Role of Tyrosine Phosphorylation in PEP1 Receptor 1(PEPR1) in Arabidopsis thaliana
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site-Directed Mutagenesis (SDM)
2.2. Recombinant Protein Production and Purification
2.3. Electrophoresis and Immunoblotting
2.4. Seedling Growth and Root Length Measurement
2.5. Liquid Culture and Ligand Treatment
2.6. Total RNA Extraction and cDNA Synthesis
2.7. Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR) and Statistical Analysis
2.8. Agrobacterium-Mediated Transformation into pepr1/2 Double Knock-Out Arabidopsis Plants
2.9. Selection of Transgenic Plants
2.10. Genes Cloning
2.11. BiFC Assay
3. Results
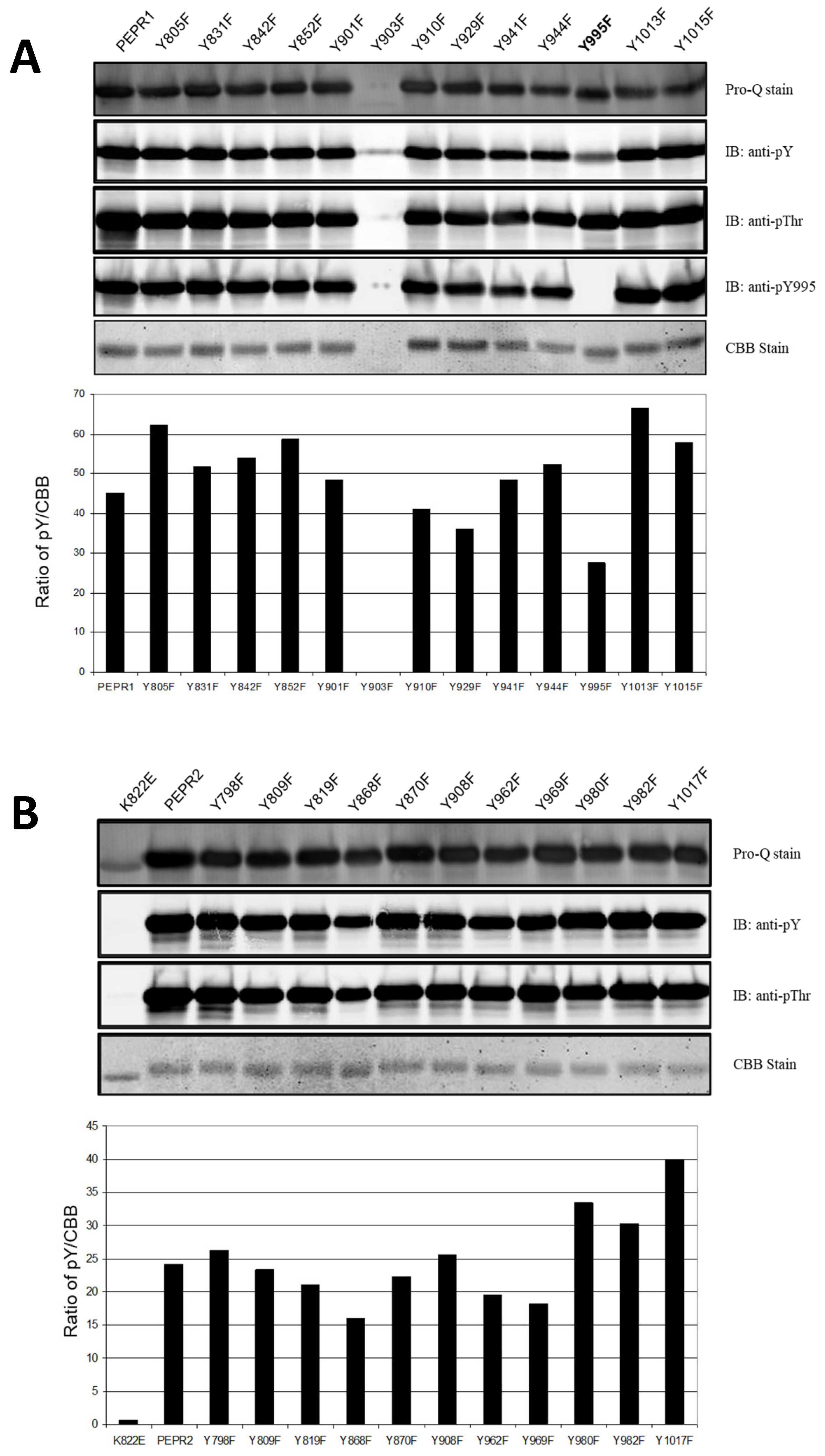
3.1. Identification of Major Tyrosine Autophosphorylation Site of PEPR1-CD and PEPR2-CD
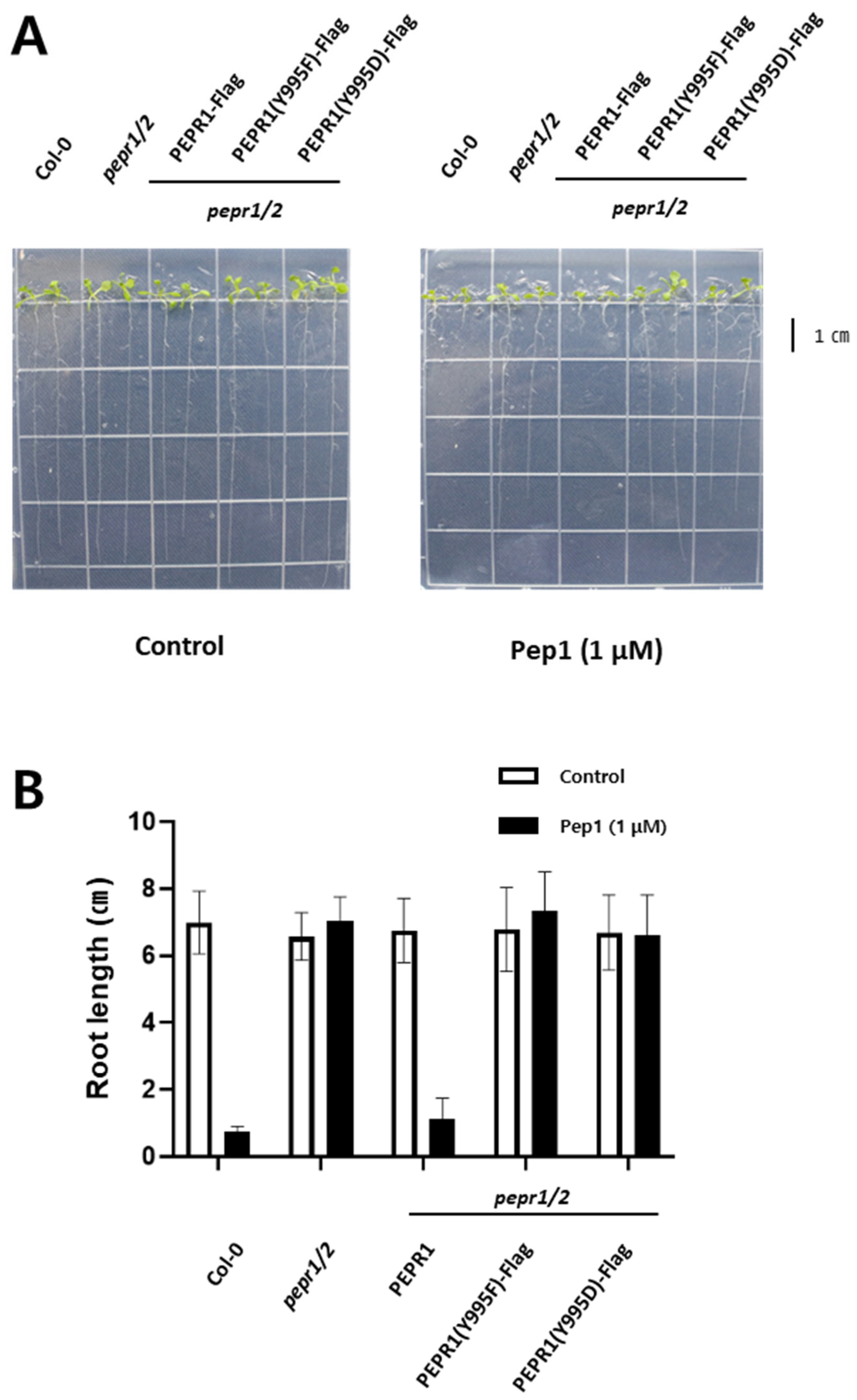
3.2. Phenotypic Analysis Under pep1 Treatment with Transgenic Plants
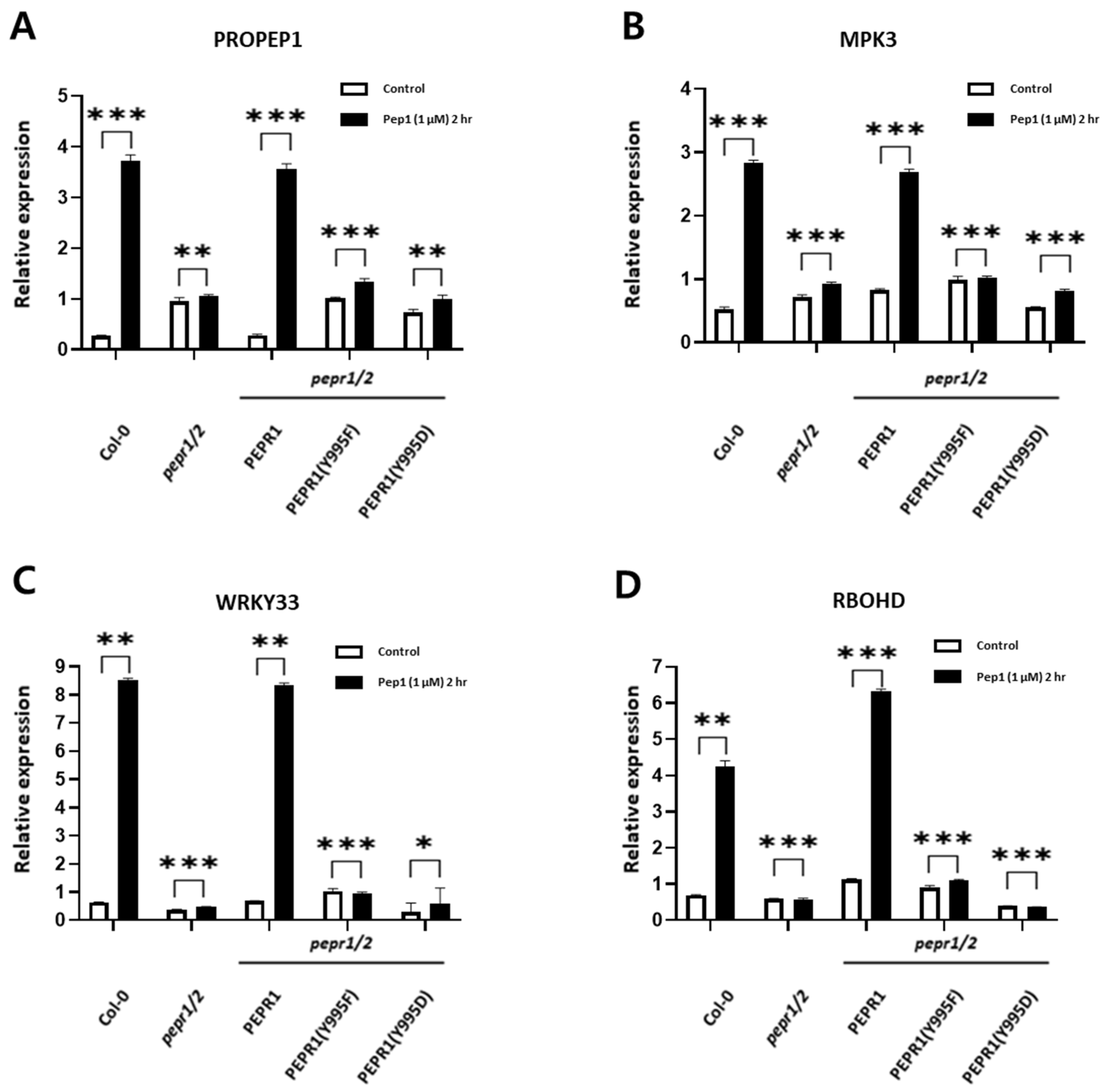
3.3. Expression Analysis of Downstream Components Involved in pep1 Signaling
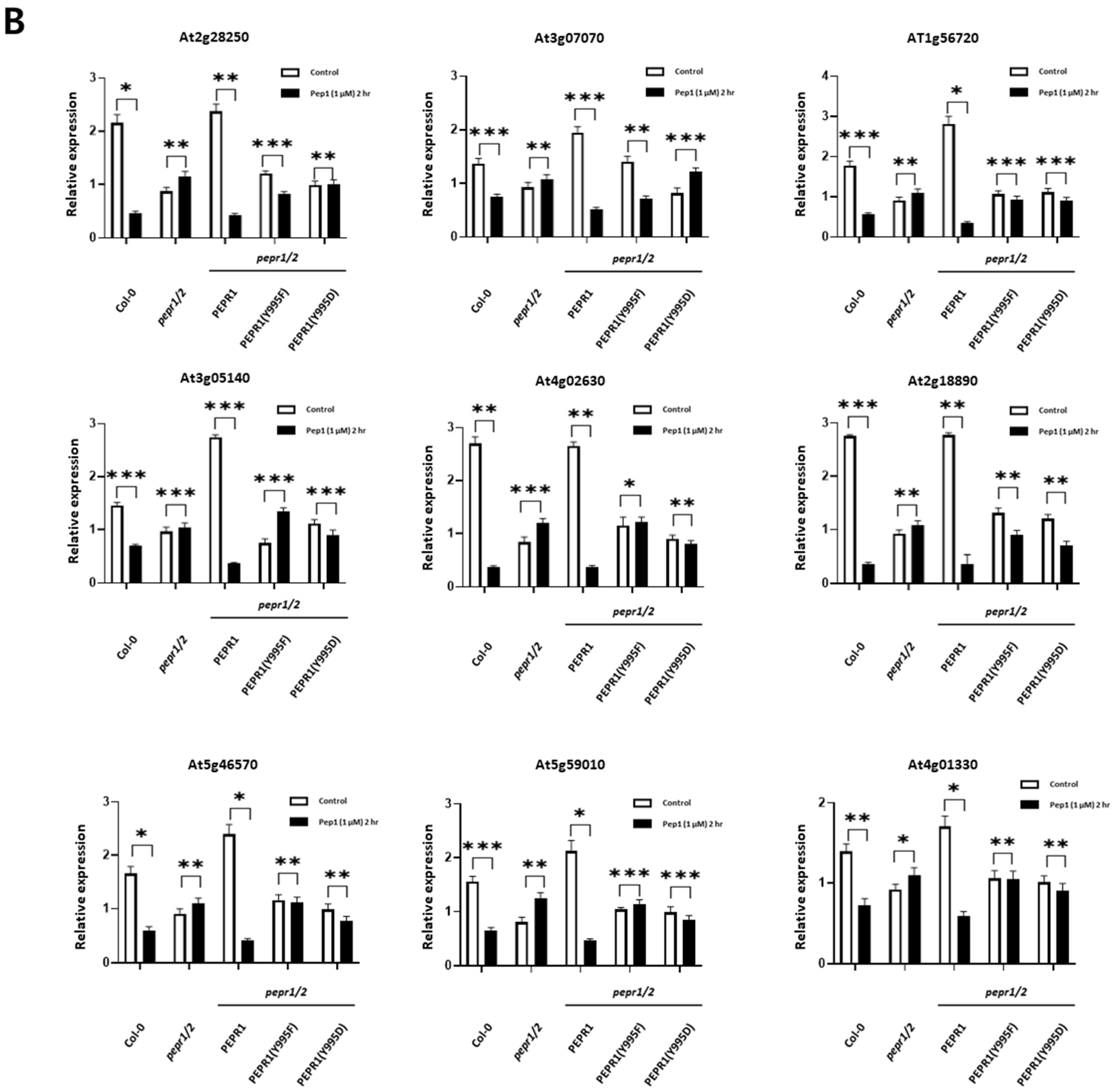
3.4. Analysis of Expression Patterns of RLCKs Under pep1 Treatment
3.5. PEPR1 and RLCKs Indirectly Interact Through BIK1
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jones, J.D.G.; Dangl, J.L. The plant immune system. Nature 2006, 444, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, C.A.; Huffaker, A.; Yamaguchi, Y. New insights into innate immunity in Arabidopsis. Cell. Microbiol. 2007, 9, 1902–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiu, S.H.; Bleecker, A.B. Receptor-like kinases from Arabidopsis form a monophyletic gene family related to animal receptor kinases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Scsi. USA 2001, 98, 10763–10768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartels, S.; Boller, T. Quo vadis, Pep? Plant elicitor peptides at the crossroads of immunity, stress, and development. J. Exp. Bot. 2015, 66, 5183–5193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartels, S.; Lori, M.; Mbengue, M.; van Verk, M.; Klauser, D.; Hander, T.; Böni, R.; Robatzek, S.; Boller, T. The family of Peps and