Virulence of Rigidoporus microporus Isolates Causing White Root Rot Disease on Rubber Trees (Hevea brasiliensis) in Malaysia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Source of White Root Rot Pathogen
2.2. Morphological Characterization of White Root Rot Pathogen
2.3. Molecular Identification of White Root Rot Pathogen
2.3.1. DNA Extraction
2.3.2. PCR Amplification
2.3.3. DNA Sequencing
2.3.4. Phylogenetic Tree Analysis
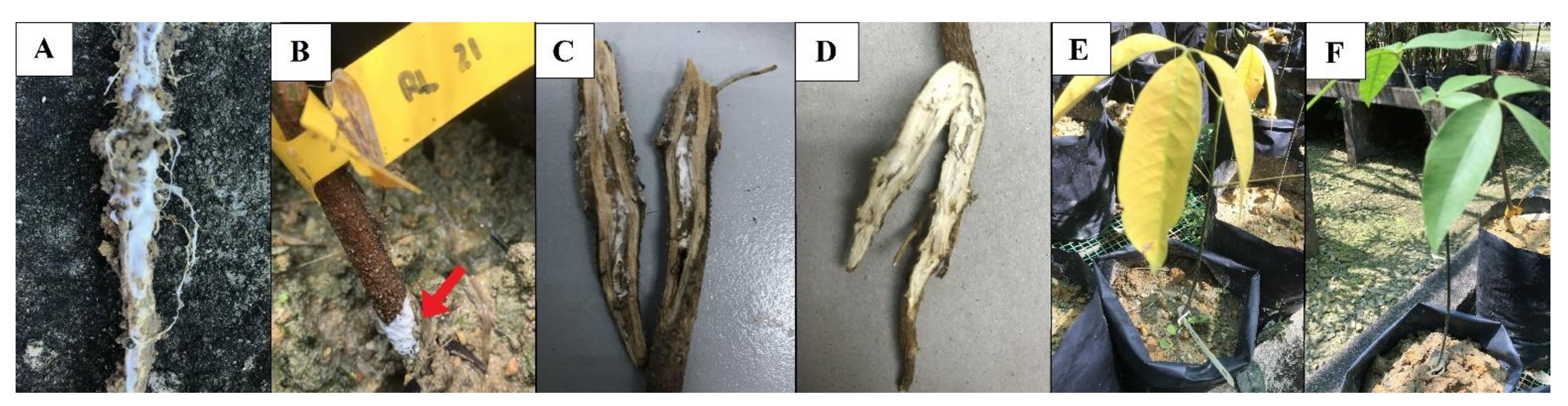
2.3.5. Pathogenicity Test
2.3.6. Disease Assessment
Xsum × SH
2.4. Cultural Characterization of R. microporus Isolates
2.4.1. Effects of pH on Mycelial Growth
2.4.2. Effects of Temperature on Mycelial Growth
2.4.3. Effects of Light Regime on Mycelial Growth
2.5. Experimental Design and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
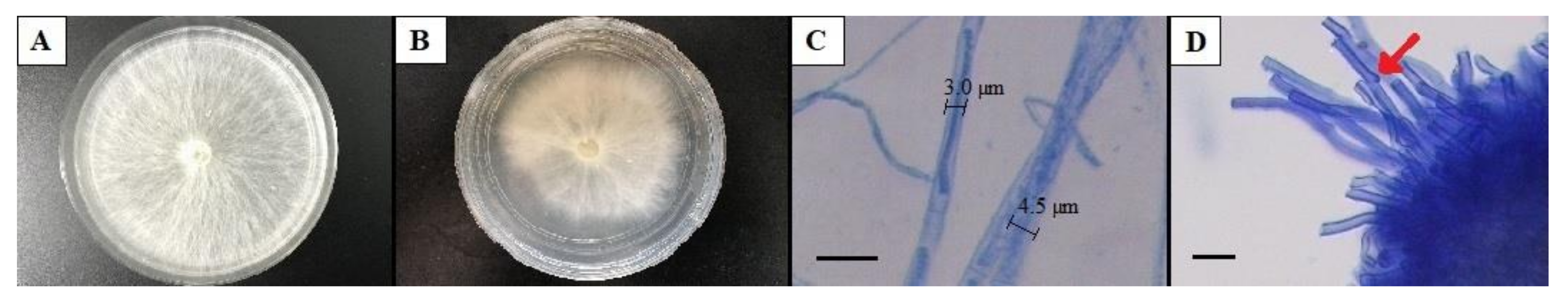
3.1. Morphological Characterization of White Root Rot Pathogen
3.2. Molecular Identification of White Root Rot Pathogen
3.3. Phylogenetic Analysis
3.4. Pathogenicity Test
3.5. Virulence of R. microporus Isolates
3.6. Cultural Characterization of R. microporus Most Virulent Isolate
3.6.1. Effects of pH on Mycelial Growth
3.6.2. Effects of Temperature on Mycelial Growth
3.6.3. Effects of Light Regime on Mycelial Growth
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kaewchai, S.; Soytong, K. Application of biofungicides against Rigidoporus microporus causing white root disease of rubber trees. J. Agric. Technol. 2010, 6, 349–363. [Google Scholar]
- Prasetyo, J.; Aeny, T.N. The Preventive Control of White Root Rot Disease in Small Holder Rubber Plantation Using Botanical, Biological and Chemical Agents. J. Hama Penyakit Tumbuh. Trop. 2013, 13, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sail, R.M.; Ahmad, M. Enhancing socio-economy of rubber smallholders through effective transfer of technology. In Proceedings of the National Rubber Economic Conference (NREC), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 23–24 June 2009; pp. 134–142. [Google Scholar]
- Chaiharn, M.; Sujada, N.; Pathom-Aree, W.; Lumyong, S. Biological control of Rigidoporus microporus the cause of white root disease in rubber using PGPRs in vivo. Chiang Mai J. Sci. 2019, 46, 850–866. [Google Scholar]
- Chee, K.H. Recent development in rubber disease management. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Plant Protection in the Tropics, Genting Highlands, Malaysia, 20–23 March 1990; Volume IV; Malaysia PLant Protection Society: Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 1990; Volume IV, pp. 88–94. [Google Scholar]
- Fatin Farhana, A.H.K.; Shamsul Bahri, A.R.; Vu Thanh, T.A.; Zakaria, L. Morphological features of Rigidoporus microporus isolated from infected malaysian rubber clones. Malays. J. Microsc. 2017, 13, 17–23. [Google Scholar]
