IMU and Multiple RGB-D Camera Fusion for Assisting Indoor Stop-and-Go 3D Terrestrial Laser Scanning
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- A novel design for a “continuous stop-and-go” indoor mapping system by fusing a low-cost 3D terrestrial laser scanner with two Microsoft Kinect sensors and a micro-electro-mechanical systems (MEMS) inertial measurement unit (IMU);
- A solution to the 5-point monocular visual odometry (VO) problem using a tightly-coupled implicit iterative extended Kalman filter (IEKF) without introducing additional states; and
- A new point-to-plane iterative closest point (ICP) algorithm suitable for triangulation-based 3D cameras solved in a tightly coupled implicit IEKF framework.
1.1. System Design
1.2. Choice of Sensors
1.3. Methods for Localization and Mapping
2. The Scannect Mobile Mapping System
2.1. Proposed System Design
Designed Robot Behavior
- Stage 1: The robot enters an unfamiliar environment without prior knowledge about the map or its current position.
- ○
- The absolute position may never be known, but an absolute orientation based on the Earth’s gravity and magnetic fields is determinable.
- ○
- The system should “look” in every direction to its maximum range possible before moving around to establish a map at this arbitrary origin.
- Stage 2: Due to occlusions and limited perceptible range, the robot needs to move and explore the area concurrently.
- ○
- When exploring new areas the map should be expanded while maintaining the localization solution based on the initial map.
- Stage 3: Occasionally when more detail is desired or the pose estimation is uncertain, the system can stop and look around again.
- ○
- As the system is for autonomous robots with no assumptions about existing localization infrastructure (e.g., LED position systems), every movement based on the dead-reckoning principle will increase the position uncertainty. Typically it is more accurate to create a map using long-range static remote sensing techniques because they are typically less than the dead-reckoning errors.
- ○
- Looking forward and backward over long ranges from the same position can possibly introduce loop-closure.
- ○
- One of the Kinects and the IMU are rigidly mounted together and force centered on the mobile platform. Through a robotic arm, quadcopter or by other means the Kinect and IMU can be dismounted from the platform during “stop” mode for mapping, making it more flexible/portable for occlusion filling. Afterwards it can return and dock at the same position and orientation and normal operations is resumed.
2.2. Proposed Choice of Sensors
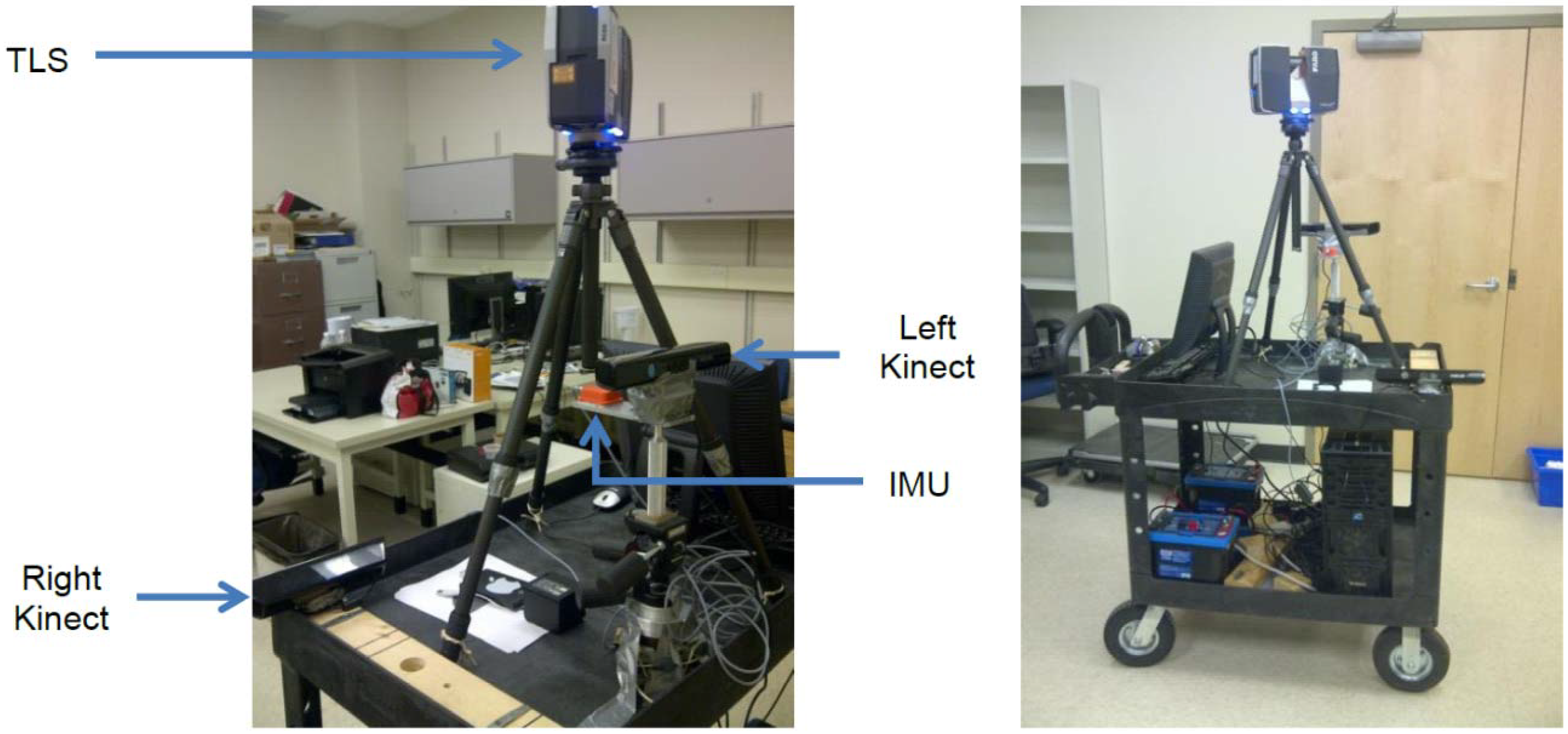
System Calibration
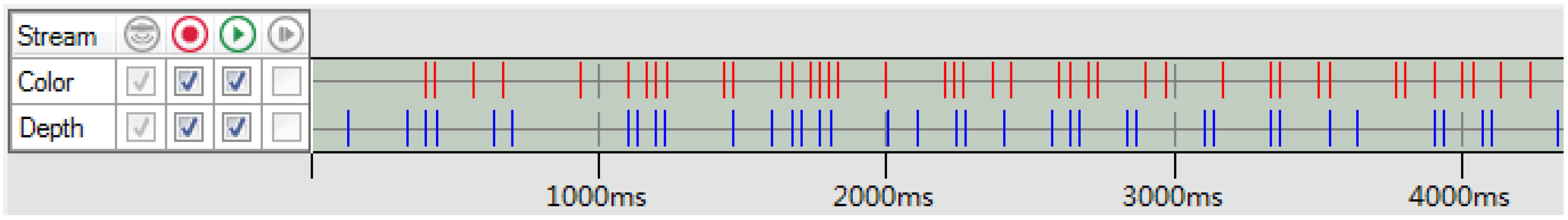
Microsoft Kinect RGB-D Camera Calibration
FARO Focus3D S 120 3D Terrestrial Laser Scanner Calibration
Boresight and Leverarm Calibration between the Kinect and Laser Scanner
Boresight and Leverarm Calibration between the Kinect and IMU

 is the observation vector for point i expressed in the RGB image space at time t;
is the observation vector for point i expressed in the RGB image space at time t;  is the scale factor for point i at time t (which can be eliminated by dividing the image measurements model by the principal distance model [20]);
is the scale factor for point i at time t (which can be eliminated by dividing the image measurements model by the principal distance model [20]);  is the relative rotation between the IR and RGB cameras;
is the relative rotation between the IR and RGB cameras;  is the relative rotation between the IMU sensor and IR camera;
is the relative rotation between the IMU sensor and IR camera;  is the orientation of the IMU sensor relative to the navigation frame at time t;
is the orientation of the IMU sensor relative to the navigation frame at time t;  is the relative rotation between the world frame defined by the checkerboard and the navigation frame;
is the relative rotation between the world frame defined by the checkerboard and the navigation frame;  is the 3D coordinates of point i in the world frame; Tn (t) is the position of the IR camera in the navigation frame at time t; Δbs is the leverarm between the IMU sensor and IR camera; ΔbIR is the relative translation between the IR and RGB cameras.
