Comprehensive Genome-Wide Investigation and Transcriptional Regulation of the bZIP Gene Family in Litchi Fruit Development
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Identification, Physicochemical Property Analysis, and Subcellular Localization of Litchi bZIP Transcription Factors
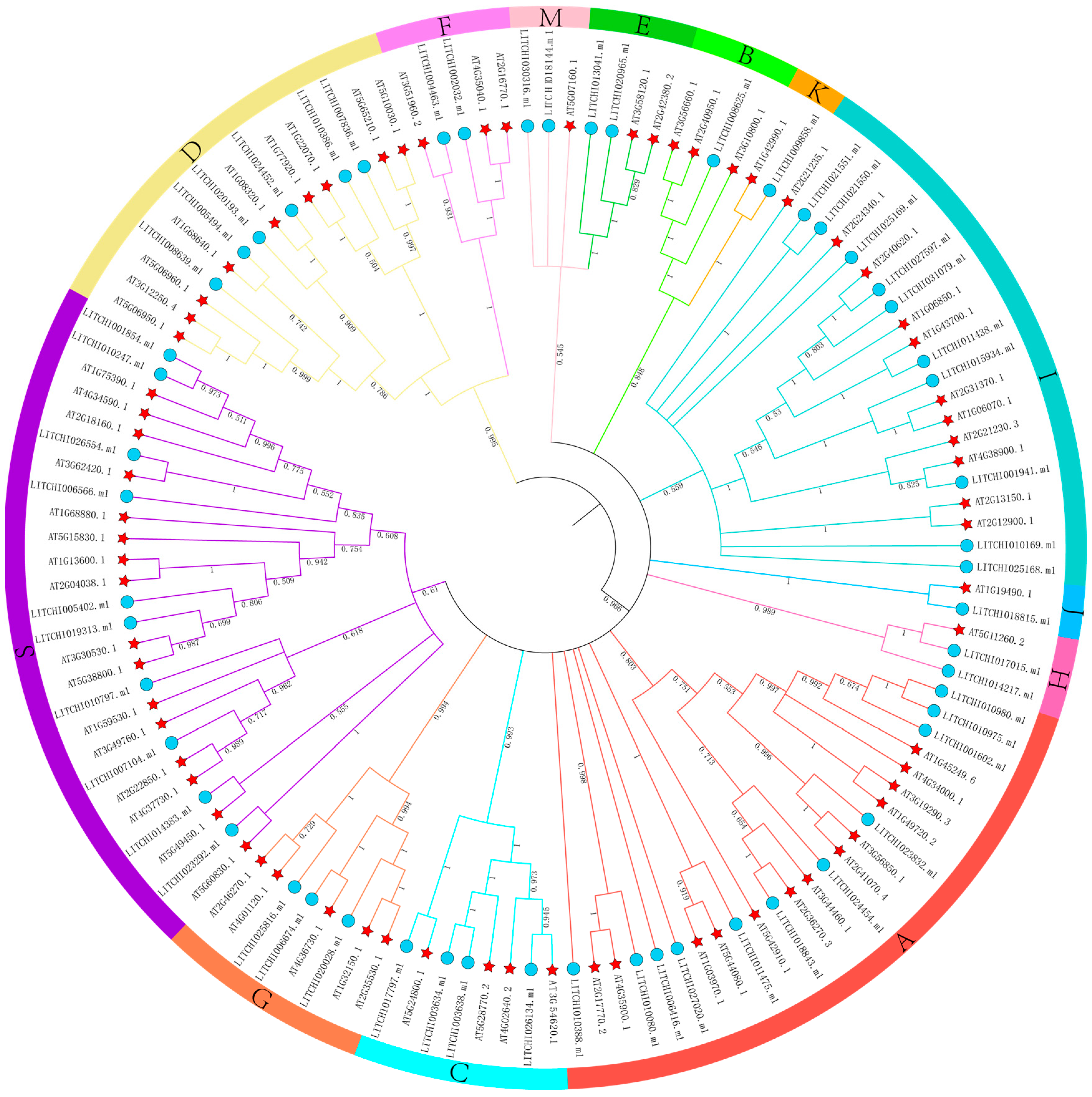
2.2. Phylogenetic Analysis of the Litchi bZIP Gene Family
2.3. Prediction of Secondary and Tertiary Structures of Litchi bZIP Transcription Factors
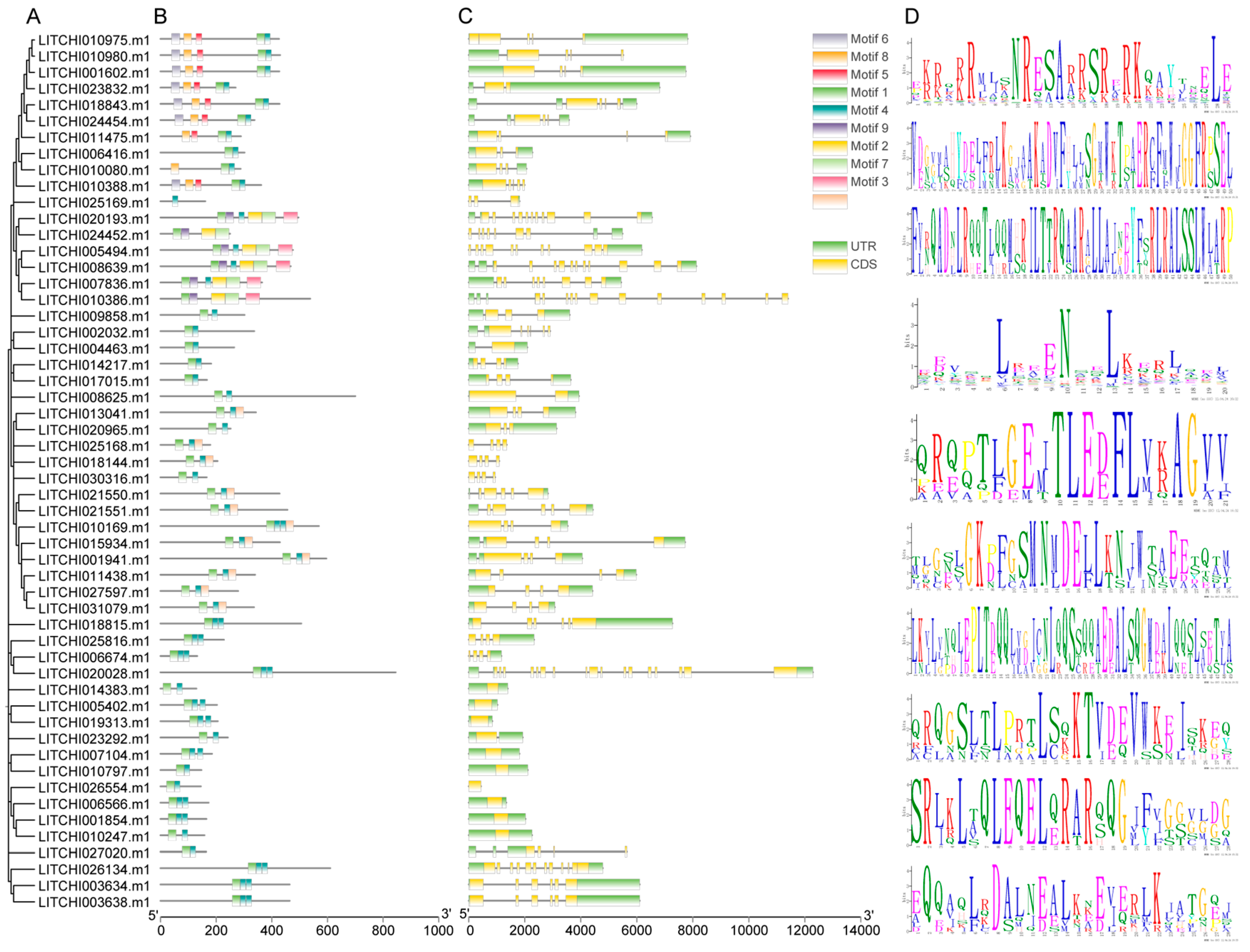
2.4. Conserved Motif and Gene Structure Analysis of the Litchi bZIP Gene Family
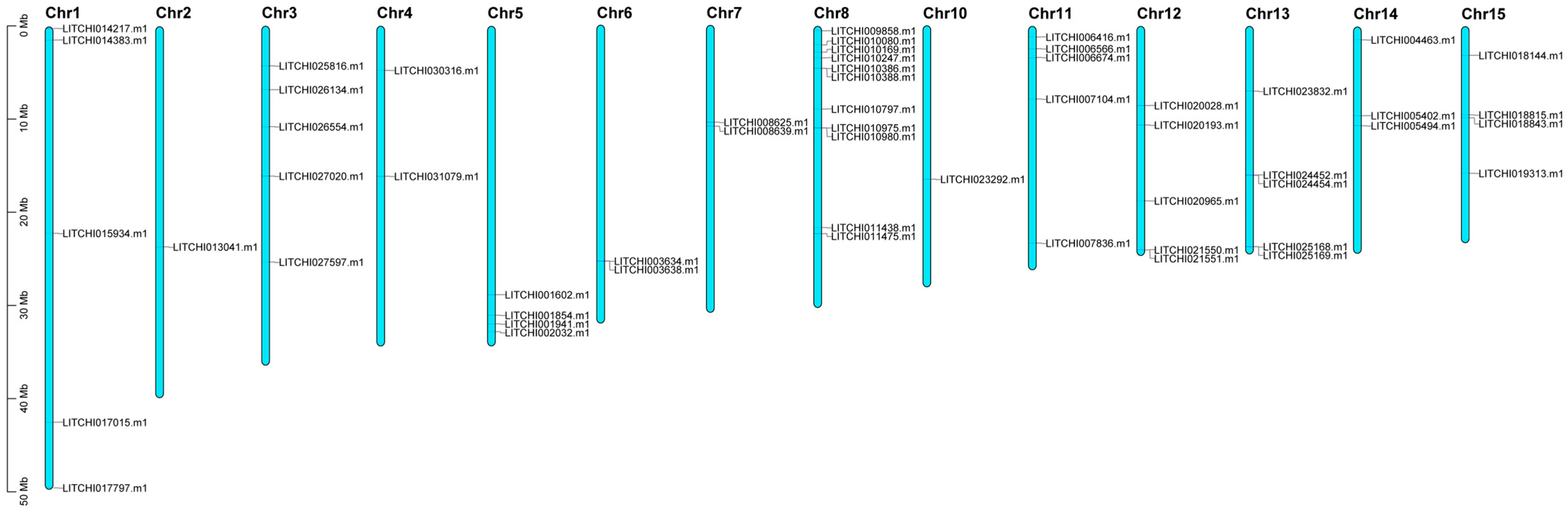
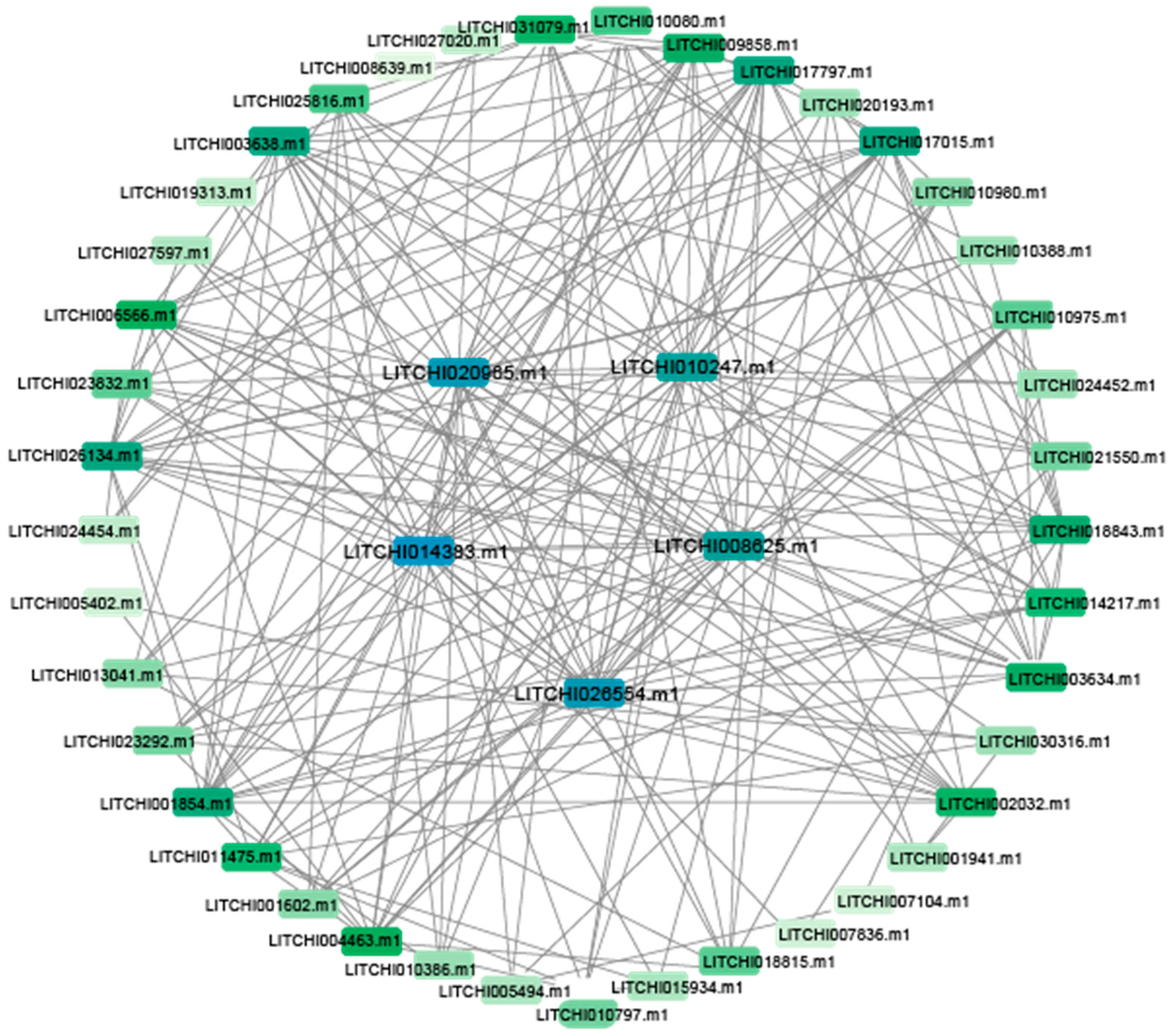
2.5. Chromosomal Localization and Interaction Analysis of Litchi bZIP Genes
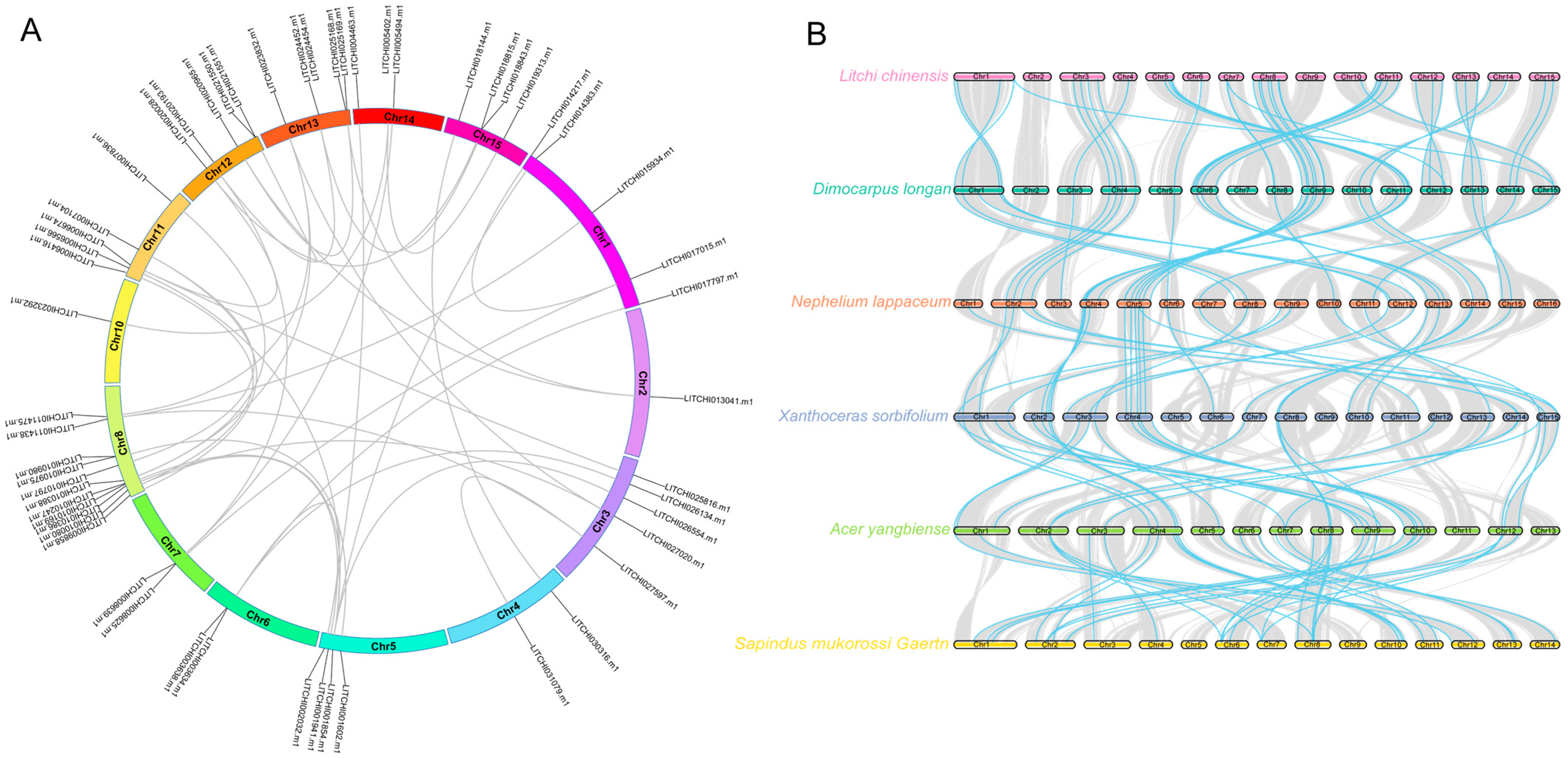
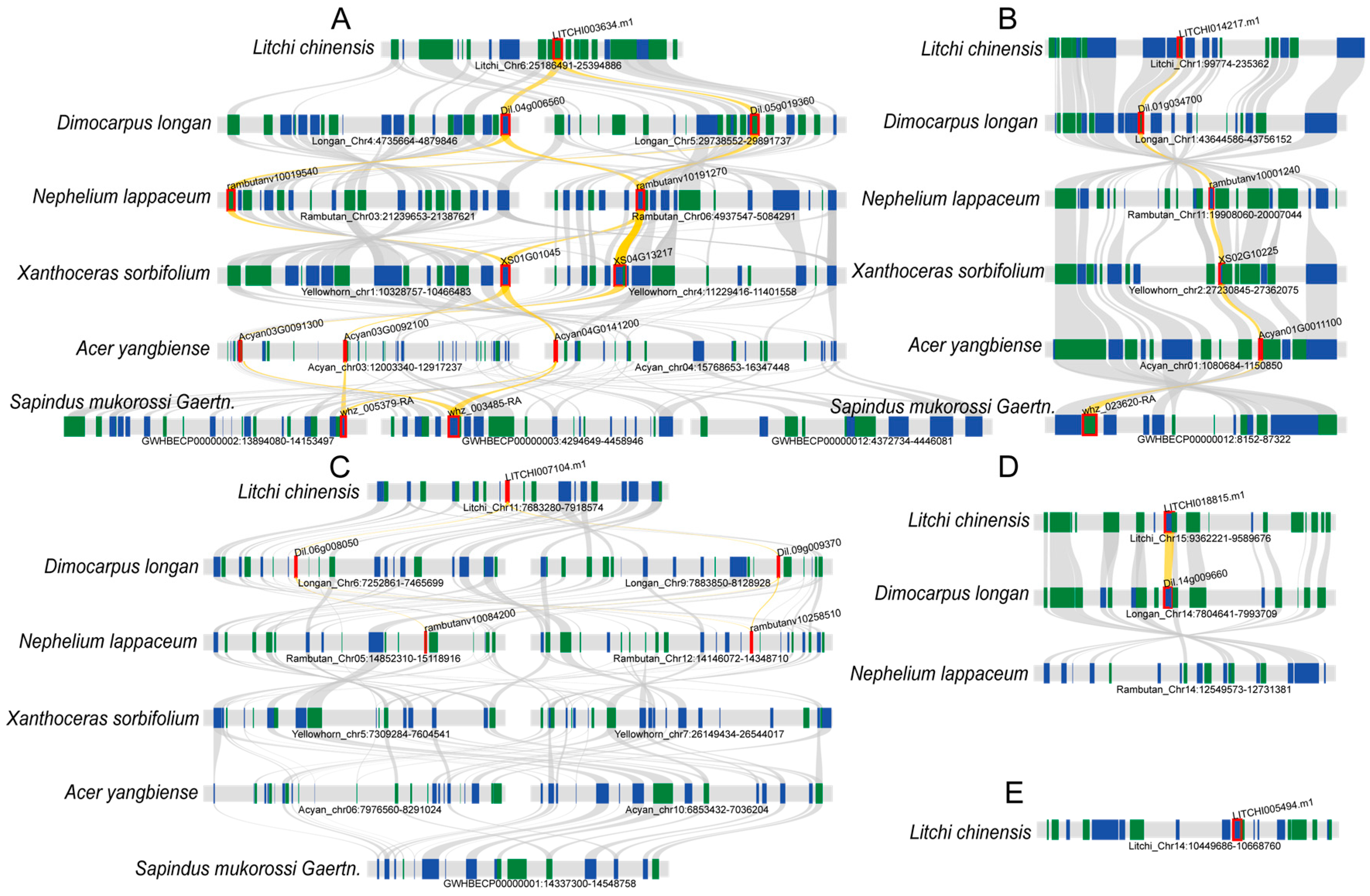
2.6. Intra- and Interspecies Synteny Analysis, Gene Duplication, and Divergence of Litchi bZIP Genes
2.7. Prediction of Cis-Acting Elements in the Litchi bZIP Gene Family
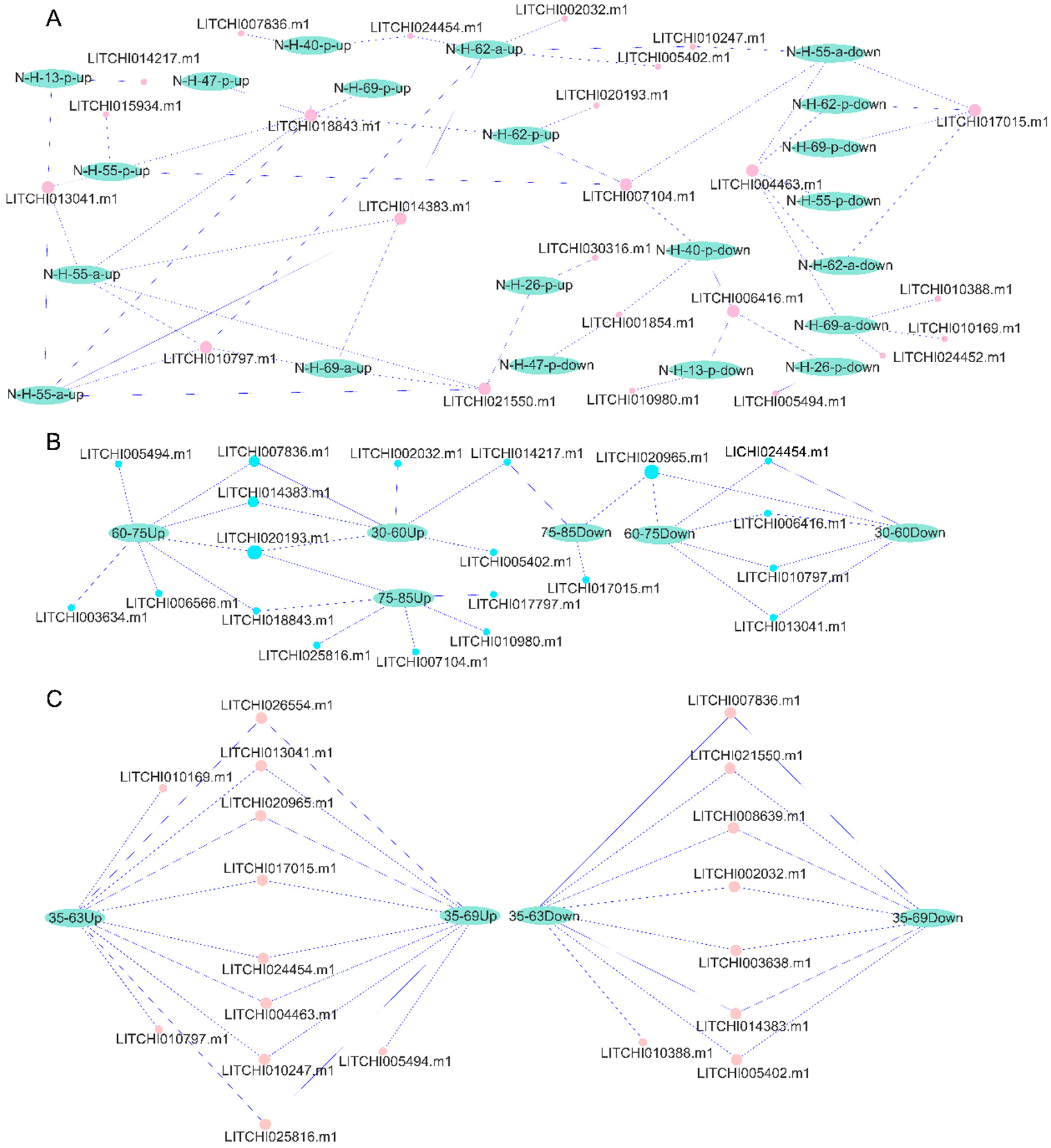
2.8. Tissue Expression Patterns of Litchi bZIP Genes and Their Differential Expression in Various Fruit Developmental Stages
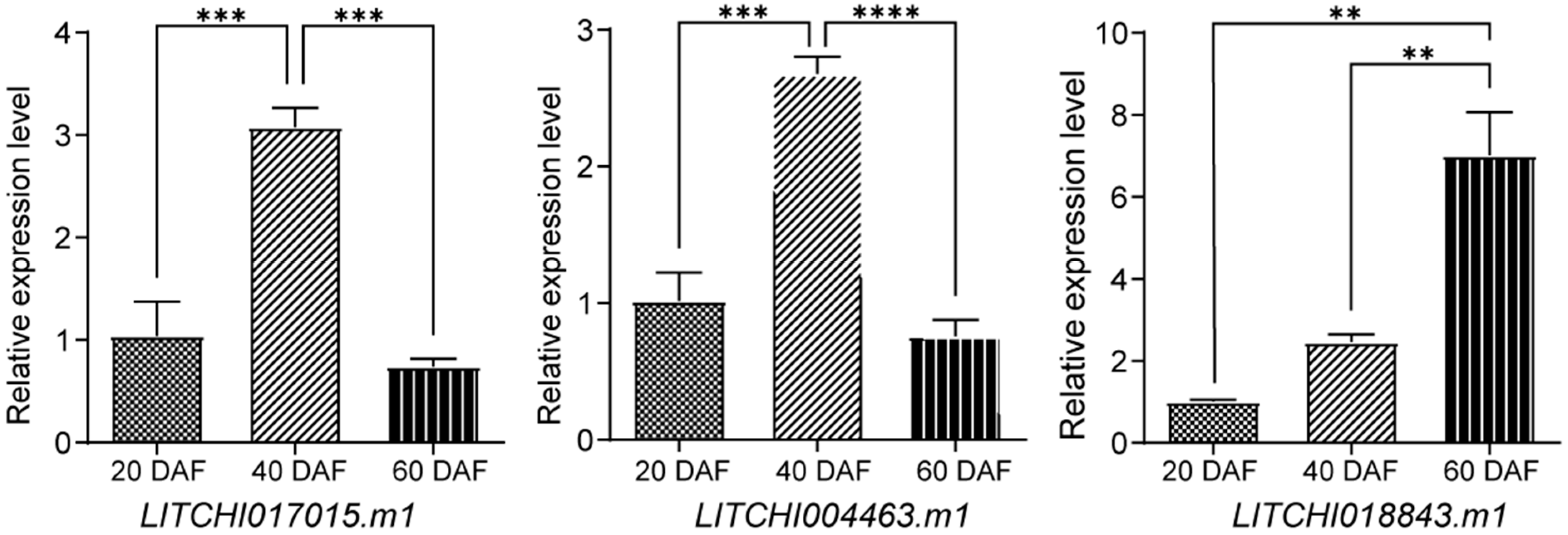
2.9. qRT-PCR Expression Analysis of the bZIP Genes
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Identification of the bZIP Gene Family
4.2. Protein Physicochemical Property Analysis and Subcellular Localization
4.3. Protein Structure Prediction and Analysis and Protein–Protein Interaction Network Analysis
4.4. Phylogenetic Analysis of the Gene Family
4.5. Conserved Domain, Gene Structure, and Motif Analysis of the Gene Family
4.6. Chromosomal Localization and Intra- and Interspecific Synteny Analysis of the Gene Family
4.7. Promoter Analysis of the Gene Family
4.8. Tissue Expression Patterns of Litchi bZIP Genes and Differential Expression Analysis During Fruit Development
4.9. Fluorescence Quantitative Verification
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pérez-Rodríguez, P.; Riano-Pachon, D.M.; Corrêa, L.G.G.; Rensing, S.A.; Kersten, B.; Mueller-Roeber, B. PlnTFDB: Updated content and new features of the plant transcription factor database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, D822–D827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, R.; Izawa, T.; Chua, N.H. Plant bZIP proteins gather at ACGT elements. FASEB J. 1994, 8, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrêa, L.G.; Riaño-Pachón, D.M.; Schrago, C.G.; dos Santos, R.V.; Mueller-Roeber, B.; Vincentz, M. The role of bZIP transcription factors in green plant evolution: Adaptive features emerging from four founder genes. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Shuman, J.D.; Guszczynski, T.; Sakchaisri, K.; Sebastian, T.; Copeland, T.D.; Miller, M.; Cohen, M.S.; Taunton, J.; Smart, R.C.; et al. RSK-mediated phosphorylation in the C/EBP{beta} leucine zipper regulates DNA binding, dimerization, and growth arrest activity. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2010, 30, 2621–2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hijazi, M.; Durand, J.; Pichereaux, C.; Pont, F.; Jamet, E.; Albenne, C. Characterization of the arabinogalactan protein 31 (AGP31) of Arabidopsis thaliana: New advances on the Hyp-O-glycosylation of the Pro-rich domain. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 9623–9632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glover, J.N.; Harrison, S.C. Crystal structure of the heterodimeric bZIP transcription factor c-Fos-c-Jun bound to DNA. Nature 1995, 373, 257–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dröge-Laser, W.; Snoek, B.L.; Snel, B.; Weiste, C. The Arabidopsis bZIP transcription factor family—An update. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2018, 45, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijhawan, A.; Jain, M.; Tyagi, A.K.; Khurana, J.P. Genomic survey and gene expression analysis of the basic leucine zipper transcription factor family in rice. Plant Physiol. 2008, 146, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, B.; Vanitha, J.; Ramachandran, S.; Jiang, S.Y. Genome-wide expansion and expression divergence of the basic leucine zipper transcription factors in higher plants with an emphasis on sorghum F. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2011, 53, 212–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Wang, M.; Zhong, M.; Luo, C.; Shi, S.; Qian, Y.; Kang, Y.; Jiang, B. Genome-wide identification of bZIP gene family and expression analysis of BhbZIP58 under heat stress in wax gourd. BMC Plant Biol. 2023, 23, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Chen, S.; Yao, W.; Cheng, Z.; Zhou, B.; Jiang, T. Genome-wide analysis and expression profile of the bZIP gene family in poplar. BMC Plant Biol. 2021, 21, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Xu, D.; Jia, L.; Huang, X.; Ma, G.; Wang, S.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, A.; Guan, M.; Lu, K. Genome-wide identification and structural analysis of bZIP transcription factor genes in Brassica napus. Genes 2017, 8, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uno, Y.; Furihata, T.; Abe, H.; Yoshida, R.; Shinozaki, K.