Controlled-Release Nitrogen Mixed with Common Nitrogen Fertilizer Can Maintain High Yield of Rapeseed and Improve Nitrogen Utilization Efficiency
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials
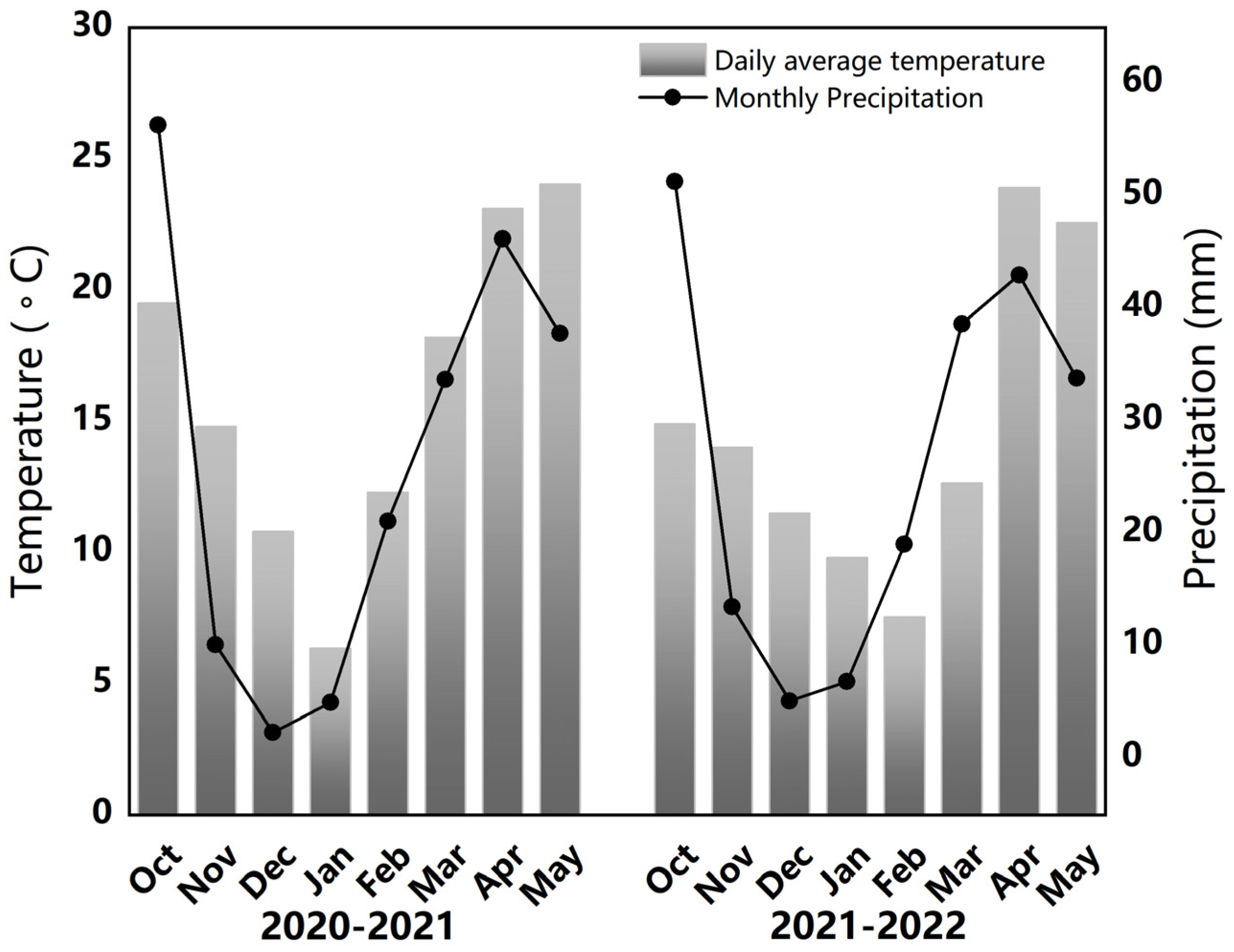
2.2. Experimental Site
2.3. Experiment Design and Field Management
2.4. Sampling and Measurements
2.4.1. Soil Sampling and Determination
2.4.2. Yield and Yield Components
2.4.3. Nitrogen Content
2.4.4. Calculation Methods for Parameters Related to Nitrogen Use
2.5. Statistics Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effects of Different Fertilization Treatments on Soil Microbial Carbon and Nitrogen Content and Enzyme Activity
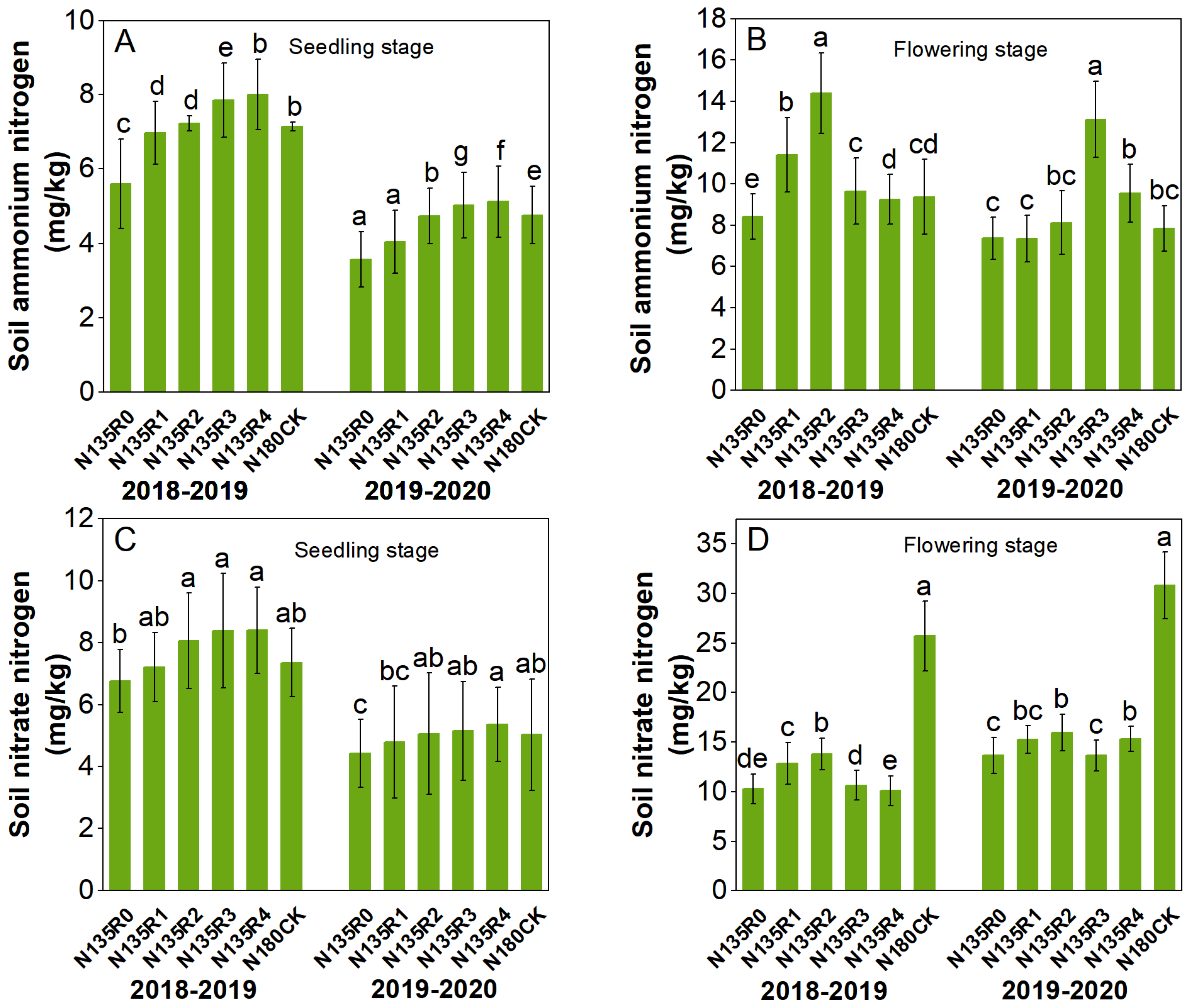
3.2. Effect of Different Fertilizer Treatments on Soil Inorganic N Content
3.3. Yield and Yield Components
3.4. Nitrogen Uptake and Utilization
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, Q.; Niu, J.; Sivakumar, B.; Ding, R.; Li, S. Accessing future crop yield and crop water productivity over the Heihe River basin in northwest China under a changing climate. Geosci. Lett. 2021, 8, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Shah, F.; Ma, B.L. Understanding of crop lodging and agronomic strategies to improve the resilience of rapeseed production to climate change. Crop. Environ. 2022, 1, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahl, A.; Vollrath, P.; Samans, B.; Frisch, M.; Wittkop, B.; Snowdon, R.J. Effect of breeding on nitrogen use efficiency-associated traits in oilseed rape. J. Exp. Bot. 2019, 70, 1969–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathke, G.-W.; Behrens, T.; Diepenbrock, W. Integrated nitrogen management strategies to improve seed yield, oil content and nitrogen efficiency of winter oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.): A review. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2006, 117, 80–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.-F.; Dou, Z.-X.; He, P.; Ju, X.-T.; Powlson, D.; Chadwick, D.; Norse, D.; Lu, Y.-L.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, L. New technologies reduce greenhouse gas emissions from nitrogenous fertilizer in China. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 8375–8380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousaf, M.; Li, X.; Zhang, Z.; Ren, T.; Cong, R.; Ata-Ul-Karim, S.T.; Fahad, S.; Shah, A.N.; Lu, J. Nitrogen fertilizer management for enhancing crop productivity and nitrogen use efficiency in a rice-oilseed rape rotation system in China. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Q.; Hua, W.; Yin, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, L.; Shi, J.; Zhao, Y.; Qin, L.; Chen, C.; Wang, H. Rapeseed research and production in China. Crop J. 2017, 5, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, H.; Tu, S.; Ge, D.; Li, T.; Liu, Y. The allocation and management of critical resources in rural China under restructuring: Problems and prospects. J. Rural. Stud. 2016, 47, 392–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vejan, P.; Khadiran, T.; Abdullah, R.; Ahmad, N. Controlled release fertilizer: A review on developments, applications and potential in agriculture. J. Control. Release 2021, 339, 321–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Lu, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Hussain, S.; Ren, T.; Cong, R.; Li, X. Nitrogen losses, use efficiency, and productivity of early rice under controlled-release urea. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 251, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, Y.; Yang, X.; Pan, H.; Zhang, X.; Cao, H.; Ulgiati, S.; Wu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, G.; Xiao, Y. Impact of fertilization schemes with different ratios of urea to controlled release nitrogen fertilizer on environmental sustainability, nitrogen use efficiency and economic benefit of rice production: A study case from Southwest China. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 293, 126198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaviv, A.; Mikkelsen, R. Controlled-release fertilizers to increase efficiency of nutrient use and minimize environmental degradation—A review. Fertil. Res. 1993, 35, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Peng, F.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhuge, Y.; Zhang, S.; Gao, H. Effect of bag-controlled release fertilizer on nitrogen loss, greenhouse gas emissions, and nitrogen applied amount in peach production. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 234, 258–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.; Liu, X.; Hu, A.; Song, H.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Z. Effects of biochar-based controlled release nitrogen fertilizer on nitrogen-use efficiency of oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.). Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 11063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghafoor, I.; Habib-ur-Rahman, M.; Ali, M.; Afzal, M.; Ahmed, W.; Gaiser, T.; Ghaffar, A. Slow-release nitrogen fertilizers enhance growth, yield, NUE in wheat crop and reduce nitrogen losses under an arid environment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 43528–43543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trenkel, M.E. Slow-and Controlled-Release and Stabilized Fertilizers: An Option for Enhancing Nutrient Use Effiiency in Agriculture; International Fertilizer Industry Association (IFA): Paris, France, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, D.; Xu, K.; Ni, X.; Xiao, Q.; Cao, B.; Liu, B.; Zou, G. Effects of mixed application of controlled-release fertilizer and common fertilizers on greenhouse tomato growth, yield, root distribution, and soil nitrate residual. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2012, 45, 3782–3791. [Google Scholar]
