Development of Single Nucleotide Polymorphism and Phylogenetic Analysis of Rhododendron Species in Zhejiang Province, China, Using ddRAD-Seq Technology
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials
2.2. DNA Extraction and Library Preparation
2.3. SNP Calling
2.4. Genetic Diversity and Genetic Differentiation
2.5. PCA and Phylogenomic Tree Reconstruction
3. Results
3.1. Sequencing Data Quality Control and Filtering
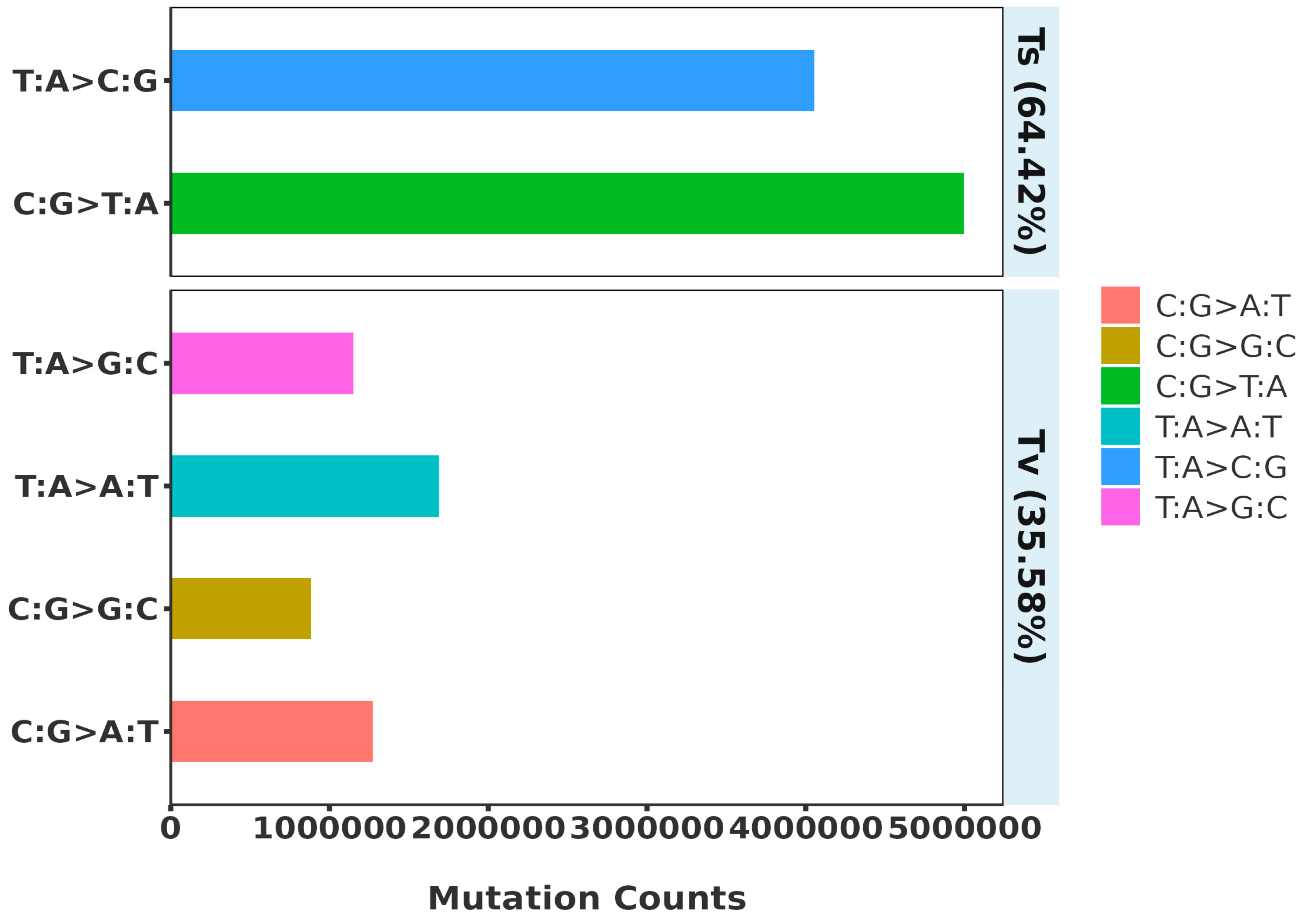
3.2. SNP Distribution and Identification
3.3. Genetic Diversity Analysis
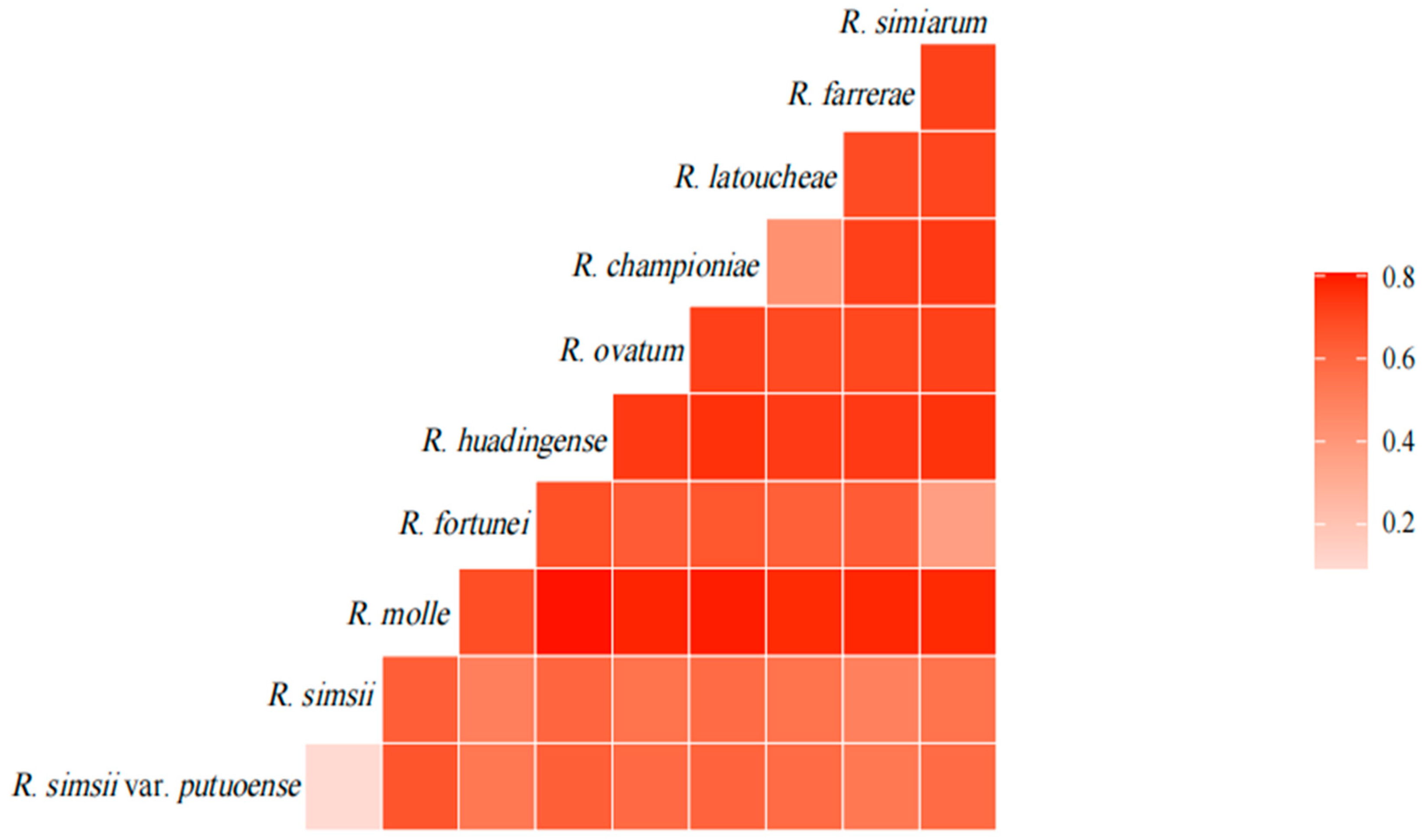
3.4. Genetic Differentiation Analysis
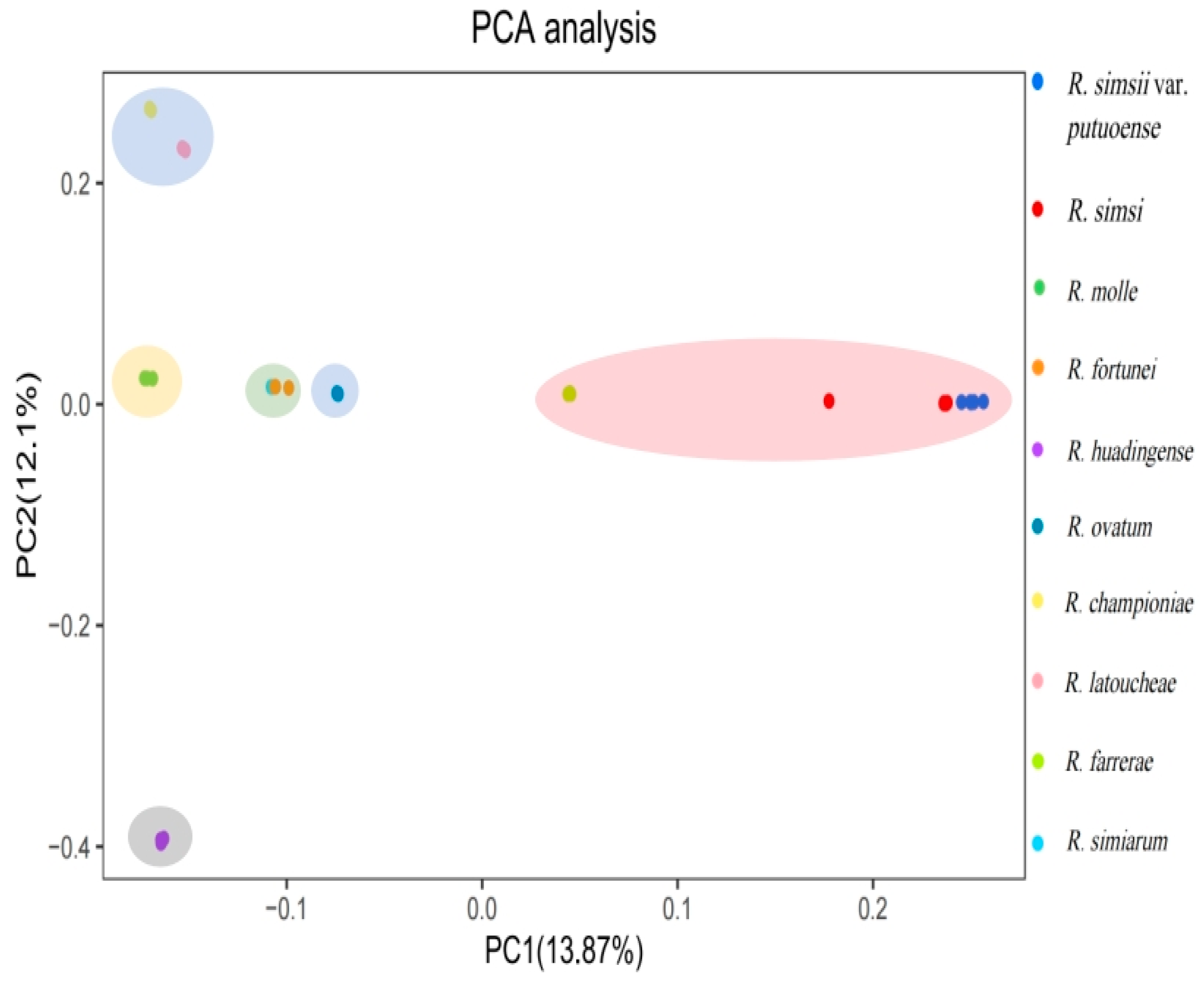
3.5. Phylogenetic Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Genetic Diversity and Genetic Differentiation of Rhododendron Species Produced in Zhejiang Province
4.2. Phylogenetic Relationships and Taxonomy of Rhododendron Species Produced in Zhejiang Province
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cheng, J.; Li, M.; Yuan, T.; Huang, H.; Yang, G.; Bai, X. A dataset on wild Rhododendron and geographical distribution information in China. Biodivers. Sci. 2021, 29, 1175–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, M.Y.; Fang, R.C.; He, M.Y. Rhododendron. In Flora of China; Wu, C.Y., Raven, P.H., Hong, D.Y., Eds.; Science Press: Beijing, China; Missouri Botanical Garden Press: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2005; Volume 14, pp. 260–455. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, F.; Skidmore, A.K.; Wang, T.; Huang, J.; Ma, K.; Groen, T.A. Rhododendron diversity patterns and priority conservation areas in China. Diver. Distrib. 2017, 23, 1143–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.; Wu, Y.; Cao, Z.; Wu, Z.; Yu, F.; Yu, H.; Wang, T. Island biogeography theory and the habitat heterogeneity jointly explain global patterns of Rhododendron diversity. Plant Divers. 