Genome-Wide Identification of Genes Encoding for Rho-Related Proteins in ‘Duli’ Pear (Pyrus betulifolia Bunge) and Their Expression Analysis in Response to Abiotic Stress
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
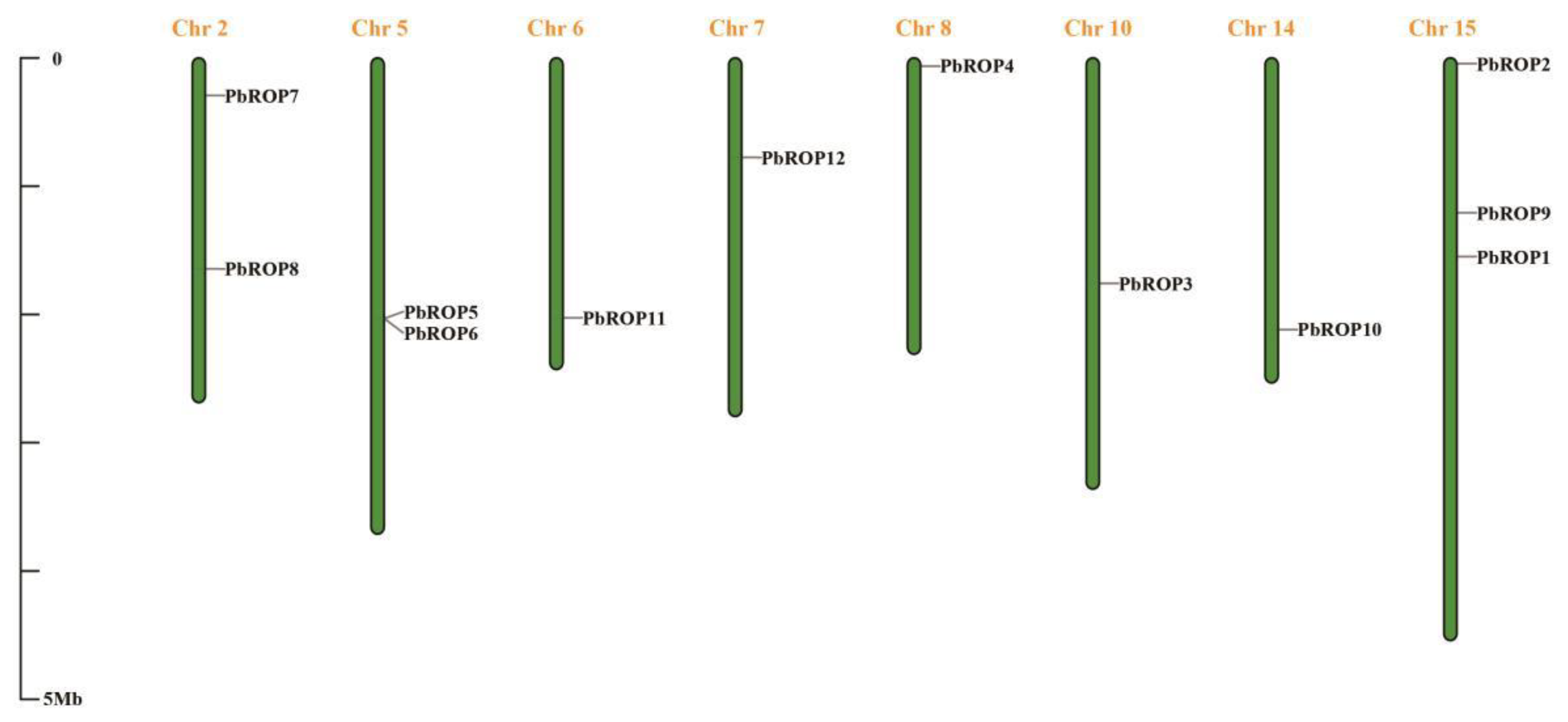
2.1. Twelve PbROPs Were Identified from ‘Duli’ Pear Genome
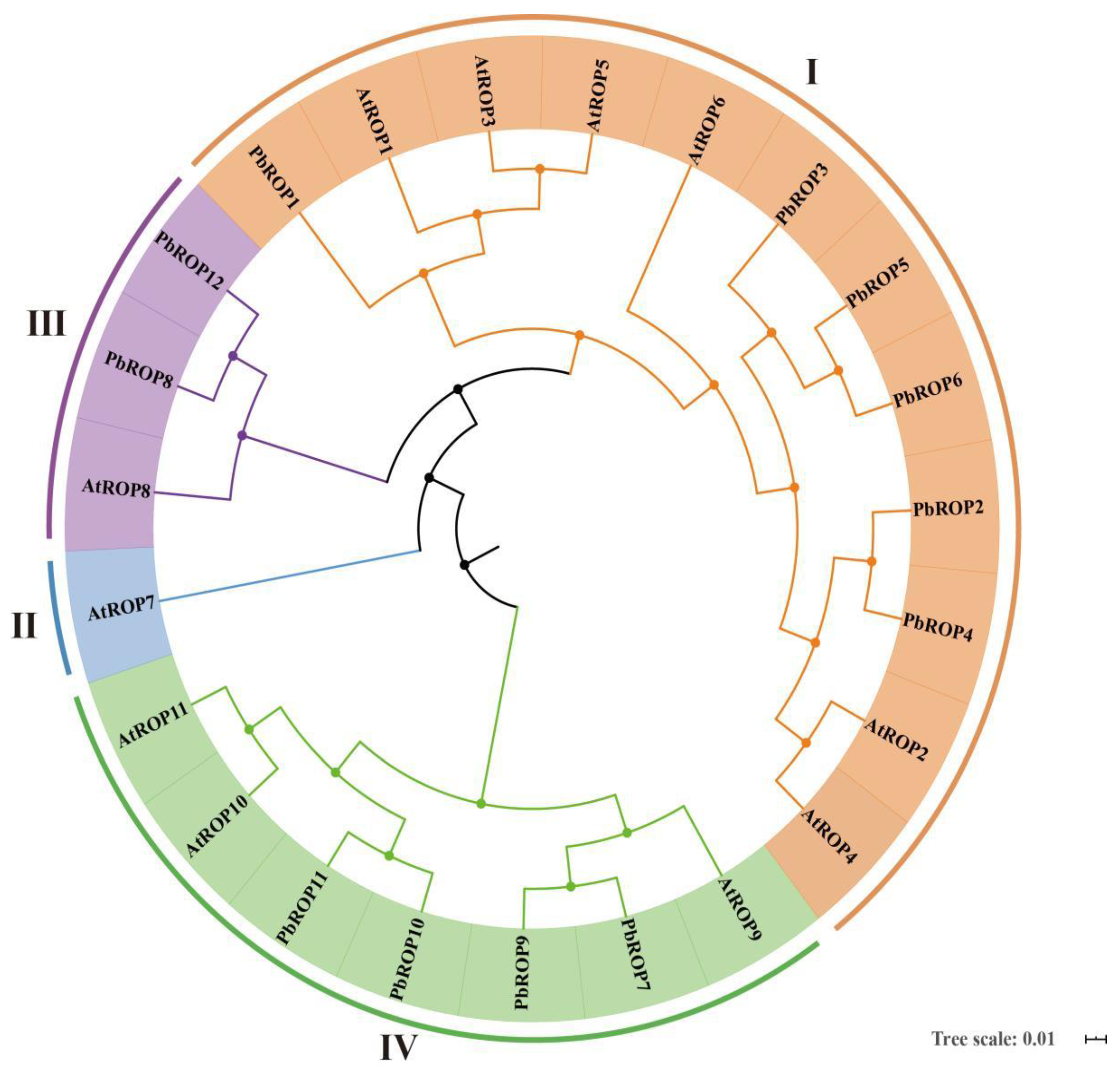
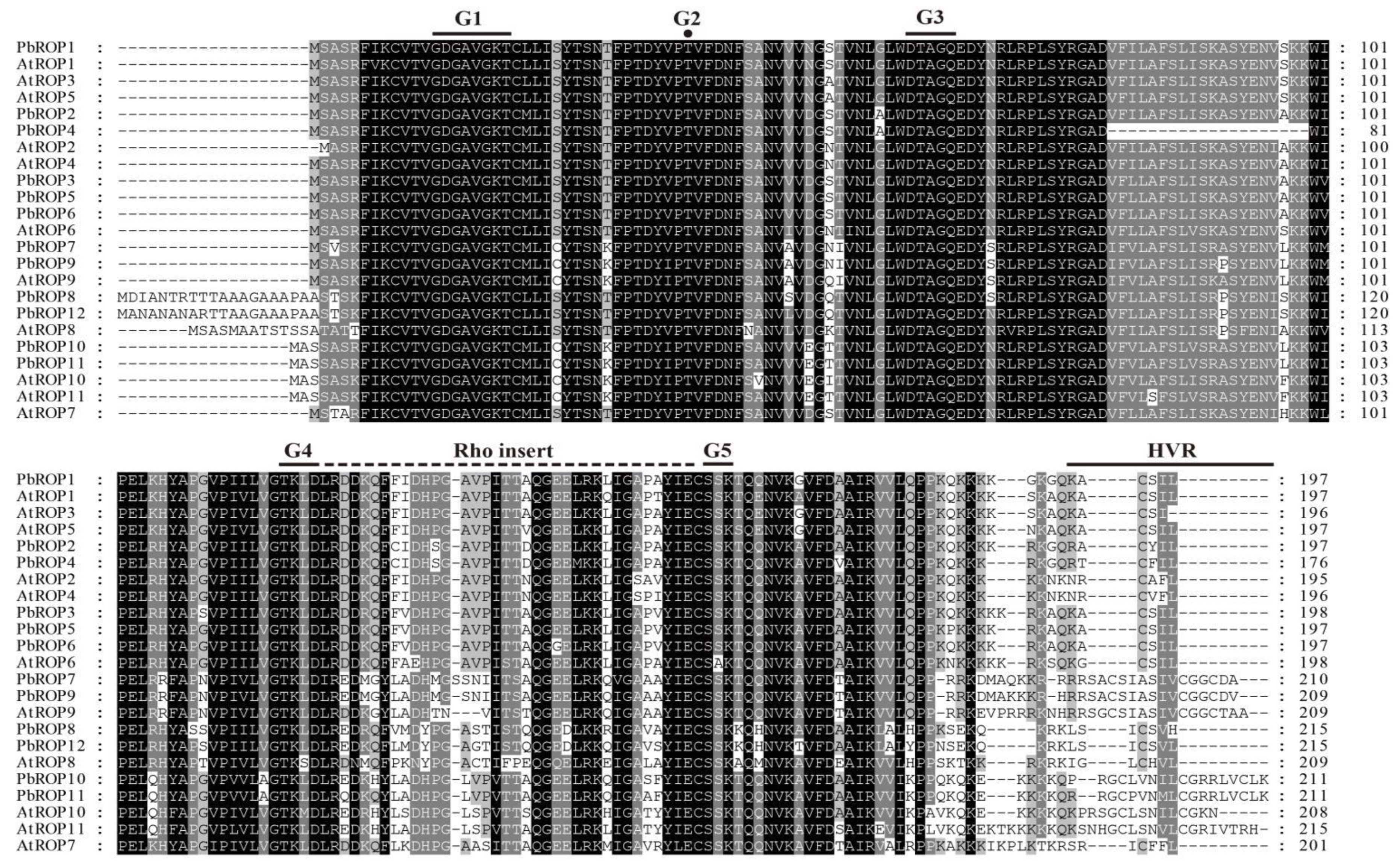
2.2. The 12 PbROPs of ‘Duli’ Pear Are Typical ROPs of Plants
2.3. The Gene Structure and Conserved Motifs Are Similar among the 12 PbROPs
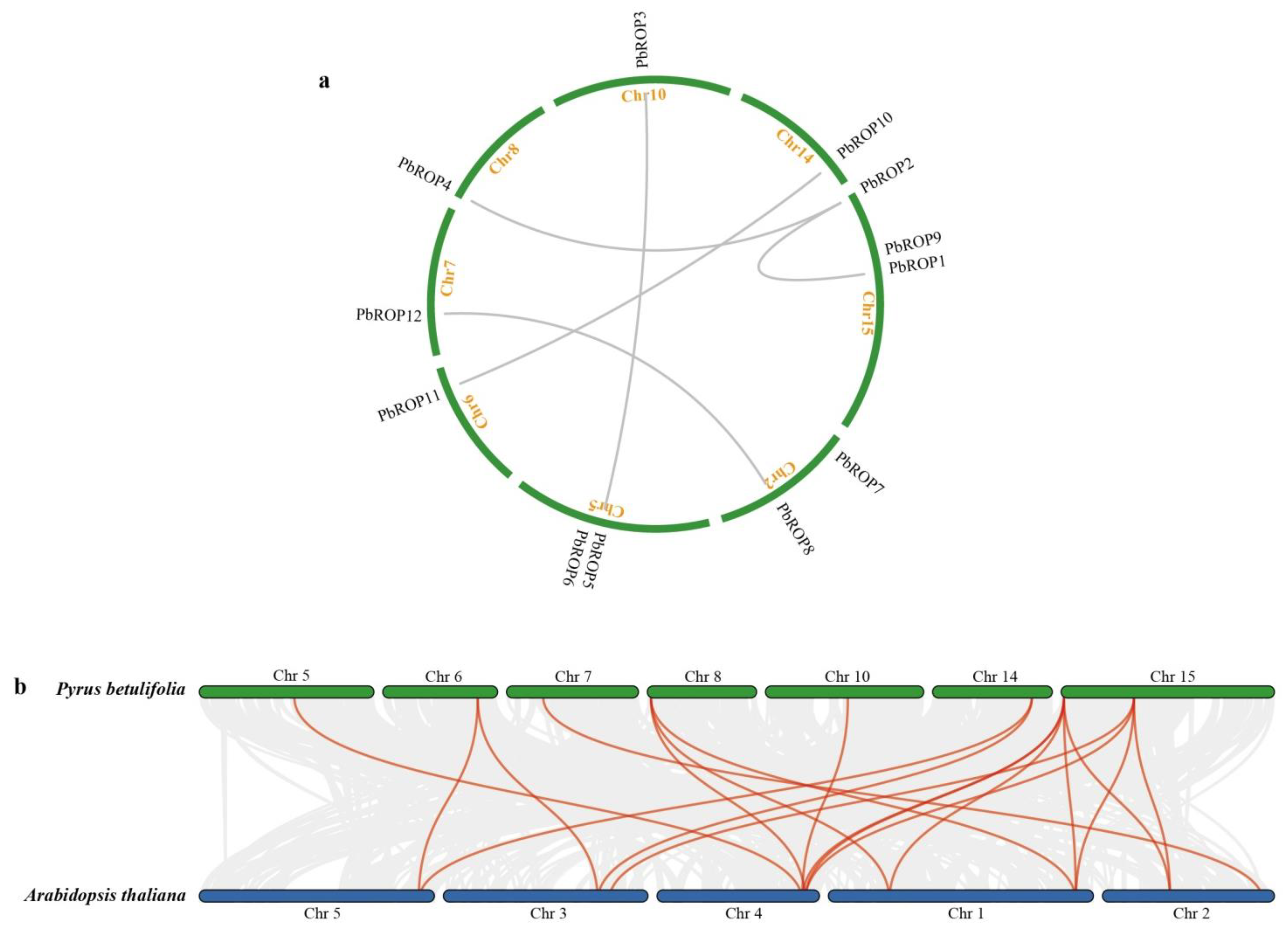
2.4. PbROPs Have Gone through Purifying Selection
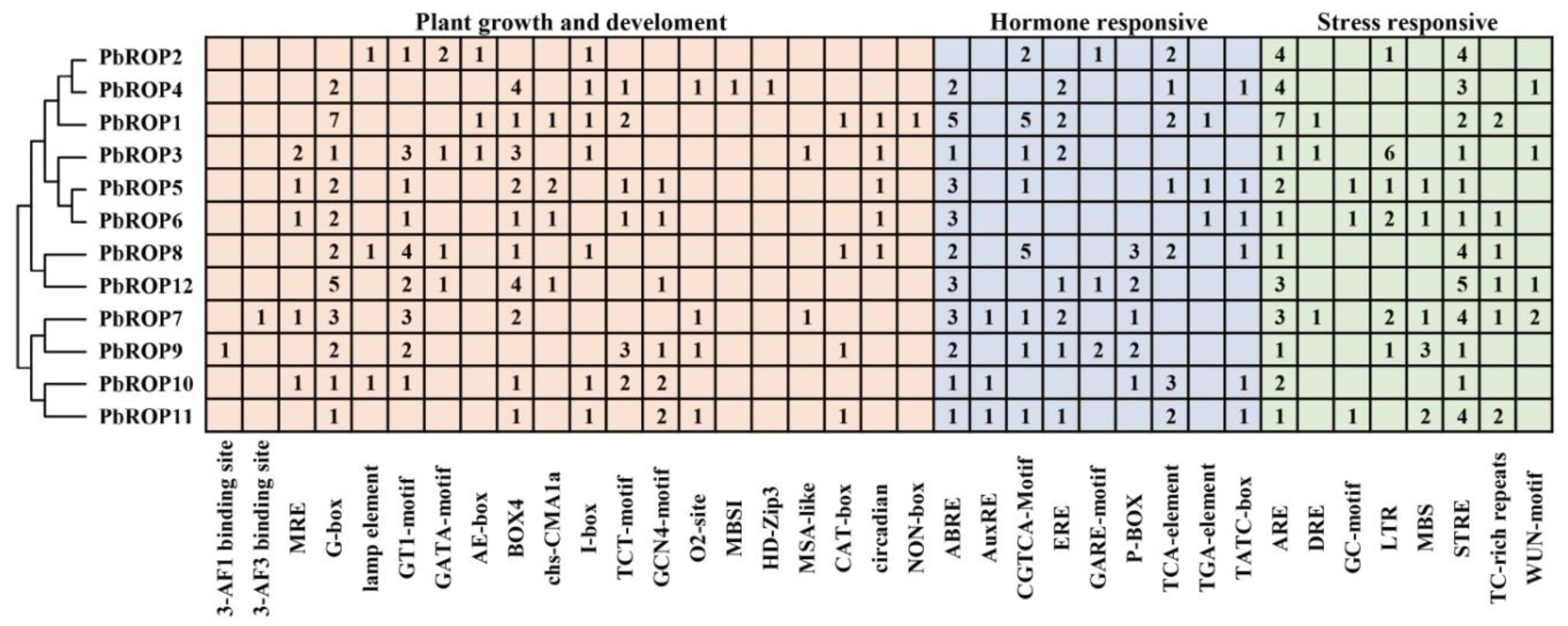
2.5. Cis-Acting Elements Related to Growth and Development, and Hormonal and Stress Response Are Present in the Promoter Regions of PbROPs
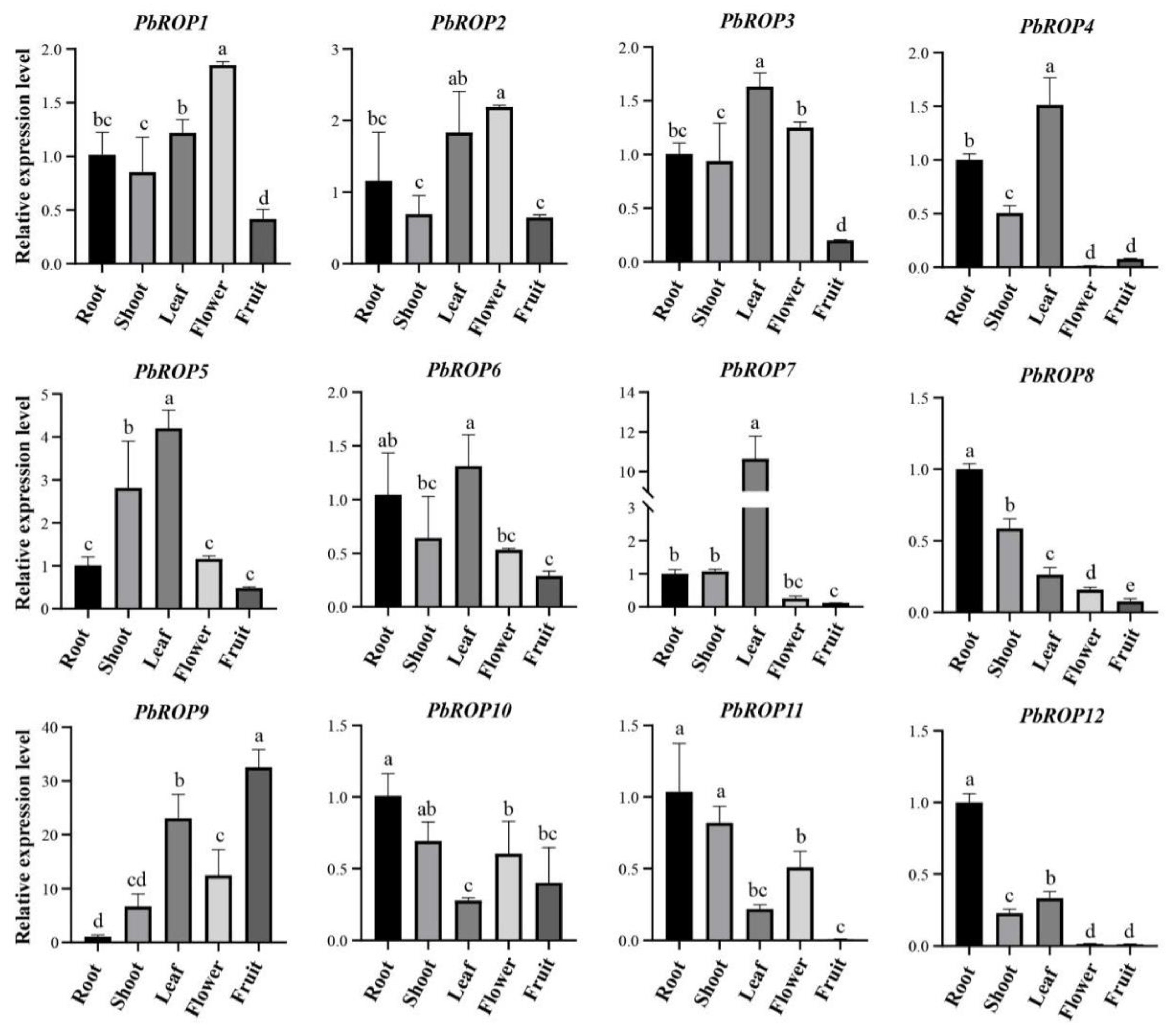
2.6. Tissue-Specific Expression Pattern of PbROP Genes
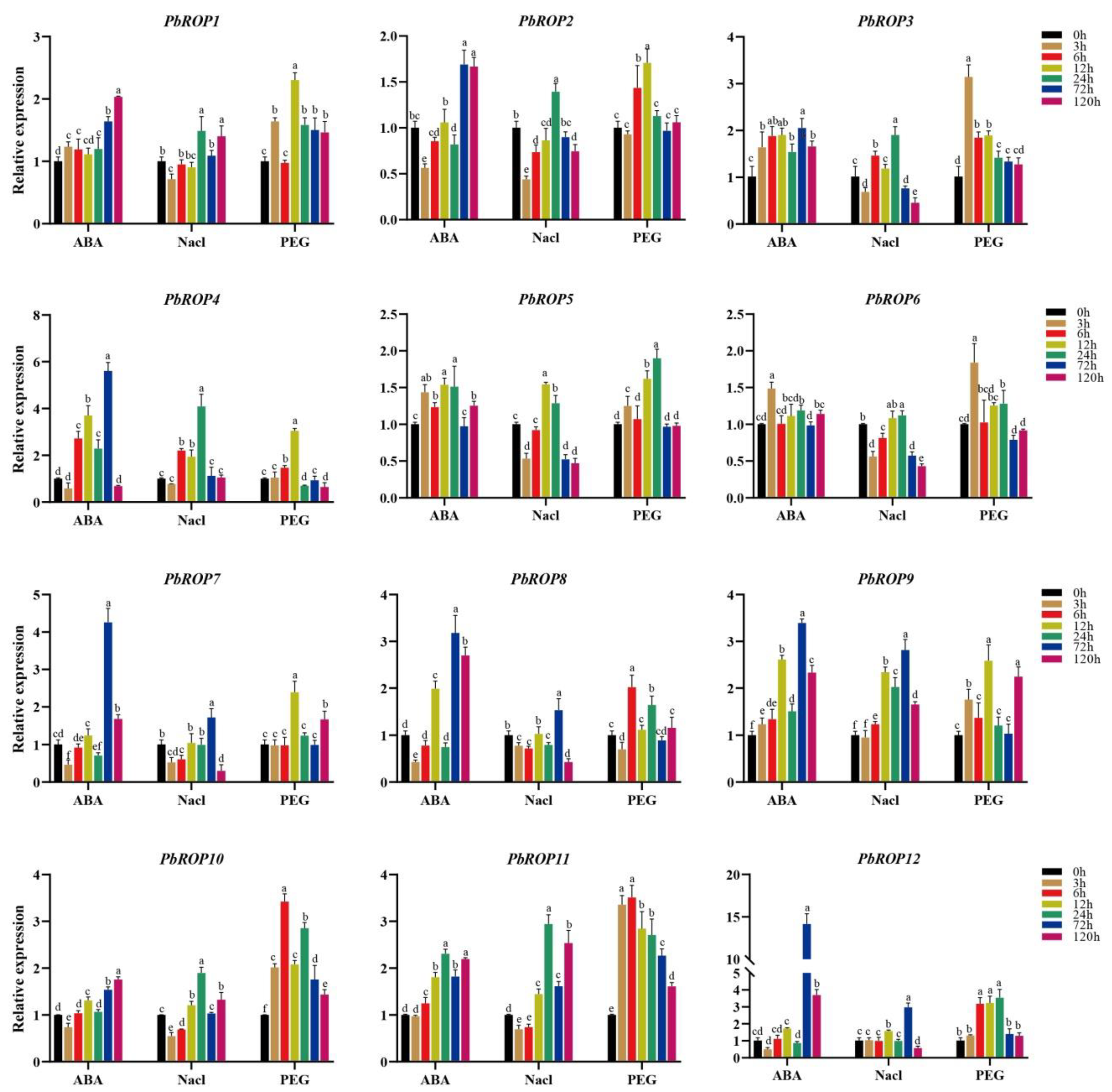
2.7. Expression Levels of PbROPs Were Elevated upon Stress
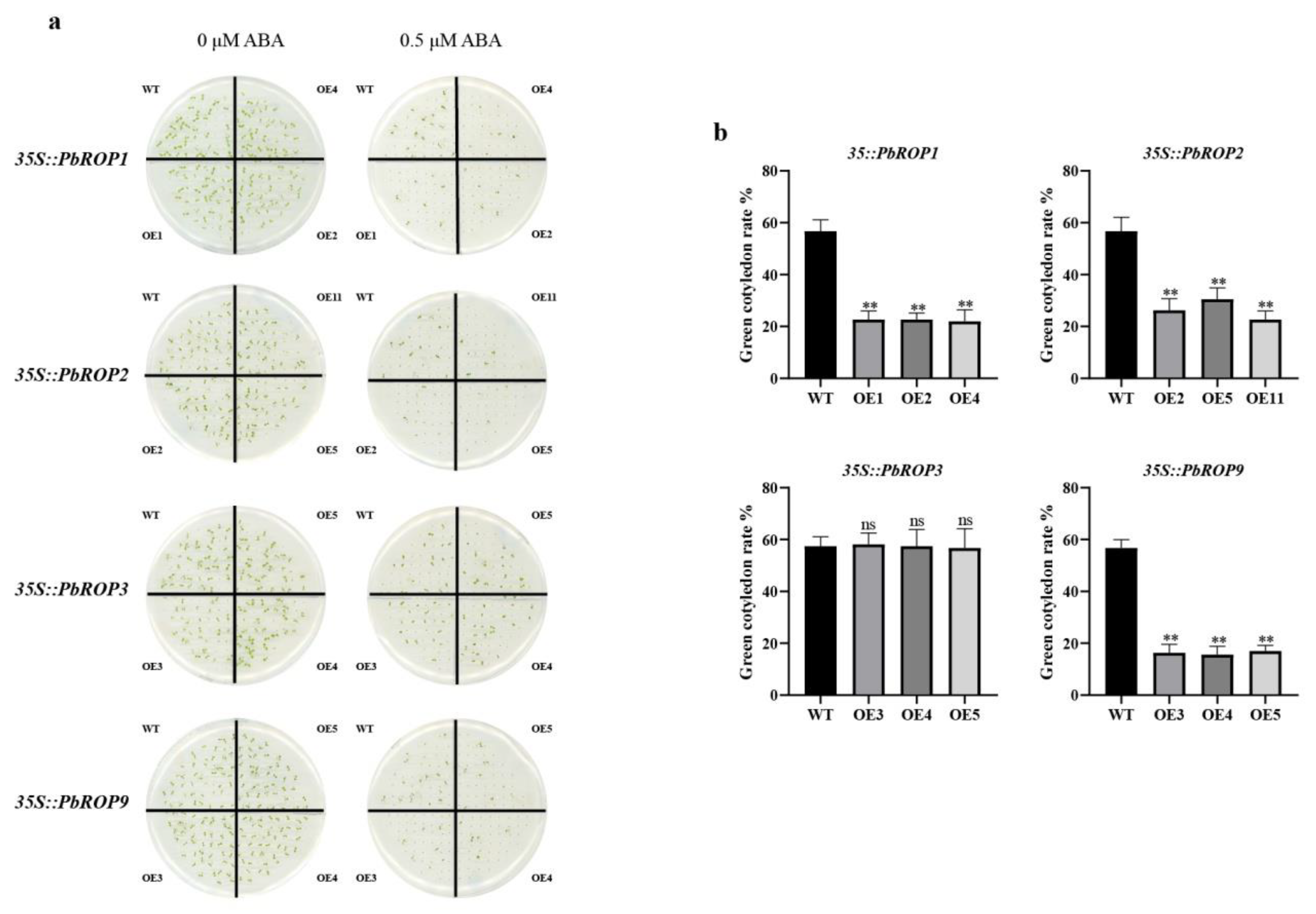
2.8. PbROP1, 2, 3, and 9 Overexpressing Transgenic Arabidopsis Seedlings Have Different Sensitivity to ABA
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Data Acquisition
4.2. Phylogenetic Tree, Gene Structure, and Sequence Analysis of PbROP Gene Family
4.3. Chromosome Location, Conserved Motifs, and the Cis-Elements in the PROMOTERS of PbROPs of ‘Duli’ Pear
4.4. Selective Pressure and Collinearity Analysis of PbROPs
4.5. Expression Patterns of PbROPs
4.6. Expression Profiles of PbROPs in Response to Different Stress Treatments
4.7. Total RNA Extraction and Synthesis of 1st-Strand cDNAs
4.8. Real-Time PCR
4.9. Over-Expression of PbROPs and ABA Sensitivity Assay of Transgenic Arabidopsis Seedlings
