A Robust Robotic Disassembly Sequence Design Using Orthogonal Arrays and Task Allocation
Abstract
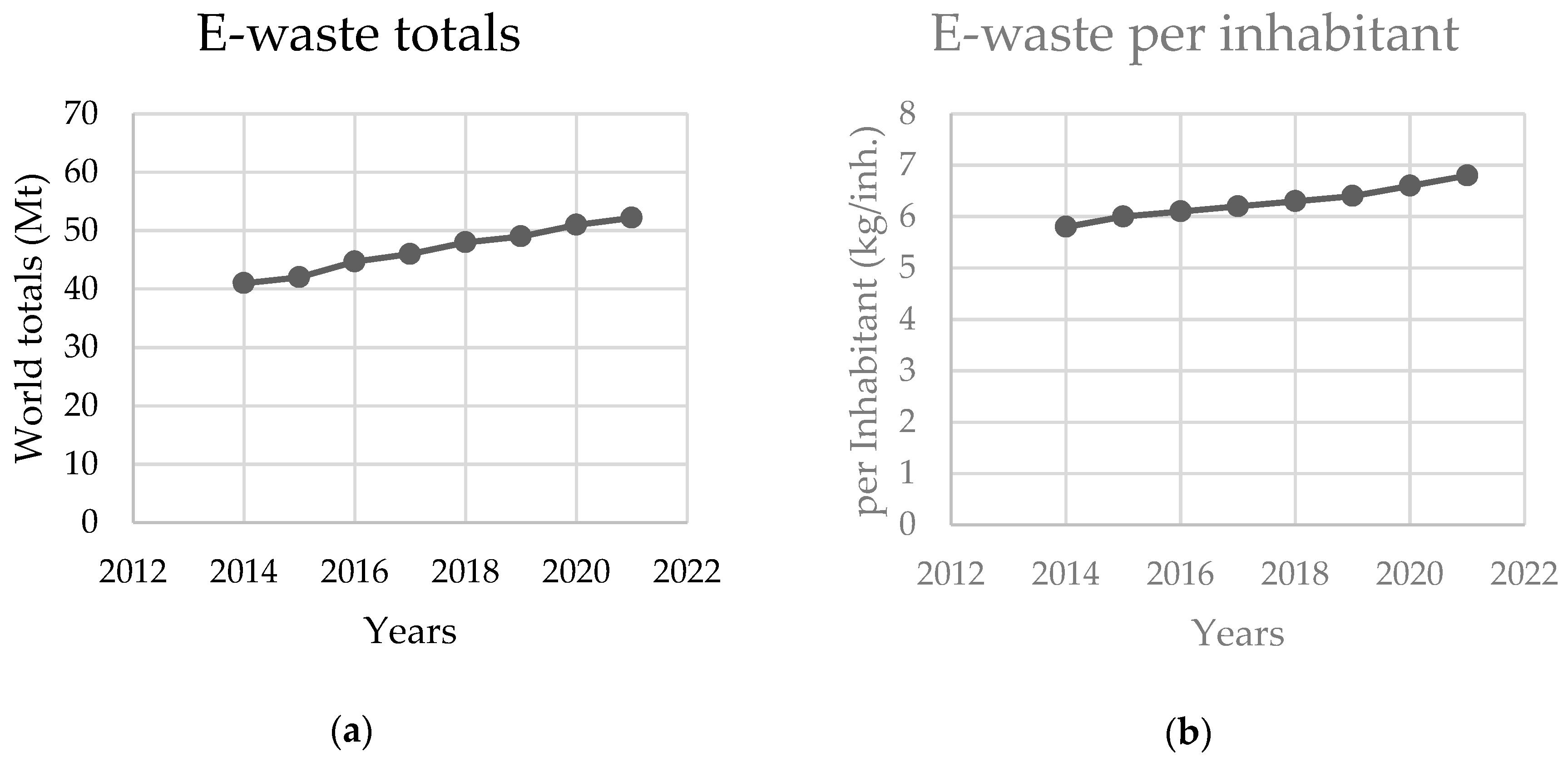
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
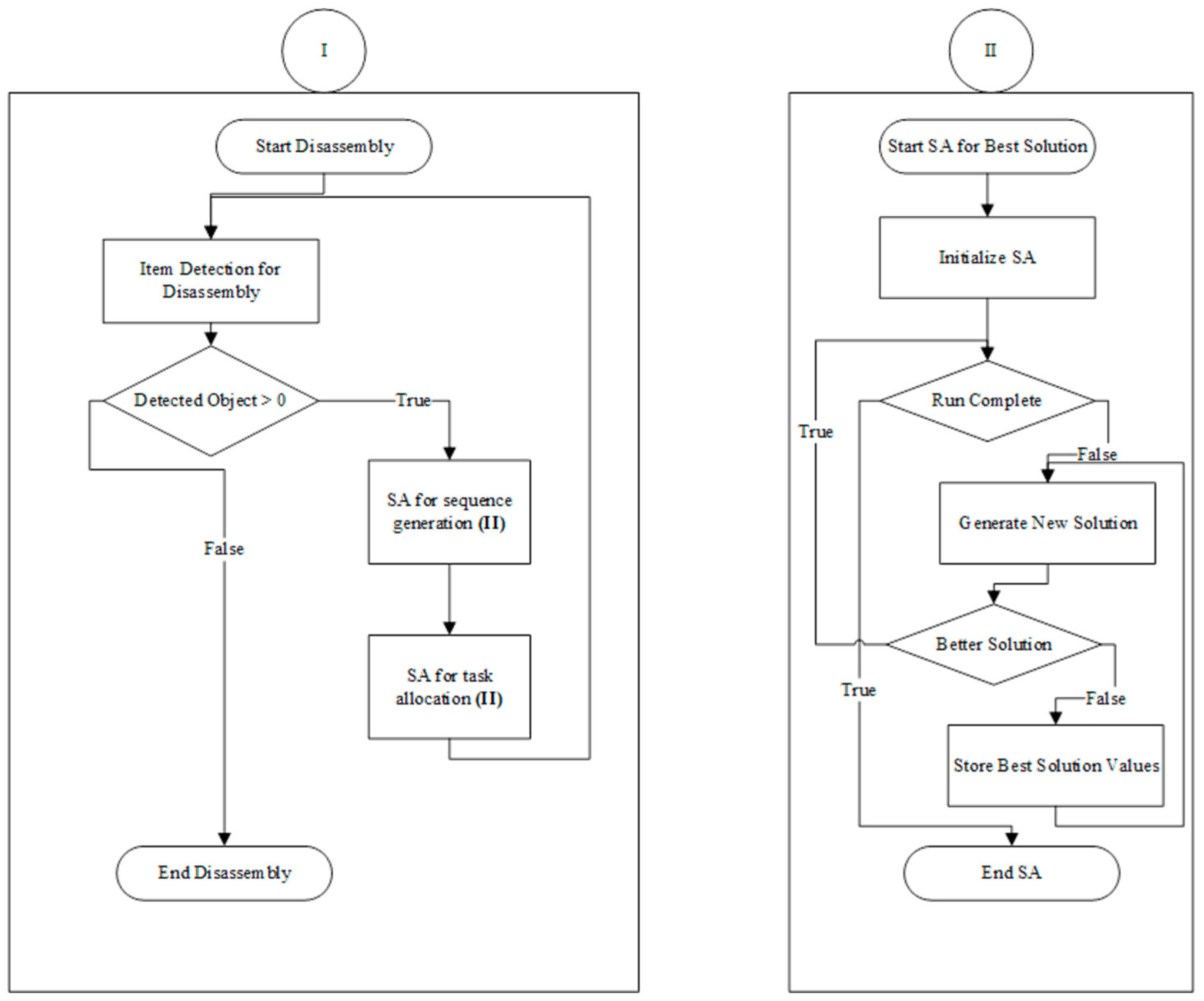
3. Robustness Design Using Orthogonal Arrays
4. Disassembly Line Balancing Using Task Allocation
5. Conclusions and Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baldé, C.P.; Forti, V.; Gray, V.; Kuehr, R.; Stegmann, P. The Global E-Waste Monitor 2017 Quantities, Flow, and Resources; The Global E-waste Monitor—2017, United Nations University (UNU); International Telecommunication Union (ITU); International Solid Waste Association (ISWA): Bonn, Germany; Geneva, Switzerland; Vienna, Austria, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- McGovern, S.M.; Gupta, S.M. A balancing method and genetic algorithm for disassembly line balancing. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2007, 179, 692–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalayci, C.B.; Gupta, S.M. Simulated annealing algorithm for solving sequence-dependent disassembly line balancing problem. IFAC Proc. Vol. 2013, 46, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshibli, M.; El Sayed, A.; Tozanli, O.; Kongar, E.; Sobh, T.M.; Gupta, S.M. A Decision Maker-Centered End-of-Life Product Recovery System for Robot Task Sequencing. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 2017, 91, 603–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Sayed, A.; Kongar, E.; Gupta, S.M. A genetic algorithm approach to end-of-life disassembly sequencing for robotic disassembly. In Proceedings of the Northeast Decision Sciences Institute Conference, NEDSI 2010, Alexandria, VA, USA, 26–28 March 2010. [Google Scholar]
- El Sayed, A.; Kongar, E.; Gupta, S.M.; Sobh, T. A Robotic-Driven Disassembly Sequence Generator for End-Of-Life Electronic Products. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 2012, 68, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Chen, M. Designing and verifying a disassembly line approach to cope with the upsurge of end-of-life vehicles in China. Waste Manag. 2018, 76, 697–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; Gao, Y.; Tian, G.; Li, Z.; Hu, H.; Zheng, H. Flexible Process Planning and End-of-Life Decision-Making for Product Recovery Optimization Based on Hybrid Disassembly. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2019, 16, 311–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshibli, M.; El Sayed, A.; Kongar, E.; Sobh, T.M.; Gupta, S.M. Disassembly Sequencing Using Tabu Search. