Pectobacterium punjabense Causing Blackleg and Soft Rot of Potato: The First Report in the Russian Federation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Isolation and Phenotypic and Biochemical Characteristics of Bacterial Strains
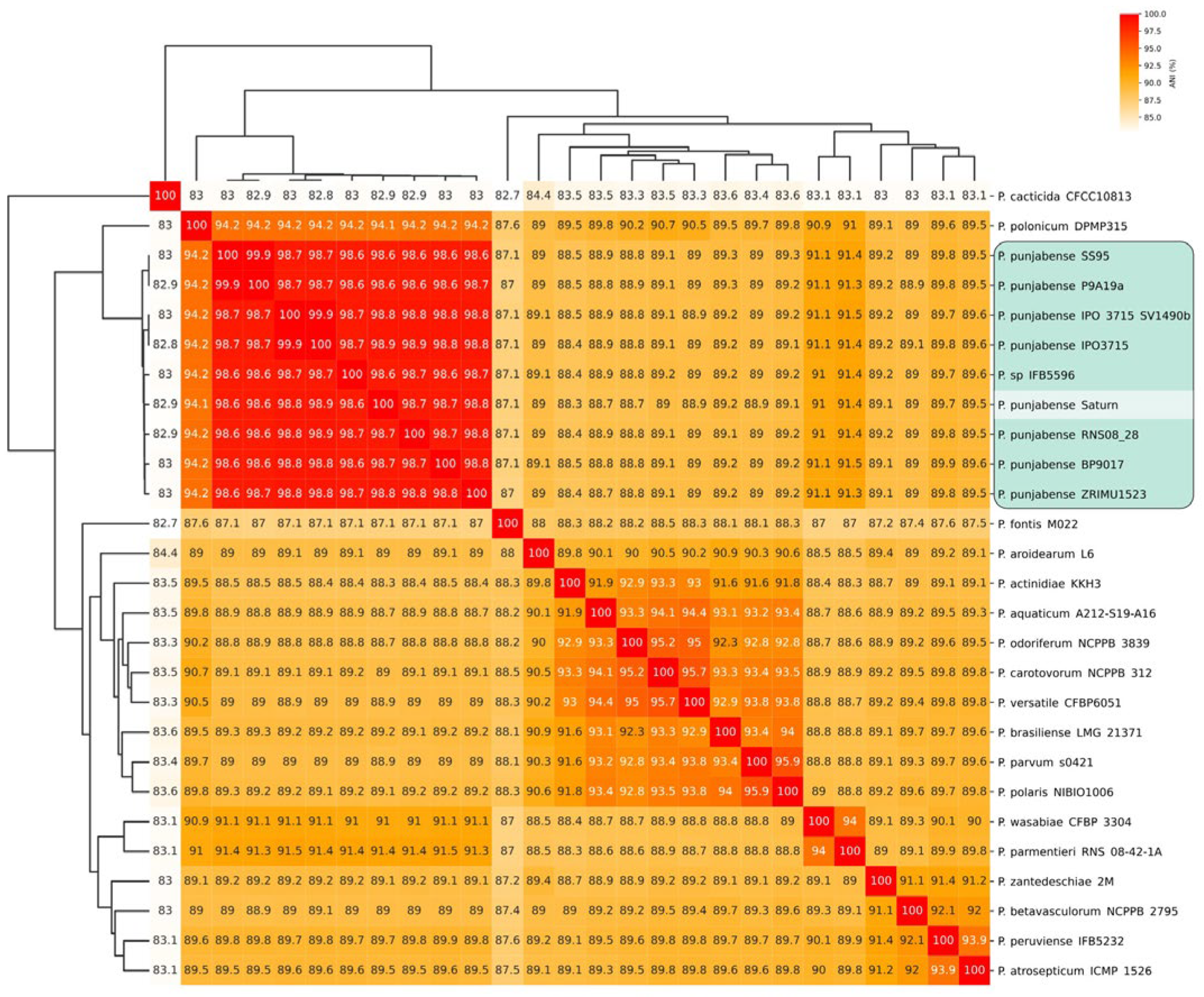
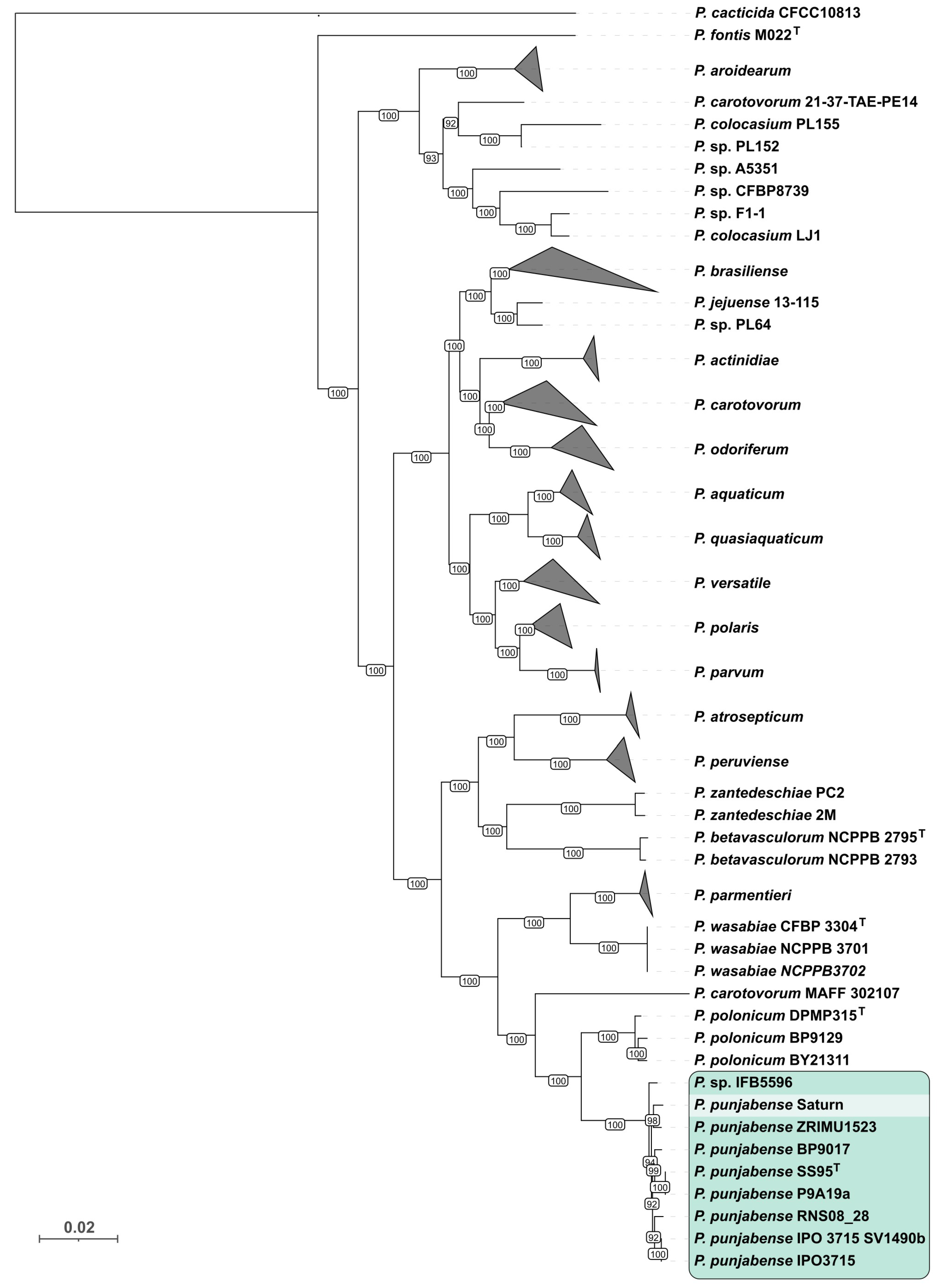
2.2. 16S rDNA, Average Nucleotide Identity (ANI), and Phylogenetic Analysis
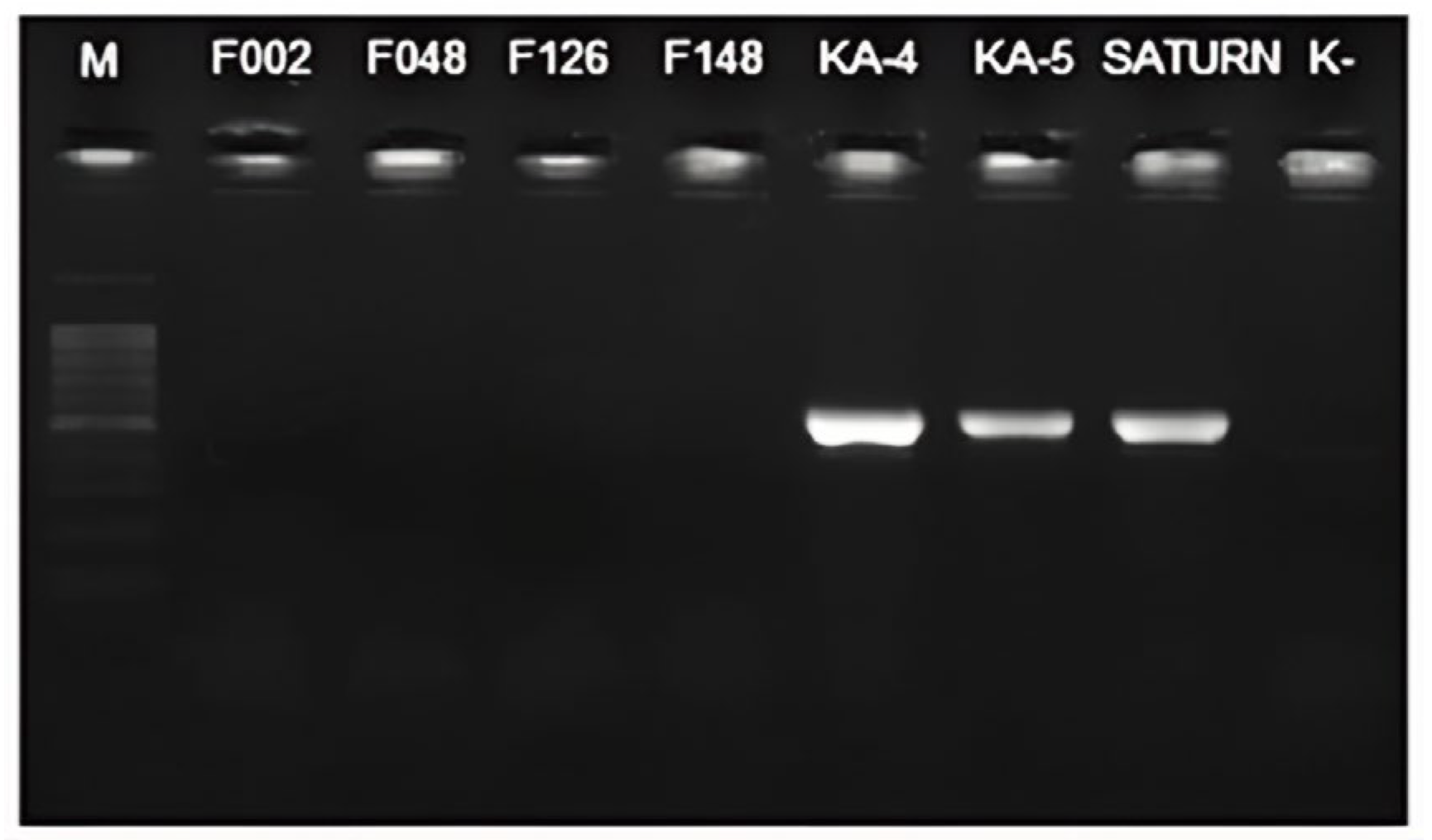
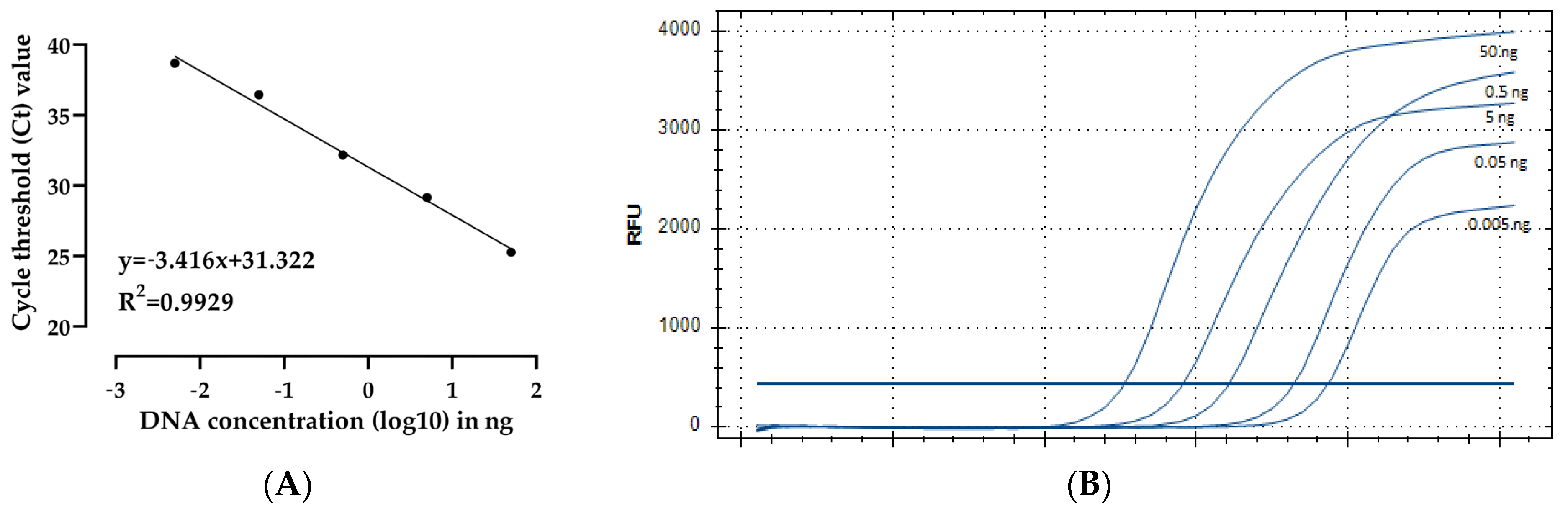
2.3. Development of a TaqMan qPCR Assay Specific to Pectobacterium punjabense
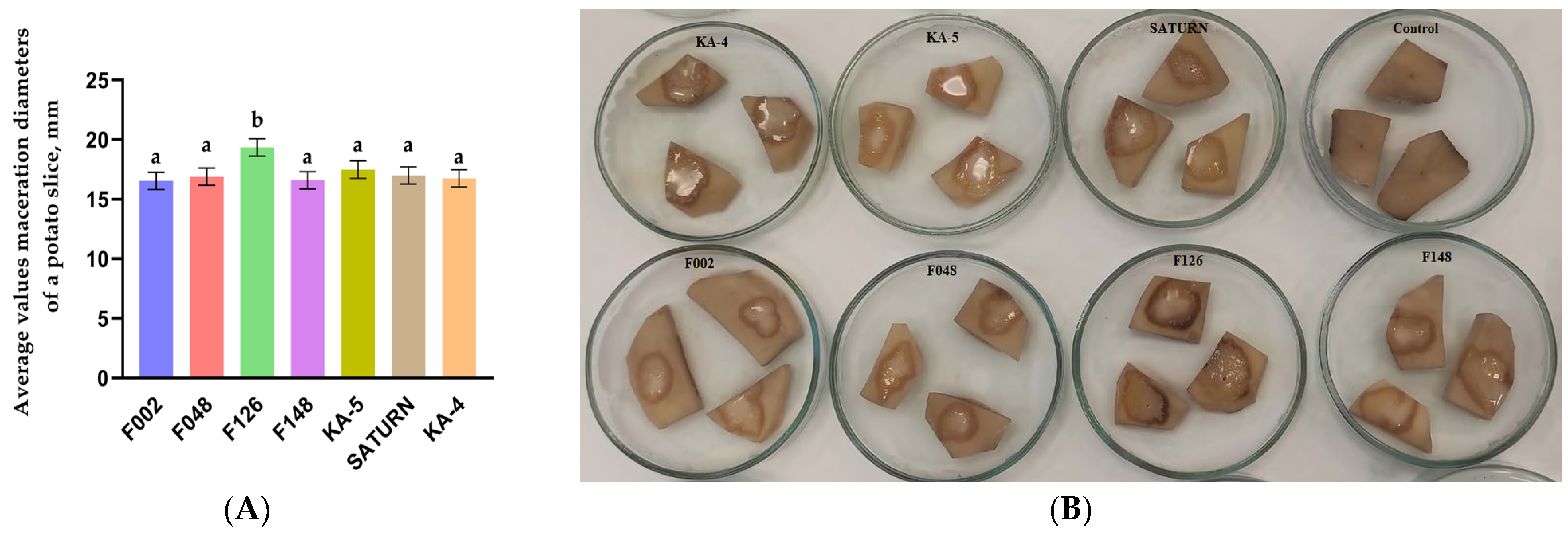
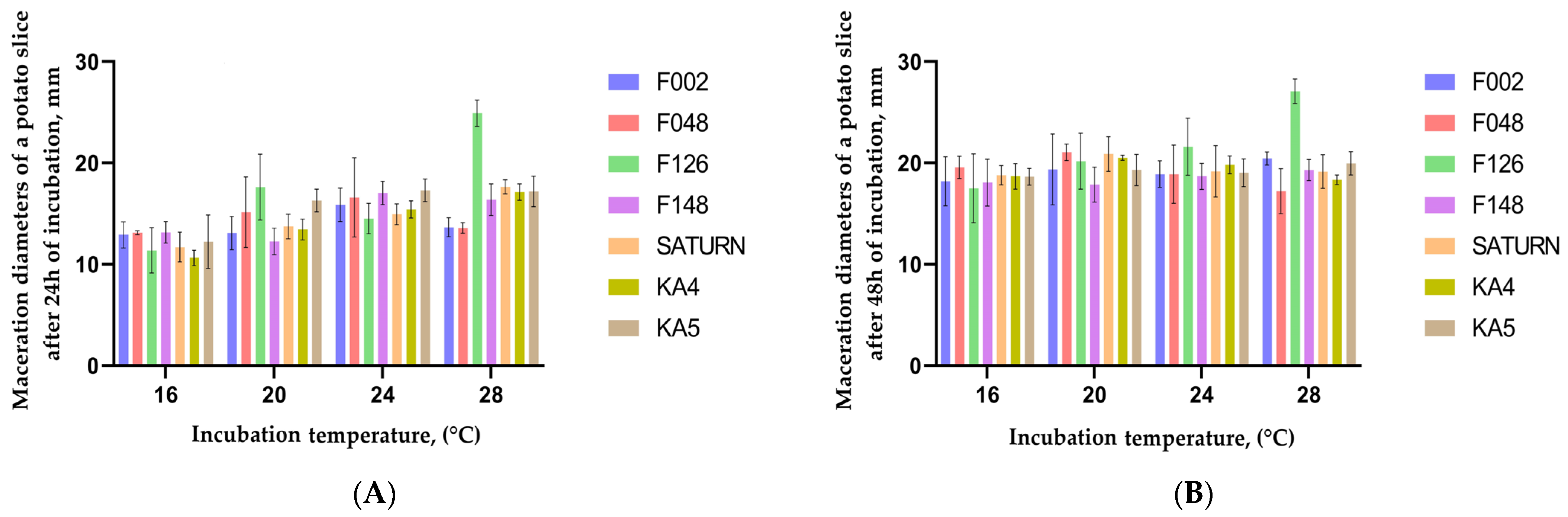
2.4. Pathogenicity of Pectobacterium Isolates on Tubers and Stems
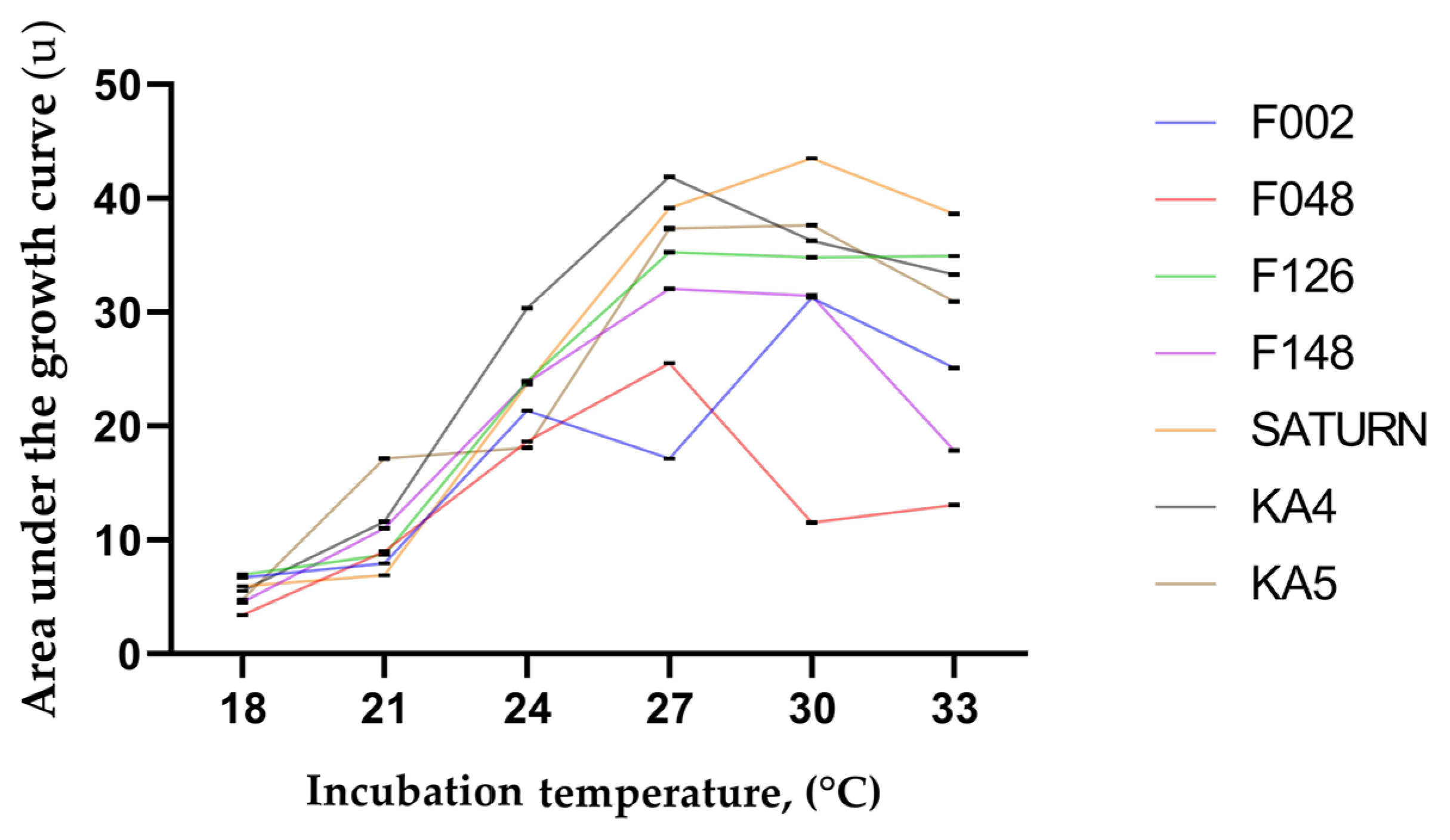
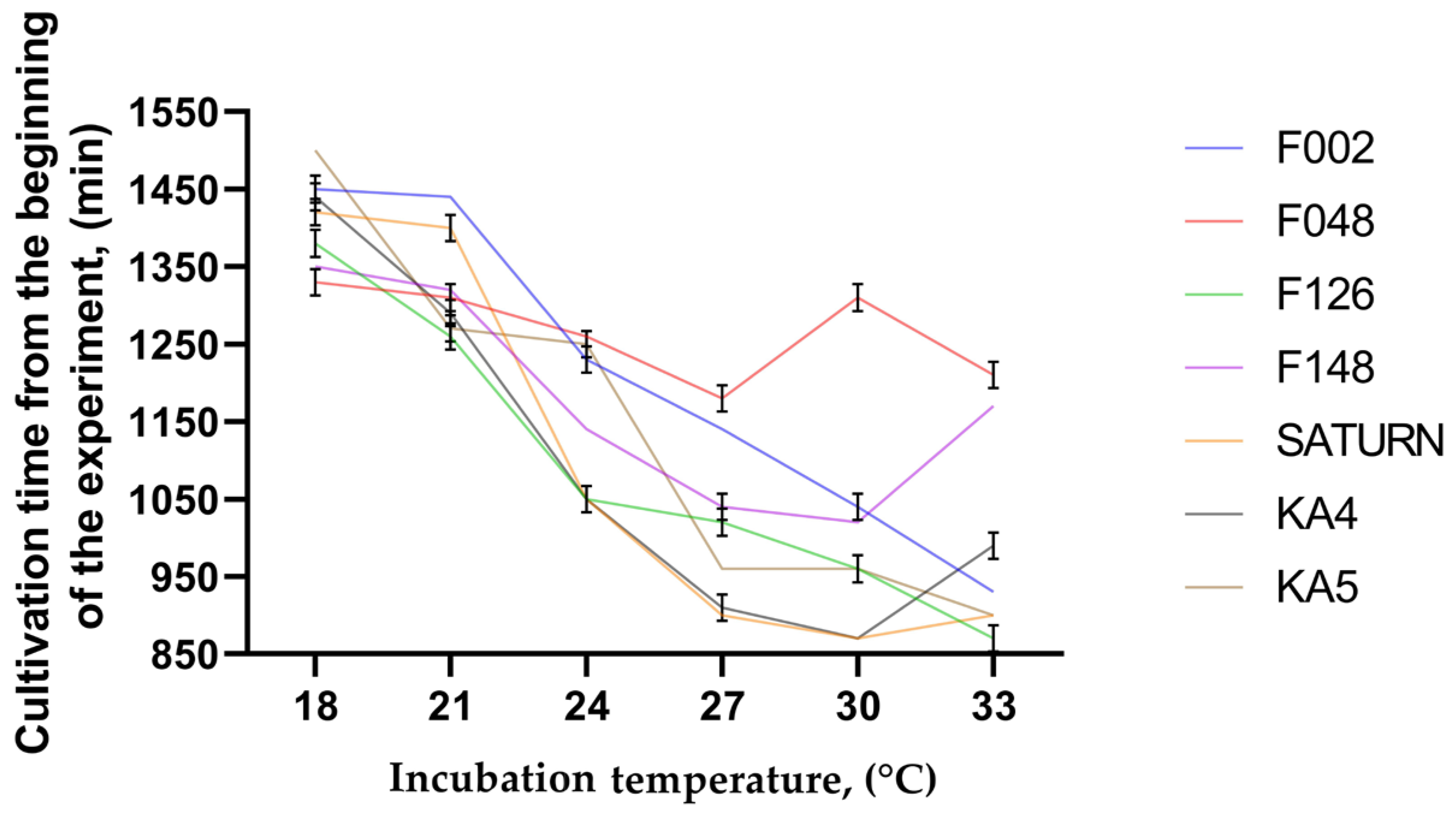
2.5. Cultivation in Liquid Nutrient Medium at Different Temperatures
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacterial Strains, Isolation, and Growth Conditions
4.2. DNA Isolation
4.3. Genetic Identification of Pectobacterium punjabense Strains
4.4. Strain SATURN Genome Sequencing and Annotation
4.5. Calculations of ANI and Phylogenetic Analysis
4.6. Development of PCR Diagnostic Kit
4.6.1. PCR Conditions
4.6.2. qPCR
4.7. Biochemical Characterisation of Pectobacterium Strains
4.8. Pathogenicity Tests
4.9. Cultivation in a Liquid Nutrient Medium
4.10. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kharumnuid, P.; Pandey, N.K.; Devarani, L.; Chauhan, J.K.; Singh, R.; Das, B.; Marbaniang, E.K. Potato production for nutritional security and doubling farmers’ Income. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. 2021, 10, 193–197. [Google Scholar]
- Andersson, R.; Akita, M.; Pirhonen, M.; Gammelgård, E.; Valkonen, J.P.T. Moss-erwinia pathosystem reveals possible similarities in pathogenesis and pathogen defense in vascular and nonvascular plants. J. Gen. Plant Pathol. 2005, 71, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansfield, J.; Genin, S.; Magori, S.; Citovsky, V.; Sriariyanum, M.; Ronald, P.; Dow, M.; Verdier, V.; Beer, S.V.; Machado, M.A.; et al. Top 10 plant pathogenic bacteria in molecular plant pathology. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2012, 13, 614–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inglis, D.; Schroeder, B.K.; Johnson, D.A. Bacterial Soft Rot and Lenticel Spot on Potato Tubers; Washington State University Extension: Pullman, WA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Czajkowski, R.; Pérombelon, M.C.M.; Jafra, S.; Lojkowska, E.; Potrykus, M.; van der Wolf, J.M.; Sledz, W. Detection, identification and differentiation of Pectobacterium and Dickeya species causing potato blackleg and tuber soft rot: A Review. Ann. Appl. Biol. 2015, 166, 18–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitman, A.R.; Wright, P.J.; Galbraith, M.D.; Harrow, S.A. Biochemical and genetic diversity of pectolytic enterobacteria causing soft rot disease of potatoes in New Zealand. Australas. Plant Pathol. 