Design of Soft Grippers with Modular Actuated Embedded Constraints
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Robotic Hands
1.2. Differential Mechanisms
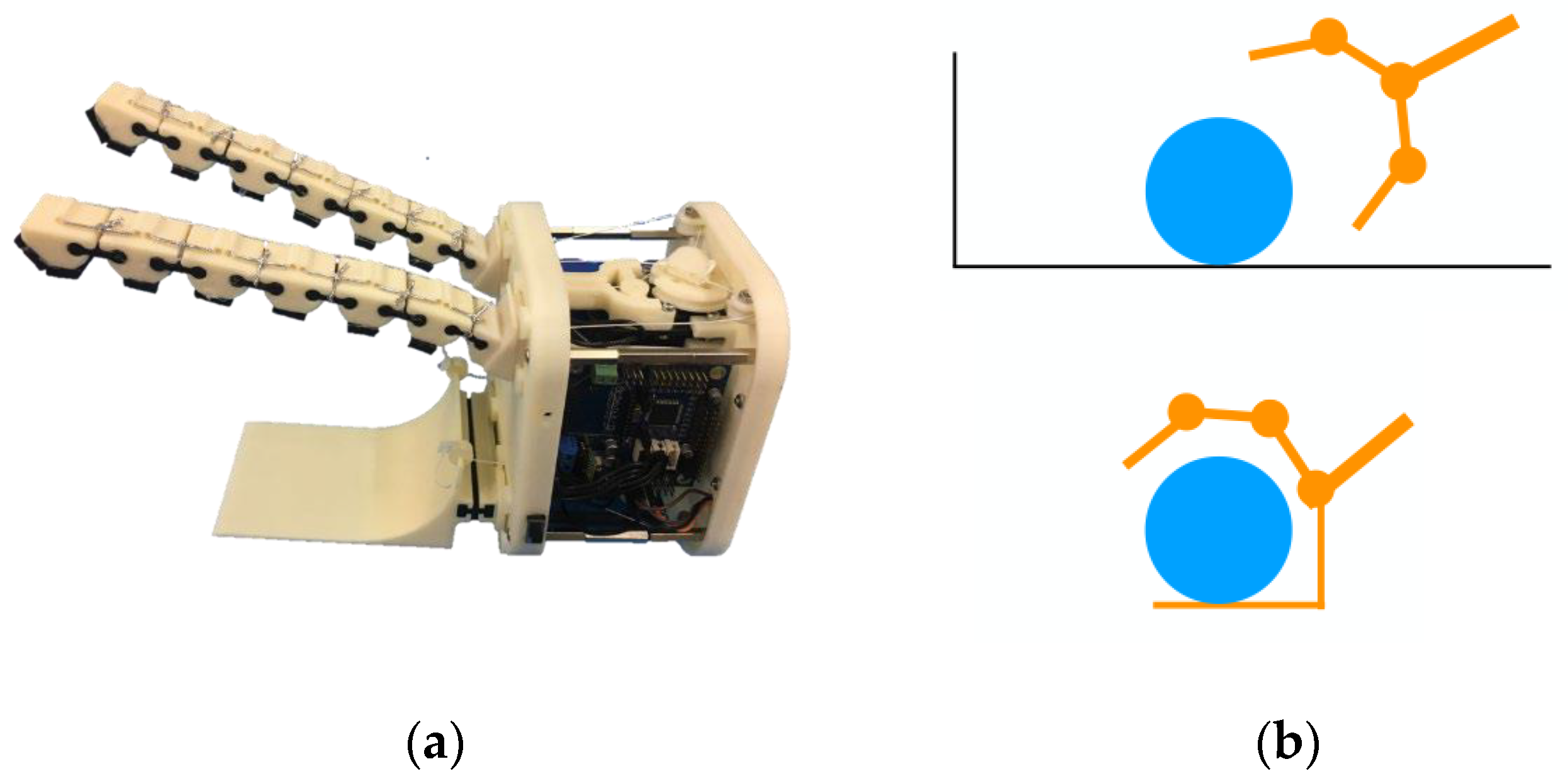
1.3. The Scoop Hand
1.4. Paper Contribution
1.5. Paper Organization
2. Motivation and Starting Point
2.1. Modular Hands
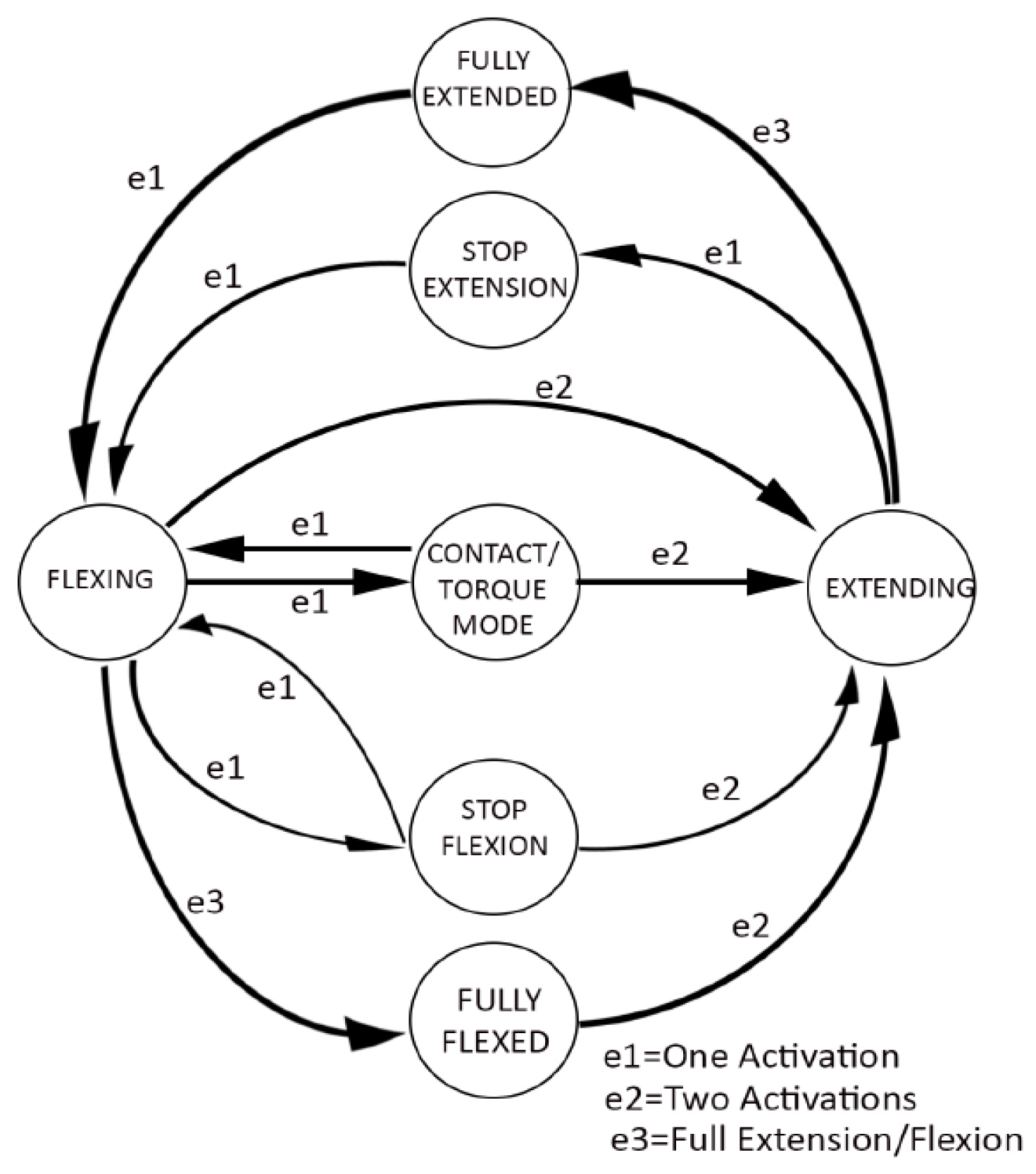
2.2. The Starting Point Solution, Main Features, and Limits
3. Design Improvements
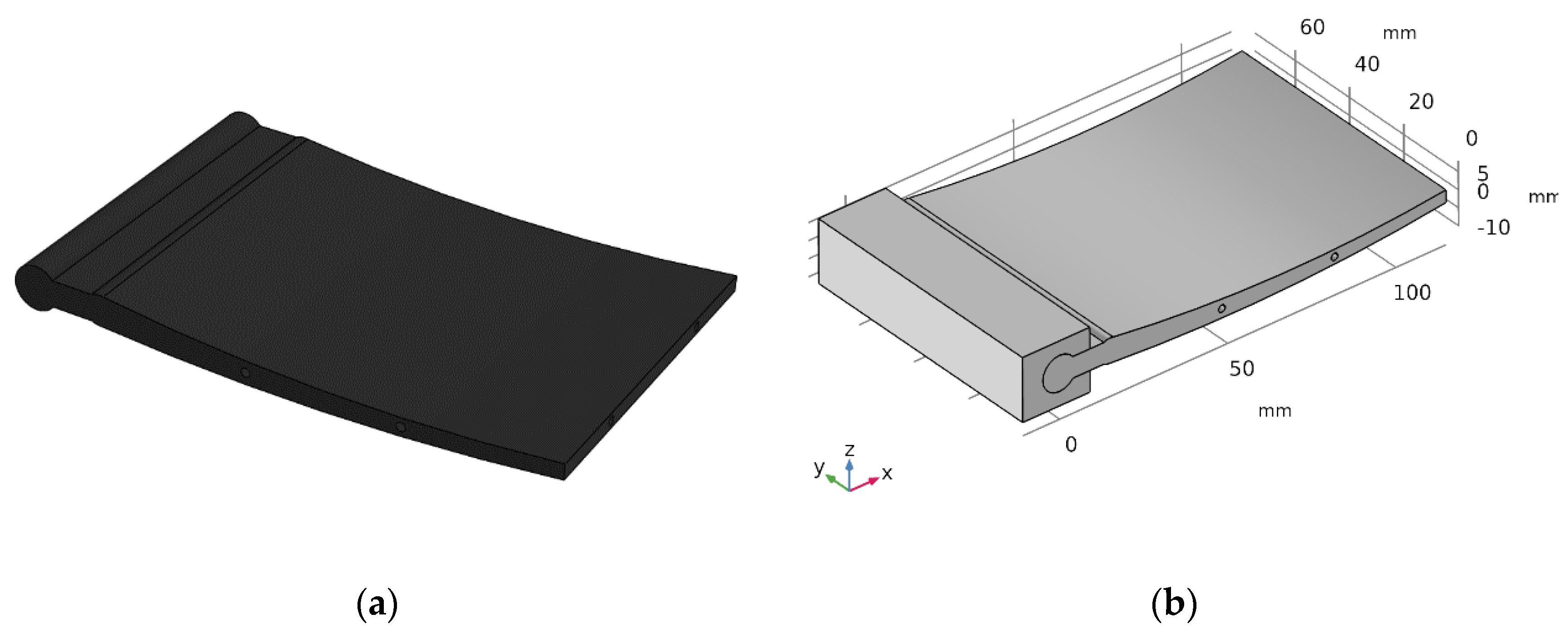
3.1. Exploiting Soft Materials
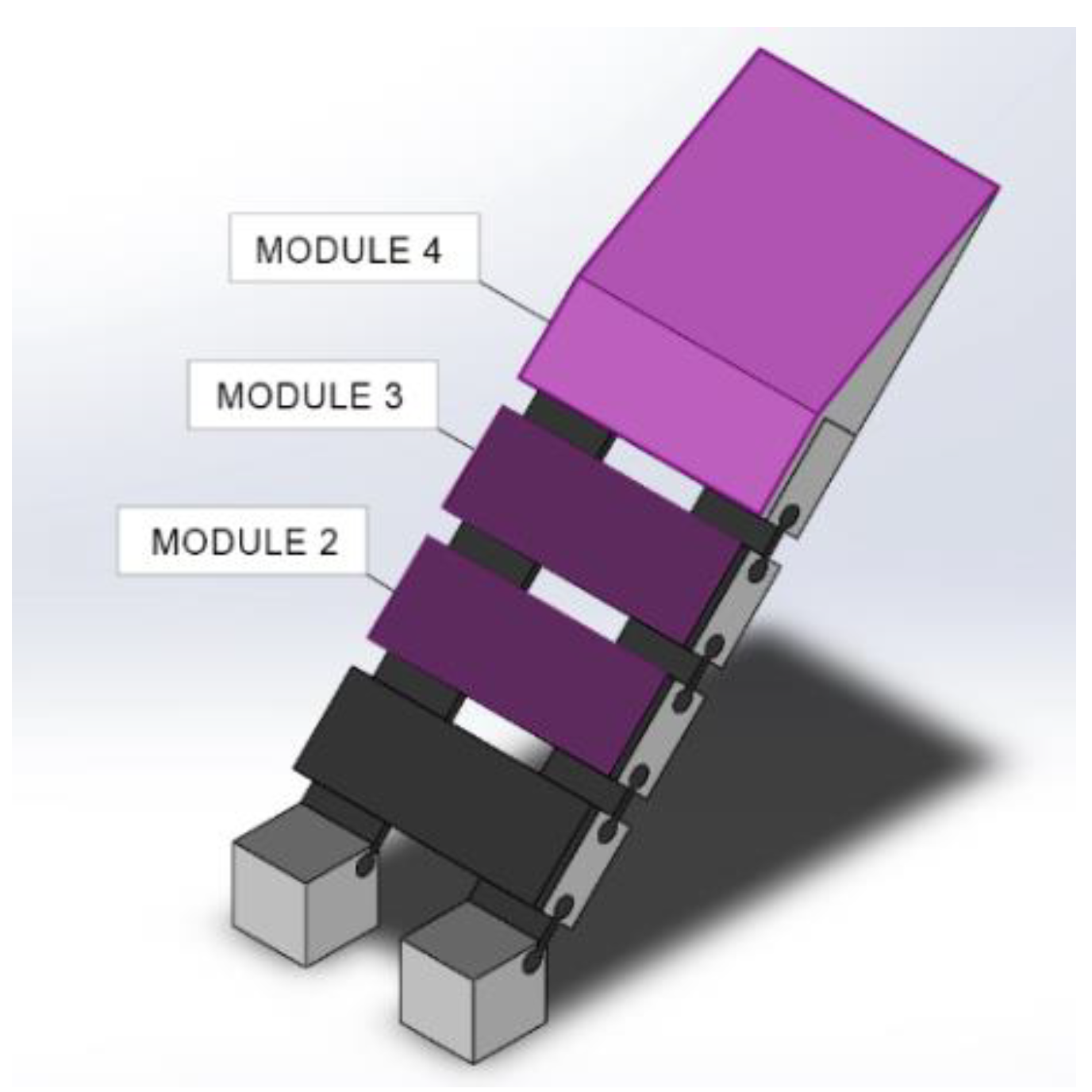
3.2. Modular Elements/1
3.3. Modular Elements/2
4. Analysis and Comparison
Numerical Evaluations with FEM Analysis
5. Prototyping and Testing
6. Conclusions and Future Work
6.1. Conclusions
6.2. Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mason, M.T.; Salisbury, J.K., Jr. Robot Hands and the Mechanics of Manipulation; The MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Carbone, G. Grasping in Robotics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; Volume 10. [Google Scholar]
- Melchiorri, C.; Kaneko, M. Robot Hands. In Springer Handbook of Robotics; Siciliano, B., Khatib, O., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 345–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shintake, J.; Cacucciolo, V.; Floreano, D.; Shea, H. Soft robotic grippers. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1707035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haidegger, T.; Galambos, P.; Rudas, I.J. Robotics 4.0–Are we there yet? In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 23rd International Conference on Intelligent Engineering Systems (INES), Gödöllő, Hungary, 25–27 April 2019; pp. 000117–000124. [Google Scholar]
- Kehoe, B.; Berenson, D.; Goldberg, K. Toward cloud-based grasping with uncertainty in shape: Estimating lower bounds on achieving force closure with zero-slip push grasps. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, St Paul, MN, USA, 14–18 May 2012; pp. 576–583. [Google Scholar]