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, Z.; Watson, J.C. Molecular cloning and characterization of rho, a ras-related small GTP-binding protein from the garden pea. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 8732–8736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nibau, C.; Wu, H.M.; Cheung, A.Y. RAC/ROP GTPases: ‘hubs’ for signal integration and diversification in plants. Trends Plant Sci. 2006, 11, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Shen, J.J.; Zheng, Z.L.; Lin, Y.; Yang, Z. The Rop GTPase switch controls multiple developmental processes in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2001, 126, 670–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, L.; Shiotani, K.; Togashi, T.; Miki, D.; Aoyama, M.; Wong, H.L.; Kawasaki, T.; Shimamoto, K. Analysis of the Rac/Rop Small GTPase Family in Rice: Expression, Subcellular Localization and Role in Disease Resistance. Plant Cell Physiol. 2010, 51, 585–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humphries, J.A.; Vejlupkova, Z.; Luo, A.; Meeley, R.B.; Sylvester, A.W.; Fowler, J.E.; Smith, L.G. ROP GTPases act with the receptor-like protein PAN1 to polarize asymmetric cell division in maize. Plant Cell 2011, 23, 2273–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Potocký, M.; Pejchar, P.; Gutkowska, M.; Jiménez-Quesada, M.J.; Potocká, A.; Alché Jde, D.; Kost, B.; Žárský, V. NADPH oxidase activity in pollen tubes is affected by calcium ions, signaling phospholipids and Rac/Rop GTPases. J. Plant Physiol. 2012, 169, 1654–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, H.; Sun, P.; Liu, J.; Wang, J.; Xu, B.; Jin, Z. Overexpression of a Novel ROP Gene from the Banana (MaROP5g) Confers Increased Salt Stress Tolerance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vernoud, V.; Horton, A.C.; Yang, Z.; Nielsen, E. Analysis of the small GTPase gene superfamily of Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2003, 131, 1191–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, Z.L.; Yang, Z. The Rop GTPase: An emerging signaling switch in plants. Plant Mol. Biol. 2000, 44, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berken, A.; Wittinghofer, A. Structure and function of Rho-type molecular switches in plants. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2008, 46, 380–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feiguelman, G.; Fu, Y.; Yalovsky, S. ROP GTPases Structure-Function and Signaling Pathways. Plant Physiol. 2018, 176, 57–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engelhardt, S.; Trutzenberg, A.; Hückelhoven, R. Regulation and Functions of ROP GTPases in Plant-Microbe Interactions. Cells 2020, 9, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Y.; Fu, Y.; Dowd, P.; Li, S.; Vernoud, V.; Gilroy, S.; Yang, Z. A Rho family GTPase controls actin dynamics and tip growth via two counteracting downstream pathways in pollen tubes. J. Cell Biol. 2005, 169, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Molendijk, A.J. Arabidopsis thaliana Rop GTPases are localized to tips of root hairs and control polar growth. EMBO J. 2001, 20, 2779–2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jones, M.A.; Shen, J.J.; Fu, Y.; Li, H.; Yang, Z.; Grierson, C.S. The Arabidopsis Rop2 GTPase is a positive regulator of both root hair initiation and tip growth. Plant Cell 2002, 14, 763–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, X.; Shi, Y.; Liu, G.; Guo, Y.; Yang, Y. Activation of ROP6 GTPase by Phosphatidylglycerol in Arabidopsis. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Kang, J.; Sui, N.; Liu, D. ROP11 GTPase is a negative regulator of multiple ABA responses in Arabidopsis. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2012, 54, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, W.; Xu, C.-J.; Li, X.; Zhang, B.; Wang, P.; Allan, A.; Chen, K. Expression of ROP/RAC GTPase genes in postharvest loquat fruit in association with senescence and cold regulated lignification. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2009, 54, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauls, J.C.P. Brassica napus Rop GTPases and their expression in microspore cultures. Planta 2007, 225, 469–484. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Q.H.; Zhu, H.H.; Han, J.Q. Wheat ROP proteins modulate defense response through lignin metabolism. Plant Sci. 2017, 262, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorek, N.; Henis, Y.I.; Yalovsky, S. How prenylation and S-acylation regulate subcellular targeting and function of ROP GTPases. Plant Signal. Behav. 2011, 6, 1026–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hemsley, P.A.; Grierson, C.S. Multiple roles for protein palmitoylation in plants. Trends Plant Sci. 2008, 13, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batistic, O. Genomics and localization of the Arabidopsis DHHC-cysteine-rich domain S-acyltransferase protein family. Plant Physiol. 2012, 160, 1597–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wan, Z.Y.; Chai, S.; Ge, F.R.; Feng, Q.N.; Zhang, Y.; Li, S. Arabidopsis PROTEIN S-ACYL TRANSFERASE4 mediates root hair growth. Plant J. 2017, 90, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Christensen, T.M.; Vejlupkova, Z.; Sharma, Y.K.; Arthur, K.M.; Spatafora, J.W.; Albright, C.A.; Meeley, R.B.; Duvick, J.P.; Quatrano, R.S.; Fowler, J.E. Conserved subgroups and developmental regulation in the monocot rop gene family. Plant Physiol. 2003, 133, 1791–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dong, X.; Wang, Z.; Tian, L.; Zhang, Y.; Qi, D.; Huo, H.; Xu, J.; Li, Z.; Liao, R.; Shi, M.; et al. De novo assembly of a wild pear (Pyrus betuleafolia Burge) genome. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2020, 18, 581–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hernandez-Garcia, C.M.; Finer, J.J. Identification and validation of promoters and cis-acting regulatory elements. Plant Sci. 2014, 217–218, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.-F.; Liao, Y.-Q.; Wang, Y.-P.; Yang, J.-W.; Zhang, N.; Si, H.-J. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of StPP2C gene family in response to multiple stresses in potato (Solanum tuberosum L.). J. Integr. Agric. 2020, 19, 1609–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubtsov, G.A. Geographical Distribution of the Genus Pyrus and Trends and Factors in Its Evolution. Am. Nat. 1944, 78, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zermiani, M.; Zonin, E.; Nonis, A.; Begheldo, M.; Ceccato, L.; Vezzaro, A.; Baldan, B.; Trentin, A.; Masi, A.; Pegoraro, M.; et al. Ethylene negatively regulates transcript abundance of ROP-GAP rheostat-encoding genes and affects apoplastic reactive oxygen species homeostasis in epicarps of cold stored apple fruits. J. Exp. Bot. 2015, 66, 7255–7270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, W.; Liu, Z.; Bao, L.J.; Zhang, S.S.; Zhang, C.G.; Li, X.; Li, H.X.; Zhang, X.L.; Bones, A.M.; Yang, Z.B.; et al. The RopGEF2-ROP7/ROP2 Pathway Activated by phyB Suppresses Red Light-Induced Stomatal Opening. Plant Physiol. 2017, 174, 717–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, C.; Lu, H.; Li, W.; Yuan, M.; Fu, Y. A ROP2-RIC1 pathway fine-tunes microtubule reorganization for salt tolerance in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Environ. 2017, 40, 1127–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, D.; Nagawa, S.; Chen, J.; Cao, L.; Chen, X.; Xu, T.; Li, H.; Dhonukshe, P.; Yamamuro, C.; Friml, J.; et al. A ROP GTPase-dependent auxin signaling pathway regulates the subcellular distribution of PIN2 in Arabidopsis roots. Curr. Biol. 2012, 22, 1319–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Li, E.; Feng, Q.N.; Zhao, X.Y.; Ge, F.R.; Zhang, Y.; Li, S. Protein palmitoylation is critical for the polar growth of root hairs in Arabidopsis. BMC Plant Biol. 2015, 15, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gendre, D.; Baral, A.; Dang, X.; Esnay, N.; Boutte, Y.; Stanislas, T.; Vain, T.; Claverol, S.; Gustavsson, A.; Lin, D.; et al. Rho-of-plant activated root hair formation requires Arabidopsis YIP4a/b gene function. Development 2019, 146, dev168559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, Y.; Li, Z.; Chen, T.