2008, 37, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardan, L.; Gouy, C.; Christen, R.; Samson, R. Elevation of three subspecies of Pectobacterium carotovorum to species level: Pectobacterium atrosepticum Sp. Nov., Pectobacterium betavasculorum Sp. Nov. and Pectobacterium wasabiae Sp. Nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2003, 53, 381–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samson, R.; Legendre, J.B.; Christen, R.; Saux, M.F.-L.; Achouak, W.; Gardan, L. Transfer of Pectobacterium chrysanthemi (Burkholder et al. 1953) Brenner et al. 1973 and Brenneria paradisiaca to the Genus Dickeya Gen. Nov. as Dickeya chrysanthemi Comb. Nov. and Dickeya paradisiaca Comb. Nov. and delineation of four novel species, Dickeya dadantii Sp. Nov., Dickeya dianthicola Sp. Nov., Dickeya dieffenbachiae Sp. Nov. and Dickeya zeae Sp. Nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2005, 55, 1415–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Hibbing, M.E.; Kim, H.-S.; Reedy, R.M.; Yedidia, I.; Breuer, J.; Breuer, J.; Glasner, J.D.; Perna, N.T.; Kelman, A.; et al. Host range and molecular phylogenies of the soft rot enterobacterial genera Pectobacterium and Dickeya. Phytopathology 2007, 97, 1150–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben Moussa, H.; Pédron, J.; Bertrand, C.; Hecquet, A.; Barny, M.-A. Pectobacterium quasiaquaticum Sp. Nov., isolated from waterways. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2021, 71, 005042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portier, P.; Pédron, J.; Taghouti, G.; Fischer-Le Saux, M.; Caullireau, E.; Bertrand, C.; Laurent, A.; Chawki, K.; Oulgazi, S.; Moumni, M.; et al. Elevation of Pectobacterium carotovorum Subsp. Odoriferum to species level as Pectobacterium odoriferum Sp. Nov., Proposal of Pectobacterium brasiliense Sp. Nov. and Pectobacterium actinidiae Sp. Nov., Emended Description of Pectobacterium carotovorum and Description of Pectobacterium versatile Sp. Nov., isolated from streams and symptoms on diverse plants. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2019, 69, 3207–3216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pédron, J.; Bertrand, C.; Taghouti, G.; Portier, P.; Barny, M.-A. Pectobacterium aquaticum Sp. Nov., Isolated from waterways. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2019, 69, 745–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nabhan, S.; De Boer, S.H.; Maiss, E.; Wydra, K. Pectobacterium aroidearum Sp. Nov., a soft rot pathogen with preference for monocotyledonous plants. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2013, 63, 2520–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alcorn, S.M.; Orum, T.V.; Steigerwalt, A.G.; Foster, J.L.M.; Fogleman, J.C.; Brenner, D.J. Taxonomy and pathogenicity of Erwinia cacticida Sp. Nov. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1991, 41, 197–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oulghazi, S.; Cigna, J.; Lau, Y.Y.; Moumni, M.; Chan, K.G.; Faure, D. Transfer of the waterfall source isolate Pectobacterium carotovorum M022 to Pectobacterium fontis Sp. Nov., a Deep-branching species within the genus Pectobacterium. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2019, 69, 470–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khayi, S.; Cigna, J.; Chong, T.M.; Quêtu-Laurent, A.; Chan, K.-G.; Hélias, V.; Faure, D. Transfer of the potato plant isolates of Pectobacterium wasabiae to Pectobacterium parmentieri Sp. Nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 5379–5383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasanen, M.; Waleron, M.; Schott, T.; Cleenwerck, I.; Misztak, A.; Waleron, K.; Pritchard, L.; Bakr, R.; Degefu, Y.; Van Der Wolf, J.; et al. Pectobacterium parvum Sp. Nov., having a Salmonella SPI-1-like type III secretion system and low virulence. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2020, 70, 2440–2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dees, M.W.; Lysøe, E.; Rossmann, S.; Perminow, J.; Brurberg, M.B. Pectobacterium polaris Sp. Nov., isolated from potato (Solanum tuberosum). Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2017, 67, 5222–5229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waleron, M.; Misztak, A.; Waleron, M.; Jonca, J.; Furmaniak, M.; Waleron, K. Pectobacterium polonicum Sp. Nov. isolated from vegetable fields. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2019, 69, 1751–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarfraz, S.; Riaz, K.; Oulghazi, S.; Cigna, J.; Sahi, S.T.; Khan, S.H.; Faure, D. Pectobacterium punjabense Sp. Nov., isolated from blackleg symptoms of potato plants in Pakistan. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2018, 68, 3551–3556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waleron, M.; Misztak, A.; Waleron, M.; Franczuk, M.; Wielgomas, B.; Waleron, K. Transfer of Pectobacterium Carotovorum Subsp. Carotovorum strains isolated from potatoes grown at high altitudes to Pectobacterium Peruviense Sp. Nov. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2018, 41, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waleron, M.; Misztak, A.; Waleron, M.; Franczuk, M.; Jońca, J.; Wielgomas, B.; Mikiciński, A.; Popović, T.; Waleron, K. Pectobacterium Zantedeschiae Sp. Nov. a new species of a soft rot pathogen isolated from Calla lily (Zantedeschia Spp.). Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 42, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cigna, J.; Laurent, A.; Waleron, M.; Waleron, K.; Dewaegeneire, P.; Van Der Wolf, J.; Andrivon, D.; Faure, D.; Hélias, V. European population of Pectobacterium punjabense: Genomic diversity, tuber maceration capacity and a detection tool for this rarely occurring potato pathogen. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mainello-Land, A.M.; Bibi, S.; Gugino, B.; Bull, C.T. Multilocus sequence and phenotypic analysis of Pectobacterium and Dickeya type strains for identification of soft rot Pectobacteriaceae from symptomatic potato stems and tubers in Pennsylvania. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2024, 47, 126476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handique, U.; Cao, Y.; Wang, D.; Zhang, R.; Li, W.; Sun, Q.; Feng, Z.; Wu, J. First report of Pectobacterium punjabense causing blackleg and soft rot on potato in Hebei and Fujian province, China. Plant Dis. 2022, 106, 1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loc, M.; Milošević, D.; Ivanović, Ž.; Ignjatov, M.; Budakov, D.; Grahovac, J.; Grahovac, M. Genetic diversity of Pectobacterium Spp. on potato in Serbia. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palafox-Leal, N.L.; Castillo Batista, J.C.; Santos-Cervantes, M.E.; Méndez-Lozano, J.; Rodríguez-Negrete, E.A.; Cervantes-Cárdenas, L.A.; Leyva-López, N.E. Pectobacterium punjabense causing soft rot and blackleg of potato in Sinaloa, Mexico. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2024, 168, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curland, R.D.; Mainello, A.; Perry, K.L.; Hao, J.; Charkowski, A.O.; Bull, C.T.; McNally, R.R.; Johnson, S.B.; Rosenzweig, N.; Secor, G.A.; et al. Species of Dickeya and Pectobacterium isolated during an outbreak of blackleg and soft rot of potato in northeastern and north central United States. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Wolf, J.M.; Acuña, I.; De Boer, S.H.; Brurberg, M.B.; Cahill, G.; Charkowski, A.O.; Coutinho, T.; Davey, T.; Dees, M.W.; Degefu, Y.; et al. diseases caused by Pectobacterium and Dickeya species around the world. In Plant Diseases Caused by Dickeya and Pectobacterium Species; Van Gijsegem, F., van der Wolf, J.M., Toth, I.K., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 215–261. ISBN 978-3-030-61459-1. [Google Scholar]
- Ossowska, K.; Motyka-Pomagruk, A.; Kaczyńska, N.; Kowalczyk, A.; Sledz, W.; Lojkowska, E.; Kaczyński, Z. Heterogenicity within the LPS structure in relation to the chosen genomic and physiological features of the plant pathogen Pectobacterium parmentieri. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babinska, W.; Motyka-Pomagruk, A.; Sledz, W.; Kowalczyk, A.; Kaczynski, Z.; Lojkowska, E. The first Polish isolate of a novel species Pectobacterium aquaticum originates from a Pomeranian lake. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 5041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maderankova, D.; Jugas, R.; Sedlar, K.; Vitek, M.; Skutkova, H. Rapid bacterial species delineation based on parameters derived from genome numerical representations. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2019, 17, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Na, S.-I.; Kim, D.; Chun, J. UBCG2: Up-to-date bacterial core genes and pipeline for phylogenomic analysis. J. Microbiol. 2021, 59, 609–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Home—Genome—NCBI. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/datasets/ (accessed on 3 May 2024).
