An Occupancy Simulator for a Smart Parking System: Developmental Design and Experimental Considerations
Abstract
1. Introduction
- The methodology we employed to increase re-usability of software development efforts for a parking simulator, applied to a related SPS development;
- how to explore the reservation guarantee concept for an SPS without physical reservation enforcement; and
- how to use the total driving distance metric for making credible comparisons when evaluating an SPS usage benefits.
2. Background
2.1. Smart Parking Systems and Parking Simulations
- building or adapting parking simulator software and not just defining a model to run in available modelers,
- working alongside the SPS development team, and
- applying software design techniques that assure robust re-usability.
2.2. Agent-Based Parking Models And Gis
2.3. SPS Evaluation Metrics
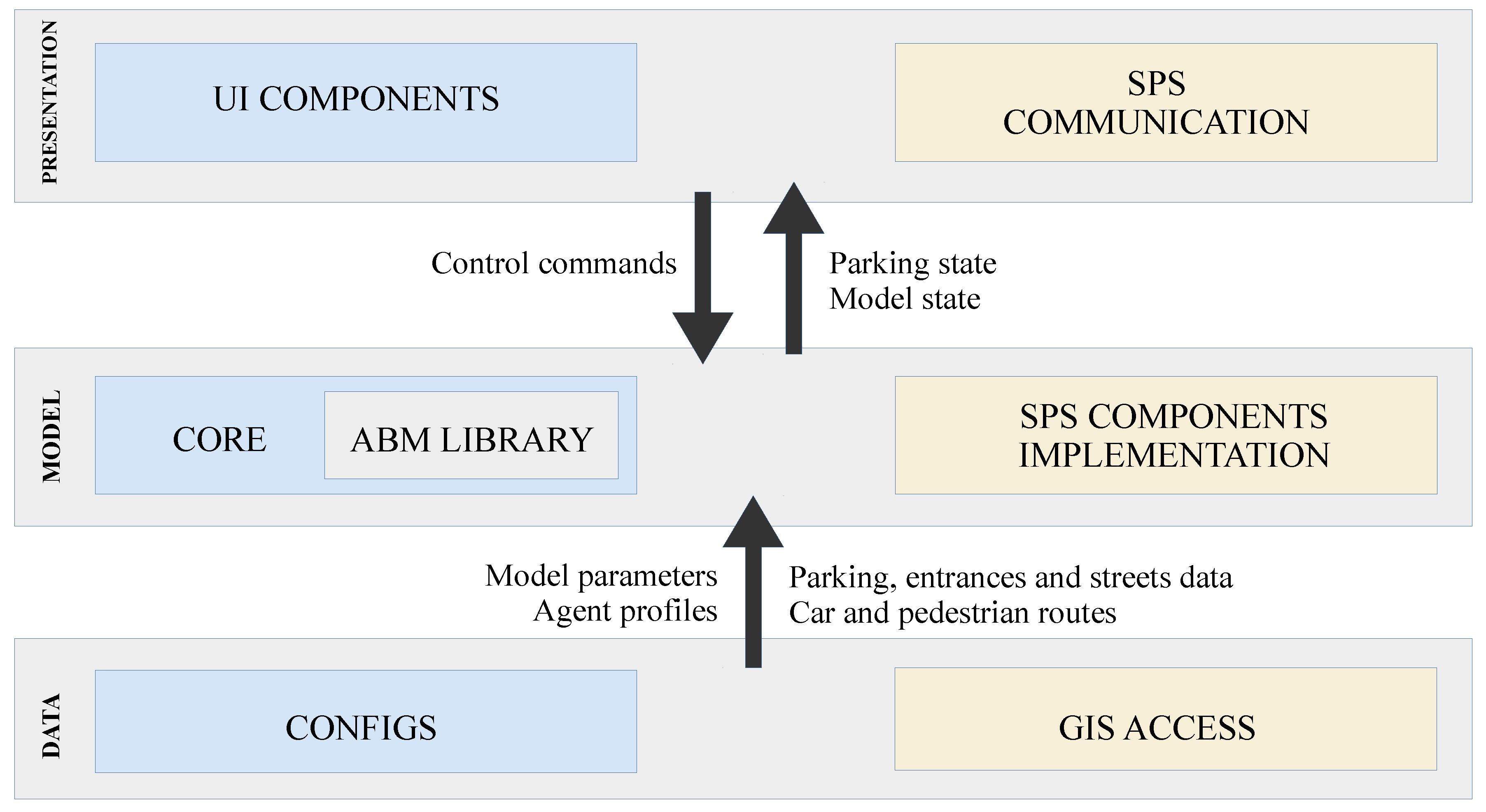
3. The SPS and the Parking Simulator
4. Parking Simulator Details
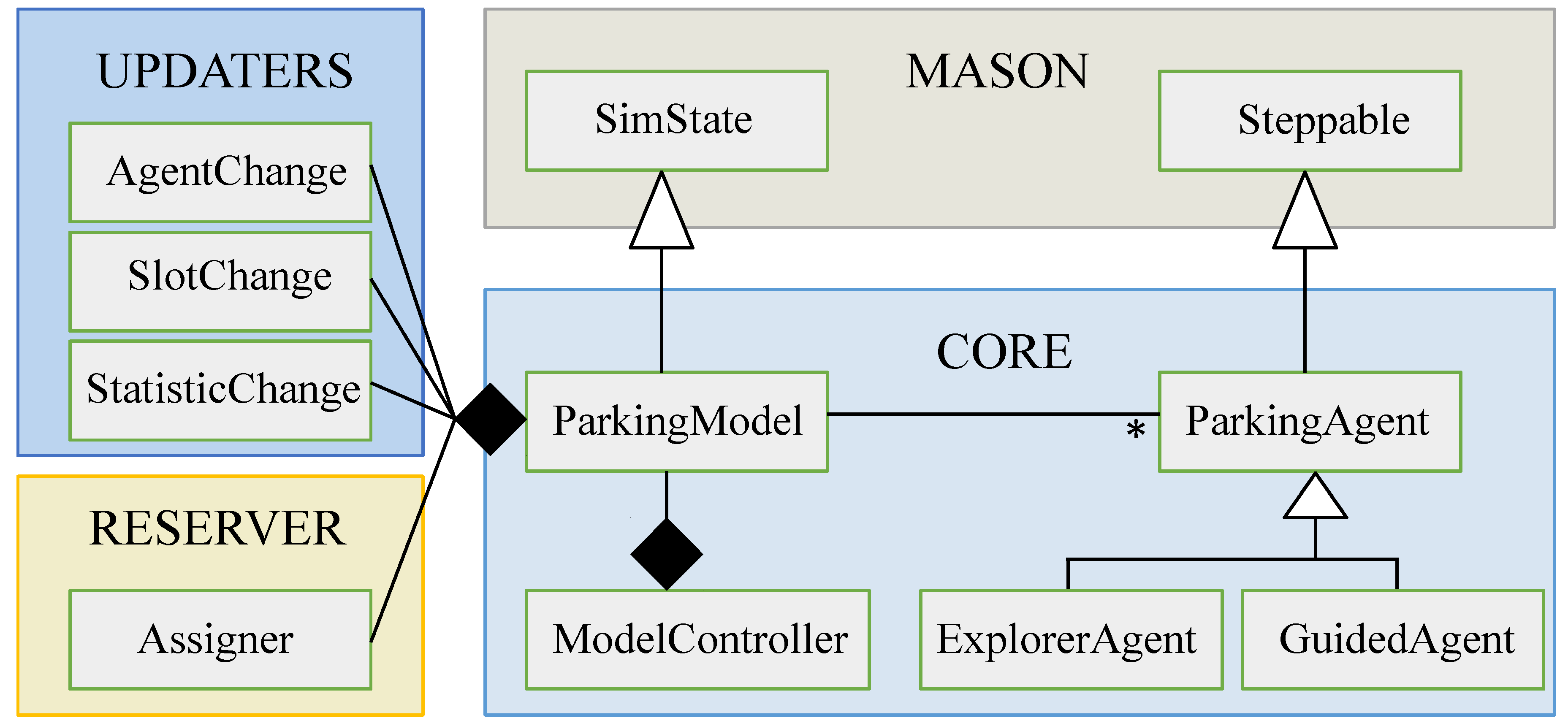
4.1. The Model
4.1.1. Agent Profiles
4.1.2. Search Behavior
Explorer
| Algorithm 1: Explorer agents decision rules |
Input:
|
Guided
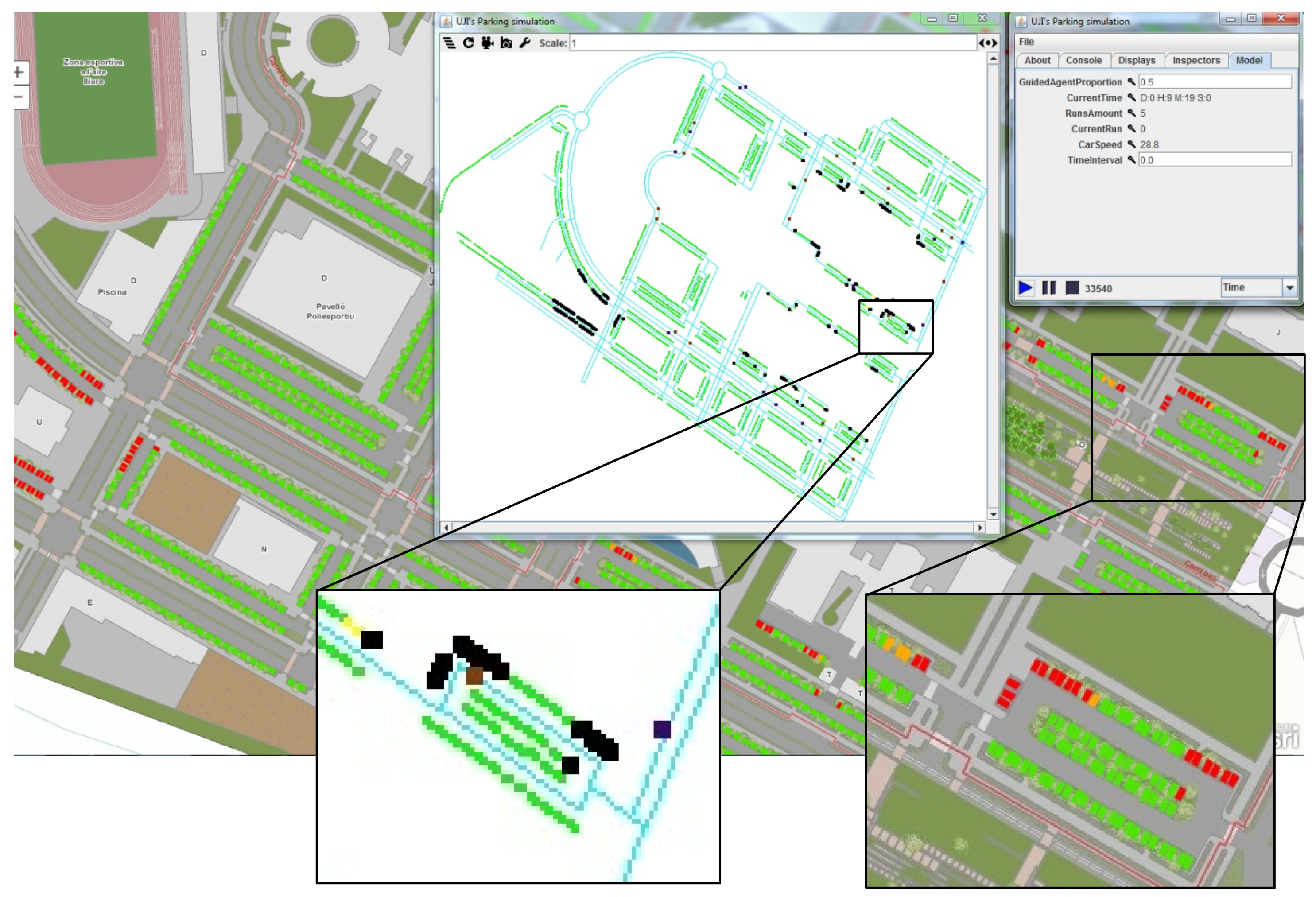
4.2. The Simulator
4.3. Parking Reservation Component
4.4. Final Development Considerations
- GIS data and services hosted in a GIS server,
- software artifacts for remote GIS data read/write operations,
- reservation component, and
- visualization components created for simulation testing.
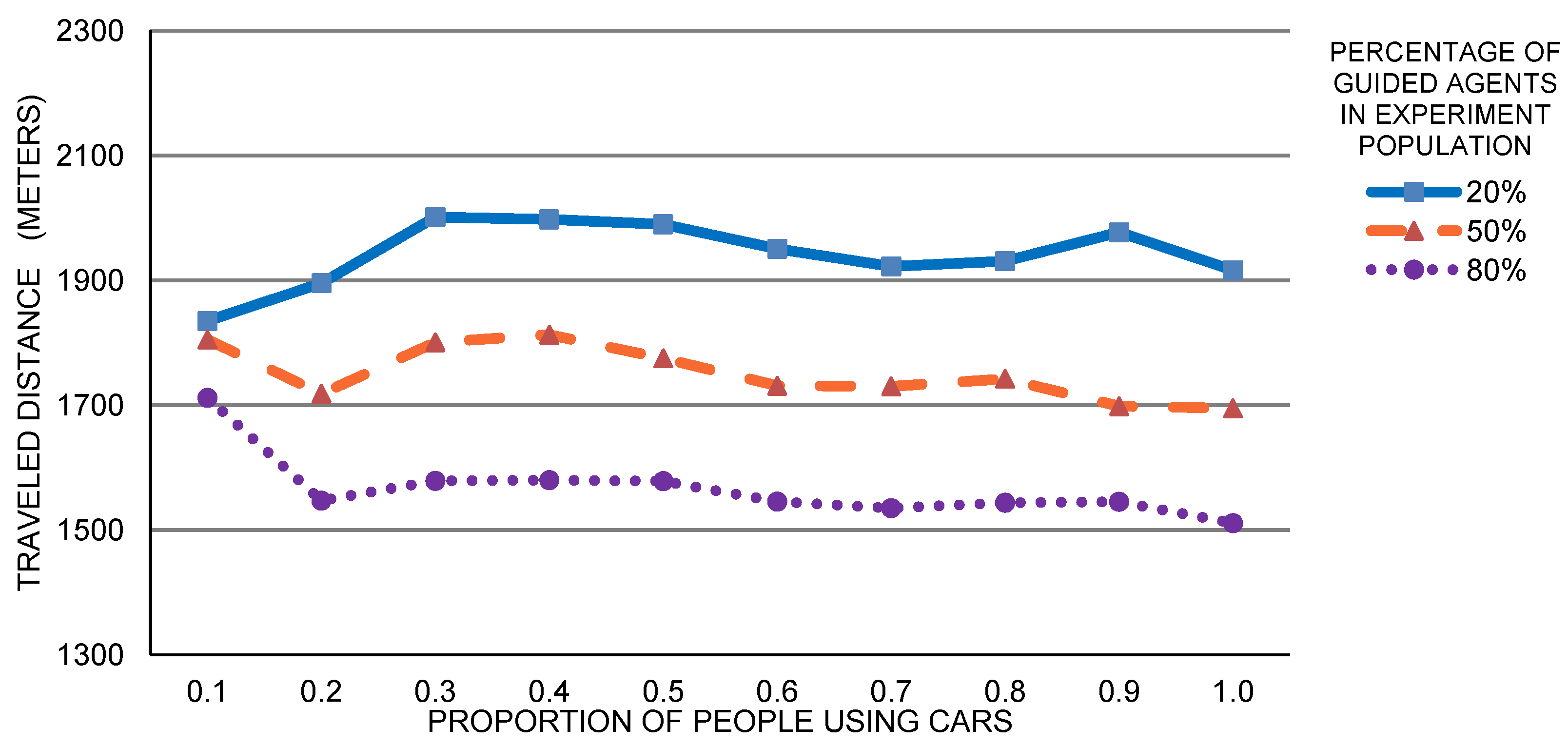
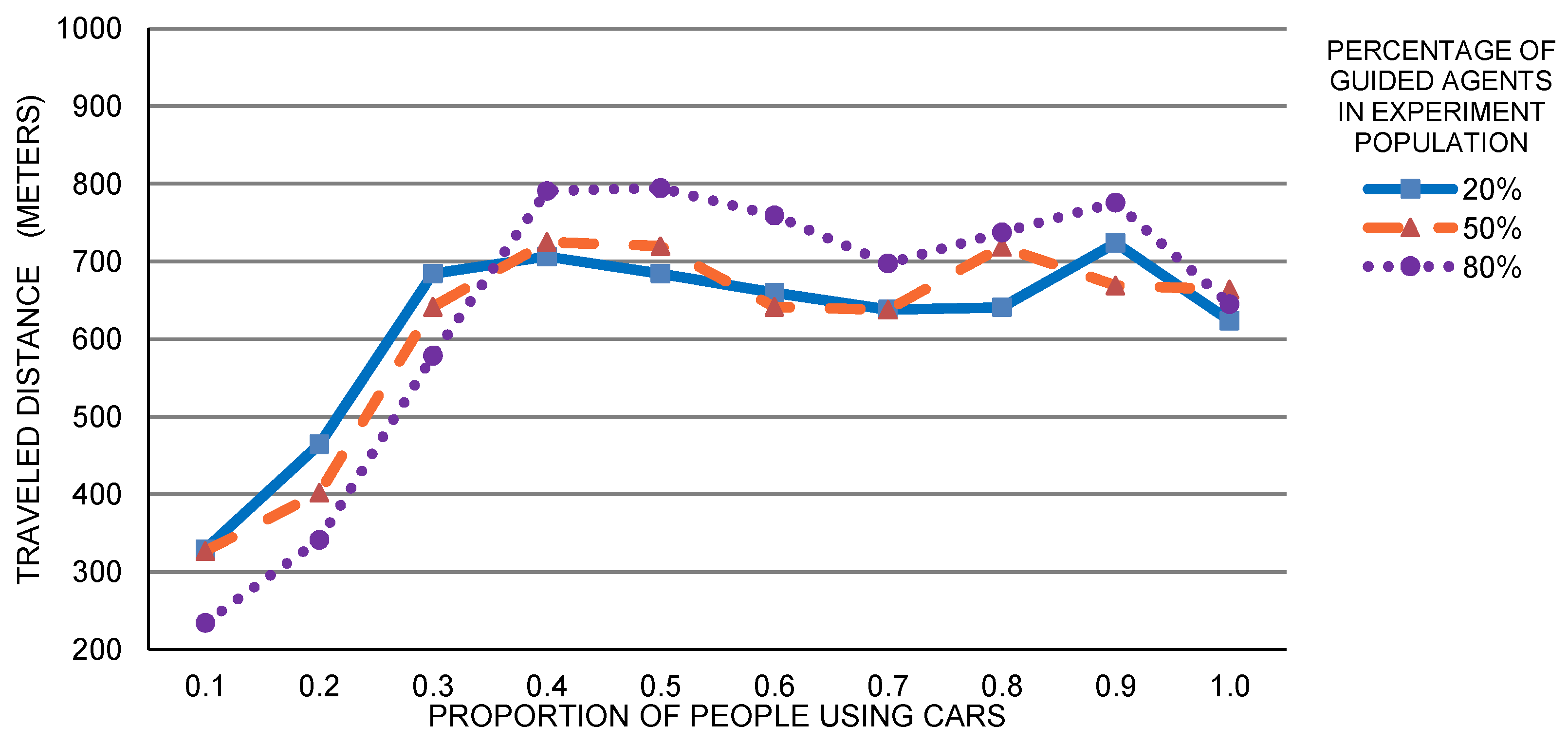
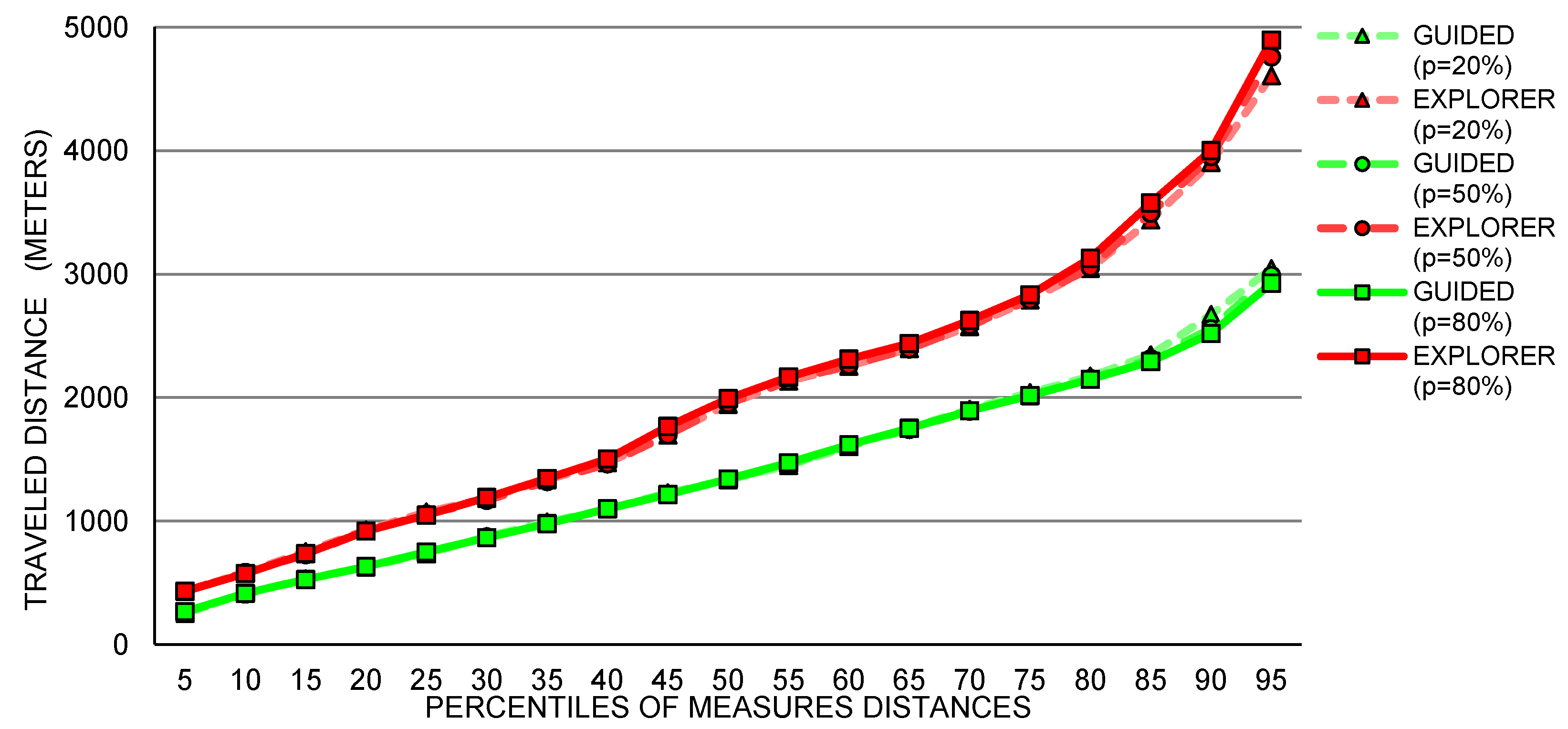
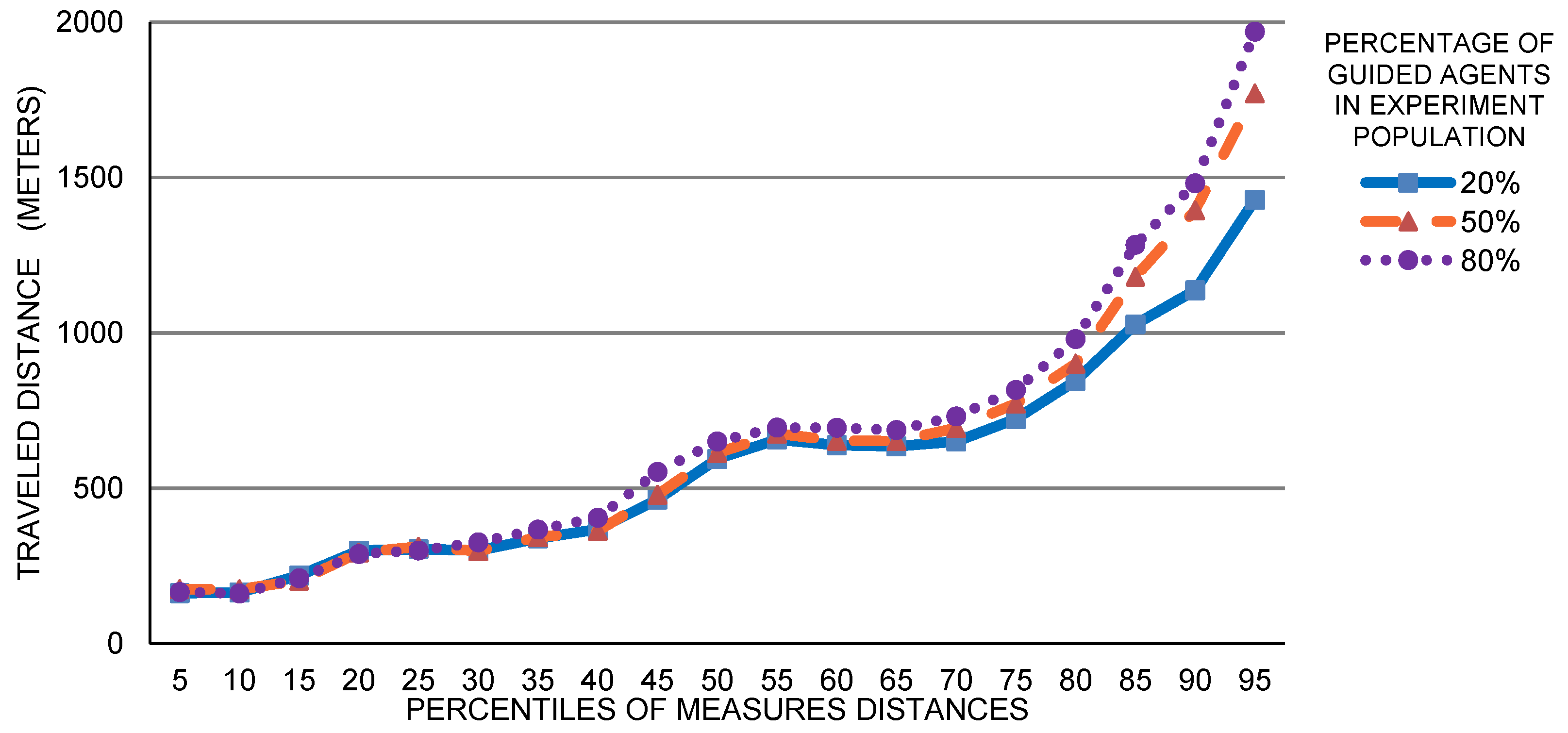
