Orphan Genes in Crop Improvement: Enhancing Potato Tuber Protein without Impacting Yield
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. No Significant Difference Was Observed in Tuber Yield, Number, and Appearance in AtQQS-E and StNF-YC4-OE Potato Plants vs. Wild-Type Control
2.2. AtQQS and StNF-YC4 Were Expressed and Overexpressed in Transgenic Potato Tubers
2.3. StNF-YC4 Expression Is Universal in Different Organs of the Potato Plant
2.4. Ectopic Expression of AtQQS and Overexpression of StNF-YC4 in Potatoes Reduces Starch Accumulation in the Tubers
2.5. AtQQS-E and StNF-YC4-OE Potato Plants Have Higher Protein Accumulation in the Tubers
2.6. Sequence Similarity to Other NF-YC4 Homologs Shows Multiple Conserved Regions among Them
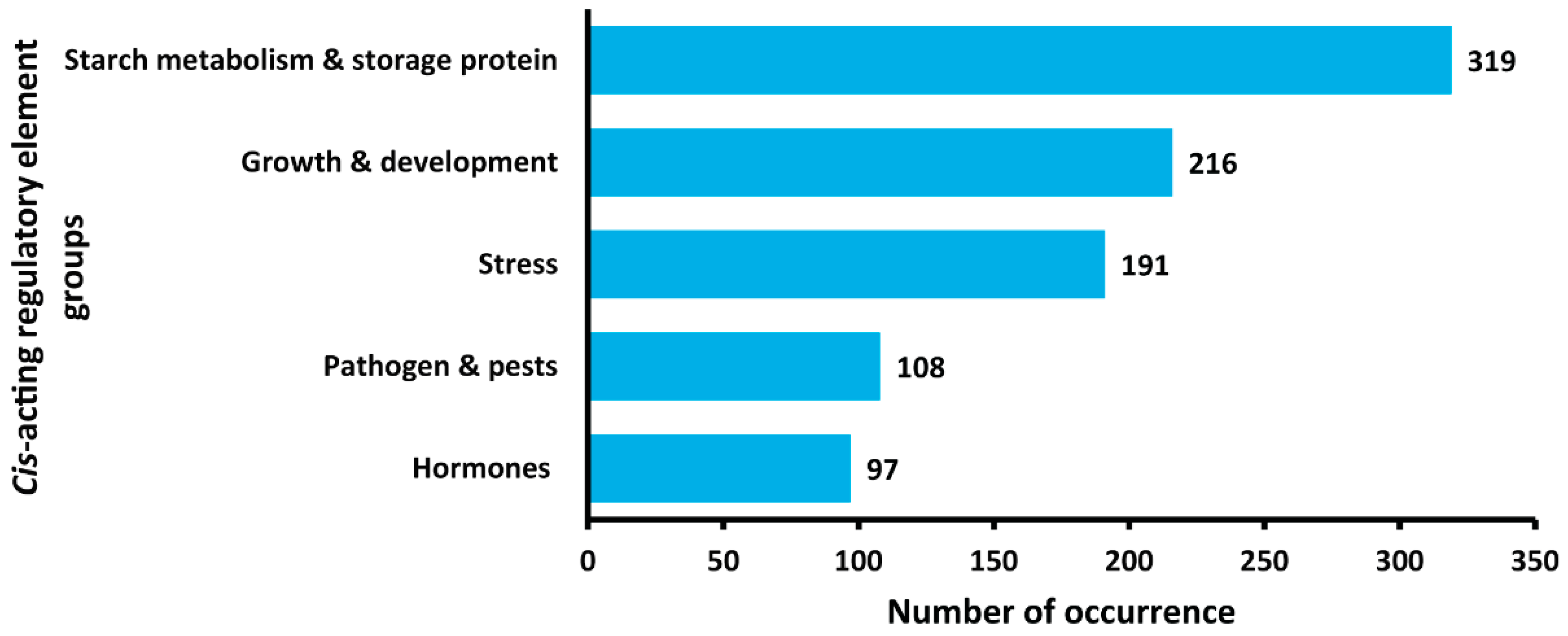
2.7. Promoter Region Analysis Demonstrates the Potential Functional Roles of StNF-YC4
2.8. Analysis of Protein–Protein Interaction Prediction Indicates StNF-YC4’s Possible Role in Stress Resistance and Flowering Time
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Plant Material
5.2. Growth Conditions
5.3. Starch Quantification
5.4. Protein Quantification and SDS-PAGE
5.5. RT-qPCR
5.6. Cis-Acting DNA Element Analysis of the Upstream Region of StNF-YC4
5.7. Multiple Sequence Alignment
5.8. Expression Data
5.9. Protein-Protein Interaction
5.10. Accession Numbers
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ezekiel, R.; Singh, N.; Sharma, S.; Kaur, A. Beneficial phytochemicals in potato—A review. Food Res. Int. 2013, 50, 487–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Harsselaar, J.K.; Lorenz, J.; Senning, M.; Sonnewald, U.; Sonnewald, S. Genome-wide analysis of starch metabolism genes in potato (Solanum tuberosum L.). BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, M. Chemistry, biochemistry, and dietary role of potato polyphenols. A review. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1997, 45, 1523–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachman, J.; Hamouz, K.; Dvorák, P.; Orsák, M. The effect of selected factors on the content of protein and nitrates in potato tubers. Plant Soil Environ. 2005, 51, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorissen, S.H.M.; Crombag, J.J.R.; Senden, J.M.G.; Waterval, W.A.H.; Bierau, J.; Verdijk, L.B.; van Loon, L.J.C. Protein content and amino acid composition of commercially available plant-based protein isolates. Amino Acids 2018, 50, 1685–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabaté, J.; Soret, S. Sustainability of plant-based diets: Back to the future. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 100, 476S–482S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Fung, T.T.; Hu, F.B.; Willett, W.C.; Longo, V.D.; Chan, A.T.; Giovannucci, E.L. Association of animal and plant protein intake with all-cause and cause-specific mortality. JAMA Intern. Med. 2016, 176, 1453–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sá, A.G.A.; Moreno, Y.M.F.; Carciofi, B.A.M. Plant proteins as high-quality nutritional source for human diet. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 97, 170–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Joshi, S.; Schlueter, R.; Cooke, J.; Brown-Tortorici, A.; Donnelly, M.; Schulman, S.; Lau, W.-L.; Rhee, C.M.; Streja, E.; et al. Plant-dominant low-protein diet for conservative management of chronic kidney disease. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahleova, H.; Fleeman, R.; Hlozkova, A.; Holubkov, R.; Barnard, N.D. A plant-based diet in overweight individuals in a 16-week randomized clinical trial: Metabolic benefits of plant protein. Nutr. Diabetes 2018, 8, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bártová, V.; Bárta, J. Chemical composition and nutritional value of protein concentrates isolated from potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) fruit juice by precipitation with ethanol or ferric chloride. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 9028–9034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arendsee, Z.W.; Li, L.; Wurtele, E.S. Coming of age: Orphan genes in plants. Trends Plant Sci. 2014, 19, 698–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Foster, C.M.; Gan, Q.; Nettleton, D.; James, M.G.; Myers, A.M.; Wurtele, E.S. Identification of the novel protein QQS as a component of the starch metabolic network in Arabidopsis leaves. Plant J. 2009, 58, 485–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Zheng, W.; Zhu, Y.; Ye, H.; Tang, B.; Arendsee, Z.W.; Jones, D.; Li, R.; Ortiz, D.; Zhao, X.; et al. QQS orphan gene regulates carbon and nitrogen partitioning across species via NF-YC interactions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 14734–14739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wurtele, E.S. The QQS orphan gene of Arabidopsis modulates carbon and nitrogen allocation in soybean. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2015, 13, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Conner, S.; Zheng, W.; Qi, M.; Kandel, Y.; Fuller, R.; Whitham, S.A.; Li, L. GmNF-YC4-2 increases protein, exhibits broad disease resistance and expedites maturity in soybean. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanvir, R.; Ping, W.; Sun, J.; Cain, M.; Li, X.; Li, L. AtQQS orphan gene and NtNF-YC4 boost protein accumulation and pest resistance in tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum). Plant Sci. 2022, 317, 111198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Conner, S.; Neudorf, A.; Zheng, W.; Qi, M.; Zhao, X.; Du, C.; Nettleton, D.; Li, L. From Arabidopsis to crops: The Arabidopsis QQS orphan gene modulates nitrogen allocation across species. In Engineering Nitrogen Utilization in Crop Plants; Shrawat, A., Zayed, A., Lightfoot, D.A., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 95–117. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, M.; Zheng, W.; Zhao, X.; Hohenstein, J.D.; Kandel, Y.; O’Conner, S.; Wang, Y.; Du, C.; Nettleton, D.; MacIntosh, G.C.; et al. QQS orphan gene and its interactor NF-YC4 reduce susceptibility to pathogens and pests. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2019, 17, 252–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenkel, S.; Turck, F.; Singer, K.; Gissot, L.; Le Gourrierec, J.; Samach, A.; Coupland, G. CONSTANS and the CCAAT box binding complex share a functionally important domain and interact to regulate flowering of Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2006, 18, 2971–2984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, W.-Z.; Song, L.-F.; Zou, J.-J.; Su, Z.; Wu, W.-H. Transcriptome analyses show changes in gene expression to accompany pollen germination and tube growth in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2008, 148, 1201–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumimoto, R.W.; Zhang, Y.; Siefers, N.; Holt III, B.F. NF–YC3, NF–YC4 and NF–YC9 are required for CONSTANS-mediated, photoperiod-dependent flowering in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 2010, 63, 379–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myers, Z.A.; Kumimoto, R.W.; Siriwardana, C.L.; Gayler, K.K.; Risinger, J.R.; Pezzetta, D.; Holt III, B.F. NUCLEAR FACTOR Y, subunit C (NF-YC) transcription factors are positive regulators of photomorphogenesis in Arabidopsis thaliana. PLoS Genet. 2016, 12, e1006333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Wu, D.; Kong, F.; Lin, K.; Zhang, H.; Li, G. The Arabidopsis thaliana Nuclear Factor Y Transcription Factors. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 7, 2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, K.; Susila, H.; Nasim, Z.; Jung, J.-Y.; Ahn, J.H. Arabidopsis ABF3 and ABF4 transcription factors act with the NF-YC complex to regulate SOC1 expression and mediate drought-accelerated flowering. Mol. Plant 2019, 12, 489–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Tang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Cai, J.; Liu, H.; Zhang, C.; Liu, X.; Hou, X. Arabidopsis NF-YCs play dual roles in repressing brassinosteroid biosynthesis and signaling during light-regulated hypocotyl elongation. Plant Cell 2021, 33, 2360–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, M.; Zhan, Z.; Li, H.; Dong, X.; Cheng, F.; Piao, Z. Brassica rapa orphan genes largely affect soluble sugar metabolism. Hort. Res. 2020, 7, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Liu, H.