Detection of Different Patterns of Genome-Wide Gene Expression Disturbance in Three Nullisomy Lines in Allotetraploid Brassica napus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
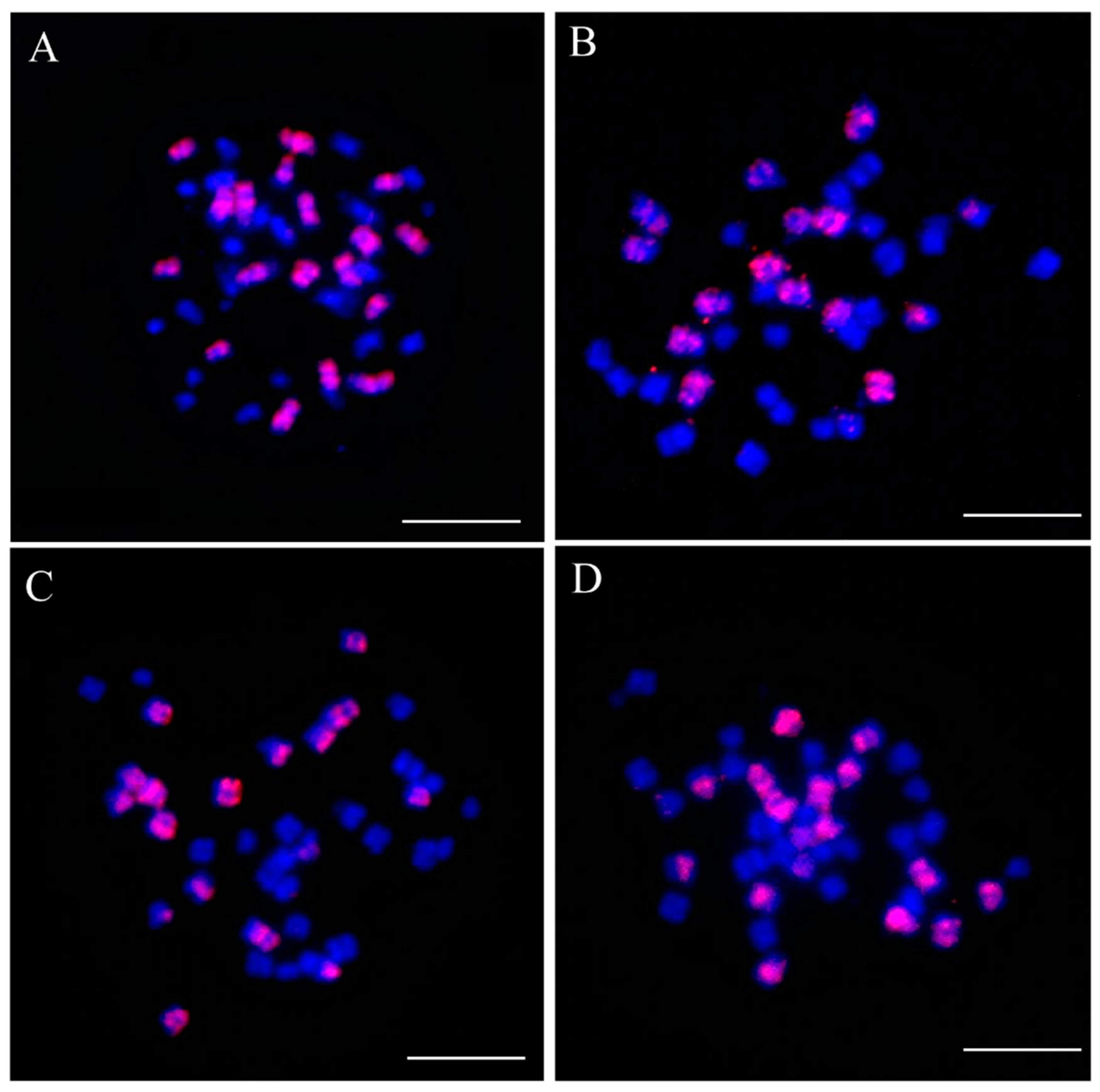
2.1. FISH Analysis of Brassica napus Nullisomy and Euploid Oro Lines
2.2. The Morphology of Nullisomy Plants
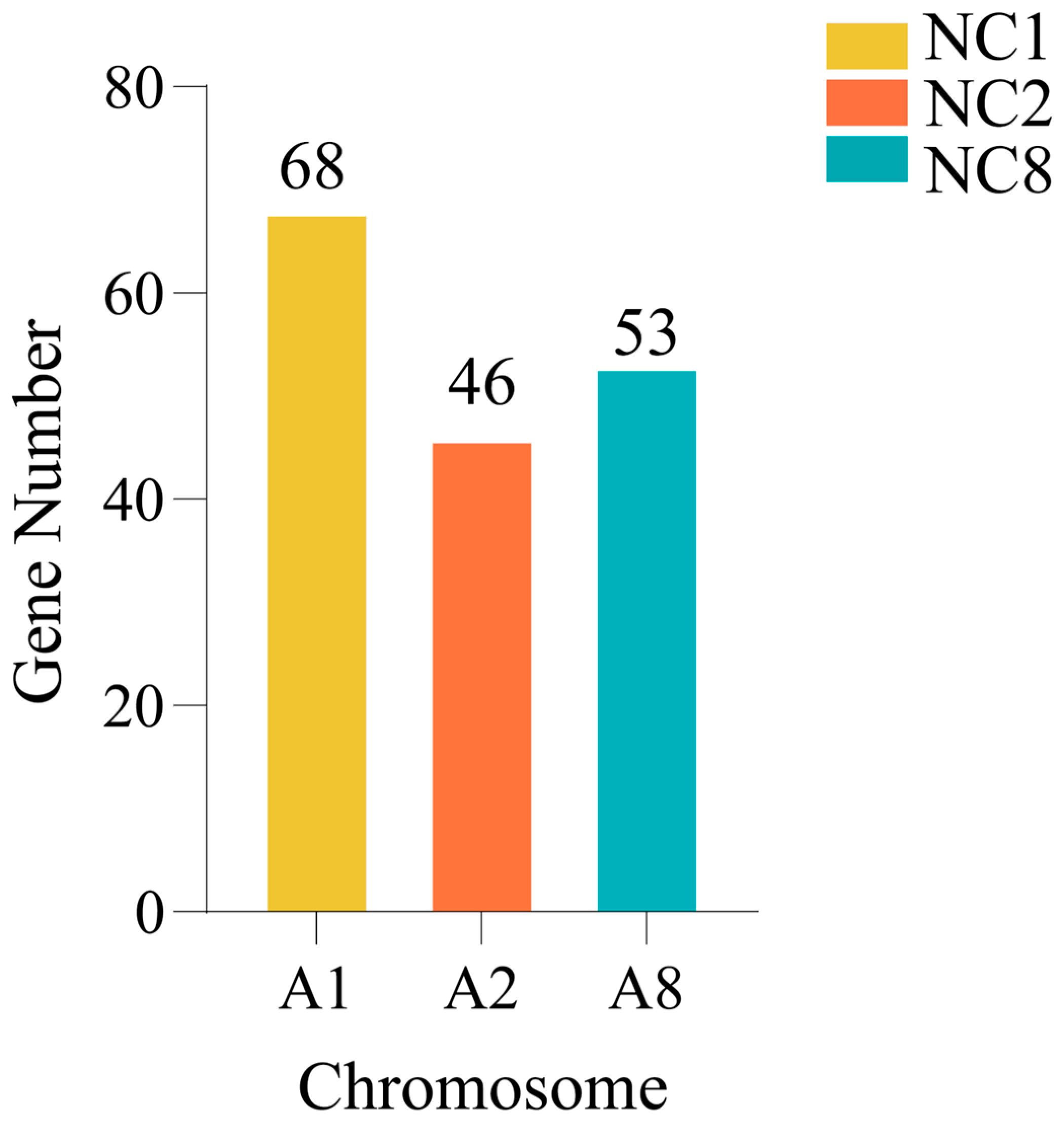
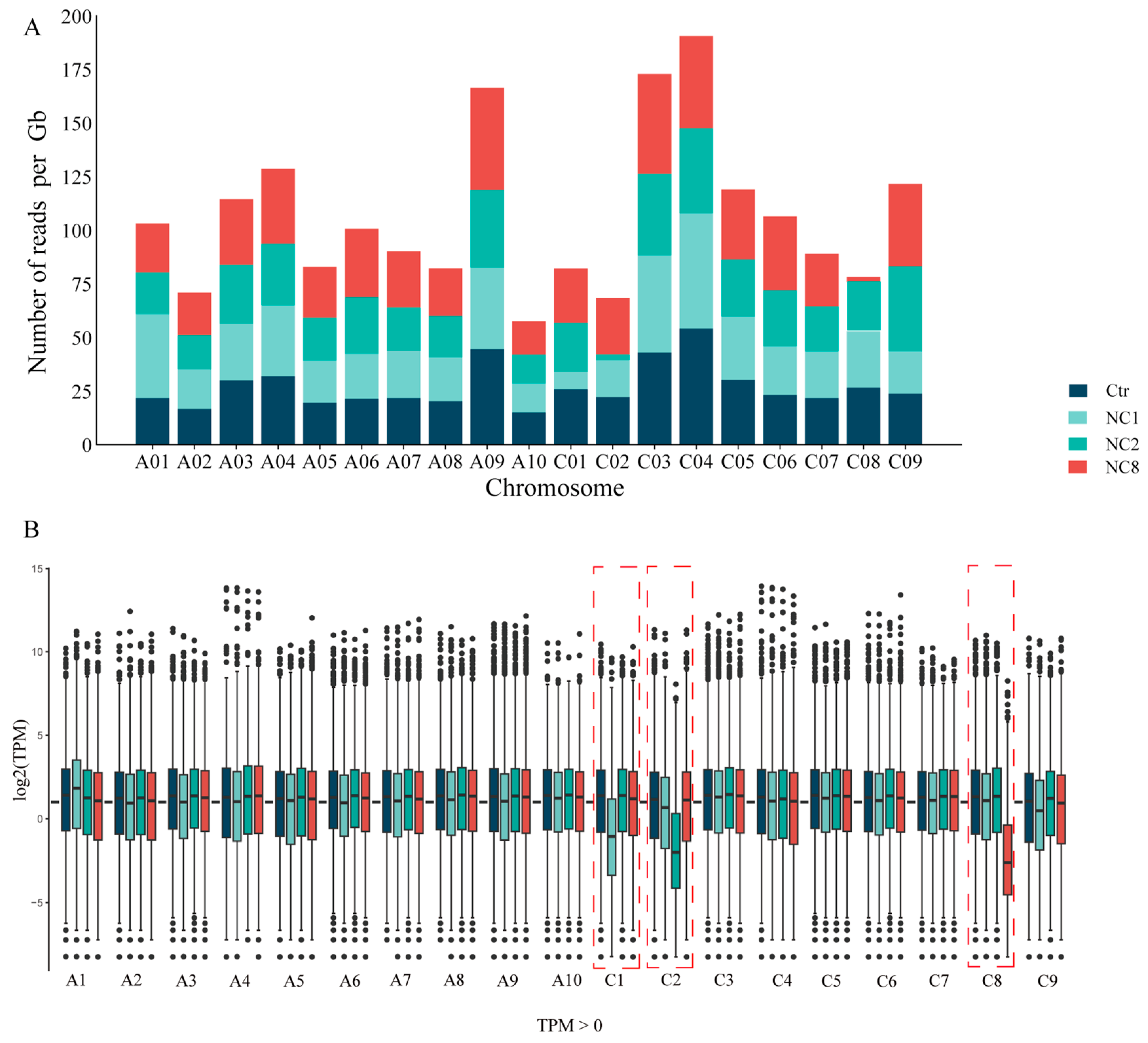
2.3. RNA-Seq Reveals the Deletion of Chromosomes C1, C2, and C8
2.4. Overall Differential Expression of Genes Between the Aneuploid and Euploid
2.5. The Effect of Hypochromatosis on the Gene Expression of the Other Chromosomes of the Plant Genome
2.6. Perturbation of Gene Expression Due to Chromosome Deletion
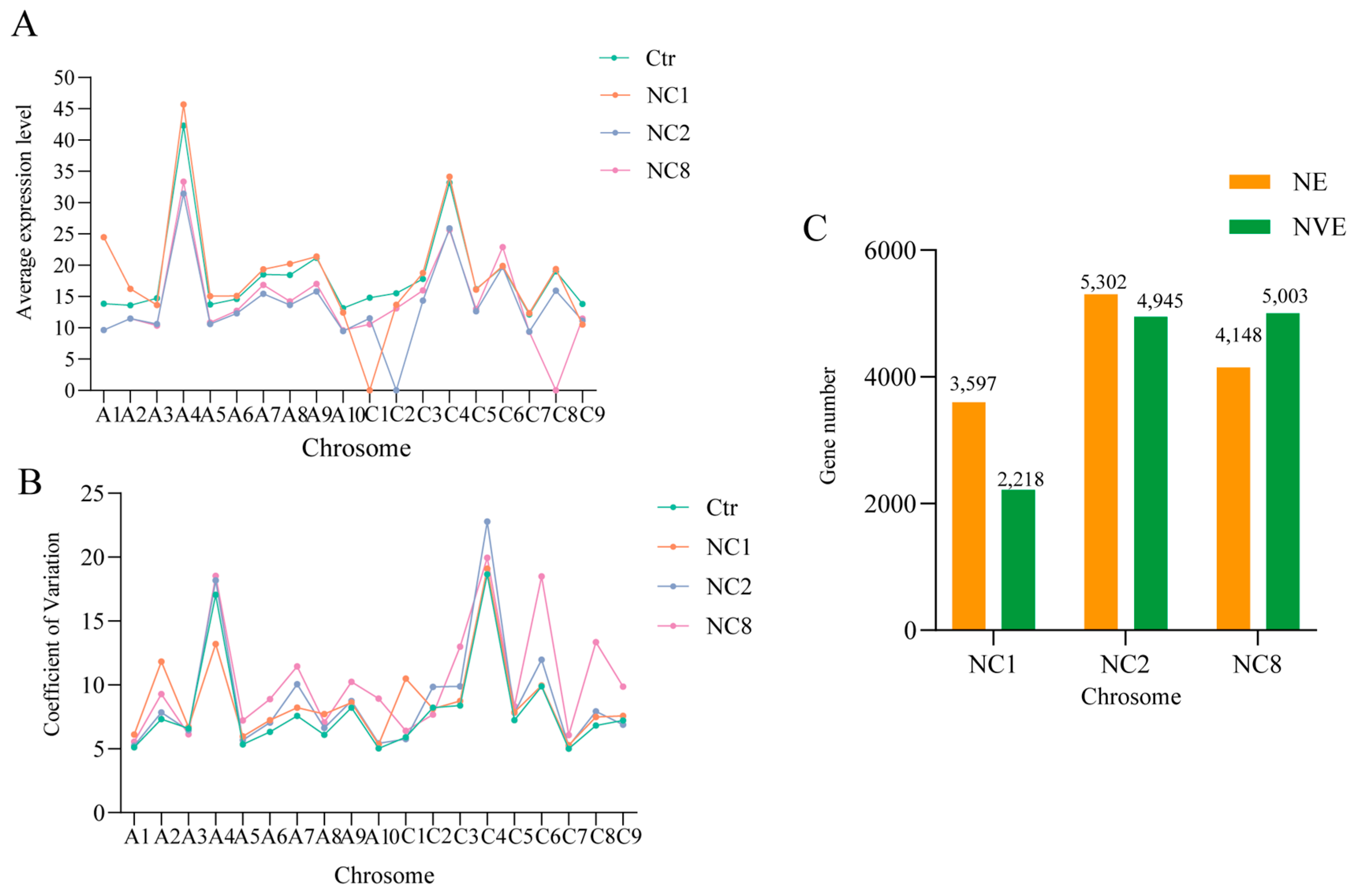
2.7. Expression Changes in Homologous Chromosomes
2.8. Enrichment Analysis of DEGs
3. Discussion
3.1. Effects of Aneuploidy on Phenotypic Variation and Function
3.2. Global Perturbation of Gene Expression
3.3. Compensatory Upregulation of Chromosomes
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials
4.2. Cytological Analysis and Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization
4.3. RNA Extraction and cDNA Library Preparation
4.4. Differential Gene Enrichment Analysis
4.5. RT-qPCR Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A

| Genome ID | Name | Forward Primer (5′-3′) | Reverse Primer (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|---|
| BnaC02g00690D | Actin-7 | GGTTCGACCATGTTCCCAGGT | GTGCTGAGGGATGCAAGGATG |
| Chromosome | Number of Reference Genes | Expressed Genes | R (%) (EGs/RGs) | DEGs | R (%) (DEGs/EGs) | Group |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A01 | 4296 | 2306 | 53.68 | 437 | 18.95 | Middle |
| A02 | 4203 | 2121 | 50.46 | 338 | 15.94 | Low |
| A03 | 5946 | 3398 | 57.15 | 546 | 16.07 | Low |
| A04 | 3014 | 1579 | 52.39 | 363 | 22.99 | High |
| A05 | 5002 | 2274 | 45.46 | 555 | 24.41 | High |
| A06 | 4533 | 2496 | 55.06 | 457 | 18.31 | Middle |
| A07 | 3904 | 2235 | 57.25 | 466 | 18.31 | Middle |
| A08 | 3222 | 1824 | 46.61 | 332 | 18.20 | Middle |
| A09 | 7218 | 3616 | 50.10 | 811 | 22.43 | High |
| A10 | 3021 | 1762 | 58.33 | 359 | 6.92 | Low |
| A | 44,359 | 23,611 | 53.23 | 4664 | 19.75 | — |
| C01 | 5168 | 2527 | 48.90 | 540 | 21.37 | Middle |
| C02 | 5574 | 1061 | 19.03 | 817 | 77.00 | — |
| C03 | 8178 | 4124 | 50.43 | 834 | 20.22 | Middle |
| C04 | 6183 | 2758 | 44.61 | 631 | 22.88 | High |
| C05 | 5761 | 2951 | 51.22 | 570 | 19.32 | Middle |
| C06 | 4597 | 2325 | 50.58 | 380 | 16.34 | Low |
| C07 | 5507 | 2732 | 49.61 | 436 | 15.96 | Low |
| C08 | 5349 | 2576 | 48.16 | 466 | 18.09 | Middle |
| C09 | 6245 | 2734 | 43.78 | 585 | 21.40 | High |
| C | 52,562 | 23,788 | 45.26 | 5259 | 22.11 | — |
| Total | 96,924 | 47,399 | 48.90 | 9921 | 20.93 | — |
