Combination of Landsat 8 OLI and Sentinel-1 SAR Time-Series Data for Mapping Paddy Fields in Parts of West and Central Java Provinces, Indonesia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
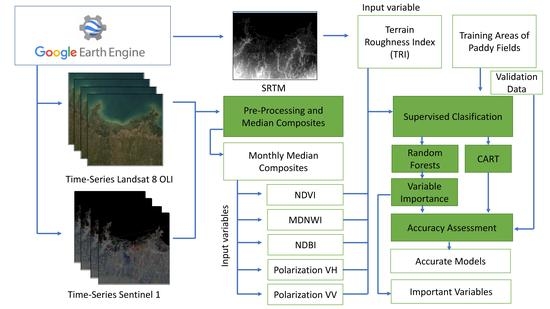
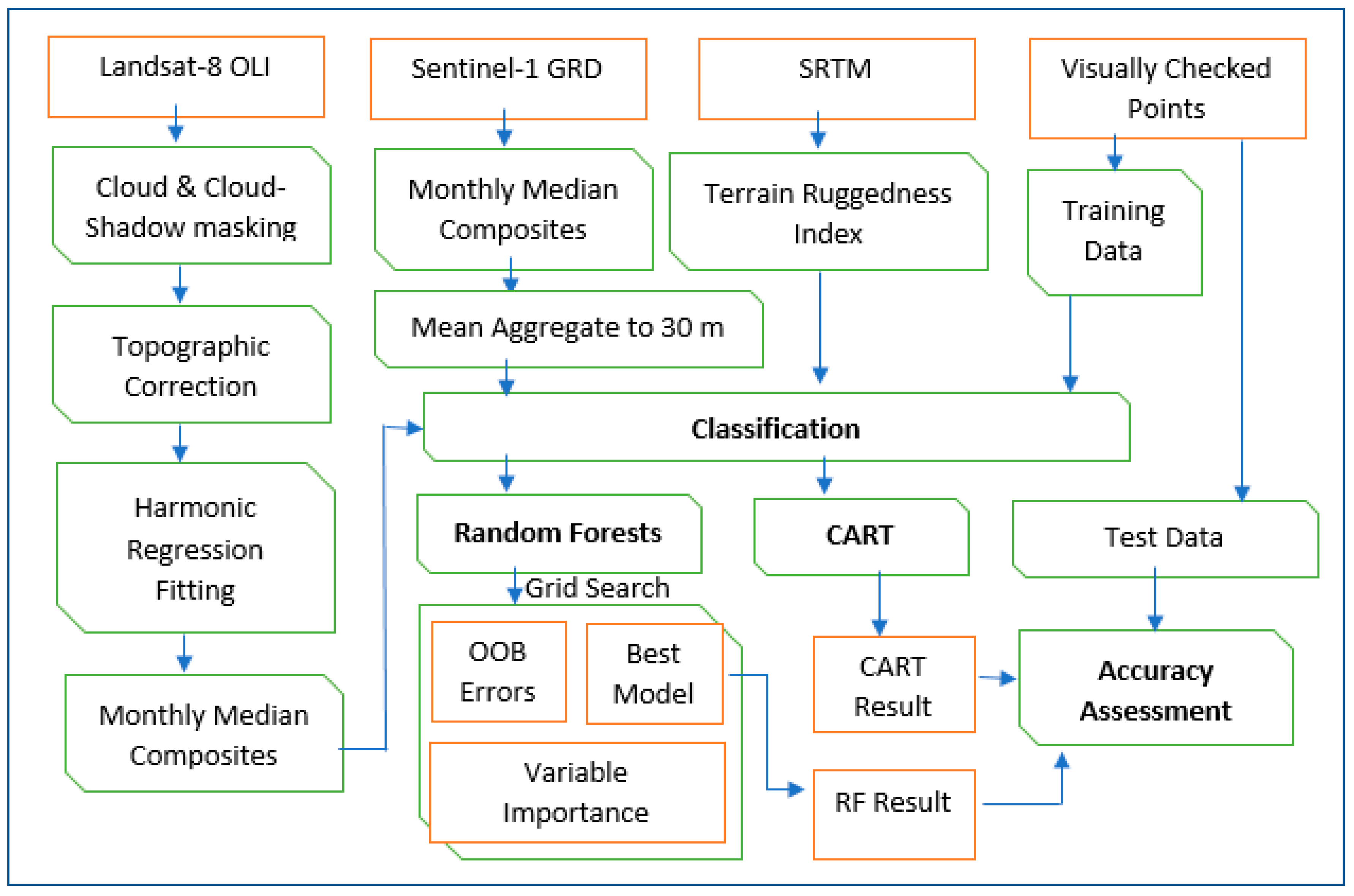
2. Materials and Methods
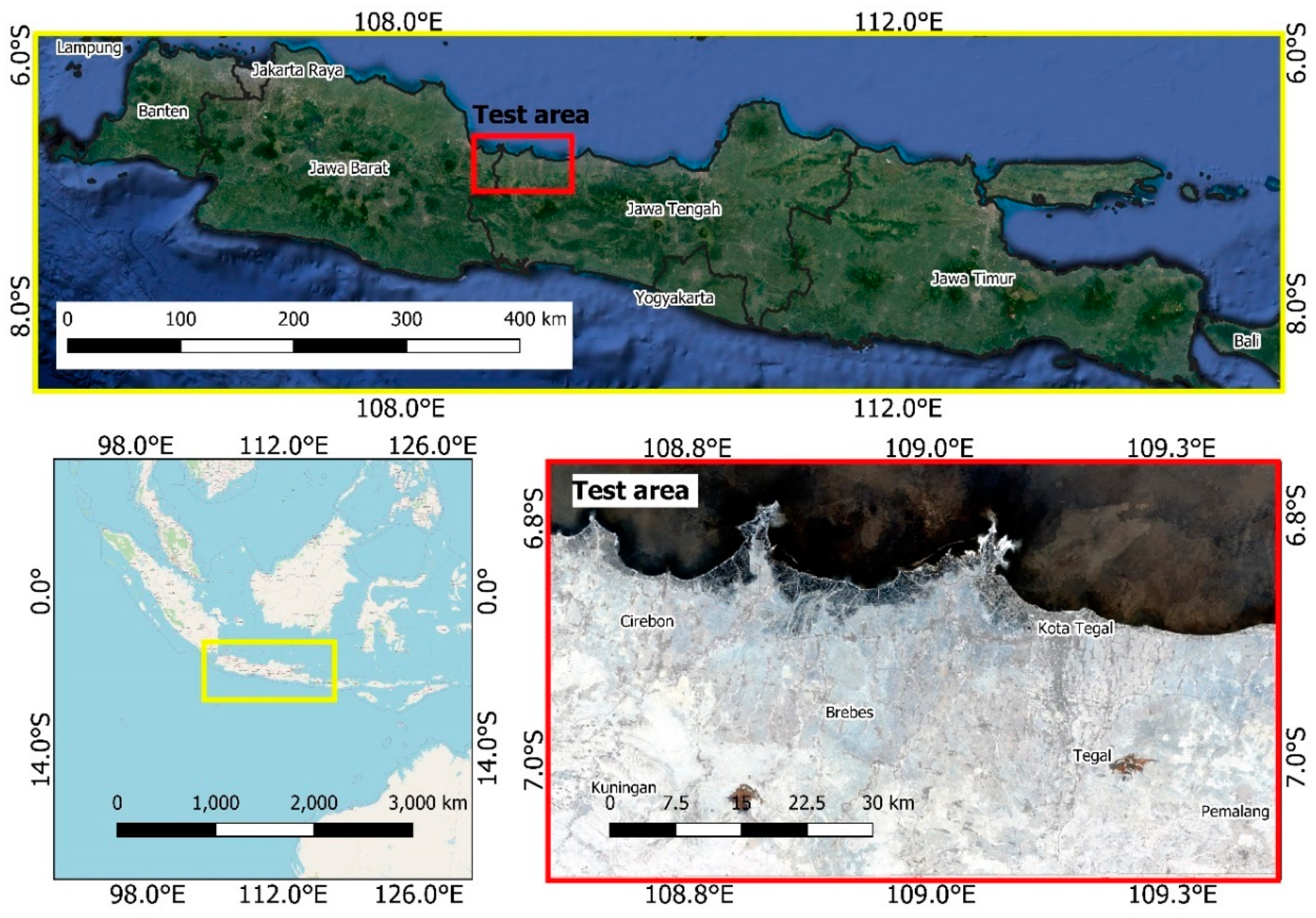
2.1. Study Area
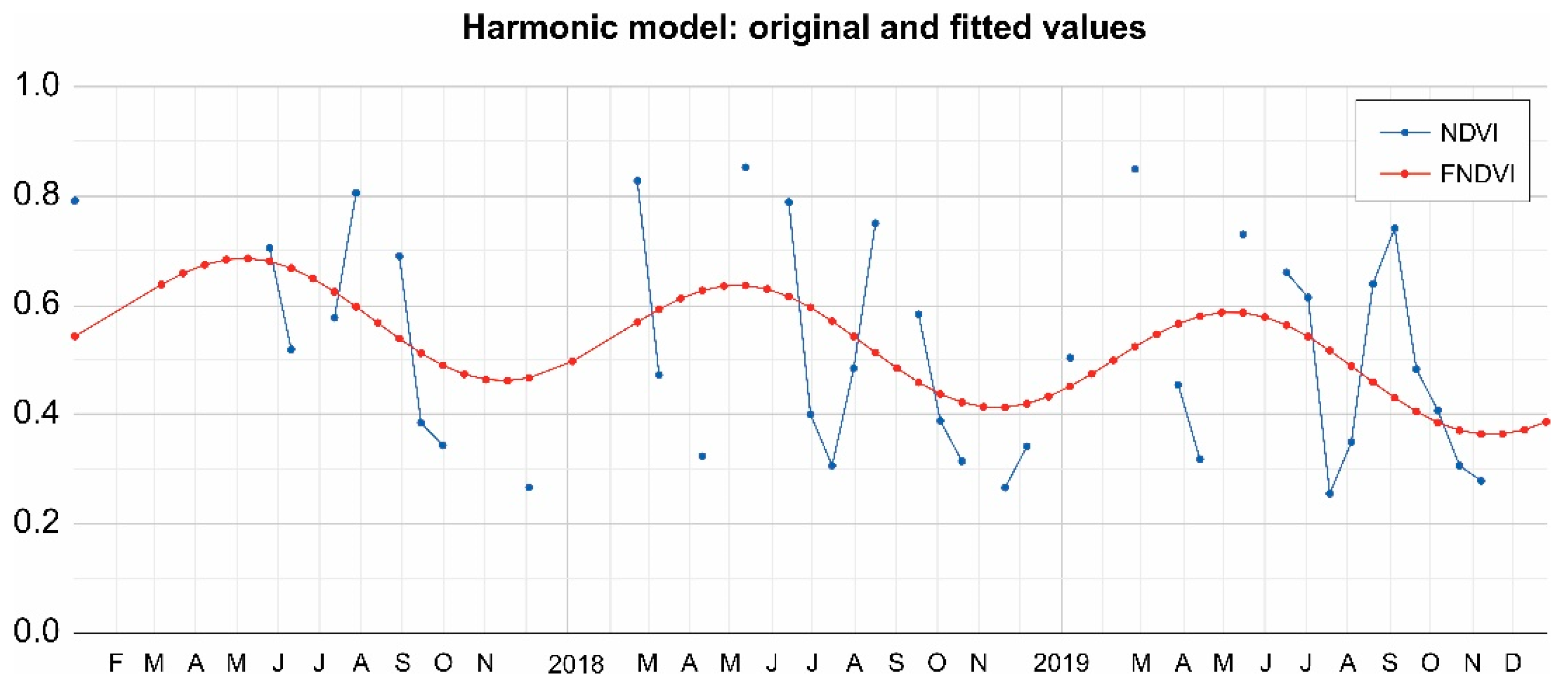
2.2. Harmonic Regression for Landsat 8 OLI
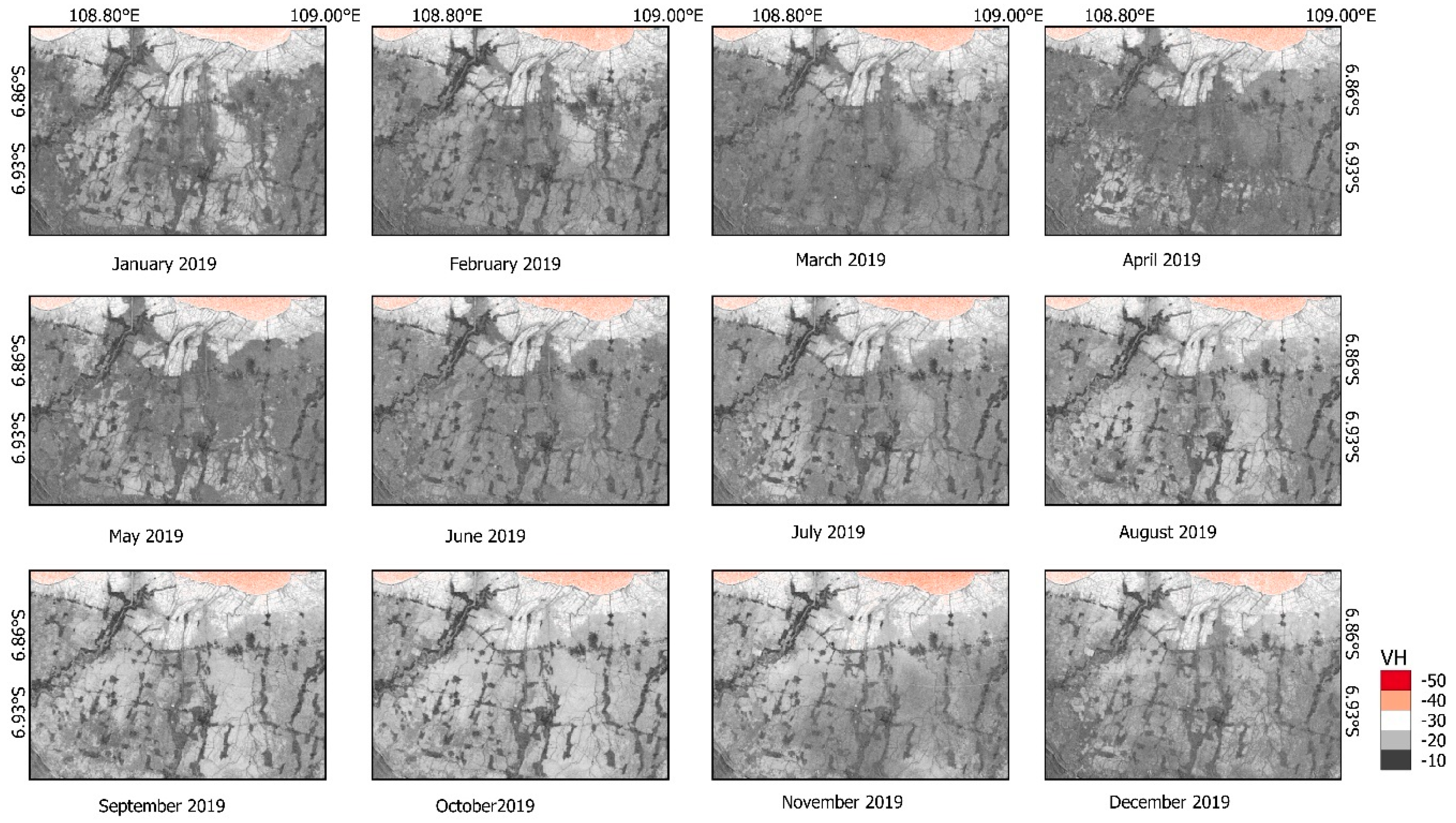
2.3. Sentinel-1 Time Series Process
2.4. Ancillary Data
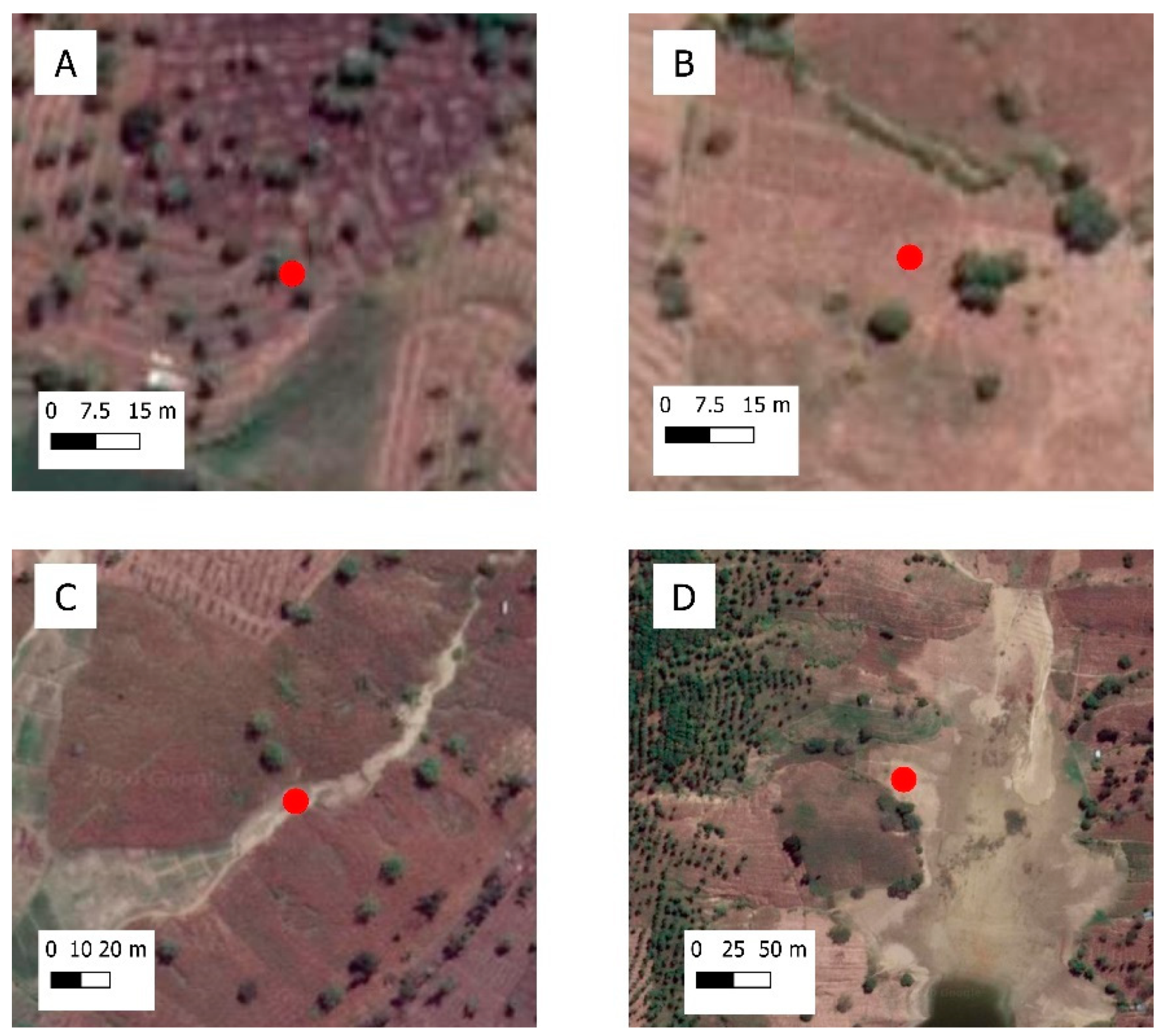
2.5. Classification and Accuracy Assessment
3. Results
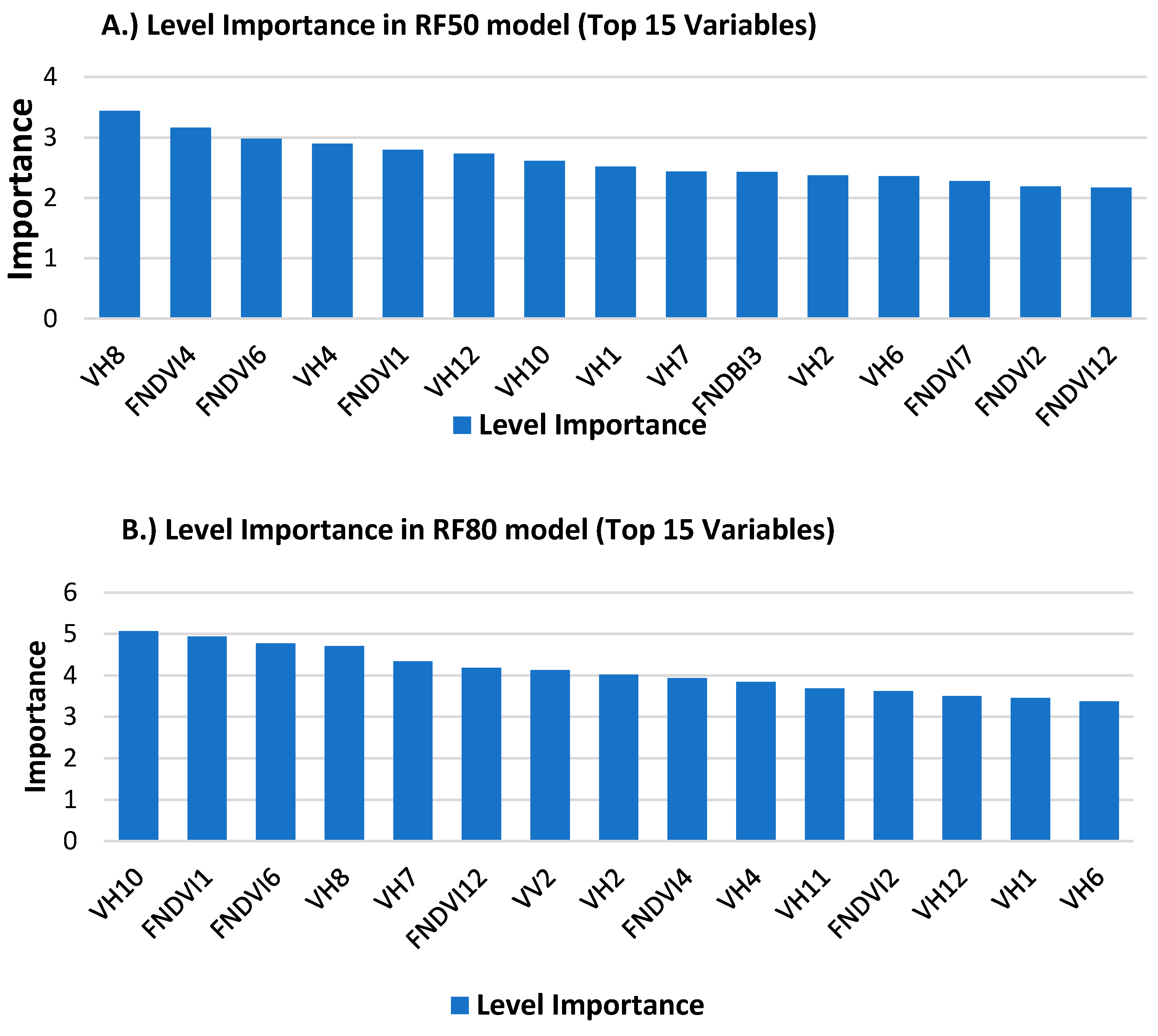
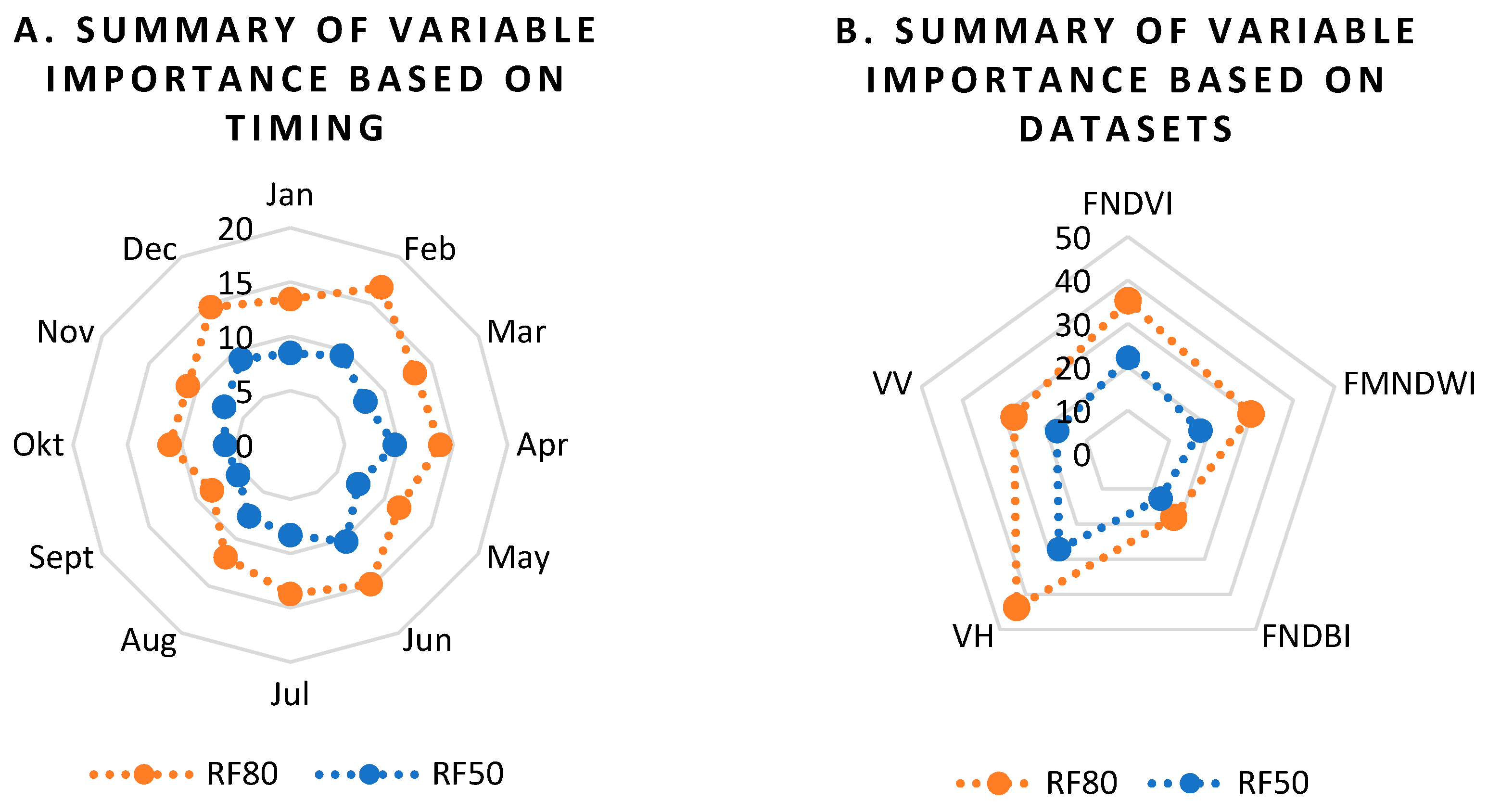
3.1. Out-of-Bag Error (OOB) and Variable Importance
3.2. Classification Results and Accuracy Assessment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| RF_50 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class | Reference | UA | |||
| Paddy Field | Non-Paddy Field | Water Body | Total | ||
| Paddy Field | 860 | 144 | 0 | 1004 | 85.66 |
| Non-Paddy Field | 60 | 932 | 4 | 996 | 93.57 |
| Water Body | 0 | 18 | 982 | 1000 | 98.20 |
| Total | 920 | 1094 | 986 | 3000 | |
| PA | 93.48 | 85.19 | 99.59 | ||
| OA | 92.47 | ||||
| RF 80 | |||||
| Paddy Field | 843 | 140 | 0 | 1004 | 83.96 |
| Non-Paddy Field | 77 | 937 | 3 | 1017 | 92.13 |
| Water Body | 0 | 17 | 983 | 1000 | 98.30 |
| Total | 920 | 1094 | 986 | 3000 | |
| PA | 91.63 | 85.65 | 1.00 | ||
| OA | 92.10 | ||||
| CART | |||||
| Paddy Field | 744 | 133 | 0 | 1004 | 74.10 |
| Non-Paddy Field | 176 | 957 | 60 | 1193 | 80.22 |
| Water Body | 0 | 8 | 926 | 1000 | 92.60 |
| Total | 920 | 1098 | 986 | 3000 | |
| PA | 80.87 | 87.16 | 0.94 | ||
| OA | 87.57 | ||||
References
- Verburg, P.H.; Bouma, J. Land use change under conditions of high population pressure: The case of Java. Glob. Environ. Chang. 1999, 9, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firman, T. Major issues in Indonesia’s urban land development. Land Use Policy 2004, 21, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimyati, M.; Mizuno, K.; Kobayashi, S.; Kitamura, T. An analysis of land use/cover change in Indonesia. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1996, 17, 931–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dirman, E.; Saleng, A.; Sapiddin, A. Food agricultural land legal protection to improve food security in Indonesia. EES 2018, 196, 012047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wikkramatileke, R. Problems of Land-Use Mapping in the Tropics. An Example from Ceylon. Geography 1959, 44, 79–95. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, D.; Huete, A.R.; Huang, J.; Wang, F.; Sun, H. Detection and estimation of mixed paddy rice cropping patterns with MODIS data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2011, 13, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Boles, S.; Frolking, S.; Li, C.; Babu, J.Y.; Salas, W.; Moore III, B. Mapping paddy rice agriculture in South and Southeast Asia using multi-temporal MODIS images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 100, 95–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Boles, S.; Liu, J.; Zhuang, D.; Frolking, S.; Li, C.; Salas, W.; Moore III, B. Mapping paddy rice agriculture in southern China using multi-temporal MODIS images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 95, 480–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sari, D.K.; Ismullah, I.H.; Sulasdi, W.N.; Harto, A.B. Detecting rice phenology in paddy fields with complex cropping pattern using time series MODIS data. J. Math. Fundam. Sci. 2010, 42, 91–106. [Google Scholar]
- Sakamoto, T.; Yokozawa, M.; Toritani, H.; Shibayama, M.; Ishitsuka, N.; Ohno, H. A crop phenology detection method using time-series MODIS data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 96, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Xiao, X.; Dong, J.; Kou, W.; Jin, C.; Qin, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, J.; Menarguez, M.A.; Biradar, C. Mapping paddy rice planting areas through time series analysis of MODIS land surface temperature and vegetation index data. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 106, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qin, Y.; Xiao, X.; Dong, J.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, G.; Du, G.; Jin, C.; Kou, W.; Wang, J.; et al. Mapping paddy rice planting area in cold temperate climate region through analysis of time series Landsat 8 (OLI), Landsat 7 (ETM+) and MODIS imagery. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 105, 220–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Y.; Xiao, X.; Qin, Y.; Dong, J.; Zhang, G.; Kou, W.; Jin, C.; Wang, J.; Li, X. Mapping paddy rice planting area in rice-wetland coexistent areas through analysis of Landsat 8 OLI and MODIS images. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2016, 46, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Xiao, X.; Qin, Y.; Dong, J.; Zhang, G.; Kou, W.; Jin, C.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y. Mapping paddy rice planting area in wheat-rice double-cropped areas through integration of Landsat-8 OLI, MODIS, and PALSAR images. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aschbacher, J.; Pongsrihadulchai, A.; Karnchanasutham, S.; Rodprom, C.; Paudyal, D.; Le Toan, T. Assessment of ERS-1 SAR data for rice crop mapping and monitoring. In Proceedings of the International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, IGARSS’95: Quantitative Remote Sensing for Science and Applications, Congress Center, Firenze, Italy, 10–14 July 1995; pp. 2183–2185. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, C.; Wu, J.; Qi, J.; Salas, W.A. Mapping paddy rice with multitemporal ALOS/PALSAR imagery in southeast China. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2009, 30, 6301–6315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyaoka, K.; Maki, M.; Susaki, J.; Homma, K.; Noda, K.; Oki, K. Rice-planted area mapping using small sets of multi-temporal SAR data. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2013, 10, 1507–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazzi, H.; Baghdadi, N.; El Hajj, M.; Zribi, M.; Minh, D.H.T.; Ndikumana, E.; Courault, D.; Belhouchette, H. Mapping paddy rice using Sentinel-1 SAR time series in Camargue, France. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kontgis, C.; Warren, M.S.; Skillman, S.W.; Chartrand, R.; Moody, D.I. Leveraging Sentinel-1 time-series data for mapping agricultural land cover and land use in the tropics. In Proceedings of the 9th International Workshop on the Analysis of Multitemporal Remote Sensing Images (MultiTemp), Bruges, Belgium, 27–29 June 2017; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Singha, M.; Dong, J.; Zhang, G.; Xiao, X. High resolution paddy rice maps in cloud-prone Bangladesh and Northeast India using Sentinel-1 data. Sci. Data 2019, 6, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasko, K.; Vadrevu, K.P.; Tran, V.T.; Justice, C. Mapping double and single crop paddy rice with Sentinel-1A at varying spatial scales and polarizations in Hanoi, Vietnam. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2018, 11, 498–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.B.; Wagner, W. European rice cropland mapping with Sentinel-1 data: The Mediterranean region case study. Water 2017, 9, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minasny, B.; Shah, R.M.; Che Soh, N.; Arif, C.; Indra Setiawan, B. Automated Near-Real-Time Mapping and Monitoring of Rice Extent, Cropping Patterns, and Growth Stages in Southeast Asia Using Sentinel-1 Time Series on a Google Earth Engine Platform. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1666. [Google Scholar]