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Xu, C.; Long, M.; Wang, S. A rice gene of de novo origin negatively regulates pathogen-induced defense response. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e4603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luhua, S.; Ciftci-Yilmaz, S.; Harper, J.; Cushman, J.; Mittler, R. Enhanced tolerance to oxidative stress in transgenic Arabidopsis plants expressing proteins of unknown function. Plant Physiol. 2008, 148, 280–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, M.A.; Silverstein, K.A.T.; Cannon, S.B.; VandenBosch, K.A. Computational identification and characterization of novel genes from legumes. Plant Physiol. 2004, 135, 1179–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Wu, X.; Hu, Y.; Muñoz-Amatriaín, M.; Luo, J.; Zhou, W.; Wang, B.; Wang, Y.; Wu, X.; Huang, L.; et al. Orphan genes are involved in drought adaptations and ecoclimatic-oriented selections in domesticated cowpea. J. Exp. Bot. 2019, 70, 3101–3110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, N.; Chen, W.; Zheng, Y.; Hasegawa, D.K.; Ling, K.S.; Fei, Z.; Wintermantel, W.M. Transcriptome analysis of the whitefly, Bemisia tabaci MEAM1 during feeding on tomato infected with the crinivirus, Tomato chlorosis virus, identifies a temporal shift in gene expression and differential regulation of novel orphan genes. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perochon, A.; Kahla, A.; Vranić, M.; Jia, J.; Malla, K.B.; Craze, M.; Wallington, E.; Doohan, F.M. A wheat NAC interacts with an orphan protein and enhances resistance to Fusarium head blight disease. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2019, 17, 1892–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhandary, P.; Seetharam, A.S.; Arendsee, Z.W.; Hur, M.; Wurtele, E.S. Raising orphans from a metadata morass: A researcher’s guide to re-use of public’omics data. Plant Sci. 2018, 267, 32–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perochon, A.; Jianguang, J.; Kahla, A.; Arunachalam, C.; Scofield, S.R.; Bowden, S.; Wallington, E.; Doohan, F.M. TaFROG encodes a Pooideae orphan protein that interacts with SnRK1 and enhances resistance to the mycotoxigenic fungus Fusarium graminearum. Plant Physiol. 2015, 169, 2895–2906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, X.-M.; Pu, X.-J.; Zhou, S.-Z.; Li, P.; Luo, T.; Chen, Z.-X.; Chen, S.-L.; Liu, L. Orphan gene PpARDT positively involved in drought tolerance potentially by enhancing ABA response in Physcomitrium (Physcomitrella) patens. Plant Sci. 2022, 319, 111222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winter, D.; Vinegar, B.; Nahal, H.; Ammar, R.; Wilson, G.V.; Provart, N.J. An “Electronic Fluorescent Pictograph” browser for exploring and analyzing large-scale biological data sets. PLoS ONE 2007, 2, e718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massa, A.N.; Childs, K.L.; Lin, H.; Bryan, G.J.; Giuliano, G.; Buell, C.R. The transcriptome of the reference potato genome Solanum tuberosum Group Phureja clone DM1-3 516R44. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e26801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Pan, S.; Cheng, S.; Zhang, B.; Mu, D.; Ni, P.; Zhang, G.; Yang, S.; Li, R.; Wang, J.; et al. Genome sequence and analysis of the tuber crop potato. Nature 2011, 475, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loppes, R.; Radoux, M.; Ohresser, M.C.P.; Matagne, R.F. Transcriptional regulation of the Nia1 gene encoding nitrate reductase in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii: Effects of various environmental factors on the expression of a reporter gene under the control of the Nia1 promoter. Plant Mol. Biol. 1999, 41, 701–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Outchkourov, N.S.; Peters, J.; De Jong, J.; Rademakers, W.; Jongsma, M.A. The promoter–terminator of chrysanthemum rbcS1 directs very high expression levels in plants. Planta 2003, 216, 1003–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, M.