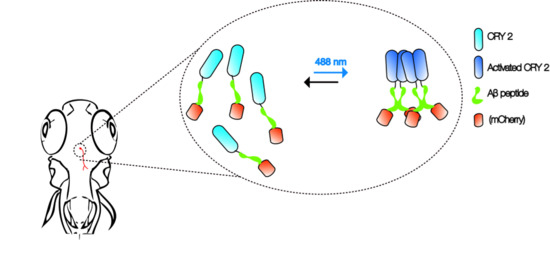
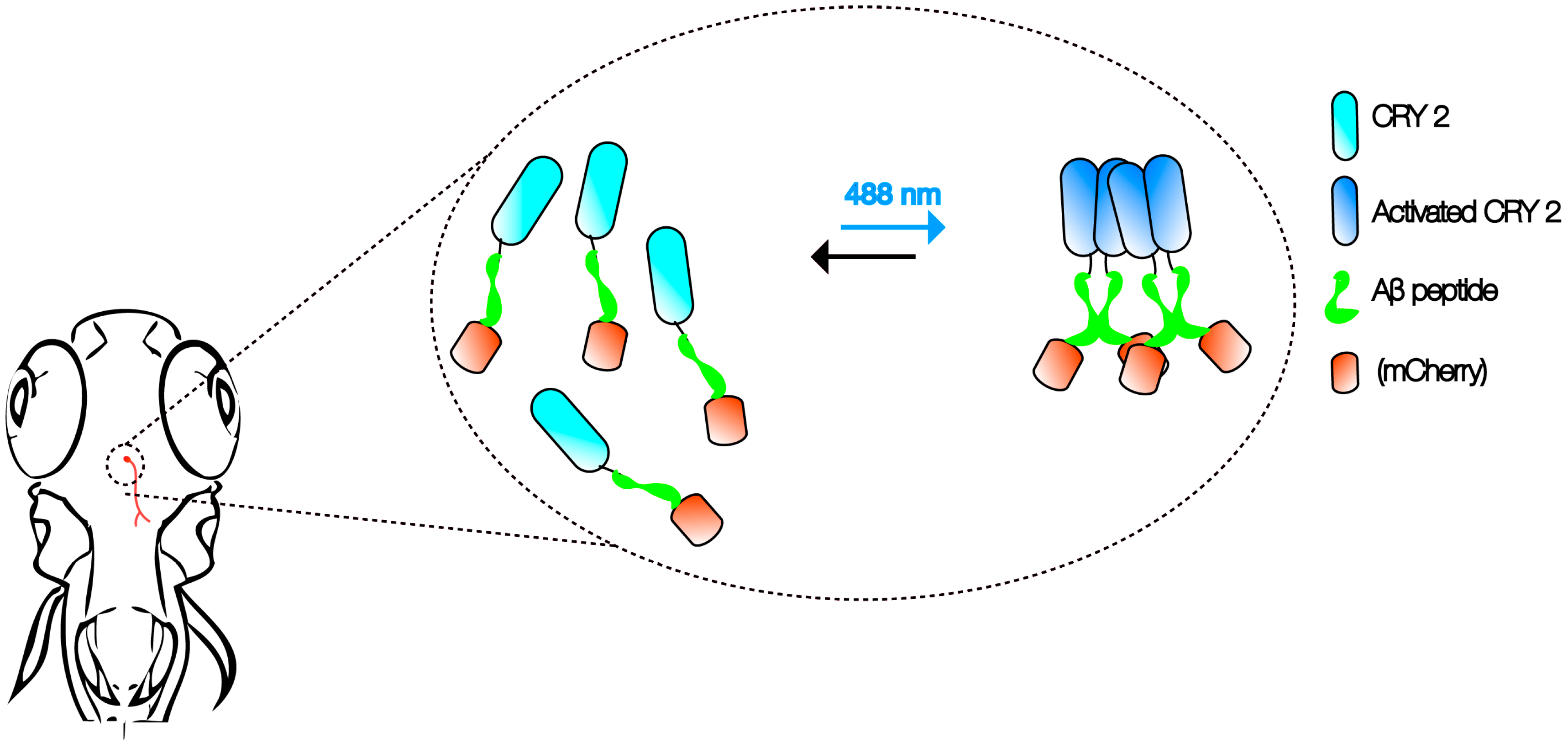
Modeling Alzheimer’s and Other Age Related Human Diseases in Embryonic Systems
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Alzheimer’s Disease: An Unresolved Problem
3. Combining Forces
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bullock, T.H. Comparative neuroscience holds promise for quiet revolutions. Science 1984, 225, 473–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bullock, T.H. “Simple” model systems need comparative studies: Differences are as important as commonalities. Trends Neurosci. 1986, 9, 470–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heiligenberg, W. The neural basis of behavior: A neuroethological view. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 1991, 14, 247–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, X.; Azpurua, J.; Hine, C.; Vaidya, A.; Myakishev-Rempel, M.; Ablaeva, J.; Mao, Z.; Nevo, E.; Gorbunova, V.; Seluanov, A. High-molecular-mass hyaluronan mediates the cancer resistance of the naked mole rat. Nature 2013, 499, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delaney, M.A.; Ward, J.M.; Walsh, T.F.; Chinnadurai, S.K.; Kerns, K.; Kinsel, M.J.; Treuting, P.M. Initial case reports of cancer in naked mole-rats (heterocephalus glaber). Vet. Pathol. 2016, 53, 691–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, U.B.; Nichols, C.D. Human disease models in drosophila melanogaster and the role of the fly in therapeutic drug discovery. Pharmacol. Rev. 2011, 63, 411–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markaki, M.; Tavernarakis, N. Modeling human diseases in caenorhabditis elegans. Biotechnol. J. 2010, 5, 1261–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santoriello, C.; Zon, L.I. Hooked! Modeling human disease in zebrafish. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 2337–2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moulton, M.J.; Letsou, A. Modeling congenital disease and inborn errors of development in drosophila melanogaster. Dis. Models Mech. 2016, 9, 253–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kessler, M.; Rottbauer, W.; Just, S. Recent progress in the use of zebrafish for novel cardiac drug discovery. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2015, 10, 1231–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Singh, A.; Ekavali. A review on alzheimer’s disease pathophysiology and its management: An update. Pharmacol. Rep. 2015, 67, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De-Paula, V.J.; Radanovic, M.; Diniz, B.S.; Forlenza, O.V. Alzheimer’s disease. Sub-Cell. Biochem. 2012, 65, 329–352. [Google Scholar]
- Alzheimer’s Association. 2017 Alzheimer’s Disease Facts and Figures. Available online: https://www.alz.org/documents_custom/2017-facts-and-figures.pdf (accessed on 10 November 2017).
- Alzheimer’s Disease International. World Alzheimer Report 2016: Improving Healthcare for People Living with Dementia; Alzheimer’s Disease International (ADI): London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Alzheimers.net. 2016 Alzheimer’s Statistics. Available online: https://www.alzheimers.net/resources/alzheimers-statistics/ (accessed on 10 November 2017).
