Semantics-Constrained Advantageous Information Selection of Multimodal Spatiotemporal Data for Landslide Disaster Assessment
Abstract
1. Introduction
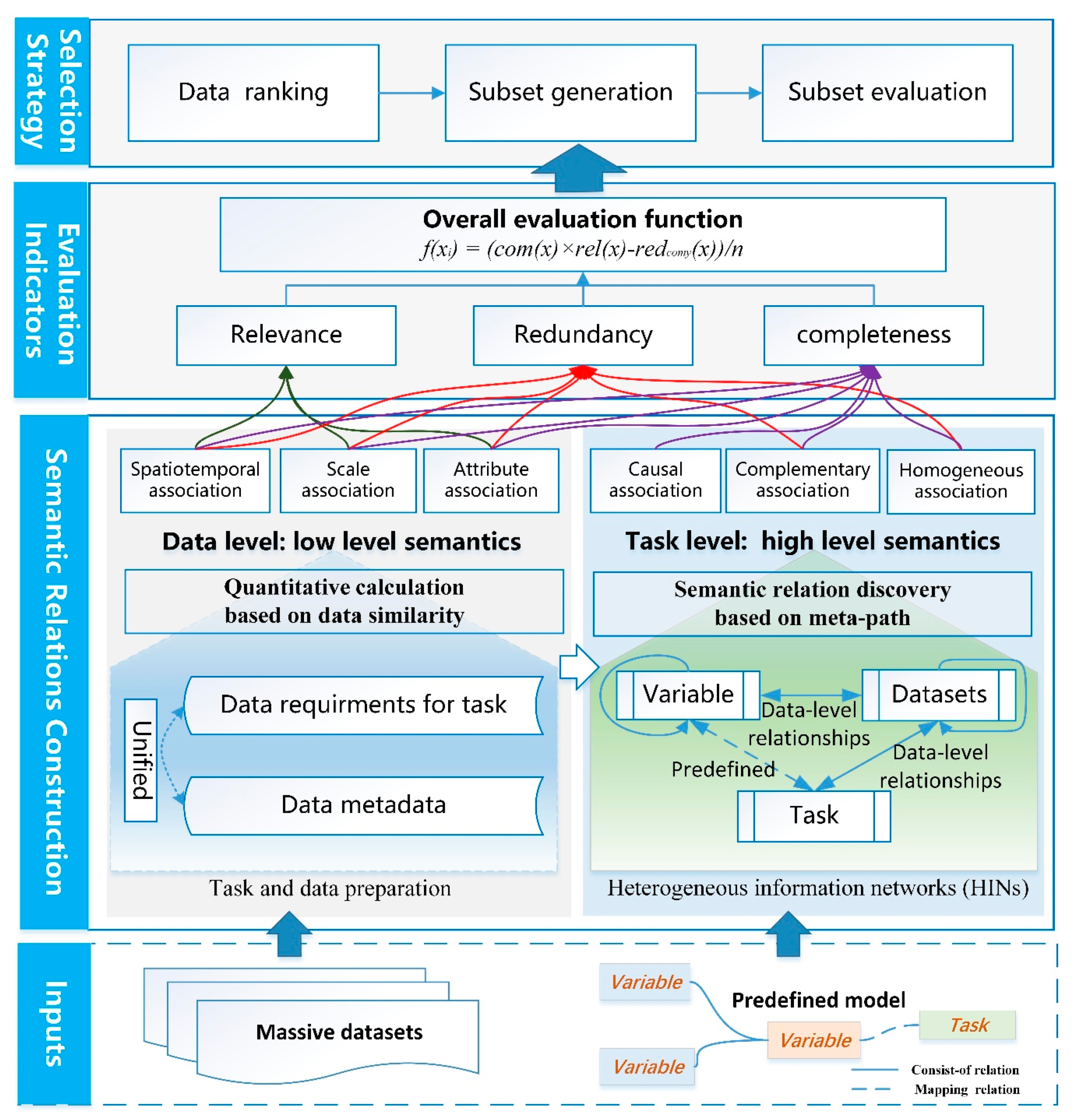
2. Methodology
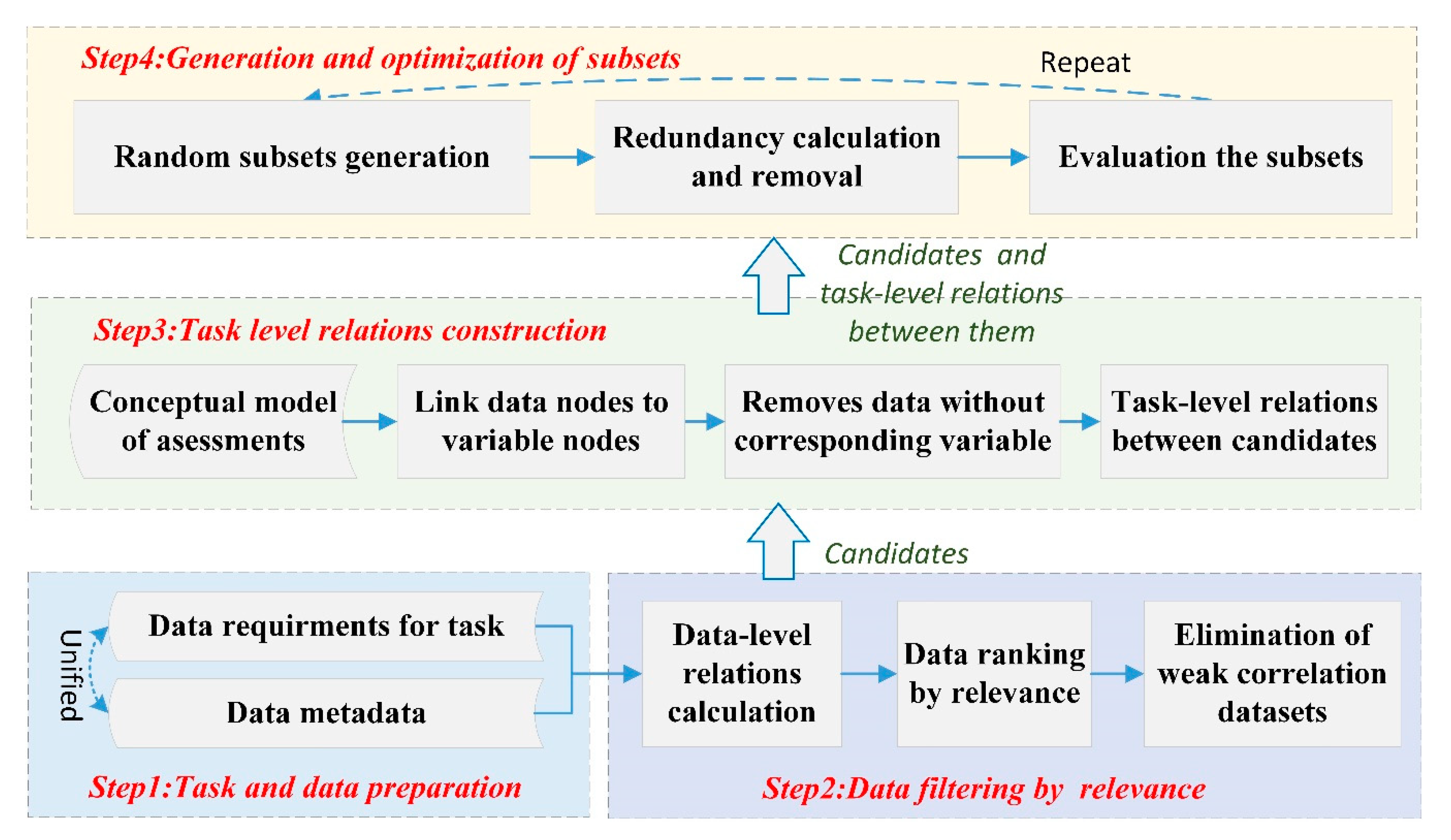
2.1. Framework of the Methodology
2.2. Construction of Multidimensional Semantic Relationships