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K. Arabidopsis basic leucine zipper transcription factors involved in an abscisic acid-dependent signal transduction pathway under drought and high-salinity conditions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 11632–11637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.; Tang, N.; Du, H.; Ye, H.; Xiong, L. Characterization of OsbZIP23 as a key player of the basic leucine zipper transcription factor family for conferring abscisic acid sensitivity and salinity and drought tolerance in rice. Plant Physiol. 2008, 148, 1938–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, F.; Maeta, E.; Terashima, A.; Takumi, S. Positive role of a wheat HvABI5 ortholog in abiotic stress response of seedlings. Physiol. Plant 2008, 134, 74–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yáñez, M.; Cáceres, S.; Orellana, S.; Bastías, A.; Verdugo, I.; Ruiz-Lara, S.; Casaretto, J.A. An abiotic stress-responsive bZIP transcription factor from wild and cultivated tomatoes regulates stress-related genes. Plant Cell Rep. 2009, 28, 1497–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.C.; Choi, H.W.; Hwang, I.S.; Choi, D.S.; Hwang, B.K. Functional roles of the pepper pathogen-induced bZIP transcription factor, CAbZIP1, in enhanced resistance to pathogen infection and environmental stresses. Planta 2006, 224, 1209–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Uribe, L.; O’Connell, M.A. A root-specific bZIP transcription factor is responsive to water deficit stress in tepary bean (Phaseolus acutifolius) and common bean (P. vulgaris). J. Exp. Bot. 2006, 57, 1391–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kusano, T.; Berberich, T.; Harada, M.; Suzuki, N.; Sugawara, K. A maize DNA-binding factor with a bZIP motif is induced by low temperature. Mol. Gen. Genet. 1995, 248, 507–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Ouyang, X.; Yang, P.; Lau, O.S.; Li, G.; Li, J.; Chen, H.; Deng, X.W. Arabidopsis FHY3 and HY5 positively mediate induction of COP1 transcription in response to photomorphogenic UV-B light. Plant Cell 2012, 24, 4590–4606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.; Feng, X.; Li, Y.; Guzmán, C.; Lin, N.; Xu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, H.; Qi, P.; Deng, M. Genome-wide identification of bZIP transcription factor genes related to starch synthesis in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Genome 2021, 64, 1067–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, B.; Deng, H.; Li, T.; Sharma, S.; Yun, Q.; Li, Q.; Zhiguo, E.; Chen, C. OsbZIP76 interacts with OsNF-YBs and regulates endosperm cellularization in rice (Oryza sativa). J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2020, 62, 1983–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sornaraj, P.; Luang, S.; Lopato, S.; Hrmova, M. Basic leucine zipper (bZIP) transcription factors involved in abiotic stresses: A molecular model of a wheat bZIP factor and implications of its structure in function. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1860, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Fu, X.; Lv, Z.; Lu, X.; Shen, Q.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, M.; Wang, G.; Sun, X.; Liao, Z.; et al. A basic leucine zipper transcription factor, AabZIP1, connects abscisic acid signaling with artemisinin biosynthesis in Artemisia annua. Mol. Plant 2015, 8, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhiguo, E.; Zhang, Y.P.; Zhou, J.H.; Wang, L. Mini review roles of the bZIP gene family in rice. Genet. Mol. Res. 2014, 13, 3025–3036. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Z.; Dzinyela, R.; Yang, L.; Hwarari, D. bZIP transcription factors: Structure, modification, abiotic stress responses and application in plant improvement. Plants 2024, 13, 2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Cao, K.; Wang, X. A conserved proline residue in the leucine zipper region of AtbZIP34 and AtbZIP61 in Arabidopsis thaliana interferes with the formation of homodimer. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 362, 425–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Xiang, L.; Yu, Q.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, T.; Zeng, J.; Geng, C.; Li, L.; Fu, X.; Shen, Q.; et al. ARTEMISININ BIOSYNTHESIS PROMOTING KINASE 1 positively regulates artemisinin biosynthesis through phosphorylating AabZIP1. J. Exp. Bot. 2018, 69, 1109–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Q.; Huang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Xie, L.; He, Q.; Zhong, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Tang, K. The Transcription Factor Aabzip9 Positively Regulates the Biosynthesis of Artemisinin in Artemisia annua. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, Z.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, F.; Jiang, W.; Shen, Q.; Fu, X.; Yan, T.; Shi, P.; Hao, X.; et al. Interaction of bZIP transcription factor TGA6 with salicylic acid signaling modulates artemisinin biosynthesis in Artemisia annua. J. Exp. Bot. 2019, 70, 3969–3979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.-Y.; Jiang, L.-L.; Jia, J.-Q.; Zhang, Z.-Z.; Chen, S.-J.; Niu, X.-L.; Wang, M.-X.; Huang, S.-X. Comparative genomics analysis of bZIP family members in Actinidia chinensis. Chin. J. Appl. Environ. Biol. 2020, 226–235. [Google Scholar]
