An Application of Cold Atmospheric Plasma to Enhance Physiological and Biochemical Traits of Basil
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussions
2.1. Microbial Load
2.2. Relative Water Content
2.3. Ion Leakage
2.4. Total Protein and Proline
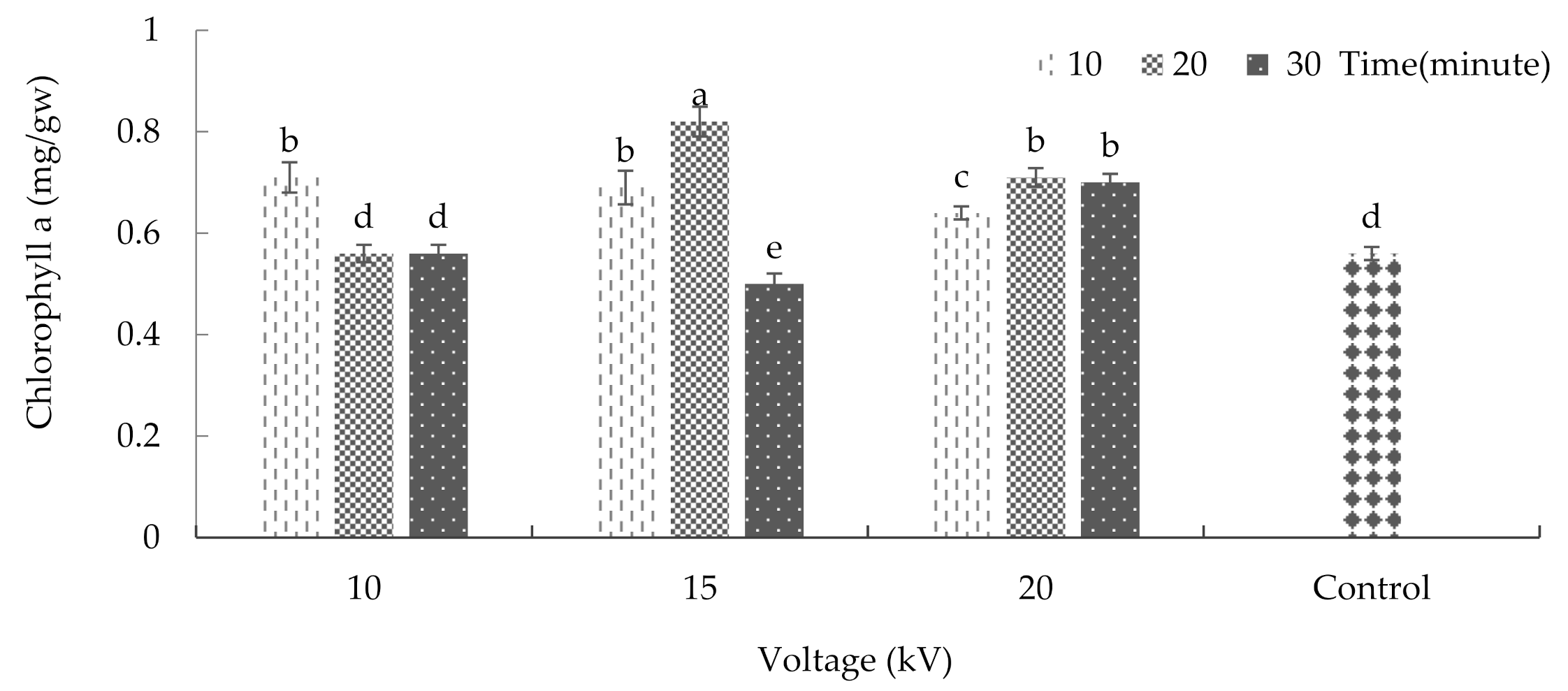
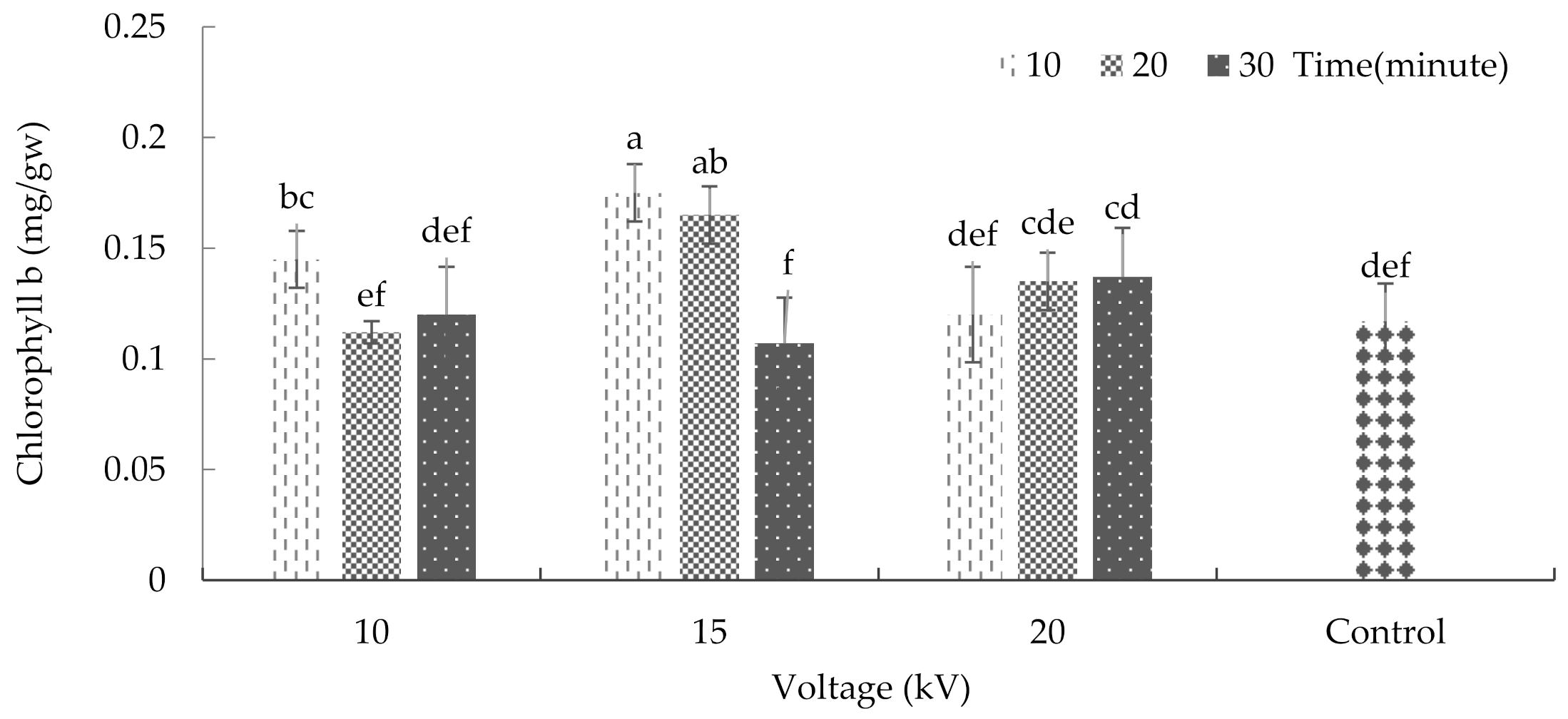
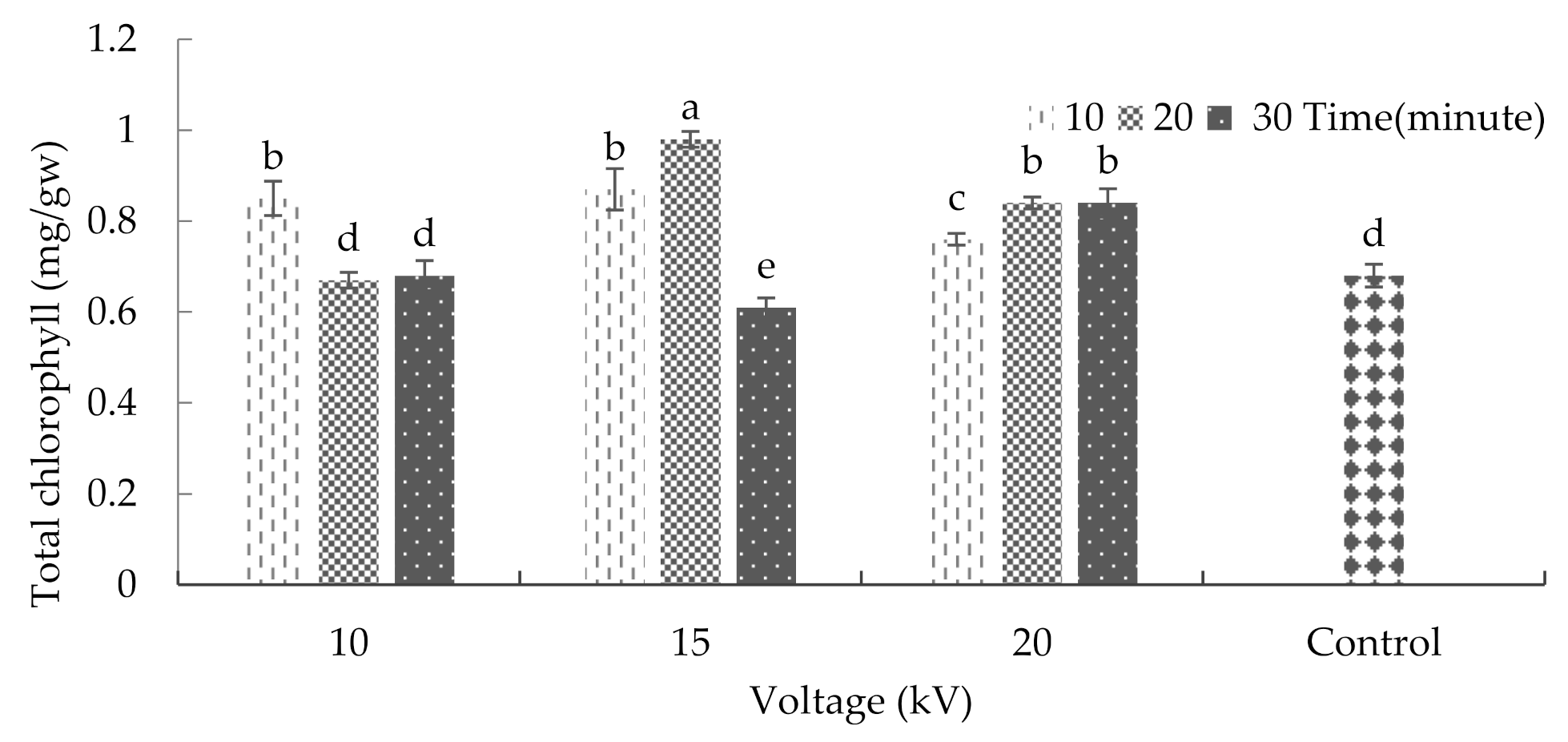
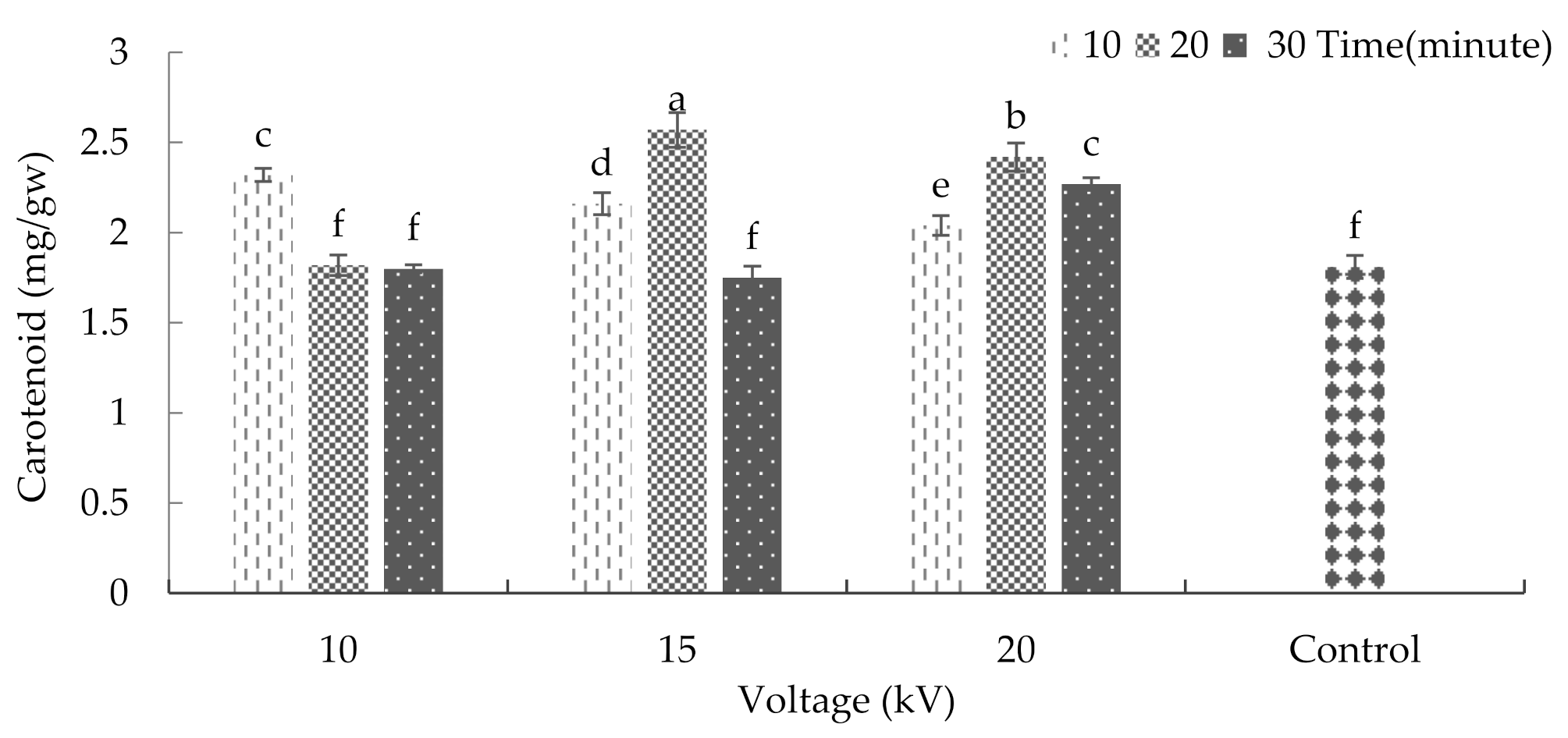
2.5. Chlorophyll and Carotenoid
2.6. Antioxidant Activity
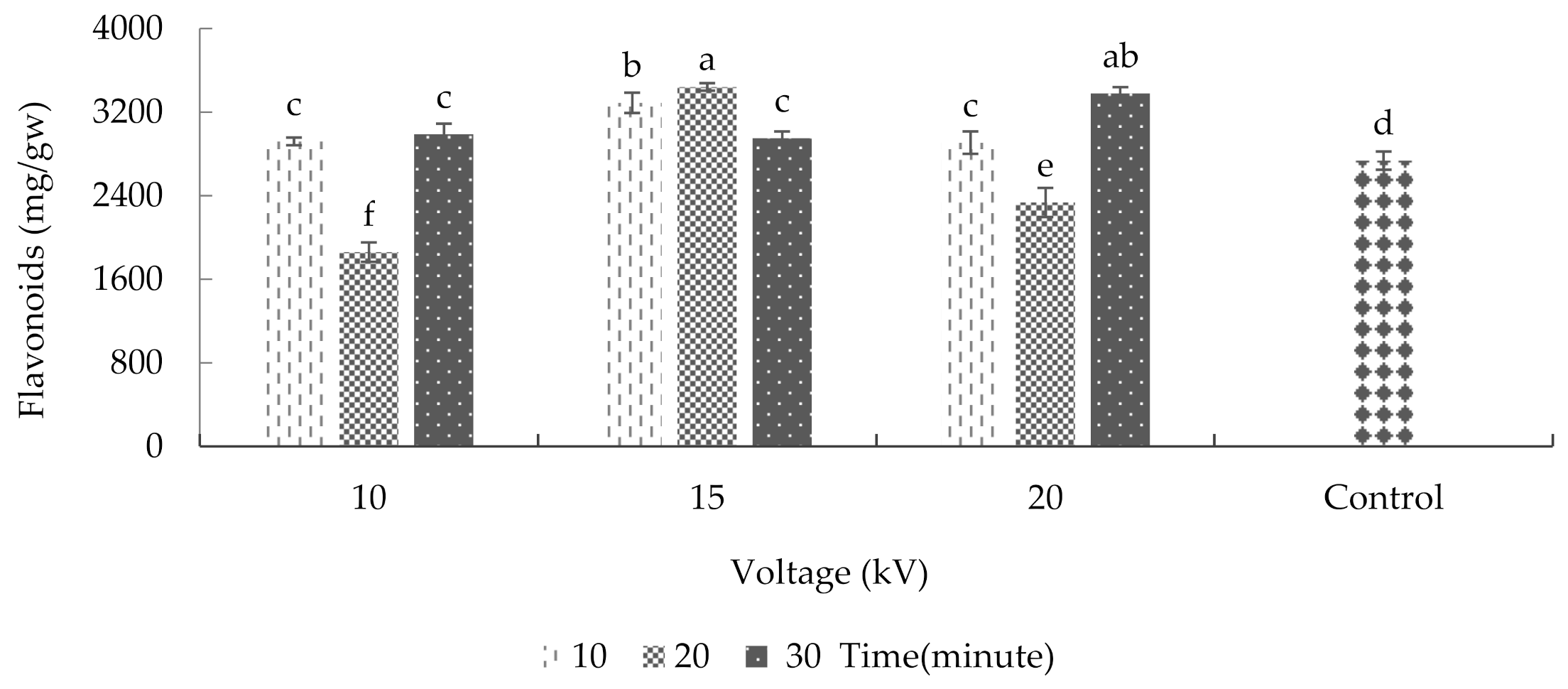
2.7. Total Flavonoid Content
2.8. Sugar, Starch, and Total Phenol
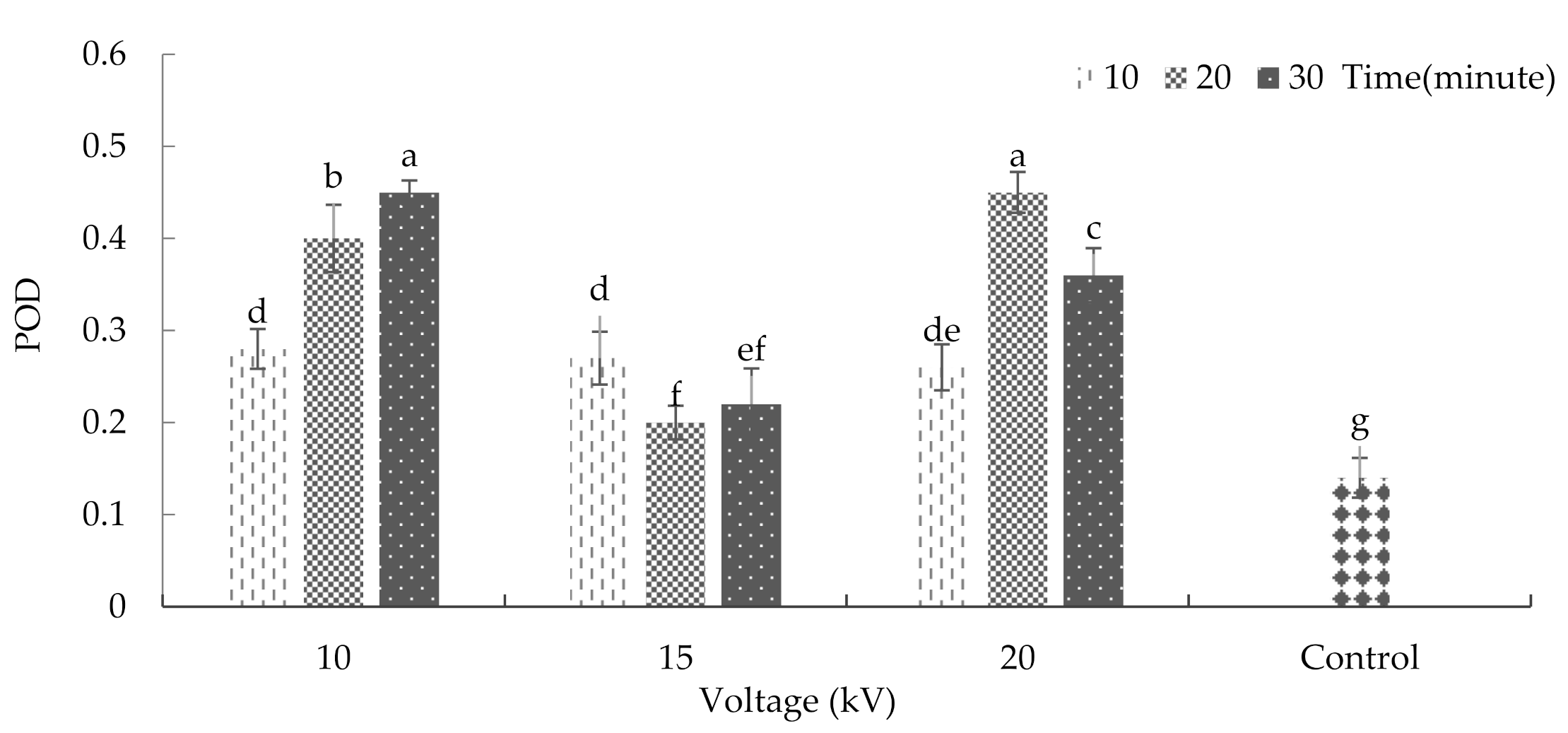
2.9. Super Oxidase Dismutase Enzyme, Catalase, and Peroxidize
3. Materials and Methods
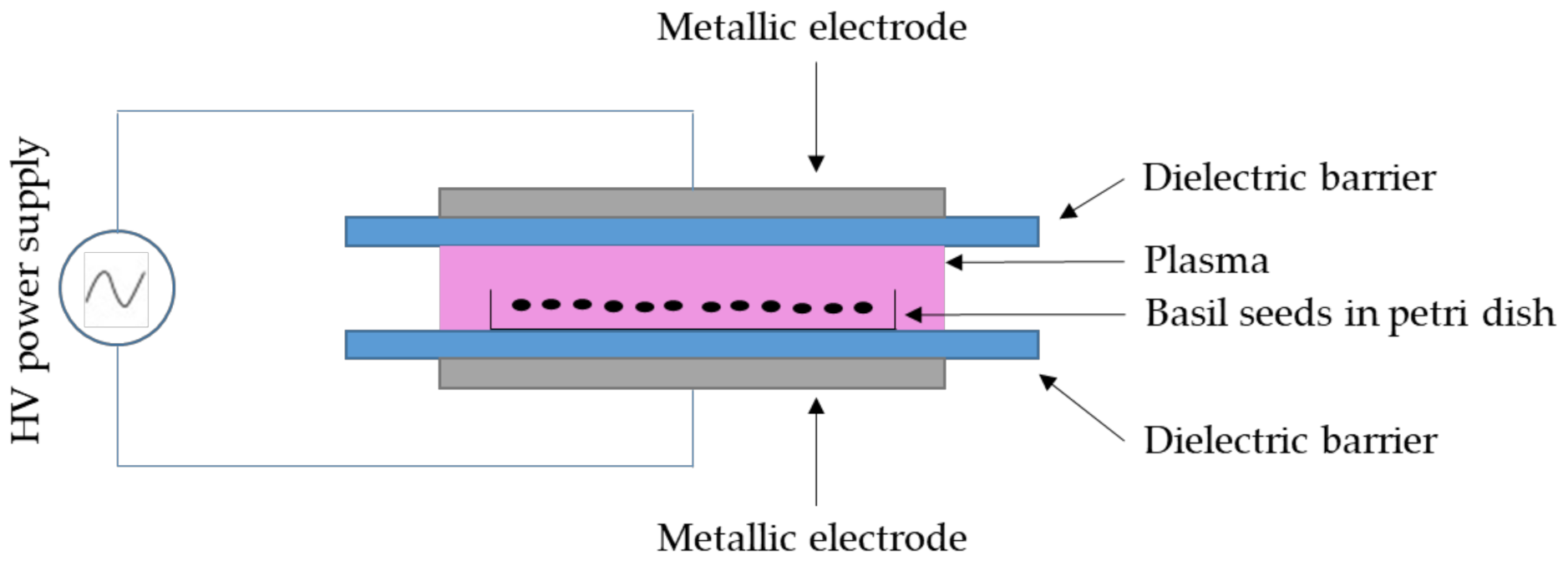
3.1. Atmospheric Cold Plasma (ACP) System
3.2. Sampling, Culturing, and Storage Conditions after Plasma Radiation
3.3. Microbial Load
3.4. Relative Water Content
3.5. Ion Leakage
3.6. Proline
3.7. Total Protein
3.8. Chlorophyll and Carotenoid of Leaf
3.9. Antioxidant Activity, Phenol, and Flavonoids
3.10. Soluble Sugars
3.11. Starch
3.12. Antioxidant Enzyme Activity
3.13. Leaf Color Analysis
3.14. Data Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mishra, L.K.; Sarkar, D.; Mentreddy, R.; Shetty, K. Evaluation of phenolic bioactive-linked anti-hyperglycemic and Helicobacter pylori inhibitory activities of Asian Basil (Ocimum spp.) varieties. J. Herb. Med. 2020, 20, 100310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahrajabian, M.H.; Sun, W.; Cheng, Q. Chemical components and pharmacological benefits of Basil (Ocimum Basilicum): A review. Int. J. Food Prop. 2020, 23, 1961–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, M.M.A.; Morais, L.C.; Luz, J.M.Q.; Pasqual, M.; Dória, J. Transatlantic and ancestral routes and the pharmacological and biological potential of Ocimum basilicum L. A Review. Eur. J. Med. Plants 2020, 31, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, H.; Kumari, P.; Bontempi, E.; Yadav, S. Medicinal plants: Treasure trove for green synthesis of metallic nanoparticles and their biomedical applications. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2020, 24, 101518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Y.; An, X.; Wang, S.; Sun, M.; Zhou, H. Basil polysaccharides: A review on extraction, bioactivities and pharmacological applications. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2020, 28, 115179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, L.; Jiafeng, J.; Jiangang, L.; Minchong, S.; Xin, H.; Hanliang, S.; Yuanhua, D. Effects of cold plasma treatment on seed germination and seedling growth of soybean. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 5859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, R.; Prasad, P.; Mohan, R.; Verma, M.K.; Kumar, B. Radiofrequency cold plasma treatment enhances seed germination and seedling growth in variety CIM-Saumya of sweet basil (Ocimum basilicum L.). J. Appl. Res. Med. Aromat. Plants 2019, 12, 78–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surowsky, B.; Fischer, A.; Schlueter, O.; Knorr, D. Cold plasma effects on enzyme activity in a model food system. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2013, 19, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullen, P.J.; Tiwari, B.K.; Valdramidis, V. (Eds.) Novel Thermal and Non-Thermal Technologies for Fluid Foods; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Puač, N.; Gherardi, M.; Shiratani, M. Plasma agriculture: A rapidly emerging field. Plasma Process. Polym. 2018, 15, 1700174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rifna, E.J.; Ramanan, K.R.; Mahendran, R. Emerging technology applications for improving seed germination. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 86, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermúdez-Aguirre, D.; Wemlinger, E.; Pedrow, P.; Barbosa-Cánovas, G.; Garcia-Perez, M. Effect of atmospheric pressure cold plasma (APCP) on the inactivation of Escherichia coli in fresh produce. Food Control. 