Antioxidant Activity of Different Hop (Humulus lupulus L.) Genotypes
Abstract
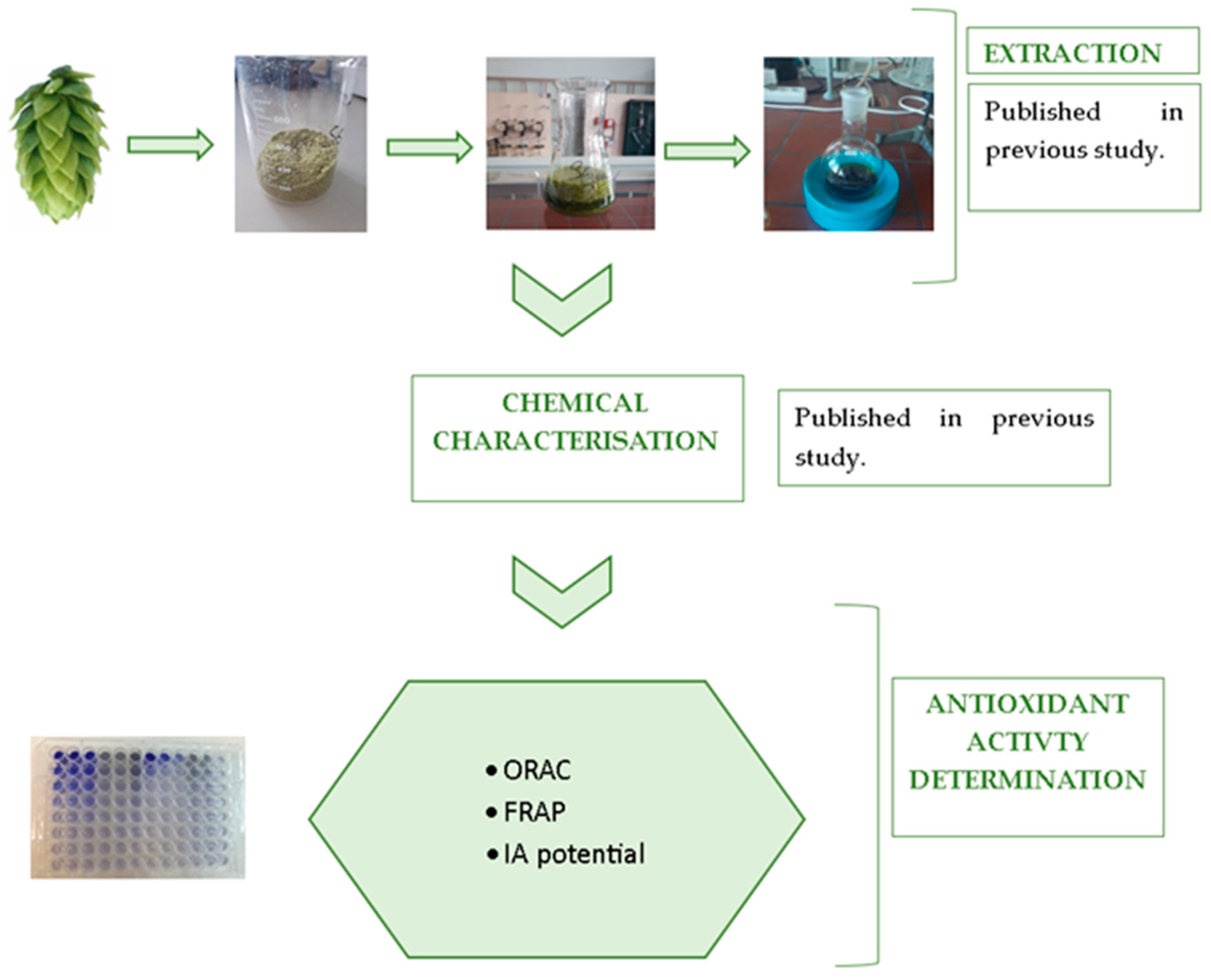
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Antioxidant Activity Using FRAP
2.2. Antioxidant Potential Using ORAC
2.3. IA Potential Determination
2.3.1. Cytotoxicity Assay
2.3.2. IA Potential Assay
2.4. Correlation between AA with Different AA Methods
2.5. Correlation between AA and Chemical Composition of Different Hop Genotypes
2.6. Association of AA with Chemical Composition
2.7. Principal Component Analysis (PCA) of Different Hop Genotype Samples according to AA
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Hop Extract Preparation and HPLC Determination of Chemical Composition
3.2. Antioxidant Activity Using FRAP
3.2.1. Chemicals
3.2.2. FRAP Assay Method
3.3. Antioxidant Activity Using ORAC
3.3.1. Chemicals
3.3.2. ORAC Assay Method
3.4. Determination of IA Potential
3.4.1. Chemicals
3.4.2. Cell Culture
3.4.3. Cytotoxicity Assay
3.4.4. IA Potential
3.5. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HAT | hydrogen atom transfer |
| SET | single electron transfer |
| FRAP | ferric reducing ability of plasma |
| ORAC | oxygen radical absorption capacity |
| IA | intracellular antioxidant |
| DCFH-DA | 2’,7’-dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate |
| DCFH | dichlorodihydrofluorescein |
| DCF | 2′,7′-dichlorofluorescein |
| AA | antioxidant activity |
| HAE | hydroacetonic extract |
| DM | dry matter |
| αβ–AF | α-acids-and-β-acids-rich fraction |
| β–AF | β-acids-rich fraction |
| DPPH | 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl |
| DMSO | dimethyl sulfoxide |
| ROS | reactive oxygen species |
| AUC | area under the curve |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium |
| HBSS | Hank’s Balanced Salt Solution |
References
- Pohl, F.; Kong Thoo Lin, P. The Potential Use of Plant Natural Products and Plant Extracts with Antioxidant Properties for the Prevention/Treatment of Neurodegenerative Diseases: In Vitro, In Vivo and Clinical Trials. Molecules 2018, 23, 3283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahidi, F.; Zhong, Y. Measurement of antioxidant activity. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 18, 757–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karadag, A.; Ozcelik, B.; Saner, S. Review of Methods to Determine Antioxidant Capacities. Food Anal. Methods 2009, 2, 41–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F.; Xu, T.; Lu, B.; Liu, R. Guidelines for antioxidant assays for food components. Food Front. 2020, 1, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amic, A.; Markovic, Z.; Dimitric Markovic, J.M.; Milenkovic, D.; Stepanic, V. Antioxidative potential of ferulic acid phenoxyl radical. Phytochemistry 2020, 170, 112218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wannenmacher, J.; Cotterchio, C.; Schlumberger, M.; Reuber, V.; Gastl, M.; Becker, T. Technological influence on sensory stability and antioxidant activity of beers measured by ORAC and FRAP. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2019, 99, 6628–6637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skroza, D.; Simat, V.; Vrdoljak, L.; Jolic, N.; Skelin, A.; Cagalj, M.; Frleta, R.; Generalic Mekinic, I. Investigation of Antioxidant Synergisms and Antagonisms among Phenolic Acids in the Model Matrices Using FRAP and ORAC Methods. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prior, R.; Wu, X.; Schaich, K. Standardizized Methods for the Determination of Antioxidant Capacity and Phenolics in Foods and Dietary Supplements. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 4290–4302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Zhu, W.; Zhang, J.; Song, D.; Zhuang, L.; Ma, Q.; Yang, X.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; et al. Antioxidant capacity of phenolic compounds separated from tea seed oil in vitro and in vivo. Food Chem. 2022, 371, 131122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munteanu, I.G.; Apetrei, C. Analytical Methods Used in Determining Antioxidant Activity: A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girard-Lalancette, K.; Pichette, A.; Legault, J. Sensitive cell-based assay using DCFH oxidation for the determination of pro- and antioxidant properties of compounds and mixtures: Analysis of fruit and vegetable juices. Food Chem. 2009, 115, 720–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Zha, Y.; Zhong, Z.; Ruan, Y.; Li, Z.; Sun, L.; Hou, S. Improved detection of reactive oxygen species by DCFH-DA: New insight into self-amplification of fluorescence signal by light irradiation. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 339, 129878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.-R.; Zhu, J.-J.; Yin, S.-W.; Yang, X.-Q. Bioaccessibility and intracellular antioxidant activity of phloretin embodied by gliadin/sodium carboxymethyl cellulose nanoparticles. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 122, 107076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashaolu, T.J. Antioxidative peptides derived from plants for human nutrition: Their production, mechanisms and applications. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2020, 246, 853–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brglez Mojzer, E.; Knez Hrncic, M.; Skerget, M.; Knez, Z.; Bren, U. Polyphenols: Extraction Methods, Antioxidative Action, Bioavailability and Anticarcinogenic Effects. Molecules 2016, 21, 901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sznarkowska, A.; Kostecka, A.; Meller, K.; Bielawski, K.P. Inhibition of cancer antioxidant defense by natural compounds. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 15996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zugravu, C.A.; Bohiltea, R.E.; Salmen, T.; Pogurschi, E.; Otelea, M.R. Antioxidants in Hops: Bioavailability, Health Effects and Perspectives for New Products. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Astray, G.; Gullón, P.; Gullón, B.; Munekata, P.E.S.; Lorenzo, J.M. Humulus lupulus L. as a Natural Source of Functional Biomolecules. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 5074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macchioni, V.; Picchi, V.; Carbone, K. Hop Leaves as an Alternative Source of Health-Active Compounds: Effect of Genotype and Drying Conditions. Plants 2021, 11, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczyk, D.; Świeca, M.; Cichocka, J.; Gawlik-Dziki, U. The phenolic content and antioxidant activity of the aqueous and hydroalcoholic extracts of hops and their pellets. J. Inst. Brew. 2013, 119, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knez Hrncic, M.; Spaninger, E.; Kosir, I.J.; Knez, Z.; Bren, U. Hop Compounds: Extraction Techniques, Chemical Analyses, Antioxidative, Antimicrobial, and Anticarcinogenic Effects. Nutrients 2019, 11, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanz, V.; Torres, M.D.; López Vilariño, J.M.; Domínguez, H. What is new on the hop extraction? Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 93, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arruda, T.R.; Pinheiro, P.F.; Silva, P.I.; Bernardes, P.C. A new perspective of a well-recognized raw material: Phenolic content, antioxidant and antimicrobial activities and α- and β-acids profile of Brazilian hop (Humulus lupulus L.) extracts. LWT 2021, 141, 110905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kores, K.; Kolenc, Z.; Furlan, V.; Bren, U. Inverse Molecular Docking Elucidating the Anticarcinogenic Potential of the Hop Natural Product Xanthohumol and Its Metabolites. Foods 2022, 11, 1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, A.; Furlan, V.; Novak, M.; Stampar, M.; Kolenc, Z.; Kores, K.; Filipic, M.; Bren, U.; Zegura, B. Chemoprotective Effects of Xanthohumol against the Carcinogenic Mycotoxin Aflatoxin B1. Foods 2021, 10, 1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.; Dunshea, F.R.; Suleria, H.A.R. LC-ESI-QTOF/MS Characterization of Phenolic Compounds from Medicinal Plants (Hops and Juniper Berries) and Their Antioxidant Activity. Foods 2019, 9, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolenc, Z.; Langerholc, T.; Hostnik, G.; Ocvirk, M.; Stumpf, S.; Pintaric, M.; Kosir, I.J.; Cerenak, A.; Garmut, A.; Bren, U. Antimicrobial Properties of Different Hop (Humulus lupulus) Genotypes. Plants 2022, 12, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothe, J.; Fischer, R.; Cotterchio, C.; Gastl, M.; Becker, T. Analytical determination of antioxidant capacity of hop-derived compounds in beer using specific rapid assays (ORAC, FRAP) and ESR-spectroscopy. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2022, 249, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tafulo, P.A.R.; Queirós, R.B.; Delerue-Matos, C.M.; Sales, M.G.F. Control and comparison of the antioxidant capacity of beers. Food Res. Int. 2010, 43, 1702–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abram, V.; Čeh, B.; Vidmar, M.; Hercezi, M.; Lazić, N.; Bucik, V.; Možina, S.S.; Košir, I.J.; Kač, M.; Demšar, L.; et al. A comparison of antioxidant and antimicrobial activity between hop leaves and hop cones. Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 64, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, N.; Satoh-Yamaguchi, K.; Ono, M. In vitro evaluation of antibacterial, anticollagenase, and antioxidant activities of hop components (Humulus lupulus) addressing acne vulgaris. Phytomedicine 2009, 16, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krofta, K.; Mikyška, A.; Hašková, D. Antioxidant Characteristics of Hops and Hop Products. J. Inst. Brew. 2008, 114, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, N.; Biehler, K.; Schwabe, K.; Haarhaus, B.; Quirin, K.W.; Frank, U.; Schempp, C.M.; Wolfle, U. Hop Extract Acts as an Antioxidant with Antimicrobial Effects against