Characteristics and Pathogenicity of Discula theae-sinensis Isolated from Tea Plant (Camellia sinensis) and Interaction with Colletotrichum spp.
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
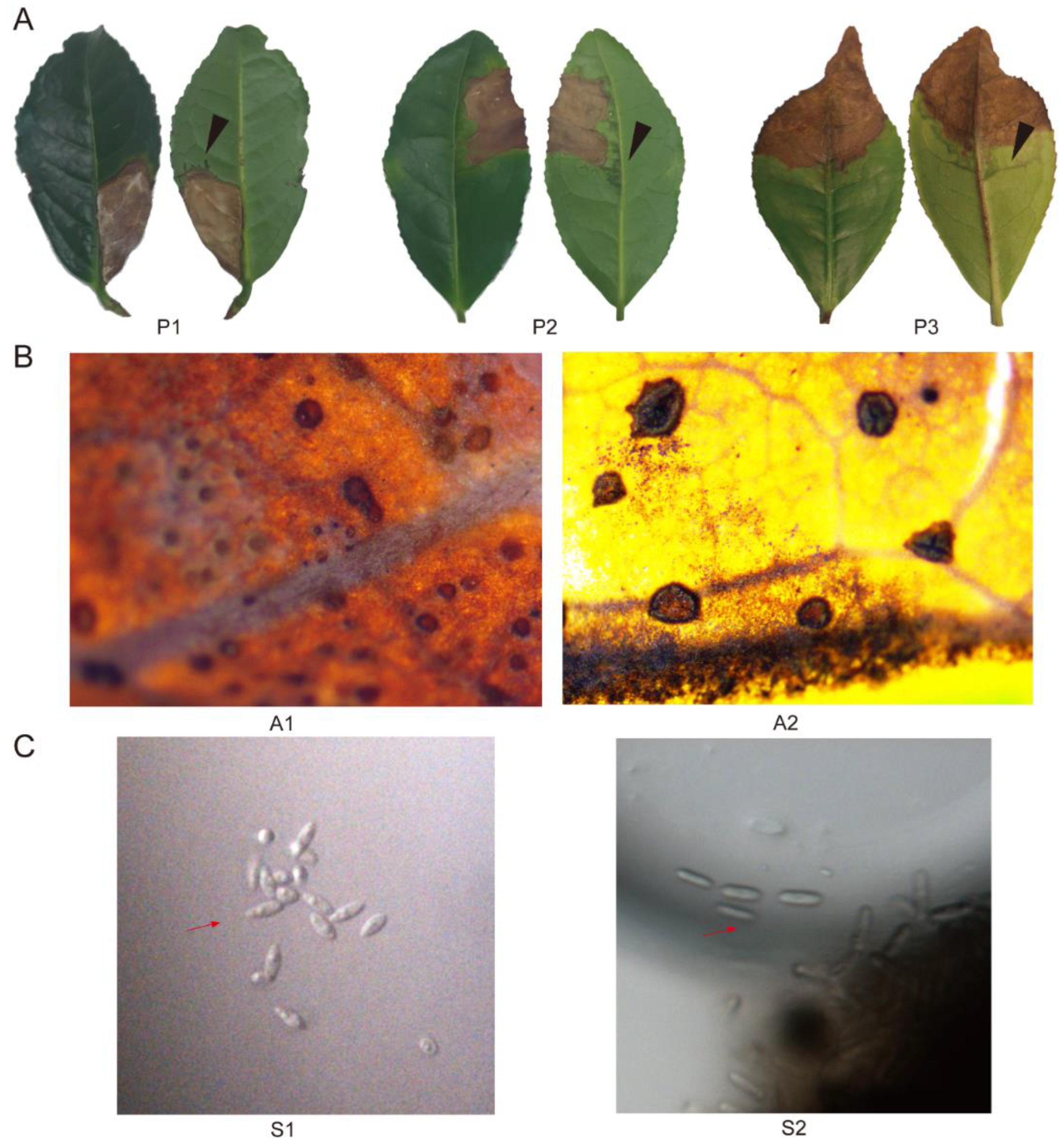
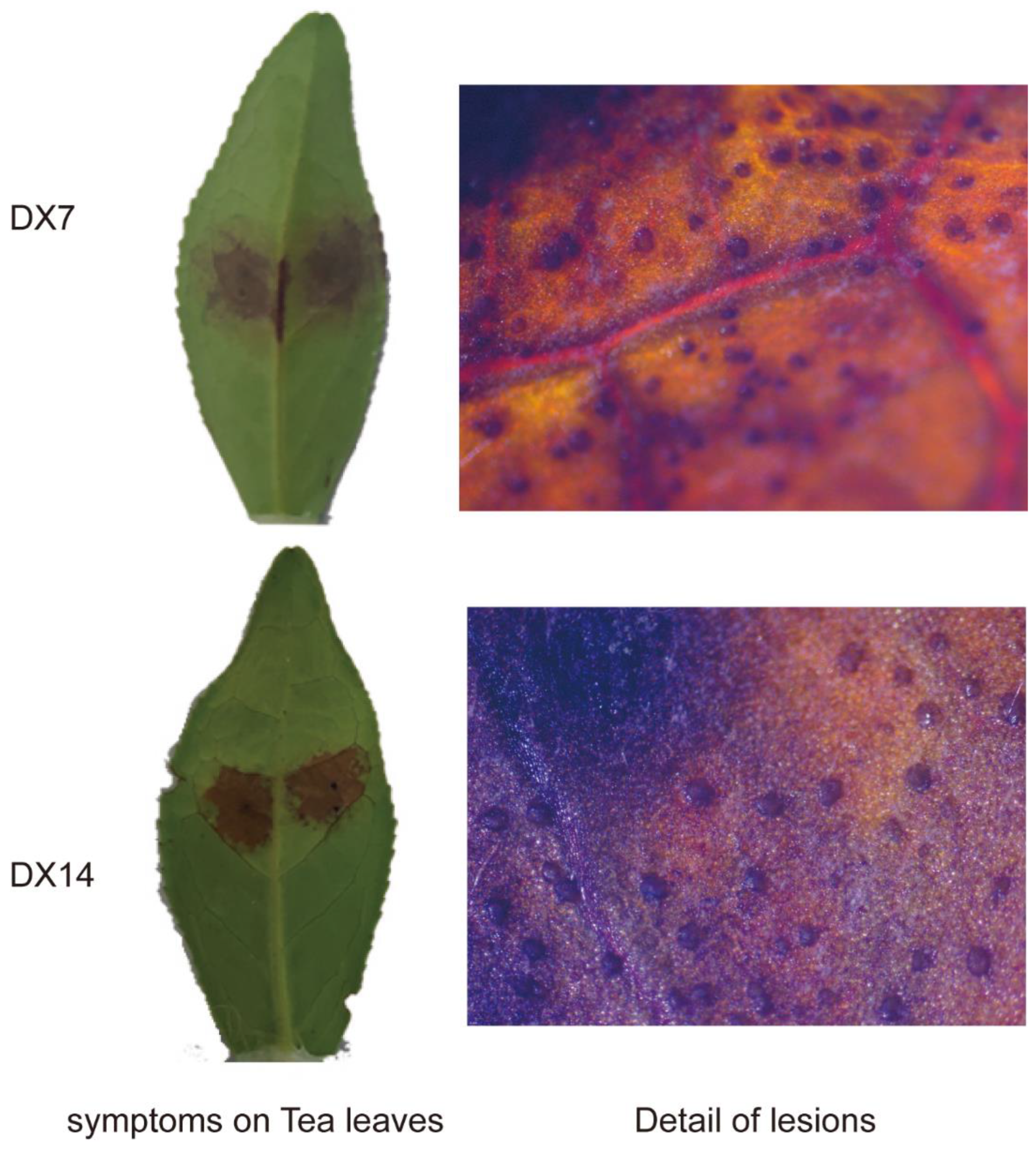
2.1. Phenotypic Characterization of Collected Tea Leaves
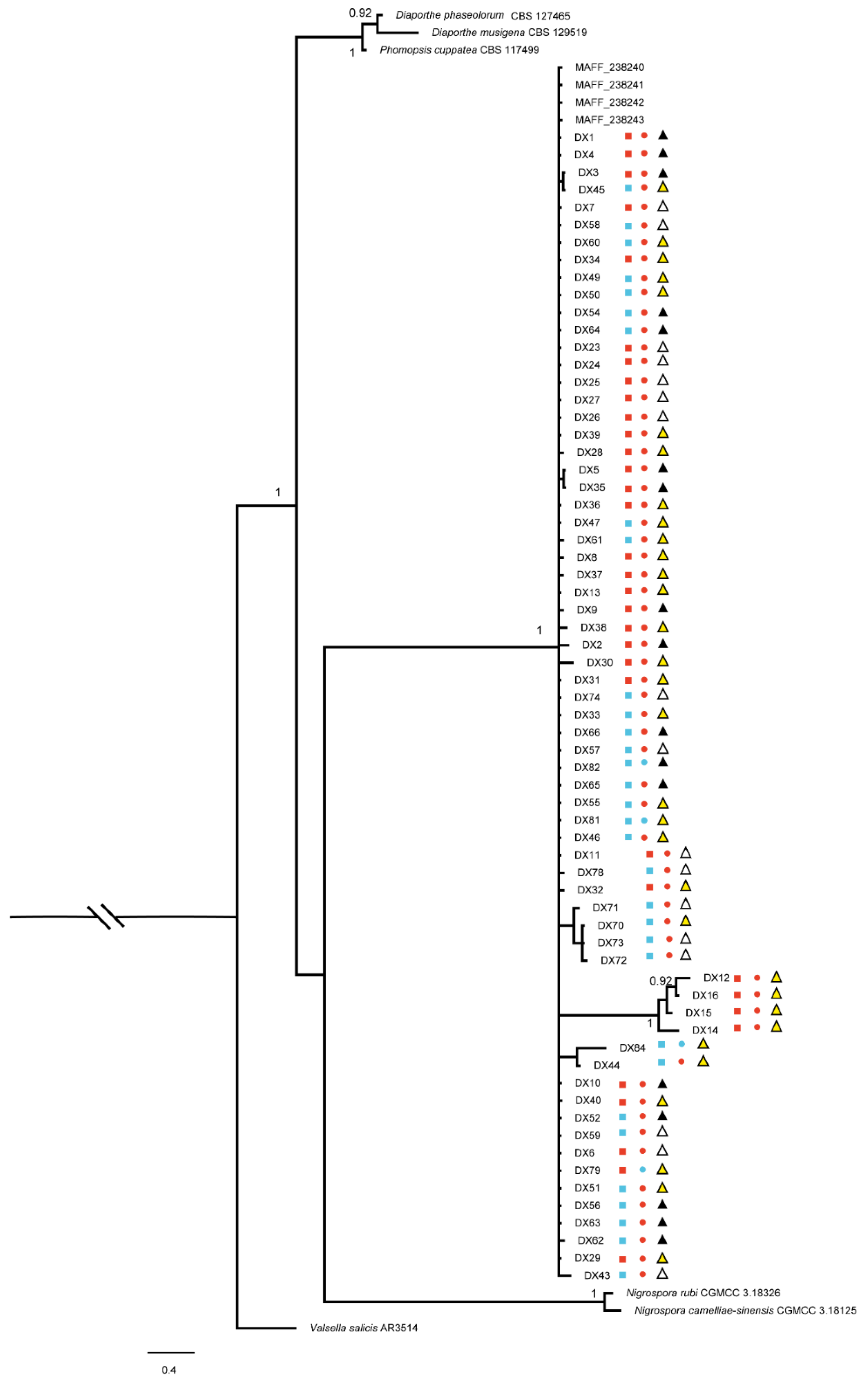
2.2. Identification and Characterization of Dt
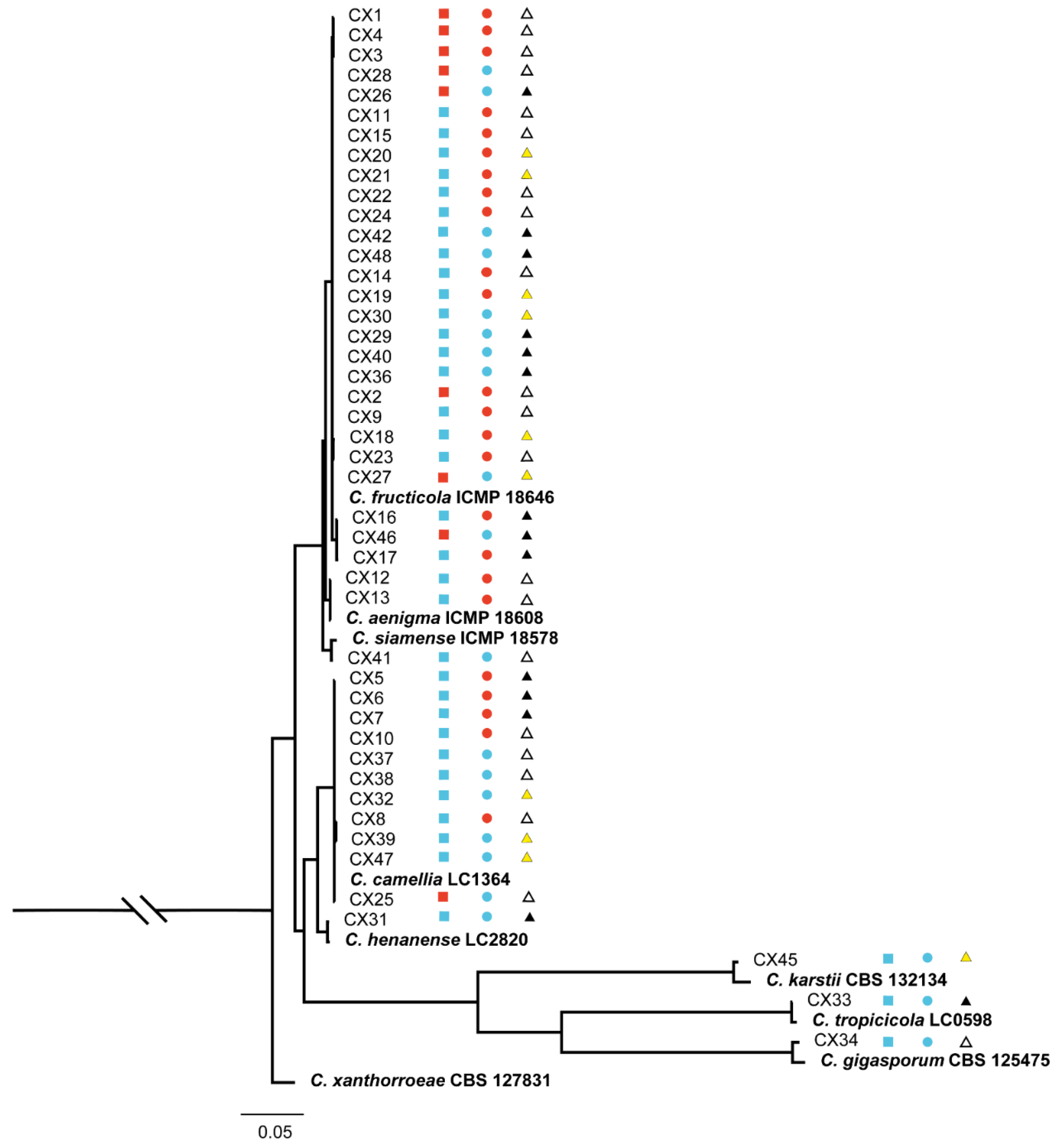
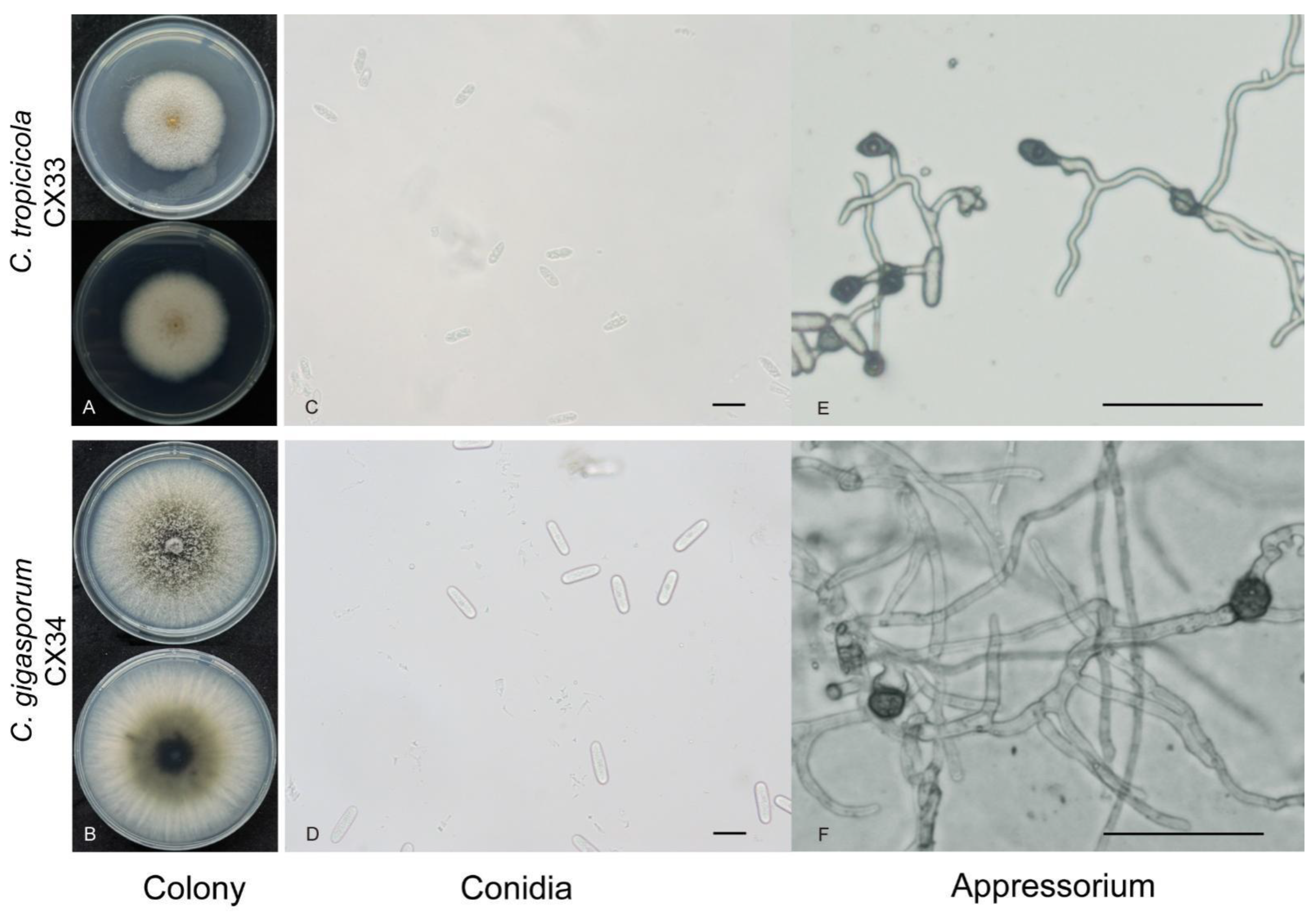
2.3. Identification and Characterization of Colletotrichum spp.
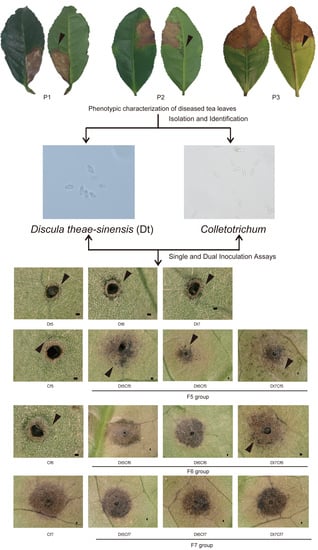
2.4. Pathogenicity Test of Dt Collected from Leaf Surface
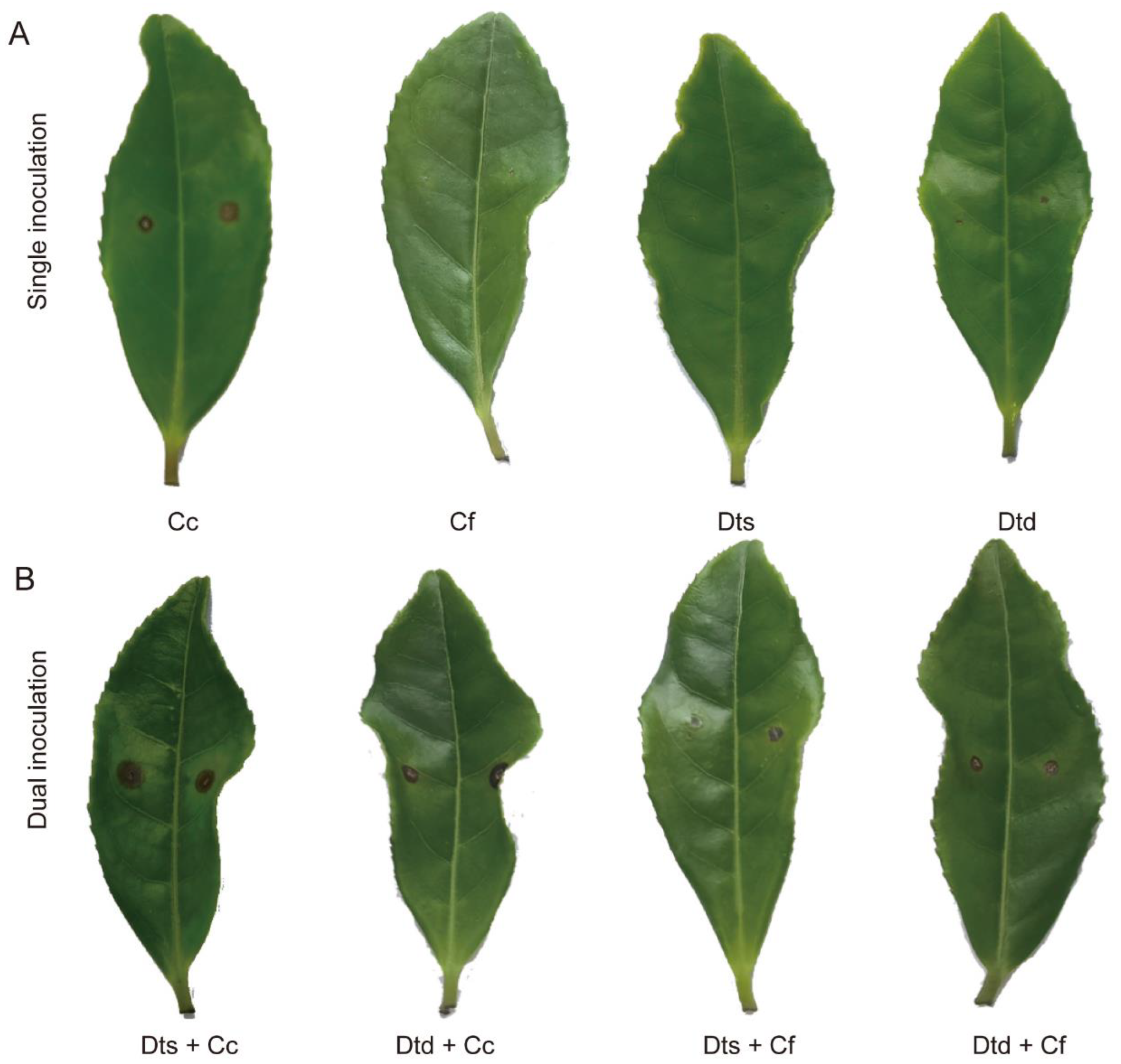
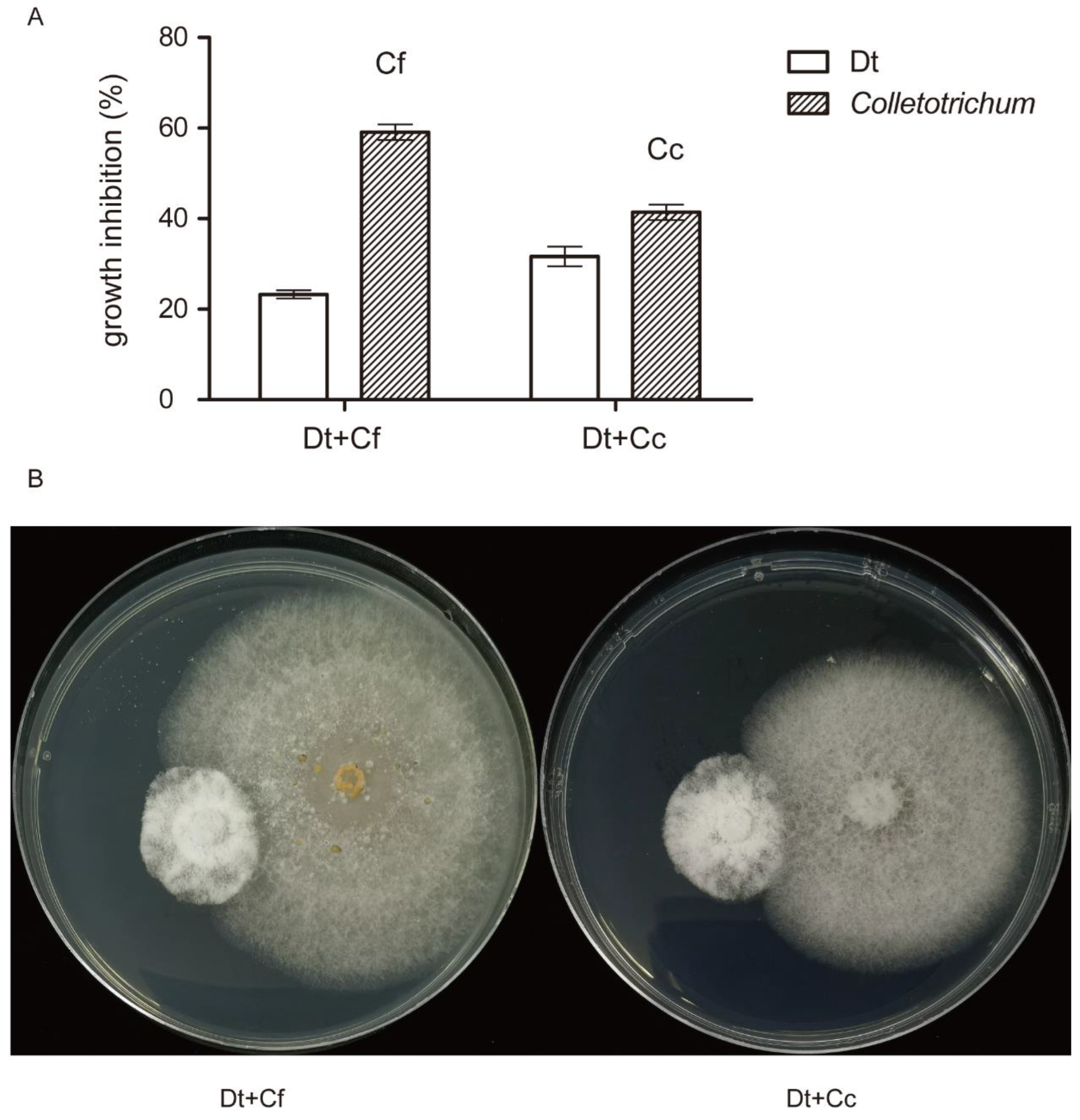
2.5. Dual Inoculation Assays of Dt and Colletotrichum
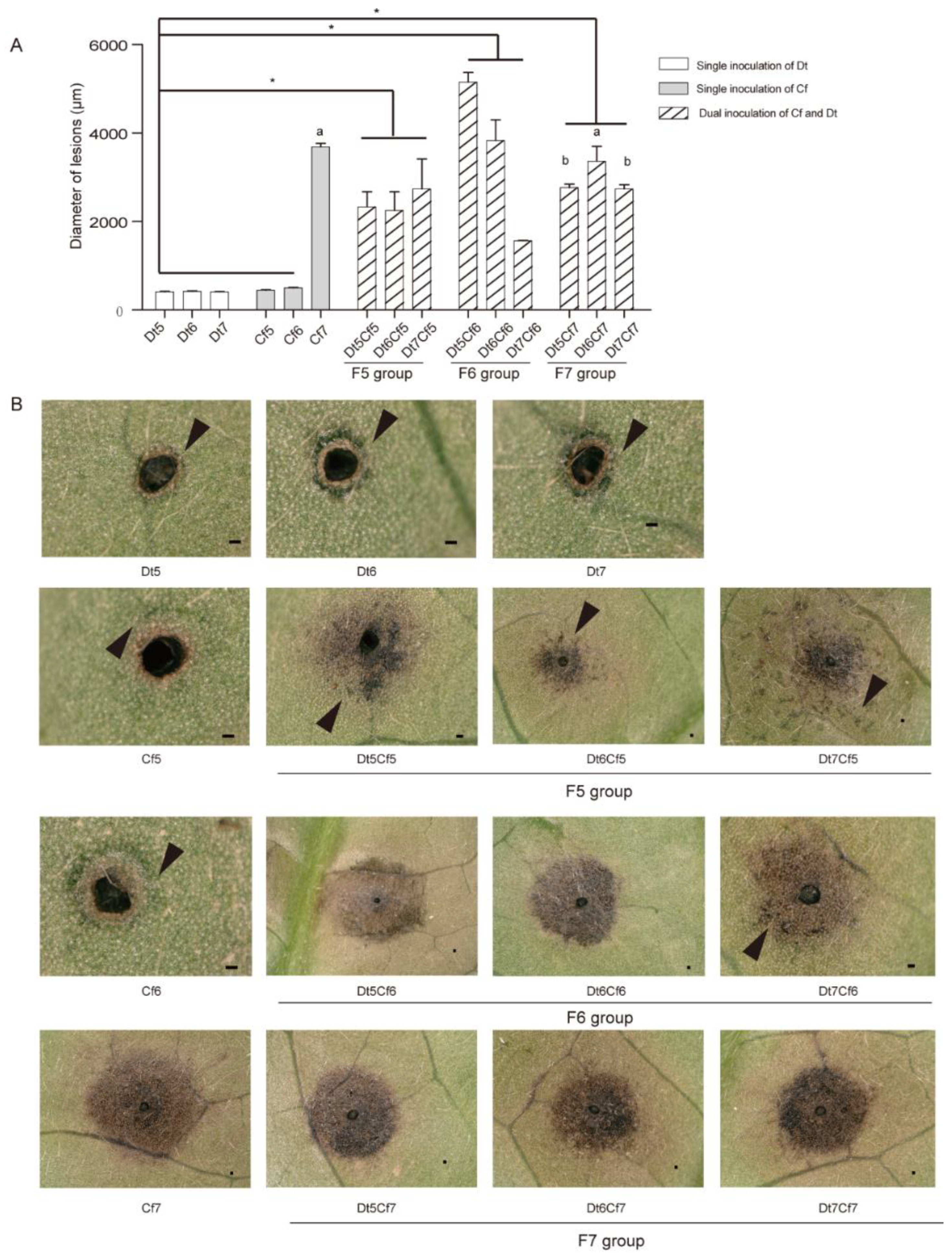
2.6. Interaction of Dt and Cf on Tea Plant Infection
3. Discussion
3.1. Phenotype and Isolated Main Fungi of Diseased Tea Leaves
3.2. Identification of Dt from Tea Plant
3.3. Interaction of Dt and Colletotrichum
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Collection and Isolation
4.2. Morphological Characterization
4.3. DNA Extraction and PCR Amplification
4.4. Phylogenetic Analysis
4.5. Pathogenicity Tests of Discula Theae-Sinensis
4.6. Dual Inoculation Assays of Dt and Colletotrichum
| Labels | Treatment Conditions |
|---|---|
| Dts | single inoculation of spore suspension of Dt |
| Dtd | single inoculation of mycelial discs of Dt |
| Cc | single inoculation of spore suspension of Cc |
| Cf | single inoculation of spore suspension of Cf |
| Dts + Cc | dual inoculation with a spore suspension of Dt and Cc |
| Dtd + Cc | dual inoculation with mycelial discs of Dt and a spore suspension of Cc |
| Dts + Cf | dual inoculation with spore suspension Dt and Cf |
| Dtd + Cf | dual inoculation with mycelial discs of Dt and spore suspension of Cf |
4.7. Impact of Spore Suspension Concentration on Combined Dt and Cf Infection Capacity
| Labels | Treatment Conditions | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Single inoculation | Dt5 | 105 spores/mL spore suspension of Dt | |
| Dt6 | 106 spores/mL spore suspension of Dt | ||
| Dt7 | 107 spores/mL spore suspension of Dt | ||
| Cf5 | 105 spores/mL spore suspension of Cf | ||
| Cf6 | 106 spores/mL spore suspension of Cf | ||
