Soil Bulk Density, Aggregates, Carbon Stabilization, Nutrients and Vegetation Traits as Affected by Manure Gradients Regimes Under Alpine Meadows of Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau Ecosystem
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
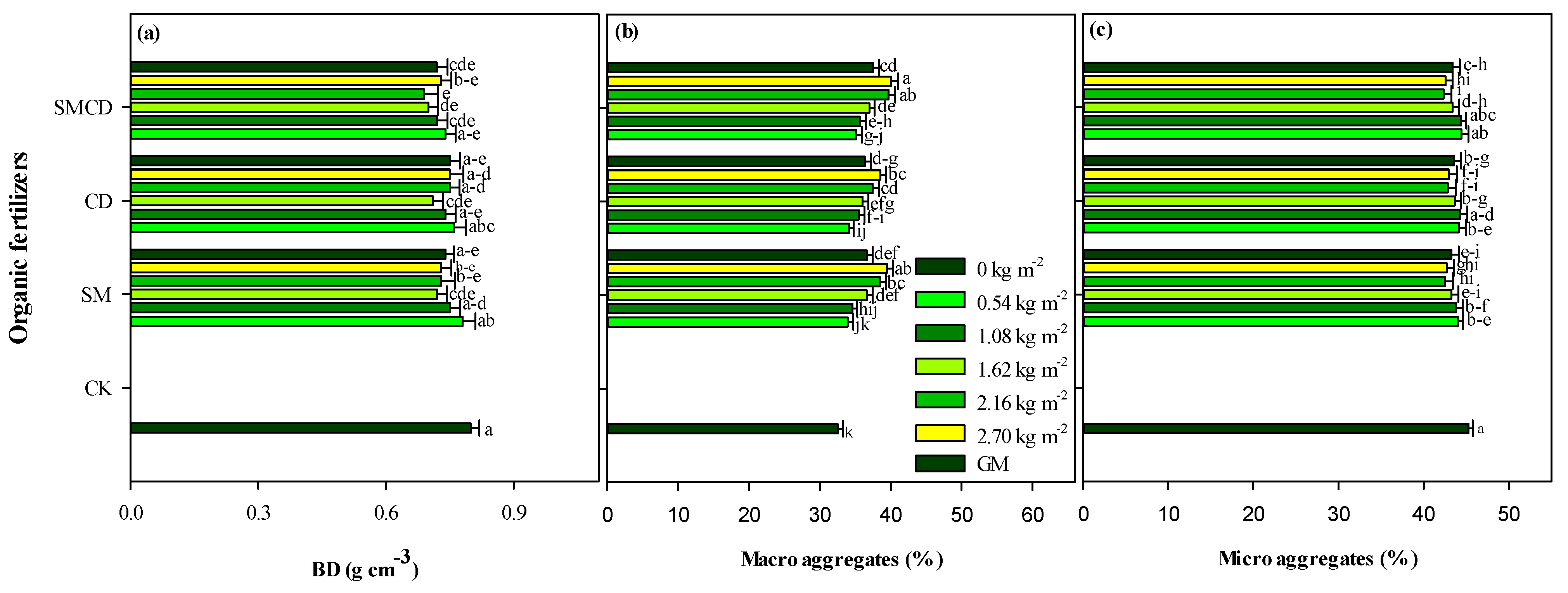
2.1. Soil Bulk Density and Aggregate Size Distribution
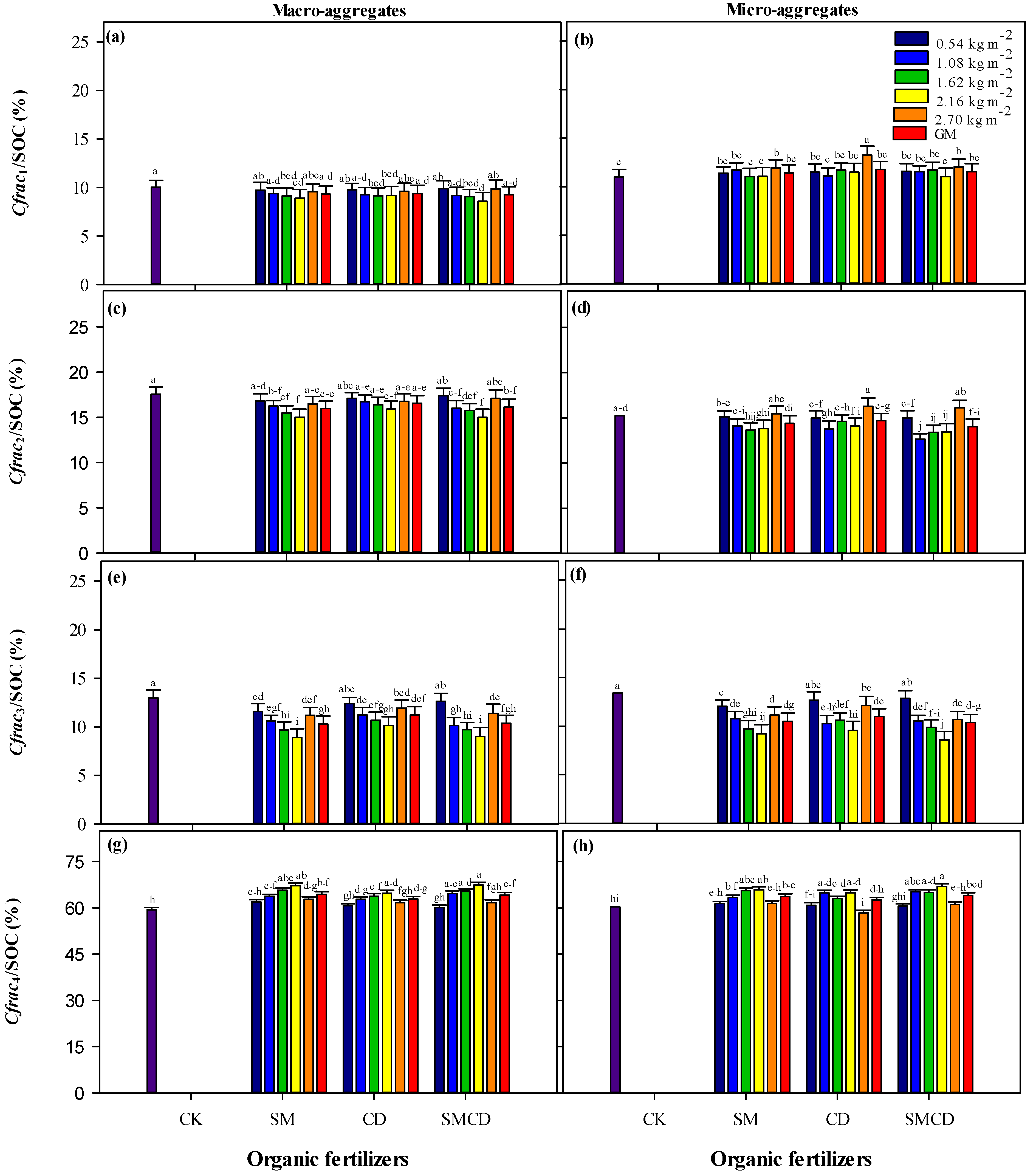
2.2. SOC Concentration, SOC Fractions and Stabilization
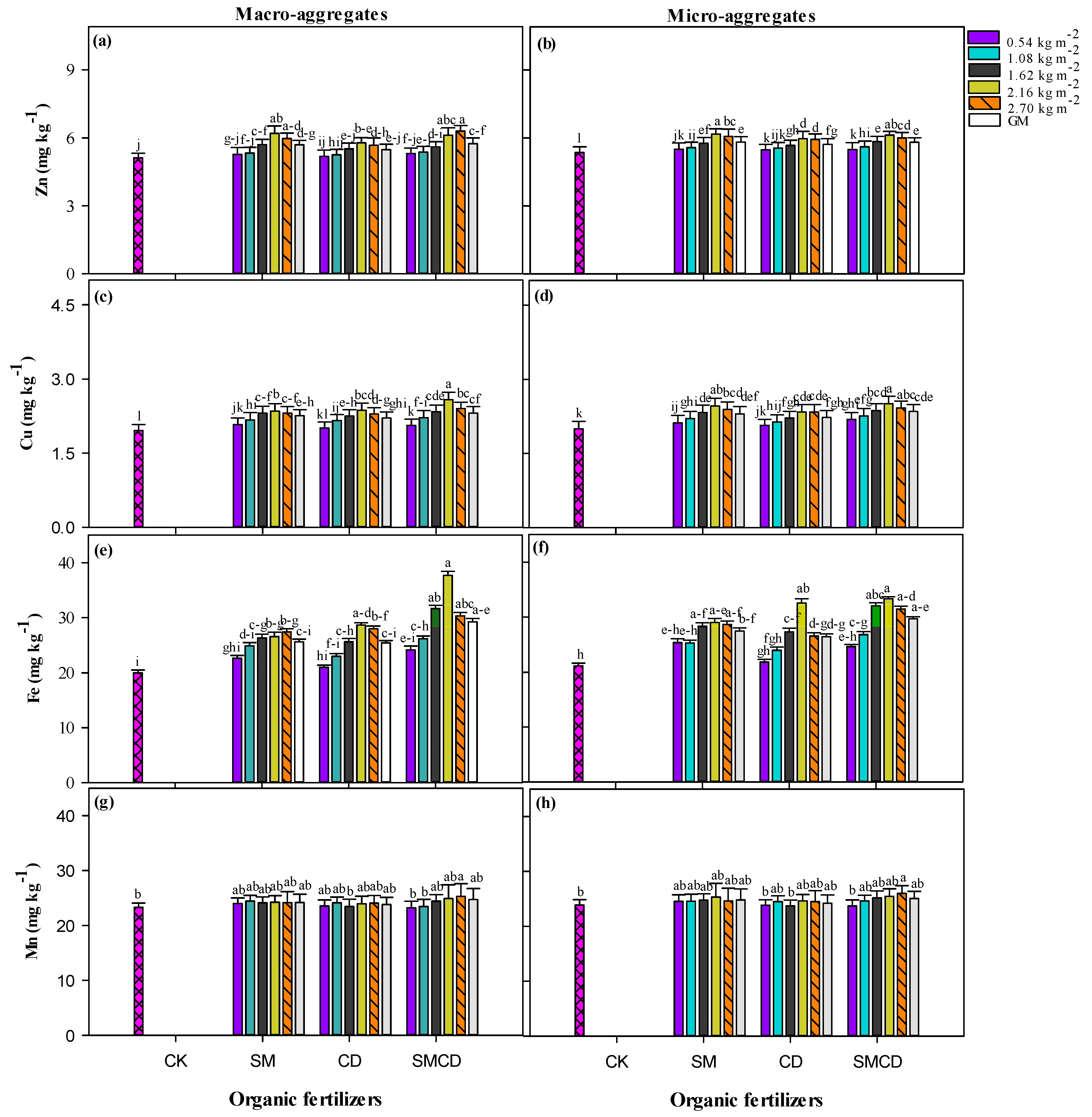
2.3. Nutrient Dynamics
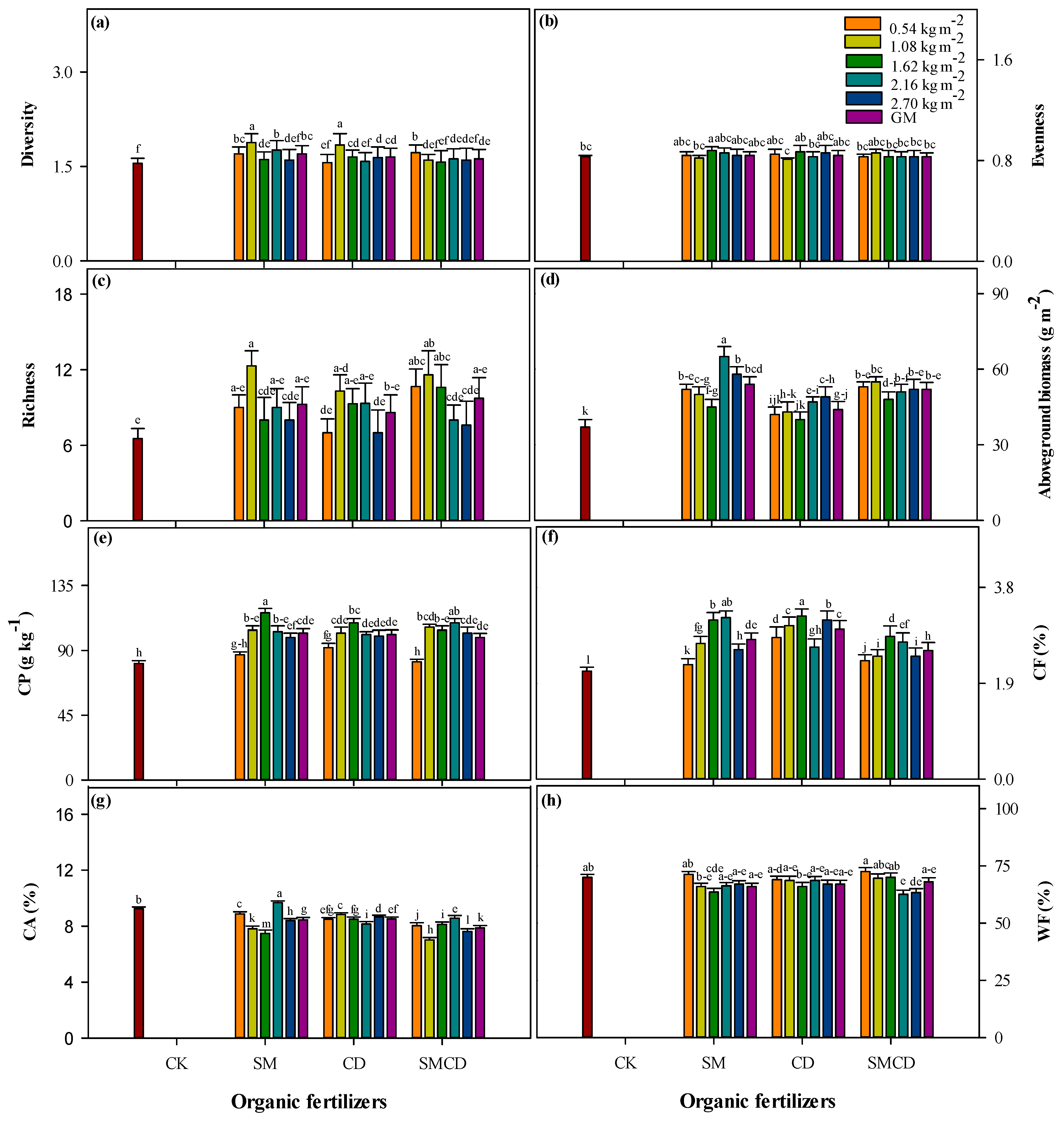
2.4. Forage Biodiversity, Productivity and Nutritional Quality