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Chen, S. Overexpression of a tobacco small G protein gene NtRop1 causes salt sensitivity and hydrogen peroxide production in transgenic plants. Sci. China C Life Sci. 2008, 51, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tardieu, F.; Simonneau, T.; Muller, B. The Physiological Basis of Drought Tolerance in Crop Plants: A Scenario-Dependent Probabilistic Approach. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2018, 69, 733–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, L.R.; Zhao, Z.J.; Hao, F.S. NADPH oxidases, essential players of hormone signalings in plant development and response to stresses. Plant Signal. Behav. 2019, 14, 1657343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.G.; Seo, P.J. MYB96 recruits the HDA15 protein to suppress negative regulators of ABA signaling in Arabidopsis. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, C.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Thomas, H.R.; Frank, M.H.; He, Y.; Xia, R. TBtools: An Integrative Toolkit Developed for Interactive Analyses of Big Biological Data. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artimo, P.; Jonnalagedda, M.; Arnold, K.; Baratin, D.; Csardi, G.; de Castro, E.; Duvaud, S.; Flegel, V.; Fortier, A.; Gasteiger, E.; et al. ExPASy: SIB bioinformatics resource portal. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, W597–W603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Peterson, D.; Filipski, A.; Kumar, S. MEGA6: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis version 6.