- Nandris, D.; Nicole, M.; Geiger, J.P. Root rot diseases of rubber trees. Plant Dis. 1987, 71, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holiday, P. Fungal diseases of tropical crops. Australas Plant Pathol. 1980, 9, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaewchai, S.; Wang, H.K.; Lin, F.; Hyde, K.D.; Soytong, K. Genetic variation among isolates of Rigidoporus microporus causing white root disease of rubber trees in Southern Thailand revealed by ISSR markers and pathogenicity. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2009, 3, 641–648. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Li, N.; Ni, D.; Yang, Y.; Wang, X. Differences in the characteristics and pathogenicity of Colletotrichum camelliae and C. fructicola isolated from the tea plant [ Camellia sinensis (L.) O. Kuntze]. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jesus Eufrade Junior, H.; Ohto, J.M.; da Silva, L.L.; Lara Palma, H.A.; Ballarin, A.W. Potential of rubberwood (Hevea brasiliensis) for structural use after the period of latex extraction: A case study in Brazil. J. Wood Sci. 2015, 61, 384–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pethin, D.; Nakkanong, K.; Nualsri, C. Performance and genetic assessment of rubber tree clones in Southern Thailand. Sci. Agric. 2015, 72, 306–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Woraathasin, N.; Nakkanong, K.; Nualsri, C. Cloning and expression analysis of HbPR-1b and HbPR-3 in Hevea brasiliensis during inoculation with Rigidoporus microporus. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 2017, 20, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaewchai, S.; Lin, F.C.; Wang, H.K.; Soytong, K.; Soytong, K. Characterization of Rigidoporus microporus isolated from rubber trees based on morphology and ITS sequencing. J. Agric. Technol. 2010, 6, 289–298. [Google Scholar]
- Go, W.Z.; H’ng, P.S.; Wong, M.Y.; Tan, G.H.; Luqman Chuah, A.; Salmiah, U.; Toczyłowska-Mamińska, R.; Soni, O.; Wong, W.Z.; Chin, K.L.; et al. Occurrence and characterisation of mycoflora in soil of different health conditions associated with white root rot disease in Malaysia rubber plantation. J. Rubber Res. 2015, 18, 159–170. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y.H.; Chang, J.Y.; Liu, E.T.; Chao, C.P.; Huang, J.W.; Chang, P.F.L. Development of a molecular marker for specific detection of Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cubense race 4. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2009, 123, 353–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 7.0 for Bigger Datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wattanasilakorn, S.; Wattanasilakorn, S.; Sdoodee, S.; Nualsri, C.; Chuenchit, S. Screening of rubber (Hevea brasiliensis Muell. Arg.) rootstocks for the white root disease resistance. Int. J. Agric. Technol. 2012, 8, 2385–2395. [Google Scholar]