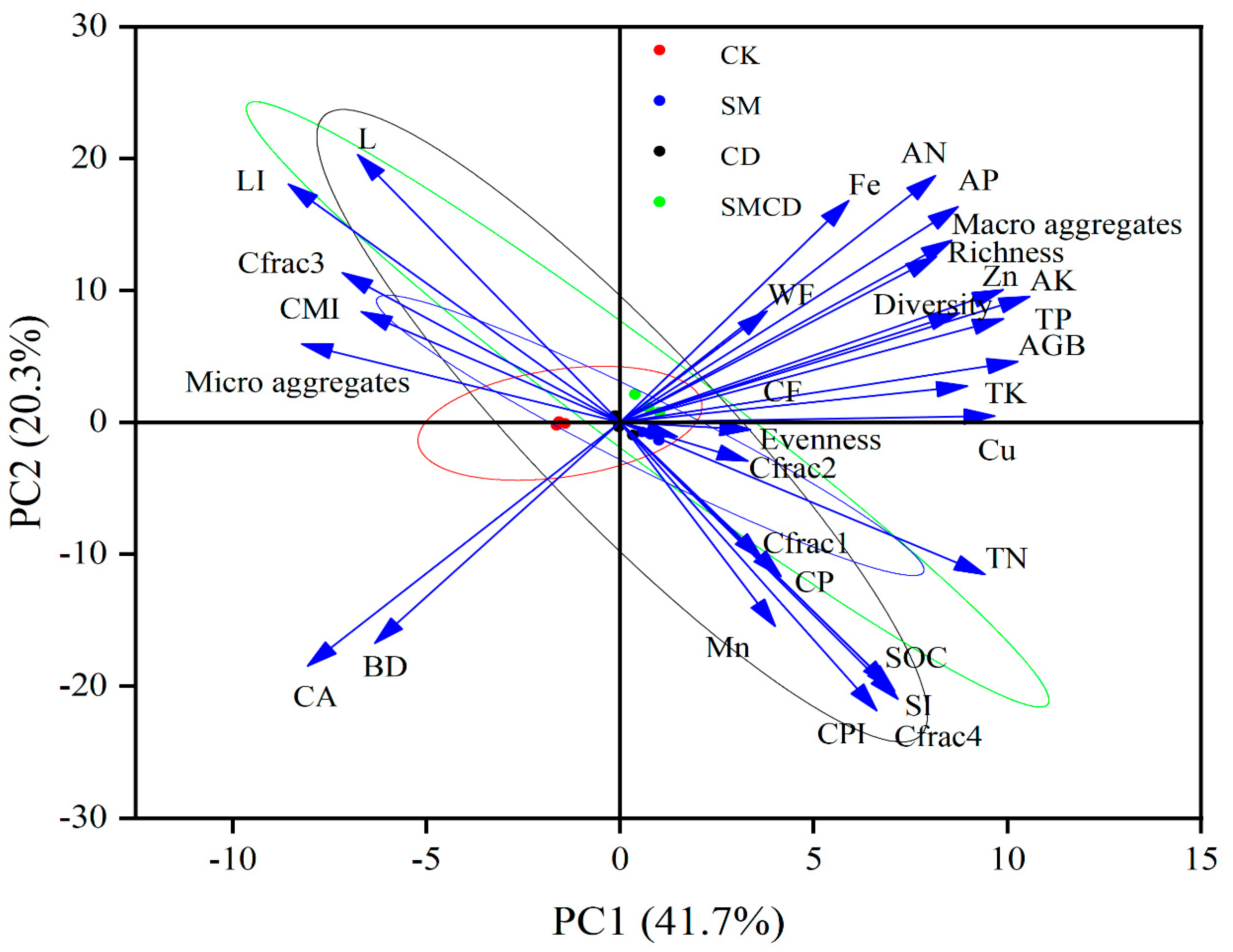
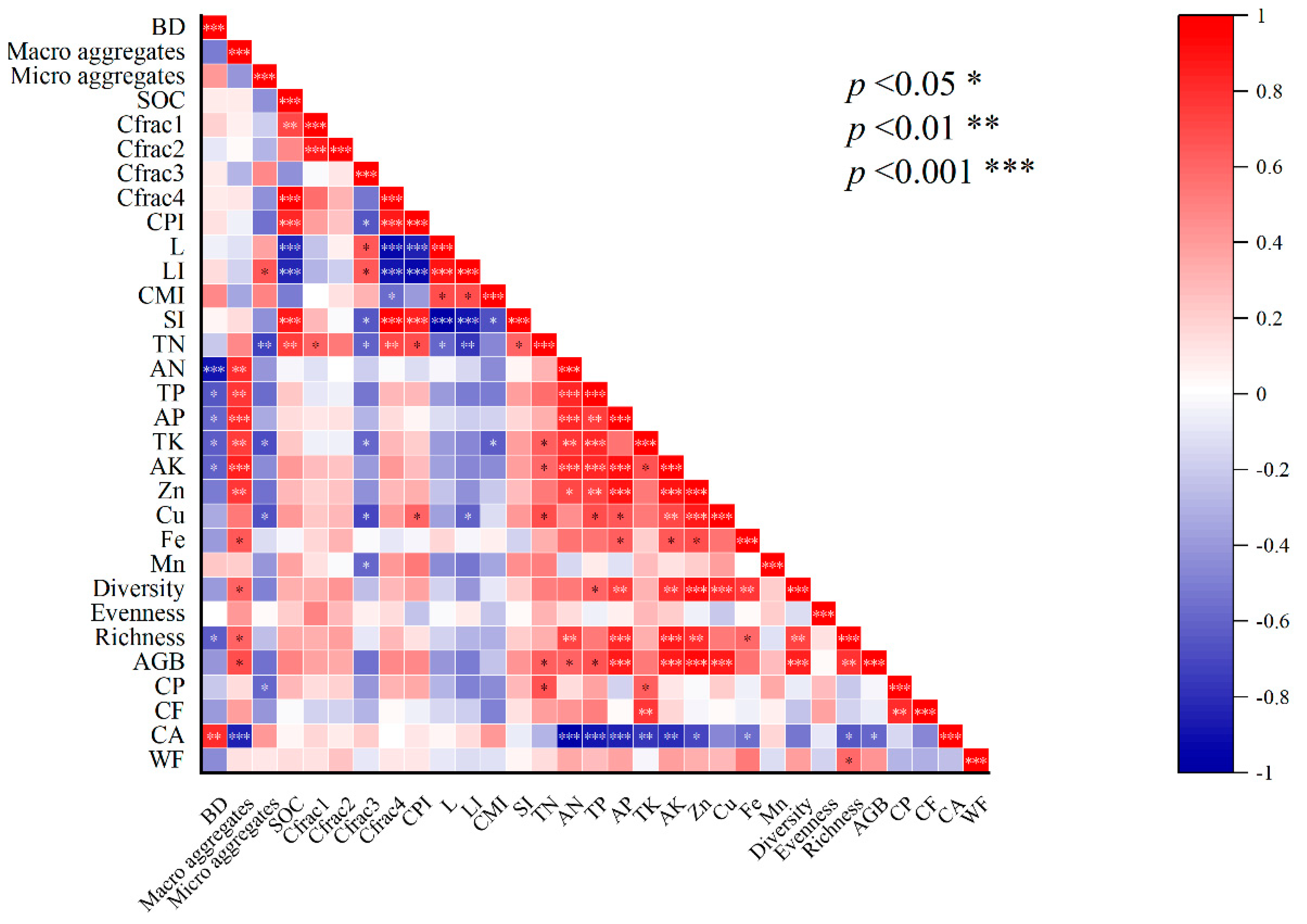
2.5. PCA and Heatmap Correlation Analysis
3. Discussion
3.1. Effect of Manure Gradient Regimes on Soil BD and Aggregation
3.2. SOC Concentration, Fractions and Stabilization Under Manure Management Practices
3.3. Influence of Manure Gradient Application on Soil Nutrient Build-Up
3.4. Forage Traits with Respect to Manure Input Rates
3.5. Correlation
3.6. Research Limitations
4. Materials and Methods
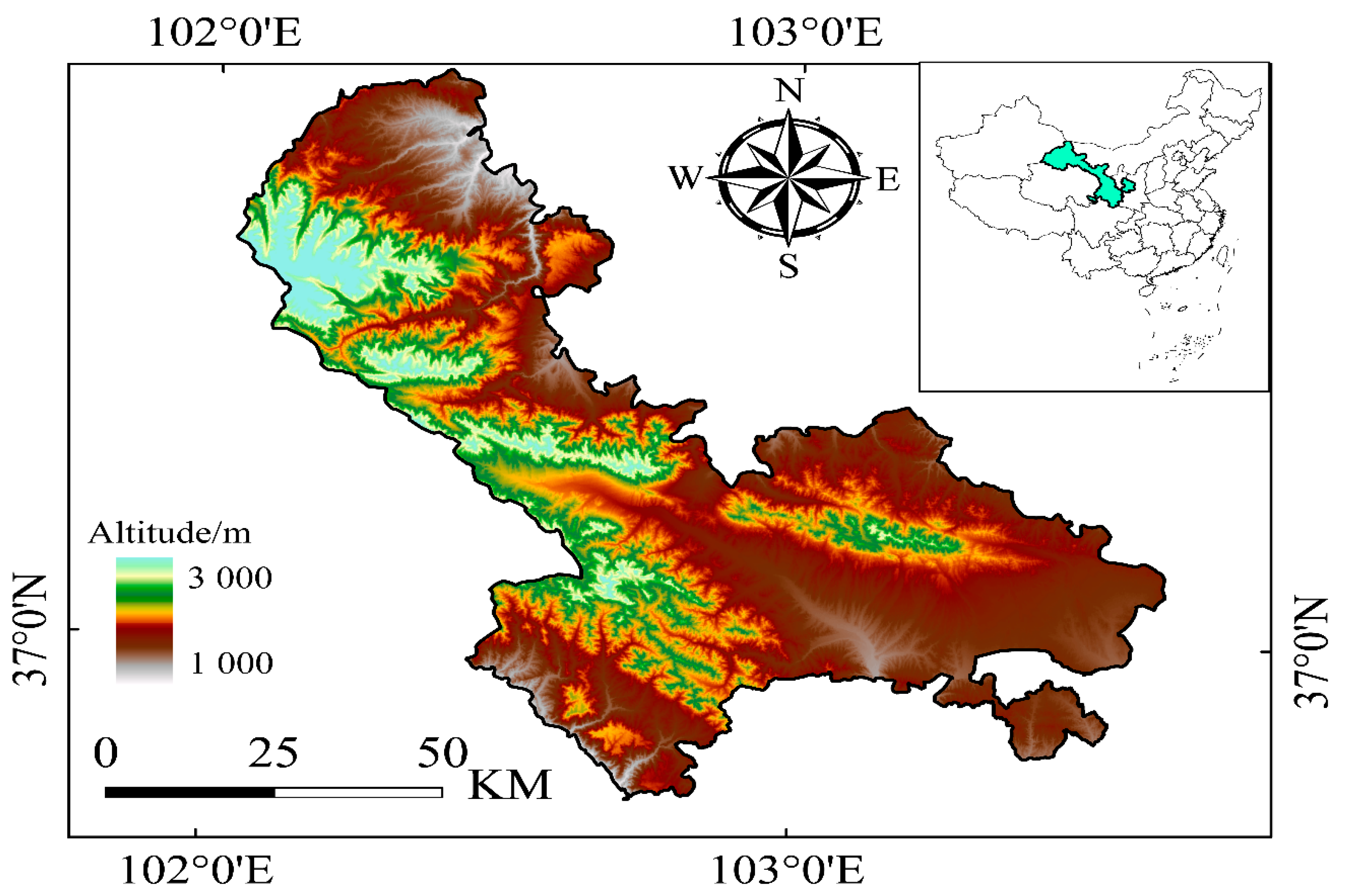
4.1. Field Site Description
4.2. Research Design and Treatment Details
4.3. Properties of Alpine Meadows Soil
4.4. Soil Sampling and Sample Preparation
4.5. Soil Measurements
4.5.1. Soil Bulk Density and Aggregate Measurement
4.5.2. Soil Organic Carbon, SOC Fractions and Nutrient Analysis
- SOC part oxidized under 33 mmol L−1 KMnO4 denoted as very-labile fraction (Cfrac1).
- Extra SOC part oxidized under 167 mmol L−1 KMnO4 defined as labile fraction (Cfrac2).
- Extra SOC part oxidized under 333 mmol L−1 KMnO4 signified as less-labile fraction (Cfrac3).
- SOC not oxidized under 333 mmol L−1 KMnO4 mentioned as non-labile/recalcitrant fraction (Cfrac4) [97].
