Characterization of Forage Quality, Phenolic Profiles, and Antioxidant Activity in Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Nutritive Forage Quality of Alfalfa
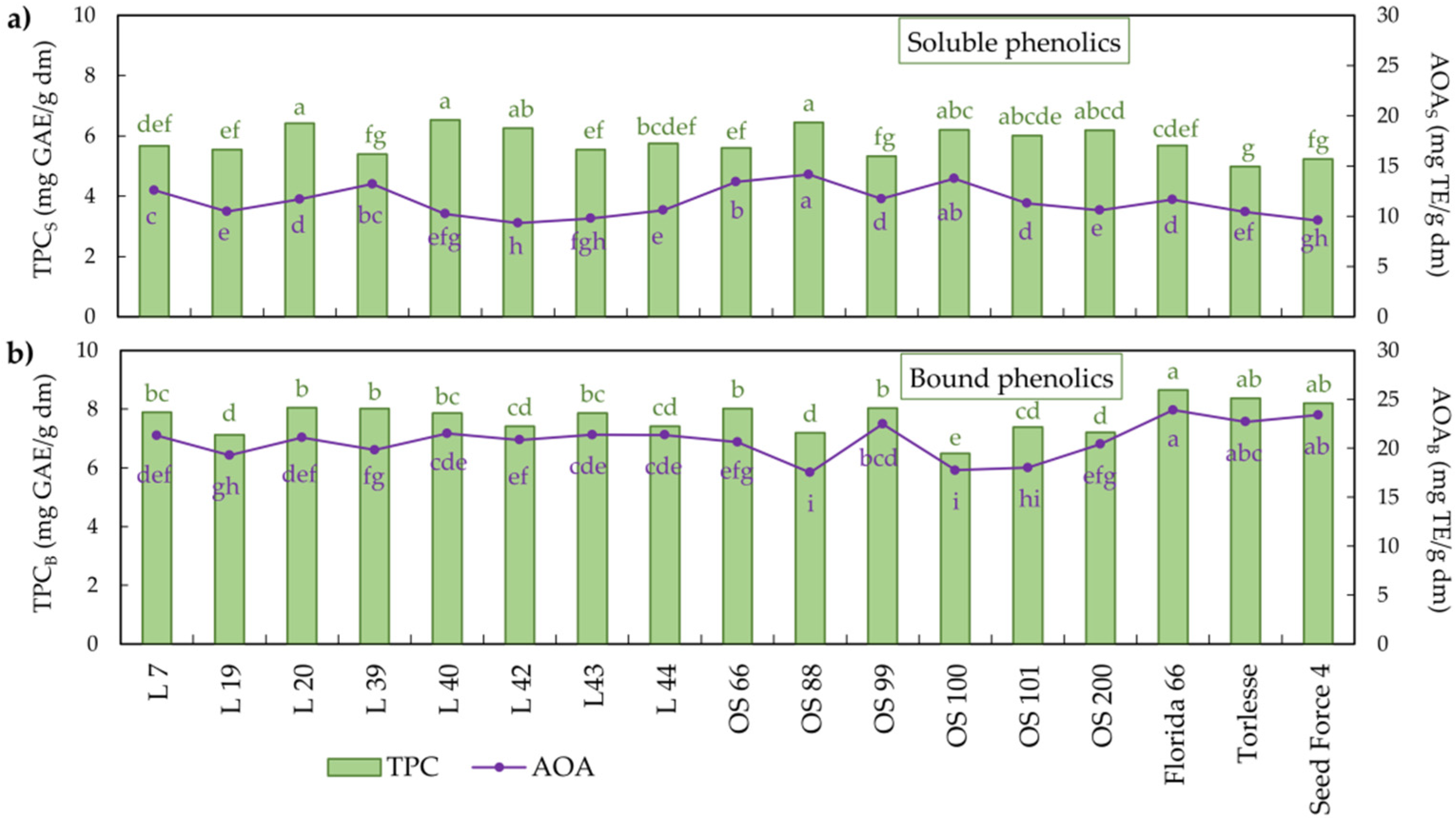
2.2. Total Phenolic Content (TPC) and Antioxidant Activity (AOA) of Alfalfa
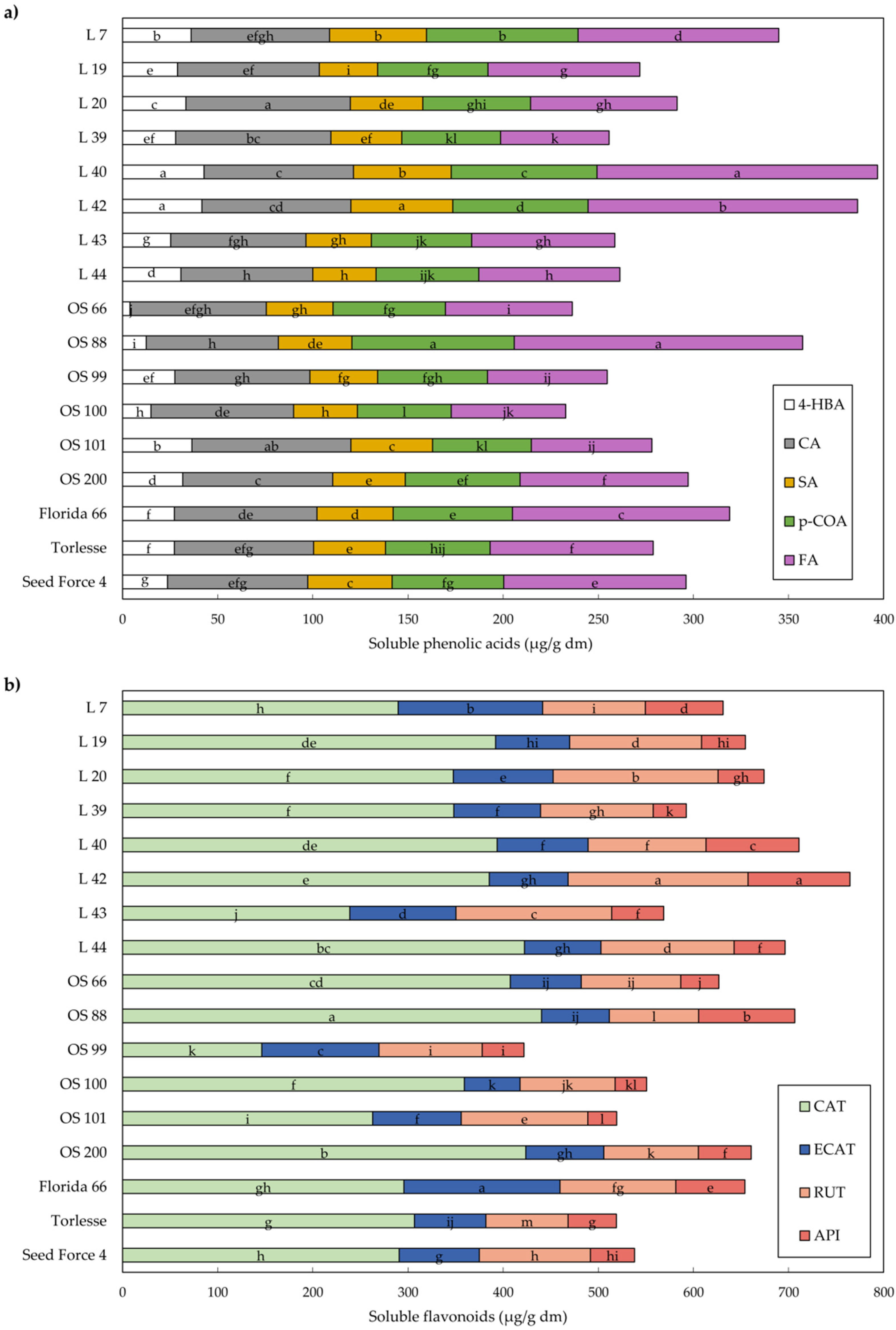
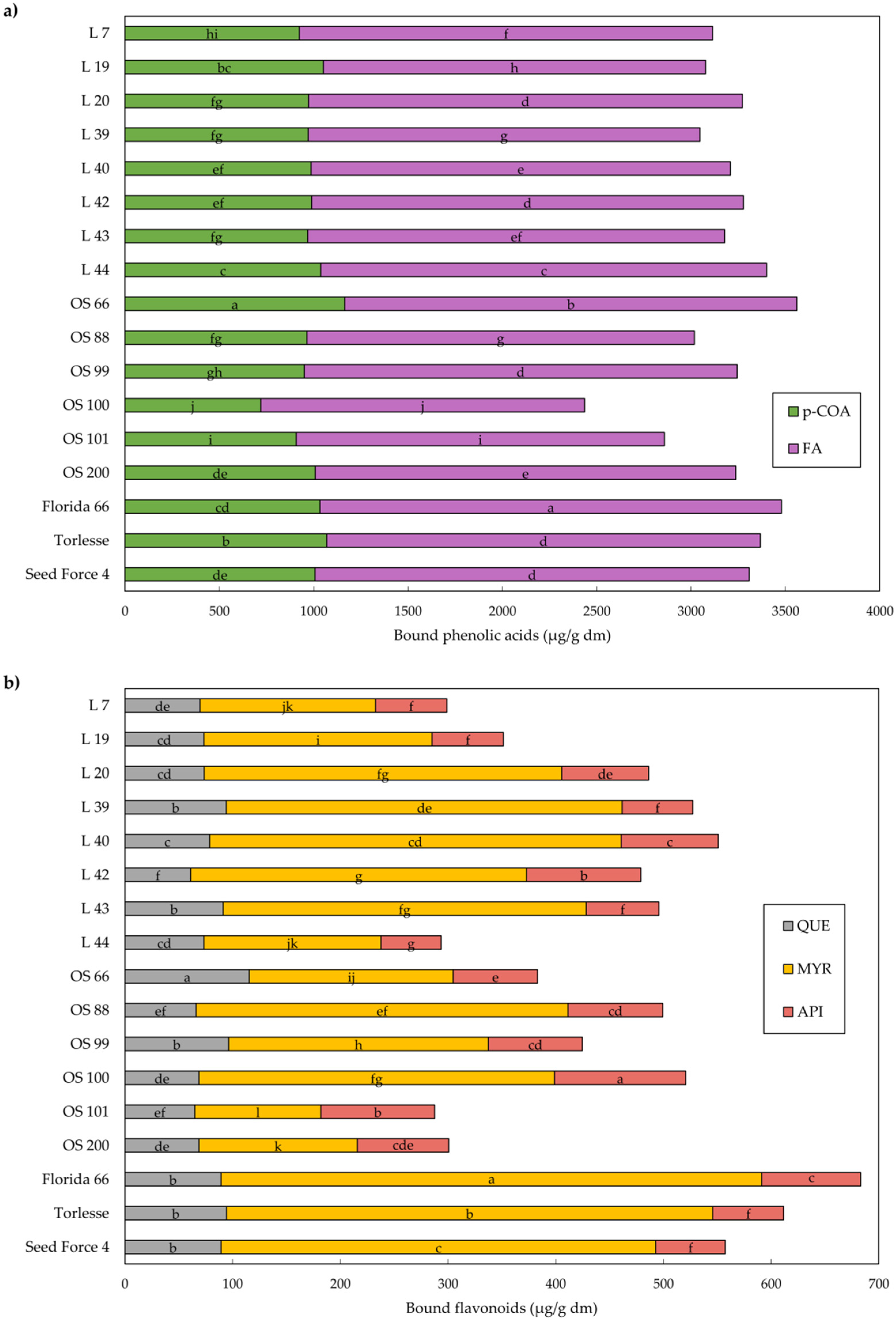
2.3. Phenolic Compounds in Alfalfa
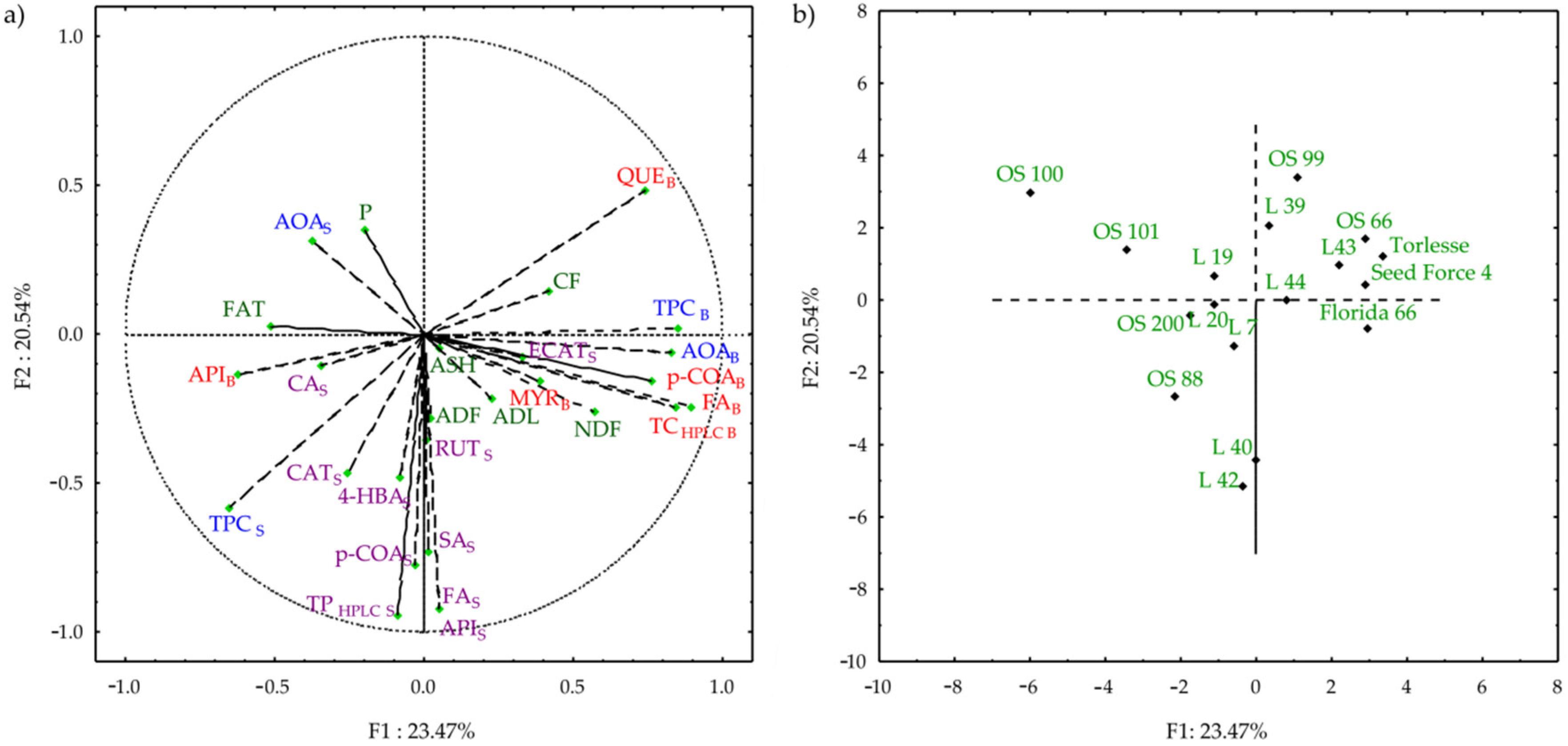
2.4. Principal Component Analysis
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Alfalfa Cultivation and Sampling
3.2. Chemicals
3.3. Nutritive Forage Analysis
3.4. Extraction of Soluble and Bound Phenolics
3.5. Total Phenolic Content (TPC)
3.6. Antioxidant Activity (AOA)
3.7. Determination and Quantitation of Phenolics by HPLC
3.8. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hrbáčková, M.; Dvořák, P.; Takáč, T.; Tichá, M.; Luptovčiak, I.; Šamajová, O.; Ovečka, M.; Šamaj, J. Biotechnological perspectives of omics and genetic engineering methods in alfalfa. Front. Plant Sci. 2000, 11, 592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fahad, S.; Bajwa, A.; Nazir, U.; Anjum, S.; Farooq, A.; Zohaib, A.; Sadia, S.; Nasim, W.; Adkins, S.; Saud, S.; et al. Crop production under drought and heat stress: Plant responses and management options. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avci, M.; Hatipoglu, R.; Çinar, S.; Kiliçalp, N. Assessment of yield and quality characteristics of alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) cultivars with different fall dormancy rating. Legume Res. 2018, 41, 369–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marković, J.; Petrović, M.; Terzić, D.; Vasić, T.; Kostić, I.; Štrbanović, R.; Grubić, G. Protein fractions as influenced by cultivars, stage of maturity and cutting dates in alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). Legume Res. 2019, 45, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucak, M.; Čupić, T.; Horvat, D.; Popović, S.; Krizmanić, G.; Ravlić, M. Variation of phytoestrogen content and major agronomic traits in alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) populations. Agronomy 2020, 10, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, D.O.; Hansen, H.H.; Hallin, O.; Nussio, L.G.; Nadeau, E. A two-year comparison on nutritive value and yield of eight lucerne cultivars and one red clover cultivar. Grass Forage Sci. 2020, 75, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabessa, T.; Bekele, K. Evaluation of alfalfa (Medicago Sativa) cultivars at highland and midland of Guji zone of Oromia. Biochem. Molec. Biol. 2021, 6, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, K.P.; Tayade, R.; Asekova, S.; Song, J.T.; Shannon, J.G.; Lee, J.D. Harnessing the potential of forage legumes, alfalfa, soybean, and cowpea for sustainable agriculture and global food security. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bora, K.S.; Sharma, A. Phytochemical and pharmacological potential of Medicago sativa: A review. Pharmac. Biol. 2011, 49, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gholami, A.; De Geyter, N.; Pollier, J.; Goormachti, S.; Goossens, A. Natural product biosynthesis in Medicago species. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2014, 31, 356–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Snafi, A.E.; Khadem, H.S.; Al-Saedy, H.A.; Alqahtani, A.M.; El-Saber, G. A review on Medicago sativa: A potential medicinal plant. Int. J. Biol. Pharm. Sci. Arch. 2021, 1, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafińska, K.; Pomastowski, P.; Wrona, O.; Górecki, R.; Buszewski, B. Medicago sativa as a source of secondary metabolites for agriculture and pharmaceutical industry. Phytochem. Lett. 2017, 20, 520–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisht, N.; Gupta, A.; Awasthi, P.; Goel, A.; Chandran, D.; Sharma, N.; Singh, N. Development of a rapid LC-MS/MS method for the simultaneous quantification of various flavonoids and phytohormones extracted from Medicago truncatula leaves. J. Liq. Chromat. Relat. Tech. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucak, M.; Ravlić, M.; Horvat, D.; Čupić, T. Improvement of Forage Nutritive Quality of Alfalfa and Red Clover through Plant Breeding. Agronomy 2021, 11, 2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igual, M.; Chis, M.S.; Socaci, S.A.; Vodnar, D.C.; Ranga, F.; Martínez-Monzó, J.; García-Segovia, P. Effect of Medicago sativa addition on physicochemical, nutritional and functional characteristics of corn extrudates. Foods 2021, 10, 928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajkacz, S.; Baranowska, I.; Buszewski, B.; Kowalski, B.; Ligor, M. Determination of flavonoids and phenolic acids in plant materials using SLE-SPE-UHPLC-MS/MS method. Food Anal. Methods 2018, 11, 3563–3575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, Y.; Ponnampalam, E.N.; Suleria, H.A.R.; Cottrell, J.J.; Dunshea, F.R. LC-ESI/QTOF-MS profiling of chicory and lucerne polyphenols and their antioxidant activities. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soto-Zarazua, M.G.; Bah, M.; Silvia Gomes Costa, A.S.; Rodrigues, F.; Botelho Pimentel, F.B.; Rojas-Molina, I.; Rojas, A.; Prior Pinto Oliveira, M.B. Nutraceutical potential of new alfalfa (Medicago sativa) ingredients for beverage preparations. J. Med. Food 2017, 20, 1039–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martens, D.A. Identification of phenolic acid composition of alkali-extracted plants and soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2002, 66, 1240–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Ma, S.; Wang, M.; Feng, X.-Y. Characterization of free, conjugated, and bound phenolic acids in seven commonly consumed vegetables. Molecules 2017, 22, 1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Li, W.; Deng, Z.; Li, H.; Zhang, B. The Composition and antioxidant activity of bound phenolics in three legumes, and their metabolism and bioaccessibility of gastrointestinal tract. Foods 2020, 7, 1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girish, T.K.; Padmaraju Vasudevaraju, P.; Rao, U.J.S. Protection of DNA and erythrocytes from free radical induced oxidative damage by black gram (Vigna mungo L.) husk extract. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2012, 50, 1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karayilanli, E.; Ayhan, V. Investigation of feed value of alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) harvested at different maturity stages. Legume Res. 2016, 39, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jungers, J.; Cherney, J.; Martinson, K.; Jaqueth, A.; Sheaffer, C. Forage nutritive value of modern alfalfa cultivars. Crop. Forage Turfgrass Manag. 