- Hood, I.A. The mycology of the basidiomycetes. In Proceedings of the Australian Centre for International Agricultural Research (ACIAR) Proceedings, Yogykarta, Indonesia, 7–9 February 2006; Volume 124, pp. 34–45. [Google Scholar]
- Zabel, R.A.; Morrell, J.J. The characteristics and classification of fungi and bacteria. In Wood Microbiology; Zabel, R.A., Morrell, J.J., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 55–98. ISBN 9780128194652. [Google Scholar]
- Oghenekaro, A.O.; Miettinen, O.; Omorusi, V.I.; Evueh, G.A.; Farid, M.A.; Gazis, R.; Asiegbu, F.O. Molecular phylogeny of Rigidoporus microporus isolates associated with white rot disease of rubber trees (Hevea brasiliensis). Fungal Biol. 2014, 118, 495–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oghenekome, U.O. Natural rubber, Hevea brasiliensis (Willd. ex A. Juss.) Müll. Arg., germplasm collection in the Amazon Basin, Brazil: A retrospective. Econ. Bot. 2004, 58, 544–555. [Google Scholar]
- Burgess, T.I.; Wingfield, M.J. Impact of Fungal Pathogens in Natural Forest Ecosystems: A Focus on Eucalyptus. In Microorganisms in Plant Conservation and Biodiversity; Sivasithamparam, K., Dixon, K.W., Barrett, R.L., Eds.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Amsterdam, Germany, 2002; pp. 285–306. ISBN 0306480999. [Google Scholar]
- Farid, A.M.; Lee, S.S.; Maziah, Z.; Patahayah, M. Pathogenicity of Rigidoporus microporus and Phellinus noxius against four major plantation tree species in Peninsular Malaysia. J. Trop. For. Sci. 2009, 21, 289–298. [Google Scholar]
- Omorusi, V.I. Effects of white root rot disease on Hevea brasiliensis (Muell. Arg.)—Challenges and control approach. In Plant Science; Dhal, N.K., Sahu, S.C., Eds.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2012; pp. 139–152. ISBN 978-953-51-0905-1. [Google Scholar]
- Prasetyo, J.; Aeny, T.N.; Suharjo, R. The corelations between white rot (Rigidoporus lignosus L.) incidence and soil characters of rubber ecosystem in Penumangan Baru, Lampung. J. Hama Penyakit Tumbuh. Trop. 2009, 9, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, J.Á.C.; Hanafi, M.M.; Syed Omar, S.R.; Rafii, Y.M. Chemical characteristics of representative high aluminium saturation soil as affected by addition of soil amendments in a closed incubation system. Malays. J. Soil. Sci. 2009, 13, 13–28. [Google Scholar]
- Liyanage, G.W.; Liyanage, A.D.S.; Peries, O.S.; Halangoda, L. Studies on the variability and pathogenicity of Rigidoporus lignosus. J. Rubber Res. Inst. Sri. Lanka 1977, 54, 363–372. [Google Scholar]
- Rodesuchit, A.; Suchatgul, S.; Klaewklong, B.; Damnoi, S. Efficacy of fertilizers to control white root disease of rubber caused by Rigidoporus microporus at the early planting stages. Rubber Thai. J. 2012, 1, 62–72. [Google Scholar]