2013, 34, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirumdas, R.; Sarangapani, C.; Annapure, U.S. Cold plasma: A novel non-thermal technology for food processing. Food Biophys. 2015, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertwig, C.; Reineke, K.; Ehlbeck, J.; Knorr, D.; Schlüter, O. Decontamination of whole black pepper using different cold atmospheric pressure plasma applications. Food Control. 2015, 55, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzegorzewski, F.; Ehlbeck, J.; Schlüter, O.; Kroh, L.W.; Rohn, S. Treating lamb’s lettuce with a cold plasma–influence of atmospheric pressure Ar plasma immanent species on the phenolic profile of Valerianella locusta. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 44, 2285–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tappi, S.; Berardinelli, A.; Ragni, L.; Rosa, M.D.; Guarnieri, A.; Rocculi, P. Atmospheric gas plasma treatment of fresh-cut apples. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2014, 21, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, F.D.L.; Cavalcante, R.S.; Cullen, P.J.; Frias, J.M.; Bourke, P.; Fernandes, F.A.; Rodrigues, S. Effects of atmospheric cold plasma and ozone on prebiotic orange juice. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2015, 32, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, B.; Adhikari, M.; Park, G. The effects of plasma on plant growth, development, and sustainability. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 6045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huijser, P.; Schmid, M. The control of developmental phase transitions in plants. Development 2011, 138, 4117–4129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stoica, M.; Stoean, S.; Alexe, P. Overview of biological hazards associated with the consumption of the meat products. J. Agroaliment. Process. Technol. 2014, 20, 192–197. [Google Scholar]