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 2725–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bailey, T.L.; Elkan, C. Fitting a mixture model by expectation maximization to discover motifs in biopolymers. Proc. Int. Conf. Intell. Syst. Mol. Biol. 1994, 2, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lescot, M.; Déhais, P.; Thijs, G.; Marchal, K.; Moreau, Y.; Van de Peer, Y.; Rouzé, P.; Rombauts, S. PlantCARE, a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 325–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xu, J.; Li, G.; Wan, S.; Batistič, O.; Sun, M.; Zhang, Y.; Scott, R.; Qi, B. Protein S-acyl transferase 15 is involved in seed triacylglycerol catabolism during early seedling growth in Arabidopsis. J. Exp. Bot. 2019, 70, 5205–5216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, B.; Doughty, J.; Hooley, R. A Golgi and tonoplast localized S-acyl transferase is involved in cell expansion, cell division, vascular patterning and fertility in Arabidopsis. New Phytol. 2013, 200, 444–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clough, S.J.; Bent, A.F. Floral dip: A simplified method for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 1998, 16, 735–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| Name | Gene Acc Number | Gene ID | Gene Location | Length of Gene (bp) | No. Amino Acid | Mol Weight (kDa) | Protein Isoelectric Point/(pI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PbROP1 | GWHPAAY-T021718 | Chr15.g02695.m2 | Chr15(−)15491640-15493489 | 1850 | 197 | 21.55 | 9.7 |
| PbROP2 | GWHPAAYT019557 | Chr15.g04856.m1 | Chr15(+)449034-450843 | 1809 | 197 | 21.74 | 9.34 |
| PbROP3 | GWHPAAYT003833 | Chr10.g15874.m1 | Chr10(+)17567259-17569896 | 2638 | 198 | 21.83 | 9.82 |
| PbROP4 | GWHPAAYT050667 | Chr8.g53635.m1 | Chr8(+)644981-646739 | 1759 | 176 | 19.46 | 8.71 |
| PbROP5 | GWHPAAYT042018 | Chr5.g07968.m1 | Chr5(+)20278696-20281398 | 2703 | 197 | 21.65 | 9.7 |
| PbROP6 | GWHPAAYT042034 | Chr5.g07952.m1 | Chr5(+)20386888-20389606 | 2719 | 197 | 21.60 | 9.83 |
| PbROP7 | GWHPAAYT031525 | Chr2.g41544.m1 | Chr2(+)2929720-2931810 | 2091 | 210 | 23.12 | 9.25 |