2024, 46, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Chen, Y.; Tang, X.; Lu, Y.; Yu, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Ji, H.; Li, Y.; Wu, P.; et al. Comprehensive evaluation of appreciation of Rhododendron based on analytic hierarchy process. Plants 2024, 13, 558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popescu, R.; Kopp, B. The genus Rhododendron: An ethnopharmacological and toxicological review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2013, 147, 42–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Mao, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, Y.; Geng, Y.; Mao, T.; Cai, L.; Huang, S.; Hollingsworth, P.; et al. Pervasive hybridization during evolutionary radiation of Rhododendron subgenus Hymenanthes in mountains of southwest China. Nat. Sci. Rev. 2022, 9, nwac276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, C.N.; Mo, Z.Q.; Yang, J.B.; Cai, J.; Ye, L.J.; Zou, J.Y.; Qin, H.T.; Zheng, W.; Hollingsworth, P.M.; Li, D.Z.; et al. Testing genome skimming for species discrimination in the large and taxonomically difficult genus Rhododendron. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2022, 22, 404–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, L.M.; Li, D.Z.; Zhang, C.Q.; Tang, J.B. Infrageneric and sectional relationships in the genus Rhododendron (Ericaceae) inferred from ITS sequence data. J. Integr. Plant. Biol. 2002, 44, 1351. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, L.J.; Liu, J.; Möller, M.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, X.M.; Li, D.Z.; Gao, L.M. DNA barcoding of Rhododendron (Ericaceae), the largest Chinese plant genus in biodiversity hotspots of the Himalaya-Hengduan Mountains. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2015, 15, 932–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.H.; Shen, S.K. De novo assembly of transcriptome and development of novel EST-SSR markers in Rhododendron rex Lévl. through Illumina sequencing. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, H.; Kumar, P.; Singh, A.; Aggarwal, K.; Roy, J.; Sharma, V.; Rawat, S. Development of polymorphic EST-SSR markers and their applicability in genetic diversity evaluation in Rhododendron arboreum. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2020, 47, 2447–2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.; Li, X.; Li, M.; Cheng, H.; Huang, X.; Jin, S. Characterization, comparative phylogenetic, and gene transfer analyses of organelle genomes of Rhododendron × pulchrum. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 969765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, W.J.; Li, H.L.; Song, W.W.; Wang, X.Q. Plastid genome structural characteristics and phylogenetic relationships of Ericaceae. J. West China For. Sci. 2023, 52, 20–28. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Y.; Yao, G.; Li, Y.; Tian, X.; Li, S.; Wang, N.; Zhang, C.; Wang, F.; Ma, Y. RAD-seq data reveals robust phylogeny and morphological evolutionary history of Rhododendron. Hortic. Plant J. 2024, 10, 866–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Huang, N.; Zhang, Z.; Luo, W.; Xiang, J.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Y. Genetic diversity analysis and prediction of potential suitable areas for the rare and endangered wild plant Henckelia longisepala. Plants 2024, 13, 2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, B.Y.; Fang, Y.Y. A new species of Rhododendron from Zhejiang, China. Bull. Bot. Res. 1990, 10, 31–33. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, B.Y.; Jin, X.F. Validation of Rhododendron huadingense (Ericaceae), the name of a species endemic to China. Taxon 2005, 54, 804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.Y.; Chen, Z.H.; Hu, J.F.; Jin, S.H.; Ma, D.D.; Ou, D.Y. Two new plant varities from Putuo Island, Zhejiang Province. J. Zhejiang A&F Univ. 2010, 27, 908–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Auwera, G.A.; Carneiro, M.O.; Hartl, C.; Poplin, R.; Del Angel, G.; Levy-Moonshine, A.; Jordan, T.; Shakir, K.; Roazen, D.; Thibalit, J.; et al. From FastQ data to high confidence variant calls: The Genome Analysis Toolkit best practices pipeline. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2013, 43, 11.10.1–11.10.33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Li, S.H.; Goddard, M.E.; Visscher, P.M. GCTA: A tool for genome-wide complex trait analysis. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2011, 88, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, M.N.; Dehal, P.S.; Arkin, A.P. FastTree 2—Approximately maximum-likelihood trees for large alignments. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Ding, B.Y.; Hu, R.Y. Study on exploitation and utilization of Rhododendron Linn. in Zhejiang. Chin. Wild Plant Res. 2005, 24, 22–25. [Google Scholar]
- Wright, S. The interpretation of population structure by F-Statistics with special regard to systems of mating. Evolution 1965, 19, 395–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Chen, B.; Chen, F.; Chen, W.J.; Chen, Z.L.; Wang, P.; Chen, H.Z.; Jin, X.F. Population structure and interspecific association of Rhododendron huadingense, a rare and endemic species in China. J. ZheJiang Univ. Sci. 2019, 46, 354–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, B.Y.; Hu, H.X.; Zhang, H.M.; Fang, Y.Y. Seed morphology of Rhododendron L. (Ericaceae) from Zhejiang and its taxonomic significance. Acta Bot. Boreal.-Occid. Sin. 1995, 15, 36–42. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.B.; Xu, Q.; He, L.P.; Xu, Z.B.; Shen, D.F. Genetic diversity and genetic relationship analysis of wild Rhododendron resources in Siming Mountain Area. For. Sci. Technol. 2023, 48, 16–19. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.J.; Jin, X.F.; Ding, B.Y.; Zhu, J.P. Pollen morphology of Rhododendron subgen. Tsutsusi and its systematic implications. J. Syst. Evol. 2009, 47, 123–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, R.; Niu, M.; Lou, X.; Huang, H.; Lin, E. The complete chloroplast genome of Rhododendron huadingense (Ericaceae). Mitochondrial DNA B Resour. 