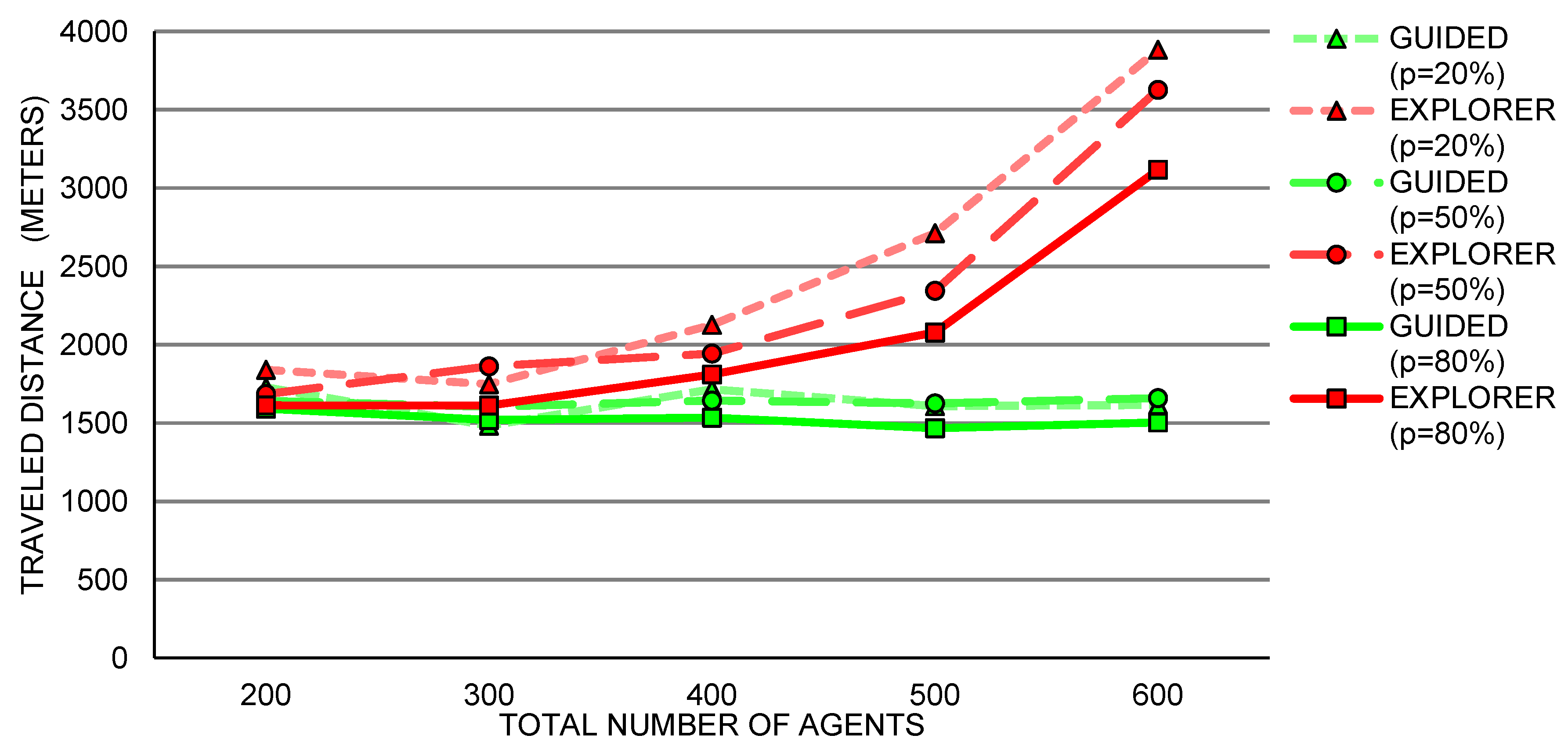
5. Case Study: Exploration of SPS Expected Usage
Single Building Analysis
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Inci, E. A review of the economics of parking. Econ. Transp. 2015, 4, 50–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotb, A.O.; Shen, Y.C.; Huang, Y. Smart Parking Guidance, Monitoring and Reservations: A Review. IEEE Intell. Transp. Syst. Mag. 2017, 9, 6–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Małecki, K. A computer simulation of traffic flow with on-street parking and drivers’ behaviour based on cellular automata and a multi-agent system. J. Comput. Sci. 2018, 28, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waraich, R.A.; Axhausen, K.W. Agent-based parking choice model. Transp. Res. Rec. 2012, 2319, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Y.; Cassandras, C.G. New ’smart parking’ system based on resource allocation and reservations. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2013, 14, 1129–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.H.; Jun, H.B. A study on smart parking guidance algorithm. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2014, 44, 299–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazzan, A.L.C.; Klügl, F. A review on agent-based technology for traffic and transportation. Knowl. Eng. Rev. 2014, 29, 375–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggi, E.; Vallino, E. Understanding urban mobility and the impact of public policies: The role of the agent-based models. Res. Transp. Econ. 2016, 55, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crooks, A.T.; Castle, C.J.E. The integration of agent-based modelling and geographical information for geospatial simulation. In Agent-Based Models of Geographical Systems; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 219–251. [Google Scholar]
