GABA Application Enhances Drought Stress Tolerance in Wheat Seedlings (Triticum aestivum L.)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
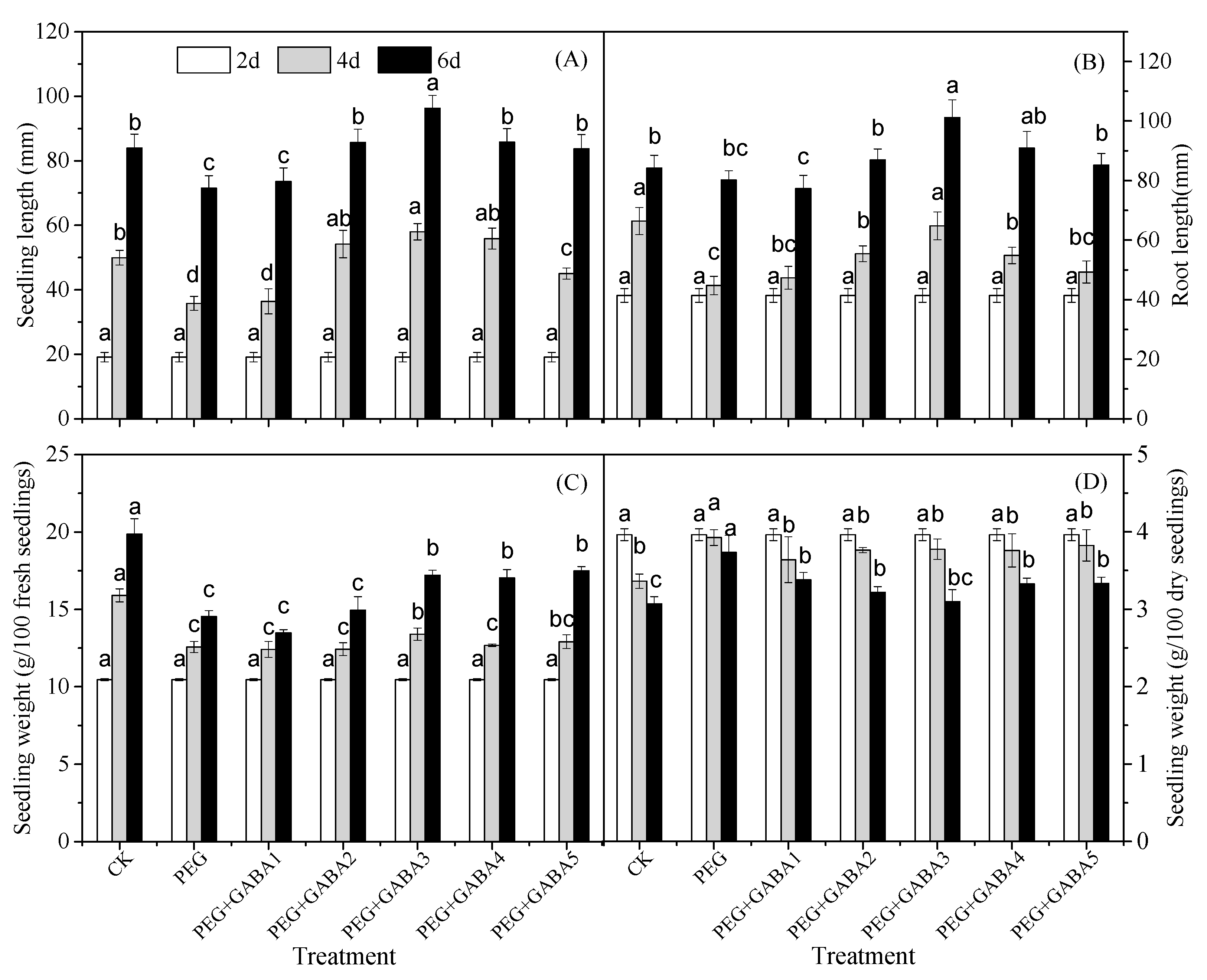
2.1. Effects of GABA on Length and Weight of Wheat Seedlings under Drought Stress
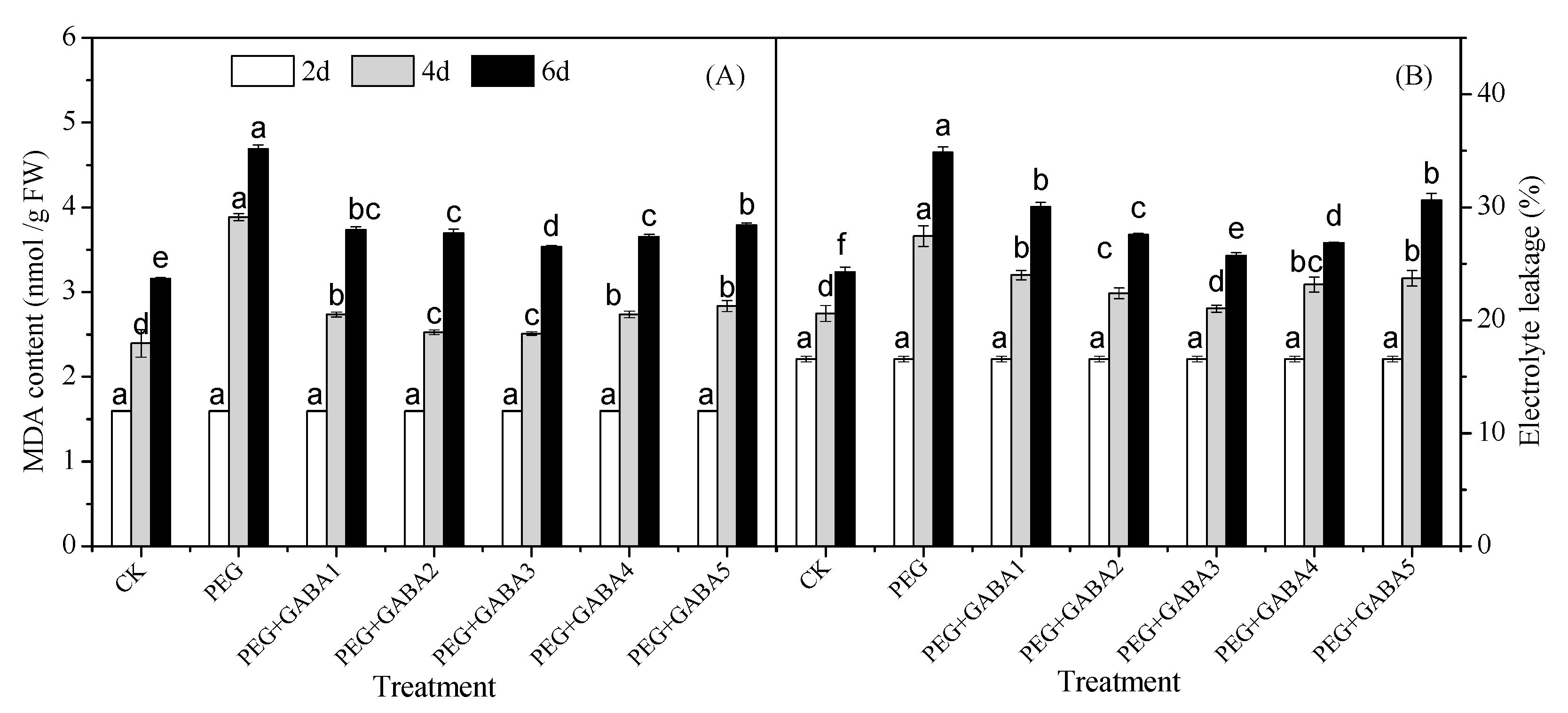
2.2. Effects of GABA on the MDA Content and Electrolyte Leakage of Wheat Seedlings under Drought Stress
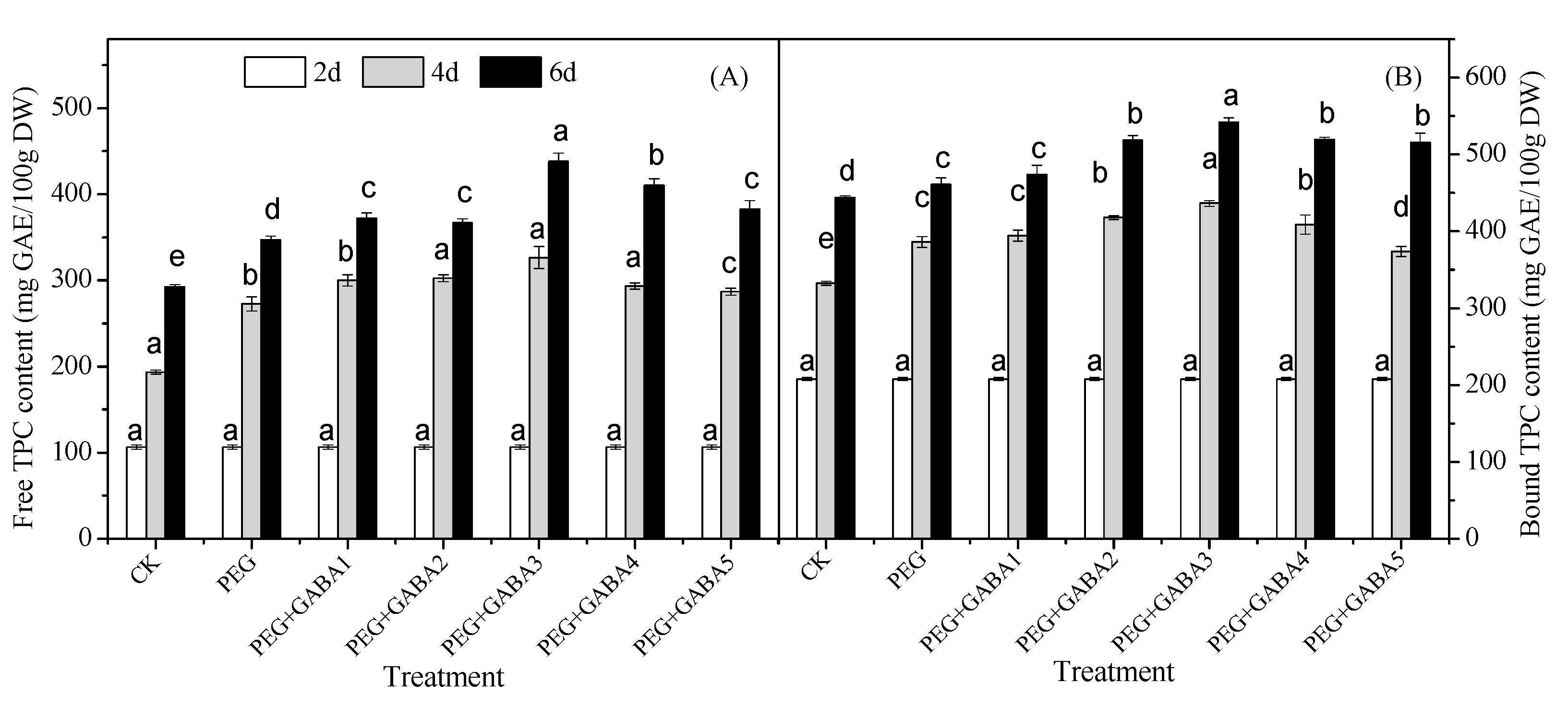
2.3. Effects of GABA on the Total Phenolic Content of Wheat Seedlings under Drought Stress
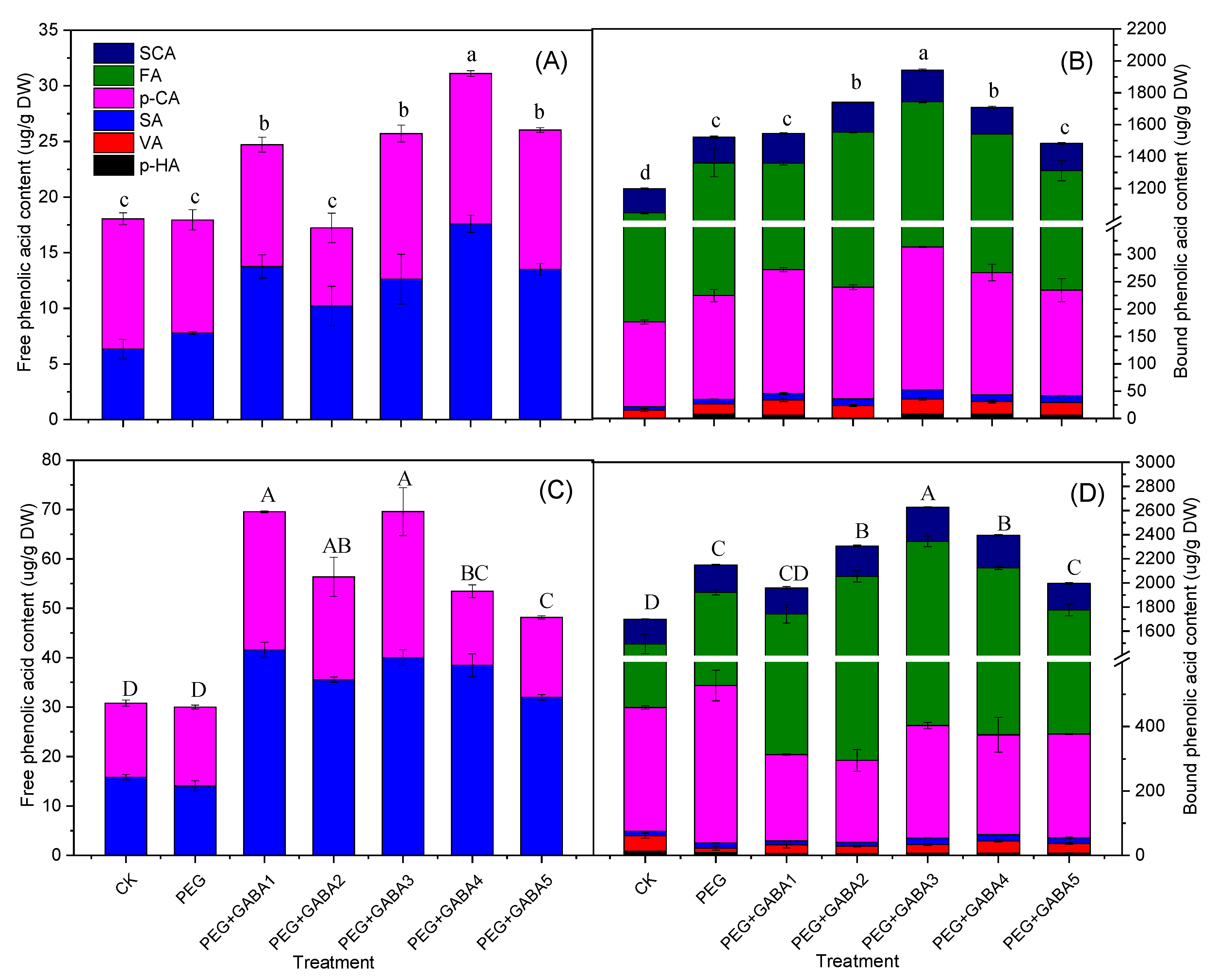
2.4. Effects of GABA the on Phenolic Acids Content of Wheat Seedlings under Drought Stress
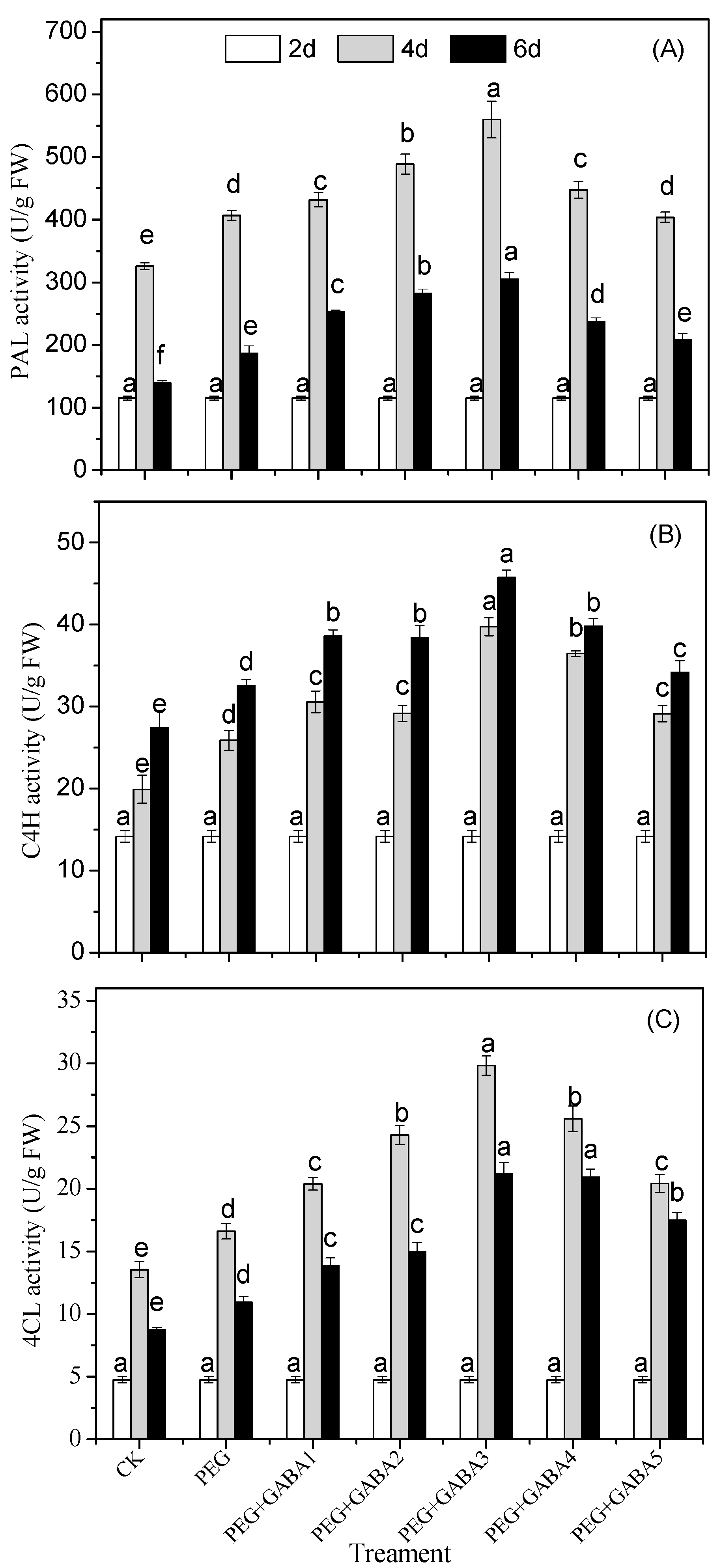
2.5. Effects of GABA on the PAL, C4H, and 4CL Activity of Wheat Seedlings under Drought Stress
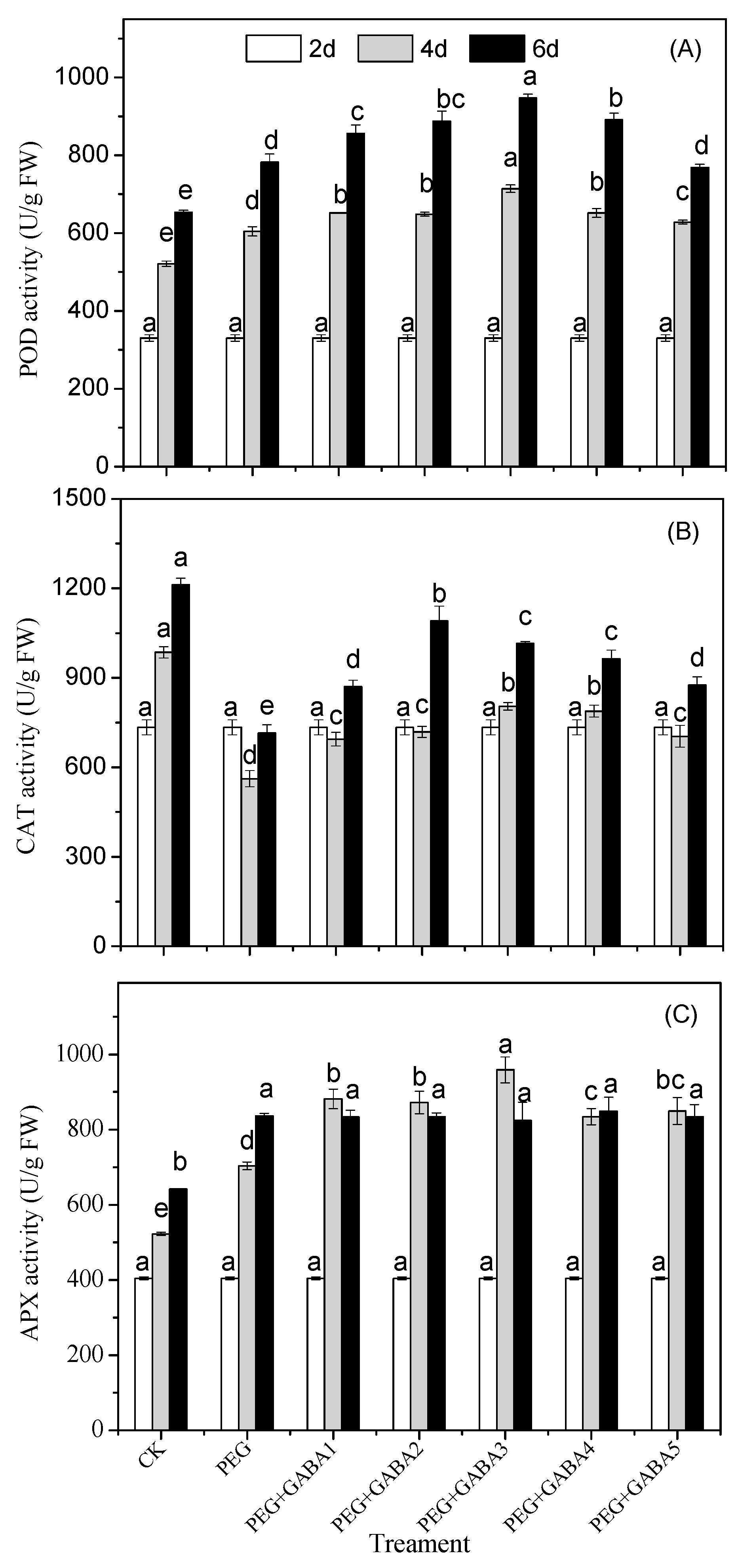
2.6. Effects of GABA on the POD, CAT and APX Activity of Wheat Seedlings under Drought Stress
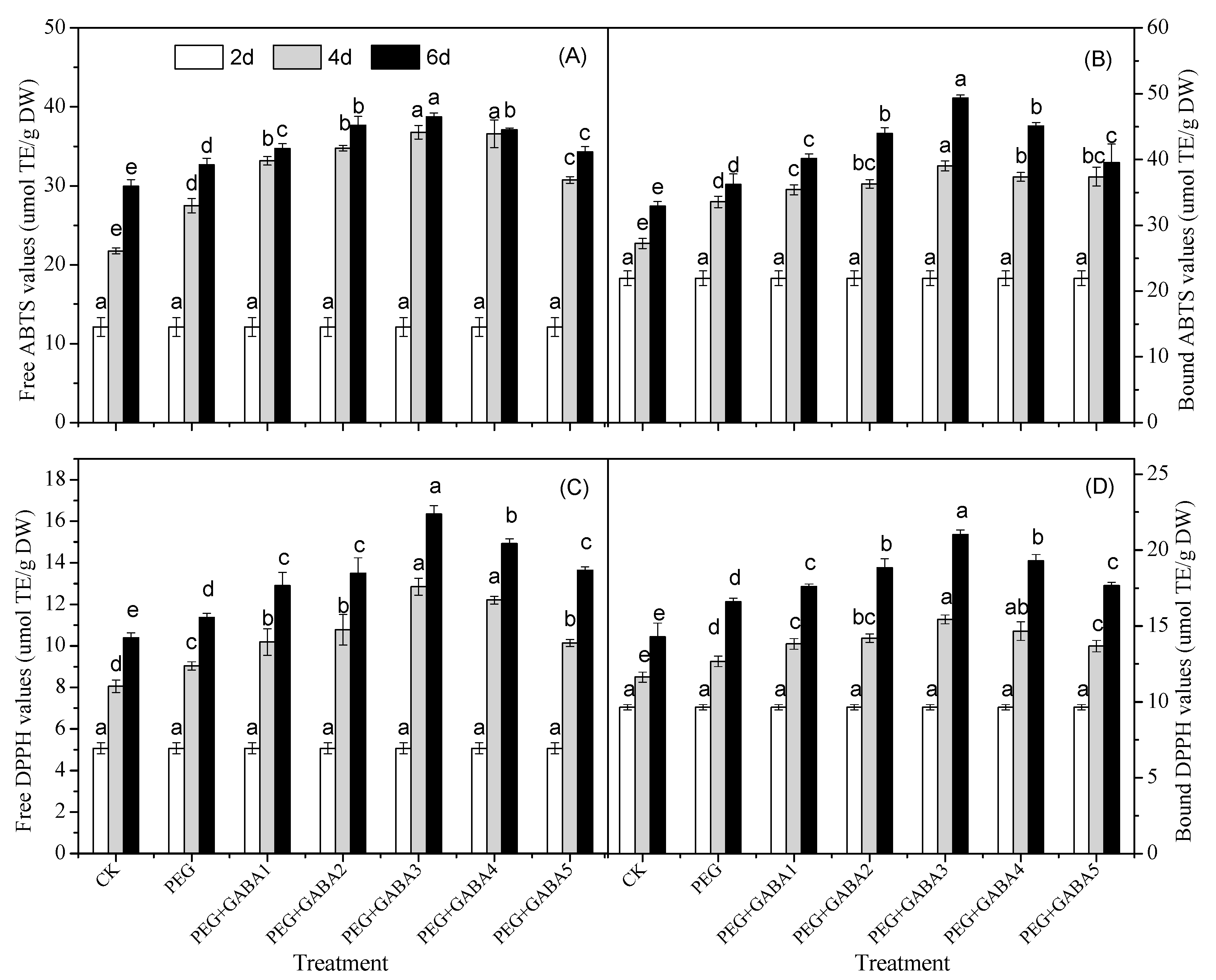
2.7. Effects of GABA on the Antioxidant Capacity of Wheat Seedlings under Drought Stress
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Material and Experimental Design
4.2. Measurement of Length and Weight
4.3. Determination of Malondialdehyde (MDA) Content and Electrolyte Leakage
4.4. Extraction of Phenolic Compounds
4.5. Determination of Total Phenolic Content
4.6. Determination of Free and Bound Phenolic Acid Content
4.7. Determination of Phenylpropanoid Metabolism-Related Enzymes Activity
4.8. Determination of Antioxidant Enzyme Activity
4.9. Determination of Antioxidant Capacity
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Márcia, C.; Irene, G.; Isaura, C.; Manuela, M.; Eduardo, R.; Carnide, V.; Ana Barros, A. Drought stress effect on polyphenolic content and antioxidant capacity of cowpea pods and seeds. J. Agron. Crop Sci. 2021, 207, 197–207. [Google Scholar]
