Examining the Causal and Heterogeneous Influence of Three-Dimensional Urban Forms on CO2 Emissions in 285 Chinese Cities
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Carbon Emissions and 3D Urban Forms Dataset
2.2. Measurement of 3D Urban Forms
2.3. Model Specification
3. Empirical Results
3.1. The Benchmark Regression Results
3.2. The Causal Effect of 3D Urban Forms on CO2 Emissions
3.3. Heterogeneity Analysis
3.4. Robustness Tests
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Root, T.L.; Price, J.T.; Hall, K.R.; Schneider, S.H.; Rosenzweig, C.; Pounds, J.A. Fingerprints of Global Warming on Wild Animals and Plants. Nature 2003, 421, 57–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Meinshausen, M.; Meinshausen, N.; Hare, W.; Raper, S.C.; Frieler, K.; Knutti, R.; Frame, D.J.; Allen, M.R. Greenhouse-Gas Emission Targets for Limiting Global Warming to 2 °C. Nature 2009, 458, 1158–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Energy Agency. CO2 Emissions in 2023; IEA: Paris, France, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Soytas, U.; Sari, R. Energy Consumption, Economic Growth, and Carbon Emissions: Challenges Faced by an EU Candidate Member. Ecol. Econ. 2009, 68, 1667–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Liu, X.; Zhou, C.; Hu, J.; Ou, J. Examining the Impacts of Socioeconomic Factors, Urban Form, and Transportation Networks on CO2 Emissions in China’s Megacities. Appl. Energy 2017, 185, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, B.; Ma, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Chen, R.; Song, Y.; Shen, M.; Xiang, R. Carbon Emissions, the Industrial Structure and Economic Growth: Evidence from Heterogeneous Industries in China. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 262, 114322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y. Path-Breaking Industrial Development Reduces Carbon Emissions: Evidence from Chinese Provinces, 1999–2011. Energy Policy 2022, 167, 113046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Deng, X.; Phillips, F.; Fang, C.; Wang, C. Impacts of Industrial Structure and Technical Progress on Carbon Emission Intensity: Evidence from 281 Cities in China. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2020, 154, 119949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Wu, R.; Wang, S. How Technological Progress Affects the Carbon Emission Efficiency? Evidence from National Panel Quantile Regression. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 307, 127133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luqman, M.; Rayner, P.J.; Gurney, K.R. On the Impact of Urbanisation on CO2 Emissions. NPJ Urban Sustain. 