Propulsion-Based Soft Robotic Actuation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods and Materials
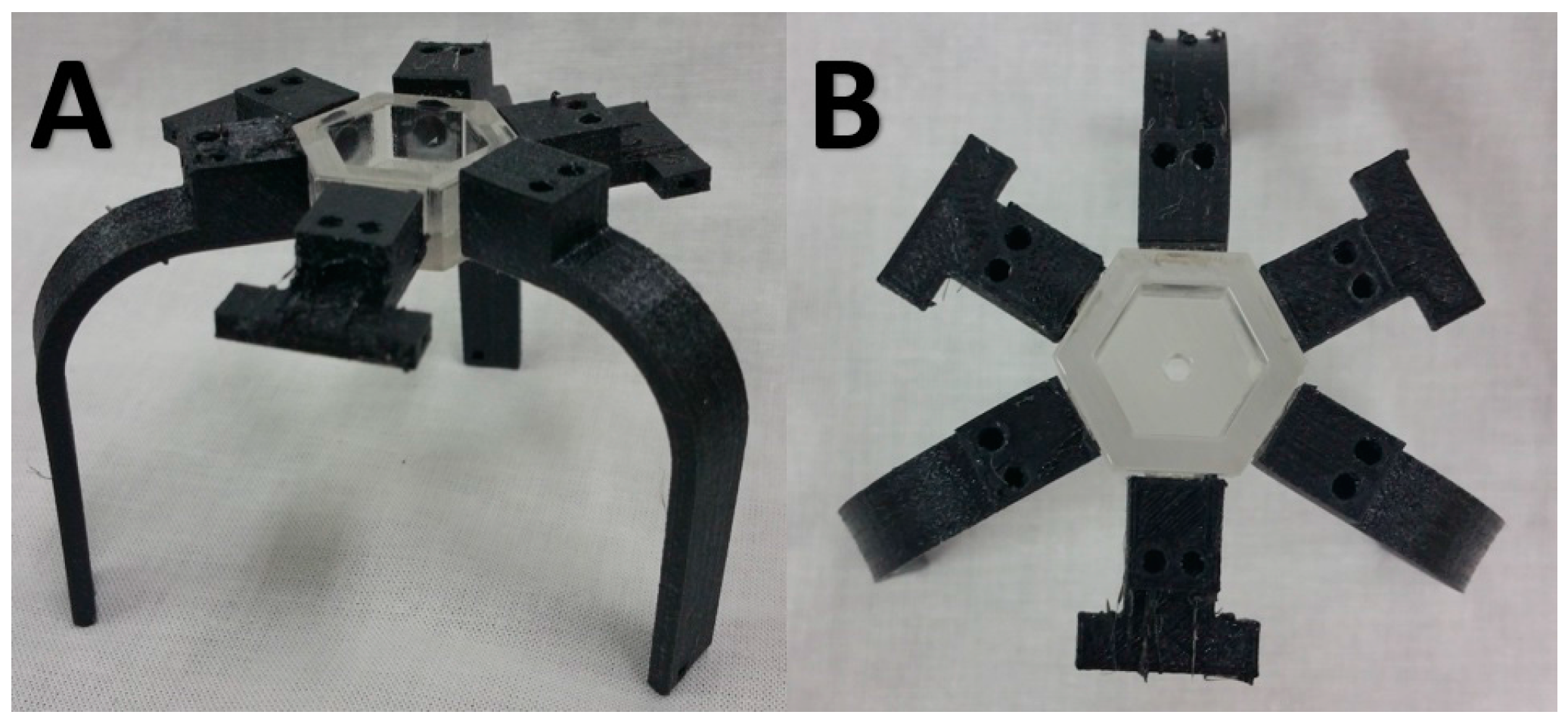
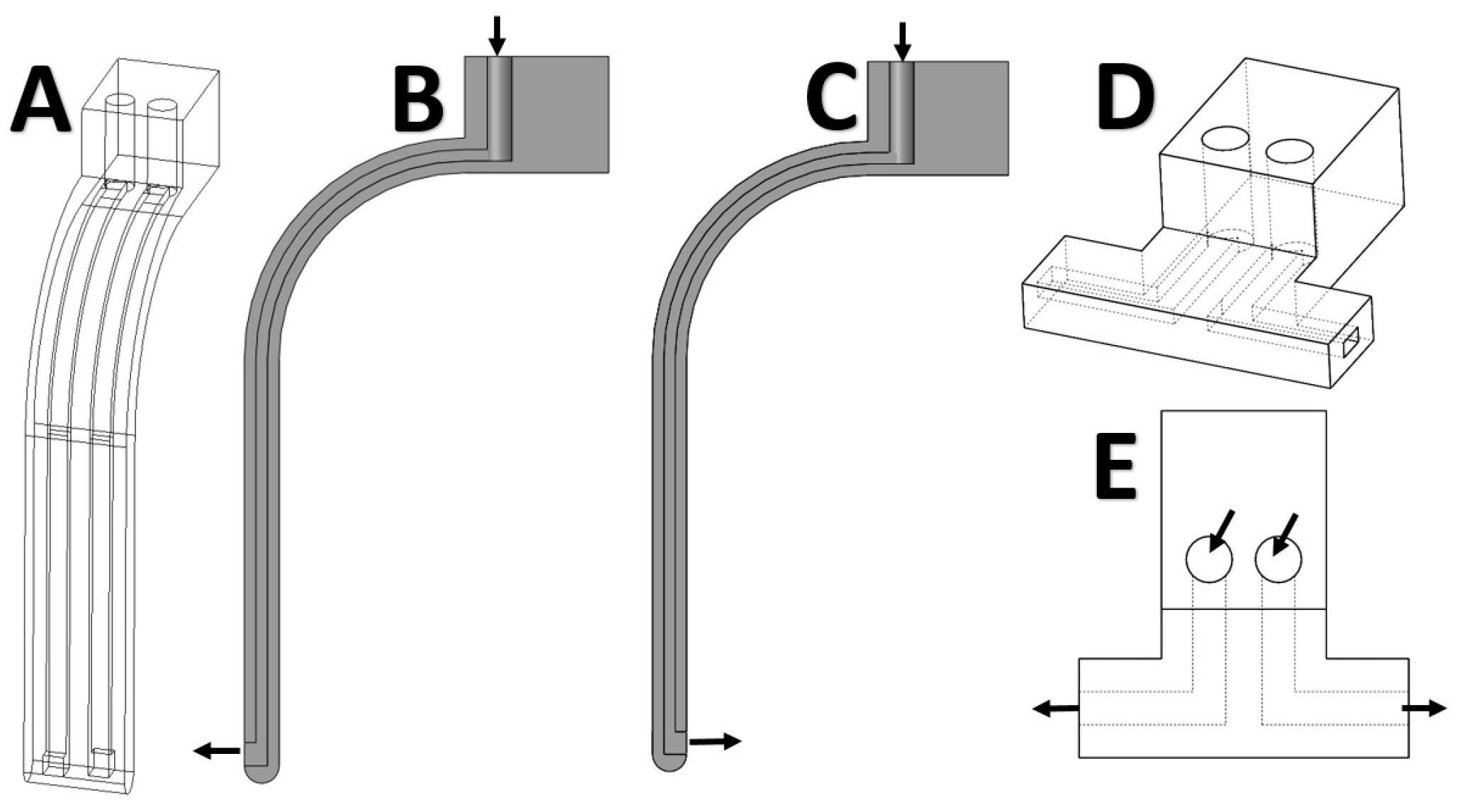
2.1. Design of Air-Driven Robot
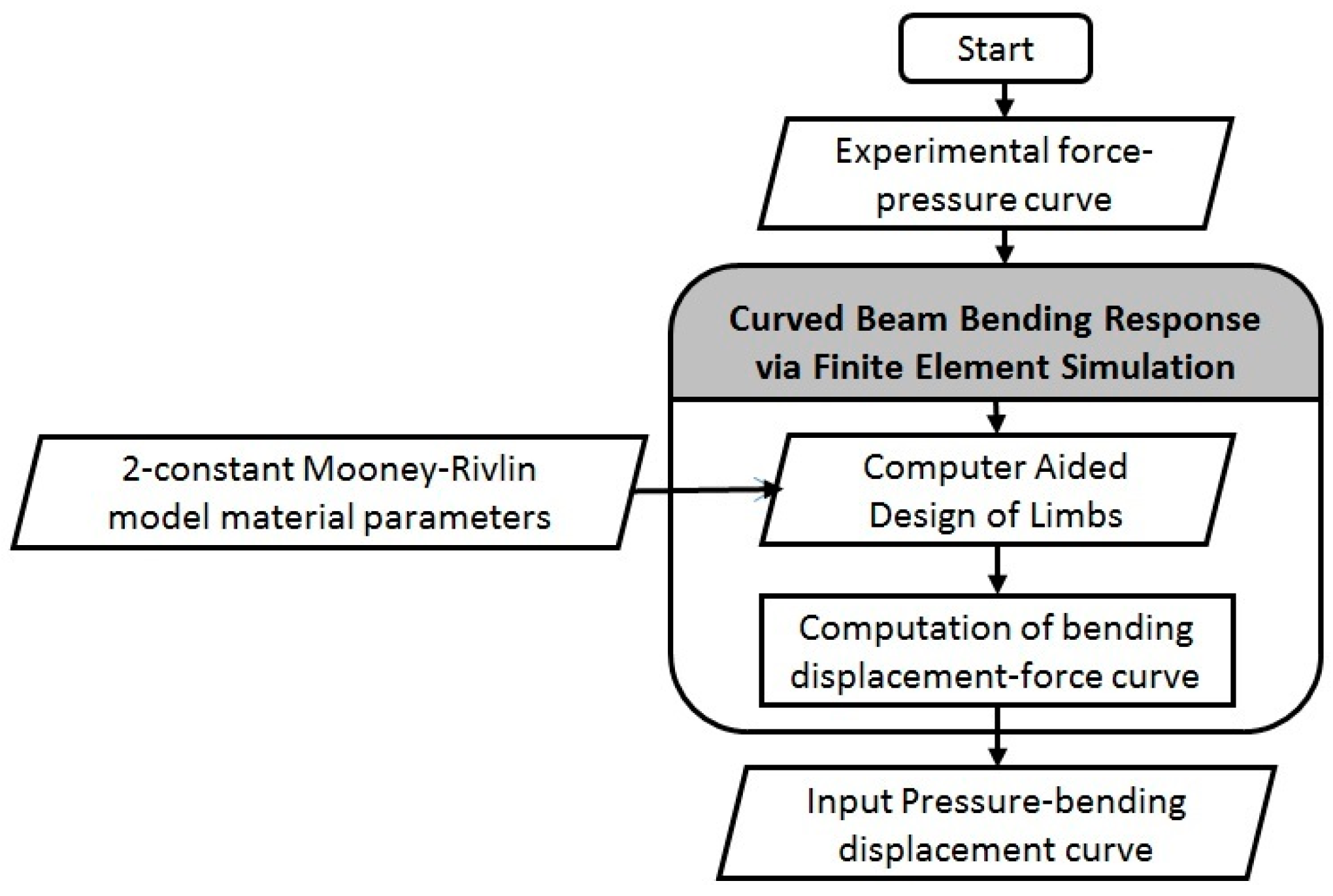
2.2. Finite Element Modeling of Limb Bending
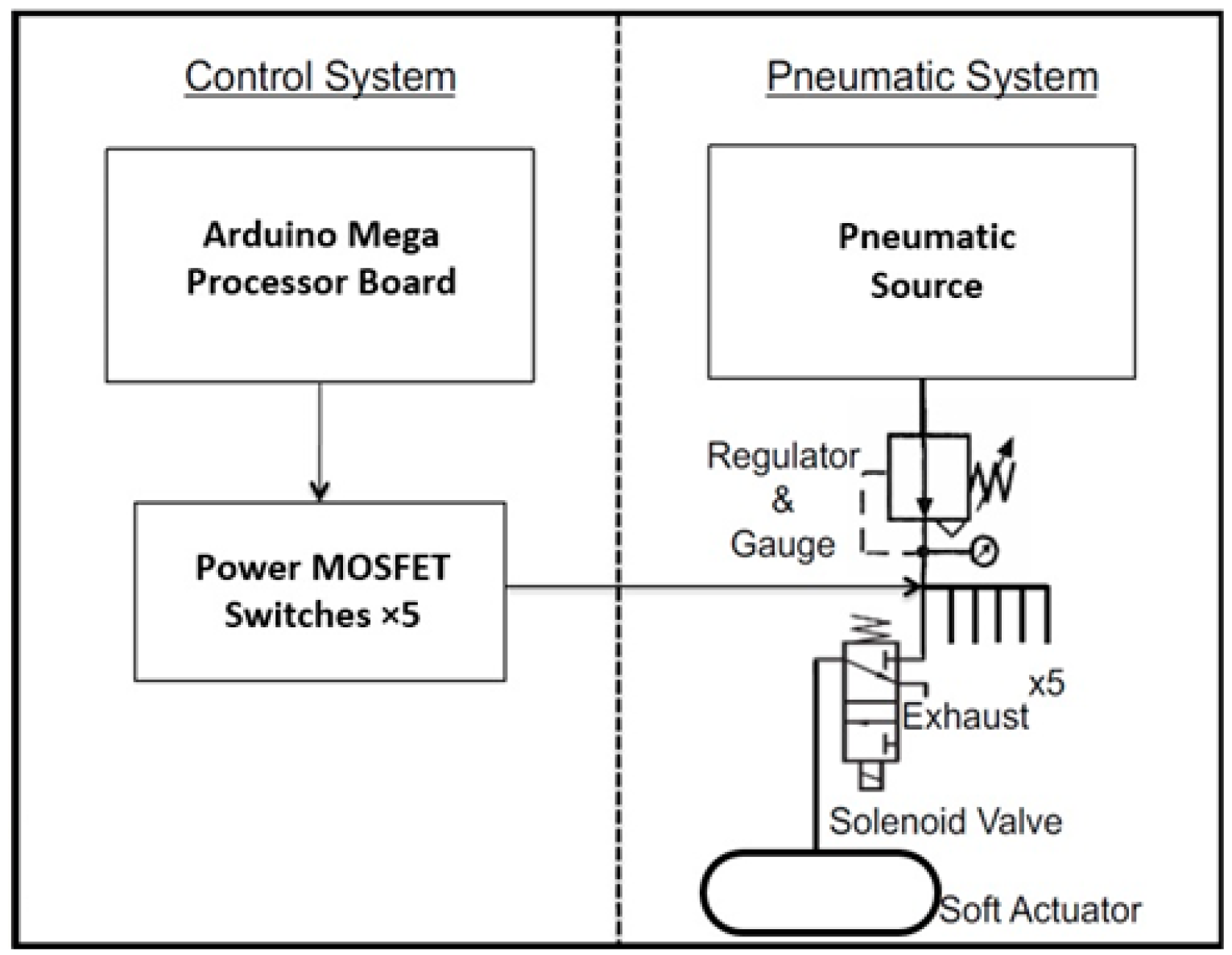
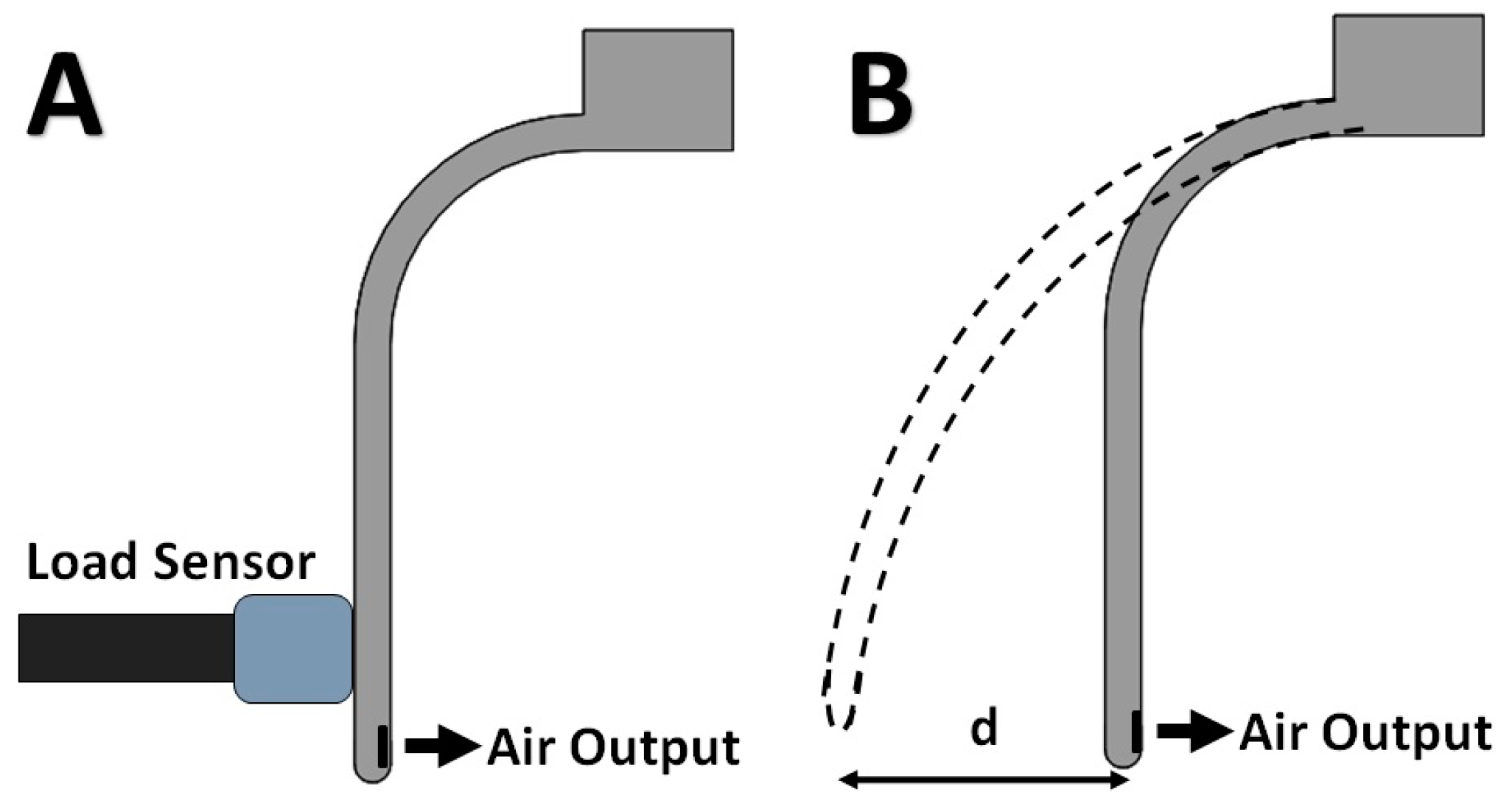
2.3. Mechanical Experimental Setup and Evaluation
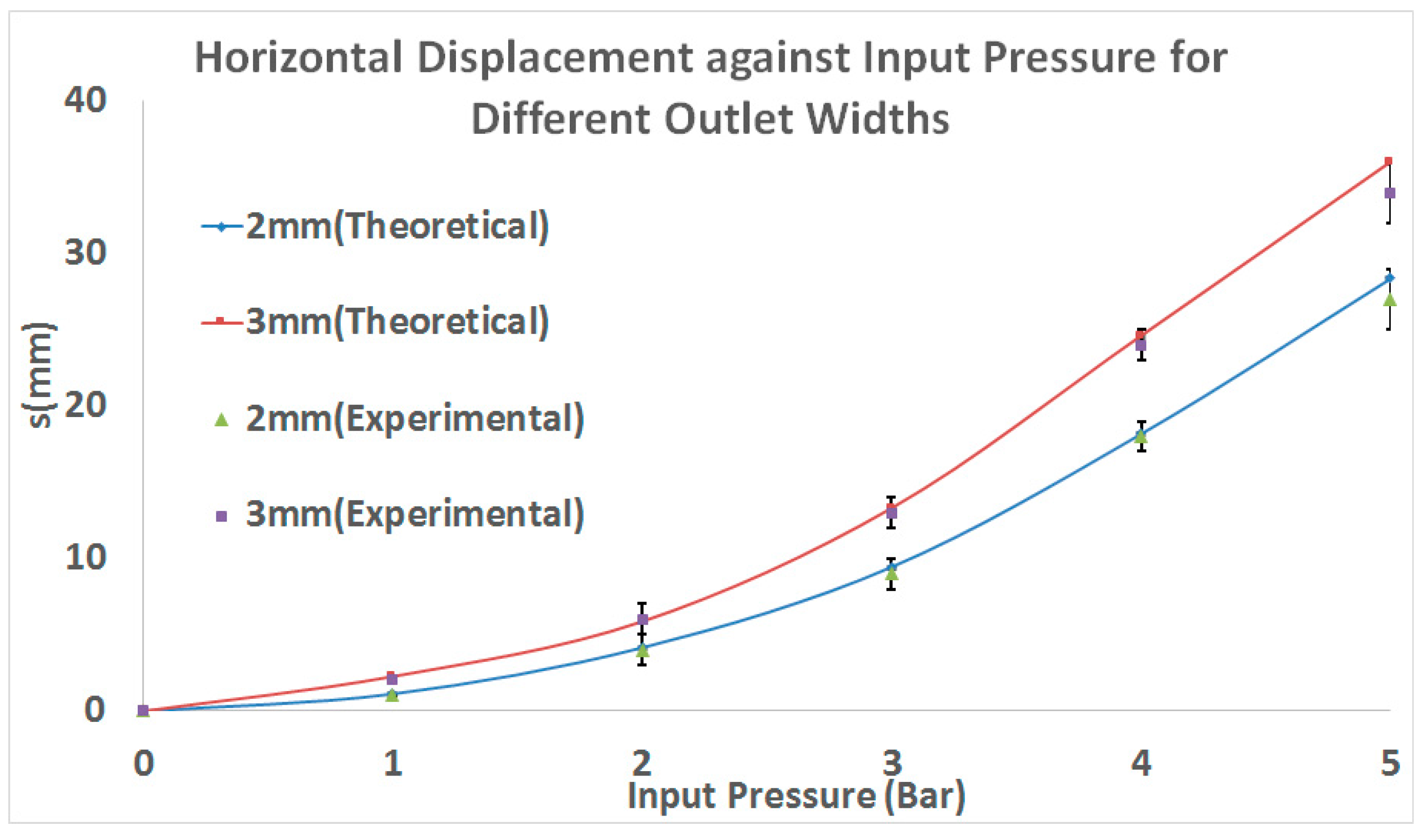
3. Results
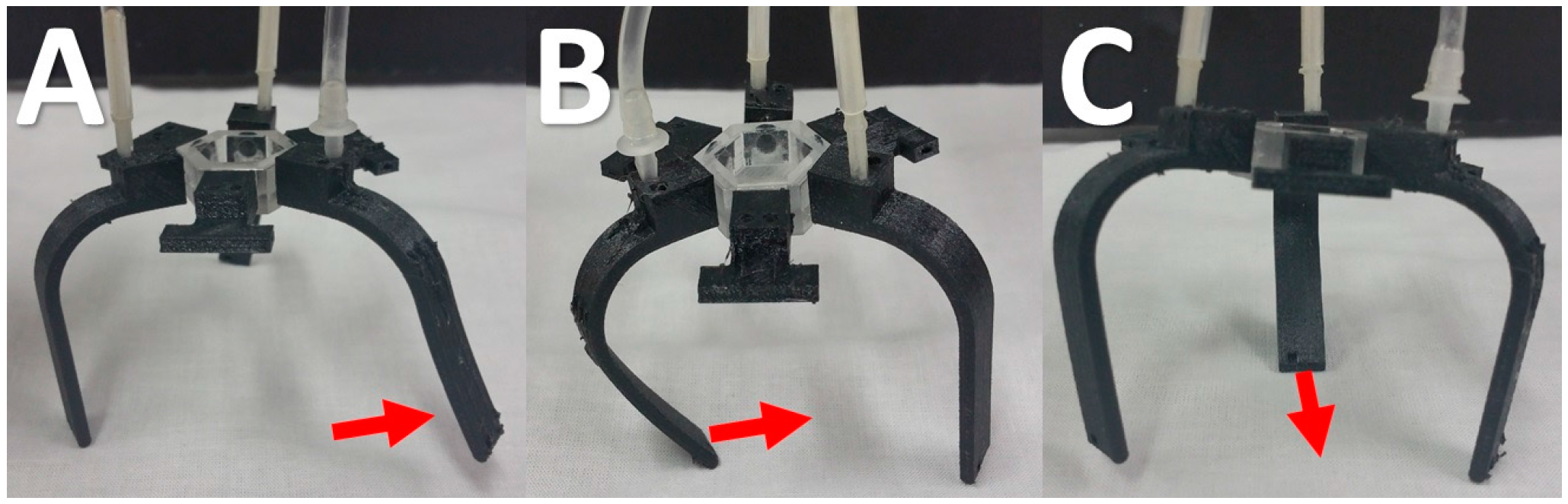
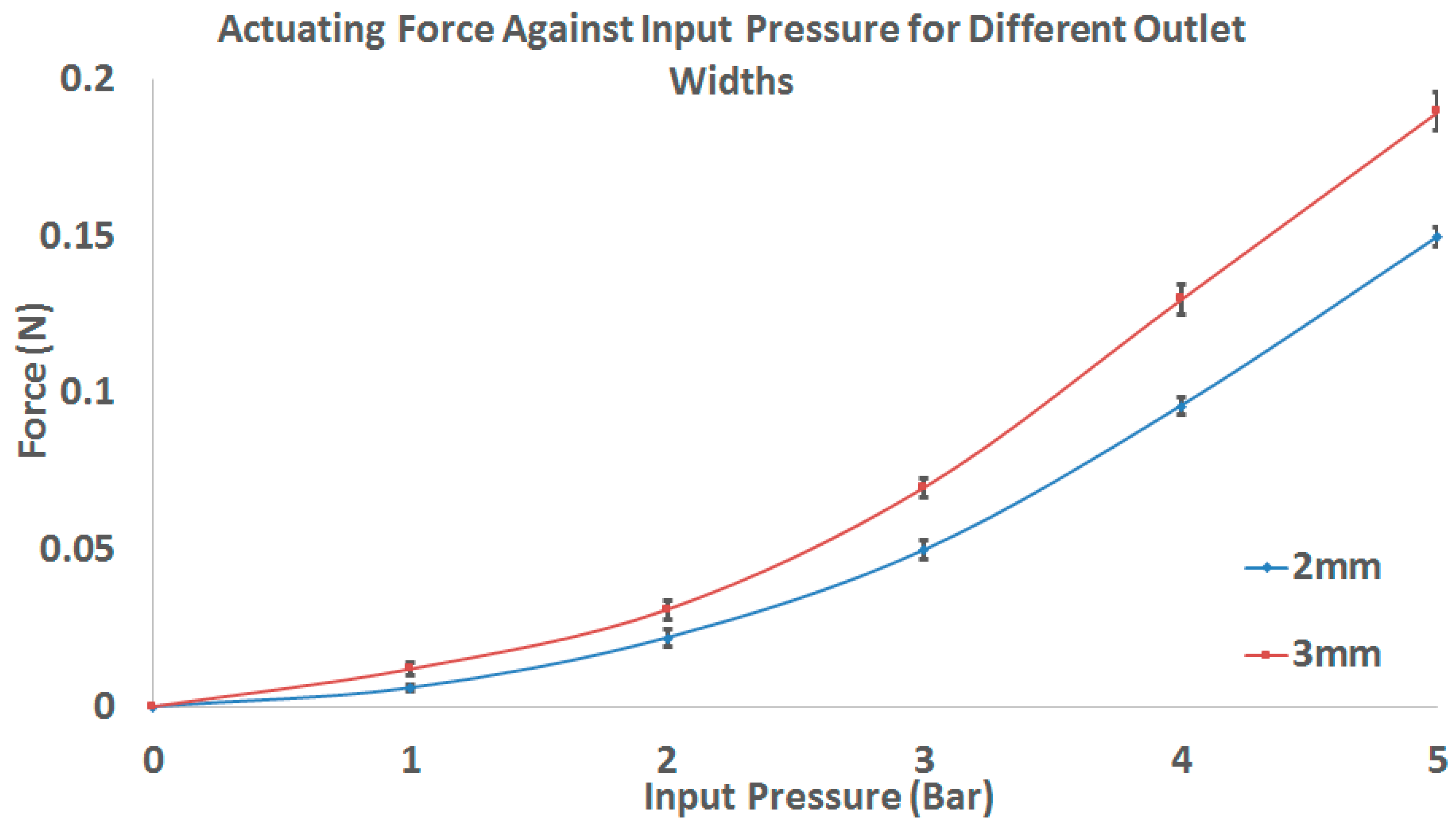
3.1. Experimental
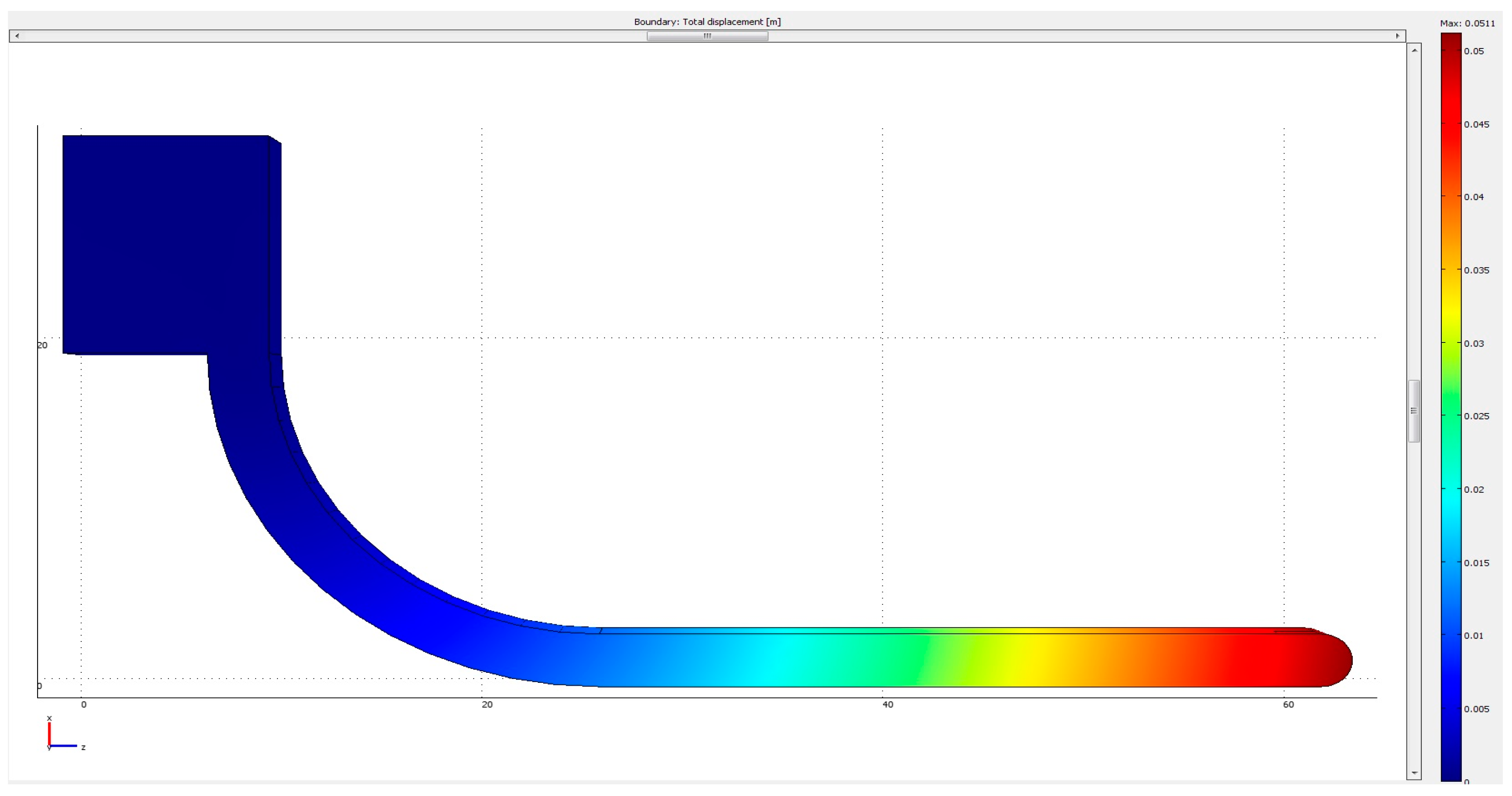
3.2. Simulation Results
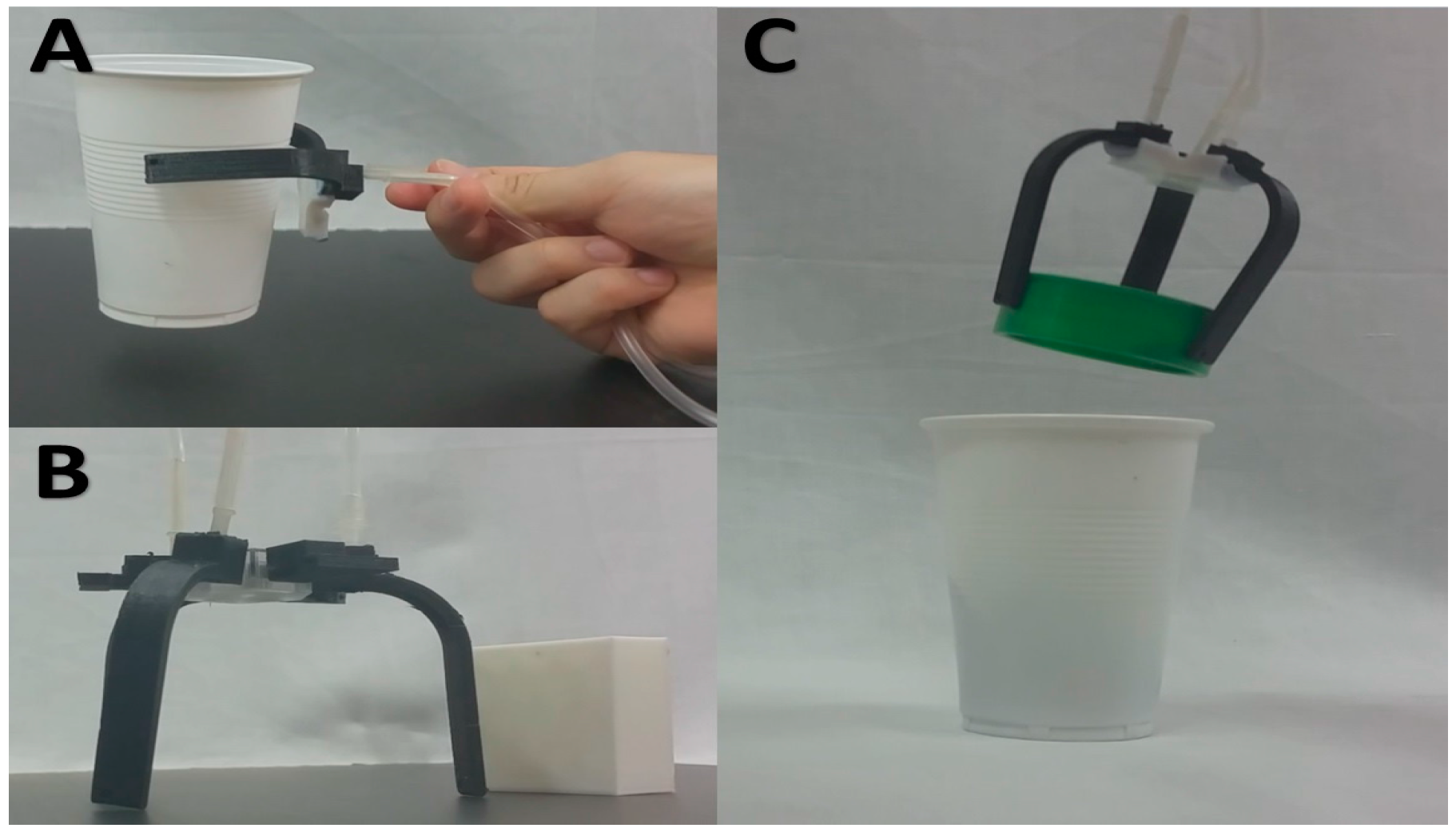
4. Application of Air-Driven Robot
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jacobson, A. Air compressor lubricants: The next generation. Tribol. Lubr. Technol. 2004, 60, 30. [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd, R.F.; Stokes, A.A.; Freake, J.; Barber, J.; Snyder, P.W.; Mazzeo, A.D.; Cademartiri, L.; Morin, S.A.; Whitesides, G.M. Using explosions to power a soft robot. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 2892–2896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucas, K.N.; Johnson, N.; Beaulieu, W.T.; Cathcart, E.; Tirrell, G.; Colin, S.P.; Gemmell, B.J.; Dabiri, J.O.; Costello, J.H. Bending rules for animal propulsion. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albertani, R.; Stanford, B.; Hubner, J.; Ifju, P. Aerodynamic coefficients and deformation measurements on flexible micro air vehicle wings. Exp. Mech. 2007, 47, 625–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Combes, S.A.; Daniel, T.L. Into thin air: Contributions of aerodynamic and inertial-elastic forces to wing bending in the hawkmoth Manduca sexta. J. Exp. Biol. 2003, 206, 2999–3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yap, H.K.; Goh, J.C.H.; Yeow, R.C.H. Design and Characterization of Soft Actuator for Hand Rehabilitation Application. In 6th European Conference of the International Federation for Medical and Biological Engineering: MBEC 2014, Dubrovnik, Croatia, 7–11 September 2014; Lacković, I., Vasic, D., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Germany, 2015; pp. 367–370. [Google Scholar]
- Yap, H.K.; Lim, J.H.; Nasrallah, F.; Goh, J.C.; Yeow, R.C. A soft exoskeleton for hand assistive and rehabilitation application using pneumatic actuators with variable stiffness. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Seattle, WA, USA, 26–30 May 2015; pp. 4967–4972. [Google Scholar]
- Yap, H.K.; Lim, J.H.; Nasrallah, F.; Goh, J.C.H.; Yeow, C.-H. Characterisation and evaluation of soft elastomeric actuators for hand assistive and rehabilitation applications. J. Med. Eng. Technol. 