Effects of Partial Replacement of Durum Wheat Re-Milled Semolina with Bean Flour on Physico-Chemical and Technological Features of Doughs and Breads during Storage
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Characteristics of Flours
2.2. Color Parameters
2.3. Technological Analysis of Flours
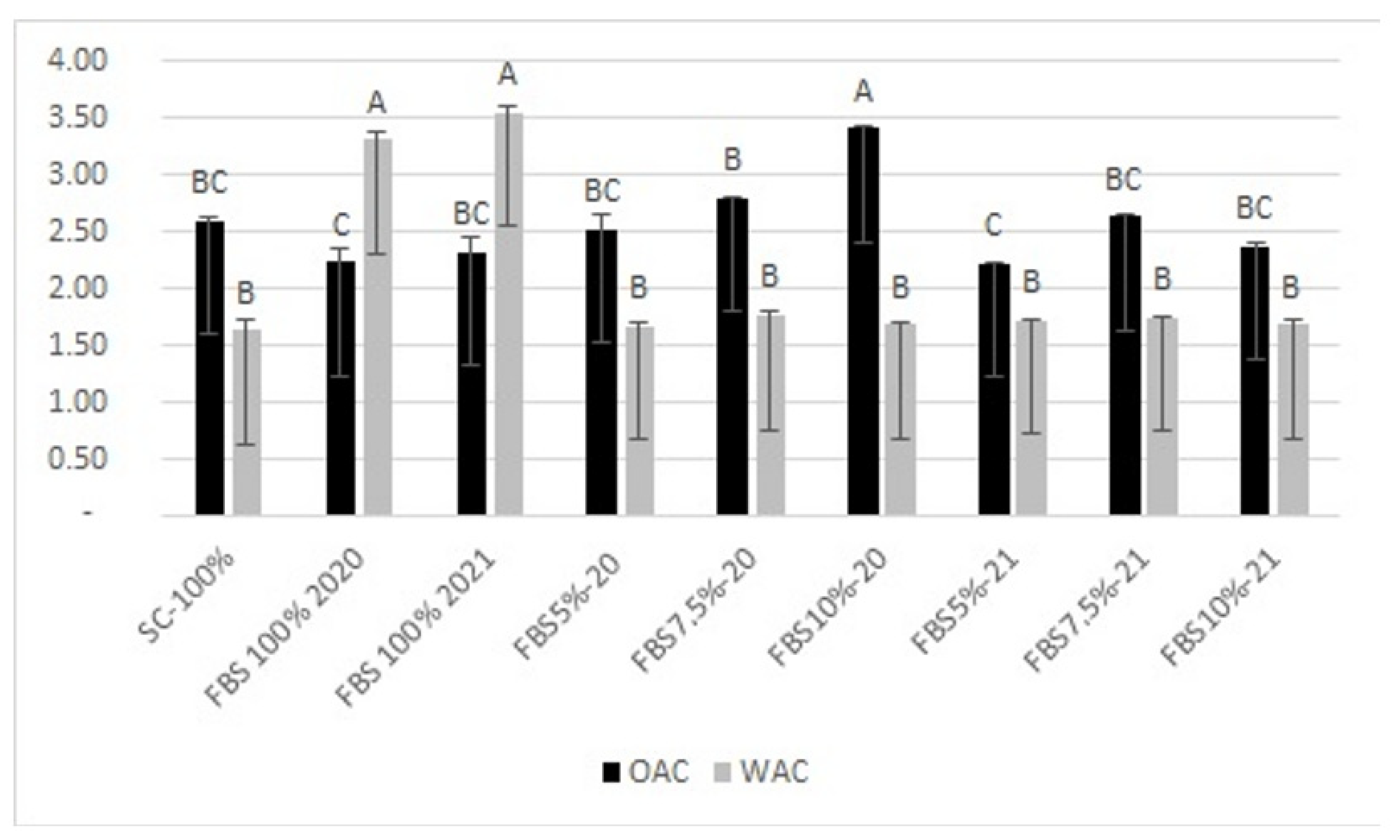
2.4. Water/Oil Absorption Capacity
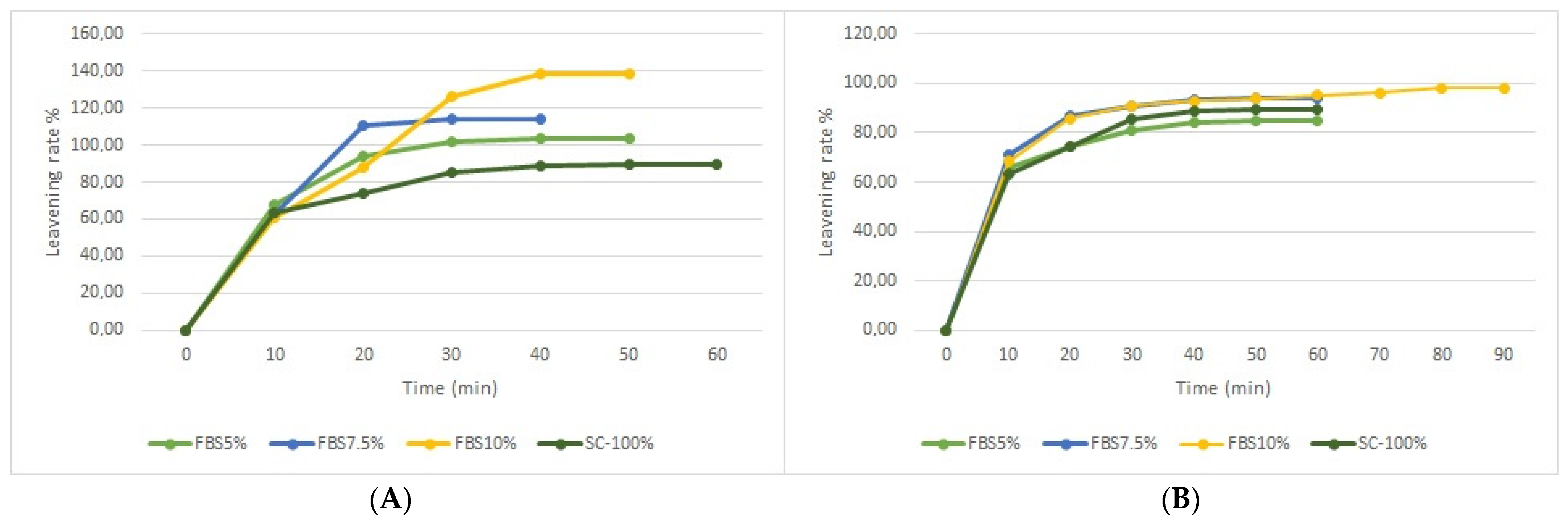
2.5. Leavening Test
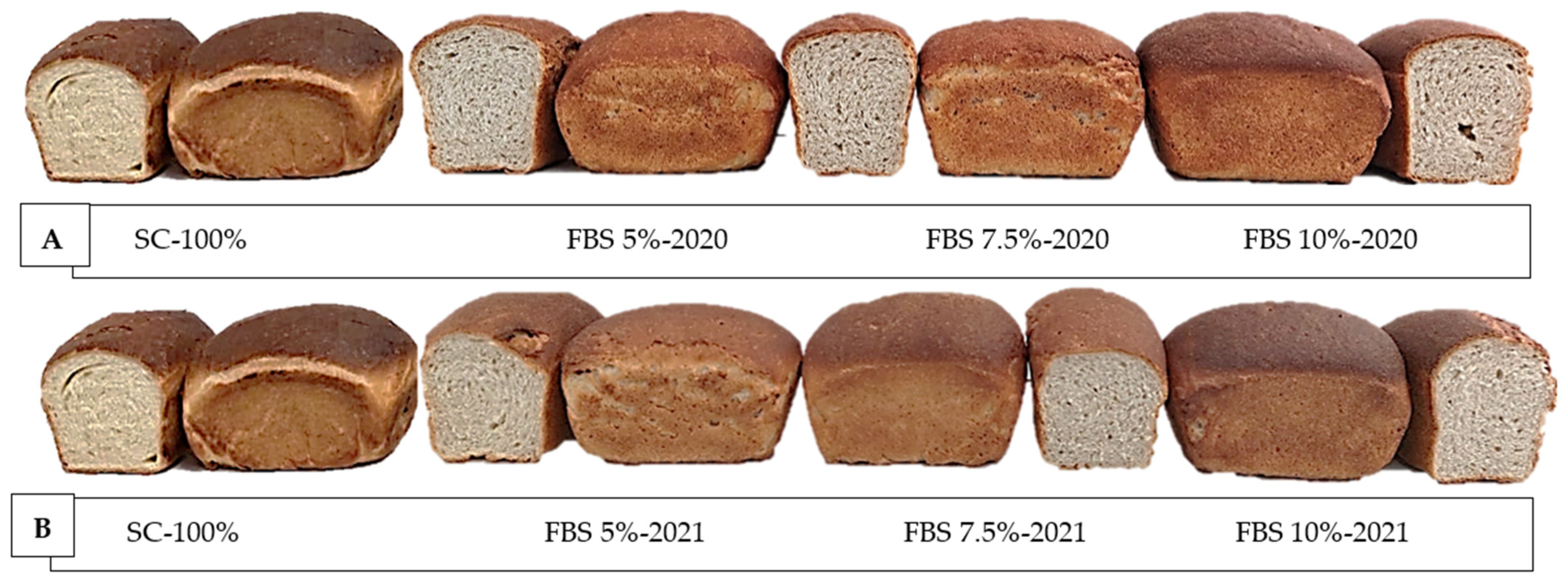
2.6. Evaluation of Quality Parameters of Bread
2.7. Bread Color
2.8. Staling Process
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Preparation of Flour from Bean Seeds
3.3. Determination of Moisture Content
3.4. Water Binding Capacity and Oil Binding Capacity
3.5. Color Determination
3.6. Farinograph and Mixograph Analyses
- -
- Phase of absorption of added water and formation of the gluten mesh;
- -
- Stability, in which disulfide bonds are broken and reformed continuously;
- -
- Gluten mesh rupture and curve slope [61].
3.7. Leavening Test
- (a)
- Control dough: 50 g semolina; 1.5 g yeast; distilled water;
- (b)
- 5% dough: 47.5 g semolina; 2.5 g bean flour; 1.5 g yeast; distilled water;
- (c)
- 7.5% dough: 46.25 g semolina; 3.75 g bean flour; 1.5 g yeast; distilled water;
- (d)
- 10% dough: 45 g semolina; 5 g bean flour; 1.5 g yeast; distilled water.
