1. Introduction
The growing demand for disassembly operations in industrial environments has driven the development of advanced solutions aimed at increasing the efficiency and safety of these processes [
1]. Industrial robot automation has been a key strategy to improve productivity in repetitive and high-risk tasks, such as disassembling components in end-of-life products [
2]. However, programming such systems remains a major challenge. Conventional methods require laborious, task-specific programming for each job, which limits the system’s flexibility and its ability to adapt quickly to product changes [
3,
4]. Beyond the complexity of programming, achieving precision and safety in disassembly operations remains a significant challenge [
5]. Many disassembly processes require specialized, delicate handling to avoid damaging reusable components, which demands robotic systems with advanced environmental perception capabilities [
6,
7].
In this context, the presence of humans in disassembly processes is indispensable. Human intervention is required for decision-making in unplanned or non-routine situations, where variability in dismantled products hinders the application of fully automated strategies [
8]. However, integrating humans into these processes introduces new challenges. Performing repetitive and physically demanding tasks increases the human’s cognitive and physical load, which can affect their performance and well-being [
9,
10].
To address these challenges, human–robot interaction (HRI) has been proposed as a key strategy [
11]. The incorporation of collaborative robots (cobots) into the workflow enables human flexibility and decision-making capacity to be combined with the precision, speed, and safety offered by these robots, thereby optimizing and modernizing industrial processes [
12,
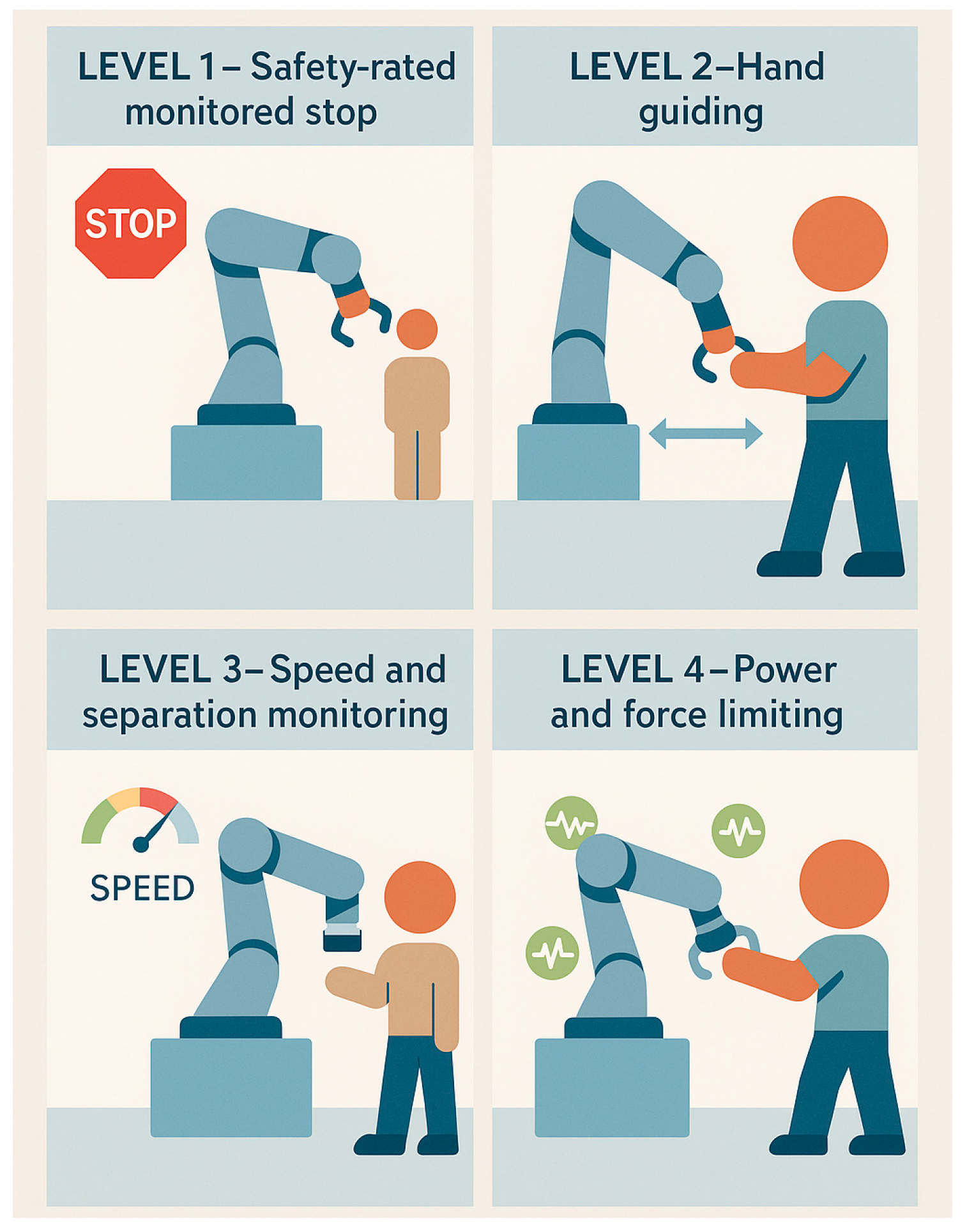
13]. According to the level of collaboration defined in ISO 10218-2:2025 [
14] and the risk assessment outlined in ISO/TS 15066:2016 [
15], robotic systems can operate in interaction modes ranging from coexistence to active collaboration in shared tasks, as shown in
Figure 1. In all cases, safety is a critical aspect, since removing physical barriers increases the risk of collisions [
16]. This necessitates the development and implementation of advanced real-time perception and adaptive control strategies that ensure a safe and efficient work environment [
17,
18].
One of the traditional solutions to safety challenges in human–robot collaboration is teleoperation, where operators control robot movements remotely [
19,
20]. However, this approach presents limitations such as the lack of haptic perception, control latency, and difficulties in operating within dynamic environments [
21,
22,
23]. Moreover, teleoperation requires an intuitive and efficient interface to minimize the impact of human error and facilitate the execution of complex tasks [
24]. In this regard, mixed reality (MR) has been explored as a promising tool to enhance HRI [
25,
26].