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 2016, 82, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sait, S.M.; Youssef, H. Iterative Computer Algorithms with Applications in Engineering: Solving Combinatorial Optimization Problems; IEEE Computer Society Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1999; p. 387. [Google Scholar]
- Alagumurthi, N.; Palaniradja, K.; Soundararajan, V. Optimization of grinding process through design of experiment (DOE)—A comparative study. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2006, 21, 19–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondapalli, S.P.; Chalamalasetti, S.R.; Damera, N.R. Application of Taguchi based design of experiments to fusion arc weld processes: A review. Int. J. Bus. Res. Dev. 2013, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freddi, A.; Salmon, M. Introduction to the Taguchi Method. In Design Principles and Methodologies: From Conceptualization to First Prototyping with Examples and Case Studies; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Germany, 2019; pp. 159–180. [Google Scholar]
- Ilgin, M.A.; Taşoğlu, G.T. Simultaneous Determination of Disassembly Sequence and Disassembly-to-Order Decisions Using Simulation Optimization. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 2016, 138, 101012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, C.-S.; Huang, H.-S.; Tsai, M.-T.; Cheng, F.-S. Bee colony optimization with Taguchi method for solving the dynamic economic dispatch. MATEC Web Conf. 2018, 185, 00033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.-P. Optimal harmonic filters design of the Taiwan high speed rail traction system of distributer generation system with specially connected transformers. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2014, 62, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gungor, A.; Gupta, S.M.; Pochampally, K.; Kamarthi, S.V. Complications in disassembly line balancing. Proc. SPIE 2001, 4193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mete, S.; Çil, Z.A.; Özceylan, E.; Ağpak, K. Resource constrained disassembly line balancing problem. IFAC Pap. Online 2016, 49, 921–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentaha, M.L.; Battaïa, O.; Dolgui, A. Disassembly line balancing and sequencing under uncertainty. Proc. CIRP 2014, 15, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, S.D.; Gagnon, R.J. A systematic literature review of