2020, 6, 20076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grev, A.M.; Wells, M.S.; Samac, D.A.; Martinson, K.L.; Sheaffer, C.C. Forage accumulation and nutritive value of reduced lignin and reference alfalfa cultivars. Agron. J. 2017, 109, 2749–2761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Min, D.; McDonald, I. Effects of harvest intervals and seeding rates on dry matter yield and nutritive value of alfalfa cultivars. J. Anim. Sci. Technol. 2021, 63, 1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohweder, D.A.; Barnes, R.F.; Jorgensen, N. Proposed hay grading standards based on laboratory analyses for evaluating quality. J. Anim. Sci. 1978, 47, 747–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholtz, G.D.J.; Van der Merwe, H.J.; Tylutki, T.P. The nutritive values of South African Medicago sativa L. hay. S. Afr. J. Anim. Sci. 2009, 39, 179–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Tang, C.; Dai, F.; Xiao, G.; Luo, G. HPLC determination of phenolic compounds in different solvent extracts of mulberry leaves and antioxidant capacity of extracts. Int. J. Food Prop. 2021, 4, 544–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastola, K.P.; Guragain, Y.N.; Bhadriraju, V.; Vadlani, P.V. Evaluation of standards and interfering compounds in the determination of phenolics by Folin-Ciocalteu assay method for effective bioprocessing of biomass. Amer. J. Anal. Chem. 2017, 8, 416–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Shi, S.; Liu, C.; Zhang, H.; Li, X.; Li, Z. Optimization of the extraction of total phenols from Medicago sativa and its antioxidant capacity. Chem. Biodivers. 2022, 19, e202100898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butleska Gjoroska, V.; Krstik, M.; Jovanovska Klincarska, I.; Cvetanovska, A.; Cvetanovska, L.; Koleva Gudeva, L. Evaluation of total phenols in alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) collected from different localities in Republic of Macedonia. J. Agric. Plant Sci. 2018, 16, 45–54. [Google Scholar]