| PbROP8 | GWHPAAYT033120 | Chr2.g43139.m1 | Chr2(−)16443373-16448921 | 5549 | 215 | 23.45 | 9.33 |
| PbROP9 | GWHPAAYT021263 | Chr15.g03150.m1 | Chr15(−)12072153-12074312 | 2160 | 209 | 23.07 | 9.24 |
| PbROP10 | GWHPAAYT018785 | Chr14.g49938.m2 | Chr14(+)21184845-21187330 | 2486 | 211 | 23.39 | 9.54 |
| PbROP11 | GWHPAAYT046524 | Chr6.g51364.m1 | Chr6(+)20257138-20259368 | 2231 | 211 | 23.42 | 9.81 |
| PbROP12 | GWHPAAYT048105 | Chr7.g33937.m1 | Chr7(+)7754549-7757181 | 2633 | 215 | 23.42 | 9.08 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, G.; Song, P.; Wang, X.; Ma, Q.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Qi, B. Genome-Wide Identification of Genes Encoding for Rho-Related Proteins in ‘Duli’ Pear (Pyrus betulifolia Bunge) and Their Expression Analysis in Response to Abiotic Stress. Plants 2022, 11, 1608. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11121608
Li G, Song P, Wang X, Ma Q, Xu J, Zhang Y, Qi B. Genome-Wide Identification of Genes Encoding for Rho-Related Proteins in ‘Duli’ Pear (Pyrus betulifolia Bunge) and Their Expression Analysis in Response to Abiotic Stress. Plants. 2022; 11(12):1608. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11121608
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Gang, Pingli Song, Xiang Wang, Qingcui Ma, Jianfeng Xu, Yuxing Zhang, and Baoxiu Qi. 2022. "Genome-Wide Identification of Genes Encoding for Rho-Related Proteins in ‘Duli’ Pear (Pyrus betulifolia Bunge) and Their Expression Analysis in Response to Abiotic Stress" Plants 11, no. 12: 1608. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11121608
APA StyleLi, G., Song, P., Wang, X., Ma, Q., Xu, J., Zhang, Y., & Qi, B. (2022). Genome-Wide Identification of Genes Encoding for Rho-Related Proteins in ‘Duli’ Pear (Pyrus betulifolia Bunge) and Their Expression Analysis in Response to Abiotic Stress. Plants, 11(12), 1608. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11121608