remanufacturing scheduling. Int. J. Product. Res. 2013, 51, 4853–4879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gungor, A.; Gupta, S.M. A solution approach to the disassembly line balancing problem in the presence of task failures. Int. J. Product. Res. 2001, 39, 1427–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, F.; Gil, P.; Puente, S.; Pomares, J.; Aracil, R. Automatic PC disassembly for component recovery. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2004, 23, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutjahr, A.L.; Nemhauser, G.L. An algorithm for the line balancing problem. Manag. Sci. 1964, 11, 308–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erel, E.; Gokcen, H. Shortest-route formulation of mixed-model assembly line balancing problem. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 1999, 116, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMullen, P.R.; Tarasewich, P. Using ant techniques to solve the assembly line balancing problem. IIE Trans. 2003, 35, 605–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duta, L.; Filip, F.G.; Henrioud, J.-M. Applying equal piles approach to disassembly line balancing problem. IFAC Proc. Vol. 2005, 38, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duta, L.; Filip, F.G.; Henrioud, J.-M. A method for dealing with multi-objective optimization problem of disassembly processes. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Assembly and Task Planning, Besancon, France, 11 July 2003; pp. 163–168. [Google Scholar]
- Avikal, S.; Mishra, P.; Jain, R.; Yadav, H. A PROMETHEE method based heuristic for disassembly line balancing problem. Ind. Eng. Manag. Syst. 2013, 12, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGrath, G.; Brenner, P.R. Serverless computing: Design, implementation, and performance. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 37th International Conference on Distributed Computing Systems Workshops (ICDCSW), Atlanta, GA, USA, 5–8 June 2017; pp. 405–410. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, T.K.; Lee, J.Y. A row-permutated data reorganization algorithm for growing server-less video-on-demand systems. In Proceedings of the CCGrid 2003, 3rd IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Cluster Computing and the Grid, Tokyo, Japan, 12–15 May 2003; pp. 44–51. [Google Scholar]