- Takács, K.; Mason, A.; Christensen, L.B.; Haidegger, T. Robotic Grippers for Large and Soft Object Manipulation. In Proceedings of the IEEE 20th International Symposium on Computational Intelligence and Informatics (CINTI 2020), Budapest, Hungary, 5–7 November 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Fukaya, N.; Toyama, S.; Asfour, T.; Dillmann, R. Design of the TUAT/Karlsruhe humanoid hand. In Proceedings of the 2000 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS 2000) (Cat. No. 00CH37113), Takamatsu, Japan, 31 October–5 November 2000; pp. 1754–1759. [Google Scholar]
- Butterfaß, J.; Grebenstein, M.; Liu, H.; Hirzinger, G. DLR-Hand II: Next generation of a dextrous robot hand. In Proceedings of the 2001 ICRA. IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (Cat. No. 01CH37164), Seoul, Korea, 21–26 May 2001; pp. 109–114. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, E.; Desbiens, A.L.; Laliberté, T.; Gosselin, C. SARAH hand used for space operation on STVF robot. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Intelligent Manipulation and Grasping, Genova, Italy, 1–2 July 2004; pp. 279–284. [Google Scholar]
- Roccella, S.; Carrozza, M.C.; Cappiello, G.; Dario, P.; Cabibihan, J.-J.; Zecca, M.; Miwa, H.; Itoh, K.; Marsumoto, M. Design, fabrication and preliminary results of a novel anthropomorphic hand for humanoid robotics: RCH-1. In Proceedings of the 2004 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS)(IEEE Cat. No. 04CH37566), Sendai, Japan, 28 September–2 October 2004; pp. 266–271. [Google Scholar]
- Dechev, N.; Cleghorn, W.; Naumann, S. Multiple finger, passive adaptive grasp prosthetic hand. Mech. Mach. Theory 2001, 36, 1157–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raparelli, T.; Mattiazzo, G.; Mauro, S.; Velardocchia, M. Design and development of a pneumatic anthropomorphic hand. J. Robot. Syst. 2000, 17, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maffiodo, D.; Raparelli, T. Three-fingered gripper with flexure hinges actuated by shape memory alloy wires. Int. J. Autom. Technol. 2017, 11, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niola, V.; Penta, F.; Rossi, C.; Savino, S. An underactuated mechanical hand: Theoretical studies and prototyping. Int. J. Mech. Control 2015, 16, 11–19. [Google Scholar]