- Alexander, A.G.; Marfil, V.; Li, C. Use of caenorhabditis elegans as a model to study alzheimer’s disease and other neurodegenerative diseases. Front. Genet. 2014, 5, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iqbal, K.; Alonso Adel, C.; Chen, S.; Chohan, M.O.; El-Akkad, E.; Gong, C.X.; Khatoon, S.; Li, B.; Liu, F.; Rahman, A.; et al. Tau pathology in alzheimer disease and other tauopathies. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2005, 1739, 198–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, J.; Lemaire, H.G.; Unterbeck, A.; Salbaum, J.M.; Masters, C.L.; Grzeschik, K.H.; Multhaup, G.; Beyreuther, K.; Muller-Hill, B. The precursor of alzheimer’s disease amyloid a4 protein resembles a cell-surface receptor. Nature 1987, 325, 733–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eskelinen, M.H.; Kivipelto, M. Caffeine as a protective factor in dementia and alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. JAD 2010, 20 (Suppl. 1), S167–S174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chartier-Harlin, M.C.; Crawford, F.; Houlden, H.; Warren, A.; Hughes, D.; Fidani, L.; Goate, A.; Rossor, M.; Roques, P.; Hardy, J.; et al. Early-onset alzheimer’s disease caused by mutations at codon 717 of the beta-amyloid precursor protein gene. Nature 1991, 353, 844–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruts, M.; Hendriks, L.; Van Broeckhoven, C. The presenilin genes: A new gene family involved in alzheimer disease pathology. Hum. Mol. Genet. 1996, 5, 1449–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugarman, M.C.; Yamasaki, T.R.; Oddo, S.; Echegoyen, J.C.; Murphy, M.P.; Golde, T.E.; Jannatipour, M.; Leissring, M.A.; LaFerla, F.M. Inclusion body myositis-like phenotype induced by transgenic overexpression of beta app in skeletal muscle. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 6334–6339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, G.P.; Clark, I.A.; Vissel, B. Inconsistencies and controversies surrounding the amyloid hypothesis of alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2014, 2, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, P.; Turola, E.; Ruiz, A.; Bergami, A.; Libera, D.D.; Benussi, L.; Giussani, P.; Magnani, G.; Comi, G.; Legname, G.; et al. Microglia convert aggregated amyloid-beta into neurotoxic forms through the shedding of microvesicles. Cell Death Differ. 2014, 21, 582–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bu, X.L.; Xiang, Y.; Jin, W.S.; Wang, J.; Shen, L.L.; Huang, Z.L.; Zhang, K.; Liu, Y.H.; Zeng, F.; Liu, J.H.; et al. Blood-derived amyloid-β protein induces alzheimer’s disease pathologies. Mol. Psychiatry 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Mims, P.N.; Roman, R.J.; Fan, F. Is beta-amyloid accumulation a cause or consequence of alzheimer’s disease? J. Alzheimer’s Parkinsonism Dement. 2016, 1, 007. [Google Scholar]
