Genetic Mapping of the HLA1 Locus Causing Hybrid Lethality in Nicotiana Interspecific Hybrids
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Segregation of the Hybrid Lethality Phenotype in the F2 Population
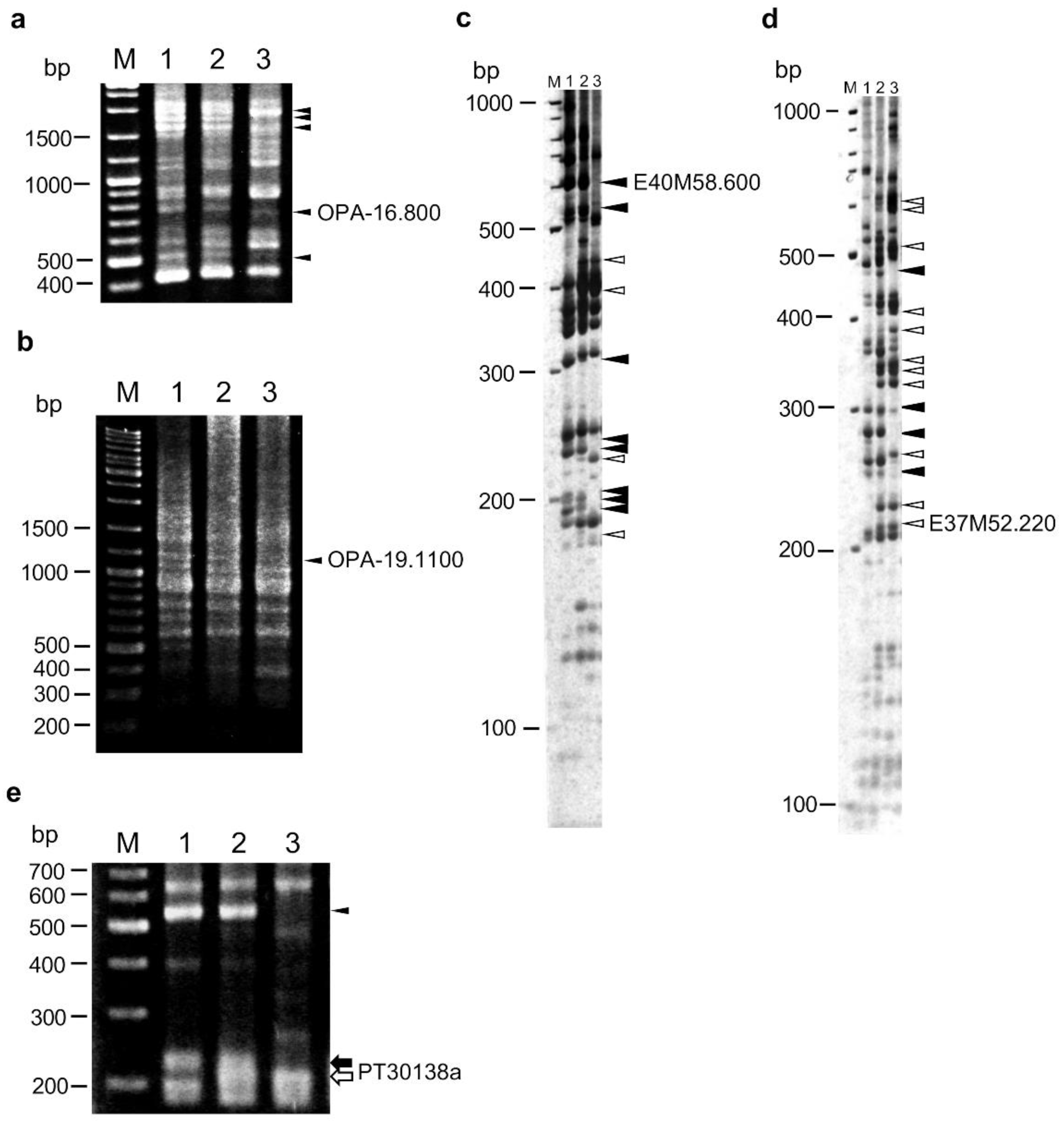
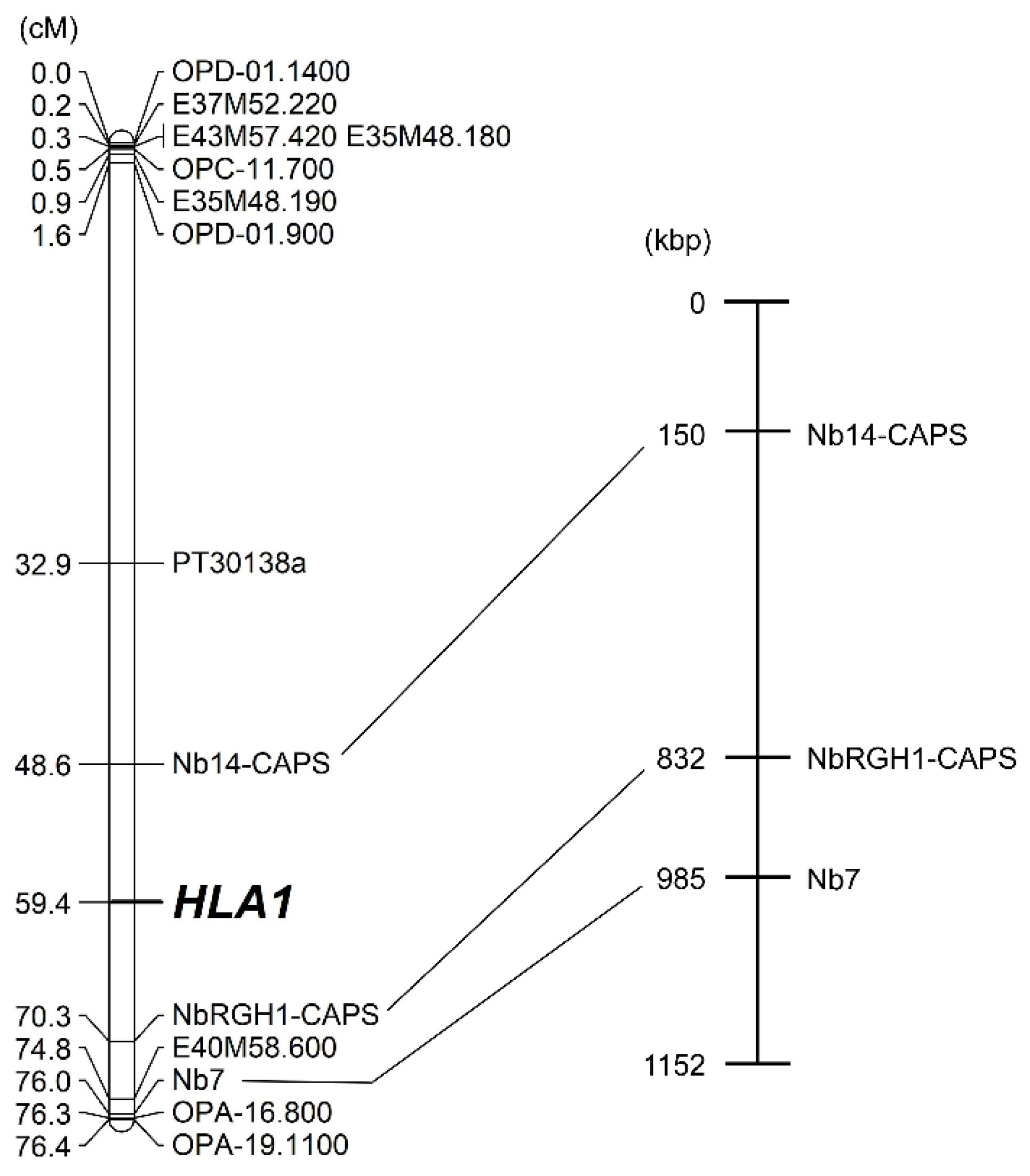
2.2. Construction of a Linkage Map Using RAPD, AFLP, and SSR Markers
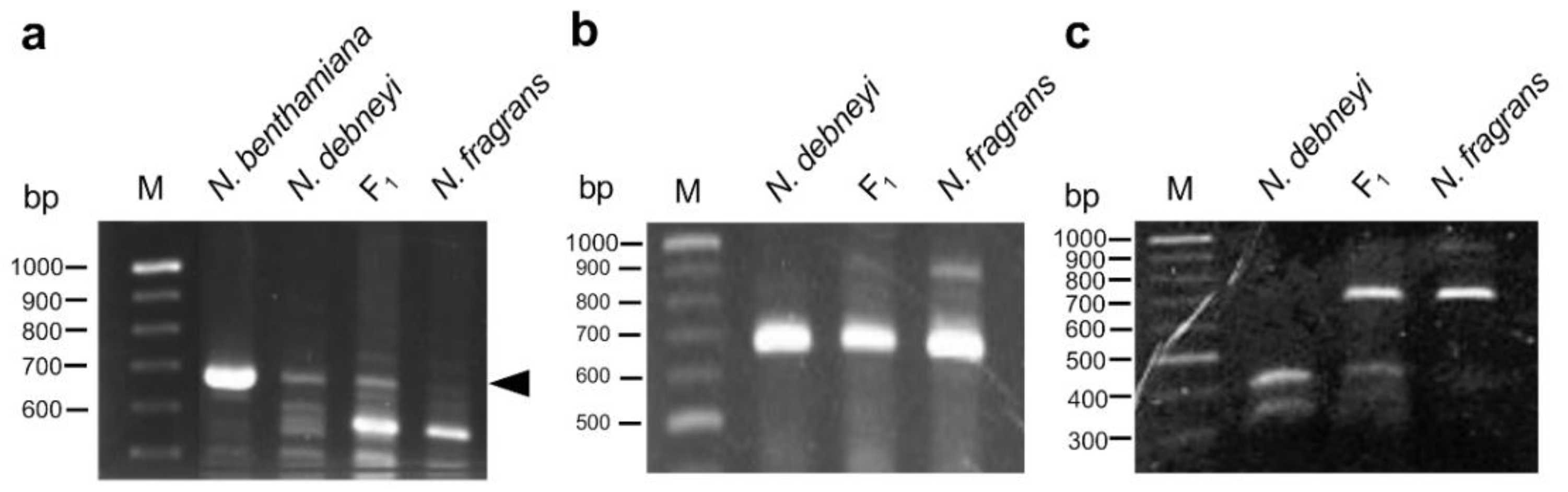
2.3. Chromosome Pairing in F1 Hybrid between N. debneyi and N. fragrans
2.4. Linkage Analysis of HLA1 Using Disease Resistance-Related Markers
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials
4.2. DNA Extraction
4.3. RAPD Analysis
4.4. AFLP Analysis
4.5. SSR Analysis
4.6. DNA Markers Related to Disease Resistance
4.7. Linkage Analysis
4.8. Cytological Analysis of Chromosome Pairing
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kulmuni, J.; Butlin, R.K.; Lucek, K.; Savolainen, V.; Westram, A.M. Towards the completion of speciation: The evolution of reproductive isolation beyond the first barriers. Philos. Trans. R Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2020, 375, 20190528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swaminathan, M.S. Overcoming cross-incompatibility among some Mexican diploid species of Solanum. Nature 1955, 176, 887–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Yokoi, S.; Tezuka, T. A high maternal genome excess causes severe seed abortion leading to ovary abscission in Nicotiana interploidy-interspecific crosses. Plant Direct 2020, 4, e00257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subhashini, U.; Venkateswarlu, T.; Anjani, K.; Prasad, G.S.R. In vitro hybridization in an incompatible cross Nicotiana glutinosa × Nicotiana megalosiphon. Theor. Appl. Genet. 1985, 71, 545–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadir, S.; Li, W.; Zhu, Q.; Khan, S.; Zhang, X.L.; Zhang, H.; Wei, Z.F.; Li, M.T.; Zhou, L.; Li, C.Y.; et al. A novel discovery of a long terminal repeat retrotransposon-induced hybrid weakness in rice. J. Exp. Bot. 2019, 70, 1197–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shiragaki, K.; Furukawa, H.; Yokoi, S.; Tezuka, T. Temperature-dependent sugar accumulation in interspecific Capsicum F1 plants showing hybrid weakness. J. Plant Res. 2021, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Liu, X.; Fang, Z.; Yang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhuang, M.; Lv, H. Transcriptome and plant hormone analyses provide new insight into the molecular regulatory networks underlying hybrid lethality in cabbage (Brassica oleracea). Planta 2021, 253, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubo, T.; Yoshimura, A. Genetic basis of hybrid breakdown in a Japonica/Indica cross of rice, Oryza sativa L. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2002, 105, 906–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsubara, K.; Ando, T.; Mizubayashi, T.; Ito, S.; Yano, M. Identification and linkage mapping of complementary recessive genes causing hybrid breakdown in an intraspecific rice cross. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2007, 115, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bomblies, K.; Weigel, D. Hybrid necrosis: Autoimmunity as a potential gene-flow barrier in plant species. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2007, 8, 382–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bomblies, K.; Lempe, J.; Epple, P.; Warthmann, N.; Lanz, C.; Dangl, J.L.; Weigel, D. Autoimmune response as a mechanism for a Dobzhansky-Muller-type incompatibility syndrome in plants. PLoS Biol. 2007, 5, e236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Fang, L.; Zhu, X.; Zhou, B.; Zhang, T. A CC-NBS-LRR gene induces hybrid lethality in cotton. J. Exp. Bot. 2019, 70, 5145–5156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Chen, H.; Lin, Y.S.; Shen, J.B.; Shan, J.X.; Qi, P.; Shi, M.; Zhu, M.Z.; Huang, X.H.; Feng, Q.; et al. A two-locus interaction causes interspecific hybrid weakness in rice. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jeuken, M.J.W.; Zhang, N.W.; McHale, L.K.; Pelgrom, K.; Den Boer, E.; Lindhout, P.; Michelmore, R.W.; Visser, R.G.F.; Niks, R.E. Rin4 causes hybrid necrosis and race-specific resistance in an interspecific lettuce hybrid. Plant Cell 2009, 21, 3368–3378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bikard, D.; Patel, D.; Le, M.C.; Giorgi, V.; Camilleri, C.; Bennett, M.J.; Loudet, O. Divergent evolution of duplicate genes leads to genetic incompatibilities within A. thaliana. Science 2009, 323, 623–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zuellig, M.P.; Sweigart, A.L. Gene duplicates cause hybrid lethality between sympatric species of Mimulus. PLoS Genet. 2018, 14, e1007130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tezuka, T.; Kuboyama, T.; Matsuda, T.; Marubashi, W. Seven of eight species in Nicotiana section Suaveolentes have common factors leading to hybrid lethality in crosses with Nicotiana tabacum. Ann. Bot. 2010, 106, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tezuka, T. Hybrid lethality in the genus Nicotiana. In Botany; Mworia, J.K., Ed.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2012; pp. 191–210. [Google Scholar]