- Cosenza, C.; Niola, V.; Savino, S. Analytical study for the capability implementation of an underactuated three-finger hand. In New Trends in Medical and Service Robotics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 161–168. [Google Scholar]
- Niola, V.; Rossi, C.; Savino, S.; Timpone, F. Study of an underactuated mechanical finger driven by tendons. Int. J. Autom. Technol. 2017, 11, 344–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maffiodo, D.; Raparelli, T. Comparison among different modular SMA actuated flexible fingers. In Advances in Italian Mechanism Science; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 324–331. [Google Scholar]
- Carbone, G.; Rossi, C.; Savino, S. Performance comparison between FEDERICA hand and LARM hand. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2015, 12, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, H.; Hyodo, K.; Ogane, D. On tendon-driven robotic mechanisms with redundant tendons. Int. J. Robot. Res. 1998, 17, 561–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laliberté, T.; Gosselin, C.M. Underactuation in space robotic hands. In Proceedings of the Sixth International Symposium on Artificial Intelligence, Robotics and Automation in Space ISAIRAS: A New Space Odyssey, St-Hubert, QC, Canada, 18–22 June 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, I.; Salvietti, G.; Spagnoletti, G.; Prattichizzo, D. The soft-sixthfinger: A wearable emg controlled robotic extra-finger for grasp compensation in chronic stroke patients. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2016, 1, 1000–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laliberte, T.; Birglen, L.; Gosselin, C. Underactuation in robotic grasping hands. Mach. Intell. Robot. Control 2002, 4, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Ceccarelli, M.; Tavolieri, C.; Lu, Z. Design considerations for underactuated grasp with a one DOF anthropomorphic finger mechanism. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Beijing, China, 9–15 October 2006; pp. 1611–1616. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L.; Carbone, G.; Ceccarelli, M. Designing an underactuated mechanism for a 1 active DOF finger operation. Mech. Mach. Theory 2009, 44, 336–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbone, G.; Yao, S.; Ceccarelli, M.; Lu, Z. Design and simulation of a new underactuated mechanism for LARM hand. Robotica 2017, 35, 483–497. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, I.; Malvezzi, M.; Gan, D.; Iqbal, Z.; Seneviratne, L.; Prattichizzo, D.; Renda, F. Compliant gripper design, prototyping, and modeling using screw theory formulation. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2020, 0278364920947818. [Google Scholar]
- Malvezzi, M.; Iqbal, Z.; Valigi, M.C.; Pozzi, M.; Prattichizzo, D.; Salvietti, G. Design of Multiple Wearable Robotic Extra Fingers for Human Hand Augmentation. Robotics 2019, 8, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malvezzi, M.; Valigi, M.C.; Salvietti, G.; Iqbal, Z.; Hussain, I.; Prattichizzo, D. Design criteria for wearable robotic extra–fingers with underactuated modular structure. In Proceedings of the International Conference of IFToMM ITALY, Naples, Italy, 29–30 November 2018; pp. 509–517. [Google Scholar]
- Birglen, L.; Gosselin, C.M. Force analysis of connected differential mechanisms: Application to grasping. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2006, 25, 1033–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zappatore, G.A.; Reina, G.; Messina, A. Analysis of a highly underactuated robotic hand. Int. J. Mech. Control 2017, 18, 17–24. [Google Scholar]
- Birglen, L.; Gosselin, C.M. On the force capability of underactuated fingers. In Proceedings of the 2003 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (Cat. No. 03CH37422), Taipei, Taiwen, 14–19 October 2003; pp. 1139–1145. [Google Scholar]
- Massa, B.; Roccella, S.; Carrozza, M.C.; Dario, P. Design and development of an underactuated prosthetic hand. In Proceedings of the 2002 IEEE international conference on robotics and automation (Cat. No. 02CH37292), Washington, DC, USA, 11–15 May 2002; pp. 3374–3379. [Google Scholar]
- Baril, M.; Laliberte, T.; Gosselin, C.; Routhier, F. On the design of a mechanically programmable underactuated anthropomorphic prosthetic gripper. J. Mech. Des. 2013, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontoudis, G.P.; Liarokapis, M.V.; Zisimatos, A.G.; Mavrogiannis, C.I.; Kyriakopoulos, K.J. Open-source, anthropomorphic, underactuated robot hands with a selectively lockable differential mechanism: Towards affordable prostheses. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Hamburg, Germany, 28 September–2 October 2015; pp. 5857–5862. [Google Scholar]