3.8. Physical Characteristics of Breads with Different Integration Levels of Bean Flour
3.9. Determination of Bread Staling Rate
3.10. Statistical Analyses
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boukid, F.; Zannini, E.; Carini, E.; Vittadini, E. Pulses for bread fortification: A necessity or a choice? Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 88, 416–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministero delle Politiche Agricole, Alimentari e Forestali. I Legumi da Granella; Ministero delle Politiche Agricole, Alimentari e Forestali: Roma, Italy, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Siddiq, M.; Ravi, R.; Harte, J.B.; Dolan, K.D. Physical and functional characteristics of selected dry bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) flours. LWT 2010, 43, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angioloni, A.; Collar, C. High legume-wheat matrices: An alternative to promote bread nutritional value meeting dough viscoelastic restrictions. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2012, 234, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miñarro, B.; Albanell, E.; Aguilar, N.; Guamis, B.; Capellas, M. Effect of legume flours on baking characteristics of gluten-free bread. J. Cereal Sci. 2012, 56, 476–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semba, R.D.; Ramsing, R.; Rahman, N.; Kraemer, K.; Bloem, M.W. Legumes as a sustainable source of protein in human diets. Glob. Food Secur. 2021, 28, 100520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dziki, D.; Różyło, R.; Gawlik-Dziki, U.; Świeca, M. Current trends in the enhancement of antioxidant activity of wheat bread by the addition of plant materials rich in phenolic compounds. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 40, 48–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litvynchuk, S.; Galenko, O.; Cavicchi, A.; Ceccanti, C.; Mignani, C.; Guidi, L.; Shevchenko, A. Conformational Changes in the Structure of Dough and Bread Enriched with Pumpkin Seed Flour. Plants 2022, 11, 2762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coţovanu, I.; Mironeasa, S. Effects of molecular characteristics and microstructure of amaranth particle sizes on dough rheology and wheat bread characteristics. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 7883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coţovanu, I.; Mironeasa, S. Influence of buckwheat seed fractions on dough and baking performance of wheat bread. Agronomy 2022, 12, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anton, A.A.; Ross, K.A.; Lukow, O.M.; Fulcher, R.G.; Arntfield, S.D. Influence of added bean flour (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) on some physical and nutritional properties of wheat flour tortillas. Food Chem. 2008, 109, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ficco, D.B.M.; Muccilli, S.; Padalino, L.; Giannone, V.; Lecce, L.; Giovanniello, V.; Del Nobile, M.A.; De Vita, P.; Spina, A. Durum wheat breads ‘high in fibre’ and with reduced in vitro glycaemic response obtained by partial semolina replacement with minor cereals and pulses. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 55, 4458–4467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Câmara, C.R.; Urrea, C.A.; Schlegel, V. Pinto beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) as a functional food: Implications on human health. Agriculture 2013, 3, 90–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, L.; Mendez, D.; Montecino, H.; Carrasco, B.; Arevalo, B.; Palomo, I.; Fuentes, E. Role of Phaseolus vulgaris L. in the prevention of cardiovascular diseases—Cardioprotective potential of bioactive compounds. Plants 2022, 11, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horax, R.; Hettiarachchy, N.S.; Chen, P.; Jalaluddin, M. Preparation and characterization of protein isolate from cowpea (Vigna unguiculata L. Walp.). J. Food Sci. 2004, 69, fct114–fct118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Różyło, R.; Dziki, D.; Gawlik-Dziki, U.; Cacak-Pietrzak, G.; Miś, A.; Rudy, S. Physical properties of gluten-free bread caused by water addition. Int. Agrophys. 