Physiological Properties of Perennial Rice Regenerating Cultivation in Two Years with Four Harvests
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
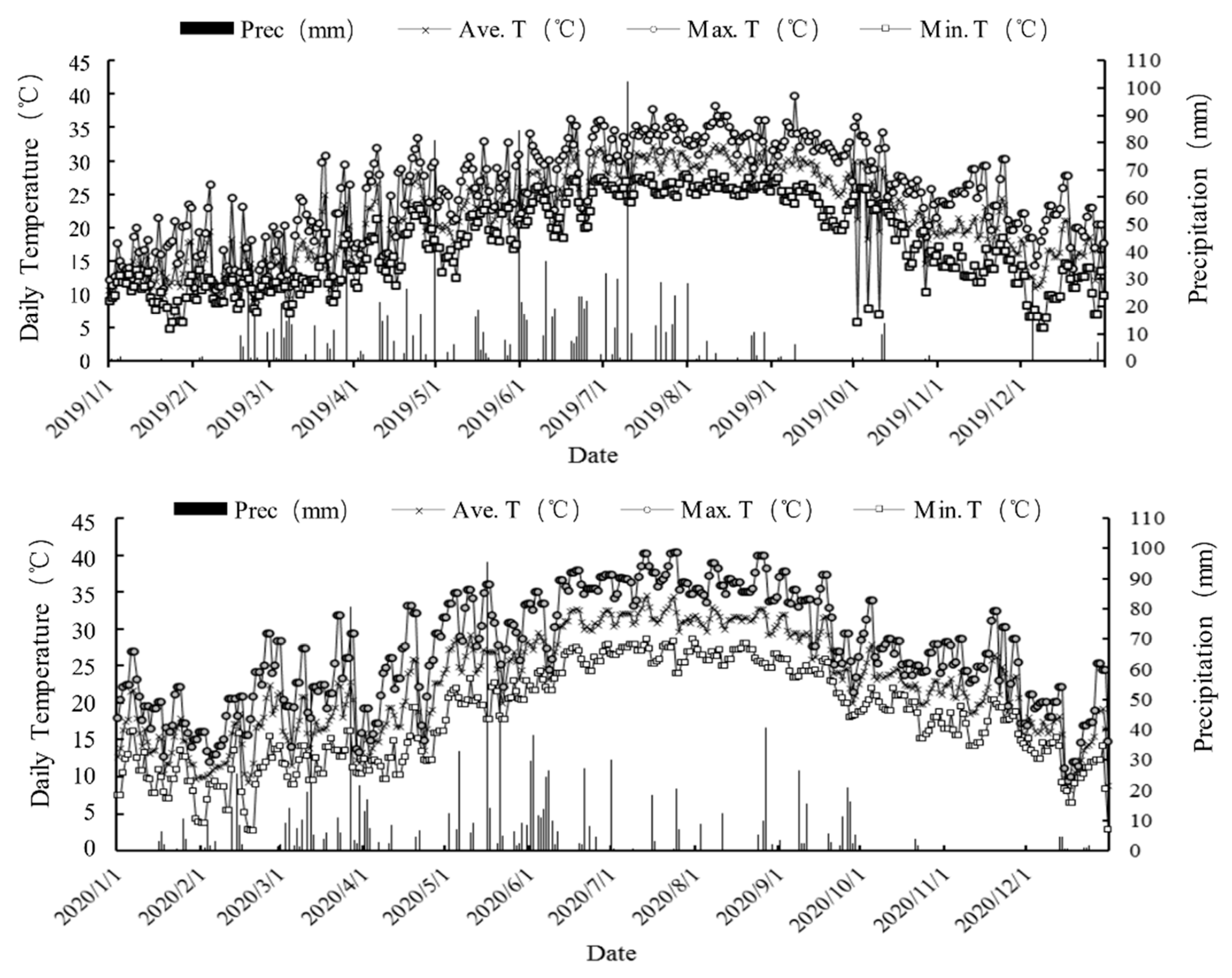
2.1. Weather Conditions and Safe Overwintering Evaluation
2.2. Yield Attributes of Perennial and Annual Rice Accessions
2.3. Relationship between Axillary Bud Sprout and Endogenous Hormones
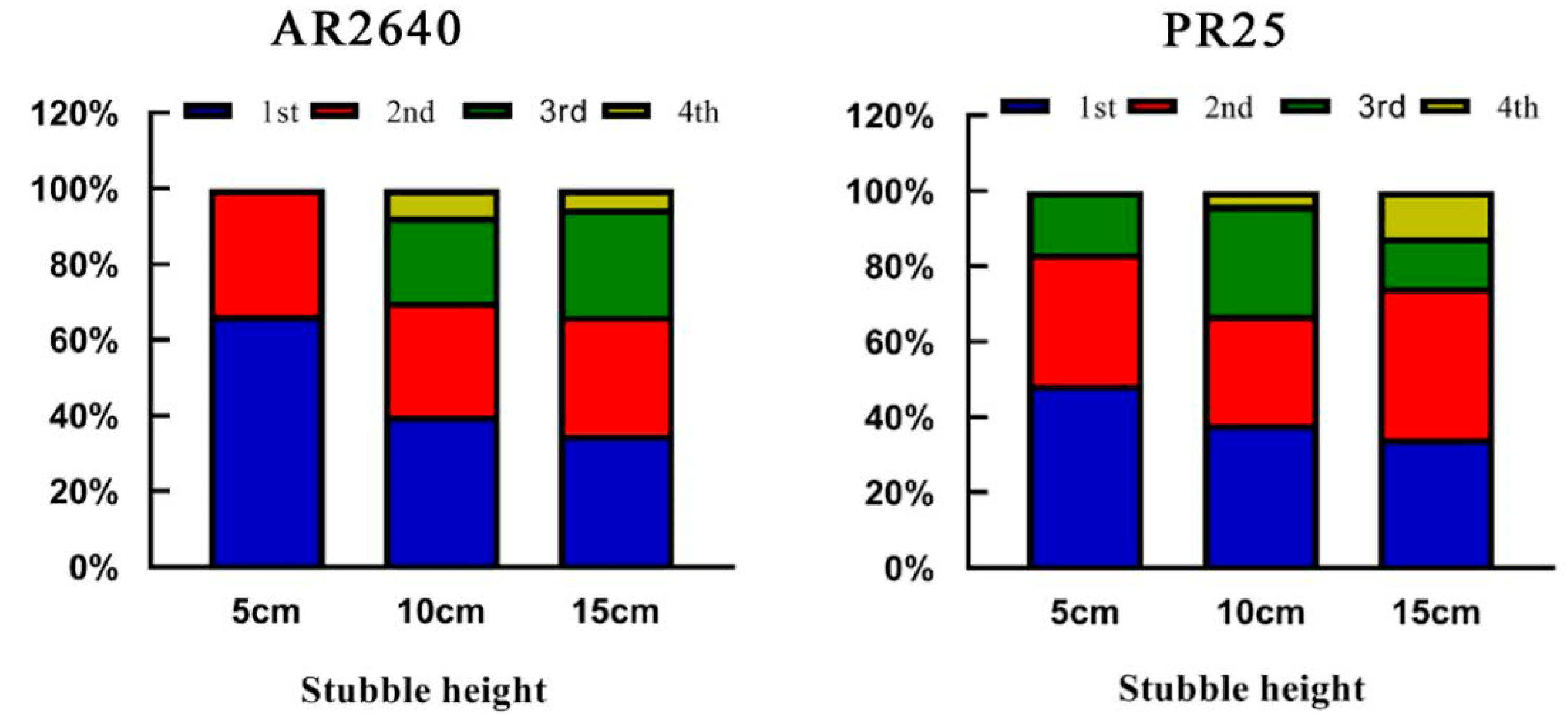
2.3.1. Effect of Stubble Height on Regeneration Rate and Effective Panicles
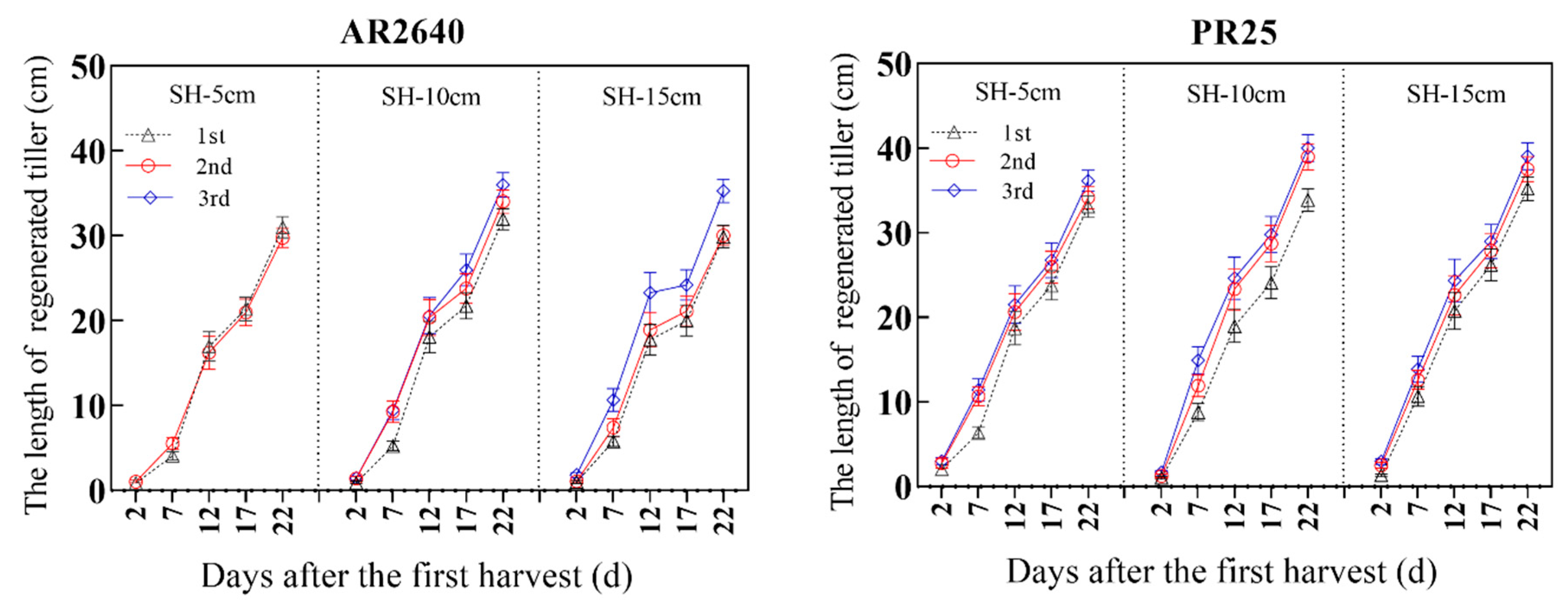
2.3.2. Sprouting and Elongating Dynamics of Axillary Buds
2.3.3. Changes in Endogenous Hormone Content of Axillary Buds
Dynamic Changes in IAA Content
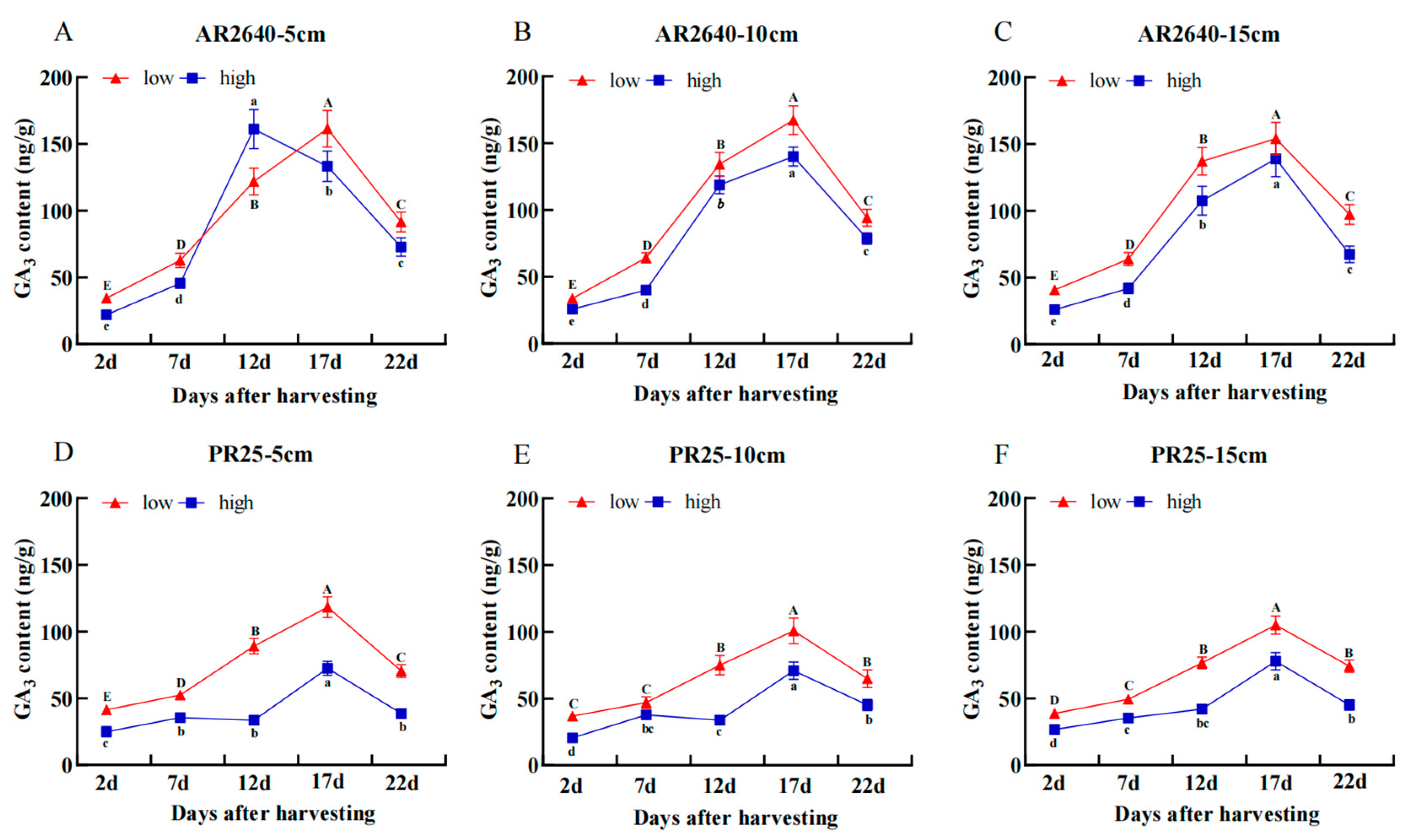
Dynamic Changes in GA3 Content
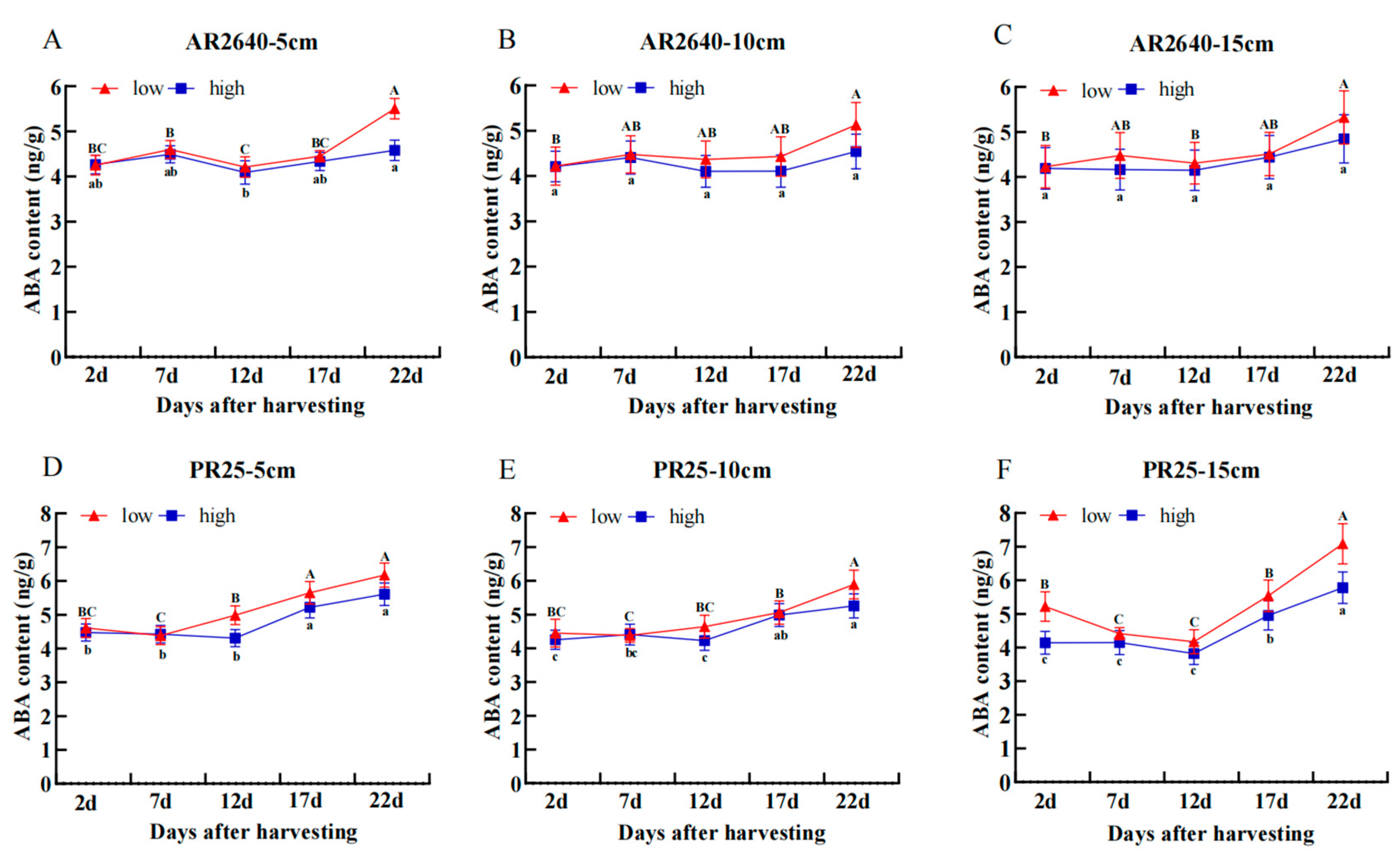
Dynamic Changes in ABA Content
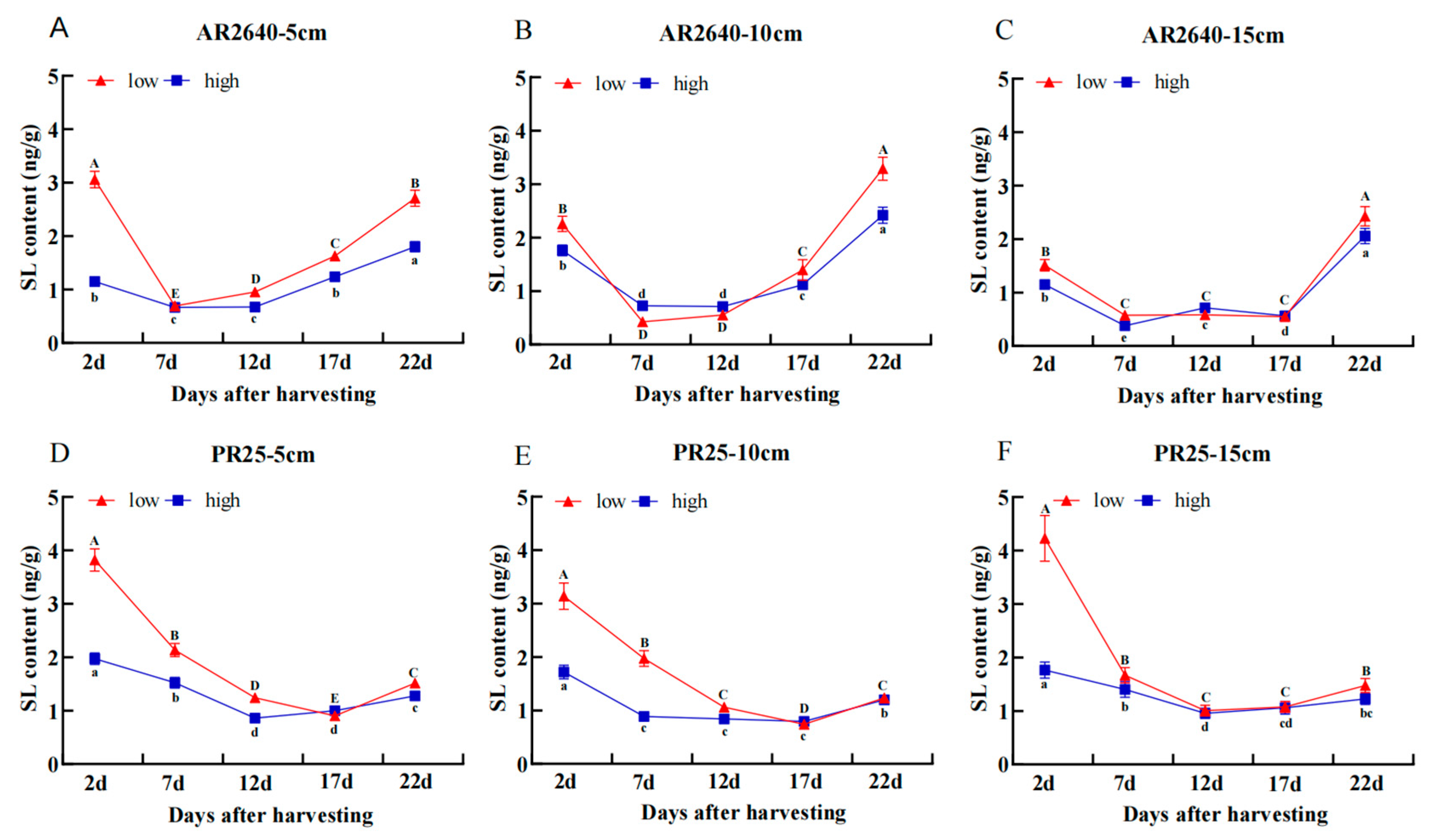
Dynamic Changes in SL Content
Correlation Analysis between the Endogenous Hormone Content and Regeneration Rate
2.4. Changing Characteristics of Rice Root Activity
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Experimental Design and Field Management
4.2. Determination Items and Methods
4.2.1. Observation of Growing Stage and Tillering Dynamics
4.2.2. Dynamic Observation on Sprout and Elongation of Axillary Buds
4.2.3. Determination of Root Activity
4.2.4. Determination of Endogenous Phytohormones
4.2.5. Determination of Rice Yield and Its Components
4.2.6. Data Processing and Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Peng, S.; Tang, Q.; Zou, Y. Current Status and Challenges of Rice Production in China. Plant Prod. Sci. 2009, 12, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Harrison, M.T.; Yan, H.; Liu, L.; Meinke, H.; Hoogenboom, G.; Wang, B.; Peng, B.; Guan, K.; Jaegermeyr, J.; et al. Silver lining to a climate crisis in multiple prospects for alleviating crop waterlogging under future climates. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otchia, C.S. Agricultural Modernization, Structural Change and Pro-poor Growth: Policy Options for the Democratic Republic of Congo. J. Econ. Struct. 2014, 3, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McArthur, J.W.; McCord, G.C. Fertilizing growth: Agricultural inputs and their effects in economic development. Glob. Econ. Dev. 2014, 27, 133–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mosier, A.R.; Syers, J.K.; Freney, J.R. Global assessment of nitrogen fertilizer: The SCOPE/IGBP nitrogen fertilizer rapid assessment project. Sci. China C Life