- AL-Quraan, N.A.; Al-Ajlouni, Z.I.; Qawasma, N.F. Physiological and Biochemical Characterization of the GABA Shunt Pathway in Pea (Pisum sativum L.) Seedlings under Drought Stress. Horticulturae 2021, 7, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajlaoui, H.; Denden, M.; El, A.N. Differential responses of two maize (Zea mays L.) varieties to salt stress: Changes on polyphenols composition of foliage and oxidative damages. Ind. Crops Prod. 2009, 30, 144–151. [Google Scholar]
- Ghumman, A.; Singh, N.; Kaur, A. Chemical, nutritional and phenolic composition of wheatgrass and pulse shoots. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 52, 2191–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Sharma, S. Bioactive components and functional properties of biologically activated cereal grains: A bibliographic review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2015, 57, 3051–3071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, N.P.; Fatma, T.; Singhal, G.S. Development of antioxidative defense system of wheat seedlings in response to high light. Physiol. Plant. 2006, 95, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charoenthaikij, P.; Jangchud, K.; Jangchud, A.; Prinyawiwatkul, W.; Tungtrakul, P. Germination Conditions Affect Selected Quality of Composite Wheat-Germinated Brown Rice Flour and Bread formulations. J. Food Sci. 2010, 75, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawlik-Dziki, U.; Dziki, D.; Nowak, R.; Świeca, M.; Olech, M.; Pietrzak, W. Influence of sprouting and elicitation on phenolic acids profile and antioxidant activity of wheat seedlings. J. Cereal Sci. 2016, 70, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, P.; Weng, Y.; Ma, Y.; Gu, Z.; Yang, R. Comparison of phenolic profiles, antioxidant capacity and relevant enzyme activity of different Chinese wheat varieties during germination. Food Biosci. 