2.2.1. Unified Description of Multiple-Association Relationships
2.2.2. Calculation of Data-Level Relationships Based on Data Similarity
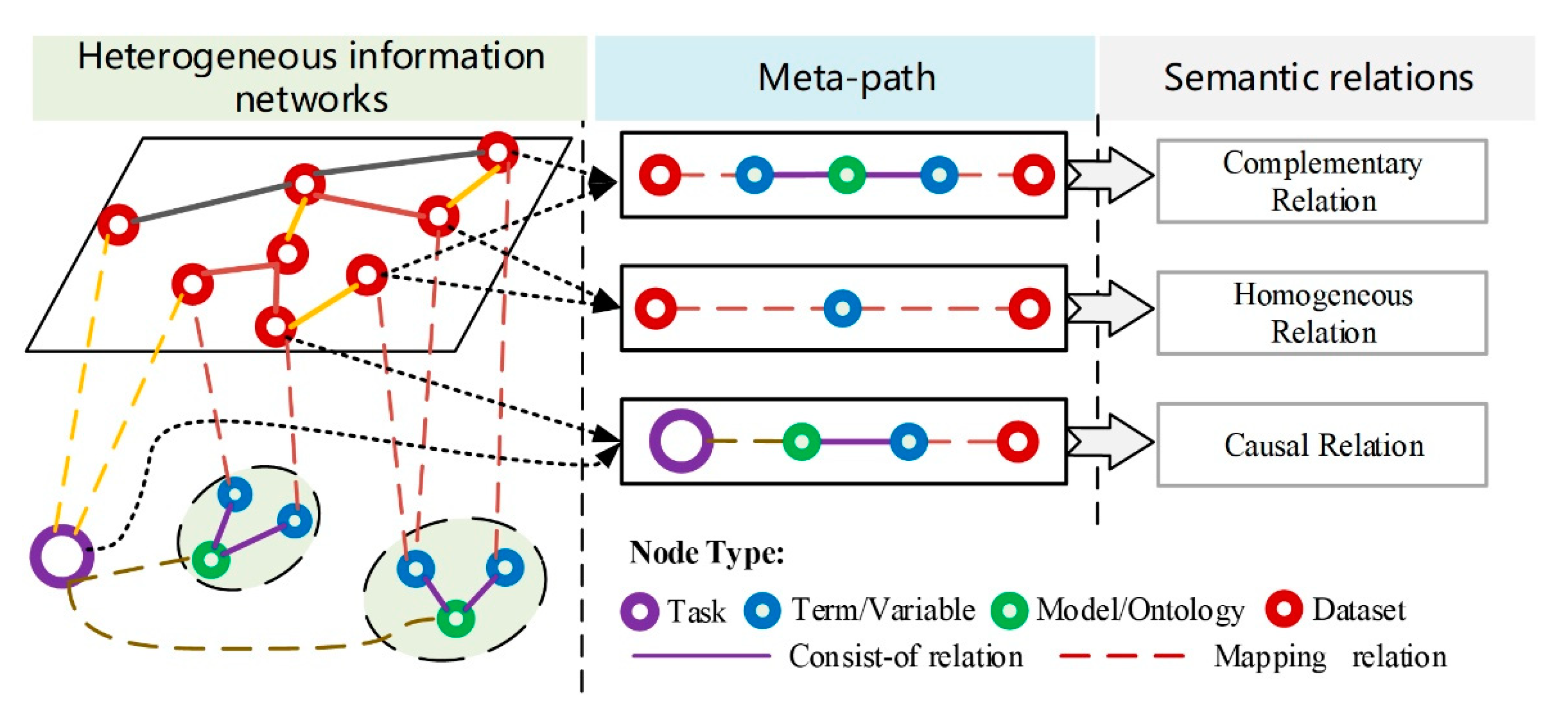
2.2.3. Task-Level Relationship Discovery Based on Meta-Paths
 , which represents a path of type .
, which represents a path of type . , which represents a path of type , where the relationships of r1 and r2 do not belong to the consist-of relationship at the same time.
, which represents a path of type , where the relationships of r1 and r2 do not belong to the consist-of relationship at the same time. , which represents a path of type .