Sci. 2005, 48, 759–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosier, A.; Syers, J.K.; Freney, J.R. Agriculture and the nitrogen cycle, assessing the impacts of fertilizer use on food production and the environment. Ecology 2006, 134, 233–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, L. Sugarcane Agriculture and Sugar Industry in China. Sugar Tech 2015, 17, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diacono, M.; Montemurro, F. Long-term effects of organic amendments on soil fertility. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2010, 30, 401–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, L.W.; Byrne, F.; Ewing, M.A.; Wade, L.J. A preliminary whole-farm economic analysis of perennial wheat in an Australian dryland farming system. Agric. Syst. 2008, 96, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, E.I.; Toensmeier, E.; Iutzi, F.; Rosenberg, N.A.; Lovell, S.T.; Jordan, N.R.; Peters, T.E.; Akwii, E.; Broad Leib, E.M. Policy pathways for perennial agriculture. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2022, 6, 983398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquardt, K.; Vico, G.; Glynn, C.; Weih, M.; Eksvard, K.; Dalin, P.; Bjorkman, C. Farmer perspectives on introducing perennial cereal in Swedish farming systems: A sustainability analysis of plant traits, farm management, and ecological implications. Agroecol. Sustain. Food 2016, 40, 432–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Huang, G.; Zhang, Y.; Lv, X.; Wan, K.; Liang, J.; Feng, Y.; Dao, J.; Wu, S.; Zhang, L.; et al. Sustained productivity and agronomic potential of perennial rice. Nat. Sustain. 2022, 6, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.; Wade, L.J. Switch to perennial rice promotes sustainable farming. Nat. Sustain. 2023, 6, 17–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Huang, G.; Shi, J.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, M.; Hu, J.; Zhang, S.; Hu, F. Yield Potential Analysis of Perennial Rice Yunda 107. China Rice 2020, 26, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Hu, J.; Yang, C.; Liu, H.; Yang, F.; Zhou, J.; Samson, B.K.; Boualaphanh, C.; Huang, L.; Huang, G.; et al. Genotype by environment interactions for grain yield of perennial rice derivatives (Oryza sativa L./Oryza longistaminata) in southern China and Laos. Field Crops Res. 2017, 207, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Huang, G.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, C.