MR enables the real-time integration of visual information about the work environment, which improves decision-making and facilitates task execution. By using advanced interfaces integrated into head-mounted display (HMD) devices, operators can visualize the robot’s trajectory and receive disassembly instructions, allowing them to anticipate and prevent potential errors before they occur [
27,
28]. Furthermore, MR-based interfaces can incorporate multiple HRI modalities, such as voice commands, hand gestures, and eye tracking [
29]. These capabilities contribute to reducing the operator’s cognitive load and improve efficiency in performing collaborative tasks with robots [
30,
31]. However, in complex industrial environments, MR alone may not be sufficient to guarantee successful disassembly operations, as these tasks require superior precision and adaptability to respond to variations in components and working conditions [
32].
It is therefore essential that collaborative systems not only feature advanced interfaces but also have the ability to recognize and respond to the operator’s actions in real time [
33]. Integrating MR with deep learning algorithms enables precise detection and tracking of components and tools, optimizing collaboration and reducing the risk of errors in human–robot collaborative disassembly tasks [
34]. To further strengthen this capability, the integration of advanced cameras and sensors facilitates the real-time collection of environmental data, which can be processed using artificial intelligence (AI) to improve trajectory planning and the precision of component manipulation [
35].
Nevertheless, to further improve the system’s flexibility and adaptability, programming by demonstration has been proposed as a complementary approach [
36]. This technique allows robots to acquire new skills by observing the actions of a human operator, which significantly reduces the need for manual programming and facilitates deployment in dynamic industrial environments [
37]. In combination with computer vision and deep learning, programming by demonstration enables robots not only to accurately detect and follow objects but also to plan optimized trajectories based on human experience, thereby improving the efficiency and safety of human–robot interaction [
38].
In this context, this research proposes an HRI system based on mixed reality and multimodal control for disassembly operations in industrial environments. The system incorporates an HMD that allows operators to interact with the robot through voice commands, gestures, and eye tracking. In addition, the system integrates a deep learning module for component detection and tracking, which improves the precision and safety of the disassembly process. The goal is to demonstrate that the use of mixed reality in disassembly environments significantly improves operational efficiency, reduces the operator’s cognitive load, and increases safety in HRI.
This document is structured as follows:
Section 2 provides an analysis of the literature relevant to this research;
Section 3 describes the architecture of the proposed system;
Section 4 presents a practical case study along with a performance evaluation of the system;
Section 5 discusses the current advantages and limitations of the system, offering suggestions for improvement; and finally,
Section 6 concludes the paper and proposes new lines of research.