-J.; Shih, M.-C. Interaction of a GATA factor with cis-acting elements involved in light regulation of nuclear genes encoding chloroplast glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase in Arabidopsis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 300, 555–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winicov, I.I.; Bastola, D.R. Transgenic overexpression of the transcription factor Alfin1 enhances expression of the endogenous MsPRP2 gene in Alfalfa and improves salinity tolerance of the plants. Plant Physiol. 1999, 120, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, B.; Xu, Y.; Ng, K.-H.; Ito, T. A timing mechanism for stem cell maintenance and differentiation in the Arabidopsis floral meristem. Genes Dev. 2009, 23, 1791–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manimaran, P.; Reddy, S.V.; Moin, M.; Reddy, M.R.; Yugandhar, P.; Mohanraj, S.S.; Balachandran, S.M.; Kirti, P.B. Activation-tagging in indica rice identifies a novel transcription factor subunit, NF-YC13 associated with salt tolerance. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Ma, C.; Xu, Y.; Wang, T.; Chen, Y.; Lü, J.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, C.-Z.; Hong, B.; Gao, J. Control of chrysanthemum flowering through integration with an aging pathway. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madeira, F.; Park, Y.M.; Lee, J.; Buso, N.; Gur, T.; Madhusoodanan, N.; Basutkar, P.; Tivey, A.R.N.; Potter, S.C.; Finn, R.D.; et al. The EMBL-EBI search and sequence analysis tools APIs in 2019. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W636–W641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higo, K.; Ugawa, Y.; Iwamoto, M.; Korenaga, T. Plant cis-acting regulatory DNA elements (PLACE) database: 1999. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999, 27, 297–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lescot, M.; Déhais, P.; Thijs, G.; Marchal, K.; Moreau, Y.; Van de Peer, Y.; Rouzé, P.; Rombauts, S. PlantCARE, a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 325–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, J.S.; Kwon, D.H.; Song, J.T.; Seo, H.S. A mutation in the pPLA-IIα gene encoding PATATIN-RELATED PHOSPHOLIPASE a causes late flowering in Arabidopsis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2021, 582, 16–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-W.; Han, C.-H.; Lee, M.-H.; Hsu, F.-L.; Hou, W.-C. Patatin, the Tuber Storage Protein of Potato (Solanum tuberosum L.), Exhibits Antioxidant Activity in Vitro. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 4389–4393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, F.-H.; Zhang, L.-P.; Cheng, F.; Yu, D.-M.; Hu, J.-Y. Accession-specific flowering time variation in response to nitrate fluctuation in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Divers. 2021, 43, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, X.; Zeng, X.; Hu, H.; Chen, L.; Zhang, F.; Liu, R.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, X.; Wang, C.; Wu, Z.; et al. Structural insights into the multivalent binding of the Arabidopsis FLOWERING LOCUS T promoter by the CO–NF–Y master transcription factor complex. Plant Cell 2021, 33, 1182–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuanyuan, G.; Lian, Q.; Jia, R.; Du, M.; Kang, L.; Pu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Qi, J.; Zhao, J. Genome-wide screening and identification of Nuclear Factor-Y family genes and exploration their function on regulating abiotic and biotic stress in potato (Solanum tuberosum). Gene 2021, 812, 146089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honeycutt, C.W. Crop rotation impacts on potato protein. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 1998, 52, 279–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartova, V.; Barta, J.; DiviŠ, J.; ŠVajner, J.; Peterka, J. Crude protein content in tubers of starch processing potato cultivars in dependence on different agro-ecological conditions. J. Cent. Eur. Agric. 