2016, 40, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belforte, G.; Eula, G.; Ivanov, A.; Sirolli, S. Soft pneumatic actuators for rehabilitation. Actuators 2014, 3, 84–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepherd, R.F.; Ilievski, F.; Choi, W.; Morin, S.A.; Stokes, A.A.; Mazzeo, A.D.; Chen, X.; Wang, M.; Whitesides, G.M. Multigait soft robot. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 20400–20403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzumori, K.; Endo, S.; Kanda, T.; Kato, N.; Suzuki, H. A bending pneumatic rubber actuator realizing soft-bodied manta swimming robot. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Roma, Italy, 10–14 April 2007; pp. 4975–4980. [Google Scholar]
- Klute, G.K.; Czerniecki, J.M.; Hannaford, B. McKibben artificial muscles: Pneumatic actuators with biomechanical intelligence. In Proceedings of the 1999 IEEE/ASME International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics, Atlanta, Georgia, 19–23 September 1999; pp. 221–226. [Google Scholar]
- Tondu, B.; Ippolito, S.; Guiochet, J.; Daidie, A. A seven-degrees-of-freedom robot-arm driven by pneumatic artificial muscles for humanoid robots. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2005, 24, 257–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polygerinos, P.; Lyne, S.; Wang, Z.; Nicolini, L.F.; Mosadegh, B.; Whitesides, G.M.; Walsh, C.J. Towards a soft pneumatic glove for hand rehabilitation. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Tokyo, Japan, 3–7 November 2013; pp. 1512–1517. [Google Scholar]