- Zhou, J.; Hu, M.; Hu, A.; Li, C.; Ren, X.; Tao, M.; Xue, Y.; Chen, S.; Tang, C.; Xu, Y.; et al. Isolation and genome analysis of Pectobacterium colocasium Sp. Nov. and Pectobacterium aroidearum, two new pathogens of taro. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 852750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acheson, J.F.; Ho, R.; Goularte, N.F.; Cegelski, L.; Zimmer, J. Molecular organization of the E. Coli cellulose synthase macrocomplex. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2021, 28, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carezzano, M.E.; Paletti Rovey, M.F.; Cappellari, L.D.R.; Gallarato, L.A.; Bogino, P.; Oliva, M.D.L.M.; Giordano, W. Biofilm-forming ability of phytopathogenic bacteria: A review of its involvement in plant stress. Plants 2023, 12, 2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lukianova, A.A.; Evseev, P.V.; Stakheev, A.A.; Kotova, I.B.; Zavriev, S.K.; Ignatov, A.N.; Miroshnikov, K.A. Development of qPCR detection assay for potato pathogen Pectobacterium atrosepticum based on a unique target sequence. Plants 2021, 10, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bustin, S.A.; Benes, V.; Garson, J.A.; Hellemans, J.; Huggett, J.; Kubista, M.; Mueller, R.; Nolan, T.; Pfaffl, M.W.; Shipley, G.L.; et al. The MIQE guidelines: Minimum information for publication of quantitative real-time PCR experiments. Clin. Chem. 2009, 55, 611–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du Raan, S.; Coutinho, T.A.; Van Der Waals, J.E. Cardinal temperature differences, determined in vitro, between closely related species and subspecies of pectinolytic bacteria responsible for blackleg and soft rot on potatoes. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2016, 144, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Moh, A.A.; Massart, S.; Jijakli, M.H.; Lepoivre, P. Models to predict the combined effects of temperature and relative humidity on Pectobacterium atrosepticum and Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. carotovorum population density and soft rot disease development at the surface of wounded potato tubers. J. Plant Pathol. 2012, 94, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarfraz, S.; Oulghazi, S.; Cigna, J.; Sahi, S.T.; Riaz, K.; Tufail, M.R.; Fayyaz, A.; Naveed, K.; Hameed, A.; Lopez-Roques, C.; et al. Complete genome sequence of the type strain Pectobacterium punjabense SS95, isolated from a potato plant with blackleg symptoms. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2020, 9, e00420-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kõiv, V.; Roosaare, M.; Vedler, E.; Ann Kivistik, P.; Toppi, K.; Schryer, D.W.; Remm, M.; Tenson, T.; Mäe, A. Microbial population dynamics in response to Pectobacterium atrosepticum infection in potato tubers. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hibbing, M.E.; Fuqua, C.; Parsek, M.R.; Peterson, S.B. Bacterial competition: Surviving and thriving in the microbial jungle. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 8, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Wolf, J.M.; Cahill, G.; Van Gijsegem, F.; Hélias, V.; Humphris, S.; Li (Sean), X.; Lojkowska, E.; Pritchard, L. Isolation, detection and characterization of Pectobacterium and Dickeya species. In Plant Diseases Caused by Dickeya and Pectobacterium Species; Van Gijsegem, F., van der Wolf, J., Toth, I., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 149–173. ISBN 978-3-030-61458-4. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez, N.; Plaza, J.; Criado, M.; Pérez-Sánchez, R.; Gómez-Sánchez, M.Á.; Morales-Corts, M.R.; Palacios, C. The second derivative of the NDVI time series as an estimator of fresh biomass: A case study of eight forage associations monitored via UAS. Drones 2023, 7, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lelekov, A.S.; Gevorgiz, R.G.; Gavrilov, P.E. Dynamic model substrate-dependent growth of microalgae butch culture. Issues Mod. Algol. 2016, 2, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Hélias, V.; Hamon, P.; Huchet, E.; Wolf, J.V.D.; Andrivon, D. Two new effective semiselective crystal violet pectate media for isolation of Pectobacterium and Dickeya. Plant Pathol. 2012, 61, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, D.J. 16S/23S rRNA Sequencing. In Nucleic Acid Techniques in Bacterial Systematic; Stackebrandt, E., Goodfellow, M., Eds.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, D.D.; Li, F.; Kirton, E.; Thomas, A.; Egan, R.; An, H.; Wang, Z. MetaBAT 2: An adaptive binning algorithm for robust and efficient genome reconstruction from metagenome assemblies. PeerJ 2019, 7, e7359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parks, D.H.; Imelfort, M.; Skennerton, C.T.; Hugenholtz, P.; Tyson, G.W. CheckM: Assessing the quality of microbial genomes recovered from isolates, single cells, and metagenomes. Genome Res. 2015, 25, 1043–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, C.; Rodriguez, -R.L.M.; Phillippy, A.M.; Konstantinidis, K.T.; Aluru, S. High throughput ANI analysis of 90K prokaryotic genomes reveals clear species boundaries. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 5114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, L.-T.; Schmidt, H.A.; Von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. IQ-TREE: A Fast and effective stochastic algorithm for estimating maximum-likelihood phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree Of Life (iTOL) v5: An online tool for phylogenetic tree display and annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W293–W296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Untergasser, A.; Cutcutache, I.; Koressaar, T.; Ye, J.; Faircloth, B.C.; Remm, M.; Rozen, S.G. Primer3—New capabilities and interfaces. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, e115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azadmanesh, S.; Mozafari, J.; Hasanzadeh, N.; Moslemkhani, C. In vitro evaluation of resistant of potato cultivars against black leg disease (Pectobacterium atrosepticum). Biol. Forum—Int. J. 2015, 7, 1087–1094. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.; Mueller, C. Factor Analysis; SAGE Publications, Inc.: Thousand Oaks, CA USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Duncan, D.B. Multiple range and multiple F tests. Biometrics 1955, 11, 1–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, R.W. Cercospora leaf spot of cowpea: Models for estimating yield loss. Phytopathology 1976, 66, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