2023, 3, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, P. Driving Effects of Urbanization on City-Level Carbon Dioxide Emissions: From Multiple Perspectives of Urbanization. Int. J. Urban Sci. 2022, 26, 108–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seto, K.C.; Dhakal, S.; Bigio, A.; Blanco, H.; Carlo Delgado, G.; Dewar, D.; Huang, A.; Inaba, A.; Kansal, S.; Zwickel, T.; et al. Human Settlements, Infrastructure, and Spatial Planning; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Seto, K.C.; Güneralp, B.; Hutyra, L.R. Global Forecasts of Urban Expansion to 2030 and Direct Impacts on Biodiversity and Carbon Pools. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 16083–16088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, W.; Wu, R.; Wang, S. The Impacts of Urban Form on Carbon Emissions: A Comprehensive Review. Land 2022, 11, 1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Yang, R.; Dong, Y.X.; Liu, Y.X.; Qiu, L.R. The Influence of Rapid Urbanization and Land Use Changes on Terrestrial Carbon Sources/Sinks in Guangzhou, China. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 70, 304–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Chen, X.; Wang, Z.; Li, W.; Zhang, C.; Yao, X. Analyzing Land Use Structure Efficiency with Carbon Emissions: A Case Study in the Middle Reaches of the Yangtze River, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 274, 123076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Lee, B. The Influence of Urban Form on GHG Emissions in the U.S. Household Sector. Energy Policy 2014, 68, 534–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Gao, C.; Lu, Y. The Impact of Urbanization on GHG Emissions in China: The Role of Population Density. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 157, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Chen, X.; Jiao, S.; Song, W.; Zong, W.; Niu, Y. Can Mixed Land Use Reduce CO2 Emissions? A Case Study of 268 Chinese Cities. Sustainability 2022, 14, 15117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Haase, D.; Su, M.; Yang, Z. The Impact of Urban Compactness on Energy-Related Greenhouse Gas Emissions across EU Member States: Population Density vs. Physical Compactness. Appl. Energy 2019, 254, 113671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Liu, G.; Cui, Y.; Wu, Y. What Urban Spatial Structure Is More Conducive to Reducing Carbon Emissions? A Conditional Effect of Population Size. Appl. Geogr. 2023, 151, 102855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, X. How Did Urban Polycentricity and Dispersion Affect Economic Productivity? A Case Study of 306 Chinese Cities. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2018, 173, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, W.; Chen, Y.; Wu, J.; Wang, Z. Will Polycentric Cities Cause More CO2 Emissions? A Case Study of 232 Chinese Cities. J. Environ. Sci. 2020, 96, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, K.; Tu, M.; Li, Y. Did Polycentric and Compact Structure Reduce Carbon Emissions? A Spatial Panel Data Analysis of 286 Chinese Cities from 2002 to 2019. Land 2022, 11, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Fang, C.; Li, S. Estimating the Impacts of Urban Form on CO2 Emission Efficiency in the Pearl River Delta, China. Cities 2019, 85, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, A. Vertical Urbanisms: Opening Up Geographies of the Three-Dimensional City. Prog. Hum. Geogr. 2015, 39, 601–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.; Hu, M.; Deetman, S.; Steubing, B.; Lin, H.X.; Hernandez, G.A.; Zhang, C.; Tukker, A.; Behrens, P. Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Residential and Commercial Building Materials and Mitigation Strategies to 2060. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Röck, M.; Saade, M.R.M.; Balouktsi, M.; Rasmussen, F.N.; Birgisdottir, H.; Frischknecht, R.; Habert, G.; Lützkendorf, T.; Passer, A. Embodied GHG Emissions of Buildings-The Hidden Challenge for Effective Climate Change Mitigation. Appl. Energy 2020, 258, 114107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perini, K.; Magliocco, A. Effects of Vegetation, Urban Density, Building Height, and Atmospheric Conditions on Local Temperatures and Thermal Comfort. Urban For. Urban Green. 2014, 13, 495–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coseo, P.; Larsen, L. How Factors of Land Use/Land Cover, Building Configuration, and Adjacent Heat Sources and Sinks Explain Urban Heat Islands in Chicago. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2014, 125, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Pan, W. Inter-Building Effect on Building Energy Consumption in High-Density City Contexts. Energy Build. 2023, 278, 112632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Q.; Luan, Q.; Liu, Y.; Wang, R. The Effects of 2D and 3D Building Morphology on Urban Environments: A Multi-Scale Analysis in the Beijing Metropolitan Region. Build. Environ. 2021, 192, 107635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camporeale, P.E.; Mercader-Moyano, P. Towards Nearly Zero Energy Buildings: Shape Optimization of Typical Housing Typologies in Ibero-American Temperate Climate Cities from a Holistic Perspective. Sol. Energy 2019, 193, 738–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Ou, J.; Liu, P.; Liu, X.; Zhang, H. Investigating the Impacts of Three-Dimensional Spatial Structures on CO2 Emissions at the Urban Scale. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 762, 143096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, S.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, W.; Liu, B. Quantifying Heterogeneous Impacts of 2D/3D Built Environment on Carbon Emissions across Urban Functional Zones: A Case Study in Beijing, China. Energy Build. 