Nutrient Composition Analysis of Maize Hybrids Affected by Different Nitrogen Fertilisation Systems
Abstract
:1. Introduction
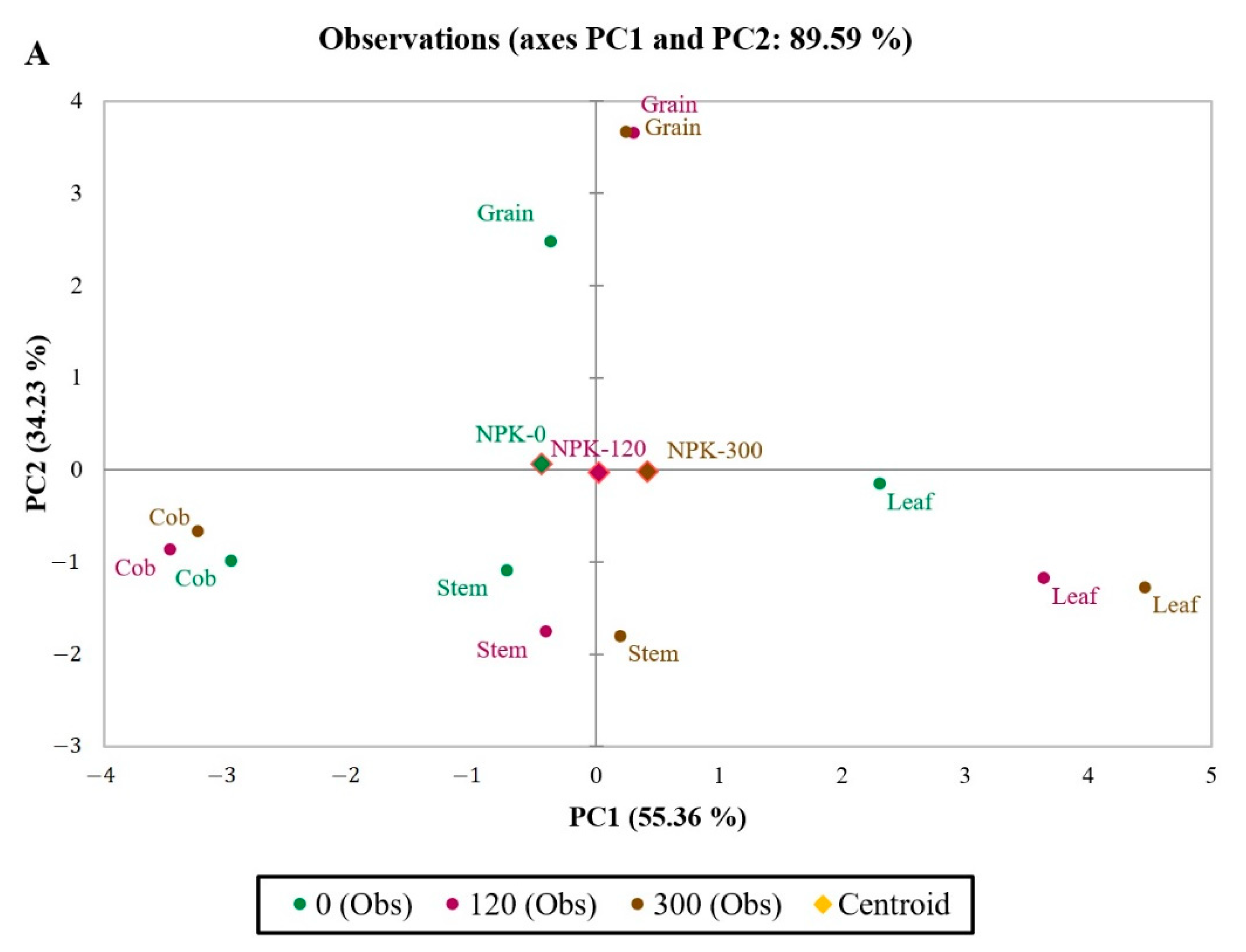
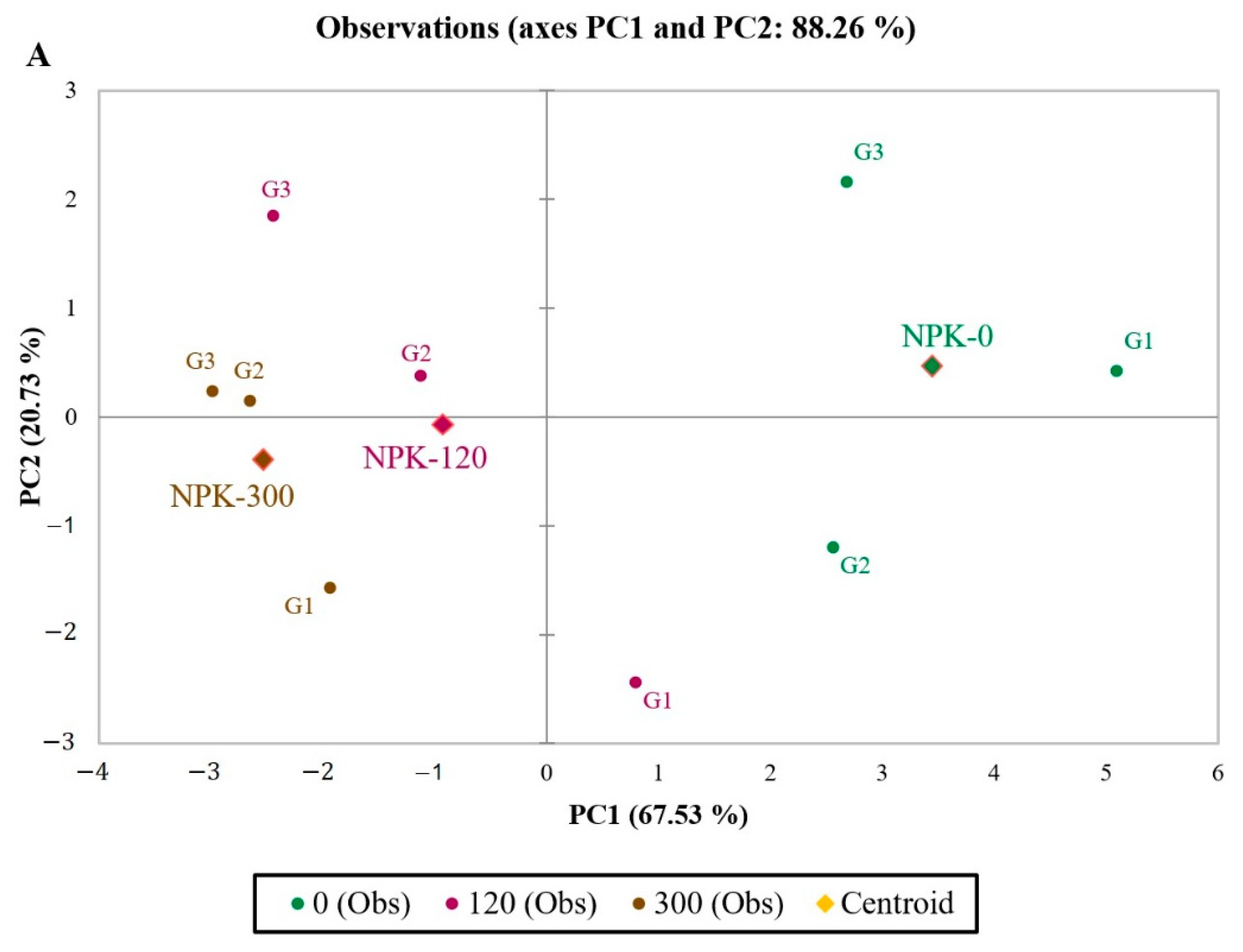
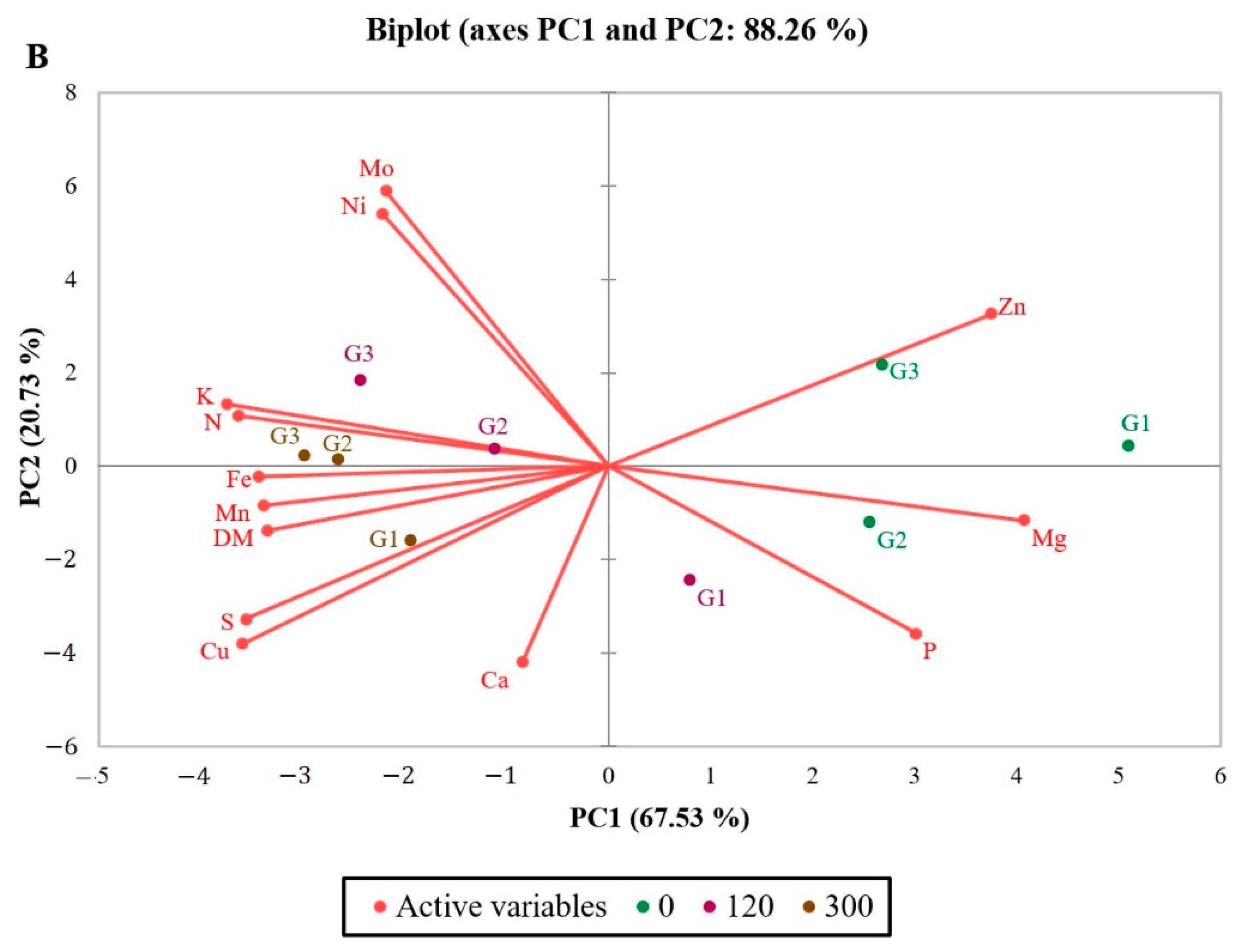
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. The Field Experiment
4.2. Sample Analysis
4.3. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nagy, J. Maize Production; Akadémiai Kiadó: Budapest, Hungary, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Ranum, P.; Peña-Rosas, J.P.; Garcia-Casal, M.N. Global maize production, utilization, and consumption. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2014, 1312, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cairns, J.E.; Sonder, K.; Zaidi, P.H.; Verhulst, N.; Mahuku, G.; Babu, R.; Prasanna, B.M. Maize production in a changing climate: Impacts, adaptation, and mitigation strategies. Adv. Agron. 2012, 114, 1–58. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, P.; Li, X.; White, P.J.; Li, C. A large and deep root system underlies high nitrogen-use efficiency in maize production. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0126293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lisuma, J.B.; Semoka, J.M.R.; Semu, E. Maize yield response and nutrient uptake after micronutrient application on a volcanic soil. Agron. J. 2006, 98, 402–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illes, A.; Bojtor, C.; Szeles, A.; Mousavi, S.M.N.; Toth, B.; Nagy, J. Analyzing the effect of intensive and low-input agrotechnical support for the physiological, phenometric, and yield parameters of different maize hybrids using multivariate statistical methods. Int. J. Agron. 2021, 2, 6682573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, S.M.N.; Bojtor, C.; Illés, Á.; Nagy, J. Genotype by Trait Interaction (GT) in Maize Hybrids on Complete Fertilizer. Plants 2021, 10, 2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bojtor, C.; Mousavi, S.M.N.; Illés, Á.; Széles, A.; Nagy, J.; Marton, C.L. Stability and adaptability of maize hybrids for precision crop production in a long-term field experiment in