- Friedrich, R.P.; Tepper, K.; Rönicke, R.; Soom, M.; Westermann, M.; Reymann, K.; Kaether, C.; Fändrich, M. Mechanism of amyloid plaque formation suggests an intracellular basis of aβ pathogenicity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 1942–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gouras, G.K.; Tampellini, D.; Takahashi, R.H.; Capetillo-Zarate, E. Intraneuronal β-amyloid accumulation and synapse pathology in alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neuropathol. 2010, 119, 523–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.-W.; Thompson, R.; Zhang, H.; Xu, H. App processing in alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Brain 2011, 4, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duffy, J.B. Gal4 system in drosophila: A fly geneticist’s swiss army knife. Genesis 2002, 34, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brenner, S. The genetics of caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics 1974, 77, 71–94. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kawashima, T.; Zwart, M.F.; Yang, C.T.; Mensh, B.D.; Ahrens, M.B. The serotonergic system tracks the outcomes of actions to mediate short-term motor learning. Cell 2016, 167, 933–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edward, D.; Levin, D.T.C. Methods of Behavior Analysis in Neuroscience, 2 ed.; CRC Press/Taylor & Francis: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Fenno, L.; Yizhar, O.; Deisseroth, K. The development and application of optogenetics. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2011, 34, 389–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guglielmi, G.; Barry, J.D.; Huber, W.; De Renzis, S. An optogenetic method to modulate cell contractility during tissue morphogenesis. Dev. Cell 2015, 35, 646–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Idevall-Hagren, O.; Dickson, E.J.; Hille, B.; Toomre, D.K.; De Camilli, P. Optogenetic control of phosphoinositide metabolism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, E2316–E2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, M.J.; Hughes, R.M.; Peteya, L.A.; Schwartz, J.W.; Ehlers, M.D.; Tucker, C.L. Rapid blue-light-mediated induction of protein interactions in living cells. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 973–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lim, C.H.; Mathuru, A.S. Modeling Alzheimer’s and Other Age Related Human Diseases in Embryonic Systems. J. Dev. Biol. 2018, 6, 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/jdb6010001
Lim CH, Mathuru AS. Modeling Alzheimer’s and Other Age Related Human Diseases in Embryonic Systems. Journal of Developmental Biology. 2018; 6(1):1. https://doi.org/10.3390/jdb6010001
Chicago/Turabian StyleLim, Chu Hsien, and Ajay S. Mathuru. 2018. "Modeling Alzheimer’s and Other Age Related Human Diseases in Embryonic Systems" Journal of Developmental Biology 6, no. 1: 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/jdb6010001
APA StyleLim, C. H., & Mathuru, A. S. (2018). Modeling Alzheimer’s and Other Age Related Human Diseases in Embryonic Systems. Journal of Developmental Biology, 6(1), 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/jdb6010001