Propionibacterium Acnes and Staphylococcus Aureus. Molecules 2019, 24, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, B.; Chung, J.W.; Bae, H.R.; Choi, J.S.; Kim, C.M.; Kim, N.D. Humulus japonicus extract exhibits antioxidative and anti-aging effects via modulation of the AMPK-SIRT1 pathway. Exp. Ther. Med. 2015, 9, 1819–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ou, B.; Huang, D.; Hampsch-Woodill, M.; Flanagan, J.A.; Deemer, E.K. Analysis of Antioxidant Activities of Common Vegetables Employing Oxygen Radical Absorbance Capacity (ORAC) and Ferric Reducing Antioxidant Power (FRAP) Assays: A comparative study. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 3122–3128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, K.; Assefa, A.D.; Kim, S.; Ko, E.Y.; Lee, E.T.; Park, S.W. Evaluation of total phenolics, flavonoids and antioxidant activity of 18 Korean onion cultivars: A comparative study. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2014, 94, 1521–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karabin, M.; Hudcova, T.; Jelinek, L.; Dostalek, P. Biologically Active Compounds from Hops and Prospects for Their Use. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2016, 15, 542–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Gu, X.-H.; Tang, J.; Liu, K. Antioxidant Activities of Hops (Humulus Lupulus) and Their Products. J. Am. Soc. Brew. Chem. 2018, 65, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, A.d.R.; Maciel, M.V.d.O.B.; Machado, M.H.; Bazzo, G.C.; Armas, R.D.; Vitorino, V.B.; Vitali, L.; Block, J.M.; Barreto, P.L.M. Bioactive compounds and antioxidant activities of Brazilian hop (Humulus lupulus L.) extracts. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 55, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Ou, B.; Hampsch-Woodill, M.; Flanagan, J.A.; Prior, R.L. High-Throughput Assay of Oxygen RAdical Absorbance Capacity (ORAC) USing a Multichannel Liquid Handling System Coupled with a Microplate Flurescence REader in 96-Well Format. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 4437–4444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langerholc, T.; Maragkoudakis, P.A.; Wollgast, J.; Gradisnik, L.; Cencic, A. Novel and established intestinal cell line models—An indispensable tool in food science and nutrition. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 22, S11–S20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosmann, T. Rapid Colorimetric Assay for Cellular Growth and Survival: Application to Proliferation and Cytotoxicity Assays. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Parameter | FRAP | ORAC | IA |
|---|---|---|---|
| FRAP | 1.000 | −0.511 * | 0.359 |
| ORAC | −0.511 * | 1.000 | 0.227 |
| IA | 0.359 | 0.227 | 1.000 |
| Chemical Components/Method | FRAP | ORAC | IA |
|---|---|---|---|
| Xanthohumol | −0.356 | 0.434 | 0.044 |
| Cohumulone | −0.121 | 0.124 | −0.129 |
| n+adhumulone | −0.168 | 0.102 | −0.268 |
| Colupulone | −0.263 | −0.166 | 0.137 |
| n+adlupulone | −0.194 | −0.184 | 0.159 |
| Unknown | 0.656 | 0.175 | 0.141 |
| α-acids * | −0.159 | 0.066 | −0.271 |
| β-acids ** | −0.215 | −0.219 | 0.109 |
| Cohumulone and colupulone | −0.271 | −0.127 | 0.112 |
| n+adhumulone and n+adlupulone | −0.129 | −0.119 | −0.176 |