2017, 20, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceccaroni, D.; Alfeo, V.; Bravi, E.; Sileoni, V.; Perretti, G.; Marconi, O. Effect of the time and temperature of germination on the phenolic compounds of Triticum aestivum, L. and Panicum miliaceum, L. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 127, 109396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crozier, A.; Jaganath, I.B.; Clifford, M.N. Phenols, Polyphenols and Tannins: An Overview; Blackwell Publishing Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Espadas, J.L.; Castaño, E.; Marina, M.L.; Rodríguez, L.C.; Plaza, M. Phenolic compounds increase their concentration in Carica papaya leaves under drought stress. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2019, 41, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zobayed, S.; Afreen, F.; Kozai, T. Phytochemical and physiological changes in the leaves of St. John’s wort plants under a water stress condition. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2007, 59, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swigonska, S.; Amarowicz, R.; Król, A.; Mostek, A.; Badowiec, A.; Weidner, S. Influence of abiotic stress during soybean germination followed by recovery on the phenolic compounds of radicles and their antioxidant capacity. Acta Soc. Bot. Pol. 2014, 83, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laddomada, B.; Blanco, A.; Mita, G.; D’Amico, L.; Singh, R.P.; Ammar, K.; Crossa, J.; Guzmán, C. Drought and heat stress impacts on phenolic acids accumulation in durum wheat cultivars. Foods 2021, 10, 2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Liu, S.; Yan, M. Synthesis of γ-Aminobutyric acid-modified chitooligosaccharide derivative and enhancing salt resistance of wheat seedlings. Molecules 2022, 27, 3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinnersley, A.M.; Turano, F.J. Gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA) and plant responses to Stress. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2000, 19, 479–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, M.R. Does GABA act as a signal in plants?: Hints from molecular studies. Plant Signal. Behav. 2007, 2, 408–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbar, O.H.A.; Elkelish, A.; Niedbała, G.; Farag, R.; Wojciechowski, T.; Mukherjee, S.; Abou-Hadid, A.F.; El-Hennawy, H.M.; El-Yazied, A.A.; El-Gawad, H.G.A.; et al. Protective effect of γ-aminobutyric acid against chilling stress during reproductive stage in tomato plants through modulation of sugar metabolism, chloroplast integrity, and antioxidative defense systems. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 663750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayakumari, K.; Puthur, J.T. γ-Aminobutyric acid (GABA) priming enhances the osmotic stress tolerance in Piper nigrum linn. plants subjected to PEG-induced stress. Plant Growth Regul. 2016, 78, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheteiwy, M.S.; Shao, H.; Qi, W.; Hamoud, Y.A.; Shaghaleh, H.; Khan, N.U.; Yang, R.; Tang, B. GABA-alleviated oxidative injury induced by salinity, osmotic stress and their combination by regulating cellular and molecular signals in rice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yu, J.; Peng, Y.; Huang, B. Metabolic pathways regulated by γ -aminobutyric acid (GABA) contributing to heat tolerance in creeping bentgrass (Agrostis stolonifera). Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, B.; Xie, H.; Li, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Nie, G.; Zhang, X.; Ma, X.; Huang, L.; Yan, Y.; et al. Exogenous application of GABA improves PEG-induced drought tolerance positively associated with GABA-shunt, polyamines, and proline metabolism in white clover. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekontso, F.N.; Duan, W.; Cisse, E.H.M.; Chen, T.; Xu, X. Alleviation of postharvest chilling injury of carambola fruit by γ-aminobutyric acid: Physiological, biochemical, and structural characterization. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 752583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, S.; Nazir, F.; Jain, K.; Khan, M.I.R. GABA and Potassium Modulates Defence Systems, Assimilation of Nitrogen and Carbon, and Yield Traits Under Salt Stress in Wheat. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Guo, S.; Yang, X.; Meng, Q.; Wei, X. Exogenous gamma-aminobutyric acid increases salt tolerance of wheat by improving photosynthesis and enhancing activities of antioxidant enzymes. Biol. Plant. 2016, 60, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, R.R.; Jahan, B.; Iqbal, N.; Khan, N.A.; AlAjmi, M.F.; Rehman, M.T.; Khan, M.I.R. GABA reverses salt-inhibited photosynthetic and growth responses through its influence on NO-mediated nitrogen-sulfur assimilation and antioxidant system in wheat. J. Biotechnol. 2021, 325, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Yu, D. Over-expression of the stress-induced OsWRKY45 enhances disease resistance and drought tolerance in Arabidopsis. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2009, 65, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Wang, P.; Wang, M.; Sun, M.; Gu, Z.; Yang, R. GABA mediates phenolic compounds accumulation and the antioxidant system enhancement in germinated hulless barley under NaCl stress. Food Chem. 2019, 270, 593–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Xie, C.; Wang, P.; Gu, Z.; Yang, R. GABA Regulates Phenolics Accumulation in Soybean Sprouts under NaCl Stress. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deikman, J.; Petracek, M.; Heard, J.E. Drought tolerance through biotechnology: Improving translation from the laboratory to farmers’ fields. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2012, 23, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Gawad, H.G.; Mukherjee, S.; Farag, R.; Abd Elbar, O.H.; Hikal, M.; Abou El-Yazied, A.; Abd Elhady, S.A.; Helal, N.; ElKelish, A.; El Nahhas, N.; et al. Exogenous γ -aminobutyric acid (GABA)-induced signaling events and field performance associated with mitigation of drought stress in Phaseolus vulgaris L. Plant Signal. Behav. 2020, 16, 1853384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caliskan, O.; Radusiene, J.; Temizel, K.E.; Staunis, Z.; Cirak, C.; Kurt, D.; Odabas, M.S. The effects of salt and drought stress on phenolic accumulation in greenhouse-grown Hypericum pruinatum. Ital. J. Agron. 2017, 12, 271–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hura, T.; Grzesiak, S.; Hura, K.; Thiemt, E.; Tokarz, K.; Wedzony, M. Physiological and biochemical tools useful in drought-tolerance detection in genotypes of winter triticale: Accumulation of ferulic acid correlates with drought tolerance. Ann. Bot. 2007, 100, 767–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarker, U.; Oba, S. Drought stress enhances nutritional and bioactive compounds, phenolic acids and antioxidant capacity of Amaranthus leafy vegetable. BMC Plant Biol. 2018, 18, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Zhu, M.; Luo, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, R.; Kou, M.