their precursors in Arabidopsis: Differential expression and localization but similar induction of pattern-triggered immune responses. J. Exp. Bot. 2013, 64, 5309–5321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boller, T.; Felix, G. A renaissance of elicitors: Perception of microbe-associated molecular patterns and danger signals by pattern-recognition receptors. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2009, 60, 379–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Gomez, L.; Boller, T. FLS2: An LRR receptor-like kinase involved in the perception of the bacterial elicitor flagellin in Arabidopsis. Mol. Cell 2000, 5, 1003–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miya, A.; Albert, P.; Shinya, T.; Desaki, Y.; Ichimura, K.; Shirasu, K.; Narusaka, Y.; Kawakami, N.; Kaku, H.; Shibuya, N. CERK1, a LysM receptor kinase, is essential for chitin elicitor signaling in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 19613–19618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Liao, C.J.; Jaiswal, N.; Lee, S.; Yun, D.J.; Lee, S.Y.; Garvey, M.; Kaplan, I.; Mengiste, T. Tomato PEPR1 ORTHOLOG RECEPTOR-LIKE KINASE1 Regulates Responses to Systemin, Necrotrophic Fungi, and Insect Herbivory. Plant Cell 2018, 30, 2214–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, K.; Yamashita-Yamada, M.; Hirase, T.; Fujiwara, T.; Tsuda, K.; Hiruma, K.; Saijo, Y. Danger peptide receptor signaling in plants ensures basal immunity upon pathogen-induced depletion of BAK1. EMBO J. 2016, 35, 46–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zipfel, C.; Kunze, G.; Chinchilla, D.; Caniard, A.; Jones, J.D.; Boller, T.; Felix, G. Perception of the bacterial PAMP EF-Tu by the receptor EFR restricts Agrobacterium-mediated transformation. Cell 2006, 125, 749–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huffaker, A.; Ryan, C.A. Endogenous peptide defense signals in Arabidopsis differentially amplify signaling for the innate immune response. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 10732–10736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huffaker, A.; Pearce, G.; Ryan, C.A. An endogenous peptide signal in Arabidopsis activates components of the innate immune response. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 10098–10103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, Y.; Huffaker, A.; Bryan, A.C.; Tax, F.E.; Ryan, C.A. PEPR2 is a second receptor for the Pep1 and Pep2 peptides and contributes to defense responses in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2010, 22, 508–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dovana, F.; Mucciarelli, M.; Mascarello, M.; Fusconi, A. In Vitro Morphogenesis of Arabidopsis to Search for Novel Endophytic Fungi Modulating Plant Growth. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0143353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Y.; Shen, N.; Zheng, X.; Fu, A.; Zhao, F.; Lan, W.; Luan, S. Danger-Associated Peptide Regulates Root Immune Responses and Root Growth by Affecting ROS Formation in Arabidopsis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecenkova, T.; Janda, M.; Ortmannova, J.; Hajna, V.; Stehlikova, Z.; Zarsky, V. Early Arabidopsis root hair growth stimulation by pathogenic strains of Pseudomonas syringae. Ann. Bot. 2017, 120, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamioudis, C.; Mastranesti, P.; Dhonukshe, P.; Blilou, I.; Pieterse, C.M. Unraveling root developmental programs initiated by beneficial Pseudomonas spp. bacteria. Plant Physiol. 2013, 162, 304–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Elmore, J.M.; Lin, Z.J.; Coaker, G. A receptor-like cytoplasmic kinase phosphorylates the host target RIN4, leading to the activation of a plant innate immune receptor. Cell Host Microbe 2011, 9, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stulemeijer, I.J.; Joosten, M.H. Post-translational modification of host proteins in pathogen-triggered defence signalling in plants. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2008, 9, 545–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, O.N. Modification-specific proteomics: Characterization of post-translational modifications by mass spectrometry. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2004, 8, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, W.; Li, B.; Lu, D.; Chen, S.; Zhu, N.; He, P.; Shan, L. Tyrosine phosphorylation of protein kinase complex BAK1/BIK1 mediates Arabidopsis innate immunity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 3632–3637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macho, A.P.; Schwessinger, B.; Ntoukakis, V.; Brutus, A.; Segonzac, C.; Roy, S.; Kadota, Y.; Oh, M.-H.; Sklenar, J.; Derbyshire, P.; et al. A bacterial tyrosine phosphatase inhibits plant pattern recognition receptor activation. Science 2014, 343, 1509–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, M.H.; Wang, X.; Kota, U.; Goshe, M.B.; Clouse, S.D.; Huber, S.C. Tyrosine phosphorylation of the BRI1 receptor kinase emerges as a component of brassinosteroid signaling in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 658–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Goshe, M.B.; Soderblom, E.J.; Phinney, B.S.; Kuchar, J.A.; Li, J.; Asami, T.; Yoshida, S.; Huber, S.C.; Clouse, S.D. Identification and functional analysis of in vivo phosphorylation sites of the Arabidopsis BRASSINOSTEROID-INSENSITIVE1 receptor kinase. Plant Cell 2005, 17, 1685–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghelis, T. Signal processing by protein tyrosine phosphorylation in plants. Plant Signal. Behav. 2011, 6, 942–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, J.V.; Blagoev, B.; Gnad, F.; Macek, B.; Kumar, C.; Mortensen, P.; Mann, M. Global, in vivo, and site-specific phosphorylation dynamics in signaling networks. Cell 2006, 127, 635–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, X.; Meisenhelder, J.; Hunter, T.; Yoshida, S.; Asami, T.; Chory, J. Autoregulation and homodimerization are involved in the activation of the plant steroid receptor BRI1. Dev. Cell 2005, 8, 855–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macho, A.P.; Zipfel, C. Plant PRRs and the activation of innate immune signaling. Mol. Cell 2014, 54, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Ma, X.; Shan, L.; He, P. Big roles of small kinases: The complex functions of receptor-like cytoplasmic kinases in plant immunity and development. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2013, 55, 1188–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Yun, K.; Park, H.Y.; Ahn, J.Y.; Yang, J.Y.; Song, H.; Lee, O.N.; Hur, Y.; Oh, M.-H. Development of Molecular Markers for Predicting Radish (Raphanus sativus) Flesh Color Based on Polymorphisms in the RsTT8 Gene. Plants 2021, 10, 1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, M.-H.; Sun, J.; Oh, D.H.; Zielinski, R.; Clouse, S.D.; Huber, S.C. Enhancing Arabidopsis Leaf Growth by Engineering the BRASSINOSTEROID INSENSITIVE 1 Receptor Kinase. Plant Physiol. 2011, 157, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.H.; Oh, E.S.; Oh, M.H. Phosphorylation of BIK1 is critical for interaction with downstream signaling components. Genes Genom. 2021, 43, 1269–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehl, C.; Waadt, R.; Kudla, J.; Mendel, R.R.; Hänsch, R. New GATEWAY vectors for high throughput analyses of protein-protein interactions by biomolecular fluorescence complementation. Mol. Plant 2009, 2, 1051–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.; Kumar, R.; Baek, D.; Hyun, T.K.; Chung, W.S.; Yun, D.J.; Kim, J.Y. Arabidopsis thaliana RECEPTOR DEAD KINASE1 Functions as a Positive Regulator in Plant Responses to ABA. Mol. Plant 2017, 10, 223–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, M.H.; Ray, W.K.; Huber, S.C.; Asara, J.M.; Gage, D.A.; Clouse, S.D. Recombinant brassinosteroid insensitive 1 receptor-like kinase autophosphorylates on serine and threonine residues and phosphorylates a conserved peptide motif in vitro. Plant Physiol. 2000, 124, 751–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Bi, G.; Liang, X.; Zhou, J.M. Early signalling mechanisms underlying receptor kinase-mediated immunity in plants. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2019, 374, 20180310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couto, D.; Niebergall, R.; Liang, X.; Bucherl, C.A.; Sklenar, J.; Macho, A.P.; Ntoukakis, V.; Derbyshire, P.; Altenbach, D.; Maclean, D.; et al. The Arabidopsis Protein Phosphatase PP2C38 Negatively Regulates the Central Immune Kinase BIK1. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Han, B.; Zhang, H.; Mariappan, K.G.; Bigeard, J.; Colcombet, J.; Hirt, H. MAP4K4 associates with BIK1 to regulate plant innate immunity. EMBO Rep. 2019, 20, e47965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Han, Z.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, H.; Gong, X.; Chai, J. Structural basis for recognition of an endogenous peptide by the plant receptor kinase PEPR1. Cell Res. 2015, 25, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, M.H.; Clouse, S.D.; Huber, S.C. Tyrosine phosphorylation in brassinosteroid signaling. Plant Signal Behav. 2009, 4, 1182–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, S.; Nguyen, B.; Wasti, S.D.; Xu, G. Plant Leucine-Rich Repeat Receptor Kinase (LRR-RK): Structure, Ligand Perception, and Activation Mechanism. Molecules 2019, 24, 3081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luan, S. Tyrosine phosphorylation in plant cell signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 11567–11569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karasov, T.L.; Chae, E.; Herman, J.J.; Bergelson, J. Mechanisms to Mitigate the Trade-Off between Growth and Defense. Plant Cell 2017, 29, 666–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Xu, J.; He, Y.; Yang, K.Y.; Mordorski, B.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, S. Phosphorylation of an ERF transcription factor by Arabidopsis MPK3/MPK6 regulates plant defense gene induction and fungal resistance. Plant Cell 2013, 25, 1126–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birkenbihl, R.P.; Diezel, C.; Somssich, I.E. Arabidopsis WRKY33 is a key transcriptional regulator of hormonal and metabolic responses toward Botrytis cinerea infection. Plant Physiol. 