| Chromosome | Number of Reference Genes | Expressed Genes | R (%) (EGs/RGs) | DEGs | R (%) (DEGs/EGs) | Group |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A01 | 4296 | 2351 | 54.73 | 323 | 13.74 | Low |
| A02 | 4203 | 2138 | 50.87 | 450 | 21.05 | High |
| A03 | 5946 | 3373 | 56.73 | 627 | 18.59 | Middle |
| A04 | 3014 | 1581 | 52.46 | 379 | 23.97 | High |
| A05 | 5002 | 2305 | 46.08 | 567 | 24.60 | High |
| A06 | 4533 | 2499 | 55.13 | 509 | 20.37 | High |
| A07 | 3904 | 2275 | 58.28 | 300 | 13.19 | Low |
| A08 | 3222 | 1832 | 56.86 | 293 | 15.99 | Middle |
| A09 | 7218 | 3639 | 50.42 | 622 | 17.09 | Middle |
| A10 | 3021 | 1820 | 60.24 | 194 | 10.66 | Low |
| A | 44,359 | 23,813 | 53.68 | 4264 | 17.91 | — |
| C01 | 5168 | 2569 | 49.71 | 361 | 14.05 | Middle |
| C02 | 5574 | 2459 | 44.12 | 368 | 14.97 | Middle |
| C03 | 8178 | 4188 | 51.21 | 586 | 13.99 | Middle |
| C04 | 6183 | 2751 | 44.49 | 563 | 20.47 | High |
| C05 | 5761 | 3019 | 52.40 | 424 | 14.04 | Middle |
| C06 | 4597 | 2348 | 51.08 | 325 | 13.84 | Middle |
| C07 | 5507 | 2781 | 50.50 | 382 | 13.74 | Low |
| C08 | 5349 | 1093 | 20.43 | 918 | 83.99 | — |
| C09 | 6245 | 2805 | 44.92 | 362 | 12.91 | Low |
| C | 52,562 | 24,013 | 45.69 | 4289 | 17.86 | — |
| Total | 96,924 | 47,826 | 49.34 | 8553 | 17.88 | — |
| Genes | Gene ID | Gene Expression (TPM) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oro | NC1 | ||
| ARF | BnaA01G0267900ZS | 8.94 | 13.08 |
| BnaA02G0396100ZS | 2.82 | 2.51 | |
| BnaA02G0396600ZS | 4.93 | 4.83 | |
| BnaA04G0008800ZS | 6.74 | 3.94 | |
| BnaA05G0014400ZS | 0.08 | 0.12 | |
| BnaA09G0077100ZS | 21.69 | 16.17 | |
| BnaA09G0559300ZS | 4.19 | 1.90 | |
| BnaA09G0702900ZS | 3.54 | 2.14 | |
| BnaC01G0174100ZS | 0.37 | 0.27 | |
| BnaC01G0328100ZS | 7.26 | 1.99 | |
| BnaC02G0529200ZS | 11.68 | 8.16 | |
| BnaC03G0559800ZS | 21.86 | 17.08 | |
| BnaC04G0014300ZS | 0.45 | 0.10 | |
| BnaC04G0265800ZS | 3.71 | 0.77 | |
| BnaC08G0407500ZS | 4.69 | 2.74 | |
| BnaC09G0068500ZS | 3.51 | 2.52 | |
| TRY | BnaA02G0140700ZS | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| BnaA03G0131600ZS | 1.59 | 0.00 | |
| BnaA10G0097300ZS | 0.00 | 1.57 | |
| BnaC01G0222200ZS | 1.66 | 0.00 | |
| BnaC01G0222400ZS | 3.82 | 0.00 | |
| BnaC02G0178400ZS | 1.46 | 0.00 | |
| BnaC03G0153000ZS | 0.10 | 1.98 | |
| BnaC09G0353000ZS | 2.30 | 0.60 | |
| R2R3 | BnaA01G0097700ZS | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| BnaA08G0111700ZS | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| BnaC01G0119400ZS | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| BnaC03G0706500ZS | 0.00 | 0.02 | |
| BnaC07G0425500ZS | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| EGL3 | BnaA09G0134400ZS | 0.32 | 0.41 |
| BnaA09G0148900ZS | 0.90 | 0.15 | |
| BnaC09G0142800ZS | 0.67 | 0.72 | |