- Bolosky, W.J.; Douceur, J.R.; Ely, D.; Theimer, M. Feasibility of a serverless distributed file system deployed on an existing set of desktop PCs. ACM SIGMETRICS Perform. Eval. Rev. 2000, 28, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendrickson, S.; Sturdevant, S.; Harter, T.; Venkataramani, V.; Arpaci-Dusseau, A.C.; Arpaci-Dusseau, R.H. Serverless computation with openlambda. Elastic 2016, 60, 80. [Google Scholar]
- Bila, N.; Dettori, P.; Kanso, A.; Watanabe, Y.; Youssef, A. Leveraging the serverless architecture for securing linux containers. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 37th International Conference on Distributed Computing Systems Workshops (ICDCSW), Atlanta, GA, USA, 5–8 June 2017; pp. 401–404. [Google Scholar]
- Baldini, I. The serverless trilemma: Function composition for serverless computing. In Proceedings of the 2017 ACM SIGPLAN International Symposium on New Ideas, New Paradigms, and Reflections on Programming and Software, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 25–27 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Adya, A.; Bolosky, W.J.; Cermak, G.; Douceur, J.R.; Theimer, M.M.; Wattenhofer, R.P. Serverless Distributed File System. U.S. Patent 7062490B2, 2006. Available online: https://patents.google.com/patent/US7062490B2/en (accessed on 8 December 2018).
- Ilgin, M.A.; Gupta, S.M. Multiple Criteria Decision Making Applications in Environmentally Conscious Manufacturing and Product Recovery; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Taguchi, G.; Wu, Y. Introduction to Off-Line Quality Control; Central Japan Quality Control Association: Nagoya, Japan, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Phadke, M.S. Quality Engineering Using Robust Design; Prentice Hall PTR: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Kalayci, C.B.; Gupta, S.M.; Nakashima, K. A simulated annealing algorithm for balancing a disassembly line. In Design for Innovative Value towards a Sustainable Society; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2012; pp. 714–719. [Google Scholar]
- Kalayci, C.B.; Gupta, S.M. Artificial bee colony algorithm for solving sequence-dependent disassembly line balancing problem. Expert Syst. Appl. 2013, 40, 7231–7241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalayci, C.B.; Gupta, S.M. A particle swarm optimization algorithm with neighborhood-based mutation for sequence-dependent disassembly line balancing problem. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2013, 69, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalayci, C.B.; Gupta, S.M. Ant colony optimization for sequence-dependent disassembly line balancing problem. J. Manuf. Technol. Manag. 