Phenotypic Genetic Analysis of Fruit Branch Angle in Upland Cotton
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
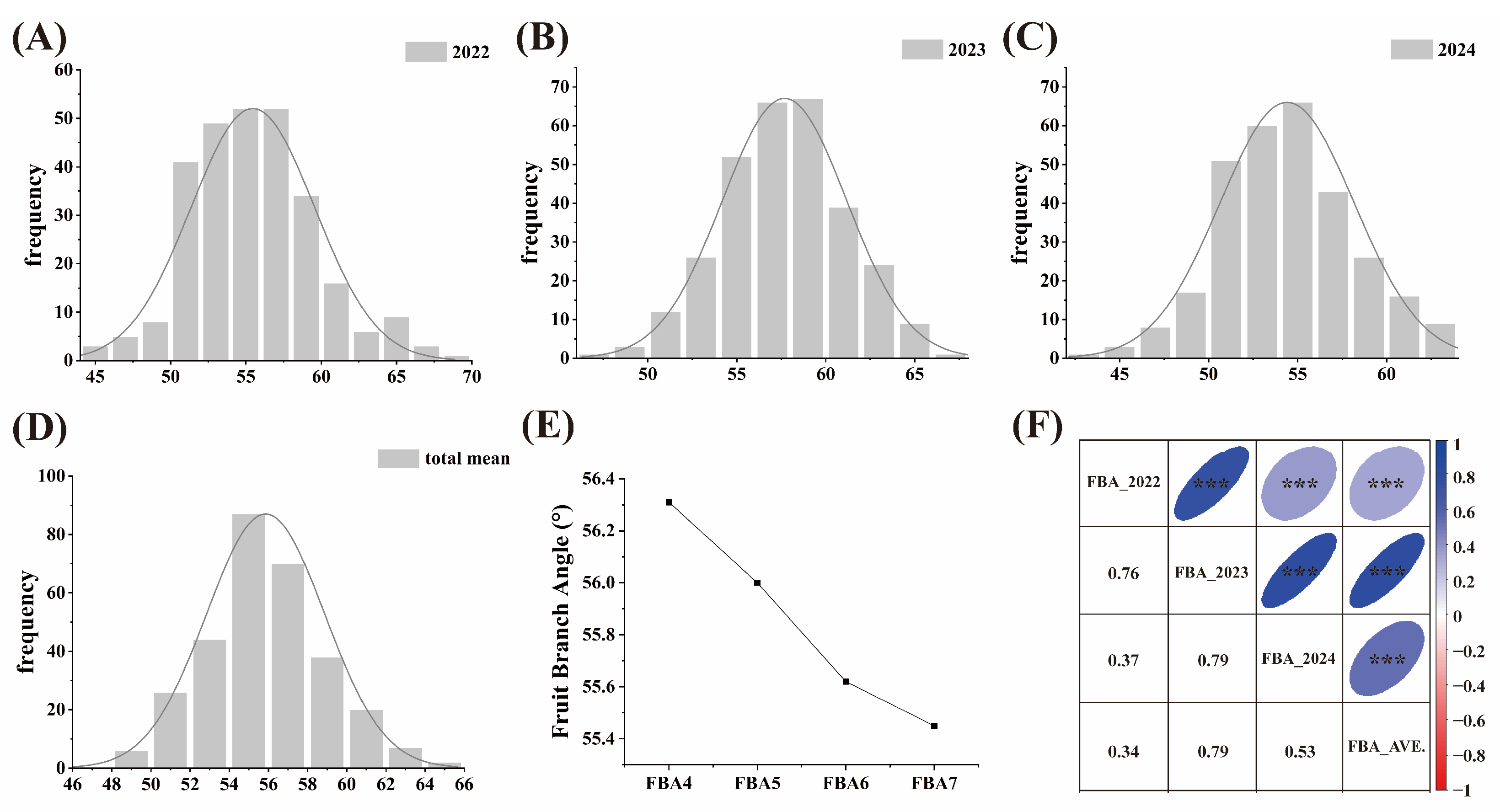
2.1. Phenotypic Analyses of Fruit Branch Angle Traits in Cotton
2.2. Variation Analysis of FBA in Cotton in the Different Regions
2.3. Variation Analysis of FBA in Cotton at Different Periods
2.4. Phenotypic Analyses of Architecture Trait and Yield Trait in Cotton
2.4.1. Variance Analysis of Architecture Trait and Yield Trait in Cotton
2.4.2. Correlation Analysis Between Architecture Traits and Yield Traits in Cotton
2.4.3. Principal Component Analysis of Architecture Traits and Yield Traits in Cotton
2.4.4. Cluster Analysis of Architecture Traits and Yield Traits in Cotton
3. Discussion
3.1. Phenotypic Variability Analysis of FBA in Cotton
3.2. Variation Analysis of FBA of Cotton in the Different Regions and Different Periods
3.3. Optimal Population Analysis of FBA in Cotton
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials
4.2. Field Trial
4.3. Phenotypic Data Measurement
4.4. Statistical and Analytical Processing of Data
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PCA | Principal Component Analysis |
| CV | Coefficients of Variation |
| FG | Foreign Germplasm |
| YRR | Yellow River Region |
| YZRR | Yangtze River Region |
| LSMR | Liaoning Special Maturing Region |
| NIR | Northwest Inland Region |
| PH | Plant Height |
| FBIN | Fruit Branch Initiation Node |
| FBIH | Fruit Branch Initiation Height |
| FBN | Number of Fruit Branches |
| EFBN | Number of Effective Fruit Branches |
| FBA | Fruit Branch Angle |
| BPP | Bell Per Plant |
| BW | Bell Weight |
| LP | Lint Percentage |
| H′ | Genetic diversity index |
| H2 | Broad-sense heritability |
References
- Wei, S.; Wu, J.; Zhang, S.; Liu, S. Advances in Crop Architecture-related Gene Research. Ningxia J. Agri. Fores. Sci. Technol. 2012, 53, 4–7, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Li, J. Molecular Basis of Plant Architecture. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2008, 59, 253–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Q.; Li, J.; Xu, S.; Chen, H.; Liu, W.; Ning, X.; Lin, H. Genetic Analysis of FBA Trait in Upland Cotton with Major Gene Plus Polygenes Mixed Genetic Model. Biotechnol. Bull. 2022, 38, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, C.; Tang, L.; Zhang, S.; Cai, X.; Li, X.; Ma, W.; Han, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, J. The influence of different planting densities on agronomic traits, yield and quality of machine—Picked cotton varieties. Xinjiang Agric. Sci. 2023, 60, 2638–2645. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y. Effects of Drip Application of Tyramine and Nitrogen on Cotton Growth and Yield. Master’s Thesis, Tarim University, Alar, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- He, Z.; Xi, H.; Yang, B.; Li, P.; Han, B. The Key to Get Good Yield of Cotton by Inducing the Response to Dpc Towards a Planned Direction and in Planned Strength. J. Beijing Univ. Agric. 