2015, 29, 353–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spina, A.; Brighina, S.; Muccilli, S.; Mazzaglia, A.; Fabroni, S.; Fallico, B.; Rapisarda, P.; Arena, E. Wholegrain durum wheat bread fortified with citrus fibres: Evaluation of quality parameters during long storage. Front. Nutr. 2019, 6, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Hu, R.; Tilley, M.; Siliveru, K.; Li, Y. Effect of Pulse Type and Substitution Level on Dough Rheology and Bread Quality of Whole Wheat-Based Composite Flours. Processes 2021, 9, 1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedier, D.F.; Salem, R.; Almashad, A.A.; Barakat, E.H. Quality assurance of functional biscuits produced from red kidney beans flour. Arch. Agri. Sci. J. 2021, 4, 251–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manonmani, D.; Bhol, S.; Bosco, S.J.D. Effect of red kidney bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) flour on bread quality. Open Access Libr. 2014, 1, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marletta, L.; Carnovale, E. Tabelle di Composizione Degli Alimenti; Istituto Nazionale di Ricerca per gli Alimenti e la Nutrizione: Milano, Italy, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Rezende, A.A.; Pacheco, M.T.B.; Silva, V.S.N.D.; Ferreira, T.A.P.D.C. Nutritional and protein quality of dry Brazilian beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 38, 421–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gomaa, E.; Elhadidy, G. Preparation of functional foods free of gluten for celiac disease patients. J. Sustain. Agric. 2020, 46, 13–24. [Google Scholar]
- Shimelis, E.A.; Meaza, M.; Rakshit, S. Physico-chemical properties, pasting behavior and functional characteristics of flours and starches from improved bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) varieties grown in East Africa. Comm. Int. Du Genie Rural. 2006, 8, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, B.J.; Yuan, S.H.; Chang, S.K.C. Comparative analyses of phenolic composition, antioxidant capacity, and colour of cool season legumes and other selected food legumes. J. Food Sci. 2007, 72, S167–S177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannone, V.; Giarnetti, M.; Spina, A.; Todaro, A.; Pecorino, B.; Summo, C.; Pasqualone, A. Physico-chemical properties and sensory profile of durum wheat Dittaino PDO (Protected Designation of Origin) bread and quality of re-milled semolina used for its production. Food Chem. 2018, 241, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bojňanská, T.; Musilová, J.; Vollmannová, A. Effects of adding legume flours on the rheological and breadmaking properties of dough. Foods 2021, 10, 1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohajdová, Z.; Karovičová, J.; Magala, M. Effect of lentil and bean flours on rheological and baking properties of wheat dough. Chem. Pap. 2013, 67, 398–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pleming, D.; Farahnaky, A.; Majzoobi, M. Effects of bread making methods, lupin variety and gluten powder on the quality of bread enriched with high percentage of lupin flour. Int. J. Food Sci. 2021, 56, 6707–6718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Des Marchais, L.P.; Foisy, M.; Mercier, S.; Villeneuve, S.; Mondor, M. Bread-making potential of pea protein isolate produced by a novel ultrafiltration/diafiltration process. Procedia Food Sci. 2011, 1, 1425–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoxha, I.; Macedonia, N.; Deliu, R.; Industry, F. The impact of flour from white bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) on rheological, qualitative and nutritional properties of the bread. Open Access Libr. 2020, 7, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohajdová, Z.; Karovicova, J. Effect of incorporation of spelt flour on the dough properties and wheat bread quality. Żywność Nauka Technol. Jakość 2007, 14, 36–45. [Google Scholar]
- Dervas, G.; Doxastakis, G.; Hadjisavva-Zinoviadi, S.; Triantafillakos, N. Lupin flour addition to wheat flour doughs and effect on rheological properties. Food Chem. 1999, 66, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinant, J.P.; Nicolas, Y.; Bouguennec, A.; Popineau, Y.; Saulnier, L.; Branlard, G. Relationships between mixograph parameters and indices of wheat grain quality. J. Cereal Sci. 1998, 27, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wani, I.A.; Sogi, D.S.; Wani, A.A.; Gill, B.S. Physico-chemical and functional properties of flours from Indian kidney bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) cultivars. LWT 2013, 53, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.Y.; Piva, M.; Labuza, T.P. Evaluation of water binding capacity (WBC) of food fibre sources. J. Cereal Sci. 1984, 49, 59–63. [Google Scholar]
- Salami, K.O.; Kayode, R.O.; Duada, A.O.; Abdulrufia, F.I. Physical, chemical and sensory properties of bread from blends of wheat and lima bean flours. Biosci. Res. 2021, 32, 87–96. [Google Scholar]
- Malekipoor, R.; Johnson, S.K.; Bhattarai, R.R. Lupin Kernel Fibre: Nutritional Composition, Processing Methods, Physicochemical Properties, Consumer Acceptability and Health Effects of Its Enriched Products. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasmadi, M.; Noorfarahzilah, M.; Noraidah, H.; Zainol, M.K.; Jahurul, M.H.A. Functional properties of composite flour: A review. Food Res. 2020, 4, 1820–1831. [Google Scholar]
