genome-Wide Identification and Gene Expression Analysis in Phytohormone and Abiotic Stress Response. Plants, 14(11), 1566. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14111566