- Mansaray, L.R.; Huang, W.; Zhang, D.; Huang, J.; Li, J. Mapping rice fields in urban Shanghai, southeast China, using Sentinel-1A and Landsat 8 datasets. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Torbick, N.; Chowdhury, D.; Salas, W.; Qi, J. Monitoring rice agriculture across myanmar using time series Sentinel-1 assisted by Landsat-8 and PALSAR-2. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mansaray, L.R.; Wang, F.; Huang, J.; Yang, L.; Kanu, A.S. Accuracies of support vector machine and random forest in rice mapping with Sentinel-1A, Landsat-8 and Sentinel-2A datasets. Geocarto Int. 2020, 35, 1088–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onojeghuo, A.O.; Blackburn, G.A.; Wang, Q.; Atkinson, P.M.; Kindred, D.; Miao, Y. Mapping paddy rice fields by applying machine learning algorithms to multi-temporal Sentinel-1A and Landsat data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 39, 1042–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Inoue, S.; Ito, A.; Yonezawa, C. Mapping Paddy Fields in Japan by Using a Sentinel-1 SAR Time Series Supplemented by Sentinel-2 Images on Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Lin, H.; Zhang, M. Mapping paddy rice by the object-based random forest method using time series Sentinel-1/Sentinel-2 data. Adv. Space Res. 2019, 64, 2233–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorelick, N.; Hancher, M.; Dixon, M.; Ilyushchenko, S.; Thau, D.; Moore, R. Google Earth Engine: Planetary-scale geospatial analysis for everyone. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 202, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, L.; Mutanga, O. Google Earth Engine applications since inception: Usage, trends, and potential. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tamiminia, H.; Salehi, B.; Mahdianpari, M.; Quackenbush, L.; Adeli, S.; Brisco, B. Google Earth Engine for geo-big data applications: A meta-analysis and systematic review. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 164, 152–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Xiao, X.; Menarguez, M.A.; Zhang, G.; Qin, Y.; Thau, D.; Biradar, C.; Moore III, B. Mapping paddy rice planting area in northeastern Asia with Landsat 8 images, phenology-based algorithm and Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 185, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kontgis, C.; Schneider, A.; Ozdogan, M. Mapping rice paddy extent and intensification in the Vietnamese Mekong River Delta with dense time stacks of Landsat data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 169, 255–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, D.J.; Atkinson, P.M.; Bhatt, S.; Mappin, B.; Hay, S.I.; Gething, P.W. An effective approach for gap-filling continental scale remotely sensed time-series. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2014, 98, 106–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kandasamy, S.; Baret, F.; Verger, A.; Neveux, P.; Weiss, M. A comparison of methods for smoothing and gap filling time series of remote sensing observations-application to MODIS LAI products. Biogeosciences 2013, 10, 4055–4071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roy, D.P.; Yan, L. Robust Landsat-based crop time series modelling. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roerink, G.; Menenti, M.; Verhoef, W. Reconstructing cloudfree NDVI composites using Fourier analysis of time series. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2000, 21, 1911–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, E.B.; Thomas, V.A.; Wynne, R.H.; Coulston, J.W. Fitting the multitemporal curve: A Fourier series approach to the missing data problem in remote sensing analysis. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 3340–3353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Heiskanen, J.; Maeda, E.E.; Pellikka, P.K. Burned area detection based on Landsat time series in savannas of southern Burkina Faso. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2018, 64, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Venkatappa, M.; Sasaki, N.; Shrestha, R.P.; Tripathi, N.K.; Ma, H.-O. Determination of vegetation thresholds for assessing land use and land use changes in Cambodia using the Google Earth Engine cloud-computing platform. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Derwin, J.M.; Thomas, V.A.; Wynne, R.H.; Coulston, J.W.; Liknes, G.C.; Bender, S.; Blinn, C.E.; Brooks, E.B.; Ruefenacht, B.; Benton, R. Estimating tree canopy cover using harmonic regression coefficients derived from multitemporal Landsat data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2020, 86, 101985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landmann, T.; Eidmann, D.; Cornish, N.; Franke, J.; Siebert, S. Optimizing harmonics from Landsat time series data: The case of mapping rainfed and irrigated agriculture in Zimbabwe. Remote Sens. Lett. 2019, 10, 1038–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surjasa, D.; Gumbira-Sa’id, E.; Arifin, B.; Jie, F. Indonesian rice supply chain analysis and supplier selection model. Int. J. Inf. Bus. Manag. 2013, 5, 198. [Google Scholar]