| AA–FRAP | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low | Medium | High | p | |||||||
| n | Mean | se | n | Mean | se | n | Mean | se | ||
| Xanthohumol (%, w/w) | 4 | 1.87 | 0.55 | 8 | 1.23 | 0.27 | 4 | 0.74 | 0.26 | 0.179 |
| Cohumulone (%, w/w) | 4 | 9.06 | 2.69 | 8 | 4.30 | 1.17 | 4 | 5.31 | 2.59 | 0.232 |
| n+adhumulone (%, w/w) | 4 | 28.45 | 8.65 | 8 | 13.91 | 5.22 | 4 | 25.01 | 16.04 | 0.469 |
| Colupulone (%, w/w) | 4 | 6.38 | 1.95 | 8 | 6.85 | 1.65 | 4 | 3.97 | 0.46 | 0.498 |
| n+adlupulone (%, w/w) | 4 | 6.17 | 1.81 | 8 | 8.59 | 1.93 | 4 | 4.76 | 0.18 | 0.354 |
| Unknown, % | 4 | 48.1 | 15.6 | 8 | 65.1 | 7.4 | 4 | 60.2 | 18.7 | 0.620 |
| AA–ORAC | ||||||||||
| low | medium | high | p | |||||||
| n | Mean | se | n | Mean | se | n | Mean | se | ||
| Xanthohumol (%, w/w) | 4 | 0.74 | 0.52 | 8 | 1.44 | 0.25 | 4 | 1.45 | 0.48 | 0.397 |
| Cohumulone (%, w/w) | 4 | 4.37 | 2.85 | 8 | 6.79 | 1.56 | 4 | 5.03 | 2.12 | 0.658 |
| n+adhumulone (%, w/w) | 4 | 22.59 | 16.85 | 8 | 21.50 | 6.21 | 4 | 15.70 | 6.54 | 0.883 |
| Colupulone (%, w/w) | 4 | 8.13 | 3.06 | 8 | 5.59 | 0.88 | 4 | 4.75 | 1.88 | 0.451 |
| n+adlupulone (%, w/w) | 4 | 9.47 | 2.87 | 8 | 6.81 | 1.40 | 4 | 5.01 | 1.84 | 0.377 |
| Unknown, % | 4 | 54.7 | 17.0 | 8 | 57.9 | 9.6 | 4 | 68.1 | 12.4 | 0.782 |
| AA–IA | ||||||||||
| low | medium | high | p | |||||||
| n | Mean | se | n | Mean | se | n | Mean | se | ||
| Xanthohumol (%, w/w) | 4 | 1.03 | 0.46 | 8 | 1.52 | 0.31 | 4 | 0.99 | 0.41 | 0.528 |
| Cohumulone (%, w/w) | 4 | 5.55 | 2.49 | 8 | 6.72 | 1.54 | 4 | 4.00 | 2.55 | 0.646 |
| n+adhumulone (%, w/w) | 4 | 26.04 | 15.66 | 8 | 19.91 | 5.35 | 4 | 15.42 | 10.89 | 0.784 |
| Colupulone (%, w/w) | 4 | 5.06 | 0.91 | 8 | 5.88 | 1.11 | 4 | 7.23 | 3.35 | 0.749 |
| n+adlupulone (%, w/w) | 4 | 6.97 | 2.21 | 8 | 6.39 | 1.48 | 4 | 8.35 | 2.88 | 0.793 |
| Unknown, % | 4 | 55.4 | 17.2 | 8 | 59.6 | 9.1 | 4 | 64.0 | 14.8 | 0.914 |
| Hop Chemical Compounds/AA Method | PC 1 | PC 2 |
|---|---|---|
| Xanthohumol | 0.907 | −0.004 |
| Cohumulone | 0.819 | 0.241 |
| n+adhumulone | 0.843 | 0.221 |
| Colupulone | 0.993 | −0.191 |
| n+adlupulone | 0.882 | −0.348 |
| Unknown | −0.948 | −0.099 |
| FRAP | −0.208 | −0.745 |
| ORAC | −0.048 | 0.814 |
| IA | −0.199 | 0.768 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kolenc, Z.; Hribernik, T.; Langerholc, T.; Pintarič, M.; Prevolnik Povše, M.; Bren, U. Antioxidant Activity of Different Hop (Humulus lupulus L.) Genotypes. Plants 2023, 12, 3436. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12193436
Kolenc Z, Hribernik T, Langerholc T, Pintarič M, Prevolnik Povše M, Bren U. Antioxidant Activity of Different Hop (Humulus lupulus L.) Genotypes. Plants. 2023; 12(19):3436. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12193436
Chicago/Turabian StyleKolenc, Zala, Tamara Hribernik, Tomaž Langerholc, Maša Pintarič, Maja Prevolnik Povše, and Urban Bren. 2023. "Antioxidant Activity of Different Hop (Humulus lupulus L.) Genotypes" Plants 12, no. 19: 3436. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12193436
APA StyleKolenc, Z., Hribernik, T., Langerholc, T., Pintarič, M., Prevolnik Povše, M., & Bren, U. (2023). Antioxidant Activity of Different Hop (Humulus lupulus L.) Genotypes. Plants, 12(19), 3436. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12193436