hungary. Agronomy 2021, 11, 2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, Z.P.; Paparozzi, E.T.; Wortmann, C.S.; Jha, P.K.; Shapiro, C.A. Effect of Foliar Micronutrients (B, Mn, Fe, Zn) on Maize Grain Yield, Micronutrient Recovery, Uptake, and Partitioning. Plants 2021, 10, 528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galani, Y.J.H.; Orfila, C.; Gong, Y.Y. A review of micronutrient deficiencies and analysis of maize contribution to nutrient requirements of women and children in Eastern and Southern Africa. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 1568–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wajid, K.; Ahmad, K.; Khan, Z.I.; Nadeem, M.; Bashir, H.; Chen, F.; Ugulu, I. Effect of organic manure and mineral fertilizers on bioaccumulation and translocation of trace metals in maize. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2020, 104, 649–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bojtor, C.; Illés, Á.; Nasir Mousavi, S.M.; Széles, A.; Tóth, B.; Nagy, J.; Marton, C.L. Evaluation of the Nutrient Composition of Maize in Different NPK Fertilizer Levels Based on Multivariate Method Analysis. Int. J. Agron. 2021, 2021, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hänsch, R.; Mendel, R.R. Physiological functions of mineral micronutrients (cu, Zn, Mn, Fe, Ni, Mo, B, cl). Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2009, 12, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Fouly, M.; Abou El-Nour, E.; Shaaban, S.; Zeidan, M. Effect of different levels of NPK and micronutrients fertilization on yield and nutrient uptake of maize plants. J. Am. Sci. 2012, 8, 209–214. [Google Scholar]
- Waters, B.M.; Sankaran, R.P. Moving micronutrients from the soil to the seeds: Genes and physiological processes from a biofortification perspective. Plant Sci. 2011, 180, 562–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Borase, C.L.; Lomte, D.M.; Thorat, S.D.; Dhonde, A.S. Response of Kharif maize (Zea mays L.) to micronutrients. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. 2018, 7, 482–484. [Google Scholar]