- Dangermond, J. Geospatial Technology and the Future of the City. 2015. Available online: http://www.esri.com/esri-news/arcnews/winter1415articles/geospatial-technology-and-the-future-of-the-city (accessed on 23 April 2019).
- Frost&Sullivan. Smart Parking to Enable Intelligent Mobility in Global Mega Cities. 2015. Available online: http://ww2.frost.com/news/press-releases/smart-parking-enable-intelligent-mobility-global-mega-cities/ (accessed on 23 April 2019).
- Rhodes, C.; Blewitt, W.; Sharp, C.; Ushaw, G.; Morgan, G. Smart Routing: A Novel Application of Collaborative Path-Finding to Smart Parking Systems. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE 16th Conference on Business Informatics, Geneva, Switzerland, 4–17 July 2014; pp. 119–126. [Google Scholar]
- Levy, N.; Render, M.; Benenson, I. Spatially explicit modeling of parking search as a tool for urban parking facilities and policy assessment. Transp. Policy 2015, 39, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, Z.; Feng, C.; Ding, W.; Zhang, L.; Wang, D. Better lucky than rich? Comparative analysis of parking reservation and parking charge. Transp. Policy 2019, 75, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leclercq, L.; Sénécat, A.; Mariotte, G. Dynamic macroscopic simulation of on-street parking search: A trip-based approach. Transp. Res. Part B Methodol. 