1984, 10, 19–28. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, Y. Effects of Water, Nitrogen and Film Mulching Mode on the Physiological Characteristics and Yield of Cotton. Master’s Thesis, Hebei Agricultural University, Baoding, China, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Pei, D.; Jia, J.; Wang, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, X. The Effects of Irrigation Quantity and Frequency of Drip Irrigation to Plastic-mulched Cotton at Critical Growing Stage. Acta Agric. Boreali Sin. 2005, 20, 76–80. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, J.; Qi, B.; Ma, B.; Li, B.; Gou, L. Effect of Altered Leaf Angle on Maize Stalk Lodging Resistance. Crop Sci. 2021, 61, 689–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Wu, Y.; Huang, N.; Zhu, X.; Guo, W.; Zhang, T. QTL Mapping for Plant Architecture Traits in Upland Cotton Using RILs and SSR Markers. J. Genet. Genom. 2006, 33, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Li, L.; Zhang, C.; Wang, C.; Gu, L.; Wang, H.; Wei, H.; Liu, Q.; Huang, L.; Yu, S. Genome-Wide Association Study Identified Genetic Variations and Candidate Genes for Plant Architecture Component Traits in Chinese Upland Cotton. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2018, 131, 1299–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Q.; Li, C. Relationship Between Plant Type Traits and Lint Yield in Upland Cotton in Different Ecological Environments. Southwest China J. Agric. Sci. 2021, 34, 1101–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q. Functional Characterization of Panicle Architecture Gene Osafb6 and Tillering Angle Gene Lazyi in Rice. Ph.D. Thesis, Huazhong Agricultural University, Wuhan, China, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godbolé, R.; Michalke, W.; Nick, P.; Hertel, R. Cytoskeletal Drugs and Gravity-Induced Lateral Auxin Transport in Rice Coleoptiles. Plant Biol. 2000, 2, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Lin, Z.; Li, H.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, Z.; Zhai, W.; Wang, X.; et al. TAC1, a Major Quantitative Trait Locus Controlling Tiller Angle in Rice. Plant J. Cell Mol. Biol. 2007, 52, 891–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, H.; Zhao, H.; Xie, W.; Han, Z.; Li, G.; Yao, W.; Bai, X.; Hu, Y.; Guo, Z.; Lu, K.; et al. A Novel Tiller Angle Gene, TAC3, Together with TAC1 and D2 Largely Determine the Natural Variation of Tiller Angle in Rice Cultivars. PLoS Genet. 2016, 12, e1006412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Sun, H.; Jiang, J.; Sun, X.; Tan, L.; Sun, C. TAC4 Controls Tiller Angle by Regulating the Endogenous Auxin Content and Distribution in Rice. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2021, 19, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Gao, H.; Liang, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, Y. Molecular Basis Underlying Rice Tiller Angle: Current Progress and Future Perspectives. Mol. Plant 2022, 15, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Xiao, N.; Chen, Z.; Wu, Y.; Yu, L.; Liu, J.; Shi, W.; Fan, C.; Li, Y.; Zhou, C.; et al. Research Progress on Molecular Mechanisms Regulating Rice Tiller Angle. J. Plant Genet. Resour. 2023, 24, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araniti, F.; Talarico, E.; Madeo, M.L.; Greco, E.; Minervino, M.; Álvarez-Rodríguez, S.; Muto, A.; Ferrari, M.; Chiappetta, A.; Bruno, L. Short-Term Exposition to Acute Cadmium Toxicity Induces the Loss of Root Gravitropic Stimuli Perception through PIN2-Mediated Auxin Redistribution in Arabidopsis thaliana (L.) Heynh. Plant Sci. 2023, 332, 111726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, D.; Zhao, H.; Wu, Y.; Qin, C.; Nie, A.; Yang, S.; Fan, Z.; Chen, Q. Mechanism of Increasing Yield and Its Technical Studies for Cotton Plant Pattern Cultivation. Cotton Sci. 1995, 14, 238–242, 222. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.; Zhao, S.; Dong, C.; Zhou, X.; Wang, X.; Li, B. Correlation Analyses between the Main Plant Ideotype Traits and the Yield of Early—Maturing Upland Cotton. Xinjiang Agric. Sci. 2018, 55, 1961–1967. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, S.; Li, X. Cotton architecture breeding. Cotton 1980, 13, 11–15. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, S.; Xiao, Y.; Yang, W. The Analysis of Raw Cotton Fiber Quality between Region and Year in China. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2006, 22, 177–183. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, X.; Sun, Z.; Feng, Y.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, F. Growth Stage and Growth Analysis on Cotton with Different Accumulate Temperature in North of Xinjiang. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2011, 27, 274–280. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, Y.; Liu, A.; Chen, Q.; Li, C.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, D.; Xu, J. Development trend and variety choice of mechanical harvest of precocious cotton in the north of Xinjiang. China Cotton 2014, 41, 44–45. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Chang, H.; Zhao, S.; Liu, R.; Yan, M.; Li, F.; El-Sheery, N.I.; Feng, Z.; Yu, S. Combining High-Throughput Deep Learning Phenotyping and GWAS to Reveal Genetic Variants of Fruit Branch Angle in Upland Cotton. Ind. Crops Prod. 2024, 220, 119180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doust, A.N. Grass Architecture: Genetic and Environmental Control of Branching. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2007, 10, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Su, J.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, F.; Guan, Z.; Chen, F.; Fang, W. Mixed inheritance analysis of branching traits in spray cut chrysanthemum. J. Nanjing Agric. Univ. 2018, 41, 440–446. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, P.; Peng, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wang, J.; Pan, Z.; Yang, Y.; Aini, N.; Guo, C.; Shui, G.; Chao, L.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Study and Transcriptome Analysis Reveal Key Genes Controlling Fruit Branch Angle in Cotton. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 988647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, W.; Xiong, Y. Studies on the Influence of Meteorological Factors on the Occurrence Pattern of Crop Pests and Diseases. J. Agric. Catastrophology 2024, 14, 211–213. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Feng, G.; Lei, X.; Liang, Q.; Qi, H. Correlation Analysis between Main Agronomic Traits and Density in Mechanical Harvest Cotton. Crops 2019, 35, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, P. Effects of Density on Boll-Forming Spatial and Temporal Distribution and Yield Formation of Short-Growth-Duration Direct Seeding Cotton. Master’s Thesis, Hunan Agricultural University, Changsha, China, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Smith, S.M.; Li, J. Genetic Regulation of Shoot Architecture. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2018, 69, 437–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Fu, C.; Ma, C.; Wang, X.; Zhao, C. Research Progress of Molecular Regulation of Branching of Crops. Biotechnol. Bull. 2021, 37, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuai, J.; Sun, Y.; Zuo, Q.; Huang, H.; Liao, Q.; Wu, C.; Lu, J.; Wu, J.; Zhou, G. The Yield of Mechanically Harvested Rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) Can Be Increased by Optimum Plant Density and Row Spacing. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 18835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Tian, J.; Xu, S.; Liu, N.; Dang, K.; Zhang, W. Plant Type Characteristics and Evolution of Main Economic Characters in Early Maturing Upland Cotton Cultivar Replacement in Xinjiang. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2019, 52, 3279–3290. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Dong, M.; Li, B.; Wang, S.; Feng, G.; Liang, Q.; Qi, H. Effects of row spacing and density on plant architecture, yield and fiber quality of machine-picked cotton in southern Hebei cotton region. J. Nanjing Agric. Univ. 2023, 46, 1022–1030. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Y.; Li, P.; Wang, H.; Wang, Q.; Li, C. Relationship of Plant Architecture Traits and Lint Yield of Upland Cotton Variety (Line) Resources. Southwest China J. Agric. Sci. 2016, 29, 2063–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Year | Min | Max | Mean | SD | CV | Skewness | Kurtosis | H2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2022 | 44.57 | 69.32 | 55.46 b | 4.11 | 7.42 | 0.41 | 0.54 | 75.50 |