, which represents a path of type .2.3. Semantics-Concerned Evaluation Indicators
2.4. Semantics-Constrained Advantageous Information Selection Strategy
3. Case Study
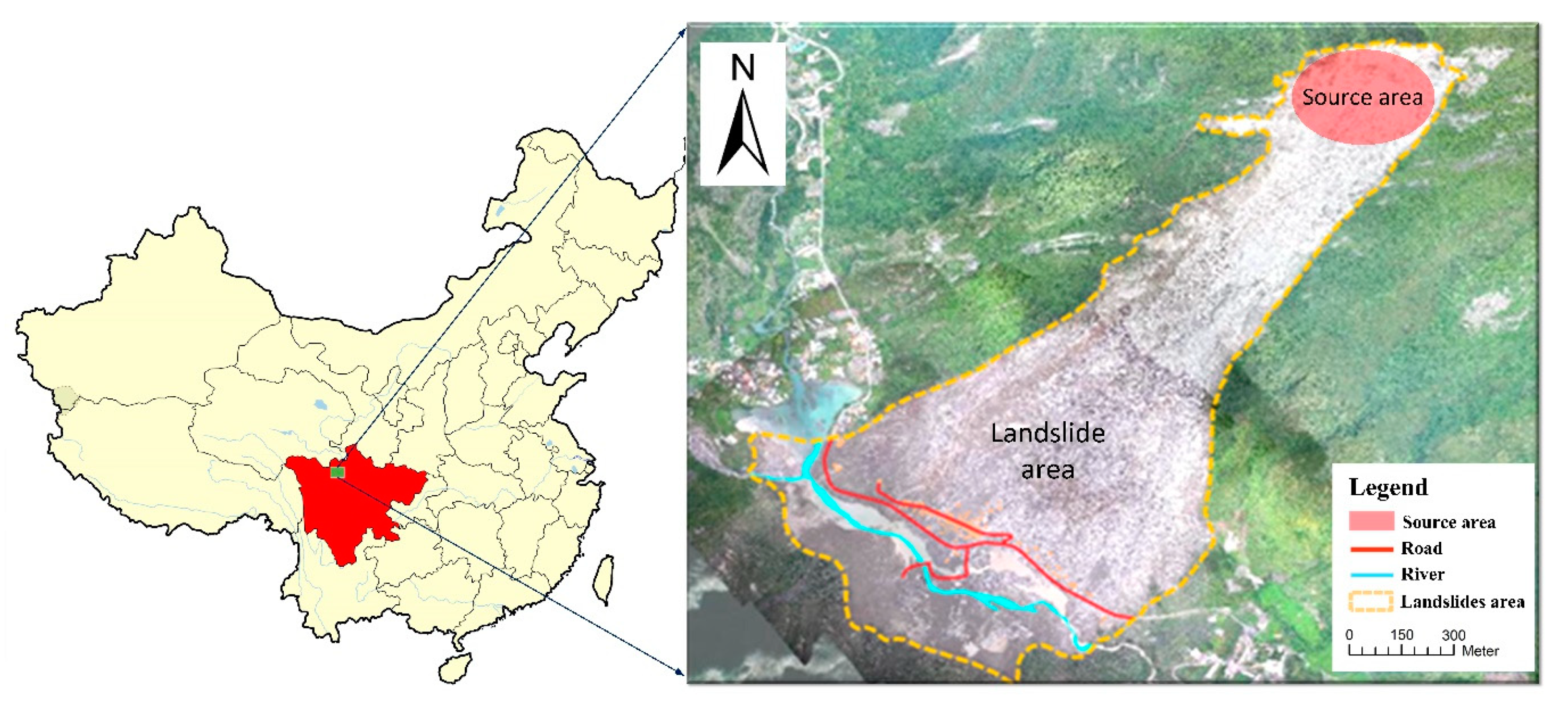
3.1. Test Data Description
3.2. Advantageous Information Selection Process
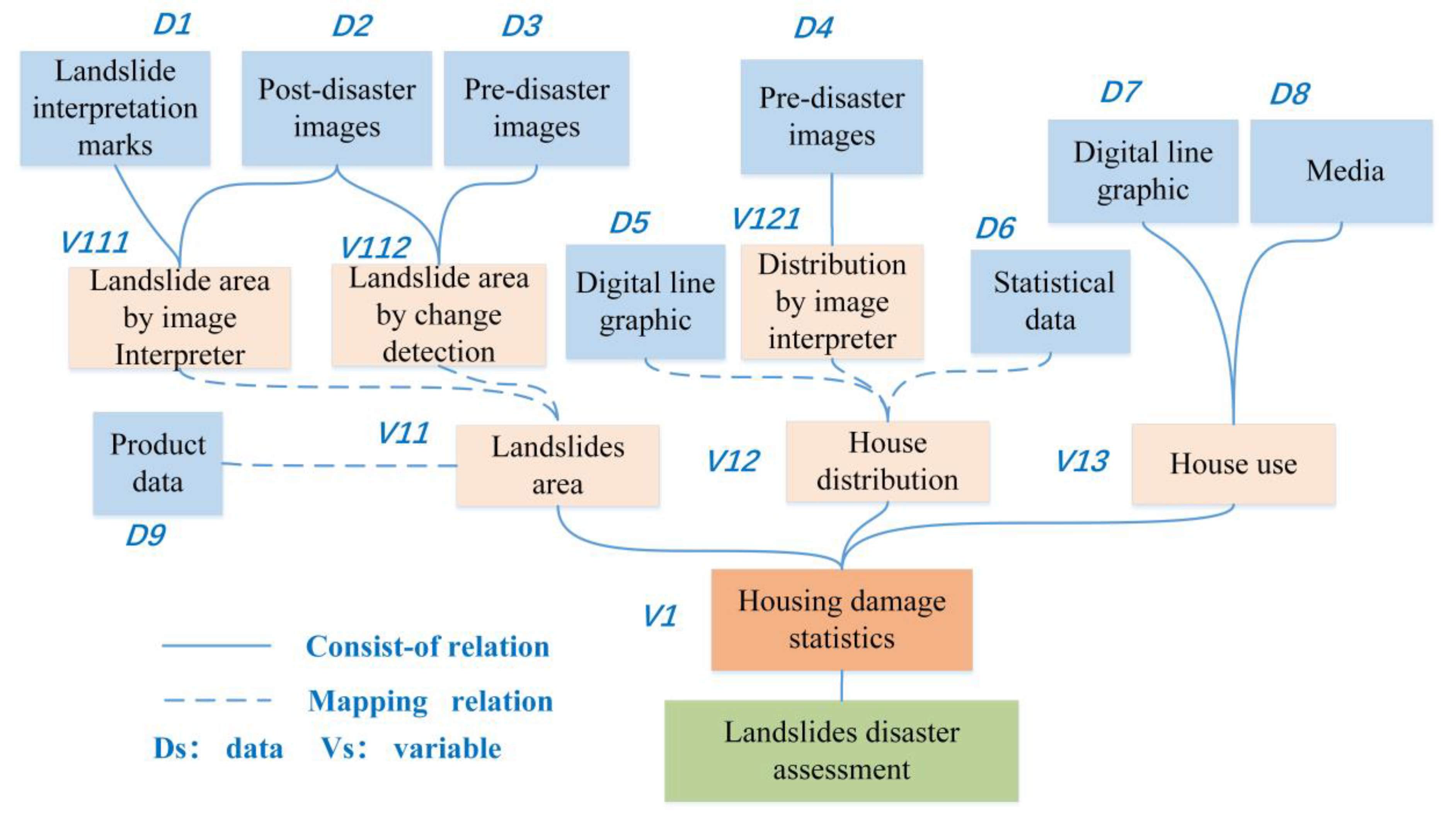
3.2.1. Task and Data Preparation
3.2.2. Data Filtering
3.2.3. Task-Level Relationship Construction
3.2.4. Selection and Optimization of Datasets
3.3. Selection Results
4. Result Analysis and Discussion
5. Conclusions and Future Studies
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kryvasheyeu, Y.; Chen, H.; Obradovich, N.; Moro, E.; Van Hentenryck, P.; Fowler, J.; Cebrian, M. Rapid assessment of disaster damage using social media activity. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1500779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, L.Y.; Zhu, Q.; Gu, J.Y.; Du, Z.Q. A task-driven disaster data link approach. Int. Arch. Photogram. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2015, 40, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velev, D.; Zlateva, P. Current state of enterprise 2.0 knowledge management. Int. J. Trade Econ. Financ. 2012, 39, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, F.; Hwang, J.H.; Chen, L.C.; Lin, T.H. Post-disaster assessment of landslides in southern Taiwan after 2009 Typhoon Morakot using remote sensing and spatial analysis. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2010, 10, 2179–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, H.; Asahara, A.; Sugaya, N.; Ogawa, Y.; Tomita, H. Spatio-temporal similarity search method for disaster estimation. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Big Data (Big Data), Santa Clara, CA, USA, 29 October–1 November 2015; Hayashi, H., Asahara, A., Sugaya, N., Ogawa, Y., Tomita, H., Eds.; IEEE: Washington, DC, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Alizadeh, M.; Ngah, I.; Hashim, M.; Pradhan, B.; Pour, B.A. A Hybrid Analytic Network Process and Artificial Neural Network (ANP-ANN) model for urban Earthquake vulnerability assessment. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, M.; Alizadeh, E.; Kotenaee, S.A.; Shahabi, H.; Pour, B.A.; Panahi, M.; Bin Ahmad, B.; Saro, L. Social vulnerability assessment using artificial neural network (ANN) model for earthquake hazard in Tabriz city, Iran. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, M.; Hashim, M.; Alizadeh, E.; Shahabi, H.; Karami, M.R.; Pour, A.B.; Paradhan, B.; Zabihi, H. Multi-criteria decision making (MCDM) model for seismic vulnerability assessment (SVA) of urban residential buildings. Isprs Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2018, 7, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillera-Arroita, G.; Lahoz-Monfort, J.J.; Elith, J.; Gordon, A.; Kujala, H.; Lentini, P.E.; McCarthy, M.A.; Tingley, R.; Wintle, B.A. Is my species distribution model fit for purpose? Matching data and models to applications. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2015, 24, 276–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarboton, D.G.; Idaszak, R.; Horsburgh, J.S.; Heard, J.; Ames, D.; Goodall, J.L.; Band, L.; Merwade, V.; Couch, A.; Arrigo, J.; et al. HydroShare: Advancing collaboration through hydrologic data and model sharing. In Proceedings of the 7th International Congress on Environmental Modelling and Software: Bold Visions for Environmental Modeling, iEMSs 2014, San Diego, CA, USA, 15–19 June 2014; Tarboton, D.G., Idaszak, R., Horsburgh, J.S., Heard, J., Ames, D., Goodall, J.L., Band, L., Merwade, V., Couch, A., Arrigo, J., et al., Eds.; International Environmental Modelling and Software Society: San Diego, CA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhu, A.X.; Feng, M.; Song, J.; Zhao, H.