2012, 159, 266–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Qamar, S.A.; Chen, Z.; Mengiste, T. Arabidopsis WRKY33 transcription factor is required for resistance to necrotrophic fungal pathogens. Plant J. 2006, 48, 592–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadota, Y.; Sklenar, J.; Derbyshire, P.; Stransfeld, L.; Asai, S.; Ntoukakis, V.; Jones, J.D.; Shirasu, K.; Menke, F.; Jones, A.; et al. Direct regulation of the NADPH oxidase RBOHD by the PRR-associated kinase BIK1 during plant immunity. Mol. Cell 2014, 54, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wu, Y.; Yang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, S.; Xie, Q.; Tian, X.; Zhou, J.M. BIK1 interacts with PEPRs to mediate ethylene-induced immunity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 6205–6210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, S.; Zhou, Z.; Miao, P.; Bi, G.; Hu, M.; Wu, Y.; Feng, F.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, J.M. Roles of Receptor-Like Cytoplasmic Kinase VII Members in Pattern-Triggered Immune Signaling. Plant Physiol. 2018, 177, 1679–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huesmann, C.; Reiner, T.; Hoefle, C.; Preuss, J.; Jurca, M.E.; Domoki, M.; Fehér, A.; Huckelhoven, R. Barley ROP binding kinase1 is involved in microtubule organization and in basal penetration resistance to the barley powdery mildew fungus. Plant Physiol. 2012, 159, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Zhou, J.M. Receptor-Like Cytoplasmic Kinases: Central Players in Plant Receptor Kinase-Mediated Signaling. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2018, 69, 267–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yang, Y.; Ortiz-Morea, F.A.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, D.; Huang, Y.; Zheng, J.; Chen, Y.; Kong, L.; Liu, Z.; et al. The antagonistic role of an E3 ligase pair in regulating plant NLR-mediated autoimmunity and fungal pathogen resistance. Cell Host Microbe 2024, 32, 1114–1128.E10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majhi, B.B.; Sreeramulu, S.; Sessa, G. BRASSINOSTEROID-SIGNALING KINASE5 Associates with Immune Receptors and Is Required for Immune Responses. Plant Physiol. 