- Eppner, C.; Deimel, R.; Alvarez-Ruiz, J.; Maertens, M.; Brock, O. Exploitation of environmental constraints in human and robotic grasping. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2015, 34, 1021–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinemann, F.; Puhlmann, S.; Eppner, C.; Élvarez-Ruiz, J.; Maertens, M.; Brock, O. A taxonomy of human grasping behavior suitable for transfer to robotic hands. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Seattle, WA, USA, 25–30 May 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Salvietti, G.; Iqbal, Z.; Malvezzi, M.; Eslami, T.; Prattichizzo, D. Soft hands with embodied constraints: The soft scoopgripper. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Montreal, QC, Canada, 20–24 May 2019; pp. 2758–2764. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Y.; Salemi, W.; Rus, B.; Moll, D.; Lipson, M. Modular self-reconfigurable robot systems. IEEE Robot. Autom. Mag. 2007, 14, 43–52. [Google Scholar]
- Prattichizzo, D.; Malvezzi, M.; Hussain, I.; Salvietti, G. The sixth-finger: A modular extra-finger to enhance human hand capabilities. In Proceedings of the 23rd IEEE International Symposium on Robot and Human Interactive Communication, Edinburgh, UK, 25–29 August 2014; pp. 993–998. [Google Scholar]
- Reppel, T.; Weinberg, K. Experimental determination of elastic and rupture properties of printed ninjaflex. Tech. Mech. Sci. J. Fundam. Appl. Eng. Mech. 2018, 38, 104–112. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, I.; Salvietti, G.; Malvezzi, M.; Prattichizzo, D. On the role of stiffness design for fingertip trajectories of underactuated modular soft hands. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Singapore, 29 May–3 June 2017; pp. 3096–3101. [Google Scholar]