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Sun, K.; Zhang, J.; Yao, L. A similarity-based automatic data recommendation approach for geographic models. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2017, 31, 1403–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodchild, M.F.; Glennon, J.A. Crowdsourcing geographic information for disaster response: A research frontier. Int. J. Digit. Earth. 2010, 3, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, C.; Kitsuregawa, M. Big Data and Disaster Management: A Report from the JST/NSF Joint Workshop; Georgia Institute of Technology, CERCS: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, H.; Wang, L.; Chen, F.; Liang, D. Scientific big data and digital earth. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2014, 59, 5066–5073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashim, M.; Misbari, S.; Pour, B.A. Landslide mapping and assessment by integrating Landsat-8, PALSAR-2 and GIS techniques: A case study from Kelantan state, peninsular Malysia. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2018, 46, 233–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pour, B.A.; Hashim, M. Application of Landsat-8 and ALOS-2 data for structural and landslide hazard mapping in Kelantan, Malaysia. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 17, 1285–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y. Geospatial semantics. In Comprehensive Geographic Information Systems, also Included in Elsevier’s Reference Module in Earth Systems and Environmental Sciences; Huang, B., Cova, T.J., Tsou, M., Eds.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2017; pp. 80–94. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Zlatanova, S.; Fabbri, A.G. Geomatics Solutions for Disaster Management; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández, M.; Cantador, I.; López, V.; Vallet, D.; Castells, P.; Motta, E. Semantically enhanced information retrieval: An ontology-based approach. J. Web Semant. 2011, 9, 434–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hristidis, V.; Chen, S.-C.; Li, T.; Luis, S.; Deng, Y. Survey of data management and analysis in disaster situations. J. Syst. Softw. 2010, 83, 1701–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiegand, N.; García, C. A task-based ontology approach to automate geospatial data retrieval. Trans. GIS 2007, 11, 355–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhong, Z.; Xiong, W.; Jing, N. Geo-Link: Correlations of heterogeneous geo-spatial entities. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2014, 39, 8811–8824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Zlatanova, S. Exploring ontologies for semantic interoperability of data in emergency response. Appl. Geomat. 2011, 3, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Du, Z.; Zhu, Q.; Fan, Y. An integrated flood management system based on linking environmental models and disaster-related data. Environ. Model. Softw. 2017, 91, 111–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, A.; Döweling, S.; Probst, F. Integrating process modeling and linked open data to improve decision making in disaster management. In International Reports on Socio-Informatics (IRSI), Proceedings of the CSCW 2012 Workshop on Collaboration and Crisis Informatics, Seattle, WA, USA, 11–15 February 2012; Pipek, V., Landgren, J., Palen, L., Eds.; International Institute for Socio-Informatics: Bonn, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, T.; Wuwongse, V.; Sharma, H.N. Disaster mitigation and preparedness using linked open data. J. Ambient Intell. Hum. Comput. 