- Semangun, H. Penyakit-Penyakit Tanaman Perkebunan di Indonesia; Gadjah Mada Universiti Press: Yogyakarta, Indonesia, 2000; ISBN 9794204625. [Google Scholar]
- Wahyuni, M.; Simanjuntak, J.H.; Sitompul, I.O. Efektivitas fungisida berbahan aktif heksakonazol terhadap penyakit jamur akar putih bibit tanaman karet (Hevea brasiliensis). Agrotekma J. Agroteknologi Ilmu Pertan. 2018, 3, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dede, A.P.O.; Akpaja, E.O.; Galillee, J.E. Effect of pH on the growth of the white root rot pathogen, Rigidoporus lignosus (Klotzsch) Imazeki, on selected para rubber sustaining soils in Nigeria. Afr. Sci. 2011, 12, 175–179. [Google Scholar]
- Hashim, I.; Azaldin, M.Y. Interaction of sulphur with soil pH and root diseases of rubber. J. Rubber Res. Inst. Malays. 1985, 33, 59–69. [Google Scholar]
- Oghenekaro, A.O.; Daniel, G.; Asiegbu, F.O. The saprotrophic wood-degrading abilities of Rigidoporus microporus. Silva Fenn. 2015, 49, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



| Isolate ID | Host (Clone) | Location |
|---|---|---|
| RL20 | RRIM2008 | RRIMINIS Seri Iskandar, Perak. |
| RL21 | PB260 | Sarikei, Sarawak. |
| RL22 | RRIM2024 | RRIM, Sungai Buloh. |
| RL25 | PB350 | Kg. Tohor, Negeri Sembilan. |
| RL26 | RRIM600 | Field 7C, Kota Tinggi, Johor. |
| Scheme | Above-Ground Symptom | Below-Ground Symptom |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | Healthy, green leaves | Not found in the root fungal infections |
| 1 | 1–25% yellow of foliage | Fungal infections on the root are less than 1% |
| 2 | 26–50% wilting | 1–10% fungal infections on the root |
| 3 | 51–75% defoliation | 11–50% fungal infections on the root |
| 4 | 76–100% death of plant | 51–90% fungal infection on the root |
| 5 | - | Fungal infections on the root of more than 90% |
| Isolate ID | Disease Severity Index * | Average DSI of Above- and Below-Ground Symptoms | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Foliar Discoloration | Root Rotting | ||
| RL20 | 52.08 | 80.00 | 66.04 |
| RL21 | 76.04 | 85.00 | 80.52 |
| RL22 | 57.29 | 80.00 | 68.65 |
| RL25 | 31.25 | 55.00 | 43.13 |
| RL26 | 43.75 | 65.00 | 54.38 |
| Isolate ID | Mortality Rate per Month (%) * | Mortality Rate 6 MAI (%) * | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | ||
| RL20 | 0.00 | 16.67 | 20.83 | 12.50 | 8.33 | 8.33 | 66.66 |
| RL21 | 0.00 | 20.83 | 25.00 | 16.67 | 12.50 | 8.33 | 83.33 |
| RL22 | 0.00 | 12.50 | 12.50 | 16.67 | 16.67 | 12.50 | 70.84 |
| RL25 | 0.00 | 4.17 | 8.33 | 12.50 | 12.50 | 12.50 | 50.00 |
| RL26 | 0.00 | 12.50 | 12.50 | 12.50 | 12.50 | 12.50 | 62.50 |
| pH Value | Colony Diameter (mm) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RL20 | RL21 | RL 22 | RL 25 | RL26 | |
| 3.5 | 15.42 f | 19.80 f | 12.19 d | 10.42 e | 8.49 f |