2013, 24, 413–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalayci, C.B.; Polat, O.; Gupta, S.M. A hybrid genetic algorithm for sequence-dependent disassembly line balancing problem. Ann. Oper. Res. 2016, 242, 321–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalayci, C.B.; Gupta, S.M. A tabu search algorithm for balancing a sequence-dependent disassembly line. Product. Plan. Control 2014, 25, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalayci, C.B.; Gupta, S.M. Tabu search for disassembly line balancing with multiple objectives. In Proceedings of the 41st International Conference on Computers and Industrial Engineering, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 23–26 October 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Kalayci, C.B.; Hancilar, A.; Gungor, A.; Gupta, S.M. Multi-objective fuzzy disassembly line balancing using a hybrid discrete artificial bee colony algorithm. J. Manuf. Syst. 2015, 37, 672–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalayci, C.B.; Gupta, S.M. River formation dynamics approach for sequence-dependent disassembly line balancing problem. In Reverse Supply Chains: Issues and Analysis; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2013; pp. 289–312. [Google Scholar]
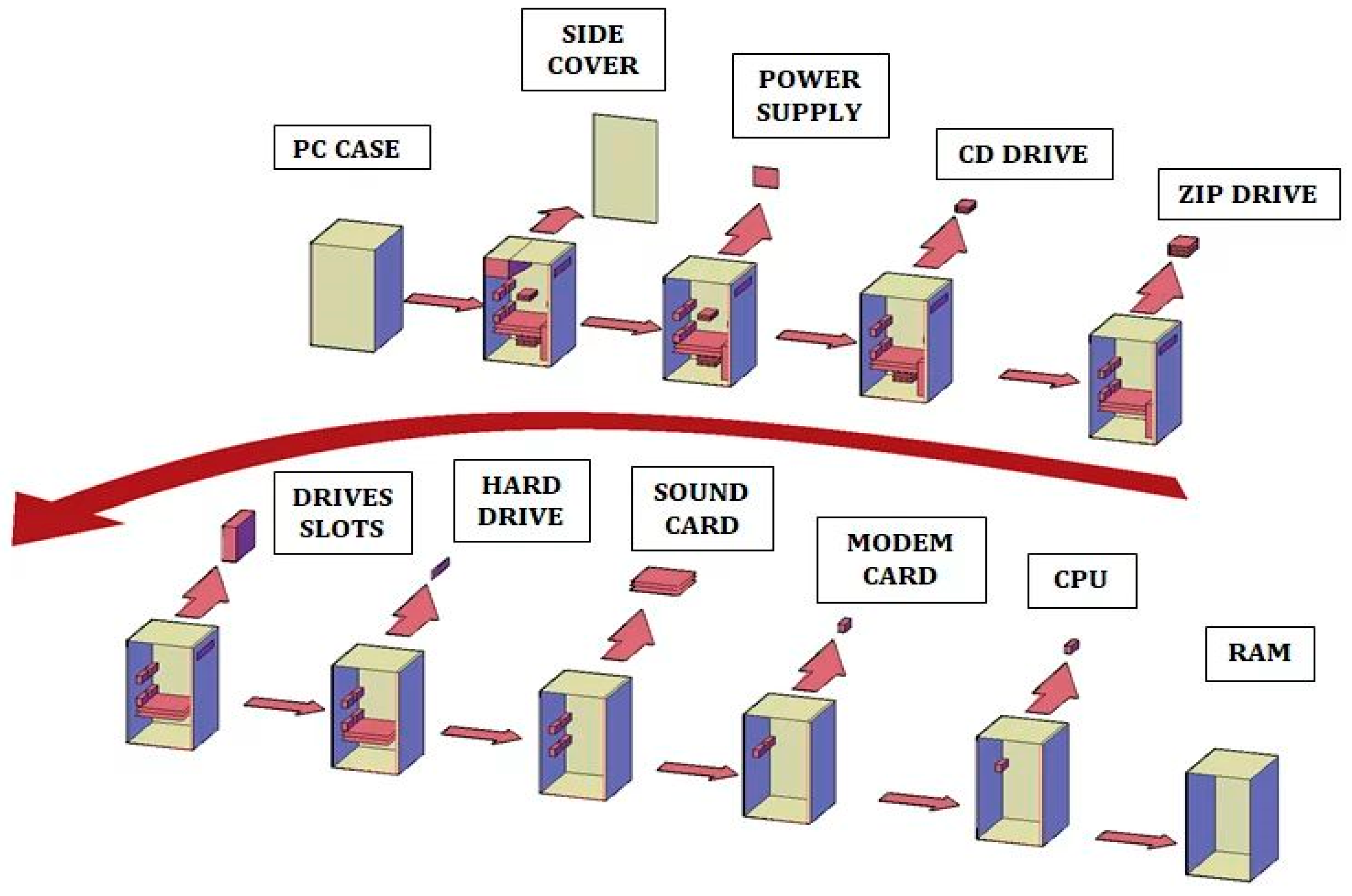

| Component Number | Description | Material | Disassembly Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Robot reference point | - | - |
| 1 | Side cover | Aluminum (A) | D |
| 2 | Power supply | Copper(C) | D |
| 3 | Sound card | Plastic (P) | ND |
| 4 | Modem card | Plastic (P) | ND |
| 5 | CPU | Plastic (P) | ND |
| 6 | Hard drive | Aluminum (A) | ND |
| 7 | CD drive | Aluminum (A) | ND |
| 8 | Zip drive | Aluminum (A) | ND |
| 9 | RAM | Plastic (P) | ND |
| 10 | Drives slot | Aluminum (A) | D |
| Expt. No. | L54 (2^1 × 3^25) Orthogonal Array Column | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| µ(dt1j) | σ(dt1j) | µ(dt2j) | σ(dt2j) | … | µ(dt9j) | σ(dt9j) | µ(dt10j) | σ(dt10j) | µ(sf) | σ(sf) | µ(mtij) | σ(mtij) | |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | |
| 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | |
| 4 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 2 | |
| 5 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | . | 1 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 3 |
| 6 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | . | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 |