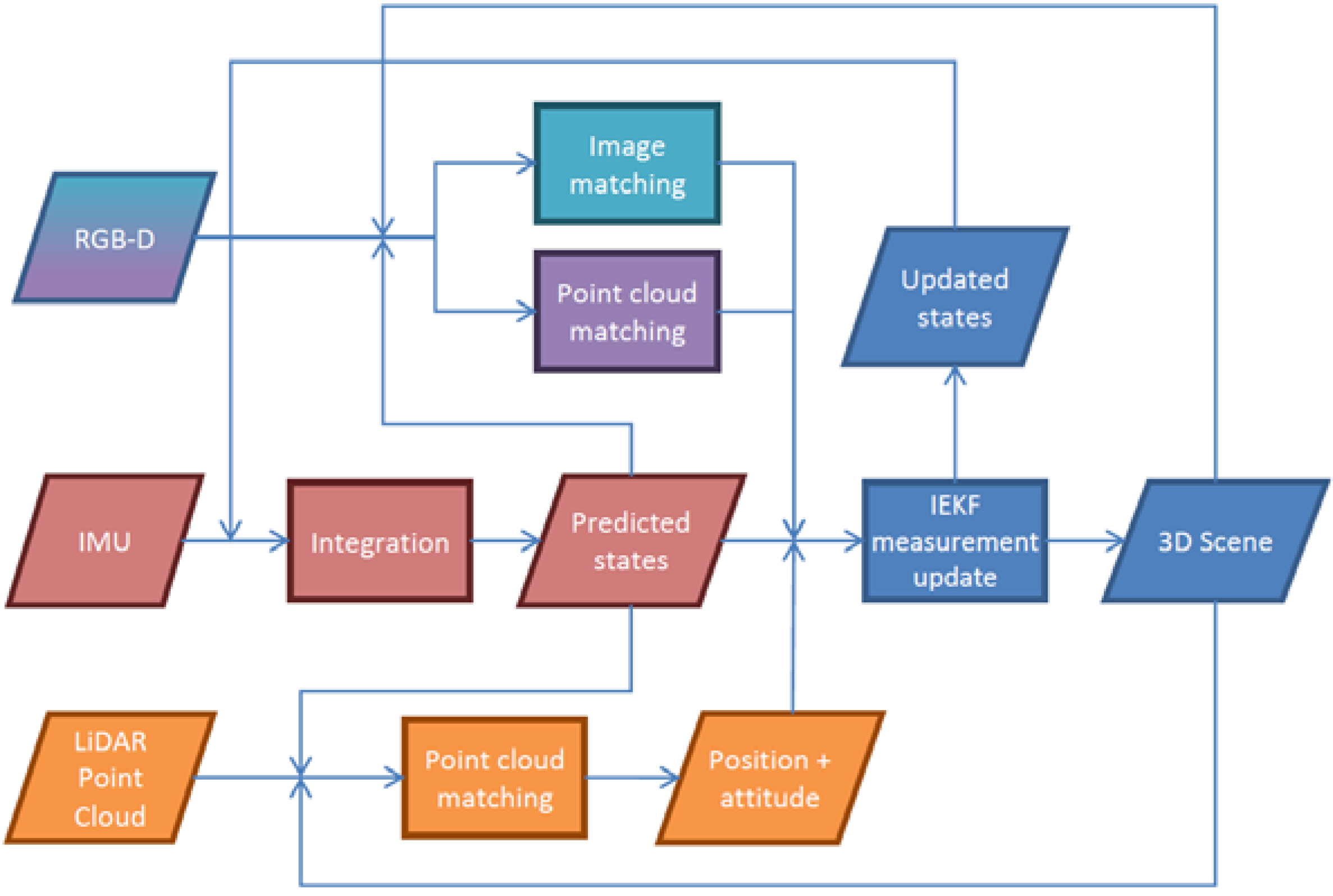
is the 3D coordinates of point i in the world frame; Tn (t) is the position of the IR camera in the navigation frame at time t; Δbs is the leverarm between the IMU sensor and IR camera; ΔbIR is the relative translation between the IR and RGB cameras.2.3. Proposed Methods for Localization and Mapping



 are the accelerometer and gyroscope measurements at time t, respectively; εa (t) and εω (t) are their corresponding measurement noises;
are the accelerometer and gyroscope measurements at time t, respectively; εa (t) and εω (t) are their corresponding measurement noises;  is the rotation rate of the earth as seen in the navigation frame; gn is the local gravity in the navigation frame; qs→n the rotation from IMU sensor frame to navigation frame expressed using quaternions; δa (t) and δω (t) are the slowly time-varying accelerometer and gyroscope biases, respectively, which are modelled as a first order Gauss-Markov process; ηa (t) and ηω (t) are the corresponding Gauss-Markov process driving noises; and Δt is the time interval between the current and previous measurement.