- Filipek-Mazur, B.; Tabak, M.; Koncewicz-Baran, M.; Bobowiec, A. Mineral fertilizers with iron influence spring rape, maize and soil properties. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2019, 65, 1575–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, I.; Javid, S.; Bibi, F.; Ehsan, S.; Niaz, A.; Ahmad, Z.A. Biofortification of maize grain with zinc and iron by using fertilizing approach. J. Agric. Ecol. Res. Int. 2016, 7, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jan, B.; Bhat, T.A.; Sheikh, T.A.; Wani, O.A.; Bhat, M.A.; Nazir, A.; Rashid, A. Agronomic Bio-fortification of Rice and Maize with Iron and Zinc: A Review. Int. Res. J. Pure Appl. Chem. 2020, 21, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuhy, Ł.; Samoraj, M.; Witkowska, Z.; Chojnacka, K. Biofortification of maize with micronutrients by Spirulina. Open Chem. 2015, 13, 1119–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phelps, J.; Carrasco, L.R.; Webb, E.L.; Koh, L.P.; Pascual, U. Agricultural intensification escalates future conservation costs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 7601–7606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kádár, I. A Növénytáplálás Alapelvei és Módszerei; MTA Talajtani és Agrokémiai Kutatóintézet (MTA ATK TAKI): Budapest, Hungary, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Kádár, I. Kölcsönhatások vizsgálata a növénytáplálási kutatásokban. Talajvédelem különszám. Talajt. Vándorgyűl. 2008, 29, 265–274. [Google Scholar]
- Izsáki, Z. The application of diagnostic plant analysis in the system of nutrient supply of sugar beet. Cukoripar 2000, 53, 141–147. [Google Scholar]
- Maňásek, J.; Lošák, T.; Prokeš, K.; Hlušek, J.; Vítězová, M.; Škarpa, P.; Filipčík, R. Effect of nitrogen and potassium fertilization on micronutrient content in grain maize (Zea mays L.). Acta Univ. Agric. Silvic. Mendel. Brun. 2013, 61, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Subedi, K.D.; Ma, B.L. Corn Crop Production: Growth, Fertilization and Yield; Nova Science Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 1–84. ISBN 978-1-60741-955-6. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, G.A.; Korndörfer, G.H.; Pereira, H.S. Methods of adding micronutrients to a NPK formulation and maize development. J. Plant Nutr. 2016, 39, 1266–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hekmat, A.W.; Mohammadi, N.K.; Ghosh, G. Effect of NPK, biofertilizer and zinc foliar nutrition on growth and growth attributes of baby corn (Zea mays L.). Int. J. Chem. Stud. 2019, 7, 2432–2436. [Google Scholar]
- Dimkpa, C.O.; White, J.C.; Elmer, W.H.; Gardea-Torresdey, J. Nanoparticle and ionic Zn promote nutrient loading of sorghum grain under low NPK fertilization. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 8552–8559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Ortiz, D.; Hernandez-Apaolaza, L.; Garate, A. Efficiency of a NPK fertilizer with adhered zinc lignosulfonate as a zinc source for maize (Zea mays L.). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 9071–9078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, R.; Shivay, Y.S.; Kumar, D. Agronomic biofortification of cereal grains with iron and zinc. Adv. Agron. 2014, 125, 55–91. [Google Scholar]
- Aajmi Salman, M.; A Kamal Al-Shibani, J.; A. Kamal Al-Shibani, J. Effect the Treatments of Biofertilizer and Mineral Fertilizer on Content of NPK of Soil Cultivated with Crop Corn (Zea Mays L). Al-Qadisiyah J. Agric. Sci. 2019, 9, 247–256. [Google Scholar]
- Masto, R.E.; Chhonkar, P.K.; Singh, D.; Patra, A.K. Alternative soil quality indices for evaluating the effect of intensive cropping, fertilisation and manuring for 31 years in the semi-arid soils of India. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2008, 136, 419–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabir, M.; Hanafi, M.M.; Malik, M.T.; Aziz, T.; Zia-ur-Rehman, M.; Ahmad, H.R.; Shahid, M. Differential effect of nitrogen forms on physiological parameters and micronutrient concentration in maize (Zea mays L.). Aust. J. Crop Sci. 2013, 7, 1836–1842. [Google Scholar]