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, J.; Hu, F. Quality Analysis of Perennial Rice in Different Altitude Regions. China Rice 2020, 26, 40–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, L.; Li, X. Impact of Tillage and Straw Treatment Methods on Rice Growth and Yields in a Rice–Ratoon Rice Cropping System. Sustainability 2022, 14, 9290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samson, B.K.; Voradeth, S.; Zhang, S.; Jackson, T.; Wade, L.J. performance and survival of perennial rice derivatives (Oryza sativa L./Oryza longistaminata) in lao pdr. Exp. Agric. 2018, 54, 592–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, F.; Lu, H.; Yuan, Y.; Chen, H.; Li, Q.; Wang, L.; Tao, Y.; Zhou, W.; Cheng, H.; Chen, Y.; et al. Accurate prediction of the eating and cooking quality of rice using artificial neural networks and the texture properties of cooked rice. Food Chem. 2023, 407, 135176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, X.; Guo, X.; Jiang, P. The ratoon rice system with high yield and high efficiency in China: Progress, trend of theory and technology. Field Crops Res. 2021, 272, 108282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.Y.; Tao, D.Y.; Sacks, E.; Fu, B.Y.; Xu, P.; Li, J.; Yang, Y.; McNally, K.; Khush, G.S.; Paterson, A.H.; et al. Convergent evolution of perenniality in rice and sorghum. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 4050–4054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, G.; Huang, J.; Cheng, L.; Wang, M.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, C.; Yu, P.; Tao, X.; et al. Genotype by environment interactions for performance of perennial rice genotypes (Oryza sativa L./Oryza longistaminata) relative to annual rice genotypes over regrowth cycles and locations in southern China. Field Crops Res. 2019, 241, 107556. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Qin, S.; Zhang, S.; Cai, X.; Wu, S.; Dao, J.; Zhang, J.; Huang, L.; Harnpichitvitaya, D.; Wade, L. Performance, Economics and Potential Impact of Perennial Rice PR23 Relative to Annual Rice Cultivars at Multiple Locations in Yunnan Province of China. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, R.J. Australian Wild Rice Populations: A Key Resource for Global Food Security. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mellor, N.; Band, L.R.; Pencik, A.; Novak, O.; Rashed, A.; Holman, T.; Wilson, M.H.; Voss, U.; Bishopp, A.; King, J.R.; et al. Dynamic regulation of auxin oxidase and conjugating enzymes AtDAO1 and GH3 modulates auxin homeostasis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 11022–11027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.; Peng, S.; Zheng, C.; Xiong, Z.; Yang, G.; Deng, S.; Wang, F. Stubble height affects the grain yield of ratoon rice under rainfed conditions. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 272, 107815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Yuan, C.; Wang, X.; Han, D.; Liao, S.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, X.; Jiang, Q.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, P. Different in the two-crop yields and main-crop rice qualities among different hybrid mid-season rice varieties in the ratooning rice region of southern Sichuan, China. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2020, 28, 990–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Wang, Y.; Tu, B.; Li, T.; Li, S. QTL Analysis of Rice Ratooning Ability and Related Agronomic Traits by. Acta Agron. Sin. 2013, 38, 1240–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, D.; Prapa, S. Preliminary Report on Transfer Traits of Vegetative Propagation from Wild Rice Species to Oryza sativa via Distant Hybridization and Embryo Rescue. Kasetsart J. 2000, 34, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Glover, J.D.; Reganold, J.P.; Bell, L.W.; Borevitz, J.; Brummer, E.C.; Buckler, E.S.; Cox, C.M.; Cox, T.S.; Crews, T.E.; Culman, S.W.; et al. Agriculture. Increased food and ecosystem security via perennial grains. Science 2010, 328, 1638–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Li, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Zheng, J. Morphologic and functional difference of root systems among ratooning rice varieties and its correlation with yield. Fujian J. Agric. Sci. 2001, 16, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ongaro, V.; Leyser, O. Hormonal control of shoot branching. J. Exp. Bot. 2008, 59, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Wu, L.; Lin, S.; Zhang, A.; Zhou, M.; Lin, R.; Wang, H.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, R. Metaproteomic analysis of ratoon sugarcane rhizospheric soil. BMC Microbiol. 2013, 13, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Yu, J.; Wen, L.; Guo, Y.; Sun, X.; Hao, Y.; Hu, D.; Zheng, C. Chrysanthemum MADS-box transcription factor CmANR1 modulates lateral root development via homo-/heterodimerization to influence auxin accumulation in Arabidopsis. Plant Sci. 2018, 266, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, J.; Zhao, M.; Chen, M.; Pan, B.; Tao, Y.; Xu, Z. Comparative transcriptome analysis of axillary buds in response to the shoot branching regulators gibberellin A3 and 6-benzyladenine in Jatropha curcas. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hytonen, T.; Elomaa, P.; Moritz, T.; Junttila, O. Gibberellin mediates daylength-controlled differentiation of vegetative meristems in strawberry (Fragaria x ananassa Duch). BMC Plant Biol. 2009, 9, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, T.; Morinaka, Y.; Ishiyama, K.; Kobayashi, M.; Itoh, H.; Kayano, T.; Iwahori, S.; Matsuoka, M.; Tanaka, H. Genetic manipulation of gibberellin metabolism in transgenic rice. Nat. Biotechnol. 2003, 21, 909–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, Y.; Chen, T.; Zhao, C.; Zhou, M. Improving Crop Lodging Resistance by Adjusting Plant Height and Stem Strength. Agronomy 2021, 11, 2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shutaro, S.; Cho, T.M.; Htay, K.M.; Yamaoka, K. Effects of the Double-Cutting Method for Ratooning Rice in the SALIBU System under Different Soil Moisture Conditions on Grain Yield and Regeneration Rate. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lymperopoulos, P.; Msanne, J.; Rabara, R. Phytochrome and Phytohormones: Working in Tandem for Plant Growth and Development. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallah, N.; Pang, Z.; Lin, Z.; Nyimbo, W.J.; Lin, W.; Mbuya, S.N.; Ishimwe, C.; Zhang, H. Sustained organic amendments utilization enhances ratoon crop growth and soil quality by enriching beneficial metabolites and suppressing pathogenic bacteria. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1273546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Liu, B.; Chen, J.; Ren, C. Effects of endogenous hormone ABA on the germination of ratooning buds in rice. J. Southwest Agric. Univ. 1997, 19, 338–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, A.; Jiang, M.; Nie, L.; Man, J.; Peng, S. Effects of source-sink regulation and nodal position of the main crop on the sprouting of regenerated buds and grain yield of ratoon rice. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1043354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Li, W.; Burritt, D.J.; Tian, H.; Zhang, H.; Liang, X.; Miao, Y.; Mostofa, M.G.; Tran, L.S.P. Strigolactones interact with other phytohormones to modulate plant root growth and development. Crop J. 2022, 10, 1517–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, C.; Carolien, R.S.; Harro, B. The interaction between strigolactones