is the rotation rate of the earth as seen in the navigation frame; gn is the local gravity in the navigation frame; qs→n the rotation from IMU sensor frame to navigation frame expressed using quaternions; δa (t) and δω (t) are the slowly time-varying accelerometer and gyroscope biases, respectively, which are modelled as a first order Gauss-Markov process; ηa (t) and ηω (t) are the corresponding Gauss-Markov process driving noises; and Δt is the time interval between the current and previous measurement.2.3.1. Tightly-Coupled Implicit Iterative Extended Kalman Filter
2.3.2. Dense 3D Point Cloud Matching for the Kinect
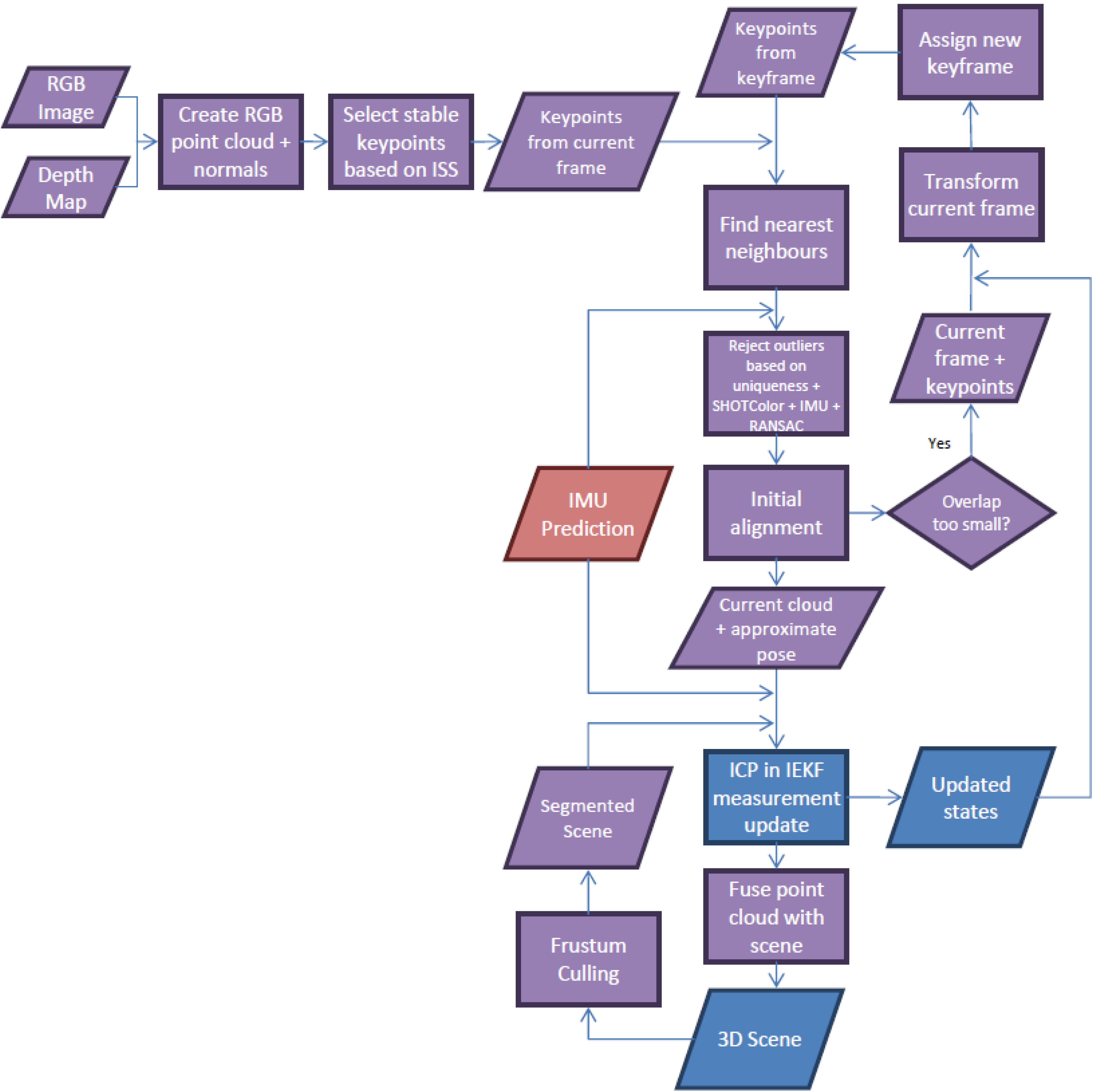
Sampling
Searching
Cost Function
 is derived by backprojecting the 3D points into the projector’s image space using its extrinsic and intrinsic parameters [65]. The inherent scale ambiguity for both the IR camera (
is derived by backprojecting the 3D points into the projector’s image space using its extrinsic and intrinsic parameters [65]. The inherent scale ambiguity for both the IR camera (  ) and the projector (
) and the projector (  ), which are traditionally eliminated from the model by dividing the first and second components by the third component of Equations (7) and (8) in parametric form [20], are solved through spatial intersection with the point-to-plane constraint (realized by substituting Equations (7) and (8) into Equation (9), respectively). The depth camera measurement update model implemented in the proposed KF framework is then obtained by equating Equations (7) and (8). It is worth noting that the functional relationship between the observations (i.e., image coordinate measures for the IR camera and projector) and unknown states (i.e., the pose) are implicitly defined. The math model presented here minimizes the reprojection errors of the Kinect’s IR camera and projector pair implicitly to reduce the orthogonal distance of every point in the source point cloud relative to the target point cloud.
), which are traditionally eliminated from the model by dividing the first and second components by the third component of Equations (7) and (8) in parametric form [20], are solved through spatial intersection with the point-to-plane constraint (realized by substituting Equations (7) and (8) into Equation (9), respectively). The depth camera measurement update model implemented in the proposed KF framework is then obtained by equating Equations (7) and (8). It is worth noting that the functional relationship between the observations (i.e., image coordinate measures for the IR camera and projector) and unknown states (i.e., the pose) are implicitly defined. The math model presented here minimizes the reprojection errors of the Kinect’s IR camera and projector pair implicitly to reduce the orthogonal distance of every point in the source point cloud relative to the target point cloud.