| BnaC09G0162100ZS | 0.81 | 0.21 | |
| WU | BnaA06G0314000ZS | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| BnaA09G0114500ZS | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| BnaC03G0508400ZS | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| BnaC09G0117600ZS | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| MYB3 | BnaA07G0121400ZS | 4.52 | 2.11 |
| BnaC07G0178800ZS | 2.86 | 2.14 | |
| CPC | BnaA04G0292300ZS | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| BnaC04G0015600ZS | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| GL1 | BnaA09G0040500ZS | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| BnaC07G0310800ZS | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| TMM | BnaA07G0224900ZS | 1.02 | 0.12 |
| BnaC06G0242000ZS | 1.63 | 0.1 | |
| GL2 | BnaC06G0240800ZS | 0.08 | 0.12 |
References
- Letourneau, A.; Santoni, F.A.; Bonilla, X.; Sailani, M.R.; Gonzalez, D.; Kind, J.; Chevalier, C.; Thurman, R.; Sandstrom, R.S.; Hibaoui, Y.; et al. Domains of genome-wide gene expression dysregulation in Down’s Syndrome. Nature 2014, 508, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, J.J.; Amon, A. New insights into the troubles of aneuploidy. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2012, 28, 189–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Xiang, Y.; Zeng, P.; Cai, B.; Huang, X.; Ge, X.; Weng, Q.; Li, Z. Genome-wide gene expression disturbance by single A1/C1 chromosome substitution in Brassica Rapa restituted from natural B. napus. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonarakis, S.E.; Lyle, R.; Dermitzakis, E.T.; Reymond, A.; Deutsch, S. Chromosome 21 and down syndrome: From genomics to pathophysiology. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2004, 5, 725–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McClintock, B. A cytological and genetical study of triploid maize. Genetics 1929, 14, 180–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, K.; Multani, D.S.; Khush, G.S. Secondary trisomics and telotrisomics of rice: Origin, characterization, and use in determining the orientation of chromosome map. Genetics 1996, 143, 517–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Shao, Y.; Pan, Q.; Ge, X.; Li, Z. Genome-wide gene expression perturbation induced by loss of C2 chromosome in allotetraploid Brassica napus L. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bin, Z.; Qi, P.; Dongao, H.; Pan, Z.; Bowei, C.; Xianhong, G.; Zaiyun, L. Transcriptional aneuploidy responses of Brassica Rapa-Oleracea Monosomic Alien Addition Lines (MAALs) derived from natural allopolyploid B. napus. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birchler, J.A.; Newton, K.J. Modulation of protein levels in chromosomal dosage series of maize: The biochemical basis of aneuploid syndromes. Genetics 1981, 99, 247–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Davis, D.; Birchler, J.A. Dosage effects on gene expression in a maize ploidy series. Genetics 1996, 142, 1349–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chester, M.; Gallagher, J.P.; Symonds, V.V.; Cruz Da Silva, A.V.; Mavrodiev, E.V.; Leitch, A.R.; Soltis, P.S.; Soltis, D.E. Extensive chromosomal variation in a recently formed natural allopolyploid species, Tragopogon miscellus (Asteraceae). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 1176–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Z.; Gaeta, R.T.; Pires, J.C. Homoeologous shuffling and chromosome compensation maintain genome balance in resynthesized allopolyploid Brassica napus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 7908–7913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Bian, Y.; Gou, X.; Zhu, B.; Xu, C.; Qi, B.; Li, N.; Rustgi, S.; Zhou, H.; Han, F.; et al. Persistent whole-chromosome aneuploidy is generally associated with nascent allohexaploid wheat. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 3447–3452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huettel, B.; Kreil, D.P.; Matzke, M.; Matzke, A.J.M. Effects of aneuploidy on genome structure, expression, and interphase organization in Arabidopsis thaliana. PLoS Genet. 2008, 4, e1000226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morard, M.; Macías, L.G.; Adam, A.C.; Lairón-Peris, M.; Pérez-Torrado, R.; Toft, C.; Barrio, E. Aneuploidy and ethanol tolerance in saccharomyces cerevisiae. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperling, A.L.; Glover, D.M. Aneuploidy during development in facultative parthenogenetic Drosophila. Heredity 2024, 132, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, I.M.; Dilkes, B.P.; Miller, E.S.; Burkart-Waco, D.; Comai, L. Phenotypic consequences of aneuploidy in Arabidopsis thaliana. Genetics 2010, 186, 1231–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, D.; Guan, J.; Luo, J.; Zhao, L.; Li, Y.; Chen, W.; Zhang, L.; Ning, S.; Yuan, Z.; Li, A.; et al. A transcriptomic view of the ability of nascent hexaploid wheat to tolerate aneuploidy. BMC Plant Biol. 2020, 20, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Li, N.; Gong, L.; Gou, X.; Wang, B.; Deng, X.; Li, C.; Dong, Q.; Zhang, H.; Liu, B. Global analysis of gene expression in response to whole-chromosome aneuploidy in hexaploid wheat. Plant Physiol. 2017, 175, 828–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udall, J.A.; Wendel, J.F. Polyploidy and crop improvement. Crop Sci. 2006, 46, S-3–S-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, J.D.; Shields, C.R.; Cohen, D.B.; Orton, T.J. Chloroplast DNA evolution and the origin of amphidiploid Brassica species. Theor. Appl. Genet. 