| 4 | 22.93 e | 34.34 e | 29.56 c | 16.63 d | 18.21 e |
| 4.5 | 25.34 de | 37.33 de | 31.16 c | 18.94 cd | 21.81 d |
| 5 | 27.53 cd | 38.24 cd | 31.41 c | 19.16 cd | 24.24 cd |
| 5.5 | 27.25 cd | 38.79 cd | 32.11 c | 21.66 c | 25.77 bc |
| 6 | 31.87 b | 43.05 b | 44.40 b | 36.89 a | 39.80 a |
| 6.5 | 38.32 a | 55.57 a | 52.65 a | 36.94 a | 39.96 a |
| 7 | 29.55 bc | 41.16 bc | 43.73 b | 29.48 b | 27.57 b |
| p-value | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
| Temperature (°C) | Colony Diameter (mm) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RL20 | RL21 | RL 22 | RL 25 | RL26 | |
| 20 | 18.51 c | 30.36 c | 21.34 c | 15.49 c | 11.93 c |
| 25 | 26.47 b | 35.57 b | 30.49 b | 20.65 b | 24.90 b |
| 30 | 30.45 a | 41.64 a | 35.62 a | 24.97 a | 27.11 a |
| 35 | 13.54 d | 21.07 d | 16.69 d | 13.62 c | 10.33 c |
| 40 | 0.00 e | 0.00 e | 0.00 e | 0.00 d | 0.00 d |
| p-value | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
| Photoperiods | Colony Diameter (mm) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RL20 | RL21 | RL 22 | RL 25 | RL26 | |
| 12 h Light and 12 h Darkness | 27.34 a | 38.12 a | 31.54 a | 22.3 a | 27.53 a |
| 24 h Darkness | 27.25 a | 38.79 a | 32.11 a | 21.66 a | 26.37 a |
| 24 h Light | 25.19 a | 38.08 a | 27.85 b | 19.19 a | 26.87 a |
| p-value | 0.337 | 0.806 | <0.01 | 1.125 | 0.738 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Go, W.Z.; Chin, K.L.; H’ng, P.S.; Wong, M.Y.; Luqman, C.A.; Surendran, A.; Tan, G.H.; Lee, C.L.; Khoo, P.S.; Kong, W.J. Virulence of Rigidoporus microporus Isolates Causing White Root Rot Disease on Rubber Trees (Hevea brasiliensis) in Malaysia. Plants 2021, 10, 2123. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10102123
Go WZ, Chin KL, H’ng PS, Wong MY, Luqman CA, Surendran A, Tan GH, Lee CL, Khoo PS, Kong WJ. Virulence of Rigidoporus microporus Isolates Causing White Root Rot Disease on Rubber Trees (Hevea brasiliensis) in Malaysia. Plants. 2021; 10(10):2123. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10102123
Chicago/Turabian StyleGo, Wen Ze, Kit Ling Chin, Paik San H’ng, Mui Yun Wong, Chuah Abdullah Luqman, Arthy Surendran, Geok Hun Tan, Chuan Li Lee, Pui San Khoo, and Wai Jern Kong. 2021. "Virulence of Rigidoporus microporus Isolates Causing White Root Rot Disease on Rubber Trees (Hevea brasiliensis) in Malaysia" Plants 10, no. 10: 2123. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10102123
APA StyleGo, W. Z., Chin, K. L., H’ng, P. S., Wong, M. Y., Luqman, C. A., Surendran, A., Tan, G. H., Lee, C. L., Khoo, P. S., & Kong, W. J. (2021). Virulence of Rigidoporus microporus Isolates Causing White Root Rot Disease on Rubber Trees (Hevea brasiliensis) in Malaysia. Plants, 10(10), 2123. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10102123