- Li, K.-Y.; Zhao, Y.-Y.; Yuan, X.-L.; Zhao, H.-B.; Wang, Z.-H.; Li, S.-X.; Malhi, S.S. Comparison of factors affecting soil nitrate nitrogen and ammonium nitrogen extraction. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2012, 43, 571–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witt, C.; Gaunt, J.L.; Galicia, C.C.; Ottow, J.C.; Neue, H.-U. A rapid chloroform-fumigation extraction method for measuring soil microbial biomass carbon and nitrogen in flooded rice soils. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2000, 30, 510–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Wang, Q.; Wang, L.; Liu, W.; Liu, X.; Huang, Y.; Christie, P. Response of soil enzymes and microbial communities to root extracts of the alien Alternanthera philoxeroides. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2018, 64, 708–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brentrup, F.; Pallière, C. Nitrogen use efficiency as an agro-environmental indicator. In Proceedings of the OECD Workshop “Agri-Environmental Indicators: Lessons Learned and Future Directions”, Leysin, Switzerland, 23–26 March 2010; pp. 23–26. [Google Scholar]
- Cong, R.; Liu, T.; Lu, P.; Ren, T.; Li, X.; Lu, J. Nitrogen fertilization compensation the weak photosynthesis of Oilseed rape (Brassca napus L.) under haze weather. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaviv, A. Advances in controlled-release fertilizers. Adv. Agron. 2001, 71, 1–49. [Google Scholar]
- Mi, W.; Gao, Q.; Guo, X.; Zhao, H.; Xie, B.; Wu, L. Evaluation of Agronomic and Economic Performance of Controlled and Slow-Release Nitrogen Fertilizers in Two Rice Cropping Systems. Agron. J. 2019, 111, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.-H.; Yang, S.-H.; Chen, J.-S.; Xu, P.-Z.; Zhang, F.-B.; Shao-ying, A.; Huang, X. Studies on the mechanism of single basal application of controlled-release fertilizers for increasing yield of rice (Oryza safiva L.). Agric. Sci. China 2007, 6, 586–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Gu, R.; Xu, K.; Guo, B.; Dai, Q.; Huo, Z.; Wei, H. Split application of a mixture of controlled-release and common urea for improving quality and agronomic and economic performance in wheat production. Crop Sci. 2021, 61, 4402–4415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Thornton, P.E.; Post, W.M. A global analysis of soil microbial biomass carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus in terrestrial ecosystems. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2013, 22, 737–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, H.; Hosen, Y.; Yagi, K.; Okada, K.; Ito, O. Soil microbial biomass and activities in a Japanese Andisol as affected by controlled release and application depth of urea. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2005, 42, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Day, S.D.; Wick, A.F.; Strahm, B.D.; Wiseman, P.E.; Daniels, W.L. Changes in soil carbon pools and microbial biomass from urban land development and subsequent post-development soil rehabilitation. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2013, 66, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, S.; Peng, Z.; Qi, J.; Gao, J.; Wei, G. Linking bacterial-fungal relationships to microbial diversity and soil nutrient cycling. Msystems 2021, 6, e01052-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Liu, C.; Tan, X.; Tan, B.; He, Y.; Li, N. Interactive effects of light and nitrogen on Pakchoi (Brassica chinensis L.) growth and soil enzyme activity in an underground environment. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Yingxue, Z.; Wang, Q.; Xu, L.; Ma, X. Effects of fertilization methods in wheat on gases emission and environmental benefit in Mollisols of Northeast China. Reseach Sq. 2022, preprint. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Ci, K.; Zhu, J.; Sun, Z.; Liu, Z.; Li, X.; Zhu, Y.; Tang, C.; Wang, P.; Liu, Z. Impacts of exogenous mineral silicon on cadmium migration and transformation in the soil-rice system and on soil health. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 759, 143501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doran, J.W.; Coleman, D.C.; Bezdicek, D.; Stewart, B. Defining Soil Quality for a Sustainable Environment; Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Glass, A.D. Nitrogen use efficiency of crop plants: Physiological constraints upon nitrogen absorption. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2003, 22, 453–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wo, F.; Chen, C.; Fang, K. Seasonal changes in the concentrations of nitrogen and phosphorus in farmland drainage and groundwater of the Taihu Lake region of China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2010, 169, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Liao, Y.; Nie, J.; Xie, J.; Yang, Z.; Zhou, X. Effects of the application of controlled release nitrogen fertilizer on rapeseed yield, agronomic characters and soil fertility. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2015, 16, 1216. [Google Scholar]
- Beig, B.; Niazi, M.B.K.; Jahan, Z.; Hussain, A.; Zia, M.H.; Mehran, M.T. Coating materials for slow release of nitrogen from urea fertilizer: A review. J. Plant Nutr. 2020, 43, 1510–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Year | Treatment | Number of Pods Per Plant | Number of Seeds Per Pod | 1000-Grain Weight (g) | Seed Yield (kg ha−1) | Biomass (kg ha −1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2018–2019 | N135R0 | 170.67 c | 19.8 b | 4.07 a | 2936.96 b | 12,768.23 b |
| N135R1 | 201.39 ab | 20.53 ab | 4.10 a | 3404.11 a | 13,816.25 ab | |
| N135R2 | 211.75 a | 19.82 b | 4.12 a | 3635.91 a | 14,146.75 a | |