- Lovisetto, A.; Guzzo, F.; Tadiello, A.; Confortin, E.; Pavanello, A.; Botton, A.; Casadoro, G. Characterization of a bZIP gene highly expressed during ripening of the peach fruit. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2013, 70, 462–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Norris, A.; Jiang, C.-Z. S1-bZIP transcription factors play important roles in the regulation of fruit quality and stress response. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 12, 802802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Hanssen, M.; Lundgren, K.; Hernández, L.; Delatte, T.; Ehlert, A.; Liu, C.M.; Schluepmann, H.; Dröge-Laser, W.; Moritz, T. The sucrose-regulated Arabidopsis transcription factor bZIP11 reprograms metabolism and regulates trehalose metabolism. New Phytol. 2011, 191, 733–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagor, G.; Berberich, T.; Tanaka, S.; Nishiyama, M.; Kanayama, Y.; Kojima, S.; Muramoto, K.; Kusano, T. A novel strategy to produce sweeter tomato fruits with high sugar contents by fruit-specific expression of a single bZIP transcription factor gene. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2016, 14, 1116–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.; Lin, S.; Wen, L.; Jiang, Y.; Zhao, M.; Chen, F.; Prasad, K.N.; Duan, X.; Yang, B. Identification of a novel phenolic compound in litchi (Litchi chinensis Sonn.) pericarp and bioactivity evaluation. Food Chem. 2013, 136, 563–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Wang, K.; Wang, K.; Zhu, J.; Hu, Z. Nutrient components, health benefits, and safety of litchi (Litchi chinensis Sonn.): A review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 2139–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, P.; Gao, Y.; Simal-Gandara, J.; Farag, M.A.; Chen, W.; Yao, D.; Delmas, D.; Chen, Z.; Liu, K.; Hu, H. Litchi (Litchi chinensis Sonn.): A comprehensive review of phytochemistry, medicinal properties, and product development. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 9527–9548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-Y.; Meng, D.; Li, M.; Cheng, L. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the bZIP gene family in apple (Malus domestica). Tree Genet. Genomes 2016, 12, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Liu, C.; Li, Z.; Ran, Q.; Xie, G.; Wang, B.; Fang, S.; Chu, J.; Zhang, J. ZmbZIP4 contributes to stress resistance in maize by regulating ABA synthesis and root development. Plant Physiol. 2018, 178, 753–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Chu, Z. Genome-wide evolutionary characterization and analysis of bZIP transcription factors and their expression profiles in response to multiple abiotic stresses in Brachypodium distachyon. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, C.; Mao, X.; Hao, J.; Wang, X.; Xue, J.; Cui, H.; Li, R. Analysis of bZIP transcription factor family and their expressions under salt stress in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakoby, M.; Weisshaar, B.; Dröge-Laser, W.; Vicente-Carbajosa, J.; Tiedemann, J.; Kroj, T.; Parcy, F. bZIP transcription factors in Arabidopsis. Trends Plant Sci. 2002, 7, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chen, N.; Chen, F.; Cai, B.; Dal Santo, S.; Tornielli, G.B.; Pezzotti, M.; Cheng, Z.M. Genome-wide analysis and expression profile of the bZIP transcription factor gene family in grapevine (Vitis vinifera). BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhang, W.-J.; Yin, Z.-G.; Li, W.-J.; Xia, C.-Y.; Sun, H.-Y.; Yang, Y.-M.; Wu, H.-B.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, H.-H. Genome-wide identification reveals the potential functions of the bZIP gene family in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) in response to salt stress during the sprouting stage. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2021, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, T.; Zhang, D.; Sofkova, S.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Y. Genome-wide analysis of the bZIP gene lineage in apple and functional analysis of MhABF in Malus halliana. Planta 2021, 254, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Li, J.; Li, H.; Yang, Y.; Guang, Y.; Zhou, Y. The bZIP gene family in watermelon: Genome-wide identification and expression analysis under cold stress and root-knot nematode infection. PeerJ 2019, 7, e7878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Lu, X.; Zhang, P.; Wang, G.; Wei, L.; Wang, T. Systematic Analysis of Differentially Expressed Maize ZmbZIP Genes between Drought and Rewatering Transcriptome Reveals bZIP Family Members Involved in Abiotic Stress Responses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azeem, F.; Tahir, H.; Ijaz, U.; Shaheen, T. A genome-wide comparative analysis of bZIP transcription factors in G. arboreum and G. raimondii (Diploid ancestors of present-day cotton). Physiol. Mol. Biol. Plants 2020, 26, 433–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Yan, B.; Hu, Y.; Cui, Z.; Wang, X. Genome-wide identification and phylogenetic analysis of rice FTIP gene family. Genomics 2020, 112, 3803–3814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huai, H.; Ning, K.; Hou, C.; Yang, S.-M.; Wang, J.-Z.; Chen, S.-L.; Dong, L.-L. The identification of bZIP gene family in Cannabis sativa L. and its preliminary research of the function in regulation of lipid metabolism. Acta Pharm. Sin. 2022, 57, 2528–2542. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, J.; Meinhardt, L.W.; Goenaga, R.; Matsumoto, T.; Zhang, D.; Yin, Y. The chromosome-level rambutan genome reveals a significant role of segmental duplication in the expansion of resistance genes. Hortic. Res. 2022, 9, uhac014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Feng, J.; Xiang, X.; Wang, J.; Salojärvi, J.; Liu, C.