and other plant hormones in the regulation of plant development. Front. Plant Sci. 2013, 4, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibasaki, K.; Takebayashi, A.; Makita, N.; Kojima, M.; Takebayashi, Y.; Kawai, M.; Hachiya, T.; Sakakibara, H. Nitrogen Nutrition Promotes Rhizome Bud Outgrowth via Regulation of Cytokinin Biosynthesis Genes and an Oryza longistaminata Ortholog of FINE CULM 1. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 670101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Li, Z.; Weng, P.; Wu, D.; Zou, J.; Pang, Z.; Lin, W. Field greenhouse gas emission characteristics and carbon footprint of ratoon rice. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2022, 33, 1340–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Wu, J.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Z.; Fang, C.; Shao, C.; Lin, W.; Weng, P.; Muhammad, U.K.; Lin, W. Optimal management of nitrogen fertilizer in the main rice crop and its carrying-over effect on ratoon rice under mechanized cultivation in Southeast China. J. Integr. Agric. 2022, 21, 351–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Pan, Y.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Z.; Fang, C.; Shao, C.; Amjad, H.; Lin, W.; Lin, W. Physiochemical mechanisms involved in the improvement of grain-filling, rice quality mediated by related enzyme activities in the ratoon cultivation system. Field Crops Res. 2020, 258, 107962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Cropping System (Year) | Variety | Stubble Height (cm) | Transplanting/Sprouting (Day/Month) | Fully Heading (Day/Month) | Ripening (Day/Month) | Growth Duration (Day) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MC (2019) | AR2640 | / | 28/4 | 14/7 | 18/8 | 147 |
| MC (2019) | PR25 | / | 28/4 | 14/7 | 22/8 | 151 |
| FRR (2019) | AR2640 | 5 | 26/8 | 3/10 | 6/11 | 80 |
| 10 | 26/8 | 1/10 | 2/11 | 76 | ||
| 15 | 26/8 | 28/9 | 30/10 | 73 | ||
| FRR (2019) | PR25 | 5 | 28/8 | 8/10 | 13/11 | 83 |
| 10 | 28/8 | 7/10 | 12/11 | 82 | ||
| 15 | 28/8 | 6/10 | 11/11 | 81 | ||
| SRR (2020) | PR25 | 5 | 2/4 | 27/6 | 6/8 | 126 |
| 10 | 2/4 | 26/6 | 6/8 | 126 | ||
| 15 | 2/4 | 26/6 | 6/8 | 126 | ||
| TRR (2020) | PR25 | 5 | 12/8 | 30/9 | 8/11 | 82 |
| 10 | 12/8 | 30/9 | 6/11 | 80 | ||
| 15 | 12/8 | 30/9 | 6/11 | 80 |
| Year | Ratooning System | Cultivar | Stubble Height (cm) | Effective Panicles (104·hm−2) | Grains Panicle−1 | 1000-Grain Weight (g) | Seed Setting Percentage (%) | Grain Yield (t·hm−2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 | MC | AR2640 | / | 200.1 d | 240.0 a | 22.1 d | 82.6 a | 8.77 b |