2022, 7, 1910–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| No. | Sample | Species | Subgenus | Section | Reads Number | Total Bases/bp | Mapping Rate/% | Sequence Depth/× |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | DJ_1 | R. simsii | subgen. Tsutsusi | sect. Tsutsusi | 7,842,910 | 1,123,802,645 | 96.84 | 2.13 |
| 2 | DJ_2 | R. simsii | subgen. Tsutsusi | sect. Tsutsusi | 8,447,614 | 1,209,526,268 | 96.58 | 2.29 |
| 3 | DJ_3 | R. simsii | subgen. Tsutsusi | sect. Tsutsusi | 6,872,262 | 983,964,165 | 96.91 | 1.86 |
| 4 | DJ_4 | R. simsii | subgen. Tsutsusi | sect. Tsutsusi | 8,227,636 | 1,178,483,283 | 91.14 | 2.23 |
| 5 | DJ_5 | R. simsii | subgen. Tsutsusi | sect. Tsutsusi | 7,468,622 | 1,069,413,995 | 93.78 | 2.02 |
| 6 | PTDJ_1 | R. simsii var. putuoense | 14,464,694 | 2,071,406,861 | 95.01 | 3.92 | ||
| 7 | PTDJ_2 | R. simsii var. putuoense | 14,516,774 | 2,079,276,661 | 83.70 | 3.93 | ||
| 8 | PTDJ_3 | R. simsii var. putuoense | 18,210,666 | 2,607,244,029 | 93.94 | 4.93 | ||
| 9 | PTDJ_4 | R. simsii var. putuoense | 9,344,540 | 2,106,199,392 | 94.93 | 3.98 | ||
| 10 | PTDJ_5 | R. simsii var. putuoense | 7,083,544 | 1,337,742,896 | 94.50 | 2.53 | ||
| 11 | DXDJ_1 | R. farrerae | subgen. Tsutsusi | sect. Brachycalyx | 7,887,388 | 1,129,332,945 | 95.82 | 2.14 |
| 12 | DXDJ_2 | R. farrerae | subgen. Tsutsusi | sect. Brachycalyx | 7,065,322 | 1,011,327,506 | 94.25 | 1.91 |
| 13 | DXDJ_3 | R. farrerae | subgen. Tsutsusi | sect. Brachycalyx | 7,406,124 | 1,060,945,460 | 95.96 | 2.01 |
| 14 | HDDJ_1 | R. huadingense | subgen. Tsutsusi | sect. Brachycalyx | 7,345,694 | 1,051,336,075 | 92.74 | 1.99 |
| 15 | HDDJ_2 | R. huadingense | subgen. Tsutsusi | sect. Brachycalyx | 7,588,046 | 1,085,558,978 | 93.62 | 2.05 |
| 16 | HDDJ_3 | R. huadingense | subgen. Tsutsusi | sect. Brachycalyx | 8,763,824 | 1,254,026,187 | 94.01 | 2.37 |