- Sathe, S.K.; Deshpande, S.S.; Salunkhe, D.K. Functional properties of winged bean [Psophocarpus tetragonolobus (L.) DC] proteins. J. Food Sci. 1982, 47, 503–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, S.K.; Jiang, H.; Yu, X.; Jane, J.L. Physicochemical and functional properties of whole legume flour. LWT 2014, 55, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravi, R.; Sushelamma, N.S. Simultaneous optimization of a multiresponse system by desirability function analysis of boondi making: A case study. J. Food Sci. 2005, 70, S539–S547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhol, S.; Bosco, S.J.D. Influence of malted finger millet and red kidney bean flour on quality characteristics of developed bread. LWT 2014, 55, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, R.; Prasad, K. Technological, processing and nutritional aspects of chickpea (Cicer arietinum)—A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 109, 448–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baardseth, P.; Kvaal, K.; Lea, P.; Ellekjær, M.R.; Færgestad, E.M. The effects of bread making process and wheat quality on French baguettes. J. Cereal Sci. 2000, 32, 73–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Zhou, W.; Isabelle, M. Comparison study of the effect of green tea extract (GTE) on the quality of bread by instrumental analysis and sensory evaluation. Food Res. Int. 2007, 40, 470–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, G.M. Bread aeration. In Bread Making: Improving Quality; Cauvin, S.P., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2003; pp. 352–374. [Google Scholar]
- Bresciani, A.; Marti, A. Using pulses in baked products: Lights, shadows, and potential solutions. Foods 2019, 8, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yellavila, S.B.; Agbenorhevi, J.K.; Asibuo, J.Y.; Sampson, G.O. Proximate Composition, Minerals Content and Functional Properties of Five Lima Bean Accessions. J. Food Secur. 2015, 3, 69–74. [Google Scholar]
- Brummer, Y.; Kaviani, M.; Tosh, S.M. Structural and functional characteristics of dietary fibre in beans, lentils, peas and chickpeas. Food Res. Int. 2015, 67, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariscal-Moreno, R.M.; Chuck-Hernández, C.; Figueroa-Cárdenas, J.D.D.; Serna-Saldivar, S.O. Physicochemical and Nutritional Evaluation of Bread Incorporated with Ayocote Bean (Phaseolus coccineus) and Black Bean (Phaseolus vulgaris). Processes 2021, 9, 1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, I.; Ahmed, A.R.; Senge, B. Effects of chickpea flour on wheat pasting properties and bread making quality. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 51, 1902–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mohammed, I.; Ahmed, A.R.; Senge, B. Dough rheology and bread quality of wheat–chickpea flour blends. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2012, 36, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasqualone, A.; Caponio, F.; Simeone, R. Quality evaluation of re-milled durum wheat semolinas used for bread-making in Southern Italy. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2004, 219, 630–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winham, D.M.; Thompson, S.V.; Heer, M.M.; Davitt, E.D.; Hooper, S.D.; Cichy, K.A.; Knoblauch, S.T. Black Bean Pasta Meals with Varying Protein Concentrations Reduce Postprandial Glycemia and Insulinemia Similarly Compared to White Bread Control in Adults. Foods 2022, 11, 1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AOAC. Official Method 935.25; AOAC International: Arlington, WA, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- He, H.; Hoseney, R.C. Changes in bread firmness and moisture during long-term storage. Cereal Chem. 1990, 67, 603–605. [Google Scholar]
- Kahraman, G.; Harsa, S.; Lucisano, M.; Cappa, C. Physicochemical and rheological properties of rice-based gluten-free blends containing differently treated chickpea flours. LWT 2018, 98, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altman, D.G.; Bland, J.M. Measurement in medicine: The analysis of method comparison studies. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. D Stat. Soc. 1983, 32, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, J.M.; Weatherall, I.L.; Litilejohn, R.P.; Seman, D.L. A comparison of two different instruments for measuring venison CIELAB values and colour assessment by a trained panel. N. Z. J. Agric. Res. 1991, 34, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Guo, Q.; Wang, C.; Ding, H.H.; Cui, S.W. Fenugreek fibre in bread: Effects on dough development and bread quality. LWT 2016, 71, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AACC. Approved Methods of Analysis, 11th ed.; The American Association of Cereal Chemists: St. Paul, MN, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Irvine, G.N.; Bradley, J.W.; Martin, G.C. A farinograph technique for macaroni doughs. Cereal Chem. 1961, 38, 153–164. [Google Scholar]