| 7 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 3 | . | 2 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 3 |
| 8 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 1 | |
| 9 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | |
| 10 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 2 | |
| … | … | … | |||||||||||
| 44 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 2 | |
| 45 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | |
| 46 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | |
| 47 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 3 | |
| 48 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 2 | . | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 1 |
| 49 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 3 | . | 1 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 3 |
| 50 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 3 | . | 2 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 1 |
| 51 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 2 | |
| 52 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 1 | |
| 53 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 2 | |
| 54 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 1 | … | 2 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 3 |
| Expt. No. | L54 (2^1 × 3^25) Orthogonal Array Column | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| µ(dt1j) | σ(dt1j) | µ(dt2j) | σ(dt2j) | … | σ(dt9j) | µ(dt10j) | σ(dt10j) | µ(sf) | σ(sf) | µ(mtij) | σ(mtij) | |
| 1 | 2.000 | 0.010 | 3.000 | 0.010 | 0.010 | 2.000 | 0.010 | 7.000 | 0.010 | 0.010 | 1.000 | |
| 2 | 2.000 | 0.010 | 3.000 | 0.010 | 0.050 | 2.250 | 0.050 | 7.250 | 0.050 | 0.050 | 1.250 | |
| 3 | 2.000 | 0.010 | 3.000 | 0.010 | 0.100 | 2.500 | 0.100 | 7.500 | 0.100 | 0.100 | 1.500 | |
| 4 | 2.000 | 0.050 | 3.250 | 0.050 | 0.050 | 2.500 | 0.050 | 7.500 | 0.050 | 0.100 | 1.250 | |
| 5 | 2.000 | 0.050 | 3.250 | 0.050 | . | 0.100 | 2.000 | 0.100 | 7.000 | 0.100 | 0.010 | 1.500 |
| 6 | 2.000 | 0.050 | 3.250 | 0.050 | . | 0.010 | 2.250 | 0.010 | 7.250 | 0.010 | 0.050 | 1.000 |
| 7 | 2.000 | 0.100 | 3.500 | 0.100 | . | 0.100 | 2.250 | 0.100 | 7.250 | 0.100 | 0.050 | 1.500 |
| 8 | 2.000 | 0.100 | 3.500 | 0.100 | 0.010 | 2.500 | 0.010 | 7.500 | 0.010 | 0.100 | 1.000 | |
| 9 | 2.000 | 0.100 | 3.500 | 0.100 | 0.050 | 2.000 | 0.050 | 7.000 | 0.050 | 0.010 | 1.250 | |
| 10 | 2.250 | 0.010 | 3.000 | 0.050 | 0.050 | 2.500 | 0.050 | 7.500 | 0.050 | 0.100 | 1.250 | |
| … | … | … | ||||||||||
| 44 | 2.250 | 0.100 | 3.000 | 0.050 | 0.100 | 2.000 | 0.010 | 7.500 | 0.100 | 0.010 | 1.250 | |