- Yamada, T.; Marubashi, W.; Niwa, M. Detection of four lethality types in interspecific crosses among Nicotiana species through the use of three rescue methods for lethality. Breed. Sci. 1999, 49, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tezuka, T.; Marubashi, W. Hybrid lethality in interspecific hybrids between Nicotiana tabacum and N. suaveolens: Evidence that the Q chromosome causes hybrid lethality based on Q-chromosome-specific DNA markers. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2006, 112, 1172–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tezuka, T.; Marubashi, W. Genes in S and T subgenomes are responsible for hybrid lethality in interspecific hybrids between Nicotiana tabacum and Nicotiana occidentalis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marubashi, W.; Yamada, T.; Niwa, M. Apoptosis detected in hybrids between Nicotiana glutinosa and N. repanda expressing lethality. Planta 1999, 210, 168–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tezuka, T.; Marubashi, W. Apoptotic cell death observed during the expression of hybrid lethality in interspecific hybrids between Nicotiana tabacum and N. suaveolens. Breed. Sci. 2004, 54, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mino, M.; Abe, S.; Suzuki, T.; Yokoyama, H.; Kaminaka, H.; Ogawa, K.; Morita, S.; Masumura, T.; Tanaka, K.; Inoue, M. Hydrogen peroxide functions as a cell death signal for hybrid lethality in the F1 of Nicotiana gossei × N. tabacum. Plant Sci. 2004, 167, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, T.; Marubashi, W. Overproduced ethylene causes programmed cell death leading to temperature-sensitive lethality in hybrid seedlings from the cross Nicotiana suaveolens × N. tabacum. Planta 2003, 217, 690–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueno, N.; Nihei, S.; Miyakawa, N.; Hirasawa, T.; Kanekatsu, M.; Marubashi, W.; van Doorn, W.G.; Yamada, T. Time course of programmed cell death, which included autophagic features, in hybrid tobacco cells expressing hybrid lethality. Plant Cell Rep. 2016, 35, 2475–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel, G. Some experiments on inoculating methods with plant viruses, and on local lesions. Ann. Appl. Biol. 1931, 18, 494–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendrix, J.W. Temperature-dependent resistance to tobacco ringspot virus in L8, a necrosis-prone tobacco cultivar. Phytopathology 1972, 62, 1376–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erickson, F.L.; Holzberg, S.; Calderon-Urrea, A.; Handley, V.; Axtell, M.; Corr, C.; Baker, B. The helicase domain of the TMV replicase proteins induces the N-mediated defence response in tobacco. Plant J. 1999, 18, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittler, R.; Lam, E. Identification, characterization, and purification of a tobacco endonuclease activity induced upon hypersensitive response cell