- Quick, J.S.; Donnelly, B.J. A Rapid for Estimating Durum Wheat Gluten Quality 1. Crop Sci. 1980, 20, 816–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walle, M.; Trentesaux, E. Studio di un metodo pratico con l’alveografo di Chopin per la valutazione dell’attitudine dei grani duri e delle semole a produrre pasta alimentare. Tec. Molitaria 1980, 12, 917–922. [Google Scholar]
- Edwards, N.M.; Gianibelli, M.C.; McCaig, T.N.; Clarke, J.M.; Ames, N.P.; Larroque, O.R.; Dexter, J.E. Relationships between dough strength, polymeric protein quantity and composition for diverse durum wheat genotypes. J. Cereal Sci. 2007, 45, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canale, M.; Spina, A.; Summo, C.; Strano, M.C.; Bizzini, M.; Allegra, M.; Sanfilippo, R.; Amenta, M.; Pasqualone, A. Waste from artichoke processing industry: Reuse in bread-making and evaluation of the physi-co-chemical characteristics of the final product. Plants 2022, 11, 3409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dallmann, H. Porentabelle, 4th ed.; Verlag Moritz Schäfer: Detmold, Germany, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Bot, B.; Sánchez, H.; de la Torre, M.; Osella, C. Mother dough in bread making. Food Sci. Nutr. 2014, 2, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


| Type of Flour | Moisture (g/100 g) | Protein (g/100 g) |
|---|---|---|
| Pure flours | ||
| SC-100% | 13.93 ± 0.13 a | 11.90 ± 0.14 b |
| FBS 100%-2020 | 10.13 ± 0.13 e | 18.81 ± 0.14 a |
| FBS 100%-2021 | 11.05 ± 0.05 de | 19.20 ± 0.28 a |
| Mixes | ||
| FBS 5%-2020 | 12.77 ± 0.16 bc | 12.23 ± 0.04 b |
| FBS 7.5%-2020 | 12.26 ± 0.13 bc | 12.40 ± 0.28 b |
| FBS 10%-2020 | 11.12 ± 0.14 de | 12.57 ± 0.05 b |
| FBS 5%-2021 | 13.18 ± 0.05 ab | 12.26 ± 0.06 b |
| FBS 7.5%-2021 | 11.91 ± 0.18 cd | 12.43 ± 0.03 b |
| FBS 10%-2021 | 11.82 ± 0.24 cd | 12.60 ± 0.28 b |
| Nutrient | ‘Signuredda’ Bean 2020 | ‘Signuredda’ Bean 2021 | Fresh Raw Bean Seed (INRAN Data) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total carbohydrates (g/100 g) | 43.1 ± 0.20 a | 42.8 ± 0.14 a | 47.5 ± 0.28 a |
| Total fats (g/100 g) | 1.4 ± 0.11 d | 1.3 ± 0.08 d | 2.0 ± 0.42 d |
| of which saturated fatty acids (g/100 g) | 0.3 ± 0.00 | 0.2 ± 0.01 | - |
| Proteins (g/100 g) | 18.8 ± 0.04 b | 19.2 ± 0.02 b | 23.6 ± 0.71 b |
| Dietary fiber (g/100 g) | 17.1 ± 0.18 c | 16.9 ± 0.10 c | 17.5 ± 0.34 c |
| Salt (g/100 g) | 0.006 ± 0.00 e | 0.006 ± 0.00 e | 0.006 ± 0.00 e |
| Energy value (Kcal) | 294.4 | 293.5 | 291.0 |
| Energy value (KJ) | 1232 | 1228 | 1216 |
| Mineral | Concentration (mg/100 g) | |
|---|---|---|
| FBS 100%-2020 | FBS 100%-2021 | |
| Calcium | 478.3 ± 0.17 d | 481.80 ± 0.30 d |
| Magnesium | 698.74 ± 0.21 c | 694.40 ± 0.88 c |
| Sodium | 95.24 ± 0.88 e | 97.84 ± 1.22 e |
| Potassium | 6742.00 ± 7.07 a | 6804.00 ± 7.07 a |
| Phosphorus | 1839.00 ± 2.12 b | 1826.00 ± 1.41 b |
| Copper | 0.52 ± 0.02 g | 0.65 ± 0.04 g |
| Manganese | 2.39 ± 0.03 g | 2.43 ± 0.20 g |
| Zinc | 22.89 ± 0.08 f | 23.37 ± 0.12 f |
| Iron | 30.02 ± 0.03 f | 28.76 ± 0.29 f |
| Type of Flour | Brown Index (100-L) | a* | b* |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pure Flours | |||
| SC-100% | 10.26 ± 0.01 f | −2.38 ± 0.00 e | 17.17 ± 0.00 a |
| FBS 100%-2020 | 13.63 ± 0.07 b | 1.08 ± 0.07 a | 7.54 ± 0.08 f |
| FBS 100%-2021 | 14.49 ± 0.02 a | 1.29 ± 0.02 a | 8.38 ± 0.01 e |
| Mixes | |||
| FBS 5%-2020 | 11.50 ± 0.01 e | −1.70 ± 0.02 d | 16.72 ± 0.01 b |
| FBS 7.5%-2020 | 12.98 ± 0.04 c | −1.37 ± 0.03 bc | 16.75 ± 0.01 b |
| FBS 10%-2020 | 12.20 ± 0.02 d | −1.23 ± 0.01 b | 15.37 ± 0.01 d |
| FBS 5%-2021 | 11.49 ± 0.02 e | −1.77 ± 0.01 d | 16.69 ± 0.02 b |
| FBS 7.5%-2021 | 12.74 ± 0.03 c | −1.57 ± 0.02 cd | 16.05 ± 0.04 c |
| FBS 10%-2021 | 12.22 ± 0.03 d | −1.31 ± 0.05 b | 15.33 ± 0.04 d |
| Year | Brown Index (100-L) | a* | b* |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | 12.58 ± 0.86 a | −0.80 ± 1.18 | 14.10 ± 4.09 |
| 2021 | 12.73 ± 1.18 a | −0.84 ± 1.32 | 14.11 ± 3.57 |
| Integration Percentage | Brown Index (100-L) | a* | b* |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pure Flours | |||
| FBS 100% | 14.06 ± 0.50 a | 1.18 ± 0.13 a | 7.96 ± 0.49 c |
| Mixes | |||
| FBS 5% | 11.49 ± 0.02 d | −1.73 ± 0.05 d | 16.70 ± 0.02 a |
| FBS 7.5% | 12.85 ± 0.14 c | −1.47 ± 0.11 c | 16.40 ± 0.41 b |
| FBS 10% | 12.21 ± 0.02 b | −1.27 ± 0.05 b | 15.35± 0.03 d |
| Type of Flour | Farinograph Data | Mixograph Data | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dough Development Time (min) | Stability (min) | Water Absorption at 500 B.U. * (%) | Mixing Time (min) | Peak Dough Height (M.U.) ** | |
| SC-100% | 1.75 ± 0.07 a | 3.15 ± 0.07 b | 61.60 ± 0.14 b | 2.65 ± 0.02 e | 5.60 ± 0.14 bc |
| FBS 5%-2020 | 1.60 ± 0.00 ab | 4.45 ± 0.07 a | 66.55 ± 0.07 a | 3.93 ± 0.02 bc | 6.30 ± 0.14 b |