4.6. Forage Traits Analysis
4.7. Statistical Analysis of Experimental Data
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brummerloh, A.; Kuka, K. The Effects of Manure Application and Herbivore Excreta on Plant and Soil Properties of Temperate Grasslands—A Review. Agronomy 2023, 13, 3010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, A.; Fallah, S.; Sourki, A.A. Organic and inorganic fertilizer effect on soil CO2 flux, microbial biomass, and growth of Nigella sativa L. Int. Agrophys. 2017, 31, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaith, M.; Tirkey, P.; Bhardwaj, D.R.; Kumar, J.; Kumar, J. Carbon sequestration potential of forest plantation soils in eastern Plateau and hill region of India: A promising approach toward climate change mitigation. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2023, 234, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Land Use, land-Use Change and Forestry. A Special Report of the IPCC; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Cooper, J.M.; Burton, D.; Daniell, T.J.; Griffiths, B.S.; Zebarth, B.J. Carbon mineralization kinetics and soil biological characteristics as influenced by manure addition in soil incubated at a range of temperatures. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2011, 47, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiemann, L.K.; Billings, S.A. Indirect effects of nitrogen amendments on organic substrate quality increase enzymatic activity driving decomposition in a Mesic Grassland. Ecosystems 2011, 14, 234–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Meng, J.; Lan, Y.; Chen, W.; Yang, T.; Yuan, J.; Liu, S.; Han, J. Effects of maize stover and its biochar on soil CO2 emissions and labile organic carbon fractions in Northeast China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2017, 240, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallenbach, C.M.; Frey, S.D.; Grandy, A.S. Direct evidence for microbial-derived soil organic matter formation and its ecophysiological controls. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panwar, P.; Mahalingappa, D.G.; Kaushal, R.; Bhardwaj, D.R.; Chakravarty, S.; Shukla, G.; Thakur, N.S.; Chavan, S.B.; Pal, S.; Nayak, B.G.; et al. Biomass production and carbon sequestration potential of different agroforestry systems in India: A critical review. Forests 2022, 13, 1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadiq, M.; Rahim, N.; Tahir, M.M.; Alasmari, A.; Alqahtani, M.M.; Albogami, A.; Ghanem, K.Z.; Abdein, M.A.; Ali, M.; Mehmood, N.; et al. Conservation tillage: A way to improve yield and soil properties and decrease global warming potential in spring wheat agroecosystems. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1356426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockmann, U.; Adams, M.A.; Crawford, J.W.; Field, D.J.; Henakaarchchi, N.; Jenkins, M.; Minasny, B.; McBratney, A.B.; de Courcelles, V.D.; Singh, K.; et al. The knowns, known unknowns and unknowns of sequestration of soil organic carbon. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2013, 164, 80–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.L.; Zhao, W.Q.; Liu, M.; Liu, Q. Responses of soil respiration and its components to experimental warming in an alpine scrub ecosystem on the eastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 643, 1427–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiem, R.; Kogel-Knabner, I. Contribution of lignin and polysaccharides to the refractory carbon pool in C-depleted arable soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2003, 35, 101–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diekow, J.; Mielniczuk, J.; Knicker, H.; Bayer, C.; Dick, D.P.; Kogel-Knaber, I. Carbon and nitrogen stocks in physical fractions of a subtropical Acrisol as influenced by long-term no-till cropping systems and N fertilization. Plant Soil 2005, 268, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigarlsford, G.; de Silva, J.; Tuwei, G.; Redfern, S.; Kulak, M.; Miah, J.H.; Sim, S. Potential management interventions to mitigate greenhouse gas emissions from tea cultivation. Carbon Manag. 2020, 11, 631–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.W.; Bai, J.H.; Xiao, R.; Wang, C.; Cui, Y.; Wu, J.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Z.M.; Zhang, M.X. Incorporating soil aggregate-associated indicators into evaluating ecological responses of degraded estuarine wetlands to freshwater replenishment at different intensity: A case study from the Yellow River Delta China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 121, 107039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Six, J.; Paustian, K.; Elliott, E.T.; Combrink, C. Soil structure and organic matter: I. Distribution of aggregate-size classes and aggregate-associated carbon. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2000, 64, 681–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Six, J.; Bossuyt, H.; Degryze, S.; Denef, K. A history of research on the link between (micro) aggregates, soil biota, and soil organic matter dynamics. Soil Tillage Res. 2004, 79, 7–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Pausch, J.; Yu, G.R.; Blagodatskaya, E.; Gao, Y.; Kuzyakov, Y. Aggregate size and their disruption affect C-14-labeled glucose mineralization and priming effect. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2015, 90, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Gao, S.Q.; Li, C.L.; Zhang, J.J.; Wang, L.C. Effects of temperature on soil organic carbon fractions contents, aggregate stability and structural characteristics of humic substances in a Mollisol. J. Soil. Sediment. 2016, 16, 1849–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakayoko, S.; Soro, D.; Nindjin, C.; Dao, D.; Tschannen, A.; Girardin, O.; Assa, A. Effects of cattle and poultry manures on organic matter content and adsorption complex of a sandy soil under cassava cultivation (Manihot esculenta, Crantz). Afr. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 3, 190–197. [Google Scholar]
- Manna, M.C.; Swarup, A.; Wanjari, R.H.; Ravankar, H.N.; Mishra, B.; Saha, M.N.; Singh, Y.V.; Sahi, D.K.; Sarap, P.A. Long-term effect of fertilizer and manure application on soil organic carbon storage, soil quality and yield sustainability under sub-humid and semi-arid tropical India. Field Crops Res. 2005, 93, 264–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.J.; Zhou, H.K.; Wu, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhao, Z.W.; Li, Y.Z.; Qiao, L.L.; Chen, K.L.; Liu, G.B.; Xue, S. Direct and indirect influences of long-term fertilization on microbial carbon and nitrogen cycles in an alpine grassland. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 149, 107922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivenshield, A.; Bassuk, N.L. Using organic amendments to decrease bulk density and increase macroporosity in compacted soils. Arboric. Urban For. 2007, 33, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzluebbers, A.J. Water infiltration and soil structure related to organic matter and its stratification with depth. Soil Tillage Res. 2002, 66, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Department of Agriculture (USDA–NRCS). Soil Quality Indicators. 2008. Available online: https://www.nrcs.usda.gov/sites/default/files/2022-10/indicator_sheet_guide_sheet.pdf (accessed on 10 July 2020).
- Khaleel, R.; Reddy, K.R.; Overcash, M.R. Changes in soil physical properties due to organic waste application: A review. J. Environ. Qual. 1981, 10, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celik, I.; Gunal, H.; Budak, M.; Akpinar, C. Effects of long-term organic and mineral fertilizers on bulk density and penetration resistance in semi-arid Mediterranean soil conditions. Geoderma 2010, 160, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linsler, D.; Geisseler, D.; Loges, R.; Taube, F.; Ludwig, B. Effects of tillage and application of cattle slurry on carbon pools and aggregate distribution in temperate grassland soils. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2014, 177, 388–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhanhui, Z.; Congzhi, Z.; Jiabao, Z.; Changhua, L.; Qicong, W. Fertilizer impacts on soil aggregation and aggregate-associated organic components. Plant Soil Environ. 2018, 64, 338–343. [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson, F.A.; Groves, S.J.; Chambers, B.J. Pathogen survival during livestock manure storage and following land application. Bioresour. Technol. 2005, 96, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motavalli, P.; Miles, R. Soil phosphorus fractions after 111 years of animal manure and fertilizer applications. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2002, 36, 35–42. [Google Scholar]
- Sindhöj, E.; Krysztoforski, M.; Kuka, K.; Luostarinen, S.; Melnalksne, Z.; Mjöfors, K.; Riiko, K.; Tamm, K.; Ylivainio, K.; Sarvi, M. Technologies and Management Practices for Sustainable Manure Use in the Baltic Sea Region; RISE Research Institutes of Sweden: Upsala, Sweden, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Shaji, H.; Chandran, V.; Mathew, L. Chapter 13—Organic Fertilizers as a Route to Controlled Release of Nutrients. In Controlled Release Fertilizers for Sustainable Agriculture; Lewu, F.B., Volova, T., Thomas, S., Rakhimol, K.R., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021; pp. 231–245. ISBN 978-0-12-819555-0. [Google Scholar]
- Lewu, F.B.; Volova, T.; Thomas, S.; Rakhimol, K.R. (Eds.) Controlled Release Fertilizers for Sustainable Agriculture; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021; ISBN 978-0-12-819555-0. [Google Scholar]
- Dhaliwal, S.S.; Vivek, S.; Arvind, K.S.; Vibha, V.; Manmeet, K.; Prabhjot, S.; Ahmed, A.H. Effect of addition of organic manures on basmati yield, nutrient content and soil fertility status in north-western India. Heliyon 2023, 9, e14514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, R.; Tian, H.; Pan, S.; Dangal, S.R.S.; Chen, J.; Chang, J.; Lu, Y.; Skiba, U.M.; Tubiello, F.N.; Zhang, B. Increased nitrogen enrichment and shifted patterns in the world’s grassland: 1860–2016. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2019, 11, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reijneveld, J.A.; Abbink, G.W.; Termorshuizen, A.J.; Oenema, O. Relationships between soil fertility, herbage quality and manure composition on grassland-based dairy farms. Eur. J. Agron. 2014, 56, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simic, A.; Marković, J.; Bojan Stojanović, S.V.; Violeta Mandić, Z.B.; Dželetović, Ž. The use of different N sources for the treatment of permanent grassland and effect on forage quality. Emir. J. Food Agric. 2019, 31, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socher, S.A.; Prati, D.; Boch, S.; Müller, J.; Klaus, V.H.; Hölzel, N.; Fischer, M. Direct and productivity-mediated indirect effects of fertilization, mowing and grazing on grassland species richness. J. Ecol. 2012, 100, 1391–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schröder, J.J.; Uenk, D.; Hilhorst, G.J. Long-term nitrogen fertilizer replacement value of cattle manures applied to cut grassland. Plant Soil 2007, 299, 83–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Štýbnarová, M.; Mičová, P.; Fiala, K.; Karabcová, H.; Látal, O.; Pozdíšek, J. Effect of Organic Fertilizers on Botanical Composition of Grassland, Herbage Yield and Quality. Agriculture 2014, 60, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Simić, A.; Stojanović, B.; Vučković, S.; Marković, J.; Božičković, A.; Bijelić, Z.; Mandić, V. Application of farmyard manure in grassland production. Agrofor 2016, 1, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pain, B.F.; Misselbrook, T.H.; Clarkson, C.R.; Rees, Y.J. Odour and ammonia emissions following the spreading of anaerobically digested pig slurry on grassland. Biol. Wastes 1990, 34, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prins, W.H.; Snijders, P.J.M. Negative Effects of Animal Manure on Grassland Due to Surface Spreading and Injection. In Animal Manure on Grassland and Fodder Crops. Fertilizer or Waste? Proceedings of an International Symposium of the European Grassland Federation, Wageningen, The Netherlands, 31 August–3 September 1987; van der Meer, H.G., Unwin, R.J., van Dijk, T.A., Ennik, G.C., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1987; pp. 119–135. ISBN 978-94-009-3659-1. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, S.K.; Rees, R.M.; Skiba, U.M.; Ball, B.C. Greenhouse gas emissions from a managed grassland. Glob. Planet. Change 2005, 47, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bicudo, J.R.; Goyal, S.M. Pathogens and manure management systems: A review. Environ. Technol. 