- Logozzo, S.; Valigi, M.C.; Canella, G. Advances in optomechatronics: An automated tilt-rotational 3D scanner for high-quality reconstructions. Photonics 2018, 5, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valigi, M.C.; Logozzo, S.; Canella, G. A new automated 2 DOFs 3D desktop optical scanner. In Advances in Italian Mechanism Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 231–238. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, C.G.; Jursik, N.J.; Rochefort, W.E.; Walker, T.W. Additive Manufacturing with Soft TPU—Adhesion Strength in Multimaterial Flexible Joints. Front. Mech. Eng. 2019, 5, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calli, B.; Walsman, A.; Singh, A.; Srinivasa, S.; Abbeel, P.; Dollar, A.M. Benchmarking in manipulation research: The YCB object and model set and benchmarking protocols. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1502.03143. [Google Scholar]





| Prototype | Infill Percentage % | E [MPa] |
|---|---|---|
| #1 | 30 | 1.38 |
| #2 | 50 | 2.07 |
| #3 | 70 | 6.53 |
| #4 | 90 | 9.45 |
| Case | Modules to which Force is Applied |
|---|---|
| 1 | Modules 2 and 3 |
| 2 | Module 3 |
| 3 | Modules 3 and 4 |
| 4 | Module 4 |
| Gripper with No Constraint | Gripper with Constraint | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case | Analysis | Min Value | Max Value | Analysis | Min Value | Max Value |
| 1 | Displacement | 0 mm | 22.3 mm | Displacement | 0 mm | 0.507 mm |
| Von Mises Stress | 5.50 × 10−4 N/mm2 | 22.7 N/mm2 | Von Mises Stress | 6.49 × 10−5 N/mm2 | 3.2 N/mm2 | |
| 2 | Displacement | 0 mm | 16.6 mm | Displacement | 0 mm | 0.604 mm |
| Von Mises Stress | 3.48 × 10−4 N/mm2 | 15.3 N/mm2 | Von Mises Stress | 6.66 × 10−5 N/mm2 | 2.82 N/mm2 | |
| 3 | Displacement | 0 mm | 22.3 mm | Displacement | 0 mm | 0.419 mm |
| Von Mises Stress | 8.13 × 10−4 N/mm2 | 27.4 N/mm2 | Von Mises Stress | 2.19 × 10−5 N/mm2 | 1.76 N/mm2 | |
| 4 | Displacement | 0 mm | 33.7 mm | Displacement | 0 mm | 22.3 mm |
| Von Mises Stress | 5.95 × 10−4 N/mm2 | 18.9 N/mm2 | Von Mises Stress | 5.90 × 10−5 N/mm2 | 1.96 N/mm2 | |
| Material Properties | ASA | TPU |
|---|---|---|
| Elastic modulus (E) | 29 N/mm2 | 15.2 N/mm2 |
| Poisson ratio | 1.03 | 1.29 |
| Density | 1070 kg/m3 | 1200 kg/m3 |
| Configuration | Rotations [deg] | Translations [mm] | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Z | Y | ||