| Cf7 | 107 spores/mL spore suspension of Cf | ||
| Dual inoculation | F5 group | Dt5Cf5 | 105 spores/mL Dt and 105 spores/mL Cf |
| Dt6Cf5 | 106 spores/mL Dt and 105 spores/mL Cf | ||
| Dt7Cf5 | 107 spores/mL Dt and 105 spores/mL Cf | ||
| F6 group | Dt5Cf6 | 105 spores/mL Dt and 106 spores/mL Cf | |
| Dt6Cf6 | 106 spores/mL Dt and 106 spores/mL Cf | ||
| Dt7Cf6 | 107 spores/mL Dt and 106 spores/mL Cf | ||
| F7 group | Dt5Cf7 | 105 spores/mL Dt and 107 spores/mL Cf | |
| Dt6Cf7 | 106 spores/mL Dt and 107 spores/mL Cf | ||
| Dt7Cf7 | 107 spores/mL Dt and 107 spores/mL Cf | ||
4.8. Statistical Analysis and Microscopic Observation
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Leng, Y.; Tong, J.W.; Huang, P.; Shang, H.G.; Zhou, Z.Y. The development of tea Industry in China during the 13th five-year plan period and prospects for the 14th five-year plan period. China Tea 2021, 43, 25–30. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.C.; Qian, W.J.; Li, N.N.; Hao, X.Y.; Wang, L.; Xiao, B.; Wang, X.C.; Yang, Y.J. Metabolic Changes of Caffeine in Tea Plant (Camellia sinensis (L.) O. Kuntze) as Defense Response to Colletotrichum fructicola. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 6685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Jiang, J.; Zhan, J.; Zhou, K.; Chen, Z. Main Diseases and Insect Pests of Tea in Meitan County. Guizhou Agric. Sci. 2011, 39, 77–80. [Google Scholar]
- Weir, B.S.; Johnston, P.R.; Damm, U. The Colletotrichum gloeosporioides species complex. Stud. Mycol. 2012, 73, 115–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, W.A. revision of the genus and species names of anthracnose fungi in Japan. Plant Prot. 1960, 14, 49–52. [Google Scholar]
- Moriwaki, J.; Sato, T. A new combination for the causal agent of tea anthracnose: Discula theae-sinensis (I. Miyake) Moriwaki & Toy. Sato, comb. nov. J. Gen. Plant Pathol. 2009, 75, 359–361. [Google Scholar]
- Castlebury, L.A.; Rossman, A.Y.; Jaklitsch, W.J.; Vasilyeva, L.N. A preliminary overview of the Diaporthales based on large subunit nuclear ribosomal DNA sequences. Mycologia 2002, 94, 1017–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sogonov, M.V.; Castlebury, L.A.; Rossman, A.Y.; White, J.F. The type species of Apiognomonia, A. veneta, with its Discula anamorph is distinct from A. Errabunda. Mycol. Res. 2007, 111, 693–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senanayake, I.C.; Crous, P.W.; Groenewald, J.Z.; Maharachchikumbura, S.S.N.; Jeewon, R.; Phillips, A.J.L.; Bhat, J.D.; Perera, R.H.; Li, Q.R.; Li, W.J.; et al. Families of Diaporthales based on morphological and phylogenetic evidence. Stud. Mycol. 