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Meng, X.; Zheng, Y.; et al. A sweet potato cinnamate 4-hydroxylase gene, IbC4H, increases phenolics content and enhances drought tolerance in tobacco. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2017, 39, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.; Kumar, S.; Rani, A.; Gulati, A.; Ahuja, P.S. Phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (PAL) and cinnamate 4-hydroxylase (C4H) and catechins (flavan-3-ols) accumulation in tea. Funct. Integr. Genom. 2009, 9, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.M.; Alabdallah, N.M.; Alharbi, B.M.; Waseem, M.; Yao, G.; Liu, X.; El-Gawad, H.G.A.; El-Yazied, A.A.; Ibrahim, M.F.M.; Jahan, M.S.; et al. GABA: A Key Player in Drought Stress Resistance in Plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirzadah, T.B.; Malik, B.; Tahir, I.; Rehman, R.U.; Hakeem, K.R.; Alharby, H.F. Aluminium stress modulates the osmolytes and enzyme defense system in Fagopyrum species. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 144, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razik, E.S.A.; Alharbi, B.M.; Pirzadah, T.B.; Alnusairi, G.S.H.; Soliman, M.H.; Hakeem, K.R. γ-Aminobutyricacid (GABA) mitigates drought and heat stress in sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.) by regulating its physiological, biochemical and molecular pathways. Physiol. Plant. 2021, 172, 505–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, P.V. Phenolic Compounds of Cereals and Their Antioxidant Capacity. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 2016, 56, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodges, D.M.; DeLong, J.M.; Forney, C.F.; Prange, R.K. Improving the thiobarbituric acid-reactive-substances assay for estimating lipid peroxidation in plant tissues containing anthocyanin and other interfering compounds. Planta 1999, 207, 604–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assis, J.S.; Maldonado, R.; Muñoz, T.; Escribano, M.A.I.; Merodio, C. Effect of high carbon dioxide concentration on PAL activity and phenolic contents in ripening cherimoya fruit. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2001, 23, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamb, C.J.; Rubery, P.H. A spectrophotometric assay for trans-cinnamic acid 4-hydroxylase activity. Anal. Biochem. 1975, 68, 554–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Li, J.; Jin, P.; Li, X.; Wang, L.; Zheng, Y. The effect of temperature on phenolic content in wounded carrots. Food Chem. 2017, 215, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, Q.; Ma, Y.; Huang, X.; Song, L.; Li, N.; Qiao, M.; Li, T.; Hai, D.; Cheng, Y. GABA Application Enhances Drought Stress Tolerance in Wheat Seedlings (Triticum aestivum L.). Plants 2023, 12, 2495. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12132495
Zhao Q, Ma Y, Huang X, Song L, Li N, Qiao M, Li T, Hai D, Cheng Y. GABA Application Enhances Drought Stress Tolerance in Wheat Seedlings (Triticum aestivum L.). Plants. 2023; 12(13):2495. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12132495
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Qiuyan, Yan Ma, Xianqing Huang, Lianjun Song, Ning Li, Mingwu Qiao, Tiange Li, Dan Hai, and Yongxia Cheng. 2023. "GABA Application Enhances Drought Stress Tolerance in Wheat Seedlings (Triticum aestivum L.)" Plants 12, no. 13: 2495. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12132495
APA StyleZhao, Q., Ma, Y., Huang, X., Song, L., Li, N., Qiao, M., Li, T., Hai, D., & Cheng, Y. (2023). GABA Application Enhances Drought Stress Tolerance in Wheat Seedlings (Triticum aestivum L.). Plants, 12(13), 2495. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12132495