- Febrina, W.D. Determinants of Paddy Field Conversion in Java 1995-2013. J. Home Aff. Gov. 2017, 9, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Poortinga, A.; Tenneson, K.; Shapiro, A.; Nquyen, Q.; San Aung, K.; Chishtie, F.; Saah, D. Mapping plantations in Myanmar by fusing landsat-8, sentinel-2 and sentinel-1 data along with systematic error quantification. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soenen, S.A.; Peddle, D.R.; Coburn, C.A. SCS+ C: A modified sun-canopy-sensor topographic correction in forested terrain. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2005, 43, 2148–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, D.; Gillespie, A. Topographic normalization of Landsat TM images of forest based on subpixel sun–canopy–sensor geometry. Remote Sens. Environ. 1998, 64, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teillet, P.; Guindon, B.; Goodenough, D. On the slope-aspect correction of multispectral scanner data. Can. J. Remote Sens. 1982, 8, 84–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han-Qiu, X. A study on information extraction of water body with the modified normalized difference water index (MNDWI). J. Remote Sens. 2005, 5, 589–595. [Google Scholar]
- Zha, Y.; Gao, J.; Ni, S. Use of normalized difference built-up index in automatically mapping urban areas from TM imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2003, 24, 583–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benbahria, Z.; Sebari, I.; Hajji, H.; Smiej, M.F. Automatic Mapping of Irrigated Areas in Mediteranean Context Using Landsat 8 Time Series Images and Random Forest Algorithm. In Proceedings of the IGARSS IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Valencia, Spain, 22–27 July 2018; pp. 7986–7989. [Google Scholar]
- Ramanathan, K.; Thenmozhi, M.; George, S.; Anandan, S.; Veeraraghavan, B.; Naumova, E.N. Assessing Seasonality Variation with Harmonic Regression: Accommodations for Sharp Peaks. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clinton, N. Lab 6: Time series analysis. In Introductory Remote Sensing Code Labs; Geospatial Analysis Lab, University of San Francisco: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Adams, B.; Iverson, L.; Matthews, S.; Peters, M.; Prasad, A.; Hix, D. Mapping Forest Composition with Landsat Time Series: An Evaluation of Seasonal Composites and Harmonic Regression. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilson, B.T.; Knight, J.F.; McRoberts, R.E. Harmonic regression of Landsat time series for modeling attributes from national forest inventory data. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2018, 137, 29–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, M.D.; Baez-Villanueva, O.M.; Bui, D.D.; Nguyen, P.T.; Ribbe, L. Harmonization of Landsat and Sentinel 2 for Crop Monitoring in Drought Prone Areas: Case Studies of Ninh Thuan (Vietnam) and Bekaa (Lebanon). Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fahsi, A.; Tsegaye, T.; Tadesse, W.; Coleman, T. Incorporation of digital elevation models with Landsat-TM data to improve land cover classification accuracy. For. Ecol. Manag. 2000, 128, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, A.; Arora, M.; Csaplovics, E.; Gupta, R. Land cover classification using IRS LISS III image and DEM in a rugged terrain: A case study in Himalayas. Geocarto Int. 2005, 20, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, S.J.; DeGloria, S.D.; Elliot, R. Index that quantifies topographic heterogeneity. Intermt. J. Sci. 1999, 5, 23–27. [Google Scholar]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Breiman, L. Out-of-bag Estimation. 1996. Available online: https://www.stat.berkeley.edu/~breiman/OOBestimation.pdf (accessed on 25 September 2020).
- Breiman, L.; Friedman, J.; Olshen, R.; Stone, C. Classification and Regression Trees; Chapman and Hall/CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Bel, L.; Allard, D.; Laurent, J.; Cheddadi, R.; Bar-Hen, A. CART algorithm for spatial data: Application to environmental and ecological data. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 2009, 53, 3082–3093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuenzer, C.; Knauer, K. Remote sensing of rice crop areas. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 2101–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Liu, X.; Ding, C.; Liu, S.; Wu, C.; Wu, L.J.G.; Sensing, R. Mapping rice paddies in complex landscapes with convolutional neural networks and phenological metrics. Gisci. Remote Sens. 2020, 57, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndikumana, E.; Ho Tong Minh, D.; Baghdadi, N.; Courault, D.; Hossard, L. Deep recurrent neural network for agricultural classification using multitemporal SAR Sentinel-1 for Camargue, France. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crisóstomo de Castro Filho, H.; Abílio de Carvalho Júnior, O.; Ferreira de Carvalho, O.L.; Pozzobon de Bem, P.; dos Santos de Moura, R.; Olino de Albuquerque, A.; Rosa Silva, C.; Guimarães Ferreira, P.H.; Fontes Guimarães, R.; Trancoso Gomes, R.A. Rice Crop Detection Using LSTM, Bi-LSTM, and Machine Learning Models from Sentinel-1 Time Series. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelletier, C.; Webb, G.I.; Petitjean, F. Temporal convolutional neural network for the classification of satellite image time series. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



| Data | Variables | Codename * | Number Variables |
|---|---|---|---|
| Landsat 8 | Harmonic-fitted NDVI | FNDVI1 to FNDVI12 | 12 |
| Harmonic-fitted MNDWI | FMNDWI1 to FMNDWI12 | 12 | |
| Harmonic-fitted NDBI | FNDBI1 to FNDBI12 | 12 | |
| Sentinel-1 | VV Polarization | VV1 to VV12 | 12 |
| VH Polarization | VH1 to VH12 | 12 | |
| SRTM | Terrain Ruggedness Index | TRI | 1 |
| Pixel Dimension: 867 × 480 pixels | Total Layer | 61 | |
| Model | PA (%) | UA (%) | OA (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CART | 80.87 | 84.83 | 87.57 |
| RF50 | 93.48 | 85.66 | 92.47 |
| RF80 | 91.63 | 85.76 | 92.10 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arjasakusuma, S.; Swahyu Kusuma, S.; Rafif, R.; Saringatin, S.; Wicaksono, P. Combination of Landsat 8 OLI and Sentinel-1 SAR Time-Series Data for Mapping Paddy Fields in Parts of West and Central Java Provinces, Indonesia. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2020, 9, 663. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi9110663
Arjasakusuma S, Swahyu Kusuma S, Rafif R, Saringatin S, Wicaksono P. Combination of Landsat 8 OLI and Sentinel-1 SAR Time-Series Data for Mapping Paddy Fields in Parts of West and Central Java Provinces, Indonesia. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information. 2020; 9(11):663. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi9110663
Chicago/Turabian StyleArjasakusuma, Sanjiwana, Sandiaga Swahyu Kusuma, Raihan Rafif, Siti Saringatin, and Pramaditya Wicaksono. 2020. "Combination of Landsat 8 OLI and Sentinel-1 SAR Time-Series Data for Mapping Paddy Fields in Parts of West and Central Java Provinces, Indonesia" ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information 9, no. 11: 663. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi9110663
APA StyleArjasakusuma, S., Swahyu Kusuma, S., Rafif, R., Saringatin, S., & Wicaksono, P. (2020). Combination of Landsat 8 OLI and Sentinel-1 SAR Time-Series Data for Mapping Paddy Fields in Parts of West and Central Java Provinces, Indonesia. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 9(11), 663. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi9110663