2019, 180, 1166–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, M.H.; Hyun, T.K.; Bahk, S.; Jo, Y.; Kumar, R.; Thiruppathi, D.; Iswanto, A.B.B.; Chung, W.S.; Shelake, R.M.; Kim, J.Y. ROS-mediated plasmodesmal regulation requires a network of an Arabidopsis receptor-like kinase, calmodulin-like proteins, and callose synthases. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1107224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Chen, H.; Ortega-Perez, M.; Miao, Y.; Ma, Y.; Henschen, A.; Lohmann, J.U.; Laubinger, S.; Bayer, M. Independent parental contributions initiate zygote polarization in Arabidopsis thaliana. Curr. Biol. 2021, 31, 4810–4816.E5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.J.; Luo, T.; Zhou, P.M.; Wang, W.Q.; Yang, W.C.; Li, H.J. Pollen-expressed RLCKs control pollen tube burst. Plant Commun. 2024, 5, 100934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, N.K.; Nagalakshmi, U.; Hurlburt, N.K.; Flores, R.; Bak, A.; Sone, P.; Ma, X.; Song, G.; Walley, J.; Shan, L.; et al. The Receptor-like Cytoplasmic Kinase BIK1 Localizes to the Nucleus and Regulates Defense Hormone Expression during Plant Innate Immunity. Cell Host Microbe 2018, 23, 485–497.E5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, J.-H.; Oh, M.-H. Role of Tyrosine Phosphorylation in PEP1 Receptor 1(PEPR1) in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plants 2025, 14, 1515. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14101515
Choi J-H, Oh M-H. Role of Tyrosine Phosphorylation in PEP1 Receptor 1(PEPR1) in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plants. 2025; 14(10):1515. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14101515
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Jae-Han, and Man-Ho Oh. 2025. "Role of Tyrosine Phosphorylation in PEP1 Receptor 1(PEPR1) in Arabidopsis thaliana" Plants 14, no. 10: 1515. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14101515
APA StyleChoi, J.-H., & Oh, M.-H. (2025). Role of Tyrosine Phosphorylation in PEP1 Receptor 1(PEPR1) in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plants, 14(10), 1515. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14101515