2024, 319, 114513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Lu, S.; He, X.; Wang, F. Analyzing the Impact of Three-Dimensional Building Structure on CO2 Emissions Based on Random Forest Regression. Energy 2021, 236, 121502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, B.; Cui, C.; Zhang, D.; Cao, L.; Wu, P.; Pang, L.; Zhang, J.; Dai, C. China City-Level Greenhouse Gas Emissions Inventory in 2015 and Uncertainty Analysis. Appl. Energy 2019, 253, 113579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, B.; Liu, H.; Zhang, X.; Pan, H.; Zhao, M.; Zheng, T.; Nie, J.; Du, M.; Dhakal, S. High-Resolution Accounting of Urban Emissions in China. Appl. Energy 2022, 325, 119896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesaresi, M.; Politis, P. GHS-BUILT-H R2023A—GHS Building Height, Derived from AW3D30, SRTM30, and Sentinel2 Composite (2018); European Commission, Joint Research Centre (JRC): Brussels, Belgium, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Pesaresi, M.; Politis, P. GHS-BUILT-S R2023A—GHS Built-Up Surface Grid, Derived from Sentinel2 Composite and Landsat, Multitemporal (1975–2030); European Commission, Joint Research Centre (JRC): Brussels, Belgium, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Pesaresi, M.; Politis, P. GHS-BUILT-V R2023A—GHS Built-Up Volume Grids Derived from Joint Assessment of Sentinel2, Landsat, and Global DEM Data, Multitemporal (1975–2030); European Commission, Joint Research Centre (JRC): Brussels, Belgium, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Qi, J. Impact of Urban Density on Carbon Emissions in China. Appl. Econ. 2021, 53, 6153–6165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, R.; Palacios, A. Why Has Europe Become Environmentally Cleaner? Decomposing the Roles of Fiscal, Trade and Environmental Policies. Environ. Resour. Econ. 2014, 58, 91–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Du, R. Polycentric Urban Structure and Innovation: Evidence from a Panel of Chinese Cities. Reg. Stud. 2022, 56, 113–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Combes, P.P.; Démurger, S.; Li, S. Migration Externalities in Chinese Cities. Eur. Econ. Rev. 2015, 76, 152–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borck, R. Will Skyscrapers Save the Planet? Building Height Limits and Urban Greenhouse Gas Emissions. Reg. Sci. Urban Econ. 2016, 58, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Hu, S.; Ren, Y.; Xu, H.; Song, W. Leverage Effect of New-Built Green Spaces on Housing Prices in a Rapidly Urbanizing Chinese City: Regional Disparities, Impact Periodicity, and Park Size. Land 2024, 13, 1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, L. Examining the Impact Factors of Urban Residential Energy Consumption and CO2 Emissions in China-Evidence from City-Level Data. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 73, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, Y.; Tu, M.; Liu, X. Third Places as Catalysts for Technological Innovation? Evidence from a Grid Cell Level Analysis of Nanjing, China. Int. J. Urban Sci. 2024, 28, 105–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Zhu, W.; Shen, X.; Bai, R.; Shi, Y.; Li, C.; Zhao, L. Exploring the Predictive Ability of the CA–Markov Model for Urban Functional Area in Nanjing Old City. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 18453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

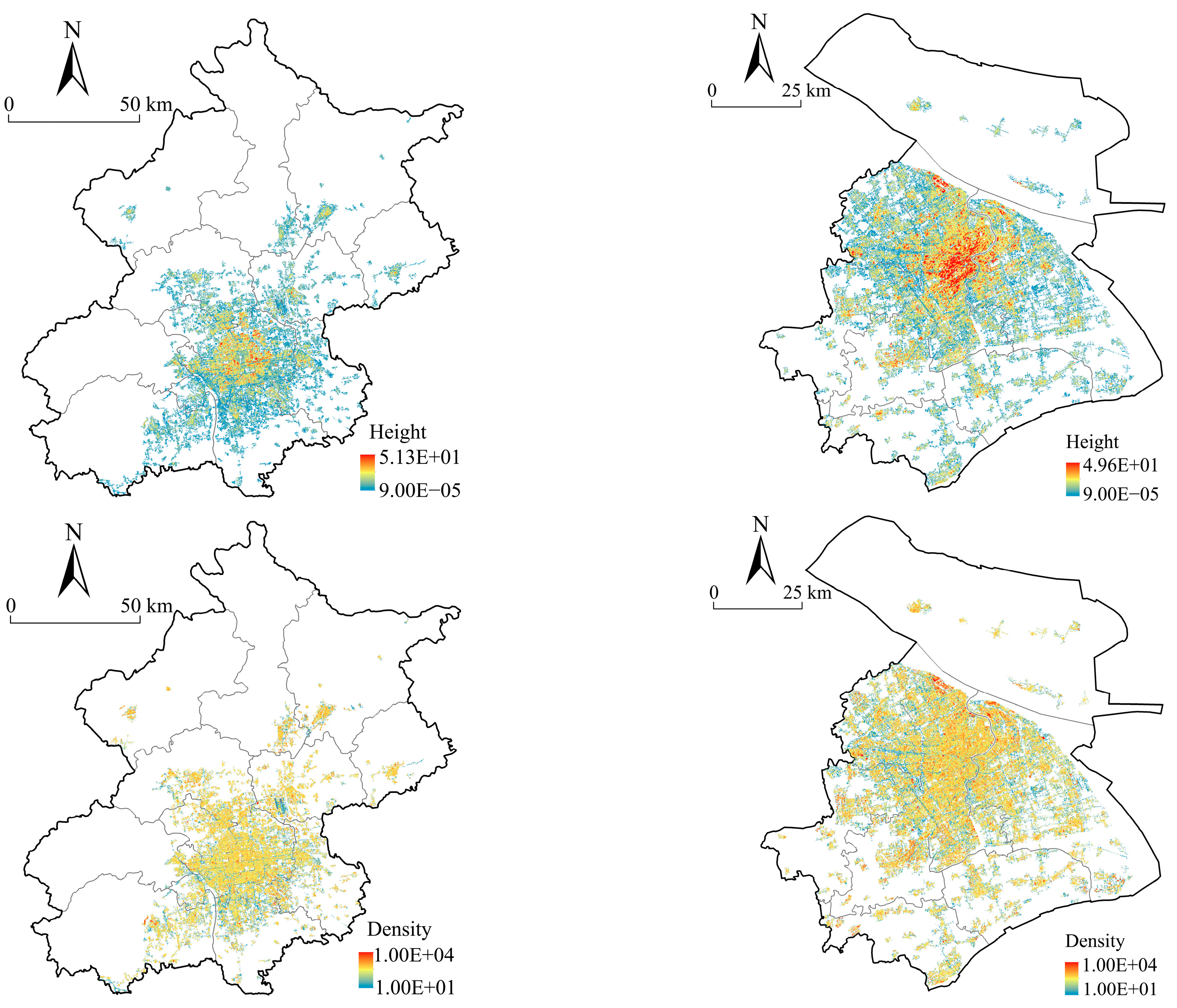
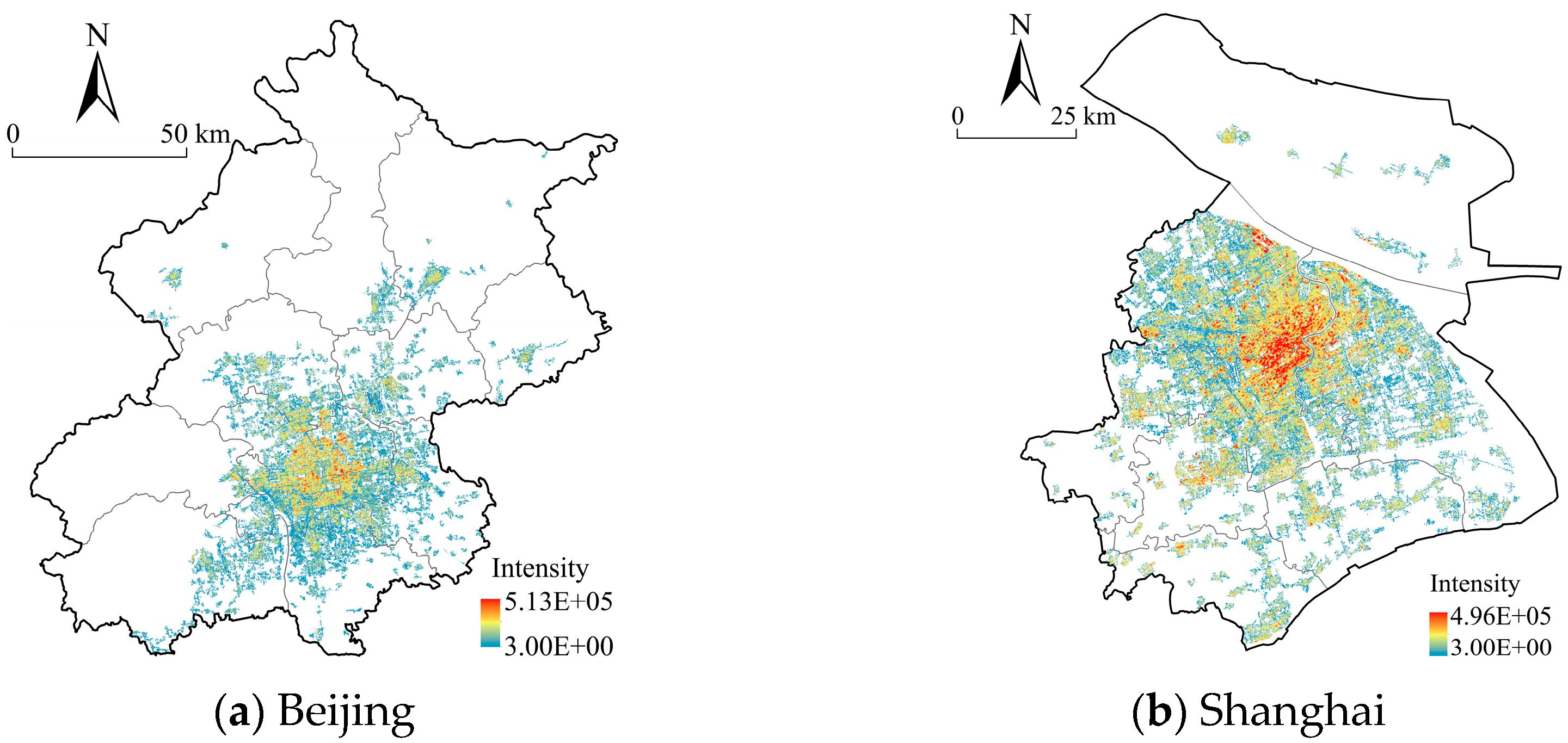

| 3D Urban Forms | Mean | S.D. | Max | Min |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Urban height | 2.434 | 0.854 | 5.138 | 0.166 |
| Urban density | 2908.456 | 551.360 | 4276 | 612 |
| Urban intensity | 25,003.320 | 8512.944 | 51,561 | 1885 |
| Variables | Description |
|---|---|
| Carbon emissions (CE) | Total CO2 emissions |
| 3D urban forms (HDI) | The principal component of city-level height, density, and intensity |
| Economic level (PGDP) | Per capita GDP |
| Population (POP) | Total population |
| Population density (POPDEN) | Permanent resident population per km2 |
| Industrial structure (INS) | Ratio of value added of the secondary sector to total GDP |
| Economic openness (OPEN) | Volume of export trade |
| Financial level (FIN) | Ratio of deposit and loan balances of financial institutions to total GDP |
| Government intervention (GOV) | Ratio of fiscal expenditure to total GDP |
| Transportation infrastructure (INF) | Per capita road areas |
| Variable | Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | Model 4 | Model 5 | Model 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HDI | 0.097 *** | 0.047 * | 0.043 * | 0.056 ** | −0.412 ** | |
| (0.028) | (0.027) | (0.024) | (0.026) | (0.206) | ||
| HDI2 | 0.027 *** | |||||
| (0.010) | ||||||
| HDI × lnPOP | 0.082 ** | |||||
| (0.036) | ||||||
| lnPGDP | 0.536 *** | 0.574 *** | 0.636 *** | 0.544 *** | 0.485 *** | |
| (0.148) | (0.150) | (0.146) | (0.148) | (0.152) | ||
| lnPOP | 0.631 *** | 0.619 *** | 0.533 *** | 0.626 *** | 0.614 *** | |
| (0.084) | (0.084) | (0.093) | (0.083) | (0.086) | ||
| lnPOPDEN | −0.104 * | −0.113 * | −0.091 | −0.112 * | −0.138 ** | |
| (0.063) | (0.063) | (0.057) | (0.063) | (0.065) | ||
| INS | 0.018 *** | 0.018 *** | 0.015 *** | 0.018 *** | 0.018 *** | |
| (0.006) | (0.006) | (0.006) | (0.005) | (0.006) | ||
| lnOPEN | 0.012 | 0.006 | 0.007 | 0.020 | 0.015 | |
| (0.035) | (0.034) | (0.033) | (0.034) | (0.034) | ||
| FIN | 0.000 | 0.000 | −0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | |
| (0.000) | (0.000) | (0.000) | (0.000) | (0.000) | ||