2017, 86, 217–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Feng, X.; Wang, M.; Wang, Y.; Kumar Awasthi, M.; Xu, P. Implications of endophytic microbiota in Camellia sinensis: A review on current understanding and future insights. Bioengineered 2020, 11, 1001–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Liu, F.; Cai, L. Unravelling Diaporthe species associated with Camellia. Syst. Biodivers. 2016, 14, 102–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayawardena, R.S.; Bhunjun, C.S.; Hyde, K.D.; Gentekaki, E.; Itthayakorn, P. Colletotrichum: Lifestyles, biology, morpho-species, species complexes and accepted species. Mycosphere 2021, 12, 519–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.C.; Hao, X.Y.; Wang, L.; Xiao, B.; Wang, X.C.; Yang, Y.J. Diverse Colletotrichum species cause anthracnose of tea plants (Camellia sinensis (L.) O. Kuntze) in China. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, X.J.; Wang, Q.C.; Zhang, S.K.; Guo, K.; Zhou, X.D. Colletotrichum species associated with Camellia anthracnose in China. Mycosphere 2023, 14, 130–157. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.; Weir, B.S.; Damm, U.; Crous, P.W.; Wang, Y.; Liu, B.; Wang, M.; Zhang, M.; Cai, L. Unravelling Colletotrichum species associated with Camellia: Employing ApMat and GS loci to resolve species in the C. gloeosporioides complex. Persoonia 2015, 35, 63–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Li, N.; Ni, D.; Yang, Y.; Wang, X. Differences in the characteristics and pathogenicity of Colletotrichum camelliae and C. fructicola Isolated from the tea plant (Camellia sinensis (L.) O. Kuntze). Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 3060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, Z.K.; Tan, W.Z.; Zhang, K.C.; Li, P.; Wang, Z.W.; Yin, L.L.; Tan, S.X. Effects of wuyiencin on growth and sporulation of Colletotrichum camelliae causing tea leaf blight. J. Southwest China Norm. Univ. 2008, 33, 42–47. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Qiao, W.L.; Zeng, L.; Shen, D.; Liu, Z.L.; Wang, X.S.; Tong, H. Characterization, pathogenicity, and phylogenetic analyses of Colletotrichum species associated with brown blight disease on Camellia sinensis in China. Plant Dis. 2017, 106, 1022–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doehlemann, G.; Ökmen, B.; Zhu, W.; Sharon, A. Plant pathogenic fungi. Microbiol. Spectr. 2017, 5, FUNK-0023-2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, K.; Sonoda, R. A fluorescence microscopic study of the infection process of Discula theae-sinensis in tea. Jpn. Agr. Res. Q 2014, 48, 399–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.W. Plant trichomes as microbial habitats and infection sites. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2019, 154, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamaya, E. Trichome infection of the tea anthracnose fungus Gloeosporium theae-sinensis. JARQ 1982, 16, 114–118. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Jiang, B.; Yang, X.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, N.; Ren, W.; Li, P.; Li, B.; Lian, S. Deficiency of the melanin biosynthesis genes CfSCD1 impedes appressoria formation and disrupts Colletotrichum fructicola infection on apple. Trop. Plant Pathol. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahara, H.; Hacquard, S.; Kombrink, A.; Hughes, H.B.; Halder, V.; Robin, G.P.; Hiruma, K.; Neumann, U.; Shinya, T.; Kombrink, E.; et al. Colletotrichum higginsianum extracellular LysM proteins play dual roles in appressorial function and suppression of chitin-triggered plant immunity. New Phytol. 2016, 211, 1323–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleemann, J.; Rincon-Rivera, L.J.; Takahara, H.; Neumann, U.; Ver Loren van Themaat, E.; van der Does, H.C.; Hacquard, S.; Stüber, K.; Will, I.; Schmalenbach, W.; et al. Sequential delivery of host-induced virulence effectors by appressoria and intracellular hyphae of the phytopathogen Colletotrichum higginsianum. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryder, L.; Talbot, N. Regulation of appressorium development in pathogenic fungi. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2015, 26, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Cai, L.; Crous, P.W.; Damm, U. The Colletotrichum gigasporum species complex. Persoonia 2014, 33, 83–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.C.; Liu, S.A.; Lu, Q.H.; Xiong, F.; Yang, Y.J.; Wang, X.C. Research progress and prospects of Colletotrichum species causing tea plant diseases in China. J. Plant Prot. Res. 2019, 46, 954–963. [Google Scholar]