1983, 65, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szadkowski, E.; Eber, F.; Huteau, V.; Lodé, M.; Huneau, C.; Belcram, H.; Coriton, O.; Manzanares-Dauleux, M.J.; Delourme, R.; King, G.J.; et al. The first meiosis of resynthesized Brassica napus, a genome blender. New Phytol. 2010, 186, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Pan, Q.; Cui, C.; Tan, C.; Ge, X.; Shao, Y.; Li, Z. Genome-specific differential gene expressions in resynthesized Brassica allotetraploids from pair-wise crosses of three cultivated diploids revealed by RNA-seq. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albertin, W.; Balliau, T.; Brabant, P.; Chèvre, A.-M.; Eber, F.; Malosse, C.; Thiellement, H. Numerous and rapid nonstochastic modifications of gene products in newly synthesized Brassica napus allotetraploids. Genetics 2006, 173, 1101–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaeta, R.T.; Pires, J.C.; Iniguez-Luy, F.; Leon, E.; Osborn, T.C. Genomic changes in resynthesized Brassica napus and their effect on gene expression and phenotype. Plant Cell 2007, 19, 3403–3417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Moshgabadi, N.; Adams, K.L. Extensive changes to alternative splicing patterns following allopolyploidy in natural and resynthesized polyploids. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 16122–16127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalhoub, B.; Denoeud, F.; Liu, S.; Parkin, I.A.P.; Tang, H.; Wang, X.; Chiquet, J.; Belcram, H.; Tong, C.; Samans, B.; et al. Early allopolyploid evolution in the post-Neolithic Brassica napus oilseed genome. Science 2014, 345, 950–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, J.; Zhang, B.; Yang, X.; Hammond, J.P.; Ding, G.; Wang, S.; Cai, H.; Wang, C.; Xu, F.; et al. Genome-wide association study dissects the genetic control of plant height and branch number in response to low-phosphorus stress in Brassica napus. Ann. Bot. 2021, 128, 919–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Yang, H.; Chen, C.; Hou, J.; Ji, T.; Cheng, J.; Birchler, J.A. Dosage-Sensitive miRNAs Trigger Modulation of Gene Expression during Genomic Imbalance in Maize. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schukken, K.M.; Sheltzer, J.M. Extensive Protein Dosage Compensation in Aneuploid Human Cancers. Genome Res. 2022, 32, 1254–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altug-Teber, Ö.; Bonin, M.; Walter, M.; Mau-Holzmann, U.A.; Dufke, A.; Stappert, H.; Tekesin, I.; Heilbronner, H.; Nieselt, K.; Riess, O. Specific transcriptional changes in human fetuses with autosomal trisomies. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2007, 119, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makarevitch, I.; Harris, C. Aneuploidy causes tissue-specific qualitative changes in global gene expression patterns in maize. Plant Physiol. 