| 17 | HDDJ_4 | R. huadingense | subgen. Tsutsusi | sect. Brachycalyx | 7,032,948 | 1,006,765,697 | 93.28 | 1.90 |
| 18 | YZZ_1 | R. molle | subgen. Pentanthera | sect. Pentanthera | 6,872,262 | 954,249,606 | 89.29 | 1.81 |
| 19 | YZZ_2 | R. molle | subgen. Pentanthera | sect. Pentanthera | 8,227,636 | 1,071,341,272 | 88.80 | 2.03 |
| 20 | YZZ_3 | R. molle | subgen. Pentanthera | sect. Pentanthera | 7,468,622 | 935,457,901 | 90.03 | 1.77 |
| 21 | MYH_1 | R. ovatum | subgen. Azaleastrum | sect. Azaleastrum | 7,156,964 | 1,024,609,279 | 95.74 | 1.94 |
| 22 | MYH_2 | R. ovatum | subgen. Azaleastrum | sect. Azaleastrum | 7,987,170 | 1,143,354,013 | 94.15 | 2.16 |
| 23 | MYH_3 | R. ovatum | subgen. Azaleastrum | sect. Azaleastrum | 6,943,508 | 994,044,215 | 94.69 | 1.88 |
| 24 | CMDJ_1 | R. championiae | subg. Azaleastrum | sect. Choniastrum | 7,001,716 | 1,002,884,795 | 91.92 | 1.90 |
| 25 | CMDJ_2 | R. championiae | subgen. Azaleastrum | sect. Choniastrum | 7,083,544 | 1,014,407,528 | 91.71 | 1.92 |
| 26 | CMDJ_3 | R. championiae | subgen. Azaleastrum | sect. Choniastrum | 6,998,250 | 1,002,294,502 | 90.80 | 1.90 |
| 27 | LJDJ_1 | R. latoucheae | subgen. Azaleastrum | sect. Choniastrum | 7,988,094 | 1,144,587,841 | 92.62 | 2.17 |
| 28 | LJDJ_2 | R. latoucheae | subgen. Azaleastrum | sect. Choniastrum | 6,100,640 | 873,849,781 | 92.48 | 1.65 |
| 29 | LJDJ_3 | R. latoucheae | subgen. Azaleastrum | sect. Choniastrum | 8,249,558 | 1,181,825,031 | 91.94 | 2.24 |
| 30 | HTDJ_1 | R. simiarum | subgen. Hymenanthes | subt. Argyrophylla | 7,336,492 | 1,050,798,076 | 90.36 | 1.99 |
| 31 | HTDJ_2 | R. simiarum | subgen. Hymenanthes | subt. Argyrophylla | 8,418,280 | 1,205,949,808 | 88.20 | 2.28 |
| 32 | YJDJ_1 | R. fortunei | subgen. Hymenanthes | subt. Fortunea | 6,998,250 | 1,071,807,669 | 90.95 | 2.03 |
| 33 | YJDJ_2 | R. fortunei | subgen. Hymenanthes | subt. Fortunea | 7,842,910 | 980,284,260 | 92.32 | 1.85 |
| 34 | YJDJ_3 | R. fortunei | subgen. Hymenanthes | subt. Fortunea | 8,447,614 | 997,989,300 | 91.97 | 1.89 |