| 1 | No object | 73.5 | 64.3 |
| 2 | Center | 53.9 | 49.3 |
| 3 | Outer edge | 72.2 | 59.7 |
| Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 | Case 4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A |  |  |  |  |
| B |  |  |  |  |
| Soft Scoop Gripper Properties | Prototypes | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | |
| Capability to adapting to non-flat rigid surfaces, where the stiffness of the material and the scoop shape make it difficult to insert it under an object. | No | Yes | Yes |
| Avoiding damage of grabbed objects, always due to the stiffness of the material of which the scoop is made. | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Enough adaptability to the shape of objects; if the shape of the object does not have a flat surface, the grip is almost exclusively performed by the fingers, and the scoop works as a constraint only. | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Good mobility of the scoop; no limited movement, which does allow a secure grip if the device is trying to grasp small objects. | No | Yes | Yes |
| Capability to selecting a particular target within a heterogeneous mix of different shape objects, as extracting a ball from inside a basket of toys. | No | Yes | Yes |
| Versatile and easily reconfigurable. | No | No | Yes |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Achilli, G.M.; Valigi, M.C.; Salvietti, G.; Malvezzi, M. Design of Soft Grippers with Modular Actuated Embedded Constraints. Robotics 2020, 9, 105. https://doi.org/10.3390/robotics9040105
Achilli GM, Valigi MC, Salvietti G, Malvezzi M. Design of Soft Grippers with Modular Actuated Embedded Constraints. Robotics. 2020; 9(4):105. https://doi.org/10.3390/robotics9040105
Chicago/Turabian StyleAchilli, Gabriele Maria, Maria Cristina Valigi, Gionata Salvietti, and Monica Malvezzi. 2020. "Design of Soft Grippers with Modular Actuated Embedded Constraints" Robotics 9, no. 4: 105. https://doi.org/10.3390/robotics9040105
APA StyleAchilli, G. M., Valigi, M. C., Salvietti, G., & Malvezzi, M. (2020). Design of Soft Grippers with Modular Actuated Embedded Constraints. Robotics, 9(4), 105. https://doi.org/10.3390/robotics9040105