2010, 152, 927–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Li, C.-Q.; Dong, Y.; Yang, X.; Wang, Y.-Z. Dosage imbalance of B- and C-class genes causes petaloid-stamen relating to F1 hybrid variation. BMC Plant Biol. 2018, 18, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The International Wheat Genome Sequencing Consortium (IWGSC); Mayer, K.F.X.; Rogers, J.; Doležel, J.; Pozniak, C.; Eversole, K.; Feuillet, C.; Gill, B.; Friebe, B.; Lukaszewski, A.J.; et al. A chromosome-based draft sequence of the hexaploid bread wheat (Triticum aestivum) genome. Science 2014, 345, 1251788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheltzer, J.M.; Torres, E.M.; Dunham, M.J.; Amon, A. Transcriptional consequences of aneuploidy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 12644–12649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muyle, A.; Marais, G.A.B.; Bačovský, V.; Hobza, R.; Lenormand, T. Dosage Compensation Evolution in Plants: Theories, Controversies and Mechanisms. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 2022, 377, 20210222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Hu, M.; Xiao, Y.; Wu, X.; Wang, J. The Activation of Gene Expression and Alternative Splicing in the Formation and Evolution of Allopolyploid Brassica Napus. Hortic. Res. 2022, 9, uhab075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Tu, Y.; Zeng, P.; Ge, X.; Li, Z. Extraction of the Constituent Subgenomes of the Natural Allopolyploid Rapeseed (Brassica Napus L.). Genetics 2016, 204, 1015–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, S.; Zhao, J.; Lei, F.; Yu, J.; Hu, Q.; Zeng, T.; Gu, L.; Wang, H.; Du, X.; Cai, M.; et al. Development and Characterization of a Complete Set of Monosomic Alien Addition Lines from Raphanus Sativus in Brassica Oleracea. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2025, 138, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, P.; Ge, X.; Li, Z. Transcriptional Interactions of Single B-Subgenome Chromosome with C-Subgenome in B. Oleracea-Nigra Additional Lines. Plants 2023, 12, 2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birchler, J.A.; Veitia, R.A. The gene balance hypothesis: From classical genetics to modern genomics. Plant Cell 2007, 19, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birchler, J.A.; Bhadra, U.; Bhadra, M.P.; Auger, D.L. Dosage-dependent gene regulation in multicellular eukaryotes: Implications for dosage compensation, aneuploid syndromes, and quantitative traits. Dev. Biol. 2001, 234, 275–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stenberg, P.; Lundberg, L.E.; Johansson, A.-M.; Rydén, P.; Svensson, M.J.; Larsson, J. Buffering of segmental and chromosomal aneuploidies in Drosophila melanogaster. PLoS Genet. 