- Nazari, Z.; Honarvar, M.; Dianat, M. Evaluation of the effects of extraction method, duration and harvesting time on qualitative and quantitative features of Medicago sativa. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2021, 15, 4868–4875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiriac, E.R.; Chiţescu, C.L.; Borda, D.; Lupoae, M.; Gird, C.E.; Geană, E.I.; Blaga, G.V.; Boscencu, R. Comparison of the polyphenolic profile of Medicago sativa L. and Trifolium pratense L. Sprouts in different germination stages using the UHPLC-Q Exactive hybrid quadrupole orbitrap high-resolution mass spectrometry. Molecules 2020, 15, 2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krakowska-Sieprawska, A.; Rafinska, K.; Walczak-Skierska, J.; Kiełbasa, A.; Buszewski, B. Promising Green Technology in Obtaining Functional Plant Preparations: Combined enzyme-assisted supercritical fluid extraction of flavonoids isolation from Medicago sativa leaves. Materials 2021, 14, 2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrona, O.; Rafińska, K.; Krakowska-Sieprawska, A.; Buszewski, B. Comparative studies of selected criteria enabling optimization of the extraction of polar biologically active compounds from alfalfa with supercritical carbon dioxide. Molecules 2021, 18, 2994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newby, V.K.; Sablon, R.M.; Van de Casteele, K.; Van Sumere, C.C. Free and bound phenolic acids of lucerne (Medicago sativa cv europe). Phytochemistry 1980, 19, 651–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohn, P.J.; Fales, S.L. Effect of two pre-treatments on phenolic acid yield in three forage species. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1991, 54, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raffrenato, E.; Fievisohn, R.; Cotanch, K.W.V.; Grant, R.J.V.; Chase, L.E.; Van Amburgh, M.E. Effect of lignin linkages with other plant cell wall components on in vitro and in vivo neutral detergent fiber digestibility and rate of digestion of grass forages. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 8119–8131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, E.; Oskoueian, E.; Oskoueian, A.; Omidvar, V.; Hendra, R.; Nazeran, H. Insight into the functional and medicinal properties of Medicago sativa (Alfalfa) leaves extract. J. Medic. Plants Res. 2013, 7, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srisaikham, S. A comparison of nutritional values, bioactive compounds, amino acids, and antioxidant activities of alfalfa (Medicago sativa) plant and Pellet for use as beneficial material ruminant feed. Walailak J. Sci. Technol. 2021, 18, 10312–10316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latif, S.; Weston, P.A.; Barrow, R.A.; Gurusinghe, S.; Piltz, J.W.; Weston, L.A. Metabolic profiling provides unique insights to accumulation and biosynthesis of key secondary metabolites in annual pasture legumes of Mediterranean origin. Metabolites 2020, 10, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zavala-López, M.; García-Lara, S. An improved microscale method for extraction of phenolic acids from maize. Plant Methods 2017, 13, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singleton, V.L.; Rossi, J.A., Jr. Colorimetry of total phenolics with phosphomolybdic-phosphotungstic acid reagents. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 1965, 16, 144–158. [Google Scholar]
- Brand-Williams, W.; Cuvelier, M.E.; Berset, C. Use of a free radical method to evaluate antioxidant activity. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 1995, 28, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Cultivar/Population | CP (%) | ASH (%) | FAT (%) | CF (%) | NDF (%) | ADF (%) | ADL (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L 7 | 23.0 bc | 11.2 cd | 1.8 bcd | 30.7 i | 42.6 h | 35.5 ij | 8.0 cde |
| L 19 | 21.7 ef | 11.6 a | 2.1 a | 31.9 fgh | 43.9 ef | 37.4 gh | 8.7 bc |
| L 20 | 22.5 cd | 11.5 ab | 1.9 bcd | 29.1 j | 40.2 i | 33.0 k | 8.0 cde |
| L 39 | 23.0 bc | 11.2 cd | 1.7 de | 33.3 cde | 44.3 cde | 39.5 cde | 8.8 bc |
| L 40 | 22.2 de | 11.4 b | 1.6 efg | 28.9 jk | 44.7 bcd | 39.7 cde | 8.7 bc |
| L 42 | 20.9 gh | 10.8 gh | 1.5 fg | 32.8 cdef | 44.3 cdef | 41.7 a | 8.7 bc |
| L 43 | 20.4 h | 11.0 ef | 1.4 g | 35.7 a | 43.6 efg | 39.3 def | 9.4 ab |