2. Related Work
Robotic disassembly has been widely studied in the context of industrial automation and the circular economy, particularly in recycling tasks. Several review studies have explored HRC solutions to optimize these processes by combining human flexibility with robotic precision.
2.1. Overview in Robotic Disassembly
In the specific domain of electric vehicle batteries, Kaarlela et al. [
39] identified critical challenges in standardization and operational efficiency. Complementary, Li et al. [
40] proposed AI-based approaches for dynamic planning and collaborative decision-making, while Beghi et al. [
41] analyzed automated and human–robot collaborative techniques to improve sustainability in lithium-ion battery recycling.
From a systemic perspective, Lee et al. [
42] emphasized the need for adaptive strategies for task allocation and sequencing in dynamic settings. Xiao and Huang [
43] expanded this approach using cyber-physical systems and digital twins, improving adaptability in human–robot interactions. In parallel, Hjorth and Chrysostomou [
44] stressed safety requirements and interface standardization, while Zang and Wang [
45] reviewed deep learning methods for sequence planning and robotic manipulation in disassembly of electrical devices.
In a recent study, Yuan et al. [
46] outlined emerging trends in HRI under the Industry 5.0 paradigm, highlighting the synergistic potential of digital twins, mixed reality, computer vision, and AI. However, they note the nascent implementation of these technologies in integrated multimodal systems.
Despite these advances, the integration of MR in robotic disassembly remains scarcely explored. Our review prioritizes works with models applicable to multimodal interaction, incorporating deep learning-based computer vision for component detection, along with key metrics of safety, precision, and user experience.
2.2. Extended Reality in Human–Robot Collaborative Disassembly
The development of advanced interfaces for HRI has become increasingly relevant in industrial disassembly, especially in processes that require greater flexibility, adaptability, and strict safety standards [
47]. In this context, various research efforts have leveraged extended reality (XR) to streamline these processes [
48]. XR encompasses virtual reality (VR), which fully immerses the user in a computer-generated environment; augmented reality (AR), which overlays virtual elements onto the real environment; and MR, which combines both to allow more seamless interaction between physical and digital elements [
49]. Recently, these technologies have been used alongside digital twins (DTs) and deep learning to improve simulation, decision-making, and detection of mechanical components [
50,
51].
Hoebert et al. [
52] describe a comprehensive framework that combines a digital twin and virtual reality to optimize collaborative disassembly of end-of-life electronic products by humans and robots. Using the Robot Operating System (ROS), the system models and synchronizes the disassembly cell in real time, allowing operators to validate trajectories in a digital twin developed in the well-known game engine Unity. To strengthen the identification of robot joints during the disassembly process, they incorporate the Fully Convolutional One-Stage (FCOS) detection model on RGB-D cameras, which more accurately localizes screws and calculates their orientation. It should be noted that VR does not provide direct real-time control over the robot but rather allows simulating and planning trajectories before execution. This strategy, in principle, promises benefits in safety and efficiency, since the operator can anticipate and correct potential collision risks or programming errors in a virtual environment. Even so, the article does not present quantitative results that empirically validate increased productivity or reduced accidents, leaving open the need for additional studies to corroborate its effectiveness.
Li et al. [
53] present a system that accelerates the disassembly of end-of-life electric vehicle batteries. Using a Microsoft HoloLens headset and a remote server, the system employs instance segmentation networks (Mask R-CNN) and Iterative Closest Point (ICP) to reconstruct the scene in 3D and display interactive instructions that guide the operator in real time. Their experiments, conducted with four groups of workers, show notable improvements: an average reduction of 13.9% in disassembly time for inexperienced personnel and 83.3% for expert personnel, along with a lower error rate by standardizing the disassembly sequence. Although the article mentions a trend toward automation supported by collaborative robotics, the described system itself does not integrate a collaborative robot; it focuses on guidance provided to the human via the HMD.
Duan et al. [
54] proposed a human–robot collaborative disassembly system that integrates MR and semantic scene perception to improve the efficiency and safety in disassembling electric vehicle batteries. Using a HoloLens 2 (HL2) headset, an RGB-D camera, and computer vision algorithms along with a robot digital twin, the system enables dynamic adaptation and real-time synchronization of the HRI. The experiments compared this system with the conventional method of predefined robot programming. Tests were conducted with 10 operators, for whom it is not specified whether they were skilled technicians or had no prior experience with the technology used. The results showed a 19% reduction in disassembly times, an increase in collaboration accuracy from 74% to 99%, and a decrease in collisions to less than 1%. Additionally, the authors indicate that the system helps reduce the operator’s cognitive load, although no quantifiable data were obtained to support this claim. The study presents some limitations, such as dependency on the capture quality of the RGB-D camera and the need to adjust system training for each environment or battery model.