2009, 10, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Zhang, T.; Jiang, W.; Li, P.; Shi, P.; Xu, G.; Cheng, S.; Cheng, Y.; Fan, Z.; Wang, X. Effects of irrigation and fertilization on different potato varieties growth, yield and resources use efficiency in the Northwest China. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 261, 107351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranowska, A.; Mystkowska, I.; Zarzecka, K.; Szczygielska, E. Impact of growth biostimulators and herbicide on the content of major protein in edible potato tubers. J. Ecol. Eng. 2019, 20, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ávila-Valdés, A.; Quinet, M.; Lutts, S.; Martínez, J.P.; Lizana, X.C. Tuber yield and quality responses of potato to moderate temperature increase during Tuber bulking under two water availability scenarios. Field Crops Res. 2020, 251, 107786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forsyth, A.; Weeks, T.; Richael, C.; Duan, H. Transcription Activator-Like Effector Nucleases (TALEN)-mediated targeted DNA insertion in potato plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butler, N.M.; Baltes, N.J.; Voytas, D.F.; Douches, D.S. Geminivirus-mediated genome editing in potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) using sequence-specific nucleases. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novy, R.G.; Whitworth, J.L.; Stark, J.C.; Love, S.L.; Corsini, D.L.; Pavek, J.J.; Vales, M.I.; James, S.R.; Hane, D.C.; Shock, C.C.; et al. Clearwater russet: A dual-purpose potato cultivar with cold sweetening resistance, high protein content, and low incidence of external defects and sugar ends. Am. J. Potato Res. 2010, 87, 458–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowry, O.H.; Rosebrough, N.J.; Farr, A.L.; Randall, R. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 1951, 193, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krohn, R.I. The colorimetric detection and quantitation of total protein. Curr. Protoc. Cell Biol. 2011, 52, A-3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicot, N.; Hausman, J.-F.; Hoffmann, L.; Evers, D. Housekeeping gene selection for real-time RT-PCR normalization in potato during biotic and abiotic stress. J. Exp. Bot. 2005, 56, 2907–2914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solovyev, V.V.; Shahmuradov, I.A.; Salamov, A.A. Identification of promoter regions and regulatory sites. In Computational Biology of Transcription Factor Binding; Ladunga, I., Ed.; Springer: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2010; pp. 57–83. [Google Scholar]
- Shahmuradov, I.A.; Solovyev, V.V. Nsite, NsiteH and NsiteM computer tools for studying transcription regulatory elements. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 3544–3545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Gable, A.L.; Nastou, K.C.; Lyon, D.; Kirsch, R.; Pyysalo, S.; Doncheva, N.T.; Legeay, M.; Fang, T.; Bork, P.; et al. The STRING database in 2021: Customizable protein-protein networks, and functional characterization of user-uploaded gene/measurement sets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D605–D612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tanvir, R.; Wang, L.; Zhang, A.; Li, L. Orphan Genes in Crop Improvement: Enhancing Potato Tuber Protein without Impacting Yield. Plants 2022, 11, 3076. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11223076
Tanvir R, Wang L, Zhang A, Li L. Orphan Genes in Crop Improvement: Enhancing Potato Tuber Protein without Impacting Yield. Plants. 2022; 11(22):3076. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11223076
Chicago/Turabian StyleTanvir, Rezwan, Lei Wang, Amy Zhang, and Ling Li. 2022. "Orphan Genes in Crop Improvement: Enhancing Potato Tuber Protein without Impacting Yield" Plants 11, no. 22: 3076. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11223076
APA StyleTanvir, R., Wang, L., Zhang, A., & Li, L. (2022). Orphan Genes in Crop Improvement: Enhancing Potato Tuber Protein without Impacting Yield. Plants, 11(22), 3076. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11223076