2003, 24, 115–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Zhang, X.; Tao, J.; Wu, J.; Wang, J.; Shi, P.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, C. The impact of climate change and anthropogenic activities on alpine grassland over the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Agric. Forest Meteorol. 2014, 189, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Singh, P.; Angmo, P.; Satpute, S. Total and labile pools of organic carbon in relation to soil biological properties under contrasting land-use systems in a dry mountainous region. Carbon Manag. 2022, 13, 352–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, D.R.; Salve, A.; Kumar, J.; Kumar, A.; Sharma, P.; Kumar, D. Biomass production and Carbon storage potential of agroforestry land use systems in high hills of north-western Himalaya: An approach towards natural based climatic solution. Biomass Convers. Biorefin. 2023, 14, 18079–18092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Sun, J.; Wu, G.L. Suitable duration of grazing exclusion for restoration of a degraded alpine meadow on the eastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. CATENA 2021, 207, 105582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.N.; Sun, G.; Zhong, B.; Wang, E.T.; Zhao, C.Z.; Wang, Y.J.; Cheng, W.; Wu, N. Impacts of wise grazing on physicochemical and biological features of soil in a sandy grassland on the Tibetan Plateau. Land Degrad. Dev. 2019, 30, 719–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichert, J.M.; Suzuki, L.E.A.S.; Reinert, D.J.; Horn, R.; Hakansson, I. Reference bulk density and critical degree-of-compactness for no-till crop production in subtropical highly weathered soils. Soil Tillage Res. 2009, 102, 242–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.B.; Hu, Y.J.; Hill, R.L.; Wu, S.F.; Song, X.L. Combined effects of biomaterial amendments and rainwater harvesting on soil moisture, structure and apple roots in a rainfed apple orchard on the Loess Plateau, China. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 248, 106776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agbede, T.M.; Adekiya, A.O.; Eifediyi, E.K. Impact of poultry manure and NPK fertilizer on soil physical properties and growth and yield of carrot. J. Hortic. Res. 2017, 25, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.P.; Li, Y.; Si, B.C.; Wang, Y.Z.; Chen, X.G.; Wang, X.F.; Chen, H.R.; Wang, H.R.; Zhang, F.C.; Bai, Y.G.; et al. Optimizing biochar application to improve soil physical and hydraulic properties in saline-alkali soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 771, 144802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brar, B.S.; Singh, K.; Dheri, G.S.; Kumar, B. Carbon sequestration and soil carbon pools in a rice–wheat cropping system: Effect of long-term use of inorganic fertilizers and organic manure. Soil Tillage Res. 2013, 128, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, X.L.; Zhang, J.B.; Zhu, A.N.; Zhang, C.Z. Effects of long-term (23 years) mineral fertilizer and compost application on physical properties of fluvo-aquic soil in the North China Plain. Soil Tillage Res. 2016, 156, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchmann, H.; Gerzabek, M.H. Relationship between soil organic matter and micropores in a long-term experiment at Ultuna, Sweden. Z. P flanzenernaehr. Bodenk. 1999, 162, 493–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhaliwal, S.S.; Naresh, R.K.; Mandal, A.; Walia, M.K.; Gupta, R.K.; Singh, R.; Dhaliwal, M.K. Effect of manures and fertilizers on soil physical properties, build-up of macro and micronutrients and uptake in soil under different cropping systems: A review. J. Plant Nutr. 2019, 42, 2873–2900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Liang, C.; Zhang, B.; Yuan, Y.; Han, X. Higher rates of manure application lead to greater accumulation of both fungal and bacterial residues in macroaggregates of a clay soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2015, 84, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wortmann, C.S.; Shapiro, C.A. The effects of manure application on soil aggregation. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2008, 80, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Liang, Y.; Li, X.; Mao, J.; Wang, G.; Ma, X.; Li, Y. Grazing Decreases Soil Aggregation and Has Different Effects on Soil Organic Carbon Storage across Different Grassland Types in Northern Xinjiang, China. Land 2023, 12, 1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denef, K.; Six, J.; Paustian, K.; Merckx, R. Importance of macroaggregate dynamics in controlling soil carbon stabilization: Short-term effects of physical disturbance induced by dry-wet cycles. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2001, 33, 2145–2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.; Qin, Y.; Jimoh, S.O.; Hou, X.Y.; Zhang, N.; Gan, Y.M.; Luo, Y.J. Impacts of livestock grazing on vegetation characteristics and soil chemical properties of alpine meadows in the eastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Ecoscience 2020, 27, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Hu, N.; Xu, M.; Li, Z.; Lou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wu, C.; Wang, Z.L. 23-year manure and fertilizer application increases soil organic carbon sequestration of a rice–barley cropping system. Biol. Fert. Soils 2015, 51, 583–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.A.; Zhao, B.Q.; Yuan, L.; So, H.B. Effects of organic manure and fertilizers long-term located application on soil fertility and crop yield. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2009, 42, 2809–2819. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lima, D.L.; Santos, S.M.; Scherer, H.W.; Schneider, R.J.; Duarte, A.C.; Santos, E.B.; Esteves, V.I. Effects of organic and inorganic amendments on soil organic matter properties. Geoderma 2009, 150, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.L.; Han, X.Z.; Liang, Y.; Qiao, Y.F.; Li, L.J.; Li, N. Changes in soil organic carbon pools after 10 years of continuous manuring combined with chemical fertilizer in a Mollisol in China. Soil Tillage Res. 2012, 122, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wu, X.P.; Gebremikael, M.T.; Wu, H.J.; Cai, D.X.; Wang, B.S.; Li, B.G.; Zhang, J.C.; Li, Y.S.; Xi, J.L. Response of soil organic carbon fractions, microbial community composition and carbon mineralization to high-input fertilizer practices under an intensive agricultural system. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0195144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.H.; Zhu, B.; Wang, S.J.; Zhu, X.Y.; Vereecken, H.; Brüggemann, N. Stimulation of N2O emission by manure application to agricultural soils may largely offset carbon benefits: A global meta-analysis. Glob. Change Biol. 2017, 23, 4068–4083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Zhu, Z.K.; Xu, X.L.; Liu, S.L.; Jones, D.L.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Shibistova, O.; Wu, J.S.; Ge, T.D. Carbon and nitrogen recycling from microbial necromass to cope with C:N stoichiometric imbalance by priming. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 142, 107720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason-Jones, K.; Schmücker, N.; Kuzyakov, Y. Contrasting effects of organic and mineral nitrogen challenge the N-Mining Hypothesis for soil organic matter priming. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 124, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sainepo, B.M.; Gachene, C.K.; Karuma, A. Assessment of soil organic carbon fractions and carbon management index under different land use types in Olesharo Catchment, Narok County, Kenya. Carbon Balance Manag. 2018, 13, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diekow, J.; Mielniczuk, J.; Knicker, H.; Bayer, C.; Dick, D.P.; Kögel-Knabner, I. Soil C and N stocks as affected by cropping systems and nitrogen fertilisation in a southern Brazil Acrisol managed under no-tillage for 17 years. Soil Tillage Res. 2005, 81, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, B.; Huang, L.; Huang, Y.N.; Ali, K.K.; Li, X.K.; Lu, J.W. Straw management influences the stabilization of organic carbon by Fe(oxyhydr)oxides in soil aggregates. Geoderma 2020, 358, 113987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Wilson, B.; Ghoshal, S.; Senapati, N.; Mandal, B. Organic amendments influence soil quality and carbon sequestration in the Indo-Gangetic plains of India. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2012, 156, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirol-Padre, A.; Ladha, J.K. Assessing the reliability of permanganate-oxidizable carbon as an index of soil labile carbon. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2004, 68, 969–978. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Wang, B.Z.; Jia, Z.J.U. Phylogenetically distinct phylotypes modulate nitrification in a paddy soil. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 3218–3227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Six, J.; Carpentier, A.; van Kessel, C.; Merckx, R.; Harris, D.; Horwath, W.R.; Luscher, A. Impact of elevated CO2 on soil organic matter dynamics as related to changes in aggregate turnover and residue quality. Plant Soil 2001, 234, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henuk, Y.; Dingle, J. Poultry manure: Source of fertilizer, fuel and feed. World’s Poult. Sci. J. 2003, 59, 350–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agbede, T.M. Effect of tillage, biochar, poultry manure and NPK 15-15-15 fertilizer, and their mixture on soil properties, growth and carrot (Daucus carota L.) yield under tropical conditions. Heliyon 2021, 6, e07391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bader, B.R.; Taban, S.K.; Fahmi, A.S.; Abood, M.A.; Hamdi, G.J. Potassium availability in soil amended with organic matter and phosphorous fertiliser under water stress during maize (Zea mays L) growth. J. Saudi Soc. Agric. Sci. 2021, 20, 390–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhaliwal, S.S.; Naresh, R.K.; Mandal, A.; Singh, R.; Dhaliwal, M.K. Dynamics and transformations of micronutrients in agricultural soils as influenced by organic matter build-up: A review. Environ. Sustain. Indic. 2019, 1, 100007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moharana, P.C.; Sharma, B.M.; Biswas, D.R.; Dwivedi, B.S.; Singh, R.V. Long-term effect of nutrient management on soil fertility and soil organic carbon pools under a 6-year-old pearl millet-wheat cropping system in an Inceptisol of sub-tropical India. Field Crops Res. 2012, 136, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, X.; Ma, Q.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Y.; Isbell, F.; Wang, D. Nitrogen addition reduced ecosystem stability regardless of its impacts on plant diversity. J. Ecol. 2019, 107, 2427–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, M.; He, S.; Yu, S.; Jin, G. Effects of experimental N addition on plant diversity in an old-growth temperate forest. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 8, 5900–5911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kacorzyk, P.; Głab, T. Effect of ten years of mineral and organic fertilization on the herbage production of a mountain meadow. J. Elem. 2012, 22, 219–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.Y. Soil Science; Chinese Agricultural Press: Beijing, China, 2000; pp. 221–241. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wu, R.G.; Tiessen, H. Effect of land use on soil degradation in alpine grassland soil. China. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2002, 66, 1648–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B. The rangeland degradation in north China and its preventive strategy. Sci. Agric. Sin. 1997, 30, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, D.A.; and Sommers, L. Total carbon, organic carbon, and organic matter. Methods soil anal. Part 2 Chem. Microbiol. Prop. 1983, 9, 539–579. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, R. Analytical Methods of Soil Agrochemistry; China Agricultural Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, S.D. Soil Agricultural Chemistry Analysis, 3rd ed.; Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- NY/T 1121.19-2008; Soil Testing—Part 19: Method for Determination of Soil Water Stable Macro-Aggregates Distribution. Ministry of Agriculture of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2008.