2009, 5, e1000465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prestel, M.; Feller, C.; Becker, P.B. Dosage compensation and the global re-balancing of aneuploid genomes. Genome Biol. 2010, 11, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenberg, P.; Larsson, J. Buffering and the evolution of chromosome-wide gene regulation. Chromosoma 2011, 120, 213–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Malone, J.H.; Powell, S.K.; Periwal, V.; Spana, E.; MacAlpine, D.M.; Oliver, B. Expression in aneuploid Drosophila S2 cells. PLoS Biol. 2010, 8, e1000320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Liu, H.L.; Luo, P. Production and cytogenetics of intergeneric hybrids between Brassica napus and Orychophragmus violaceus. Theor. Appl. Genet. 1995, 91, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, C.; Ge, X.; Gautam, M.; Kang, L.; Li, Z. Cytoplasmic and genomic effects on meiotic pairing in Brassica hybrids and allotetraploids from pair crosses of three cultivated diploids. Genetics 2012, 191, 725–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.-B.; De Jong, J.H.; Zabel, P. Preparation of tomato meiotic pachytene and mitotic metaphase chromosomes suitable for fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH). Chromosome Res. 1996, 4, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anders, S.; Huber, W. Differential expression analysis for sequence count data. Genome Biol. 2010, 11, R106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Wang, L.-G.; Han, Y.; He, Q.-Y. clusterProfiler: An R package for comparing biological themes among gene clusters. OMICS A J. Integr. Biol. 2012, 16, 284–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogata, H.; Goto, S.; Sato, K.; Fujibuchi, W.; Bono, H.; Kanehisa, M. KEGG: Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999, 27, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klopfenstein, D.V.; Zhang, L.; Pedersen, B.S.; Ramírez, F.; Warwick Vesztrocy, A.; Naldi, A.; Mungall, C.J.; Yunes, J.M.; Botvinnik, O.; Weigel, M.; et al. GOATOOLS: A Python library for gene ontology analyses. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



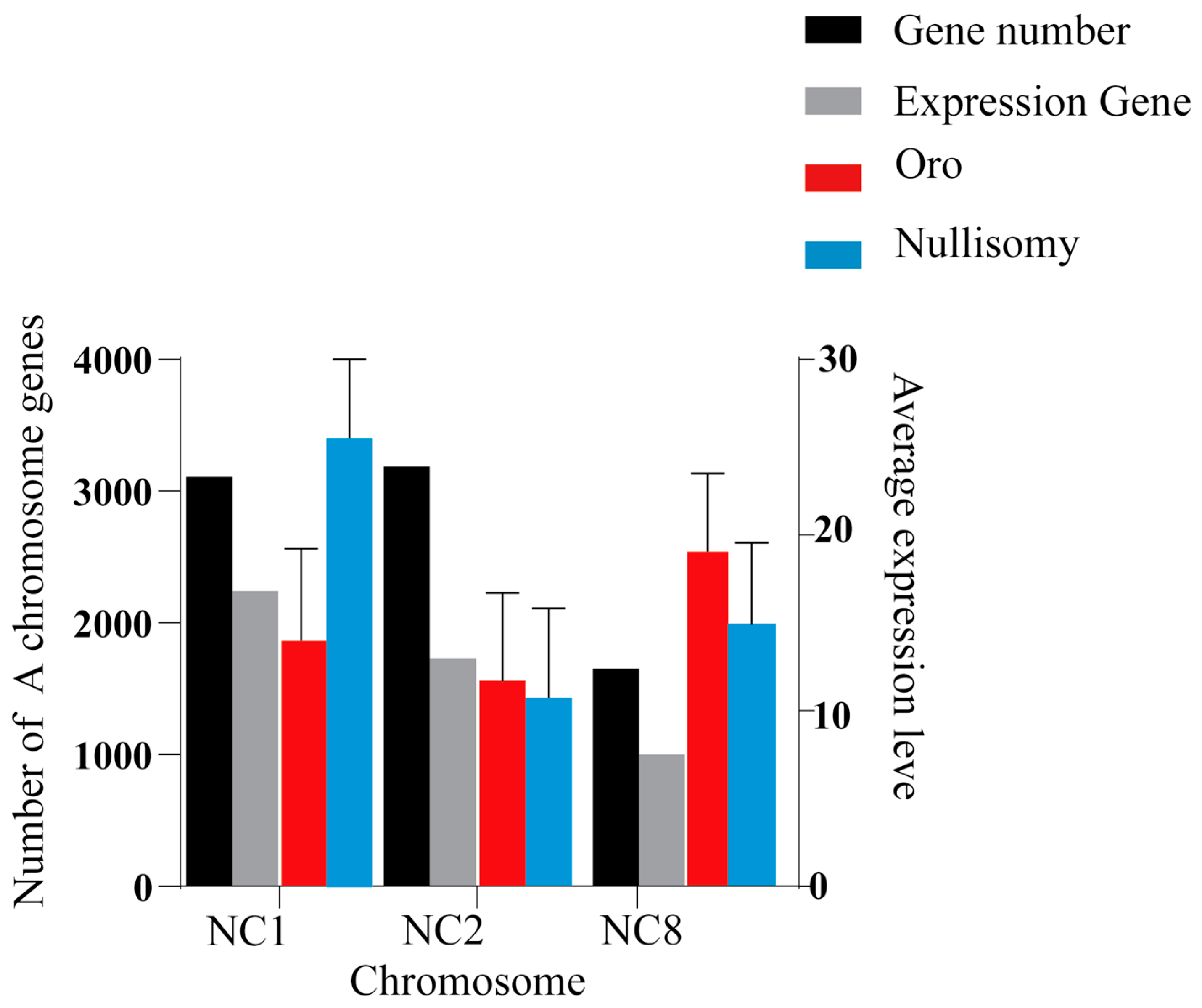
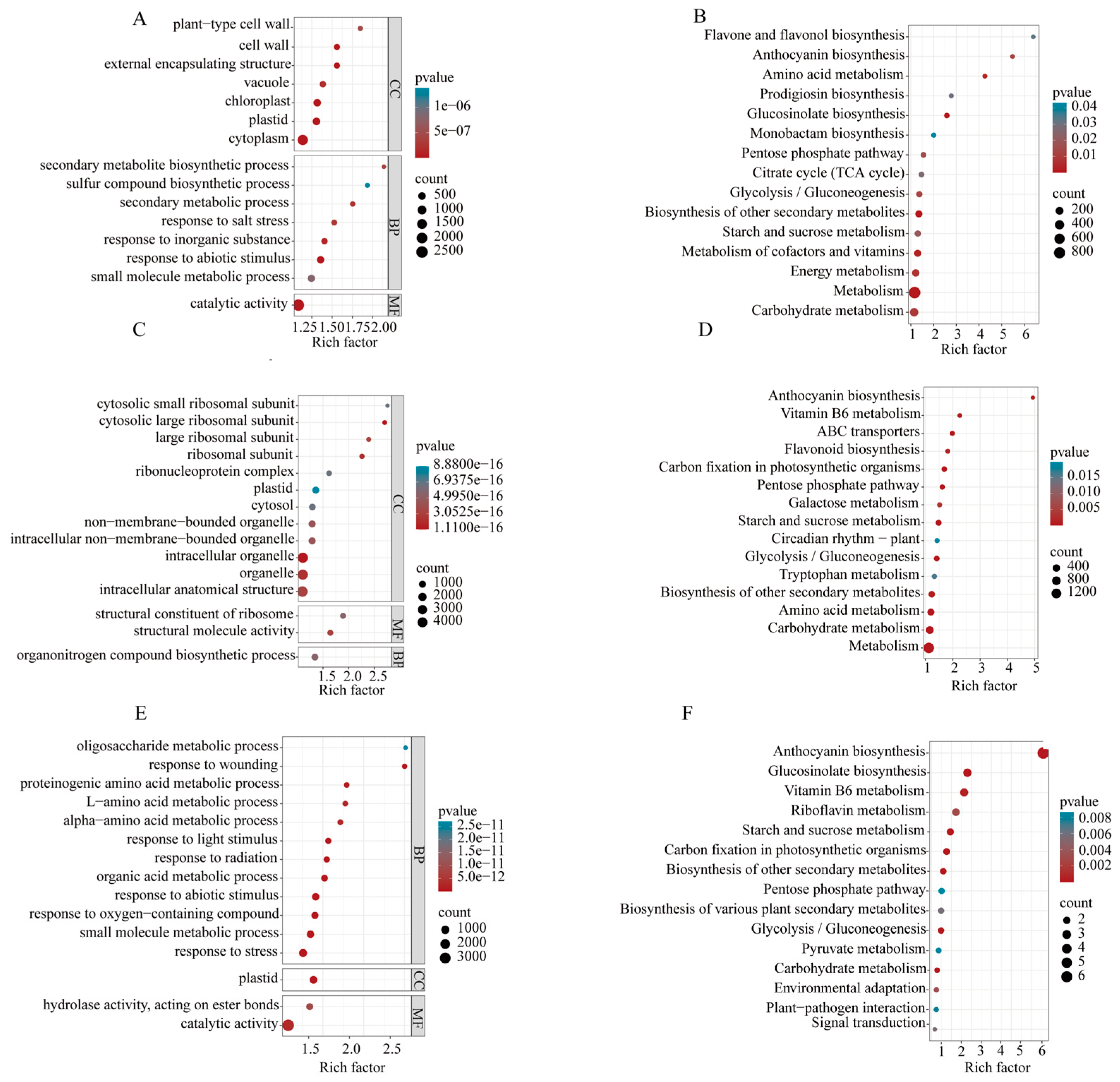
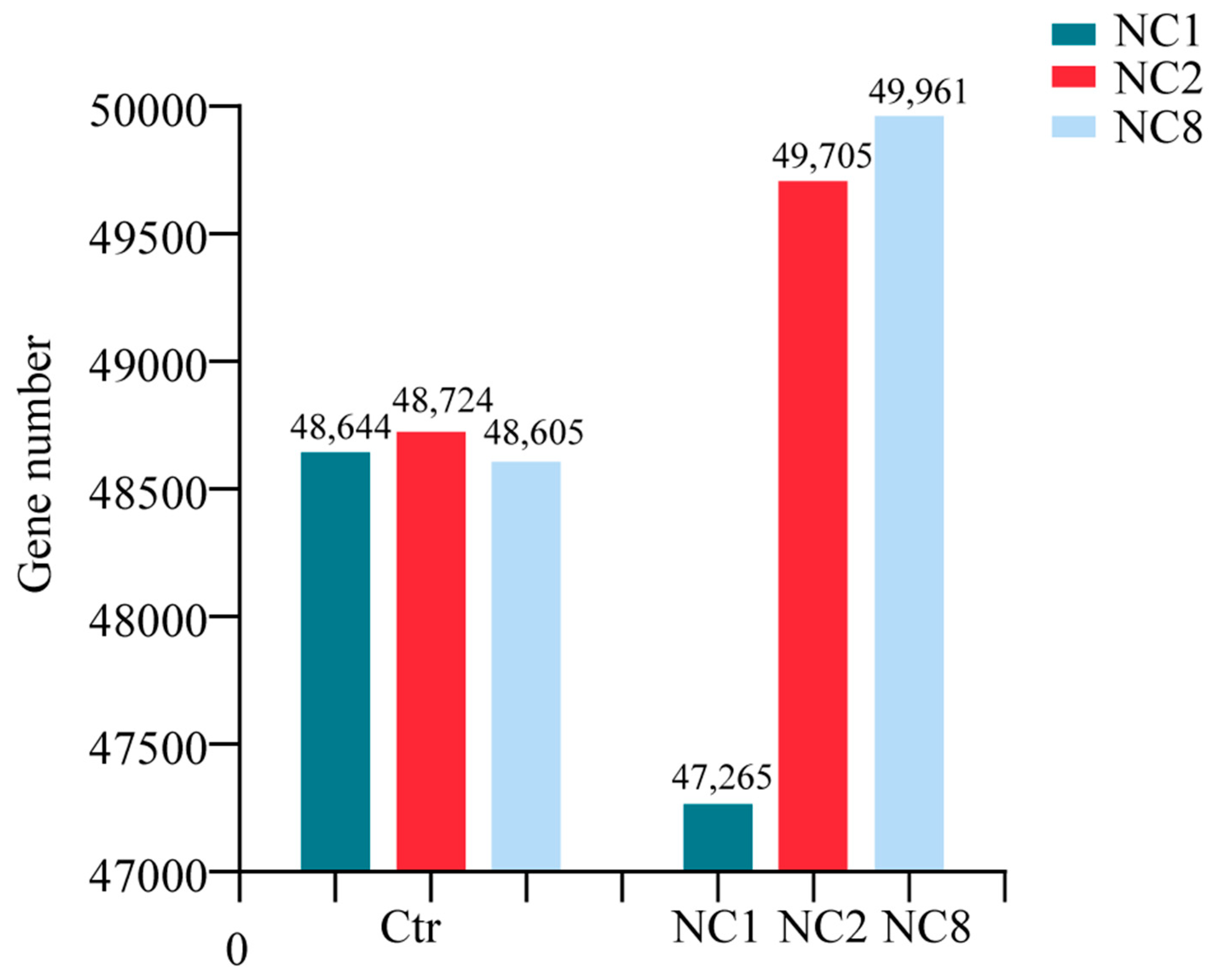
| Oro_vs_NC1 | Oro_vs_NC2 | Oro_vs_NC8 | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UP | Ratio (%) | Down | Ratio (%) | Total | UP | Ratio (%) | Down | Ratio (%) | Total | UP | Ratio (%) | Down | Ratio (%) | Total | |
| DEGs | 3253 | 51.41 | 3043 | 48.59 | 6296 | 6314 | 55.11 | 5144 | 44.89 | 11,458 | 4967 | 53.24 | 4363 | 46.76 | 9330 |
| FC ≥ 10 | 921 | 49.84 | 927 | 50.16 | 1848 | 1932 | 61.31 | 1219 | 38.69 | 3151 | 1259 | 56.11 | 985 | 43.89 | 2244 |