- Izsáki, Z. A N-trágyázás hatása a kukorica levél tápelem-koncentrációjára és a tápelemek közötti kölcsönhatásokra. Növénytermelés 2011, 60, 43–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruns, H.A.; Ebelhar, M.W. Nutrient uptake of maize affected by nitrogen and potassium fertility in a humid subtropical environment. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2006, 37, 275–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyszkowski, M.; Brodowska, M.S. Content of trace elements in soil fertilized with potassium and nitrogen. Agriculture 2020, 10, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, C.A.; Ferguson, R.; Wortmann, C.S.; Maharjan, B.; Krienke, B.T. Nutrient Management Suggestions for Corn; University of Nebraska-Lincoln Extension Circular EC117: Lincoln, NE, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Nagy, J. Complex long-term experiments on soil use, water and nutrient management at the University of Debrecen since 1983. Növénytermelés 2019, 68, 5–28. [Google Scholar]
- Tarantino, T.B.; Barbosa, I.S.; de C Lima, D.; de G Pereira, M.; Teixeira, L.S.; Korn, M.G.A. Microwave-assisted digestion using diluted nitric acid for multi-element determination in rice by ICP OES and ICP-MS. Food Anal. Methods 2017, 10, 1007–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebeling, M.E. The Dumas method for nitrogen in feeds. J. Assoc. Off. Anal. Chem. 1968, 51, 766–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Df | F | Df | F | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DM | NPK | 2 | 90.25 ** | S | NPK | 2 | 51.89 ** |
| Genotype | 2 | 11.8 ** | Genotype | 2 | 1.45 | ||
| Tissue | 3 | 4387.79 ** | Tissue | 3 | 397.53 ** | ||
| NPK * Genotype | 4 | 4.91 ** | NPK * Genotype | 4 | 0.5 | ||
| NPK * Tissue | 6 | 12.09 ** | NPK * Tissue | 6 | 11.77 ** | ||
| Genotype * Tissue | 6 | 11.11 ** | Genotype * Tissue | 6 | 3.59 ** | ||
| NPK * Genotype * Tissue | 12 | 1.48 | NPK * Genotype * Tissue | 12 | 1.8 | ||
| N | NPK | 2 | 6.45 ** | Zn | NPK | 2 | 83.46 ** |
| Genotype | 2 | 2.38 * | Genotype | 2 | 2.52 | ||
| Tissue | 3 | 23.2 ** | Tissue | 3 | 1.74 | ||
| NPK * Genotype | 4 | 0.85 | NPK * Genotype | 4 | 6.32 ** | ||
| NPK * Tissue | 6 | 1.34 | NPK * Tissue | 6 | 5.41 ** | ||
| Genotype * Tissue | 6 | 0.72 | Genotype * Tissue | 6 | 2.14 * | ||
| NPK * Genotype * Tissue | 12 | 0.71 | NPK * Genotype * Tissue | 12 | 2.22 * | ||