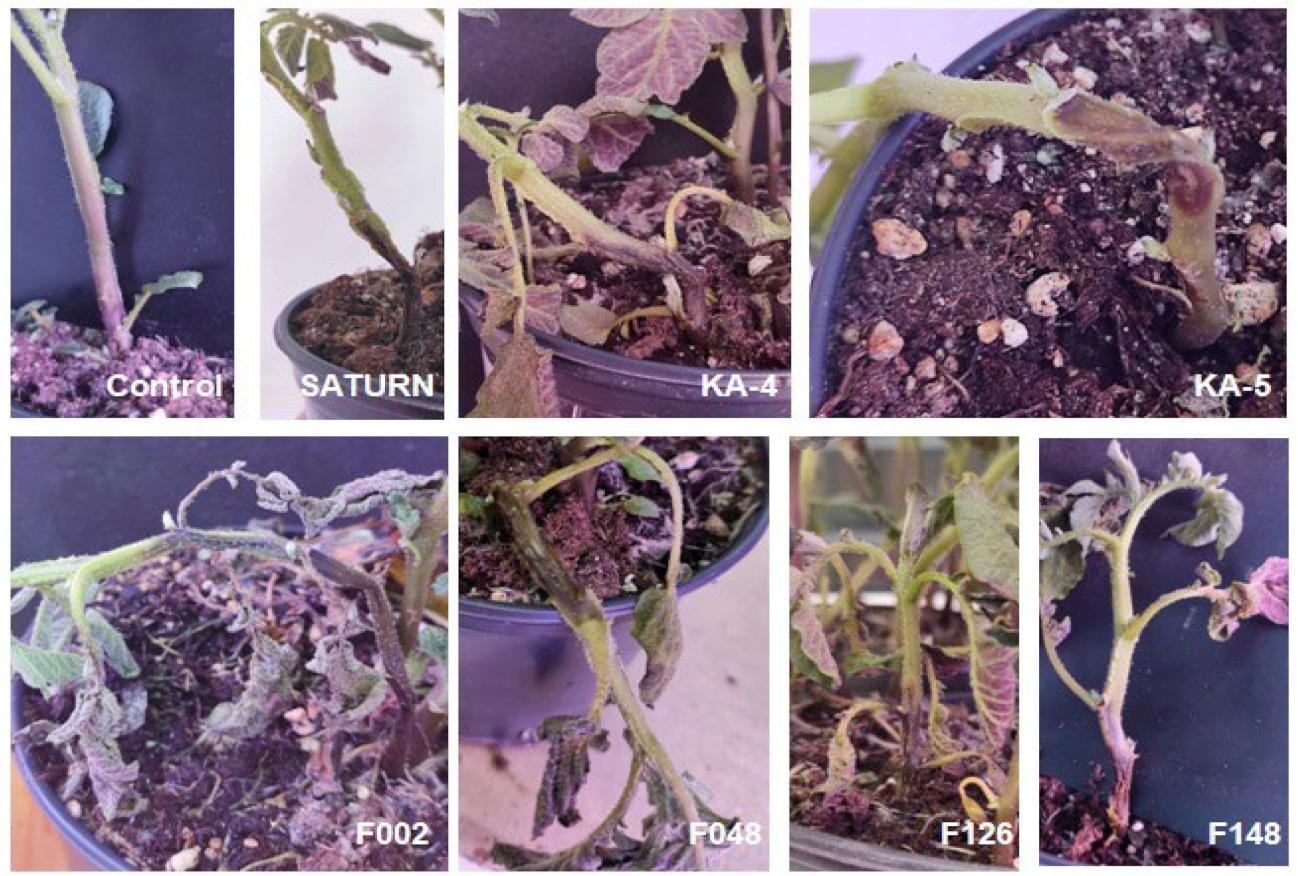

| Strain | Year of Isolation | Origin | NCBI GenBank Accession Number |
|---|---|---|---|
| P. punjabense SATURN * | 2021 | Kemerovo region | this study |
| P. punjabense KA-4 * | 2021 | Moscow region | this study |
| P. punjabense KA-5 * | 2021 | Moscow region | this study |
| P. versatile F002 | 2012 | Moscow region | NZ_PDVY00000000.1 |
| P. atrosepticum F048 | 2012 | Tver region | NZ_PDDK00000000.1 |
| P. brasiliense F126 | 2012 | Samara region | NZ_RRYQ01000010.1 |
| P. parmentieri F148 | 2013 | Moscow region | NZ_PDDJ01000001.1 |
| Chemical Reaction | P. punjabense SATURN | P. punjabense KA-4 | P. punjabense KA-5 | P. versatile F002 | P. atrosepticum F048 | P. brasiliense F126 | P. parmentieri F148 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| β-galactosidase activity | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| Arginine dihydrolase activity | − | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| Lysine decarboxylase activity | − | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| Ornithine decarboxylase activity | − | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| Citrate utilization | − | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| H2S production | − | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| Urease production | − | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| Tryptophane deaminase activity | − | − | − | − | + | − | + |
| Indole production | − | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| Acetoin production (VP) | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| Liquefaction of gelatine | + | − | − | + | − | + | − |
| Fermentation of glucose | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| Fermentation of mannitol | − | − | − | + | + | + | + |
| Fermentation of inositol | − | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| Fermentation of sorbitol | − | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| Fermentation of rhamnose | + | + | + | − | + | + | + |
| Fermentation of saccharose | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| Fermentation of melibiose | + | + | + | − | − | + | − |
| Fermentation of amygdalin | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| Fermentation of arabinose | + | + | + | + | − | + | + |
| NO3 reduction to NO2 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| Primer/Probe | Nucleotide Sequence (5′–3′ Direction) | Amplicon Sequence for the Type Strain |
|---|---|---|