| PR25 | / | 185.6 e | 180.0 b | 25.2 a | 86.5 a | 7.28 c | ||
| FRR | AR2640 | 5 | 205.1 d | 88.5 i | 21.8 d | 62.9 d | 2.49 g | |
| 10 | 225.1 c | 86.1 i | 21.9 d | 70.8 c | 3.01 f | |||
| 15 | 270.1 b | 83.5 ij | 22.1 d | 78.9 b | 3.93 e | |||
| PR25 | 5 | 265.1 b | 110.3 f | 24.6 b | 79.0 b | 5.68 d | ||
| 10 | 260.1 b | 126.5 e | 24.2 b | 75.0 b | 5.97 d | |||
| 15 | 230.1 c | 97.3 gh | 24.3 b | 60.0 e | 3.26 f | |||
| 2020 | SRR | AR2640 | 5 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| 10 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | |||
| 15 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | |||
| PR25 | 5 | 331.6 a | 167.9 c | 23.4 c | 82.1 a | 10.70 a | ||
| 10 | 307.4 a | 170.5 c | 23.8 c | 82.4 a | 10.28 a | |||
| 15 | 290.6 b | 154.3 cd | 23.3 c | 83.4 a | 8.71 b | |||
| TRR | PR25 | 5 | 185.6 e | 112.3 f | 24.5 b | 76.5 b | 3.91 e | |
| 10 | 192.6 e | 120.5 e | 23.5 c | 73.8 b | 4.15 e | |||
| 15 | 185.6 e | 102.6 g | 24.5 b | 67.8 d | 3.15 f | |||
| df | ||||||||
| F-value | 15 | 71.4 *** | 88.9 *** | 60.8 *** | 63.1 *** | 99.4 *** | ||
| Year | Cultivar | Ratoon Crop System | SH | MS | HT | EP | RR | PEP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (cm) | (104·hm−2) | (104·hm−2) | (104·hm−2) | (%) | (%) | |||
| 2019 | AR2640 | FRR | 5 | 200.1 d | 282.6 d | 205.1 e | 102.5 e | 72.6 c |
| 10 | 200.1 d | 315.2 c | 225.1 e | 112.5 d | 71.4 c | |||
| 15 | 200.1 d | 337.7 c | 270.1 d | 135.0 b | 80.0 a | |||
| PR25 | FRR | 5 | 185.6 e | 332.6 c | 265.1 d | 142.8 a | 79.7 a | |
| 10 | 185.6 e | 326.6 c | 260.1 d | 140.1 a | 79.6 a | |||
| 15 | 185.6 e | 300.2 d | 230.1 e | 124.0 c | 76.6 b | |||
| 2020 | PR25 | SRR | 5 | 265.1 b | 432.7 a | 331.6 a | 125.1 c | 76.6 b |
| 10 | 260.1 b | 431.5 a | 307.4 b | 118.2 d | 74.2 b | |||
| 15 | 230.1 c | 387.2 b | 290.6 c | 126.3 d | 76.6 b | |||
| PR25 | TRR | 5 | 331.6 a | 264.8 e | 185.6 f | 55.97 f | 70.1 c | |
| 10 | 325.2 a | 274.1 e | 192.5 f | 59.19 f | 70.5 c | |||
| 15 | 290.6 a | 260.7 e | 185.6f | 62.79 f | 71.2 c |
| Cultivar | Basal Node | BS | HS | RS | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BL (mm) | BL (mm) | BL (mm) | INL (cm) | ||
| 3rd | 8.08 a | 14.33 a | 22.24 a | 7.80 a | |
| AR2640 | 2nd | 5.52 b | 6.90 c | 15.63 b | 5.23 b |
| 1st | 6.28 b | 9.88 b | 21.69 a | 1.40 d | |
| 3rd | 6.80 b | 13.25 a | 12.75 c | 6.04 b | |
| PR25 | 2nd | 8.87 a | 6.43 c | 12.53 c | 4.05 c |