| GOV | 0.666 | 0.759 | 0.709 | 0.743 | 0.414 | |
| (0.744) | (0.762) | (0.627) | (0.731) | (0.742) | ||
| lnINF | 0.038 | 0.069 | 0.038 | 0.101 | 0.058 | |
| (0.123) | (0.125) | (0.116) | (0.123) | (0.122) | ||
| lnCE × W | 0.036 ** | |||||
| (0.018) | ||||||
| Constant | −3.072 | 7.982 *** | −3.492 * | −3.632 ** | −3.555 * | 0.485 *** |
| (1.879) | (0.049) | (1.915) | (1.689) | (1.860) | (0.152) | |
| Observations | 285 | 285 | 285 | 285 | 285 | 285 |
| R2/Pseudo R2 | 0.410 | 0.038 | 0.418 | 0.414 | 0.434 | 0.432 |
| Variable | First Stage: HDI | Second Stage: lnCE |
|---|---|---|
| DIS | −0.022 *** | |
| (0.005) | ||
| HDI | 0.253 ** | |
| (0.122) | ||
| lnPGDP | −0.634 ** | 0.740 *** |
| (0.299) | (0.165) | |
| lnPOP | 0.071 | 0.570 *** |
| (0.202) | (0.099) | |
| lnPOPDEN | 0.020 | −0.149 ** |
| (0.151) | (0.074) | |
| INS | −0.015 | 0.019 *** |
| (0.014) | (0.007) | |
| lnOPEN | 0.109 | −0.018 |
| (0.094) | (0.038) | |
| FIN | −0.000 | 0.000 |
| (0.000) | (0.000) | |
| GOV | −2.287 | 1.165 |
| (1.667) | (0.855) | |
| lnINF | −0.828 *** | 0.203 |
| (0.301) | (0.165) | |
| Constant | 10.756 *** | −5.332 ** |
| (3.797) | (2.114) | |
| Kleibergen–Paap rk LM statistic | 19.478 *** | |
| Kleibergen–Paap rk Wald F statistic | 20.267 | |
| Stock–Yogo critical value (10% maximal IV) | 16.38 | |
| Observations | 285 | 285 |
| R2 | 0.192 | 0.270 |
| Variable | By Geography | By Sector | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model 1: Eastern | Model 2: Non-Eastern | Model 3: Industry | Model 4: Household | Model 5: Transportation | |
| HDI | 0.696 *** | 0.212 * | 0.270 | 0.435 *** | 0.031 |
| (0.269) | (0.124) | (0.166) | (0.166) | (0.052) | |
| lnPGDP | 0.367 | 0.707 ** | 0.583 *** | 0.477 ** | 0.590 *** |
| (0.281) | (0.279) | (0.217) | (0.201) | (0.082) | |
| lnPOP | 0.422 | 0.490 *** | 0.595 *** | 1.045 *** | 0.844 *** |
| (0.350) | (0.115) | (0.136) | (0.115) | (0.055) | |
| lnPOPDEN | −0.644 *** | −0.140 | −0.282 ** | −0.125 | 0.121 *** |
| (0.249) | (0.088) | (0.111) | (0.089) | (0.045) | |
| INS | −0.001 | 0.023 *** | 0.033 *** | 0.008 | −0.007 * |
| (0.013) | (0.009) | (0.011) | (0.008) | (0.003) | |
| lnOPEN | −0.010 | −0.031 | −0.001 | −0.161 *** | 0.013 |
| (0.097) | (0.049) | (0.051) | (0.050) | (0.019) | |
| FIN | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 ** | −0.000 ** |
| (0.000) | (0.000) | (0.000) | (0.000) | (0.000) | |
| GOV | −4.086 | 0.934 | 1.111 | 0.471 | 1.499 *** |
| (2.972) | (1.068) | (1.017) | (1.162) | (0.318) | |
| lnINF | −0.275 | 0.197 | 0.189 | 0.168 | −0.123 * |
| (0.311) | (0.216) | (0.204) | (0.197) | (0.069) | |
| Constant | 1.421 | −4.797 | −5.260 ** | −6.449 ** | −5.540 *** |
| (4.301) | (3.472) | (2.523) | (2.648) | (0.874) | |
| Kleibergen–Paap rk LM statistic | 8.930 *** | 16.481 *** | 19.478 *** | 19.478 *** | 19.478 *** |