death. Plant Cell 1995, 7, 1951–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Masuda, Y.; Yamada, T.; Kuboyama, T.; Marubashi, W. Identification and characterization of genes involved in hybrid lethality in hybrid tobacco cells (Nicotiana suaveolens × N. tabacum) using suppression subtractive hybridization. Plant Cell Rep. 2007, 26, 1595–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mino, M.; Kubota, M.; Nogi, T.; Zhang, S.; Inoue, M. Hybrid lethality in interspecific F1 hybrid Nicotiana gossei × N. tabacum involves a MAP-kinases signalling cascade. Plant Biol. 2007, 9, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiragaki, K.; Nakamura, R.; Nomura, S.; He, H.; Yamada, T.; Marubashi, W.; Oda, M.; Tezuka, T. Phenylalanine ammonia-lyase and phenolic compounds are related to hybrid lethality in the cross Nicotiana suaveolens × N. tabacum. Plant Biotechnol. 2020, 37, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsuyama, Y.; Doi, M.; Shioya, S.; Hane, S.; Yoshioka, M.; Date, S.; Miyahara, C.; Ogawa, T.; Takada, R.; Okumura, H.; et al. The role of chaperone complex HSP90-SGT1-RAR1 as the associated machinery for hybrid inviability between Nicotiana gossei Domin and N. tabacum L. Gene 2021, 776, 145443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawaguchi, K.; Ohya, Y.; Maekawa, M.; Iizuka, T.; Hasegawa, A.; Shiragaki, K.; He, H.; Oda, M.; Morikawa, T.; Yokoi, S.; et al. Two Nicotiana occidentalis accessions enable gene identification for Type II hybrid lethality by the cross to N. sylvestris. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 17093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tezuka, T.; Kuboyama, T.; Matsuda, T.; Marubashi, W. Possible involvement of genes on the Q chromosome of Nicotiana tabacum in expression of hybrid lethality and programmed cell death during interspecific hybridization to Nicotiana debneyi. Planta 2007, 226, 753–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tezuka, T.; Matsuo, C.; Iizuka, T.; Oda, M.; Marubashi, W. Identification of Nicotiana tabacum linkage group corresponding to the Q chromosome gene(s) involved in hybrid lethality. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, J.; Hancock, W.G.; Nifong, J.M.; Kernodle, S.P.; Lewis, R.S. Identification and editing of a hybrid lethality gene expands the range of interspecific hybridization potential in Nicotiana. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2020, 133, 2915–2925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iizuka, T.; Kuboyama, T.; Marubashi, W.; Oda, M.; Tezuka, T. Nicotiana debneyi has a single dominant gene causing hybrid lethality in crosses with N. tabacum. Euphytica 2012, 186, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, H.M. A contribution to the cytology of the Australian-South Pacific species of Nicotiana. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1945, 31, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, Y.I.; Chang, F.C.; Chung, M.C. Chromosome pairing affinities in interspecific hybrids reflect phylogenetic distances among lady’s slipper orchids (Paphiopedilum). Ann. Bot. 2011, 108, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Williams, J.G.K.; Kubelik, A.R.; Livak, K.J.; Rafalski, J.A.; Tingey, S.V. DNA polymorphisms amplified by arbitrary primers are useful as genetic markers. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990, 18, 6531–6535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vos, P.; Hogers, R.; Bleeker, M.; Reijans, M.; Van De Lee, T.; Hornes, M.; Frijters, A.; Pot, J.; Paleman, J.; Kuiper, M.; et al. AFLP: A new technique for DNA fingerprinting. Nucleic Acids Res. 1995, 23, 4407–4414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bindler, G.; Plieske, J.; Bakaher, N.; Gunduz, I.; Ivanov, N.; Van Der Hoeven, R.; Ganal, M.; Donini, P. A high density genetic map of tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.) obtained from large scale microsatellite marker development. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2011, 123, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Valleau, W.D. Breeding tobacco for disease resistance. Econ. Bot. 1952, 6, 69–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burk, L.G.; Heggestad, H.E. The genus Nicotiana: A source of resistance to diseases of cultivated tobacco. Econ. Bot. 1966, 20, 76–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.C.; Bass, W.T.; Cornelius, P.L. Resistance to tobacco black shank in Nicotiana species. Crop. Sci. 2006, 46, 554–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Milla, S.R.; Levin, J.S.; Lewis, R.S.; Rufty, R.C. RAPD and SCAR markers linked to an introgressed gene conditioning resistance to Peronospora tabacina D.B. Adam. in tobacco. Crop. Sci. 2005, 45, 2346–2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julio, E.; Verrier, J.L.; De Borne, F.D. Development of SCAR markers linked to three disease resistances based on AFLP within Nicotiana tabacum L. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2006, 112, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bombarely, A.; Rosli, H.G.; Vrebalov, J.; Moffett, P.; Mueller, L.A.; Martin, G.B. A draft genome sequence of Nicotiana benthamiana to enhance molecular plant-microbe biology research. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2012, 25, 1523–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chase, M.W.; Knapp, S.; Cox, A.V.; Clarkson, J.J.; Butsko, Y.; Joseph, J.; Savolainen, V.; Parokonny, A.S. Molecular systematics, GISH and the origin of hybrid taxa in Nicotiana (Solanaceae). Ann. Bot. 2003, 92, 107–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dodsworth, S.; Christenhusz, M.J.M.; Conran, J.G.; Guignard, M.S.; Knapp, S.; Struebig, M.; Leitch, A.R.; Chase, M.W. Extensive plastid-nuclear discordance in a recent radiation of Nicotiana section Suaveolentes (Solanaceae). Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 2020, 193, 546–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.Y.; Kao, Y.Y.; Lin, S.; Lin, R.F.; Chen, C.M.; Huang, C.H.; Wang, C.K.; Lin, Y.Z.; Chen, C.C. A genetic linkage map of Nicotiana plumbaginifolia/Nicotiana longiflora based on RFLP and RAPD markers. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2001, 103, 905–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, W.P.; Schupp, J.M.; Keim, P. DNA methylation and AFLP marker distribution in the soybean genome. Theor. Appl. Genet. 1999, 99, 785–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, H.S.; Nicholson, J.S.; Lewis, R.S. Use of transferable Nicotiana tabacum L. microsatellite markers for investigating genetic diversity in the genus Nicotiana. Genome 2008, 51, 547–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Harushima, Y.; Nakagahra, M.; Yano, M.; Sasaki, T.; Kurata, N. Diverse variation of reproductive barriers in three intraspecific rice crosses. Genetics 2002, 160, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toyomoto, D.; Uemura, M.; Taura, S.; Sato, T.; Henry, R.; Ishikawa, R.; Ichitani, K. Segregation distortion observed in the progeny of crosses between Oryza sativa and O. meridionalis caused by abortion during seed development. Plants 2019, 8, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Murashige, T.; Skoog, F. A revised medium for rapid growth and bio assays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol. Plant. 1962, 15, 473–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, M.G.; Thompson, W.F. Rapid isolation of high molecular weight plant DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980, 8, 4321–4325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bassam, B.J.; Caetano-Anollés, G.; Gresshoff, P.M. Fast and sensitive silver staining of DNA in polyacrylamide gels. Anal. Biochem. 1991, 196, 80–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Pozo, N.; Menda, N.; Edwards, J.D.; Saha, S.; Tecle, I.Y.; Strickler, S.R.; Bombarely, A.; Fisher-York, T.; Pujar, A.; Foerster, H.; et al. The Sol Genomics Network (SGN)—from genotype to phenotype to breeding. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, D1036–D1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamesch, P.; Berardini, T.Z.; Li, D.; Swarbreck, D.; Wilks, C.; Sasidharan, R.; Muller, R.; Dreher, K.; Alexander, D.L.; Garcia-Hernandez, M.; et al. The Arabidopsis Information Resource (TAIR): Improved gene annotation and new tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, D1202–D1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozen, S.; Skaletsky, H.J. Primer3 on the WWW for general users and for biologist programmers. Bioinform. Methods Protoc. Methods Mol. Biol. 2000, 132, 365–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neff, M.M.; Turk, E.; Kalishman, M. Web-based primer design for single nucleotide polymorphism analysis. Trends Genet. 2002, 18, 613–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Ooijen, J.W. JoinMap® 4, Software for the Calculation of Genetic Linkage Maps in Experimental Populations; Kyazma B.V.: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2006. [Google Scholar]

| Marker Type | No. of Primers | No. of Bands Detected | Percentage of Polymorphic Bands | Total No. of Polymorphic Markers | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | N. debneyi-Specific Dominant | N. fragrans-Specific Dominant | Codominant | ||||
| RAPD | 80 | 385 | 42 | 36 | 0 | 20.3% | 78 |
| AFLP | 256 sets | 5191 | 1176 | 1151 | 0 | 44.8% | 2327 |
| SSR | 66 sets | 112 | 22 | 12 | 14 (7 sets) | 42.9% | 41 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tezuka, T.; Kitamura, N.; Imagawa, S.; Hasegawa, A.; Shiragaki, K.; He, H.; Yanase, M.; Ogata, Y.; Morikawa, T.; Yokoi, S. Genetic Mapping of the HLA1 Locus Causing Hybrid Lethality in Nicotiana Interspecific Hybrids. Plants 2021, 10, 2062. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10102062
Tezuka T, Kitamura N, Imagawa S, Hasegawa A, Shiragaki K, He H, Yanase M, Ogata Y, Morikawa T, Yokoi S. Genetic Mapping of the HLA1 Locus Causing Hybrid Lethality in Nicotiana Interspecific Hybrids. Plants. 2021; 10(10):2062. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10102062
Chicago/Turabian StyleTezuka, Takahiro, Naoto Kitamura, Sae Imagawa, Akira Hasegawa, Kumpei Shiragaki, Hai He, Masanori Yanase, Yoshiyuki Ogata, Toshinobu Morikawa, and Shuji Yokoi. 2021. "Genetic Mapping of the HLA1 Locus Causing Hybrid Lethality in Nicotiana Interspecific Hybrids" Plants 10, no. 10: 2062. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10102062
APA StyleTezuka, T., Kitamura, N., Imagawa, S., Hasegawa, A., Shiragaki, K., He, H., Yanase, M., Ogata, Y., Morikawa, T., & Yokoi, S. (2021). Genetic Mapping of the HLA1 Locus Causing Hybrid Lethality in Nicotiana Interspecific Hybrids. Plants, 10(10), 2062. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10102062