- Olatunde, O.O.; Benjakul, S.; Vongkamjan, K. High voltage cold atmospheric plasma: Antibacterial properties and its effect on quality of Asian sea bass slices. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2019, 52, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Shi, J.; Kong, M.G. Physical mechanisms of inactivation of Bacillus subtilis spores using cold atmospheric plasmas. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2006, 34, 1310–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lugojan, C.; Ciulca, S. Evaluation of relative water content in winter wheat. J. Hortic. Fores. Biotechnol. 2011, 15, 173–177. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, H.; Zhu, X.; Chen, K.; Wang, S.; Zhang, C. Silicon alleviates oxidative damage of wheat plants in pots under drought. Plant Sci. 2005, 169, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilík, P.; Špundová, M.; Šicner, M.; Melkovičová, H.; Kučerová, Z.; Krchňák, P.; Trtílek, M. Estimating heat tolerance of plants by ion leakage: A new method based on gradual heating. New Phytol. 2018, 218, 1278–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Wang, G.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, L. Protective effect of nitric oxide against oxidative stress under ultraviolet-B radiation. Nitric Oxide 2005, 13, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, R.W.; Campbell, B.D.; Bloor, S.J.; Swinny, E.E.; Markham, K.R.; Ryan, K.G.; Fountain, D.W. Responses to UV-B radiation in Trifolium repens L. physiological links to plant productivity and water availability. Plant Cell Environ. 2003, 26, 603–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mujahid, Z.; Tounekti, T.; Khemira, H. Cold plasma treatment to release dormancy and improve growth in grape buds: A promising alternative to natural chilling and rest breaking chemicals. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, M.; Foolad, M. Roles of glycine betaine and proline in improving plant abiotic stress resistance. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2007, 59, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinari, H.B.C.; Marur, C.J.; Daros, E.; De Campos, M.K.F.; De Carvalho, J.F.R.P.; Filho, J.C.B.; Vieira, L.G.E. Evaluation of the stress-inducible production of proline in transgenic sugarcane (Saccharum spp.): Osmotic adjustment, chlorophyll fluorescence and oxidative stress. Physiol. Plant. 2007, 130, 218–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maroneze, M.M.; Zepka, L.Q.; Lopes, E.J.; Pérez-Gálvez, A.; Roca, M. Chlorophyll oxidative metabolism during the phototrophic and heterotrophic growth of Scenedesmus obliquus. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reigosa, M.J.; Pedrol, N.; González, L. (Eds.) Allelopathy: A physiological Process with Ecological Implications; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Faragher, J.D.; Mor, Y.; Johnson, F. Role of aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid (ACC) in control of ethylene production in fresh and cold-stored cut roses. J. Exp. Bot. 1987, 38, 1839–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramazzina, I.; Berardinelli, A.; Rizzi, F.; Tappi, S.; Ragni, L.; Sacchetti, G.; Rocculi, P. Effect of cold plasma treatment on physico-chemical parameters and antioxidant activity of minimally processed kiwifruit. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2015, 107, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirgedaitė-Šėžienė, V.; Mildažienė, V.; Žemaitis, P.; Ivankov, A.; Koga, K.; Shiratani, M.; Baliuckas, V. Long-term response of Norway spruce to seed treatment with cold plasma: Dependence of the effects on the genotype. Plasma Process. Polym. 2021, 18, 2000159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, M.Y.; Lee, S.J.; Min, S.C. Mandarin preservation by microwave-powered cold plasma treatment. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2017, 39, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, M.; Ghoranneviss, M. Effects of cold plasma treatment on antioxidants activity, phenolic contents and shelf life of fresh and dried walnut (Juglans regia L.) cultivars during storage. LWT 2016, 73, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, A.I.; Liao, X.; Cullen, P.J.; Liu, D.; Xiang, Q.; Wang, J.; Ding, T. Effects of nonthermal plasma technology on functional food components. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2018, 17, 1379–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, B.; Xiong, S.; Li, X.; Li, L.; Xie, F.; Chen, L. Effect of oxygen glow plasma on supramolecular and molecular structures of starch and related mechanism. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 37, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorram, S.; Zakerhamidi, M.S.; Karimzadeh, Z. Polarity functions’ characterization and the mechanism of starch modification by DC glow discharge plasma. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 127, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirumdas, R.; Deshmukh, R.R.; Annapure, U.S. Effect of low temperature plasma processing on physicochemical properties and cooking quality of basmati rice. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2015, 31, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herceg, Z.; Kovačević, D.B.; Kljusurić, J.G.; Jambrak, A.R.; Zorić, Z.; Dragović-Uzelac, V. Gas phase plasma impact on phenolic compounds in pomegranate juice. Food Chem. 2016, 190, 665–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, B.; Adhikari, M.; Ghimire, B.; Park, G.; Choi, E.H. Cold atmospheric plasma-activated water irrigation induces defense hormone and gene expression in tomato seedlings. Sci. Reports. 2019, 9, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Xu, Z.; Shen, J.; Li, X.; Ding, L.; Ma, J.; Zhang, Z. Effects and mechanism of atmospheric-pressure dielectric barrier discharge cold plasma on lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) enzyme. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meiqiang, Y.; Mingjing, H.; Buzhou, M.; Tengcai, M. Stimulating effects of seed treatment by magnetized plasma on tomato growth and yield. Plasma Sci. Technol. 2005, 7, 3143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, D.D.; Cameron, A.C. Postharvest shelf life of sweet basil (Ocimum basilicum). HortScience 1994, 29, 102–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Valverde, J.M.; Valero, D.; Martínez-Romero, D.; Guillén, F.; Castillo, S.; Serrano, M. Novel edible coating based on Aloe vera gel to maintain table grape quality and safety. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 7807–7813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritchie, S.W.; Nguyen, H.T.; Holaday, A.S. Leaf water content and gas-exchange parameters of two wheat genotypes differing in drought resistance. Crop. Sci. 1990, 30, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, H.R.; Nasrolahpour-Moghadam, S. Male pistachio seedlings exhibit more efficient protective mechanisms than females under salinity stress. Sci. Hortic. 2016, 211, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiscox, J.T.; Israelstam, G.F. A method for the extraction of chlorophyll from leaf tissue without maceration. Can. J. Bot. 1979, 57, 1332–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, J. Pigments in Vegetables: Chlorophylls and Carotenoids; Van Nostrand Reinhold: New York, NY, USA, 1991; p. 351. [Google Scholar]
- Wojdyło, A.; Oszmiański, J.; Czemerys, R. Antioxidant activity and phenolic compounds in 32 selected herbs. Food Chem. 2007, 105, 940–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oke, F.; Aslim, B.; Ozturk, S.; Altundag, S. Essential oil composition, antimicrobial and antioxidant activities of Satureja cuneifolia Ten. Food Chem. 2009, 112, 874–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menichini, F.; Tundis, R.; Bonesi, M.; Loizzo, M.R.; Conforti, F.; Statti, G.; Di Cindi, B.; Houghton, P.J.; Menichini, F. The influence of fruit ripening on the phytochemical content and biological activity of Capsicum chinense Jacq. cv Habanero. Food Chem. 2009, 114, 553–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, M.; Gilles, K.A.; Hamilton, J.K.; Rebers, P.A.T.; Smith, F. Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal. Chem. 1956, 28, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mc-Cready, R.M.; Guggolz, J.; Silviera, V.; Owens, H.S. Determination of starch and amylase in vegetables. Anal. Chem. 1950, 22, 1156–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozden, M.; Demirel, U.; Kahraman, A. Effects of proline on antioxidant system in leaves of grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.) exposed to oxidative stress by H2O2. Sci. Hortic. 2009, 119, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abarghuei, F.M.; Etemadi, M.; Ramezanian, A.; Esehaghbeygi, A.; Alizargar, J. An Application of Cold Atmospheric Plasma to Enhance Physiological and Biochemical Traits of Basil. Plants 2021, 10, 2088. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10102088
Abarghuei FM, Etemadi M, Ramezanian A, Esehaghbeygi A, Alizargar J. An Application of Cold Atmospheric Plasma to Enhance Physiological and Biochemical Traits of Basil. Plants. 2021; 10(10):2088. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10102088
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbarghuei, Faezeh Mirazimi, Mohammad Etemadi, Asghar Ramezanian, Ali Esehaghbeygi, and Javad Alizargar. 2021. "An Application of Cold Atmospheric Plasma to Enhance Physiological and Biochemical Traits of Basil" Plants 10, no. 10: 2088. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10102088
APA StyleAbarghuei, F. M., Etemadi, M., Ramezanian, A., Esehaghbeygi, A., & Alizargar, J. (2021). An Application of Cold Atmospheric Plasma to Enhance Physiological and Biochemical Traits of Basil. Plants, 10(10), 2088. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10102088