- Kheiri, A.; Moosawi-Jorf, S.A.; Malihipour, A. Infection process and wheat response to Fusarium head blight caused by Fusarium graminearum. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2018, 153, 489–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamichhane, J.R.; Fabi, A.; Ridolfi, R.; Varvaro, L. Epidemiological study of hazelnut bacterial blight in central Italy by using laboratory analysis and geostatistics. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhavan, A.; Bahar, M.; Askarian, H.; Lak, M.R.; Nazemi, A.; Zamani, Z. Bean common bacterial blight: Pathogen epiphytic life and effect of irrigation practices. Springerplus 2013, 2, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Kashyap, P.L.; Mahapatra, S.; Jasrotia, P.; Singh, G.P. New and emerging technologies for detecting Magnaporthe oryzae causing blast disease in crop plants. Crop Prot. 2021, 143, 105473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potnis, N.; Colee, J.; Jones, J.B.; Barak, J.D. Plant pathogen induced water-soaking promotes Salmonella enterica growth on tomato leaves. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 8126–8134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aung, K.; Jiang, Y.; He, S.Y. The role of water in plant-microbe interactions. Plant J. 2018, 93, 771–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schornack, S.; Minsavage, G.V.; Stall, R.E.; Jones, J.B.; Lahaye, T. Characterization of AvrHah1, a novel AvrBs3-like effector from Xanthomonas gardneri with virulence and avirulence activity. New Phytol. 2008, 179, 546–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, A.R.; Morbitzer, R.; Lahaye, T.; Staskawicz, B.J. TALE-induced bHLH transcription factors that activate a pectate lyase contribute to water soaking in bacterial spot of tomato. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E897–E903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, R.R.; Glienke, C.; Videira, S.I.R.; Lombard, L.; Groenewald, J.Z.; Crous, P.W. Diaporthe: A genus of endophytic, saprobic and plant pathogenic fungi. Persoonia 2013, 31, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.M.; Correia, V.G.; Phillips, A.J.L. Primers for mating-type diagnosis in Diaporthe and Phomopsis: Their use in teleomorph induction in vitro and biological species definition. Fungal. Biol. 2010, 114, 255–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostert, L.; Groenewald, J.Z.; Summerbell, R.; Gams, W.; Crous, P.W. Taxonomy and Pathology of Togninia (Diaporthales) and its Phaeoacremonium Anamorphs. Stud. Mycol. 2006, 54, 1–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Rensburg, J.C.J.; Lamprecht, S.C.; Groenewald, J.Z.; Castlebury, L.A.; Crous, P.W. Characterization of Phomopsis spp. associated with die-back of rooibos (Aspalathus linearis) in South Africa. Stud. Mycol. 2006, 55, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyde, K.D.; Nilsson, R.H.; Alias, S.A.; Ariyawansa, H.A.; Blair, J.E.; Cai, L.; Cock, A.; Dissanayake, A.; Glockling, S.; Goonasekara, I.; et al. One stop shop: Backbones trees for important phytopathogenic genera: I. Fungal. Divers. 2014, 67, 21–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senanayake, I.C.; Jeewon, R.; Chomnunti, P.; Wanasinghe, D.N.; Norphanphoun, C.; Karunarathna, A.; Pem, D.; Perera, R.H.; Camporesi, E.; McKenzie, E.H.C.; et al. Taxonomic circumscription of Diaporthales based on multigene phylogeny and morphology. Fungal Divers. 2018, 93, 241–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitt, B.D.L.; Huang, Y.J.; Bosch, F.V.D.; West, J.S. Coexistence of related pathogen species on arable crops in space and time. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2006, 44, 163–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le May, C.; Potage, G.; Andrivon, D.; Tivoli, B.; Outreman, Y. Plant disease complex: Antagonism and synergism between pathogens of the Ascochyta blight complex on Pea. J. Phytopathol. 2009, 157, 715–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Tian, Q.; Zeng, D.; Xu, M.; Wang, Y.; Dong, S.; Ma, Z.; et al. Fusarium-produced vitamin B6 promotes the evasion of soybean resistance by Phytophthora sojae. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2023, 65, 2204–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitelaw-Weckert, M.A.; Rahman, L.; Appleby, L.M.; Hall, A.; Clark, A.C.; Waite, H.; Hardie, W.J. Co-infection by Botryosphaeriaceae and Ilyonectria spp. fungi during propagation causes decline of young grafted grapevines. Plant Pathol. 2013, 62, 1226–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, P.; Sivasithamparam, K.; Li, H.; Barbetti, M.J. Pre-inoculation with Hyaloperonospora parasitica reduces incubation period and increases severity of disease caused by Albugo candida in a Brassica juncea variety resistant to downy mildew. J. Gen. Plant Pathol. 2011, 77, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.J.; Xiao, Q. Colored Pictorial Handbook of Tea Plant Pests and Natural Enemies; China Agricultural University Press: Beijing, China, 2019; pp. 4–5. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, L.; Hyde, K.D.; Taylor, P.; Weir, B.S.; Waller, J.M.; Abang, M.M.; Zhang, J.Z.; Yang, Y.L.; Phoulivong, S.; Liu, Z.Y.; et al. A polyphasic approach for studying Colletotrichum. Fungal Divers. 2009, 39, 183–204. [Google Scholar]
- Kjer, J.; Debbab, A.; Aly, A.H.; Proksch, P. Methods for isolation of marine-derived endophytic fungi and their bioactive secondary products. Nat. Protoc. 2010, 5, 479–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-González, R.C.; Gómez-Cornelio, S.; Rosa-García, D.; Garrido, E.; Oropeza-Mariano, O.; Heil, M.; Partida-Martínez, L. The age oflima bean leaves influences the richness and diversity of the endophytic fungal community, but not the antagonistic effect of endophytes against Colletotrichum lindemuthianum. Fungal Ecol. 2017, 26, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Templeton, M.D.; Rikkerink, E.; Solon, S.L.; Crowhurst, R.N. Cloning and molecular characterization of the glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase-encoding gene and cDNA from the plant pathogenic fungus Glomerella cingulata. Gene 1992, 122, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardes, M.; Bruns, T.D. ITS primers with enhanced specificity for basidiomycetes—Application to the identification of mycorrhizae and rusts. Mol. Ecol. 1993, 2, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, T.; Bruns, T.; Lee, S.; Taylor, J. Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. Pcr. Protocols. 1990, 18, 315–322. [Google Scholar]