 is the relative rotation from the IR camera of Kinect k to the IR camera of the reference Kinect;
is the relative rotation from the IR camera of Kinect k to the IR camera of the reference Kinect;  (t) and
(t) and  (t) are the scale factors for point i observed by the IR camera and projector of Kinect k at time t, respectively;
(t) are the scale factors for point i observed by the IR camera and projector of Kinect k at time t, respectively;  and
and  are the image measurement vectors of point i observed by the IR camera and projector of Kinect k at time t, respectively;
are the image measurement vectors of point i observed by the IR camera and projector of Kinect k at time t, respectively;  is the relative rotation between the IR camera and projector of Kinect k; Δbk is the relative translation between the IR camera of Kinect k and the reference Kinect; Δck is the relative translation between the IR camera and projector of Kinect k; ai, bi, ci, and di are the best-fit plane parameters of point i in the navigation frame.
is the relative rotation between the IR camera and projector of Kinect k; Δbk is the relative translation between the IR camera of Kinect k and the reference Kinect; Δck is the relative translation between the IR camera and projector of Kinect k; ai, bi, ci, and di are the best-fit plane parameters of point i in the navigation frame.Outlier Rejection
Rejection When Estimating Correspondences
Rejection Using RANSAC
Rejection in the Kalman Filtering
Weighting
Initial Alignment
Loop-Closure
2.3.3. RGB Visual Odometry
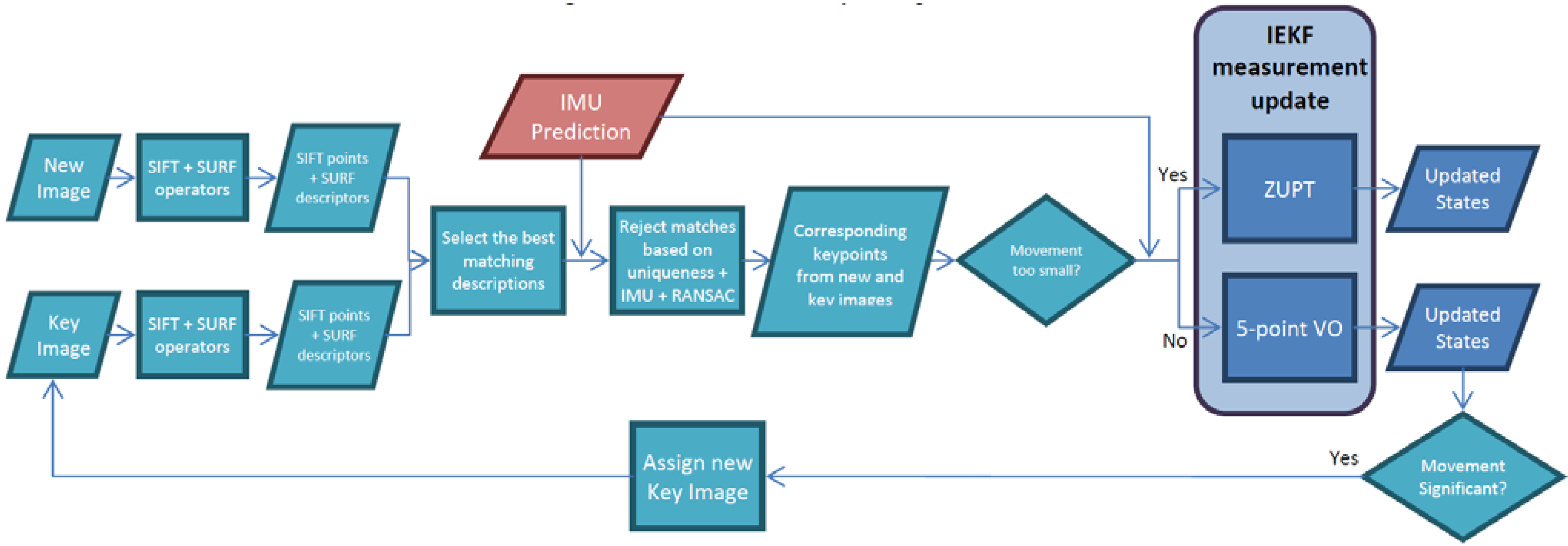

 is the relative rotation between the RGB and IR camera of Kinect k; Δdk is the relative translation between the RGB and IR camera of Kinect k.
is the relative rotation between the RGB and IR camera of Kinect k; Δdk is the relative translation between the RGB and IR camera of Kinect k.3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Boresight and Leverarm Calibration between the Kinect and Laser Scanner
3.2. Boresight and Leverarm Calibration between the Kinect and IMU
| Before Calibration | After Calibration | Improvements | |
|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE x | 29.1 pix | 0.8 pix | 97% |
| RMSE y | 23.1 pix | 1.1 pix | 95% |
3.3. Point-to-Plane ICP for the Kinect


3.4. 2D-to-2D Visual Odometry for Monocular Vision

3.5. Scannect Testing at the University of Calgary

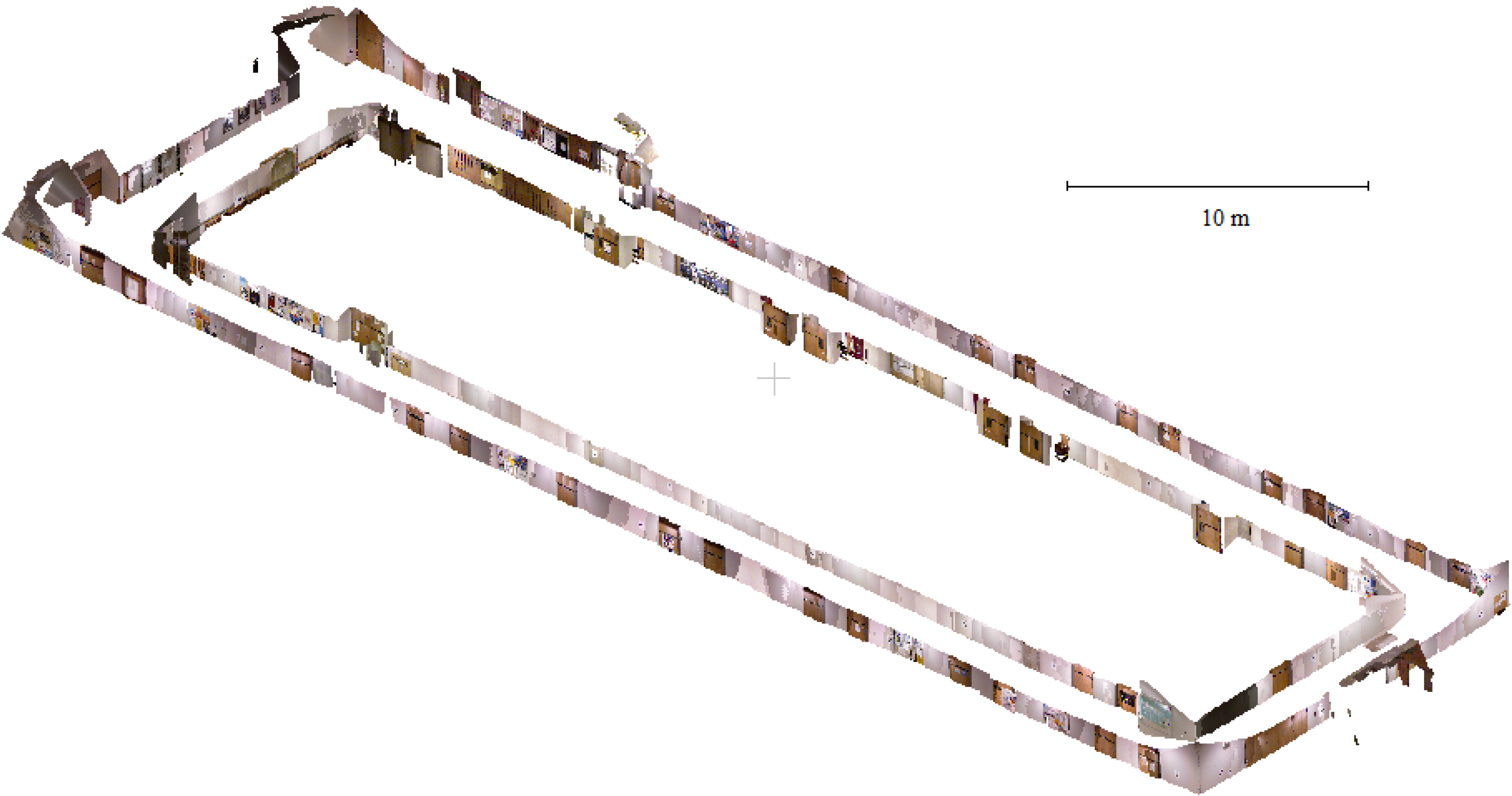
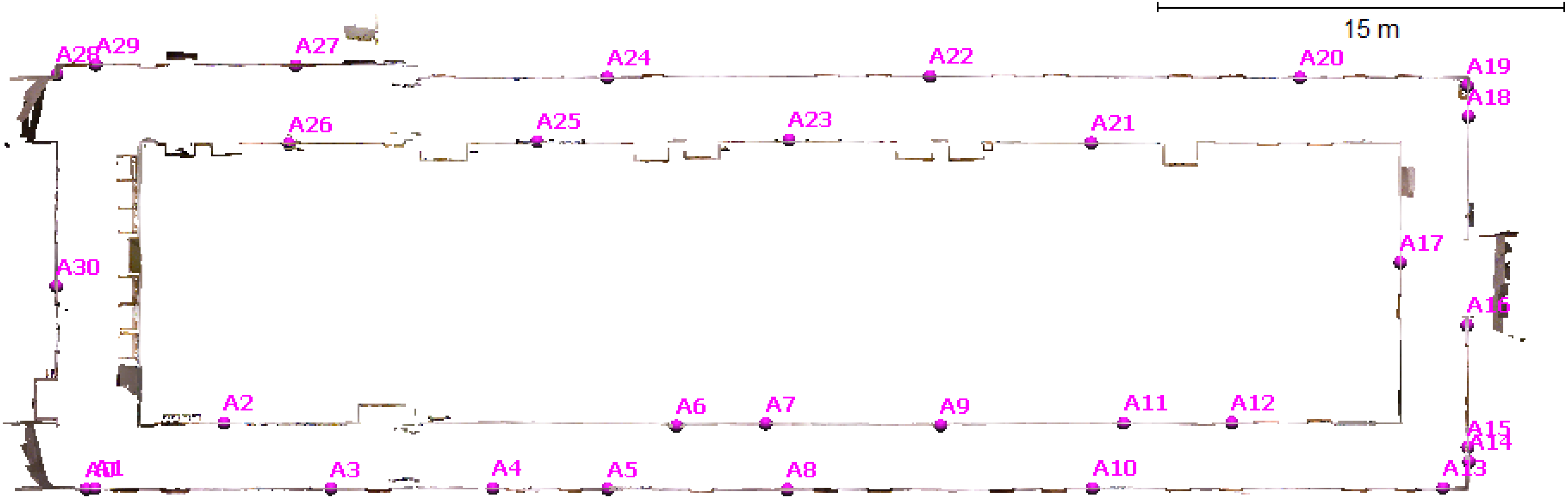
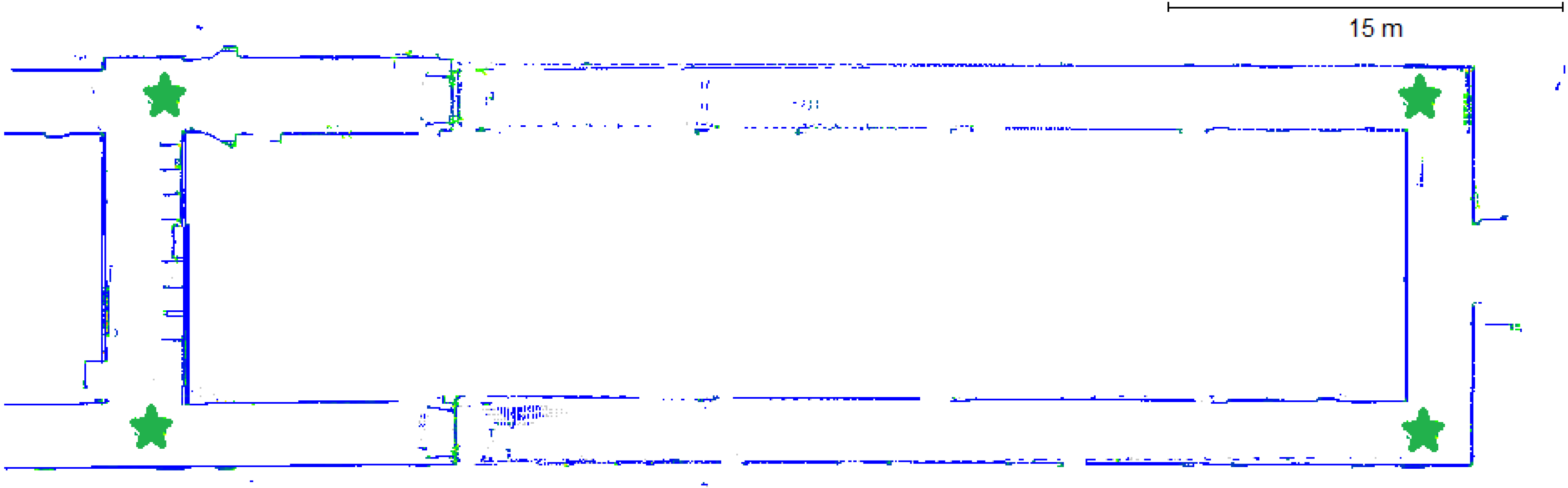
4. Conclusions and Future Work
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gadeke, T.; Schmid, J.; Zahnlecker, M.; Stork, W.; Muller-Glaser, K. Smartphone pedestrian navigation by foot-IMU sensor fusion. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Ubiquitous Positioning, Indoor Navigation, and Location Based Service, Helsinki, Finland, 3–4 October 2012; pp. 1–8.