- Chaudhary, S.; Dheri, G.S.; Brar, B.S. Long-term effects of NPK fertilizers and organic manures on carbon stabilization and management index under rice-wheat cropping system. Soil Tillage Res. 2017, 166, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefroy, R.D.B.; Blair, G.J.; Strong, W.M. Changes in soil organic matter with cropping as measured by organic carbon fractions and 13C natural isotope abundance. Plant Soil 1993, 155, 399–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, G.J.; Lefroy, R.D.B.; Lisle, L. Soil carbon fractions, based on their degree of oxidation and the development of a carbon management index for agricultural systems. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 1995, 46, 1459–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.W.; Qu, Q.; Lu, B.B.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, G.B.; Xue, S. Variation in soil organic carbon stability and driving factors after vegetation restoration in different vegetation zones on the Loess Plateau China. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 204, 104727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.B.; Qu, Y.Y.; Zhang, Z.J.; Zhao, J.G.; Hou, R.; Wang, H.R. Composition and nutrient analysis of captive giant panda diet. Acta Theriol. Sin. 2015, 35, 65–73. [Google Scholar]
| Fertilization Gradients (kg m−2) | Treatments | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soil Aggregate Fraction | SM | CD | SMCD | SM | CD | SMCD | SM | CD | SMCD | SM | CD | SMCD | SM | CD | SMCD |
| Macro-aggregates | SOC (g kg −1) | Cfrac1 (g kg −1) | Cfrac2 (g kg −1) | Cfrac3 (g kg −1) | Cfrac4 (g kg −1) | ||||||||||
| CK | 88 j ± 2.6 | - | - | 8.83 f ± 0.2 | - | - | 15.46 g ± 0.5 | - | - | 11.45 a ± 0.4 | - | - | 52.31 h ± 1.1 | - | - |
| 0.54 | 96.3 ghi ± 1.3 | 90 ij ± 2.4 | 89.5 j ± 1.2 | 9.37 cde ± 0.3 | 8.86 f ± 0.2 | 8.84 f ± 0.1 | 16.18 de ± 0.4 | 15.50 g ± 0.5 | 15.57 fg ± 0.8 | 11.15 abc ± 0.5 | 11.22 ab ± 0.4 | 11.30 ab ± 0.6 | 59.61 d–g ± 1.2 | 55.04 fgh ± 1.8 | 53.85 gh ± 1.9 |
| 1.08 | 101 d–g ± 2.5 | 98 fgh ± 3.7 | 104 cde ± 2.8 | 9.50 b–e ± 0.2 | 9.08 ef ± 0.4 | 9.62 bcd ± 0.3 | 16.47 b–e ± 0.6 | 16.39 cde ± 0.4 | 16.76 a–d ± 0.7 | 10.74 d–i ± 0.6 | 11.01 b–e ± 0.5 | 10.59 g–j ± 0.6 | 64.62 bcd ± 2.3 | 61.51 c–f ± 3.2 | 67.68 bc ± 2.4 |
| 1.62 | 108 abc ± 3.4 | 102 c–g ± 2.8 | 107 bcd ± 1.9 | 9.86 ab ± 0.4 | 9.23 def ± 0.3 | 9.69 abc ± 0.5 | 16.73 a–d ± 0.7 | 16.55 a–e ± 0.9 | 16.90 abc ± 0.7 | 10.46 h–k ± 0.7 | 10.80 c–h ± 0.8 | 10.39 ijk ± 0.7 | 70.94 ab ± 3.1 | 64.41 bcd ± 2.7 | 70.01 ab ± 2.6 |
| 2.16 | 113 a ± 2.2 | 104.2 cde ± 3.2 | 112 ab ± 1.6 | 10.10 a ± 0.5 | 9.61 bcd ± 0.4 | 9.76 abc ± 0.4 | 17.06 ab ± 0.9 | 16.67 a–e ± 0.6 | 17.08 a ± 0.9 | 10.10 k ± 0.8 | 10.60 f–j ± 0.9 | 10.24 jk ± 0.9 | 76.27 a ± 2.6 | 67.84 bc ± 2.9 | 76.69 a ± 2.7 |
| 2.70 | 98.8 e–h ± 3.6 | 92.7 hij ± 1.6 | 96.4 ghi ± 1.5 | 9.45 b–e ± 0.3 | 8.90 f ± 0.2 | 9.49 b–e ± 0.10 | 16.30 de ± 0.8 | 15.56 fg ± 0.6 | 16.46 b–e ± 0.4 | 11.05 bcd ± 0.6 | 11.07 bcd ± 0.4 | 10.97 b–f ± 0.9 | 62.03 cde ± 2.7 | 57.19 e–h ± 3.3 | 59.38 d–g ± 1.4 |
| GM | 103 c–f ± 2.6 | 97.6 fgh ± 2.7 | 102 c–g ± 1.8 | 9.65 bcd ± 0.34 | 9.13 ef ± 0.3 | 9.47 b–e ± 0.28 | 16.54 a–e ± 0.68 | 16.13 ef ± 0.6 | 16.55 a–e ± 0.7 | 10.65 e–i ± 0.64 | 10.94 b–g ± 0.6 | 10.61 f–j ± 0.7 | 66.75 bc ± 2.4 | 61.21 c–f ± 2.8 | 65.61 bcd ± 2.2 |
| Micro-aggregates | |||||||||||||||
| CK | 82 j ± 1.1 | - | - | 9.00 m ± 0.2 | - | - | 12.5 k ± 0.4 | - | - | 11 bc ± 0.2 | - | - | 49.50 k ± 1.4 | - | - |
| 0.54 | 90 hi ± 1.5 | 88.2 ij ± 2.1 | 86.3 ij ± 1.3 | 10.25 k ± 0.9 | 10.15 kl ± 0.4 | 10.00 l ± 0.2 | 13.60 i ± 0.6 | 13.20 j ± 0.9 | 12.95 j ± 0.8 | 10.86 cd ± 0.5 | 11.21 a ± 0.4 | 11.11 ab ± 0.5 | 55.27 h–k ± 1.9 | 53.70 ijk ± 2.1 | 52.26 jk ± 3.2 |
| 1.08 | 97.7 d–g ± 2.3 | 101 c–f ± 2.6 | 103 bcd ± 2.1 | 11.45 fgh ± 0.8 | 11.22 ij ± 0.6 | 11.89 cd ± 0.5 | 13.81 hi ± 0.5 | 13.93 gh ± 0.7 | 13.03 j ± 0.6 | 10.53 e ± 0.6 | 10.37 fgh ± 0.5 | 10.87 cd ± 0.6 | 61.94 d–g ± 2.8 | 65.48 b–e ± 3.6 | 67.21 bcd ± 4.3 |
| 1.62 | 105 bc ± 1.8 | 97 d–g ± 1.4 | 104 bcd ± 2.7 | 11.60 ef ± 0.8 | 11.36 ghi ± 0.5 | 12.11 b ± 0.4 | 14.31 def ± 0.6 | 14.15 efg ± 0.8 | 13.83 hi ± 0.5 | 10.21 ij ± 0.6 | 10.30 hij ± 0.5 | 10.19 jk ± 0.7 | 68.86 bc ± 3.3 | 61.17 d–h ± 3.5 | 67.19 bcd ± 3.6 |
| 2.16 | 109 ab ± 2.5 | 102 cde ± 1.7 | 113 a ± 2.9 | 12.04 bc ± 0.7 | 11.76 de ± 0.8 | 12.54 a ± 0.9 | 15.07 ab ± 0.7 | 14.40 de ± 0.8 | 15.30 a ± 0.8 | 10.05 kl ± 0.5 | 9.81 mn ± 0.4 | 9.73 n ± 0.8 | 71.83 ab ± 4.2 | 66.36 bcd ± 4.7 | 76.09 a ± 3.9 |
| 2.70 | 96.1 e–h ± 3.6 | 89.7 hi ± 2.8 | 92.6 ghi ± 3.2 | 11.48 fgh ± 0.4 | 11.87 d ± 0.9 | 11.14 j ± 0.6 | 14.85 bc ± 0.8 | 14.57 cd ± 0.9 | 14.92 b ± 0.9 | 10.72 d ± 0.4 | 10.89 c ± 0.7 | 9.90 lm ± 0.9 | 59.04 f–i ± 3.4 | 52.36 jk ± 4.4 | 56.69 g–j ± 4.7 |
| GM | 99.5 c–f ± 2.3 | 95.4 fgh ± 2.1 | 100 c–f ± 2.4 | 11.36 ghi ± 0.7 | 11.27 ij ± 0.6 | 11.53 fg ± 0.5 | 14.32 def ± 0.6 | 14.04 fgh ± 0.8 | 14.00 gh ± 0.7 | 10.47 efg ± 0.5 | 10.51 ef ± 0.5 | 10.35 ghi ± 0.7 | 63.40 c–f ± 3.1 | 59.83 e–i ± 3.6 | 63.90 c–f ± 3.9 |
| Fertilization Gradients (kg m−2) | Treatments | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soil Aggregate Fraction | SM | CD | SMCD | SM | CD | SMCD | SM | CD | SMCD | SM | CD | SMCD | SM | CD | SMCD |
| Macro-aggregates | CPI | L | LI | CMI | SI | ||||||||||