| 1st | 5.89 b | 7.90 c | 14.79 b | 1.15 d | |
| R2d | R7d | R12d | R17d | R22d | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GA | −0.413 * | −0.230 | −0.350 | 0.580 * | −0.263 |
| IAA | −0.434 * | 0.091 | −0.325 | 0.202 | −0.363 |
| ABA | −0.490 * | −0.029 | −0.047 | −0.318 | 0.083 |
| SL | −0.617 * | 0.516 * | −0.125 | 0.677 * | 0.046 |
| IAA/ABA | −0.404 | 0.101 | −0.384 | 0.346 | −0.517 * |
| (IAA + GA)/ABA | −0.364 | −0.151 | −0.435 * | 0.550 * | −0.321 |
| IAA + GA | −0.451 * | −0.148 | −0.446 * | 0.549 * | −0.292 |
| GA/ABA | −0.301 | −0.241 | −0.338 | 0.568 * | −0.319 |
| Cultivar | MBS | MHS | MMS | SH (cm) | RBS | RHS | RMS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AR2640 | 9.94 b | 5.83 b | 4.53 b | 5 | 10.00 b | 8.82 b | 7.35 b |
| 10 | 9.98 b | 8.63 b | 7.12 b | ||||
| 15 | 10.2 b | 8.98 b | 7.41 b | ||||
| PR25 | 12.4 a | 7.34 a | 5.91 a | 5 | 12.86 a | 11.62 a | 10.03 a |
| 10 | 12.83 a | 11.58 a | 9.97 a | ||||
| 15 | 12.78 a | 11.42 a | 9.72 a |
| Item | R-MBS | R-MHS | R-MRS | R-RBS | R-RHS | R-RRS | RR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RR | 0.952 ** | 0.887 ** | 0.935 ** | 0.861 * | 0.869 ** | 0.971 ** | 1.000 |
| RY | 0.857 * | 0739 * | 0.846 ** | 0.700 * | 0.546 * | 0.695 * | 0.921 ** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, C.; Lin, W.; Gao, W.; Lan, C.; Xu, H.; Zou, J.; Fallah, N.; Wang, W.; Lin, W.; Chen, T.; et al. Physiological Properties of Perennial Rice Regenerating Cultivation in Two Years with Four Harvests. Plants 2023, 12, 3910. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12223910
Guo C, Lin W, Gao W, Lan C, Xu H, Zou J, Fallah N, Wang W, Lin W, Chen T, et al. Physiological Properties of Perennial Rice Regenerating Cultivation in Two Years with Four Harvests. Plants. 2023; 12(22):3910. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12223910
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Chunlin, Weiwei Lin, Wujie Gao, Chaojie Lan, Hailong Xu, Jingnan Zou, Nyumah Fallah, Wenfei Wang, Wenfang Lin, Ting Chen, and et al. 2023. "Physiological Properties of Perennial Rice Regenerating Cultivation in Two Years with Four Harvests" Plants 12, no. 22: 3910. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12223910
APA StyleGuo, C., Lin, W., Gao, W., Lan, C., Xu, H., Zou, J., Fallah, N., Wang, W., Lin, W., Chen, T., & Lin, W. (2023). Physiological Properties of Perennial Rice Regenerating Cultivation in Two Years with Four Harvests. Plants, 12(22), 3910. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12223910