- Durrant-Whyte, H.; Bailey, T. Simultaneous localization and mapping: Part I. IEEE Robot. Autom. Mag. 2006, 13, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, T.; Durrant-Whyte, H. Simultaneous localisation and mapping (SLAM): Part II state of the art. IEEE Robot. Autom. Mag. 2006, 13, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, A.; Bachrach, A.; Henry, P.; Krainin, M.; Maturana, D.; Fox, D.; Roy, N. Visual odometry and mapping for autonomous flight using an RGB-D camera. In Proceedings of the 15th International Symposium on Robotics Research, Flagstaff, AZ, USA, 28 August–1 September 2011.
- He, B.; Yang, K.; Zhao, S.; Wang, Y. Underwater simultaneous localization and mapping based on EKF and point features. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Mechatronics and Automation, Changchun, China, 9–12 August 2009; pp. 4845–4850.
- Kuo, B.; Chang, H.; Chen, Y.; Huang, S. A light-and-fast SLAM algorithm for robots in indoor environments using line segment map. J. Robot. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, P.; Cole, D.; Ho, K. Outdoor SLAM using visual appearance and laser ranging. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Orlando, FL, USA, 15–19 May 2006; pp. 1180–1187.
- Georgiev, A.; Allen, P. Localization methods for a mobile robot in urban environments. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2004, 20, 851–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kümmerle, R.; Steder, B.; Dornhege, C.; Kleiner, A.; Grisetti, G.; Burgard, W. Large scale graph-based SLAM using aerial images as prior information. J. Auton. Robots 2011, 30, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vosselman, G.; Maas, H.-G. Airborne and Terrestrial Laser Scanning; Whittles Publishing: Caithness, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Nüchter, A. Parallelization of scan matching for robotic 3D mapping. In Proceedings of the 3rd European Conference on Mobile Robots, Freiburg, Germany, 19–21 September 2007.
- Lin, Y.; Hyyppä, J.; Kukko, A. Stop-and-go mode: Sensor manipulation as essential as sensor development in terrestrial laser scanning. Sensors 2013, 13, 8140–8154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferris, B.; Fox, D.; Lawrence, N. WiFi-SLAM using Gaussian process latent variable models. In Proceedings of the 20th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Hyderabad, India, 6–12 January 2007; pp. 2480–2485.
- Des Bouvrie, B. Improving rgbd indoor mapping with imu data. Master’s Thesis, Delft University of Technology, Delft, The Netherlands, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Strasdat, H.; Montiel, J.; Davison, A. Real-time monocular SLAM: Why filter? In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Anchorage, AK, 3–7 May 2010; pp. 2657–2664.
- Tomono, M. Robust 3D SLAM with a stereo camera based on an edge-point ICP algorithm. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Kobe, Japan, 12–17 May 2009; pp. 4306–4311.
- Borrmann, D.; Elseberg, J.; Lingemann, K.; Nüchter, A.; Hertzberg, J. Globally consistent 3D mapping with scan matching. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2008, 56, 130–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, S.; Fuchs, S.; Droeschel, D.; Holz, D.; Nüchter, A. Robust 3D-mapping with time-of-flight cameras. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, St. Louis, MO, USA, 10–15 October 2009; pp. 1673–1678.
- Siegwart, R.; Nourbakhsh, I.; Scaramuzza, D. Introduction to Autonomous Mobile Robots, 2nd ed.; The MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Luhmann, T.; Robson, S.; Kyle, S.; Harley, I. Close Range Photogrammetry: Principles, Techniques and Applications; Whittles Publishing: Caithness, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, R.; Zhang, Y. A review of optical imagery and airborne LiDAR data registration methods. Open Remote Sens. J. 2012, 5, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurz, T.; Buckley, S.; Schneider, D.; Sima, A.; Howell, J. Ground-based hyperspectral and lidar scanning: A complementary method for geoscience research. In Proceedings of the International Association for Mathematical Geosciences, Salzburg, Austria, 5–9 September 2011.
- Han, J.; Shao, L.; Xu, D.; Shotton, J. Enhanced computer vision with Microsoft Kinect sensor: A review. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2013, 43, 1318–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zug, S.; Penzlin, F.; Dietrich, A.; Nguyen, T.; Albert, S. Are laser scanners replaceable by Kinect sensors in robotic applications? In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Robotic and Sensors Environments (ROSE), Magdeburg, Germany, 16–18 November 2012; pp. 144–149.
- Meister, S.; Kohli, P.; Izadi, S.; Hämmerle, M.; Rother, C.; Kondermann, D. When can we use KinectFusion for ground truth acquisition? In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Workshop on Color-Depth Camera Fusion in Robotics, Vilamoura, Algarve, Portugal, 7–11 October 2012.
- Smisek, J.; Jancosek, M.; Pajdla, T. 3D with kinect. In Proceedings of the Consumer Depth Cameras for Computer Vision, Barcelona, Spain, 12 November 2011.
- Stoyanov, T.; Louloudi, A.; Andreasson, H.; Lilienthal, A. Comparative evaluation of range sensor accuracy for indoor environments. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Mobile Robots, Örebro, Sweden, 7–9 September 2011; pp. 19–24.
- Chow, J.; Ang, K.; Lichti, D.; Teskey, W. Performance analysis of a low-cost triangulation-based 3D camera: Microsoft Kinect system. In Proceedings of the International Society of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing Congress, Melbourne, Australia, 25 August–1 September 2012.
- Renaudin, V.; Yalak, O.; Tomé, P.; Merminod, B. Indoor navigation of emergency agents. Eur. J. Navig. 2007, 5, 36–45. [Google Scholar]
- Ghilani, C.; Wolf, P. Elementary Surveying: An Introduction to Geomatics, 12th ed.; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Grisetti, G.; Stachniss, C.; Burgard, W. Improving grid-based SLAM with with Rao-Blackwellized particle filters by adaptive proposals and selective resampling. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Barcelona, Spain, 18–22 April 2005; pp. 2432–2437.