| FBS 7.5%-2020 | 1.45 ± 0.07 b | 4.60 ± 0.14 a | 67.30 ± 0.14 a | 3.79 ± 0.01 c | 5.05 ± 0.07 c |
| FBS 10%-2020 | 1.65 ± 0.07 ab | 4.75 ± 0.07 a | 68.30 ± 0.42 a | 4.27 ± 0.02 a | 4.90 ± 0.14 c |
| FBS 5%-2021 | 1.55 ± 0.07 ab | 4.30 ± 0.14 a | 66.50 ± 0.14 a | 2.73 ± 0.01 e | 7.65 ± 0.07 a |
| FBS 7.5%-2021 | 1.45 ± 0.07 b | 4.60 ± 0.14 a | 67.20 ± 0.28 a | 3.40 ± 0.02 d | 5.00 ± 0.14 c |
| FBS 10%-2021 | 1.65 ± 0.07 ab | 4.75 ± 0.07 a | 68.40 ± 0.71 a | 4.10 ± 0.02 ab | 5.05 ± 0.07 c |
| Year | Farinograph | Mixograph | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dough Development Time (min) | Stability (min) | Water Absorption at 500 B.U. * (%) | Mixing Time (min) | Peak Dough Height (M.U.) ** | |
| 2020 | 1.57 ± 0.10 | 4.60 ± 0.15 | 66.38 ± 0.81 | 3.99 ± 0.22 a | 5.42 ± 0.69 b |
| 2021 | 1.55 ± 0.10 | 4.55 ± 0.23 | 67.37 ± 1.00 | 3.41 ± 0.62 b | 5.90 ± 1.35 a |
| Integration Percentage | Farinograph | Mixograph | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dough Development Time (min) | Stability (min) | Water Absorption at 500 B.U. * (%) | Mixing Time (min) | Peak Dough Height (M.U.) ** | |
| FBS 5% | 1.58 ± 0.05 ab | 4.38 ± 0.13 ab | 66.48 ± 0.05 a | 3.33 ± 0.70 c | 6.98 ± 0.78 a |
| FBS 7.5% | 1.45 ± 0.06 b | 4.60 ± 0.06 b | 67.25 ± 0.06 a | 3.59 ± 0.23 b | 5.03 ± 0.10 b |
| FBS 10% | 1.65 ± 0.06 a | 4.75 ± 0.06 a | 68.40 ± 0.06 a | 4.18 ±0.10 a | 4.98 ± 0.13 b |
| Type of Bread | Specific Volume (cm3/g) | Specific Weight (g/cm3) | Porosity * |
|---|---|---|---|
| SC-100% | 3.05 ± 0.05 a | 0.33 ± 0.01 ab | 7.00 ± 0.00 a |
| FBS5%-2020 | 3.29 ± 0.00 a | 0.30 ± 0.00 ab | 5.00 ± 0.00 b |
| FBS7.5%-2020 | 3.25 ± 0.12 a | 0.31 ± 0.01 ab | 5.00 ± 0.00 b |
| FBS10%-2020 | 3.30 ± 0.18 a | 0.30 ± 0.02 ab | 5.50 ± 0.00 b |
| FBS5%-2021 | 2.97 ± 0.12 a | 0.34 ± 0.01 a | 5.50 ± 0.00 b |
| FBS7.5%-2021 | 3.40 ± 0.06 a | 0.29 ± 0.00 b | 6.00 ± 0.00 ab |
| FBS10%-2021 | 3.35 ± 0.13 a | 0.30 ± 0.01 ab | 5.25 ± 0.35 b |
| Year | Specific Volume (cm3/g) | Specific Weight (g/cm3) | Porosity * |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | 3.28 ± 0.10 | 0.31 ± 0.01 | 5.17 ± 0.26 b |
| 2021 | 3.24 ± 0.22 | 0.31 ± 0.02 | 5.58 ± 0.38 a |
| Integration Percentage | Specific Volume (cm3/g) | Specific Weight (g/cm3) | Porosity * |
|---|---|---|---|
| FBS 5% | 3.15 ± 0.17 | 0.32 ± 0.02 | 5.00 ± 0.00 |
| FBS 7.5% | 3.31 ± 0.10 | 0.30 ± 0.01 | 5.50 ± 0.58 |
| FBS 10% | 3.31 ± 0.15 | 0.30 ± 0.01 | 5.75 ± 0.29 |
| Crust | Crumb | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample | Brown Index (100-L) | a* | b* | Brown Index (100-L) | a* | b* |
| SC-100% | 62.54 ± 1.10 | 12.85 ± 1.27 | 17.82 ± 4.11 | 23.78 ± 2.14 b | −2.92 ± 0.28 b | 19.34 ± 2.04 a |
| FBS5%-2020 | 61.97 ± 1.51 | 14.95 ± 1.54 | 20.08 ± 1.73 | 28.79 ± 0.25 ab | −0.24 ± 0.17 a | 10.83 ± 0.06 b |
| FBS7.5%-2020 | 61.93 ± 2.96 | 15.62 ± 0.35 | 20.88 ± 1.27 | 31.39 ± 0.40 a | 0.09 ± 0.08 a | 11.20 ± 0.28 b |
| FBS10%-2020 | 63.15 ± 3.18 | 14.80 ± 1.40 | 18.43 ± 3.38 | 31.06 ± 0.52 ab | 0.40 ± 0.03 a | 11.87 ± 0.02 b |
| FBS5%-2021 | 60.40 ± 0.02 | 15.00 ± 0.86 | 19.63 ± 0.54 | 26.59 ± 3.06 ab | −0.49 ± 0.01 a | 12.30 ± 0.63 b |
| FBS7.5%-2021 | 59.93 ± 0.21 | 14.83 ± 1.39 | 20.37 ± 0.65 | 29.35 ± 2.59 ab | 0.27 ± 0.49 a | 11.06 ± 0.30 b |
| FBS10%-2021 | 66.05 ± 0.42 | 12.38 ± 0.18 | 14.03 ± 0.59 | 31.70 ± 1.74 a | 0.75 ± 0.04 a | 12.27 ± 0.12 b |
| Crust | Crumb | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | Brown Index (100-L) | a* | b* | Brown Index (100-L) | a* | b* |
| 2020 | 62.35 ± 2.15 | 15.12 ± 1.02 | 19.80 ± 2.11 | 30.41 ± 1.30 | 0.08 ± 0.30 | 11.30 ± 0.49 b |
| 2021 | 62.13 ± 3.05 | 14.07 ± 1.51 | 18.01 ± 3.13 | 29.21 ± 3.01 | 0.18 ± 0.60 | 11.87 ± 0.70 a |
| Crust | Crumb | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Integration Percentage | Brown Index (100-L) | a* | b* | Brown Index (100-L) | a* | b* |
| FBS 5% | 61.18 ± 1.26 | 14.98 ± 1.02 | 19.86 ± 1.08 ab | 27.69 ± 2.18 | −0.36 ± 0.17 b | 11.56 ± 0.92 ab |
| FBS 7.5% | 60.93 ± 2.06 | 15.22 ± 0.94 | 20.62 ± 0.87 a | 30.37 ± 1.91 | 0.18 ± 0.31 ab | 11.13 ± 0.25 b |
| FBS 10% | 64.60 ± 2.50 | 13.59 ± 1.62 | 16.23 ± 3.22 b | 31.38 ± 1.11 | 0.58 ± 0.20 a | 12.07 ± 0.24 a |
| Days After Baking | Type of Bread | Moisture (g/100 g) | Volume (cm3) | Weight (g) | Height (mm) | Hardness (N) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T0 | SC-100% | 31.5 ± 2.12 b(a) | 440.0 ± 3.54 b(a) | 144.5 ± 1.13 b(a) | 82.0 ± 1.20 | 12.1 ± 0.64 a(c) |
| FBS5%-2020 | 37.5 ± 0.71 a(a) | 480.0 ± 0.00 a(a) | 146.0 ± 0.18 ab(a) | 78.7 ± 0.21 | 9.0 ± 1.33 ab(b) | |
| FBS7.5%-2020 | 36.0 ± 1.41 a(a) | 485.0 ± 17.68 a(a) | 149.4± 0.21 a(a) | 78.0 ± 1.91 | 6.8 ± 1.03 b(b) | |
| FBS10%-2020 | 35.5 ± 0.01 ab(a) | 480.0 ± 28.28 a | 145.5 ± 0.67 ab(a) | 79.9 ± 4.24 | 7.5 ± 0.23 b(b) | |
| FBS5%-2021 | 34.5 ± 0.71 ab(a) | 437.5 ± 10.61 b(a) | 147.1 ± 2.37 ab(a) | 74.1 ± 4.67 | 9.2 ± 1.64 ab(b) | |