2012, 4, 591–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janowicz, K.; Raubal, M.; Kuhn, W. The semantics of similarity in geographic information retrieval. J. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2011, 2, 29–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Wang, L.; Ranjan, R.; Wu, A. Semantic analysis and retrieval of spatial data based on the uncertain ontology model in digital earth. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2015, 8, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhu, A.X.; Song, J.; Yang, J.; Feng, M.; Sun, K.; Zhang, J.; Hou, Z.; Zhao, H. Multidimensional and quantitative interlinking approach for linked geospatial data. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2017, 10, 923–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyon, I.; Elisseeff, A.; Kaelbling, L.P. An introduction to variable and feature selection. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2003, 3, 1157–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Alelyani, S.; Liu, H. Feature selection for classification: A review. In Data Classification: Algorithms and Applications; Aggarwal, C., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014; pp. 37–64. [Google Scholar]
- Bolón-Canedo, V.; Sánchez-Maroño, N.; Alonso-Betanzos, A. Recent advances and emerging challenges of feature selection in the context of big data. Knowl. Based Syst. 2015, 86, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Cheng, K.; Wang, S.; Morstatter, F.; Trevino, R.P.; Tang, J.; Liu, H. Feature selection. ACM Comput. Surv. 2016, 50, 1–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Long, F.; Ding, C. Feature selection based on mutual information: Criteria of max-dependency, max-relevance, and min-redundancy. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2005, 27, 1226–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramírez-Gallego, S.; Lastra, I.; Martínez-Rego, D.; Bolón-Canedo, V.; Benítez, J.M.; Herrera, F.; Alonso-Betanzos, A. Fast-mRMR: Fast minimum redundancy maximum relevance algorithm for high-dimensional big data. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 2016, 32, 134–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovic, A.; Brkic, K.; Bogunovic, N. A review of feature selection methods with applications. In Proceedings of the 2015 38th International Convention on Information and Communication Technology, Electronics and Microelectronics (MIPRO), Opatija, Croatia, 25–29 May 2015; Jovic, A., Brkic, K., Bogunovic, N., Eds.; IEEE: Opatija, Croatia, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Q.; Shao, J.; Scholz, M.; Plant, C. Feature selection methods for characterizing and classifying adaptive sustainable flood retention basins. Water Res. 2011, 45, 993–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Z.; Ran, B.; Zhong, M.; Lyu, N. Feature selection with redundancy-complementariness dispersion. Knowl. Based Syst. 2015, 89, 203–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, R.; Yin, C. A novel feature selection method considering feature interaction. Pattern Recognit. 2015, 48, 2656–2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bratasanu, D.; Nedelcu, I.; Datcu, M. Bridging the semantic gap for satellite image annotation and automatic mapping applications. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2011, 4, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; He, J.; Yao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liang, H.; Wang, H.; Hong, Y. Classifying urban land use by integrating remote sensing and social media data. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2017, 31, 1675–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, P.M.; Aplin, P. Spatial variation in land cover and choice of spatial resolution for remote sensing. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2004, 25, 3687–3702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhu, X.; Guo, W.; Yue, P.; Fan, Y. A case-based reasoning approach for task-driven remote sensing image discovery under spatial–temporal constraints. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2016, 9, 454–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Albuquerque, J.P.; Herfort, B.; Brenning, A.; Zipf, A. A geographic approach for combining social media and authoritative data towards identifying useful information for disaster management. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2015, 29, 667–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosser, J.F.; Leibovici, D.G.; Jackson, M.J. Rapid flood inundation mapping using social media, remote sensing and topographic data. Nat. Hazards 2017, 87, 103–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Tinghua, A.; Peng, Z.; Wang, G. The LOD representation and proximity measurement of semantic about geographic information. Geomat. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 2016, 41, 1299–1306. [Google Scholar]
- Resnik, P. Semantic similarity in a taxonomy: An information-based measure and its application to problems of ambiguity in natural language. J. Artif. Intell. Res. 1999, 11, 95–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, M.A.; Egenhofer, M.J. Comparing geospatial entity classes: An asymmetric and context-dependent similarity measure. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2004, 18, 229–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Vasardani, M.; Winter, S. Similarity matching for integrating spatial information extracted from place descriptions. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2017, 31, 56–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Han, J. Mining heterogeneous information networks: Principles and methodologies. Synth. Lect. Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 2012, 3, 1–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Sun, Y.; Yu, P.S. A survey of heterogeneous information network analysis. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2015, 29, 17–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Han, J.; Yan, X.; Yu, P.S.; Wu, T. Pathsim: Meta path-based top-k similarity search in heterogeneous information networks. Proc. Vldb Endow. 2011, 4, 992–1003. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, X.; Xu, Q.; Scaringi, G.; Dai, L.; Li, W.; Dong, X.; Zhu, X.; Pei, X.; Dai, K.; Havenith, H.B. Failure mechanism and kinematics of the deadly June 24th 2017 Xinmo landslide, Maoxian, Sichuan, China. Landslides 2017, 14, 2129–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.T.; Wu, J.H. Simulating the failure process of the Xinmo landslide using discontinuous deformation analysis. Eng. Geol. 2018, 239, 269–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| No. | Data Title/Description | Spatiotemporal Similarity | Scale Similarity | Attribute Similarity | Corresponding Variables | Relevance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2017.6.25 Diexi Town, Mao County landslide interpretation results. 1:500 | 1.000 | 1 | 1.000 | D9 | 1.0000 |