- Gustafsson, F. Statistical Sensor Fusion, 2nd ed.; Studentlitteratur AB: Lund, Sweden, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Scaramuzza, D.; Fraundorfer, F. Visual odometry part I: The first 30 years and fundamentals. IEEE Robot. Autom. Mag. 2011, 18, 80–92. [Google Scholar]
- Besl, P.; McKay, N. A method for registration of 3D shapes. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1992, 14, 239–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn, B. Closed-form solution of absolute orientation using unit quaternions. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 1987, 4, 629–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Medioni, G. Object modelling by registration of multiple range images. Image Vis. Comput. 1992, 10, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusinkiewicz, S.; Levoy, M. Efficient variants of the ICP algorithm. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on 3-D Digital Imagining and Modeling, Quebec, QC, Canada, 28 May–1 June 2001; pp. 145–152.
- Klein, G.; Murray, D. Parallel tracking and mapping for small AR workspaces. In Proceedings of the 6th IEEE and ACM International Symposium on Mixed and Augmented Reality, Nara, Japan, 13–16 November 2007; pp. 225–234.
- Nützi, G.; Weiss, S.; Scaramuzza, D.; Siegwart, R. Fusion of IMU and vision for absolute scale estimation in monocular SLAM. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 2011, 61, 287–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherer, S.; Dube, D.; Zell, A. Using depth in visual simultanesous localisation and mapping. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, St. Paul, MN, USA, 14–18 May 2012.
- Henry, P.; Krainin, M.; Herbst, E.; Ren, X.; Fox, D. RGB-D mapping: Using Kinect-style depth cameras for dense 3D modeling of indoor environments. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2012, 31, 647–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, P.; Krainin, M.; Herbst, E.; Ren, X.; Fox, D. RGB-D mapping: Using depth cameras for dense 3d modeling of indoor environments. In Proceedings of the RGB-D: Advanced Reasoning with Depth Cameras in Conjunction with Robotics Science and Systems, Zaragoza, Spain, 27 June 2010.
- Johnson, A.; Kang, S. Registration and integration of textured 3D data. Image Vis. Comput. 1999, 17, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izadi, S.; Kim, D.; Hilliges, O.; Molyneaux, D.; Newcombe, R.; Kohli, P.; Shotton, J.; Hodges, S.; Freeman, D.; Davison, A.; et al. KinectFusion: Real-time 3D reconstruction and interaction using a moving depth camera. In Proceedings of the 24th ACM Symposium on User Interface Software and Technology, Santa Barbara, CA, USA, 16–19 October 2011; pp. 559–568.
- Curless, B.; Levoy, M. A volumetric method for building complex odels from range images. In Proceedings of the 23rd Annual Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques—SIGGRAPH, New York, NY, USA, 4–9 August 1996; pp. 303–312.
- Whelan, T.; McDonald, J.; Kaess, M.; Fallon, M.; Johannsson, H.; Leonard, J. Kintinuous: Spatially extended KinectFusion. In Proceedings of the 3rd RSS Workshop on RGB-D: Advanced Reasoning with Depth Cameras, Sydney, Australia, 9–10 July 2012.
- Whelan, T.; Johannsson, H.; Kaess, M.; Leonard, J.; McDonald, J. Robust real-time visual odometry for dense RGB-D mapping. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Karlsruhe, Germany, 6–10 May 2013; pp. 5724–5731.
- Whelan, T.; Kaess, M.; Leonard, J.; McDonald, J. Deformation-based loop closure for large scale dense RGB-D SLAM. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Tokyo, Japan, 3–8 November 2013.
- Keller, M.; Lefloch, D.; Lambers, M.; Izadi, S.; Weyrich, T.; Kolb, A. Real-time 3D reconstruction in dynamic scenes using point-based fusion. In Proceedings of the International Conference on 3D Vision, Seattle, WA, USA, 29 June–1 July 2013; pp. 1–8.
- Khoshelham, K.; Dos Santos, D.; Vosselman, G. Generation and weighting of 3D point correspondences for improved registration of RGB-D data. In Proceedings of the ISPRS Annals of the Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, Antalya, Turkey, 11–13 November 2013; Volume II-5/W2.
- Leutenegger, S.; Furgale, P.; Rabaud, V.; Chli, M.; Konolige, K.; Siegwart, R. Keyframe-based visual-inertial SLAM using nonlinear optimization. In Proceedings of the Robotics: Science and Systems, Berlin, Germany, 24–28 June 2013.
- Li, L.; Cheng, E.; Burnett, I. An iterated extended Kalman filter for 3D mapping via Kinect camera. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Vancouver, Canada, 26–31 May 2013; pp. 1773–1777.
- Aghili, F.; Kuryllo, M.; Okouneva, G.; McTavish, D. Robust pose estimation of moving objects using laser camera data for autonomous rendezvous and docking. In Proceedings of the International Society of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing Archives, Paris, France, 1–3 September 2009; Volume XXXVIII-3/W8, pp. 253–258.
- Hervier, T.; Bonnabel, S.; Goulette, F. Accurate 3D maps from depth images and motion sensors via nonlinear Kalman filtering. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Vilamoura, Portugal, 7–12 October 2012; pp. 5291–5297.
- Kottas, D.; Roumeliotis, S. Exploiting urban scenes for vision-aided inertial navigation. In Proceedings of the Robotics: Science and Systems, Berlin, Germany, 24–28 June 2013.
- Li, M.; Kim, B.; Mourikis, A. Real-time motion tracking on a cellphone using inertial sensing and a rolling shutter camera. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Karlsruhe, Germany, 6–10 May 2013.
- Burens, A.; Grussenmeyer, P.; Guillemin, S.; Carozza, L.; Lévêque, F.; Mathé, V. Methodological developments in 3D scanning and modelling of archaeological French heritage site: The bronze age painted cave of Les Fraux, Dordogne (France). In Proceedings of the International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, Strasbourg, France, 2–6 September 2013; Volume XL-5/W2, pp. 131–135.
- Chiabrando, F.; Spanò, A. Point clouds generation using TLS and dense-matching techniques. A test on approachable accuracies of different tools. In Proceedings of the ISPRS Annals of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, Strasbourg, France, 2–6 September 2013; Volume II-5/W1, pp. 67–72.
- Khoshelham, K.; Oude Elberink, S. Accuracy and resolution of kinect depth data for indoor mapping applications. Sensors 2012, 12, 1437–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dal Mutto, C.; Zanuttigh, P.; Cortelazzo, G. Time-of-Flight Cameras and Microsoft Kinect; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Kainz, B.; Hauswiesner, S.; Reitmayr, G.; Steinberger, M.; Grasset, R.; Gruber, L.; Veas, E.; Kalkofen, D.; Seichter, H.; Schmalstieg, D. OmniKinect: Real-time dense volumetric data acquisition and applications. In Proceedings of the 18th ACM Symposium on Virtual Reality Software and Technology, Toronto, ON, Canada, 10–12 December 2012; pp. 25–32.