| Species | Num Indv | Ho | He | π | Fis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R. simsii var. putuoense | 4.8102 | 0.0549 | 0.0574 | 0.0642 | 0.0199 |
| R. simsii | 4.7006 | 0.0474 | 0.0611 | 0.0685 | 0.0466 |
| R. molle | 2.8409 | 0.0293 | 0.0199 | 0.0241 | −0.0087 |
| R. fortunei | 2.7522 | 0.0362 | 0.0432 | 0.0528 | 0.0306 |
| R. huadingense | 3.7156 | 0.0345 | 0.0280 | 0.0323 | −0.0035 |
| R. ovatum | 2.8092 | 0.0355 | 0.0301 | 0.0365 | 0.0019 |
| R. championiae | 2.8421 | 0.0379 | 0.0301 | 0.0364 | −0.0023 |
| R. latoucheae | 2.8224 | 0.0372 | 0.0318 | 0.0386 | 0.0028 |
| R. farrerae | 2.7556 | 0.0318 | 0.0325 | 0.0395 | 0.0140 |
| R. simiarum | 1.9170 | 0.0374 | 0.0245 | 0.0330 | −0.0066 |
| Mean value | 3.1966 | 0.0382 | 0.0359 | 0.0426 | 0.0193 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, H.; Li, D.; Yue, C.; Li, H. Development of Single Nucleotide Polymorphism and Phylogenetic Analysis of Rhododendron Species in Zhejiang Province, China, Using ddRAD-Seq Technology. Plants 2025, 14, 1548. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14101548
Zhu H, Li D, Yue C, Li H. Development of Single Nucleotide Polymorphism and Phylogenetic Analysis of Rhododendron Species in Zhejiang Province, China, Using ddRAD-Seq Technology. Plants. 2025; 14(10):1548. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14101548
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Hong, Dongbin Li, Chunlei Yue, and Hepeng Li. 2025. "Development of Single Nucleotide Polymorphism and Phylogenetic Analysis of Rhododendron Species in Zhejiang Province, China, Using ddRAD-Seq Technology" Plants 14, no. 10: 1548. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14101548
APA StyleZhu, H., Li, D., Yue, C., & Li, H. (2025). Development of Single Nucleotide Polymorphism and Phylogenetic Analysis of Rhododendron Species in Zhejiang Province, China, Using ddRAD-Seq Technology. Plants, 14(10), 1548. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14101548