- O’Donnell, K.; Cigelnik, E. Two divergent intragenomic rDNA ITS2 types within a monophyletic lineage of the fungus Fusarium are nonorthologous. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 1997, 7, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glass, N.L.; Donaldson, G.C. Development of primer sets designed for use with the PCR to amplify conserved genes from filamentous ascomycetes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol 1995, 61, 1323–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carbone, I.; Kohn, L.M. A method for designing primer sets for speciation studies in filamentous ascomycetes. Mycologia 1999, 91, 553–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.J.; Whelen, S.; Hall, B.D. Phylogenetic relationships among ascomycetes: Evidence from an RNA polymerse II subunit. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1999, 16, 1799–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilgalys, R.; Hester, M. Rapid genetic identification and mapping of enzymatically amplified ribosomal DNA from several Cryptococcus species. J. Bacteriol. 1990, 172, 4238–4246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Q.; Zhu, J.; Ren, N.; Li, D.; Jin, Y.; Lu, W.; Lu, Q. Characteristics and Pathogenicity of Discula theae-sinensis Isolated from Tea Plant (Camellia sinensis) and Interaction with Colletotrichum spp. Plants 2023, 12, 3427. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12193427
Li Q, Zhu J, Ren N, Li D, Jin Y, Lu W, Lu Q. Characteristics and Pathogenicity of Discula theae-sinensis Isolated from Tea Plant (Camellia sinensis) and Interaction with Colletotrichum spp. Plants. 2023; 12(19):3427. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12193427
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Qingsheng, Junyan Zhu, Ning Ren, Da Li, Ya Jin, Wenyuan Lu, and Qinhua Lu. 2023. "Characteristics and Pathogenicity of Discula theae-sinensis Isolated from Tea Plant (Camellia sinensis) and Interaction with Colletotrichum spp." Plants 12, no. 19: 3427. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12193427
APA StyleLi, Q., Zhu, J., Ren, N., Li, D., Jin, Y., Lu, W., & Lu, Q. (2023). Characteristics and Pathogenicity of Discula theae-sinensis Isolated from Tea Plant (Camellia sinensis) and Interaction with Colletotrichum spp. Plants, 12(19), 3427. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12193427