2017, 101, 268–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leephakpreeda, T. Car-parking guidance with fuzzy knowledge-based decision making. Build. Environ. 2007, 42, 803–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kravari, K.; Bassiliades, N. A survey of agent platforms. J. Artif. Soc. Soc. Simul. 2015, 18, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudali, I.; Ouada, M.B. Smart Parking Reservation System Based on Distributed Multicriteria Approach. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2017, 31, 518–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, X.Y.; Sun, D.J. Agent-Based Modelling and Simulation to Assess the Impact of Parking Reservation System. J. Adv. Transp. 2017, 2017, 2576094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Spana, S.; Yin, Y.; Du, Y. An Advanced Parking Navigation System for Downtown Parking. Netw. Spat. Econ. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.; Rivano, H.; Le Mouël, F. A survey of smart parking solutions. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2017, 18, 3229–3253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crooks, A.; Malleson, N.; Manley, E.; Heppenstall, A. Agent-Based Modelling and Geographical Information Systems: A Practical Primer; SAGE Publications Limited: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Taillandier, P.; Gaudou, B.; Grignard, A.; Huynh, Q.N.; Marilleau, N.; Caillou, P.; Philippon, D.; Drogoul, A. Building, composing and experimenting complex spatial models with the GAMA platform. GeoInformatica 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieussaert, K.; Aerts, K.; Steenberghen, T.; Maerivoet, S.; Spitaels, K. SUSTAPARK: An