| CK | 1.00 i ± 0.00 | - | - | 0.68 a ± 0.02 | - | - | 1.00 a ± 0.00 | - | - | 100 a ± 0.00 | - | - | 1.46 g ± 0.04 | - | - |
| 0.54 | 1.09 fgh ± 0.04 | 1.02 hi ± 0.03 | 1.01 i ± 0.02 | 0.61 a–d ± 0.02 | 0.64 ab ± 0.02 | 0.66 ab ± 0.02 | 0.90 a–d ± 0.04 | 0.94 ab ± 0.02 | 0.97 ab ± 0.03 | 98.58 a ± 4.30 | 97.39 ab ± 3.55 | 98.77 a ± 6.45 | 1.62 d–g ± 0.06 | 1.54 fg ± 0.04 | 1.50 fg ± 0.08 |
| 1.08 | 1.15 c–f ± 0.02 | 1.11 efg ± 0.02 | 1.18 bcd ± 0.05 | 0.56 cde ± 0.02 | 0.59 b–e ± 0.03 | 0.54 c–f ± 0.02 | 0.83 cde ± 0.05 | 0.86 b–e ± 0.03 | 0.79 d–g ± 0.03 | 95.70 ab ± 8.20 | 96.59 ab ± 7.23 | 95.05 ab ± 7.12 | 1.76 b–e ± 0.05 | 1.69 c–f ± 0.06 | 1.82 bc ± 0.07 |
| 1.62 | 1.22 ab ± 0.05 | 1.14 c–f ± 0.03 | 1.21 bc ± 0.07 | 0.52 ef ± 0.03 | 0.56 cde ± 0.02 | 0.51 ef ± 0.03 | 0.76 efg ± 0.03 | 0.84 cde ± 0.03 | 0.77 efg ± 0.04 | 93.76 ab ± 6.90 | 95.30 ab ± 7.66 | 93.93 ab ± 5.97 | 1.91 ab ± 0.04 | 1.77 b–e ± 0.07 | 1.89 ab ± 0.09 |
| 2.16 | 1.28 a ± 0.06 | 1.19 bcd ± 0.04 | 1.29 a ± 0.06 | 0.48 f ± 0.02 | 0.54 def ± 0.03 | 0.47 f ± 0.02 | 0.71 fg ± 0.04 | 0.79 d–g ± 0.04 | 0.70 g ± 0.04 | 92.19 b ± 9.40 | 94.62 ab ± 8.88 | 91.39 b ± 8.76 | 2.04 a ± 0.07 | 1.83 bc ± 0.06 | 2.06 a ± 0.08 |
| 2.70 | 1.12 d–g ± 0.05 | 1.05 ghi ± 0.04 | 1.09 fgh ± 0.06 | 0.59 b–e ± 0.02 | 0.62 abc ± 0.03 | 0.63 abc ± 0.03 | 0.87 b–e ± 0.04 | 0.91 abc ± 0.04 | 0.92 abc ± 0.06 | 97.44 ab ± 9.80 | 95.76 ab ± 7.44 | 99.57 a ± 8.81 | 1.68 c–f ± 0.08 | 1.61 efg ± 0.04 | 1.60 efg ± 0.09 |
| GM | 1.17 b–e ± 0.04 | 1.10 efg ± 0.03 | 1.16 b–f ± 0.05 | 0.55 c–f ± 0.02 | 0.59 b–e ± 0.03 | 0.56 cde ± 0.02 | 0.80 c–g ± 0.04 | 0.86 b–e ± 0.03 | 0.82 c–f ± 0.04 | 94.78 ab ± 7.72 | 95.74 ab ± 6.95 | 94.88 ab ± 7.42 | 1.81 bcd ± 0.06 | 1.69 c–f ± 0.05 | 1.79 b–e ± 0.08 |
| Micro-aggregates | |||||||||||||||
| CK | 1.00 j ± 0.00 | - | - | 0.65 abc ± 0.03 | - | - | 1.00 ab ± 0.00 | - | - | 100 e ± 0.00 | - | - | 1.52 ij ± 0.03 | - | - |
| 0.54 | 1.09 hi ± 0.02 | 1.07 ij ± 0.04 | 1.05 ij ± 0.05 | 0.62 b–f ± 0.04 | 0.64 bcd ± 0.03 | 0.65 abc ± 0.02 | 0.95 b–e ± 0.02 | 0.98 bc ± 0.03 | 0.99 ab ± 0.04 | 105.07 cd ± 5 | 105.56 cd ± 4 | 104.57 cde ± 6 | 1.59 f–i ± 0.05 | 1.55 g–j ± 0.04 | 1.53 hij ± 0.09 |
| 1.08 | 1.19 d–g ± 0.03 | 1.23 c–f ± 0.06 | 1.25 bcd ± 0.03 | 0.57 d–h ± 0.02 | 0.54 ghi ± 0.04 | 0.53 ghi ± 0.03 | 0.88 c–g ± 0.04 | 0.83 fgh ± 0.02 | 0.80 gh ± 0.03 | 104.90 cde ± 7 | 101.73 de ± 6 | 101.84 de ± 5 | 1.73 c–g ± 0.05 | 1.84 b–e ± 0.08 | 1.87 a–d ± 0.07 |
| 1.62 | 1.29 bc ± 0.06 | 1.18 d–g ± 0.05 | 1.26 bcd ± 0.05 | 0.52 hi ± 0.03 | 0.58 c–h ± 0.03 | 0.55 f–i ± 0.02 | 0.80 gh ± 0.05 | 0.89 b–g ± 0.04 | 0.81 fgh ± 0.02 | 102.36 de ± 8 | 105.51 cd ± 5 | 103.24 de ± 8 | 1.90 abc ± 0.06 | 1.70 d–h ± 0.09 | 1.85 a–d ± 0.09 |
| 2.16 | 1.33 ab ± 0.04 | 1.24 cde ± 0.03 | 1.38 a ± 0.07 | 0.51 hi ± 0.04 | 0.55 f–i ± 0.02 | 0.49 i ± 0.03 | 0.78 gh ± 0.04 | 0.82 fgh ± 0.03 | 0.75 h ± 0.05 | 104.74 cde ± 7 | 103.05 de ± 9 | 104.23 de ± 8 | 1.93 ab ± 0.07 | 1.84 a–e ± 0.06 | 2.02 a ± 0.08 |
| 2.70 | 1.17 e–h ± 0.05 | 1.08 hi ± 0.06 | 1.13 ghi ± 0.06 | 0.61 b–f ± 0.02 | 0.71 a ± 0.03 | 0.62 b–e ± 0.01 | 0.94 b–e ± 0.04 | 1.09 a ± 0.02 | 0.96 bcd ± 0.03 | 112.02 b ± 8 | 118.98 a ± 9 | 109.27 bc ± 8 | 1.60 f–i ± 0.07 | 1.40 j ± 0.08 | 1.57 f–j ± 0.09 |
| GM | 1.22 c–f ± 0.04 | 1.16 fgh ± 0.05 | 1.21 c–f ± 0.05 | 0.56 e–h ± 0.03 | 0.59 b–g ± 0.03 | 0.55 f–i ± 0.02 | 0.86 d–g ± 0.04 | 0.91 b–f ± 0.03 | 0.84 e–h ± 0.3 | 105.50 cd ± 7 | 105.40 cd ± 6 | 104.10 de ± 7 | 1.75 b–f ± 0.06 | 1.66 e–i ± 0.07 | 1.78 b–e ± 0.08 |
| Fertilization Gradients (kg m−2) | Treatments | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soil Aggregate Fraction | SM | CD | SMCD | SM | CD | SMCD | SM | CD | SMCD |
| Macro-aggregates | TN (g kg −1) | AN (mg kg −1) | TP (g kg −1) | ||||||
| CK | 7.40 k ± 0.20 | - | - | 514 j ± 10 | - | - | 0.71 h ± 0.02 | - | - |
| 0.54 | 8.14 ghi ± 0.25 | 7.97 j ± 0.29 | 8.17 gh ± 0.24 | 538 i ± 16 | 563 h ± 10 | 595 g ± 15 | 0.82 g ± 0.03 | 0.85 fg ± 0.04 | 0.89 d–g ± 0.02 |
| 1.08 | 8.18 g ± 0.30 | 8.05 hij ± 0.30 | 7.97 j ± 0.20 | 564 h ± 13 | 590 g ± 12 | 610 fg ± 18 | 0.91 c–g ± 0.05 | 0.90 d–g ± 0.03 | 0.86 efg ± 0.01 |
| 1.62 | 9.12 ab ± 0.28 | 8.34 f ± 0.50 | 9.22 a ± 0.30 | 602 fg ± 11 | 635 cde ± 17 | 655 c ± 12 | 0.99 abc ± 0.04 | 1.02 ab ± 0.05 | 0.97 a–d ± 0.03 |
| 2.16 | 8.99 c ± 0.36 | 8.07 g–j ± 0.45 | 9.00 bc ± 0.43 | 643 cd ± 12 | 676 b ± 14 | 704 a ± 20 | 0.96 a–d ± 0.08 | 1.00 abc ± 0.07 | 1.01 a ± 0.05 |
| 2.70 | 8.81 d ± 0.40 | 8.02 ij ± 0.35 | 8.54 e ± 0.54 | 618 ef ± 19 | 632 de ± 11 | 650 cd ± 14 | 0.95 a–e ± 0.06 | 0.84 fg ± 0.04 | 0.83 g ± 0.07 |
| GM | 8.64 e ± 0.31 | 8.09 ghi ± 0.36 | 8.58 e ± 0.32 | 593 g ± 14 | 619 ef ± 12 | 643 cd ± 16 | 0.93 b–f ± 0.05 | 0.92 c–g ± 0.04 | 0.91 c–g ± 0.03 |
| Micro-aggregates | |||||||||
| CK | 7.34 l ± 0.25 | - | - | 507 i ± 12 | - | - | 0.70 h ± 0.03 | - | - |
| 0.54 | 8.10 fh ± 0.50 | 7.87 hij ± 0.60 | 7.69 k ± 0.45 | 532 h ± 15 | 582 h ± 13 | 583 g ± 10 | 0.76 e–h ± 0.04 | 0.74 gh ± 0.03 | 0.83 cd ± 0.05 |
| 1.08 | 8.29 e ± 0.40 | 7.98 ghi ± 0.20 | 7.85 ij ± 0.30 | 550 h ± 18 | 585 g ± 16 | 601 fg ± 14 | 0.81 def ± 0.02 | 0.86 cd ± 0.04 | 0.73 e–h ± 0.04 |
| 1.62 | 9.01 b ± 0.36 | 8.15 f ± 0.35 | 9.15 a ± 0.32 | 594 fg ± 13 | 628 cd ± 18 | 639 c ± 13 | 1.01 a ± 0.05 | 0.95 ab ± 0.04 | 0.84 cd ± 0.01 |