- Martinez, R.V.; Fish, C.R.; Chen, X.; Whitesides, G.M. Elastomeric Origami: Programmable Paper-Elastomer Composites as Pneumatic Actuators. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 1376–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laschi, C.; Mazzolai, B.; Mattoli, V.; Cianchetti, M.; Dario, P. Design of a biomimetic robotic octopus arm. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2009, 4, 015006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosadegh, B.; Polygerinos, P.; Keplinger, C.; Wennstedt, S.; Shepherd, R.F.; Gupta, U.; Shim, J.; Bertoldi, K.; Walsh, C.J.; Whitesides, G.M. Pneumatic networks for soft robotics that actuate rapidly. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 2163–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, C.-P.; Hannaford, B. Static and dynamic characteristics of McKibben pneumatic artificial muscles. In Proceedings of the 1994 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, San Diego, CA, USA, 8–13 May 1994; pp. 281–286. [Google Scholar]
- Kingsley, D.A.; Quinn, R.D. Fatigue life and frequency response of braided pneumatic actuators. In Proceedings of the ICRA’02. IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Washington, DC, USA, 11–15 May 2002; pp. 2830–2835. [Google Scholar]
- Bahr, R.; Le, T.; Tentzeris, M.M.; Moscato, S.; Pasian, M.; Bozzi, M.; Perregrini, L. RF characterization of 3D printed flexible materials-NinjaFlex Filaments. In Proceedings of the 2015 European Microwave Conference (EuMC), Paris, France, 7–10 September 2015; pp. 742–745. [Google Scholar]
- Soe, S.; Theobald, P. Energy Absorbing Characteristics of Additively Manufactured TPE Cellular Structures. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Sustainable Design and Manufacturing, Seville, Spain, 12–14 April 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Boyce, M.C.; Arruda, E.M. Constitutive models of rubber elasticity: A review. Rubber Chem. Technol. 2000, 73, 504–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Deng, T.; Zhao, S.-G. Determination for Material Constants of Rubber Mooney-Rivlin Model. Spec. Purp. Rubber Prod. 2004, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Yap, H.K.; Ng, H.Y.; Yeow, C.-H. High-Force Soft Printable Pneumatics for Soft Robotic Applications. Soft Robot. 2016, 3, 144–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, R.R.; Tadokoro, S.; Nardi, D.; Jacoff, A.; Fiorini, P.; Choset, H.; Erkmen, A.M. Search and rescue robotics. In Springer Handbook of Robotics; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2008; pp. 1151–1173. [Google Scholar]