| FBS7.5%-2021 | 35.0 ± 0.00 ab(a) | 497.5 ± 16.61 a(a) | 146.4 ± 0.71 ab(a) | 80.0 ± 3.04 | 7.0 ± 0.97 b(c) | |
| FBS10%-2021 | 35.5 ± 0.71 ab(a) | 487.5 ± 17.68 a(a) | 145.5 ± 0.25 ab(a) | 82.9 ± 0.49 (a) | 8.3 ± 0.85 ab(b) | |
| T1 | SC-100% | 27.5 ± 0.71 (ab) | 408.2 ± 3.28 b(ab) | 134.4 ± 1.05 b(ab) | 79.9 ± 1.17 | 33.7 ± 0.03 a(ab) |
| FBS5%-2020 | 27.5 ± 2.12 (ab) | 445.3 ± 0.35 ab(b) | 141.0 ± 0.74 ab(ab) | 76.5 ± 3.32 | 12.5 ± 2.35 b(ab) | |
| FBS7.5%-2020 | 30.0 ± 0.00 (ab) | 462.5 ± 21.21 a(a) | 144.6 ± 0.00 a(ab) | 75.9 ± 1.56 | 9.7 ± 2.13 b(ab) | |
| FBS10%-20 | 31.0 ± 0.00 (ab) | 462.3 ± 28.64 a | 141.8 ± 0.14 a(a) | 78.1 ± 3.46 | 11.3 ± 1.76 b(b) | |
| FBS5%-2021 | 28.0 ± 1.41 (b) | 412.5 ± 7.07 b(ab) | 140.4 ± 1.22 ab(ab) | 71.4 ± 3.39 | 14.3 ± 0.94 b(b) | |
| FBS7.5%-2021 | 30.0 ± 1.41 (ab) | 467.3 ± 6.72 a(a) | 138.5 ± 1.28 ab(ab) | 78.9 ± 1.56 | 11.1 ± 1.87 b(bc) | |
| FBS10%-2021 | 29.5 ± 0.71 (a) | 462.8 ± 24.40 a(ab) | 138.6 ± 0.22 ab(ab) | 78.9 ± 0.35 (ab) | 14.7 ± 3.29 b(b) | |
| T4 | SC-100% | 26.0 ± 0.00 (b) | 400.2 ± 3.22 abc(ab) | 124.4 ± 0.97 ab(bc) | 78.7 ± 1.15 | 28.2 ± 0.24 (b) |
| FBS5%-2020 | 28.5 ± 3.54 (ab) | 380.8 ± 1.06 bc(c) | 127.6 ± 3.25 ab(bc) | 75.5 ± 4.67 | 23.4 ± 1.27 (ab) | |
| FBS7.5%-2020 | 30.0 ± 4.24 (ab) | 390.0 ± 14.14 bc (b) | 129.7 ± 2.55 a(bc) | 75.1 ± 2.12 | 24.7 ± 0.13 (a) | |
| FBS10%-2020 | 26.0 ± 4.24 (b) | 440.0 ± 21.21 ab | 129.5 ± 0.09 a(b) | 77.0 ± 3.89 | 22.0 ± 2.67 (ab) | |
| FBS5%-2021 | 25.5 ± 0.71 (b) | 360.0 ± 7.07 c(bc) | 129.2 ± 0.07 a(ab) | 70.7 ± 2.40 | 28.3 ± 0.76 (ab) | |
| FBS7.5%-2021 | 31.0 ± 0.00 (a) | 460.0 ± 7.07 a(a) | 122.3 ± 0.30 b(bc) | 77.9 ± 0.92 | 25.3 ± 3.35 (ab) | |
| FBS10%-2021 | 31.0 ± 0.00 (a) | 412.5 ± 17.68 abc(b) | 122.4 ± 0.05 b(bc) | 77.9 ± 0.28 (b) | 23.7 ± 1.84 (ab) | |
| T6 | SC-100% | 25.0 ± 0.00 a(b) | 386.3 ± 3.10 ab(b) | 119.4 ± 0.93 (c) | 77.5 ± 1.14 | 39.0 ± 1.00 (a) |
| FBS5%-2020 | 22.5 ± 0.71 ab(b) | 351.0 ± 1.41 c(d) | 120.3 ± 3.08 (c) | 74.3 ± 3.89 | 37.2 ± 3.26 (a) | |
| FBS7.5%-2020 | 22.5 ± 3.54 ab(b) | 383.8 ± 8.84 abc(b) | 124.0 ± 5.42 (c) | 73.4 ± 1.34 | 26.9 ± 1.44 (a) | |
| FBS10%-2020 | 24.0 ± 0.00 ab(b) | 392.5 ± 3.54 a | 122.0 ± 0.47 (c) | 76.2 ± 3.68 | 30.6 ± 4.85 (a) | |
| FBS5%-2021 | 24.5 ± 0.71 a(b) | 355.0 ± 7.07 bc(c) | 122.9 ± 2.32 (b) | 69.9 ± 1.84 | 35.3 ± 2.57 (a) | |
| FBS7.5%-2021 | 22.0 ± 0.00 ab(b) | 403.8 ± 8.84 a(b) | 119.8 ± 2.42 (c) | 76.7 ± 0.42 | 32.0 ± 3.75 (a) | |
| FBS10%-2021 | 18.5 ± 0.71 b(b) | 394.5 ± 7.78 a(b) | 119.1 ± 5.15 (c) | 77.4 ± 0.14 (b) | 32.6 ± 3.42 (a) |
| Bread Type | Re-Milled Semolina | FBS 2020 | FBS 2021 | Yeast | NaCl | Ascorbic Acid | Sugar | Shortening | Water * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SC-100% | 100 | - | - | 0.6 | 0.4 | 8 × 10−4 | 1.2 | 3.5 | 61.6 |
| FBS 5%-2020 | 95 | 5 | - | 0.6 | 0.4 | 8 × 10−4 | 1.2 | 3.5 | 66.6 |
| FBS 7.5%-2020 | 92.5 | 7.5 | - | 0.6 | 0.4 | 8 × 10−4 | 1.2 | 3.5 | 67.3 |
| FBS 10%-2020 | 90 | 10 | - | 0.6 | 0.4 | 8 × 10−4 | 1.2 | 3.5 | 68.3 |
| FBS 5%-2021 | 95 | - | 5 | 0.6 | 0.4 | 8 × 10−4 | 1.2 | 3.5 | 66.5 |
| FBS 7.5%-2021 | 92.5 | - | 7.5 | 0.6 | 0.4 | 8 × 10−4 | 1.2 | 3.5 | 67.2 |
| FBS 10%-2021 | 90 | - | 10 | 0.6 | 0.4 | 8 × 10−4 | 1.2 | 3.5 | 68.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sanfilippo, R.; Canale, M.; Dugo, G.; Oliveri, C.; Scarangella, M.; Strano, M.C.; Amenta, M.; Crupi, A.; Spina, A. Effects of Partial Replacement of Durum Wheat Re-Milled Semolina with Bean Flour on Physico-Chemical and Technological Features of Doughs and Breads during Storage. Plants 2023, 12, 1125. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12051125
Sanfilippo R, Canale M, Dugo G, Oliveri C, Scarangella M, Strano MC, Amenta M, Crupi A, Spina A. Effects of Partial Replacement of Durum Wheat Re-Milled Semolina with Bean Flour on Physico-Chemical and Technological Features of Doughs and Breads during Storage. Plants. 2023; 12(5):1125. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12051125
Chicago/Turabian StyleSanfilippo, Rosalia, Michele Canale, Giacomo Dugo, Cinzia Oliveri, Michele Scarangella, Maria Concetta Strano, Margherita Amenta, Antonino Crupi, and Alfio Spina. 2023. "Effects of Partial Replacement of Durum Wheat Re-Milled Semolina with Bean Flour on Physico-Chemical and Technological Features of Doughs and Breads during Storage" Plants 12, no. 5: 1125. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12051125
APA StyleSanfilippo, R., Canale, M., Dugo, G., Oliveri, C., Scarangella, M., Strano, M. C., Amenta, M., Crupi, A., & Spina, A. (2023). Effects of Partial Replacement of Durum Wheat Re-Milled Semolina with Bean Flour on Physico-Chemical and Technological Features of Doughs and Breads during Storage. Plants, 12(5), 1125. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12051125