| 45 | 2.250 | 0.100 | 3.000 | 0.050 | 0.010 | 2.250 | 0.050 | 7.000 | 0.010 | 0.050 | 1.500 | |
| 46 | 2.500 | 0.010 | 3.500 | 0.050 | 0.050 | 2.500 | 0.100 | 7.250 | 0.010 | 0.010 | 1.250 | |
| 47 | 2.500 | 0.010 | 3.500 | 0.050 | 0.100 | 2.000 | 0.010 | 7.500 | 0.050 | 0.050 | 1.500 | |
| 48 | 2.500 | 0.010 | 3.500 | 0.050 | . | 0.010 | 2.250 | 0.050 | 7.000 | 0.100 | 0.100 | 1.000 |
| 49 | 2.500 | 0.050 | 3.000 | 0.100 | . | 0.100 | 2.250 | 0.010 | 7.000 | 0.050 | 0.100 | 1.500 |
| 50 | 2.500 | 0.050 | 3.000 | 0.100 | . | 0.010 | 2.500 | 0.050 | 7.250 | 0.100 | 0.010 | 1.000 |
| 51 | 2.500 | 0.050 | 3.000 | 0.100 | 0.050 | 2.000 | 0.100 | 7.500 | 0.010 | 0.050 | 1.250 | |
| 52 | 2.500 | 0.100 | 3.250 | 0.010 | 0.010 | 2.000 | 0.050 | 7.500 | 0.100 | 0.050 | 1.000 | |
| 53 | 2.500 | 0.100 | 3.250 | 0.010 | 0.050 | 2.250 | 0.100 | 7.000 | 0.010 | 0.100 | 1.250 | |
| 54 | 2.500 | 0.100 | 3.250 | 0.010 | … | 0.100 | 2.500 | 0.010 | 7.250 | 0.050 | 0.010 | 1.500 |
| Iteration | Sequence | Allocation | Fitness Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 1 D r A 24.7381 | [1 0 0] [3 0 0] | 1, 3, 0, 0 |
| 2 | 0 2 3 4 DNN ruu CPP 49.1646 | [1 0 0] [0 1 0] [0 0 1] [6 0 0] [0 3 0] [0 0 3] | 3, 6, 0, 0 |
| 3 | 0 7 8 6 5 NNNN rrru AAAP 73.8853 | [1 0 0] [0 1 0] [0 0 1] [0 1 0] [5 0 0] [0 3 0] [0 0 4] [0 4 0] | 3, 5, 0, 0 |
| 4 | 0 10 9 DN rs AP 53.2419 | [1 0 0] [0 1 0] [3 0 0] [0 2 0] | 2, 6, 0, 0 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alshibli, M.; ElSayed, A.; Kongar, E.; Sobh, T.; Gupta, S.M. A Robust Robotic Disassembly Sequence Design Using Orthogonal Arrays and Task Allocation. Robotics 2019, 8, 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/robotics8010020
Alshibli M, ElSayed A, Kongar E, Sobh T, Gupta SM. A Robust Robotic Disassembly Sequence Design Using Orthogonal Arrays and Task Allocation. Robotics. 2019; 8(1):20. https://doi.org/10.3390/robotics8010020
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlshibli, Mohammad, Ahmed ElSayed, Elif Kongar, Tarek Sobh, and Surendra M. Gupta. 2019. "A Robust Robotic Disassembly Sequence Design Using Orthogonal Arrays and Task Allocation" Robotics 8, no. 1: 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/robotics8010020
APA StyleAlshibli, M., ElSayed, A., Kongar, E., Sobh, T., & Gupta, S. M. (2019). A Robust Robotic Disassembly Sequence Design Using Orthogonal Arrays and Task Allocation. Robotics, 8(1), 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/robotics8010020