- Hougen, D.F.; Benjaafar, S.; Bonney, J.C.; Budenske, J.R.; Dvorak, M.; Gini, M.; French, H.; Krantz, D.G.; Li, P.Y.; Malver, F. A miniature robotic system for reconnaissance and surveillance. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, San Francisco, CA, USA, 24–28 April 2000; pp. 501–507. [Google Scholar]
- Matthies, L.; Xiong, Y.; Hogg, R.; Zhu, D.; Rankin, A.; Kennedy, B.; Hebert, M.; Maclachlan, R.; Won, C.; Frost, T. A portable, autonomous, urban reconnaissance robot. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2002, 40, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarfogliero, U.; Stefanini, C.; Dario, P. A bioinspired concept for high efficiency locomotion in micro robots: The jumping Robot Grillo. In Proceedings of the ICRA 2006 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Orlando, FL, USA, 15–19 May 2006; pp. 4037–4042. [Google Scholar]
- Buksh, S.R.; Chen, X.; Wang, W. Study of flea jumping mechanism for biomimetic robot design. J. Biomech. Sci. Eng. 2010, 5, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsagarakis, N.; Caldwell, D.; Medrano-Cerda, G. A 7 DOF pneumatic muscle actuator (pMA) powered exoskeleton. In Proceedings of the 8th IEEE International Workshop on Robot and Human Interaction, Pisa, Italy, 27–29 September 1999; pp. 327–333. [Google Scholar]