| 2023 | 46.23 | 66.07 | 57.68 a | 3.50 | 6.06 | −0.07 | −0.13 | |
| 2024 | 43.59 | 63.54 | 54.41 c | 3.77 | 6.93 | 0.06 | −0.13 | |
| Total mean | 47.60 | 65.16 | 55.84 b | 2.97 | 5.31 | 0.17 | 0.25 |
| Region | No. of Line | Min | Max | Mean | SD | CV | H′ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YRR | 99 | 49.92 | 63.32 | 56.24 ab | 3.01 | 5.35 | 2.04 |
| LSMR | 43 | 48.14 | 59.65 | 55.35 b | 2.30 | 4.15 | 1.99 |
| NIR | 89 | 48.51 | 65.27 | 55.25 b | 3.32 | 6.02 | 1.94 |
| YZRR | 42 | 49.2 | 61.38 | 56.16 ab | 2.84 | 5.06 | 1.91 |
| FG | 27 | 48.43 | 61.41 | 56.77 a | 2.94 | 5.18 | 1.93 |
| Period | No. of Line | Min | Max | Mean | SD | CV | H′ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 19 | 53.43 | 61.61 | 57.28 a | 2.06 | 3.60 | 1.79 |
| S2 | 10 | 54.90 | 60.07 | 56.55 a | 1.41 | 2.49 | 1.42 |
| S3 | 14 | 48.43 | 60.20 | 54.64 ab | 3.19 | 5.84 | 1.97 |
| S4 | 15 | 50.00 | 60.77 | 55.77 ab | 2.89 | 5.19 | 1.84 |
| S5 | 34 | 50.27 | 59.07 | 54.59 b | 2.23 | 4.09 | 2.04 |
| S6 | 65 | 48.51 | 65.27 | 55.48 ab | 3.05 | 5.50 | 2.00 |
| S7 | 70 | 51.13 | 63.32 | 56.80 a | 2.99 | 5.27 | 2.03 |
| S8 | 20 | 48.14 | 62.44 | 55.21 ab | 3.99 | 7.22 | 1.94 |
| FBA | S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | S5 | S6 | S7 | S8 | Range | Mean | SD | CV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FBA4 | 57.60 | 56.24 | 54.95 | 56.48 | 55.37 | 55.97 | 57.01 | 56.51 | 2.65 | 56.27 | 0.85 | 1.51 |
| FBA5 | 57.23 | 56.93 | 54.98 | 56.12 | 54.44 | 55.68 | 56.90 | 55.74 | 2.79 | 56.00 | 0.99 | 1.77 |
| FBA6 | 57.05 | 56.57 | 54.33 | 55.10 | 54.37 | 55.34 | 56.76 | 54.21 | 2.84 | 55.47 | 1.17 | 2.11 |
| FBA7 | 57.13 | 56.43 | 54.25 | 55.38 | 54.06 | 54.91 | 56.60 | 54.11 | 3.07 | 55.36 | 1.22 | 2.21 |
| Trait | Min | Max | Mean | SD | CV | Skewness | Kurtosis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PH | 53.38 | 98.47 | 72.60 | 6.91 | 9.52 | 0.57 | 0.98 |
| FBIN | 4.52 | 8.31 | 6.05 | 0.57 | 9.48 | 0.44 | 1.37 |
| FBIH | 19.52 | 42.64 | 29.24 | 4.30 | 14.70 | 0.45 | 0.03 |
| FBN | 7.29 | 11.17 | 8.71 | 0.63 | 7.25 | 0.56 | 0.97 |
| EFBN | 3.98 | 7.75 | 5.59 | 0.60 | 10.80 | 0.05 | 0.07 |
| FBA | 47.60 | 65.16 | 55.84 | 2.97 | 5.31 | 0.17 | 0.25 |
| BPP | 5.65 | 15.45 | 8.50 | 1.49 | 17.55 | 1.22 | 2.89 |
| BW | 4.79 | 7.95 | 6.06 | 0.45 | 7.34 | 0.18 | 1.03 |
| LP | 0.31 | 0.48 | 0.41 | 0.03 | 6.37 | −0.70 | 0.79 |
| PH | FBIN | FBIH | FBN | EFBN | FBA | BPP | BW | LP | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PH | 1 | ||||||||
| FBIN | 0.335 ** | 1 | |||||||
| FBIH | 0.771 ** | 0.672 ** | 1 | ||||||
| FBN | 0.060 | −0.434 ** | −0.370 ** | 1 | |||||
| EFBN | 0.201 ** | −0.115 * | −0.019 | 0.329 ** | 1 | ||||
| FBA | −0.014 | 0.046 | −0.048 | −0.039 | 0.200 ** | 1 | |||
| BPP | 0.123 * | −0.085 | −0.086 | 0.360 ** | 0.675 ** | 0.080 | 1 | ||
| BW | 0.024 | 0.041 | −0.035 | −0.044 | −0.011 | 0.131 * | 0.044 | 1 | |
| LP | 0.183 ** | 0.084 | 0.182 ** | −0.186 ** | 0.127 * | 0.110 | 0.058 | −0.090 | 1 |