| PecpunF | CAC AAC CTT AAC AAT ACC GGC G | CAC AAC CTT AAC AAT ACC GGC GGT CAC CGC ACC AAC CAC AAG AGA TGC CGT CTG CTT CCC CAT CCA AAA AGT TGT CTT TCA TGA TGC AGA GTC GCT CCC AGC GAA AGA TCG CAC GGC CAT TCA GCA ACG CTA CCA AAG CCG CTG CCT TGA TTT AGC CAC AAT CCA TAA CGC CGT GAG GGA AAC CAC CAA TGC CTA CCT CAA TCG TGG CTT TGT CAC CAG TCA GGC CTA TTT ACA GGA GCA AGA CCT CTC CGG CGG CAC GCT CAT CAT CAG CGT CAG CGA GGG AAA GAT AGA AGC TAT TCG CAT GGA AGG GGA AAC GCC ACT CGC AAT CAA GAT GGC CTT CCC TAG GCT GGA AGGAC ATA TTC TTA ATC TGC GCG ACA TCG AAC AAG GGA TGG AAC AGT TGA ATC GTC TGC CTT CGC AGC AGG TTG CCA TTG ATA TTC AAC CGG GAA AAC AAG CAG GGA GTT CGA TTG TTT ATC TCA AGC GCA CCA CGC AAG CCC GTC CTG TCA CCC TCT CTC TCA GCG |
| PecpunR | CGC TGA GAG AGA GGG TGA CA | |
| ProbePecpun | (FAM)-TCA TGA TGC AGA GTC GCT CC-(RTQ1) |
| Strain | Geographical Origin | NCBI GenBank Accession Number | Detection in TaqMan Assay (Ct Value) |
|---|---|---|---|
| P. punjabense SATURN | Kemerovo | this study | 28.04 |
| P. punjabense KA-4 | Moscow | this study | 28.17 |
| P. punjabense KA-5 | Moscow | this study | 27.56 |
| P. versatile F002 | Moscow | NZ_PDVY00000000.1 | ND |
| P. versatile F016 | Ryazan | NZ_RRYR00000000.1 | ND |
| P. versatile F135 | Moscow | NZ_PDVX00000000.1 | ND |
| P. atrosepticum F048 | Tver | NZ_PDDK00000000.1 | ND |
| P. atrosepticum F162 | Scotland | NC_004547 | ND |
| P. atrosepticum F163 | Belarus | NZ_CP009125 | ND |
| P. brasiliense F126 | Samara | NZ_RRYQ01000010.1 | ND |
| P. brasiliense F157 | Moscow | NZ_PJDL00000000.1 | ND |
| P. parmentieri F148 | Moscow | NZ_PDDJ01000001.1 | ND |
| D. solani DFil | Voronezh | NZ_PGOJ00000.1 | ND |
| D. chrysanthemi DSM 4610 T | USA | GCA_000406105.1 | ND |
| D. dadantii DSM 18020 T | Comoros | NZ_CP023467.1 | ND |
| DNA Concentration | Ct Mean | Standard Deviation |
|---|---|---|
| 50 ng | 25.27 | 0.17 |
| 5 ng | 29.15 | 0.87 |
| 0.5 ng | 32.18 | 0.08 |
| 0.05 ng | 36.45 | 0.05 |
| 0.005 ng | 38.7 | 0.07 |
| Control | ND | ND |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vasilyeva, A.A.; Evseev, P.V.; Ignatov, A.N.; Dzhalilov, F.S.-U. Pectobacterium punjabense Causing Blackleg and Soft Rot of Potato: The First Report in the Russian Federation. Plants 2024, 13, 2144. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13152144
Vasilyeva AA, Evseev PV, Ignatov AN, Dzhalilov FS-U. Pectobacterium punjabense Causing Blackleg and Soft Rot of Potato: The First Report in the Russian Federation. Plants. 2024; 13(15):2144. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13152144
Chicago/Turabian StyleVasilyeva, Anna A., Peter V. Evseev, Alexandr N. Ignatov, and Fevzi S.-U. Dzhalilov. 2024. "Pectobacterium punjabense Causing Blackleg and Soft Rot of Potato: The First Report in the Russian Federation" Plants 13, no. 15: 2144. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13152144
APA StyleVasilyeva, A. A., Evseev, P. V., Ignatov, A. N., & Dzhalilov, F. S.-U. (2024). Pectobacterium punjabense Causing Blackleg and Soft Rot of Potato: The First Report in the Russian Federation. Plants, 13(15), 2144. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13152144