- Malcolm, P.; Derave, W.; Galle, S.; de Clercq, D. A simple exoskeleton that assists plantarflexion can reduce the metabolic cost of human walking. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heaston, J.; Hong, D.; Morazzani, I.; Ren, P.; Goldman, G. STriDER: Self-excited tripedal dynamic experimental robot. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Roma, Italy, 10–14 April 2007; pp. 2776–2777. [Google Scholar]
- Morazzani, I.; Hong, D.; Lahr, D.; Ren, P. Novel tripedal mobile robot and considerations for gait planning strategies based on kinematics. In Recent Progress in Robotics: Viable Robotic Service to Human; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2007; pp. 35–48. [Google Scholar]
- Daerden, F.; Lefeber, D. Pneumatic artificial muscles: Actuators for robotics and automation. Eur. J. Mech. Environ. Eng. 2002, 47, 11–21. [Google Scholar]
- Trivedi, D.; Rahn, C.D.; Kier, W.M.; Walker, I.D. Soft robotics: Biological inspiration, state of the art, and future research. Appl. Bionics Biomech. 2008, 5, 99–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, J.-H.; Ang, M.H.; Yeow, C.-H. Customizable soft pneumatic finger actuators for hand orthotic and prosthetic applications. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics (ICORR), Singapore, 11–14 August 2015; pp. 380–385. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Yap, H.K.; Liang, X.; Guo, J.; Qi, P.; Ang, M.H., Jr.; Yeow, C.H. Stiffness Customization and Patterning for Property Modulation of Silicone-Based Soft Pneumatic Actuators. Soft Robot. 2017, 4, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Bulk Properties | Values |
|---|---|
| Bulk Density | 600 kg/m3 |
| Young’s Modulus [21] | 7.5 MPa |
| Compressive Modulus [21] | 20 MPa |
| Specific Gravity | 1.2 |
| Features | Air-Propelled Actuators | Pneumatic Bladder Actuators [34,35] |
|---|---|---|
| Speed of actuation | Very Fast | Moderately Fast |
| Hysteresis effect | Low | High |
| Force generated | Small | Moderate |
| Minimum wall thickness | Low | Moderate |
| Size to stiffness ratio | Large | Small |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chua, M.C.H.; Yeow, R.C.H. Propulsion-Based Soft Robotic Actuation. Robotics 2017, 6, 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/robotics6040034
Chua MCH, Yeow RCH. Propulsion-Based Soft Robotic Actuation. Robotics. 2017; 6(4):34. https://doi.org/10.3390/robotics6040034
Chicago/Turabian StyleChua, Matthew Chin Heng, and Raye Chen Hua Yeow. 2017. "Propulsion-Based Soft Robotic Actuation" Robotics 6, no. 4: 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/robotics6040034
APA StyleChua, M. C. H., & Yeow, R. C. H. (2017). Propulsion-Based Soft Robotic Actuation. Robotics, 6(4), 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/robotics6040034