| Kleibergen–Paap rk Wald F statistic | 10.075 | 19.272 | 20.267 | 20.267 | 20.267 |
| Stock–Yogo critical value (10% maximal IV) | 16.38 | 16.38 | 16.38 | 16.38 | 16.38 |
| Observations | 86 | 199 | 285 | 285 | 285 |
| R2 | 0.012 | 0.182 | 0.174 | 0.196 | 0.775 |
| Variable | Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| HDI | 0.257 ** | 0.221 ** | 0.242 ** |
| (0.125) | (0.111) | (0.105) | |
| lnPGDP | 0.632 *** | 0.628 *** | 0.522 *** |
| (0.171) | (0.189) | (0.194) | |
| lnPOP | 0.513 *** | 0.609 *** | 0.536 *** |
| (0.104) | (0.102) | (0.108) | |
| lnPOPDEN | −0.152 ** | −0.195 *** | −0.160 ** |
| (0.073) | (0.073) | (0.073) | |
| INS | 0.019 *** | 0.027 *** | 0.023 *** |
| (0.007) | (0.007) | (0.008) | |
| lnOPEN | −0.018 | −0.025 | −0.022 |
| (0.039) | (0.037) | (0.038) | |
| FIN | 0.000 * | 0.000 ** | 0.000 |
| (0.000) | (0.000) | (0.000) | |
| GOV | 0.760 | 0.871 | 0.342 |
| (0.863) | (0.981) | (0.864) | |
| lnINF | 0.266 | 0.273 * | 0.286 * |
| (0.173) | (0.156) | (0.162) | |
| Constant | −3.943 * | −5.368 ** | −3.293 |
| (2.169) | (2.250) | (2.368) | |
| Kleibergen–Paap rk LM statistic | 18.722 *** | 16.319 *** | 23.685 *** |
| Kleibergen–Paap rk Wald F statistic | 19.524 | 17.883 | 29.894 |
| Stock–Yogo critical value (10% maximal IV) | 16.38 | 16.38 | 16.38 |
| Observations | 281 | 258 | 264 |
| R2 | 0.230 | 0.323 | 0.231 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the International Society for Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiong, W.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J. Examining the Causal and Heterogeneous Influence of Three-Dimensional Urban Forms on CO2 Emissions in 285 Chinese Cities. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2024, 13, 372. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi13110372
Xiong W, Zhang Y, Li J. Examining the Causal and Heterogeneous Influence of Three-Dimensional Urban Forms on CO2 Emissions in 285 Chinese Cities. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information. 2024; 13(11):372. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi13110372
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiong, Weiting, Yedong Zhang, and Jingang Li. 2024. "Examining the Causal and Heterogeneous Influence of Three-Dimensional Urban Forms on CO2 Emissions in 285 Chinese Cities" ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information 13, no. 11: 372. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi13110372
APA StyleXiong, W., Zhang, Y., & Li, J. (2024). Examining the Causal and Heterogeneous Influence of Three-Dimensional Urban Forms on CO2 Emissions in 285 Chinese Cities. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 13(11), 372. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi13110372