| FC ≥ 100 | 368 | 55.76 | 292 | 44.24 | 660 | 587 | 58.41 | 418 | 41.59 | 1005 | 269 | 44.98 | 329 | 55.02 | 598 |
| FC ≥ 1000 | 46 | 63.01 | 27 | 36.99 | 73 | 110 | 62.15 | 67 | 37.85 | 177 | 32 | 33.68 | 63 | 66.32 | 95 |
| Chromosome | Number of Reference Genes | Expressed Genes | R (%) (EGs/RGs) | DEGs | R (%) (DEGs/EGs) | Group |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A01 | 4296 | 2350 | 54.70 | 824 | 35.06 | High |
| A02 | 4203 | 2066 | 49.17 | 301 | 14.57 | High |
| A03 | 5946 | 3210 | 53.99 | 421 | 13.12 | Middle |
| A04 | 3014 | 1527 | 50.66 | 220 | 14.41 | High |
| A05 | 5002 | 2007 | 40.12 | 256 | 12.76 | Middle |
| A06 | 4533 | 2388 | 52.68 | 339 | 14.20 | High |
| A07 | 3904 | 2185 | 55.97 | 185 | 8.47 | Middle |
| A08 | 3222 | 1732 | 53.76 | 150 | 8.66 | Middle |
| A09 | 7218 | 3479 | 48.20 | 393 | 11.30 | Middle |
| A10 | 3021 | 1748 | 57.86 | 121 | 6.92 | Middle |
| A | 44,359 | 22,692 | 51.16 | 3210 | 14.15 | — |
| C01 | 5168 | 1509 | 29.20 | 827 | 54.80 | — |
| C02 | 5574 | 2218 | 39.79 | 334 | 15.06 | High |
| C03 | 8178 | 4067 | 49.73 | 232 | 5.70 | Low |
| C04 | 6183 | 2841 | 45.95 | 195 | 6.86 | Middle |
| C05 | 5761 | 2922 | 50.72 | 160 | 5.48 | Low |
| C06 | 4597 | 2270 | 49.38 | 125 | 5.51 | Low |
| C07 | 5507 | 2683 | 46.72 | 151 | 5.63 | Low |
| C08 | 5349 | 2548 | 47.64 | 131 | 5.14 | Low |
| C09 | 6245 | 2607 | 41.75 | 226 | 8.67 | Middle |
| C | 52,562 | 23,665 | 45.02 | 2381 | 10.06 | — |
| Total | 96,924 | 46,357 | 47.83 | 5591 | 12.03 | — |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lei, S.; Wei, B.; Hu, Q.; Liu, L.; Yu, F.; Zeng, T.; Du, X.; Gu, L.; Wang, H. Detection of Different Patterns of Genome-Wide Gene Expression Disturbance in Three Nullisomy Lines in Allotetraploid Brassica napus. Plants 2025, 14, 1434. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14101434
Lei S, Wei B, Hu Q, Liu L, Yu F, Zeng T, Du X, Gu L, Wang H. Detection of Different Patterns of Genome-Wide Gene Expression Disturbance in Three Nullisomy Lines in Allotetraploid Brassica napus. Plants. 2025; 14(10):1434. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14101434
Chicago/Turabian StyleLei, Shaolin, Bo Wei, Qi Hu, Lang Liu, Feng Yu, Tuo Zeng, Xuye Du, Lei Gu, and Hongcheng Wang. 2025. "Detection of Different Patterns of Genome-Wide Gene Expression Disturbance in Three Nullisomy Lines in Allotetraploid Brassica napus" Plants 14, no. 10: 1434. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14101434
APA StyleLei, S., Wei, B., Hu, Q., Liu, L., Yu, F., Zeng, T., Du, X., Gu, L., & Wang, H. (2025). Detection of Different Patterns of Genome-Wide Gene Expression Disturbance in Three Nullisomy Lines in Allotetraploid Brassica napus. Plants, 14(10), 1434. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14101434