| N135R3 | 205.83 ab | 23.05 a | 4.11 a | 3447.18 a | 13,490.25 ab | |
| N135R4 | 196.5 ab | 21.58 ab | 4.09 a | 3027.54 b | 12,869.17 b | |
| N180CK | 208.42 ab | 19.87 b | 4.08 a | 3492.47 a | 13,449 ab | |
| 2019–2020 | N135R0 | 161.83 c | 21.11 b | 4.09 a | 3449.77 b | 12,378.75 c |
| N135R1 | 171.11 bc | 21.49 b | 4.12 a | 3556.72 ab | 13,458 ab | |
| N135R2 | 185.5 a | 23.04 a | 4.12 a | 3859.11 a | 13,796.5 a | |
| N135R3 | 173.83 b | 22.61 a | 4.09 a | 3780.82 ab | 12,626 bc | |
| N135R4 | 171.17 bc | 21.73 b | 4.11 a | 3547.04 ab | 12,180.25 c | |
| N180CK | 182.44 ab | 21.11 b | 4.12 a | 3822.93 a | 12,520 bc |
| Year | Treatment | Plant N (kg ha−1) | AEN (kg kg−1) | PFPN (kg kg−1) | NHI (%) | AREN (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N135R0 | 162.33 c | 4.88 c | 19.4 b | 68.76 b | 49.11 d | |
| N135R1 | 185.33 b | 7.71 a | 25.59 a | 76.96 a | 78.58 a | |
| 2018–2019 | N135R2 | 207.50 a | 8.31 a | 26.19 2 a | 78.86 a | 83.07 a |
| N135R3 | 212.73 a | 7.66 a | 25.53 a | 78.48 a | 68.73 b | |
| N135R4 | 189.20 b | 7.49 a | 25.37 a | 76.61 a | 58.52 c | |
| N180CK | 182.05 b | 5.99 b | 21.76 ab | 75.04 ab | 59.26 c | |
| N135R0 | 154.2 b | 6.83 a | 21.11 b | 69.83 b | 44.67 d | |
| N135R1 | 199.35 a | 8.11 a | 27.92 ab | 73.32 ab | 78.74 a | |
| 2019–2020 | N135R2 | 212.52 a | 9.2 a | 28.73 a | 76.86 a | 74.71 a |
| N135R3 | 201.73 a | 7.62 a | 26.35 ab | 77.23 a | 70.22 a | |
| N135R4 | 168.57 b | 7.55 a | 26.27 ab | 73.99 ab | 62.95 b | |
| N180CK | 194.09 a | 7.43 a | 25.55 b | 73.28 ab | 56.35 c |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, Y.; Zhang, F.; Hassan Javed, H.; Peng, X.; Chen, H.; Tang, W.; Lai, Y.; Wu, Y. Controlled-Release Nitrogen Mixed with Common Nitrogen Fertilizer Can Maintain High Yield of Rapeseed and Improve Nitrogen Utilization Efficiency. Plants 2023, 12, 4105. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12244105
Hu Y, Zhang F, Hassan Javed H, Peng X, Chen H, Tang W, Lai Y, Wu Y. Controlled-Release Nitrogen Mixed with Common Nitrogen Fertilizer Can Maintain High Yield of Rapeseed and Improve Nitrogen Utilization Efficiency. Plants. 2023; 12(24):4105. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12244105
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Yue, Fangfang Zhang, Hafiz Hassan Javed, Xiao Peng, Honglin Chen, Weiqun Tang, Ying Lai, and Yongcheng Wu. 2023. "Controlled-Release Nitrogen Mixed with Common Nitrogen Fertilizer Can Maintain High Yield of Rapeseed and Improve Nitrogen Utilization Efficiency" Plants 12, no. 24: 4105. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12244105
APA StyleHu, Y., Zhang, F., Hassan Javed, H., Peng, X., Chen, H., Tang, W., Lai, Y., & Wu, Y. (2023). Controlled-Release Nitrogen Mixed with Common Nitrogen Fertilizer Can Maintain High Yield of Rapeseed and Improve Nitrogen Utilization Efficiency. Plants, 12(24), 4105. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12244105