| 2.16 | 8.76 c ± 0.41 | 7.99 gh ± 0.56 | 8.88 c ± 0.11 | 631 c ± 17 | 661 b ± 20 | 695 a ± 16 | 0.92 bc ± 0.07 | 0.85 cd ± 0.06 | 1.02 a ± 0.06 |
| 2.70 | 8.59 d ± 0.40 | 7.80 jk ± 0.25 | 8.40 e ± 0.36 | 606 ef ± 20 | 624 cde ± 15 | 638 c ± 15 | 0.81 d–g ± 0.08 | 0.75 e–h ± 0.08 | 0.71 fgh ± 0.06 |
| GM | 8.55 d ± 0.30 | 7.95 hi ± 0.32 | 8.39 e ± 0.47 | 582 g ± 16 | 610 def ± 17 | 631 c ± 13 | 0.86 cd ± 0.05 | 0.83 de ± 0.05 | 0.82 cd ± 0.04 |
| Macro-aggregates | AP (mg kg−1) | TK (g kg−1) | AK (mg kg−1) | ||||||
| CK | 17.26 f ± 0.5 | - | - | 6.76 i ± 0.12 | - | - | 557 i ± 12 | - | - |
| 0.54 | 19.81 c–f ± 0.6 | 18.80 ef ± 0.2 | 22.53 a–d ± 0.7 | 7.07 h ± 0.17 | 7.14 gh ± 0.17 | 7.18 g ± 0.20 | 583 fgh ± 14 | 580 gh ± 19 | 596 a–e ± 18 |
| 1.08 | 20.00 c–f ± 0.7 | 19.86 c–f ± 0.3 | 19.43 def ± 0.9 | 7.15 gh ± 0.22 | 7.11 gh ± 0.23 | 7.21 g ± 0.13 | 584 e–h ± 17 | 587 d–h ± 14 | 599 a–d ± 25 |
| 1.62 | 20.73 cde ± 0.9 | 20.80 b–e ± 0.5 | 20.70 cde ± 0.5 | 7.55 de ± 0.08 | 7.44 ef ± 0.21 | 7.75 c ± 0.11 | 606 ab ± 19 | 609 a ± 12 | 602 abc ± 11 |
| 2.16 | 24.13 ab ± 0.8 | 23.00 abc ± 0.6 | 24.66 a ± 0.6 | 7.87 b ± 0.15 | 7.74 c ± 0.16 | 8.03 a ± 0.18 | 600 a–d ± 20 | 587 d–h ± 11 | 592 c–g ± 16 |
| 2.70 | 23.13 abc ± 0.9 | 22.06 a–e ± 0.8 | 19.16 ef ± 0.8 | 7.88 b ± 0.19 | 7.65 cd ± 0.18 | 7.87 b ± 0.14 | 597 a–e ± 22 | 579 h ± 23 | 598 a–e ± 18 |
| GM | 21.56 a–e ± 0.8 | 20.90 b–e ± 0.5 | 21.30 b–e ± 0.7 | 7.50 ef ± 0.16 | 7.41 f ± 0.19 | 7.60 d ± 0.15 | 594 b–f ± 18 | 588 d–h ± 15 | 597 a–e ± 17 |
| Micro-aggregates | |||||||||
| CK | 17.00 f ± 0.4 | - | - | 6.71 h ± 0.10 | - | - | 550 h ± 8 | - | - |
| 0.54 | 19.30 def ± 0.8 | 18.36 ef ± 0.7 | 21.91 abc ± 0.6 | 6.81 gh ± 0.14 | 6.87 fg ± 0.20 | 6.84 fg ± 0.08 | 576 fg ± 10 | 567 g ± 13 | 587 c–f ± 11 |
| 1.08 | 19.33 def ± 0.5 | 18.90 def ± 0.6 | 18.26 ef ± 0.7 | 6.92 ef ± 0.13 | 6.93 ef ± 0.14 | 6.94 ef ± 0.17 | 586 c–f ± 12 | 581 efg ± 16 | 596 abcd ± 17 |
| 1.62 | 20.06 b–e ± 0.7 | 19.49 cde ± 0.9 | 18.70 def ± 0.9 | 6.98 e ± 0.19 | 7.09 d ± 0.11 | 7.11 d ± 0.19 | 600 abc ± 17 | 590 b–f ± 19 | 607 a ± 14 |
| 2.16 | 23.76 a ± 0.6 | 21.10 bcd ± 0.7 | 20.26 b–e ± 0.9 | 7.30 c ± 0.20 | 7.42 b ± 0.09 | 7.28 c ± 0.22 | 588 c–f ± 20 | 583 def ± 15 | 585 c–f ± 18 |
| 2.70 | 22.02 ab ± 0.8 | 21.00 bcd ± 0.4 | 18.13 ef ± 0.5 | 7.50 b ± 0.16 | 7.65 a ± 0.16 | 7.75 a ± 0.12 | 604 ab ± 16 | 578 efg ± 10 | 580 efg ± 14 |
| GM | 20.89 bcd ± 0.7 | 19.77 b–e ± 0.6 | 19.45 c–f ± 0.6 | 7.10 d ± 0.16 | 7.19 d ± 0.14 | 7.17 d ± 0.15 | 591 b–e ± 15 | 580 efg ± 14 | 590b–e ± 14 |
| Soil Parameter | Values | Measurement Method | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| SOC (g kg−1) | 3.20 ± 78.3 | Walkley–Black dichromate oxidation | Nelson and Sommers [92] |
| TN (g kg−1) | 0.50 ± 7.12 | Semimicro-Kjeldahl method | Lu [93] |
| TP (g kg−1) | 0.04 ± 0.70 | Colorimetric method | Lu [93] |
| TK (g kg−1) | 0.33 ± 6.55 | Colorimetric method | Lu [93] |
| pH | 0.22 ± 7.8 | pH meter | Lu [93] |
| BD (g cm−3) | 0.03 ± 0.78 | Core sampler method | Bao [94] |
| P (%) | 0.40 ± 70.8 | (1 − (BD/PD)) × 100 equation | Bao [94] |
| Parameters | Zn | Cu | Fe | Mn |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Current of lamp (mA) | 10 | 7.5 | 10 | 3 |
| Wavelength analysis (nm) | 213.9 | 324.8 | 248.3 | 279.5 |
| Width of slit (nm) | 1.3 | 1.3 | 0.2 | 0.5 |
| Type of atomizer flame | Standard burner air-acetylene | Standard burner air-acetylene | Standard burner air-acetylene | Standard burner air-acetylene |
| Velocity of gas (L/h) | 1.6 | 1.6 | 1.6 | 50 |
| Type of consumption head (mm) | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 100 |
| Height of consumption head (mm) | 7.5 | 7.5 | 7.5 | 6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sadiq, M.; Rahim, N.; Tahir, M.M.; Shaheen, A.; Ran, F.; Chen, G.; Bai, X. Soil Bulk Density, Aggregates, Carbon Stabilization, Nutrients and Vegetation Traits as Affected by Manure Gradients Regimes Under Alpine Meadows of Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau Ecosystem. Plants 2025, 14, 1442. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14101442
Sadiq M, Rahim N, Tahir MM, Shaheen A, Ran F, Chen G, Bai X. Soil Bulk Density, Aggregates, Carbon Stabilization, Nutrients and Vegetation Traits as Affected by Manure Gradients Regimes Under Alpine Meadows of Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau Ecosystem. Plants. 2025; 14(10):1442. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14101442
Chicago/Turabian StyleSadiq, Mahran, Nasir Rahim, Majid Mahmood Tahir, Aqila Shaheen, Fu Ran, Guoxiang Chen, and Xiaoming Bai. 2025. "Soil Bulk Density, Aggregates, Carbon Stabilization, Nutrients and Vegetation Traits as Affected by Manure Gradients Regimes Under Alpine Meadows of Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau Ecosystem" Plants 14, no. 10: 1442. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14101442
APA StyleSadiq, M., Rahim, N., Tahir, M. M., Shaheen, A., Ran, F., Chen, G., & Bai, X. (2025). Soil Bulk Density, Aggregates, Carbon Stabilization, Nutrients and Vegetation Traits as Affected by Manure Gradients Regimes Under Alpine Meadows of Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau Ecosystem. Plants, 14(10), 1442. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14101442