| L 44 | 21.3 fg | 10.6 i | 1.7 cde | 32.6 def | 43.5 fg | 38.0 g | 9.7 a |
| OS 66 | 21.7 ef | 10.7 hi | 1.1 h | 33.7 bc | 45.5 b | 41.6 ab | 8.4 cde |
| OS 88 | 21.4 f | 10.9 fg | 1.8 bcd | 33.6 bcd | 45.0 bc | 40.7 abc | 7.7 ef |
| OS 99 | 24.7 a | 11.0 f | 1.5 efg | 30.6 i | 42.9 gh | 34.7 j | 6.9 f |
| OS 100 | 22.3 d | 10.8 gh | 2.0 ab | 31.2 hi | 40.8 i | 38.0 fg | 7.6 ef |
| OS 101 | 23.1 b | 11.1 de | 1.7 def | 31.0 hi | 42.4 h | 40.4 bcd | 8.3 cde |
| OS 200 | 23.3 b | 10.4 j | 1.7 de | 27.9 k | 44.0 def | 38.6 efg | 8.0 cde |
| Florida 66 | 23.1 b | 11.2 cd | 1.7 bcde | 31.4 ghi | 43.6 efg | 36.6 hi | 7.8 def |
| Torlesse | 21.5 f | 11.3 c | 1.4 g | 32.4 efg | 43.9 def | 39.3 def | 8.6 bcd |
| Seed Force 4 | 21.4 f | 10.8 gh | 1.9 abc | 34.5 b | 47.2 a | 38.0 g | 7.7 ef |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Horvat, D.; Viljevac Vuletić, M.; Andrić, L.; Baličević, R.; Kovačević Babić, M.; Tucak, M. Characterization of Forage Quality, Phenolic Profiles, and Antioxidant Activity in Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). Plants 2022, 11, 2735. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11202735
Horvat D, Viljevac Vuletić M, Andrić L, Baličević R, Kovačević Babić M, Tucak M. Characterization of Forage Quality, Phenolic Profiles, and Antioxidant Activity in Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). Plants. 2022; 11(20):2735. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11202735
Chicago/Turabian StyleHorvat, Daniela, Marija Viljevac Vuletić, Luka Andrić, Renata Baličević, Marija Kovačević Babić, and Marijana Tucak. 2022. "Characterization of Forage Quality, Phenolic Profiles, and Antioxidant Activity in Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.)" Plants 11, no. 20: 2735. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11202735
APA StyleHorvat, D., Viljevac Vuletić, M., Andrić, L., Baličević, R., Kovačević Babić, M., & Tucak, M. (2022). Characterization of Forage Quality, Phenolic Profiles, and Antioxidant Activity in Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). Plants, 11(20), 2735. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11202735