- Butler, A.; Izadi, S.; Hilliges, O.; Molyneaux, D.; Hodges, S.; Kim, D. Shake and sense: Reducing interference for overlapping structured light depth cameras. In Proceedings of the SIGCHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Austin, TX, USA, 5–10 May 2012; pp. 1933–1936.
- Aggarwal, P.; Syed, Z.; Noureldin, A.; El-Sheimy, N. MEMS-Based Integrated Navigation; Artech House: Norwood, MA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Herrera, D.; Kannala, J.; Heikkilä, J. Joint depth and color camera calibration with distortion correction. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2012, 34, 2058–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, J.; Lichti, D. Photogrammetric bundle adjustment with self-calibration of the PrimeSense 3D camera technology: Microsoft Kinect. IEEE Access 2013, 1, 465–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichti, D. Error modelling, calibration and analysis of an AM-CW terrestrial laser scanner system. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2007, 61, 307–324. [Google Scholar]
- Reshetyuk, Y. A unified approach to self-calibration of terrestrial laser scanners. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2010, 65, 445–456. [Google Scholar]
- Chow, J.; Lichti, D.; Glennie, C.; Hartzell, P. Improvements to and comparison of static terrestrial LiDAR self-calibration methods. Sensors 2013, 13, 7224–7249. [Google Scholar]
- Chow, J.; Lichti, D.; Teskey, W. Accuracy assessment of the Faro Focus3D and Leica HDS6100 panoramic type terrestrial laser scanner through point-based and plane-based user self-calibration. In Proceedings of the FIG Working Week 2012: Knowing to Manage the Territory, Protect the Environment, Evaluate the Cultural Heritage, Rome, Italy, 6–10 May 2012.
- Al-Manasir, K.; Fraser, C. Registration of terrestrial laser scanner data using imagery. Photogramm. Rec. 2006, 21, 255–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobo, J.; Dias, J. Relative pose calibration vetween visual and inertial sensors. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2007, 26, 561–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hol, J.; Schön, T.; Gustafsson, F. Modeling and calibration of inertial and vision sensors. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2009, 29, 231–244. [Google Scholar]
- Mirzaei, F.; Roumeliotis, S. A Kalman filter-based algorithm for IMU-camera calibration: Observability analysis and performance evaluation. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2008, 24, 1143–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titterton, D.; Weston, J. Strapdown Inertial Navigation Technology; IEE Radar, Sonar, Navigation and Avionics Series; Peter Peregrinus Ltd.: Stevenage, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Gelb, A. Applied Optimal Estimation; The MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Steffen, R.; Beder, C. Recursive estimation with implicit constraints. In Proceedings of the 29th DAGM Conference on Pattern Recognition, Heidelberg, Germany, 12–14 September 2007; pp. 194–203.
- Steffen, R. A robust iterative Kalman filter based on implicit measurement equations. Photogramm. Fernerkund. Geoinf. 2013, 2013, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OpenNI Programmer’s Guide. OpenNI 2.0 API. Available online: http://www.openni.org/openni-programmers-guide/ (accessed on 16 December 2013).
- Muja, M.; Lowe, D. Fast approximate nearest neighbors with automatic algorithm configuration. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications (VISAPP’09), Lisboa, Portugal, 5–9 February 2009; pp. 331–340.
- Luck, J.; Little, C.; Hoff, W. Registration of range data using a hybrid simulated annealing and iterative closest point algorithm. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, San Francisco, CA, USA, 24–28 April 2000; pp. 3739–3733.
- Bradski, G.; Kaehler, A. Learning OpenCV; O’Reilly Media: Sabastopol, CA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, Y. Intrinsic shape signatures: A shape descriptor for 3D object recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE 12th International Conference on Computer Vision, Kyoto, Japan, 29 September–2 October 2009; pp. 689–696.
- Filipe, S.; Alexandre, L. A comparative Evaluation of 3D keypoint detectors. In Proceedings of the 9th Conference on Telecommunications, Castelo Branco, Portugal, 8–10 May 2013; pp. 145–148.
- Tombari, F.; Salti, S.; Di Stefano, L. A combined texture-shape descriptor for enhanced 3D feature matching. In Proceedings of the 18th IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Brussels, Belgium, 11–14 September 2011; pp. 809–812.
- Fraundorfer, F.; Scaramuzza, D. Visual odometry part II: Matching, robustness, optimization, and applications. IEEE Robot. Autom. Mag. 2012, 19, 78–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chow, J.; Ebeling, A.; Teskey, W. Point-based and plane-based deformation monitoring of indoor environments using terrestrial laser scanners. J. Appl. Geod. 2012, 6, 193–202. [Google Scholar]
- Pfister, H.; Zwicker, M.; van Baar, J.; Gross, M. Surfels: Surface elements as rendering primitives. In Proceedings of the 27th Annual Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques, New Orleans, LA, USA, 23–28 July 2000; pp. 335–342.
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Chow, J.C.K.; Lichti, D.D.; Hol, J.D.; Bellusci, G.; Luinge, H. IMU and Multiple RGB-D Camera Fusion for Assisting Indoor Stop-and-Go 3D Terrestrial Laser Scanning. Robotics 2014, 3, 247-280. https://doi.org/10.3390/robotics3030247
Chow JCK, Lichti DD, Hol JD, Bellusci G, Luinge H. IMU and Multiple RGB-D Camera Fusion for Assisting Indoor Stop-and-Go 3D Terrestrial Laser Scanning. Robotics. 2014; 3(3):247-280. https://doi.org/10.3390/robotics3030247
Chicago/Turabian StyleChow, Jacky C.K., Derek D. Lichti, Jeroen D. Hol, Giovanni Bellusci, and Henk Luinge. 2014. "IMU and Multiple RGB-D Camera Fusion for Assisting Indoor Stop-and-Go 3D Terrestrial Laser Scanning" Robotics 3, no. 3: 247-280. https://doi.org/10.3390/robotics3030247
APA StyleChow, J. C. K., Lichti, D. D., Hol, J. D., Bellusci, G., & Luinge, H. (2014). IMU and Multiple RGB-D Camera Fusion for Assisting Indoor Stop-and-Go 3D Terrestrial Laser Scanning. Robotics, 3(3), 247-280. https://doi.org/10.3390/robotics3030247