| 2 | 2017.6.25 Diexi Town, Mao County landslide UAV optical images 0.1 m | 1.000 | 1 | 1.000 | D2 | 1.0000 |
| 3 | 2017.6.24 Gaofen-3 satellite radar image 1 m | 1.000 | 0.875 | 0.500 | null | 0.7917 |
| 4 | 2017.4.8 Gaofen-2 satellite optical image 1 m | 0.590 | 0.875 | 0.750 | D3,D4 | 0.7383 |
| 5 | 2016.12 Gaofen-2 satellite optical image 1 m | 0.430 | 0.875 | 0.750 | D4 | 0.6850 |
| 6 | Multimedia datasets | 1.000 | 0.875 | 0.000 | D8 | 0.6250 |
| 7 | 2017.6.24 Diexi Town, Mao County landslide UAV optical images 0.1 m | 0.400 | 1 | 1.000 | D3,D4 | 0.6000 |
| 8 | 2017.6.24 Diexi Town, Mao County landslide interpretation results. 1:500 | 0.400 | 1 | 1.000 | D9 | 0.6000 |
| 9 | 2017.5.31 ZY-3 satellite optical image 2.1 m | 0.729 | 0.125 | 0.750 | D3,D4 | 0.5347 |
| 10 | 2017.5.16 ZY-3 satellite optical image 2.1 m | 0.656 | 0.125 | 0.750 | D3,D4 | 0.5103 |
| 11 | 2014.11.1 Diexi Town, Mao County DLG 1:10000 | 0.254 | 0.125 | 0.667 | D5,D7 | 0.3486 |
| 12 | 2015.1 Diexi Town, Mao County DLG 1:50000 | 0.254 | 0.125 | 0.667 | D5,D7 | 0.3486 |
| 13 | 2014.12 Diexi Town, Mao County DLG 1:50000 | 0.206 | 0.125 | 0.667 | D5,D7 | 0.3326 |
| 14 | 2013 Diexi Town, Mao County DLG 1:50000 | 0.185 | 0.125 | 0.667 | D5,D7 | 0.3256 |
| 15 | 2011 Diexi Town, Mao County DLG 1:50000 | 0.119 | 0.125 | 0.667 | D5,D7 | 0.3036 |
| 16 | 2015.12 Mao County DLG | 0 | 0.875 | 0.333 | D5,D7 | 0.1111 |
| 17 | 2014.8 Mao County DLG | 0 | 1 | 0.333 | D5,D7 | 0.1111 |
| Results: selected items (Nos. 1, 4, 5, 6, and 11), irrelevant items (Nos. 3, 16, and 17), and redundant items (others). | ||||||
| Query Method | Result Number | Relevant Number | Redundant Number | Irrelevant Number | Recall | Precision | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Relevance-based | 0.7 | 4 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 40% | 75% |
| 0.5 | 10 | 9 | 5 | 1 | 80% | 40% | |
| 0.3 | 15 | 14 | 8 | 1 | 100% | 33% | |
| Keyword-based | 15 | 12 | 9 | 3 | 100% | 33% | |
| Semantics-constrained (proposed method) | 5 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 100% | 100% | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Ding, Y.; Liu, M.; Li, Y.; Feng, B.; Miao, S.; Yang, W.; He, H.; Zhu, J. Semantics-Constrained Advantageous Information Selection of Multimodal Spatiotemporal Data for Landslide Disaster Assessment. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2019, 8, 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi8020068
Zhu Q, Zhang J, Ding Y, Liu M, Li Y, Feng B, Miao S, Yang W, He H, Zhu J. Semantics-Constrained Advantageous Information Selection of Multimodal Spatiotemporal Data for Landslide Disaster Assessment. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information. 2019; 8(2):68. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi8020068
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Qing, Junxiao Zhang, Yulin Ding, Mingwei Liu, Yun Li, Bin Feng, Shuangxi Miao, Weijun Yang, Huagui He, and Jun Zhu. 2019. "Semantics-Constrained Advantageous Information Selection of Multimodal Spatiotemporal Data for Landslide Disaster Assessment" ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information 8, no. 2: 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi8020068
APA StyleZhu, Q., Zhang, J., Ding, Y., Liu, M., Li, Y., Feng, B., Miao, S., Yang, W., He, H., & Zhu, J. (2019). Semantics-Constrained Advantageous Information Selection of Multimodal Spatiotemporal Data for Landslide Disaster Assessment. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 8(2), 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi8020068