Zhao et al. [
55] proposed a robotic teleoperation system that integrates MR and digital twins to improve safety and efficiency in the disassembly of end-of-life electric vehicle batteries. Using a KUKA LBR IIWA 14 R820 collaborative robot operated via an HL2, the system allows remote control through gestures and real-time visualization of the robot and critical data, such as torque graphs to detect anomalies during the task. Experiments were conducted with 20 participants, all of whom had robotics knowledge but no prior experience with the HL2. Three teleoperation methods were compared: control with a smartpad, AR without informative feedback, and AR enhanced with a digital twin, evaluating disassembly time and workload using the NASA Task Load Index (NASA-TLX). The results showed that the proposed system reduced disassembly time to 29.7 s, compared to 42.1 s with basic AR and 65.8 s with the smartpad, and significantly decreased perceived workload (38.24 NASA-TLX points versus 49.19 and 60.44 in the other methods). Although the system improves HRI and task efficiency, no data were obtained on disassembly accuracy or errors committed.
From the above literature, it is evident that the application of XR in industrial disassembly has shown benefits in efficiency, safety, and reduction in operator cognitive load. However, existing literature has mainly focused on trajectory planning and simulation, visual assistance, or teleoperation, while downplaying the integration of direct and dynamic real-time robot control. Furthermore, the lack of quantitative studies on the impact of these technologies on productivity and safety highlights the need for more in-depth research in this area.
This work addresses that gap by developing an MR system that enables real-time multimodal interaction between the operator and the cobot. Unlike previous approaches, our proposal integrates dynamic control through voice, gesture, and gaze tracking, combined with computer vision for precise component detection. This approach optimizes the execution of disassembly tasks, improving efficiency, reducing cognitive load, and increasing safety in collaborative manufacturing environments.
3. Methodology
We propose a human–robot collaborative disassembly system that employs MR and multimodal control of collaborative robots. The architecture of this system is detailed in
Section 3.1, describing the integration of hardware and software, as well as the publisher/subscriber-based communication.
Section 3.2 describes the methods used for component recognition and robotic action planning.
Section 3.3 focuses on the implementation of the MR interface and its role in HRI, while
Section 3.4 outlines the analytical computations that synchronize the real and digital worlds during the activity. Finally,
Section 3.5 addresses the management of communication and real-time task execution.
3.1. Overall System Architecture
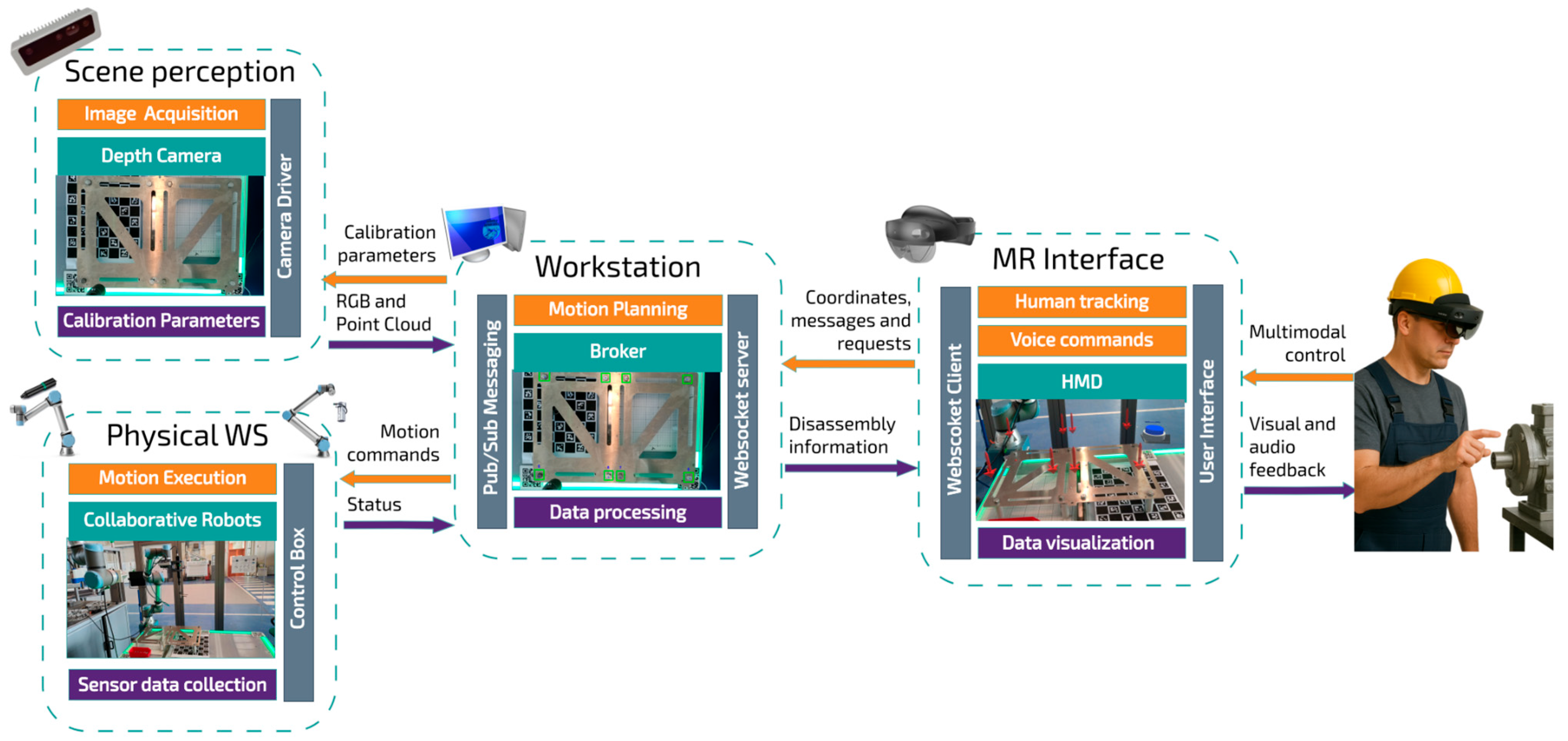
The proposed system integrates an MR interface with a collaborative robotic environment to optimize disassembly tasks in complex industrial environments. As shown in