| Trait | Eigenvector | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Principal Component No. 1 | Principal Component No. 2 | Principal Component No. 3 | Principal Component No. 4 | |
| PH | 0.62 | 0.56 | −0.27 | 0.18 |
| FBIN | 0.80 | 0.06 | 0.10 | 0.14 |
| FBIH | 0.91 | 0.27 | −0.16 | 0.10 |
| FBN | −0.61 | 0.41 | −0.35 | 0.19 |
| EFBN | −0.25 | 0.84 | 0.08 | −0.07 |
| FBA | −0.02 | 0.23 | 0.78 | −0.10 |
| BPP | −0.31 | 0.79 | 0.02 | 0.05 |
| BW | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.54 | 0.68 |
| LP | 0.28 | 0.26 | 0.23 | −0.71 |
| Group | No. | PH | FFNP | FFNH | FBN | EFBN | FBA | BPP | BW | LP | PCA Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 9 | 87.98 a | 5.96 b | 36.04 a | 9.41 a | 6.06 a | 52.58 c | 9.56 a | 6.01 ba | 0.43 a | 0.71 a |
| C2 | 24 | 67.21 d | 5.31 c | 23.89 d | 9.47 a | 5.80 a | 54.58 b | 8.74 b | 5.73 c | 0.39 bc | −0.82 d |
| C3 | 35 | 77.80 b | 6.90 a | 35.52 a | 8.17 c | 5.14 b | 54.74 b | 7.75 c | 5.83 bc | 0.42 ab | 0.51 ab |
| C4 | 114 | 68.06 d | 5.87 b | 26.65 c | 8.68 b | 5.30 b | 55.93 ba | 7.88 c | 6.14 a | 0.41 ac | −0.34 c |
| C5 | 118 | 75.13 c | 6.12 b | 30.46 b | 8.69 b | 5.92 a | 56.75 a | 9.20 ab | 6.13 a | 0.41 ac | 0.29 b |
| Trait | Criteria for Investigation | |
|---|---|---|
| Architecture | PH | Distance from the cotyledonary node of cotton to the tip of the main stem |
| FBIN | Node at which the first fruit branch appears on the main stem of cotton | |
| FBIH | Height from the ground to the first fruit branch | |
| FBN | FBN per cotton plant | |
| EFBN | FBN with cotton bolls | |
| Yield | BPP | Number of effective bolls of cotton per plant |
| BW | At harvest, 10 middle bolls were collected from each plot, dried, weighed, and divided by 10 to obtain the BW | |
| LP | At harvest, 10 central bolls were collected from each plot, and the lint weight was divided by the seed cotton weight to give the LP in percent |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tan, Y.; Long, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Jin, S.; Ai, X. Phenotypic Genetic Analysis of Fruit Branch Angle in Upland Cotton. Plants 2025, 14, 1512. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14101512
Tan Y, Long Y, Yang Y, Wang Y, Jin S, Ai X. Phenotypic Genetic Analysis of Fruit Branch Angle in Upland Cotton. Plants. 2025; 14(10):1512. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14101512
Chicago/Turabian StyleTan, Yanping, Yilei Long, Yinan Yang, Yin Wang, Shen Jin, and Xiantao Ai. 2025. "Phenotypic Genetic Analysis of Fruit Branch Angle in Upland Cotton" Plants 14, no. 10: 1512. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14101512
APA StyleTan, Y., Long, Y., Yang, Y., Wang, Y., Jin, S., & Ai, X. (2025). Phenotypic Genetic Analysis of Fruit Branch Angle in Upland Cotton. Plants, 14(10), 1512. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14101512