agent-based model for simulating parking search. In Proceedings of the AGILE International Conference on Geographic Information Science, Hannover, Germany, 2–5 June 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, K.S.; Eom, J.K.; seop Moon, D. Applications of TRANSIMS in Transportation: A Literature Review. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2014, 32, 769–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horni, A.; Nagel, K.; Axhausen, K.W. The Multi-Agent Transport Simulation MATSim; Ubiquity Press: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Fulman, N.; Benenson, I. Agent-Based Modeling for Transportation Planning: A Method for Estimating Parking Search Time Based on Demand and Supply. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1806.10874. [Google Scholar]
- Benenson, I.; Martens, K.; Birfir, S. PARKAGENT: An agent-based model of parking in the city. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2008, 32, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, N.; Martens, K.; Benenson, I. Exploring cruising using agent-based and analytical models of parking. Transp. A Transp. Sci. 2013, 9, 773–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surpris, G.; Liu, D.; Vincenzi, D. How Much Can a Smart Parking System Save You? Ergon. Des. Q. Hum. Factors Appl. 2014, 22, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; He, W. A Reservation-based Smart Parking System. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE Conference on Computer Communications Workshops (INFOCOM WKSHPS), Shanghai, China, 10–15 April 2011; pp. 690–695. [Google Scholar]