| P | NPK | 2 | 3.31 * | Fe | NPK | 2 | 10.96 ** |
| Genotype | 2 | 5.8 ** | Genotype | 2 | 3.31 * | ||
| Tissue | 3 | 164.98 ** | Tissue | 3 | 185.68 ** | ||
| NPK * Genotype | 4 | 1.89 | NPK * Genotype | 4 | 1.95 | ||
| NPK * Tissue | 6 | 1.91 | NPK * Tissue | 6 | 2.13 | ||
| Genotype * Tissue | 6 | 2.98 * | Genotype * Tissue | 6 | 1.03 | ||
| NPK * Genotype * Tissue | 12 | 1.23 | NPK * Genotype * Tissue | 12 | 1.67 | ||
| K | NPK | 2 | 14.36 ** | Cu | NPK | 2 | 66.4 ** |
| Genotype | 2 | 3.87 * | Genotype | 2 | 3.54 * | ||
| Tissue | 3 | 222.98 ** | Tissue | 3 | 250.45 ** | ||
| NPK * Genotype | 4 | 1.05 | NPK * Genotype | 4 | 0.82 | ||
| NPK * Tissue | 6 | 6.63 ** | NPK * Tissue | 6 | 17.67 ** | ||
| Genotype * Tissue | 6 | 1.15 | Genotype * Tissue | 6 | 1.88 | ||
| NPK * Genotype * Tissue | 12 | 1.02 | NPK * Genotype * Tissue | 12 | 0.6 | ||
| Mg | NPK | 2 | 14.99 ** | Mn | NPK | 2 | 7.1 ** |
| Genotype | 2 | 7.25 ** | Genotype | 2 | 4.47 * | ||
| Tissue | 3 | 426.93 ** | Tissue | 3 | 107.91 ** | ||
| NPK * Genotype | 4 | 1.24 | NPK * Genotype | 4 | 3.87 ** | ||
| NPK * Tissue | 6 | 4.99 ** | NPK * Tissue | 6 | 6.6 ** | ||
| Genotype * Tissue | 6 | 6.84 ** | Genotype * Tissue | 6 | 0.5 | ||
| NPK * Genotype * Tissue | 12 | 0.84 | NPK * Genotype * Tissue | 12 | 0.86 | ||
| Ca | NPK | 2 | 0.43 | Mo | NPK | 2 | 0.85 |
| Genotype | 2 | 10.53 ** | Genotype | 2 | 5.89 ** | ||
| Tissue | 3 | 1442.54 ** | Tissue | 3 | 18.74 ** | ||
| NPK * Genotype | 4 | 2.31 * | NPK * Genotype | 4 | 1.14 | ||
| NPK * Tissue | 6 | 2.58 * | NPK * Tissue | 6 | 2.7 | ||
| Genotype * Tissue | 6 | 6.26 ** | Genotype * Tissue | 6 | 2.08 | ||
| NPK * Genotype * Tissue | 12 | 2.61 ** | NPK * Genotype * Tissue | 12 | 0.18 | ||
| Ni | NPK | 2 | 1.26 | ||||
| Genotype | 2 | 3.07 | |||||
| Tissue | 3 | 12.28 ** | |||||
| NPK * Genotype | 4 | 1.3 | |||||
| NPK * Tissue | 6 | 1.02 | |||||
| Genotype * Tissue | 6 | 2.64 * | |||||
| NPK * Genotype * Tissue | 12 | 0.68 | |||||
| Tissue | Grouping | Tissue | Grouping | Tissue | Grouping | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DM | Grain | A | N | Grain | A | P | Grain | A |
| Stem | B | Leaf | A | Leaf | B | |||