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Liang, X.; Jiang, Z. Two divergent haplotypes from a highly heterozygous lychee genome suggest independent domestication events for early and late-maturing cultivars. Nat. Genet. 2022, 54, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, M.; Saito, K. Differential display analysis of gene expression in plants. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. CMLS 2002, 59, 1246–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, S.; Wu, Z.; Cheng, Z.; Zhang, S.; Liu, H.; Huang, Q. Genome-wide identification, evolutionary patterns, and expression analysis of bZIP gene family in olive (Olea europaea L.). Genes 2020, 11, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xu, K.; Li, X.; Blanco-Ulate, B.; Yang, Q.; Yao, G.; Wei, Y.; Wu, J.; Sheng, B.; Chang, Y. A pear S1-bZIP transcription factor PpbZIP44 modulates carbohydrate metabolism, amino acid, and flavonoid accumulation in fruits. Hortic. Res. 2023, 10, uhad140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mounet, F.; Moing, A.; Garcia, V.; Petit, J.; Maucourt, M.; Deborde, C.; Bernillon, S.; Le Gall, G.; Colquhoun, I.; Defernez, M. Gene and metabolite regulatory network analysis of early developing fruit tissues highlights new candidate genes for the control of tomato fruit composition and development. Plant Physiol. 2009, 149, 1505–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Wang, L.; Tie, W.; Yan, Y.; Ding, Z.; Liu, J.; Li, M.; Peng, M.; Xu, B.; Jin, Z. Genome-wide analyses of the bZIP family reveal their involvement in the development, ripening and abiotic stress response in banana. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.; Ren, H.; Xie, H.; Ma, Z.; Chen, F. Identification and characterization of bZIP-type transcription factors involved in carrot (Daucus carota L.) somatic embryogenesis. Plant J. 2009, 60, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artimo, P.; Jonnalagedda, M.; Arnold, K.; Baratin, D.; Csardi, G.; De Castro, E.; Duvaud, S.; Flegel, V.; Fortier, A.; Gasteiger, E. ExPASy: SIB bioinformatics resource portal. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, W597–W603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, K.-C.; Shen, H.-B. Cell-PLoc 2.0: An improved package of web-servers for predicting subcellular localization of proteins in various organisms. Nat. Sci. 2010, 2, 1090–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 7.0 for Bigger Datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Thomas, H.R.; Frank, M.H.; He, Y.; Xia, R. TBtools: An Integrative Toolkit Developed for Interactive Analyses of Big Biological Data. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Krishnakumar, V.; Zeng, X.; Xu, Z.; Taranto, A.; Lomas, J.S.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yim, W.C. JCVI: A versatile toolkit for comparative genomics analysis. Imeta 2024, 3, e211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wu, X.F.; Tang, Y.; Li, J.G.; Zhao, M.L. RNA-Seq provides new insights into the molecular events involved in “Ball-Skin versus Bladder Effect” on fruit cracking in litchi. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, R.; Wei, J.; Liu, B.; Luo, H.; Zhang, Z.; Pang, X.; Fang, F. Metabolite and transcriptome profiles of proanthocyanidin biosynthesis in the development of litchi fruit. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 24, 532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Du, J.; Wuqiang, M.; Chen, T.; Shui, X.; Liao, H.; Lin, X.; Zhou, K. Transcriptomics-based analysis of the causes of sugar receding in Feizixiao litchi (Litchi chinensis Sonn.) pulp. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1083753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. HISAT: A fast spliced aligner with low memory requirements. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Chan, C.-K.K. Analysis of RNA-Seq data using TopHat and Cufflinks. Plant Bioinform. Methods Protoc. 2016, 1374, 339–361. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, M.; Chen, T.; Liu, Y.X.; Huang, L. Visualizing set relationships: EVenn’s comprehensive approach to Venn diagrams. Imeta 2024, 3, e184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, J.; Silaiyiman, S.; Wu, J.; Ouyang, L.; Cao, Z.; Shen, C. Comprehensive Genome-Wide Investigation and Transcriptional Regulation of the bZIP Gene Family in Litchi Fruit Development. Plants 2025, 14, 1453. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14101453
Liu J, Silaiyiman S, Wu J, Ouyang L, Cao Z, Shen C. Comprehensive Genome-Wide Investigation and Transcriptional Regulation of the bZIP Gene Family in Litchi Fruit Development. Plants. 2025; 14(10):1453. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14101453
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Jiaxuan, Saimire Silaiyiman, Jiaxin Wu, Lejun Ouyang, Zheng Cao, and Chao Shen. 2025. "Comprehensive Genome-Wide Investigation and Transcriptional Regulation of the bZIP Gene Family in Litchi Fruit Development" Plants 14, no. 10: 1453. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14101453
APA StyleLiu, J., Silaiyiman, S., Wu, J., Ouyang, L., Cao, Z., & Shen, C. (2025). Comprehensive Genome-Wide Investigation and Transcriptional Regulation of the bZIP Gene Family in Litchi Fruit Development. Plants, 14(10), 1453. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14101453