- Tasseron, G.; Martens, K. Urban parking space reservation through bottom-up information provision: An agent-based analysis. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2017, 64, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Menendez, M. System dynamics of urban traffic based on its parking-related-states. Transp. Res. Part B Methodol. 2015, 81, 718–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, M. Patterns of Enterprise Application Architecture; Addison-Wesley Longman Publishing Co., Inc.: Reading, MA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Torres-Sospedra, J.; Avariento, J.; Rambla, D.; Montoliu, R.; Casteleyn, S.; Benedito-Bordonau, M.; Gould, M.; Huerta, J. Enhancing integrated indoor/outdoor mobility in a smart campus. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2015, 29, 1955–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baqueri, S.F.A.; Adnan, M.; Kochan, B.; Bellemans, T. Activity-based model for medium-sized cities considering external activity–travel: Enhancing FEATHERS framework. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2019, 96, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaniotakis, E.; Pel, A.J. Drivers’ parking location choice under uncertain parking availability and search times: A stated preference experiment. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2015, 82, 228–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Li, S.; Wang, W.; Li, X.; Du, Y. Advanced Parking Space Management Strategy Design: An Agent-Based Simulation Optimization Approach. Transp. Res. Rec. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antolín, G.; Ibeas, Á.; Alonso, B.; dell’Olio, L. Modelling parking behaviour considering users heterogeneities. Transp. Policy 2018, 67, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bischoff, J.; Maciejewski, M.; Schlenther, T.; Nagel, K. Autonomous vehicles and their impact on parking search. IEEE Intell. Transp. Syst. Mag. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaliq, A.; van der Waerden, P.; Janssens, D.; Wets, G. A Conceptual Framework for Forecasting Car Driver’s On-Street Parking Decisions. Transp. Res. Procedia 2019, 37, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Du, Y.; Li, Y.C.; Wong, S.C. Modeling heterogeneous parking choice behavior on university campuses. Transp. Plan. Technol. 2018, 41, 154–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martens, K.; Benenson, I.; Levy, N. The dilemma of on-street parking policy: Exploring cruising for parking using an agent-based model. In Geospatial Analysis and Modelling of Urban Structure and Dynamics; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2010; pp. 121–138. [Google Scholar]
- Luke, S. Multiagent simulation and the MASON library. 2015. Available online: https://cs.gmu.edu/~eclab/projects/mason/manual.pdf (accessed on 23 April 2019).
- Coletti, M. The GeoMason Cookbook. 2013. Available online: https://cs.gmu.edu/~eclab/projects/mason/extensions/geomason/geomason.pdf (accessed on 23 April 2019).
- Kastanakis, B. Mapbox Cookbook; Packt Publishing Ltd.: Birmingham, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- GeoTools: The Open Source Java GIS Toolkit. 2019. Available online: https://geotools.org/ (accessed on 23 April 2019).