| Leaf | C | Stem | B | Stem | C | |||
| Cob | D | Cob | C | Cob | D | |||
| K | Stem | A | Mg | Leaf | A | Ca | Leaf | A |
| Leaf | B | Stem | B | Stem | B | |||
| Grain | C | Grain | B | Grain | C | |||
| Cob | C | Cob | C | Cob | D | |||
| S | Leaf | A | Zn | Grain | A | Fe | Leaf | A |
| Grain | B | Leaf | B | Stem | B | |||
| Stem | C | Stem | B | Grain | C | |||
| Cob | D | Cob | B | Cob | C | |||
| Cu | Leaf | A | Mn | Leaf | A | Mo | Grain | A |
| Stem | B | Grain | A | Cob | B | |||
| Cob | C | Cob | B | Leaf | B | |||
| Grain | C | Stem | C | Stem | C | |||
| Ni | Cob | A | ||||||
| Stem | B | |||||||
| Grain | B | |||||||
| Leaf | B | |||||||
| Fertilisation Level | N (kg ha−1) | P (kg ha−1) | K (kg ha−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| N0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| N1 | 120 | 80.41 | 179.28 |
| N2 | 300 | 80.41 | 179.28 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bojtor, C.; Mousavi, S.M.N.; Illés, Á.; Golzardi, F.; Széles, A.; Szabó, A.; Nagy, J.; Marton, C.L. Nutrient Composition Analysis of Maize Hybrids Affected by Different Nitrogen Fertilisation Systems. Plants 2022, 11, 1593. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11121593
Bojtor C, Mousavi SMN, Illés Á, Golzardi F, Széles A, Szabó A, Nagy J, Marton CL. Nutrient Composition Analysis of Maize Hybrids Affected by Different Nitrogen Fertilisation Systems. Plants. 2022; 11(12):1593. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11121593
Chicago/Turabian StyleBojtor, Csaba, Seyed Mohammad Nasir Mousavi, Árpád Illés, Farid Golzardi, Adrienn Széles, Atala Szabó, János Nagy, and Csaba L. Marton. 2022. "Nutrient Composition Analysis of Maize Hybrids Affected by Different Nitrogen Fertilisation Systems" Plants 11, no. 12: 1593. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11121593
APA StyleBojtor, C., Mousavi, S. M. N., Illés, Á., Golzardi, F., Széles, A., Szabó, A., Nagy, J., & Marton, C. L. (2022). Nutrient Composition Analysis of Maize Hybrids Affected by Different Nitrogen Fertilisation Systems. Plants, 11(12), 1593. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11121593