- Arnott, R.; Williams, P. Cruising for parking around a circle. Transp. Res. Part B Methodol. 2017, 104, 357–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| maxWalkDist (m) | [50 to 100] |
| criticalRatio | 0.25 |
| criticalReduc | 0.15 |
| visDistance (m) | 40 |
| carSpeed (km/h) | 30 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mendoza-Silva, G.M.; Gould, M.; Montoliu, R.; Torres-Sospedra, J.; Huerta, J. An Occupancy Simulator for a Smart Parking System: Developmental Design and Experimental Considerations. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2019, 8, 212. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi8050212
Mendoza-Silva GM, Gould M, Montoliu R, Torres-Sospedra J, Huerta J. An Occupancy Simulator for a Smart Parking System: Developmental Design and Experimental Considerations. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information. 2019; 8(5):212. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi8050212
Chicago/Turabian StyleMendoza-Silva, Germán Martín, Michael Gould, Raul Montoliu, Joaquín Torres-Sospedra, and Joaquín Huerta. 2019. "An Occupancy Simulator for a Smart Parking System: Developmental Design and Experimental Considerations" ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information 8, no. 5: 212. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi8050212
APA StyleMendoza-Silva, G. M., Gould, M., Montoliu, R., Torres-Sospedra, J., & Huerta, J. (2019). An Occupancy Simulator for a Smart Parking System: Developmental Design and Experimental Considerations. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 8(5), 212. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi8050212