Figure 2, the system architecture is composed of four main modules: environment perception, physical execution, workstation, and MR interface, which operate synchronously to ensure efficient and safe human–robot interaction.
The environment perception module is responsible for acquiring images of the various components to be disassembled. This information is collected using a calibrated depth camera capable of capturing both RGB images and point clouds in real time. The acquired data, along with calibration parameters, are transmitted to the workstation for processing and component identification.
The physical execution module is responsible for performing the disassembly of the components, guided by spatial information provided by the depth camera. In the human–robot collaborative disassembly, robotic manipulators equipped with specialized tools are used to adapt to various geometries and types of mechanical joints. Although such tasks can be executed through the collaboration between an operator and a single robot, in this work we opted for a dual architecture with two cobots to improve process efficiency and continuity. In this configuration, the first robot performs the extraction of the component, while the second handles its removal and transfer to a storage area located outside the reach of the first. This separation of functions is essential to avoid interference, keep the main work area clear, and ensure an uninterrupted and safe workflow. Status feedback is continuously provided from this module back to the workstation.
HRI is implemented through an MR module that allows the system to be controlled via hand gestures, voice, and eye gaze while projecting supporting digital information for the operator. To meet these requirements of intuitive interaction and visual assistance, an HMD is used that reconstructs the environment with passthrough technology to provide the user with a direct perception of the workspace, without latency or distortion. This is critical in industrial environments, where clarity and accuracy in viewing the physical environment are essential for manipulating digital information smoothly and safely.
Finally, the workstation serves as the operational core of the system’s architecture, as it centralizes data management, task planning, and the coordination of the various functional modules. This element acts as the central control system, enabling real-time communication between the different modules, such as the perception components, robotic execution, and mixed-reality interface. To ensure smooth and efficient interaction, a publish-subscribe broker architecture is used, allowing rapid, robust, and decoupled data transmission between processes, thereby facilitating system synchronization and scalability. Calibration data, spatial coordinates, operator commands, motion instructions, and status messages are managed and routed effectively through this central node.
3.2. Detection, Segmentation, and Pose Estimation of Target Components for Disassembly
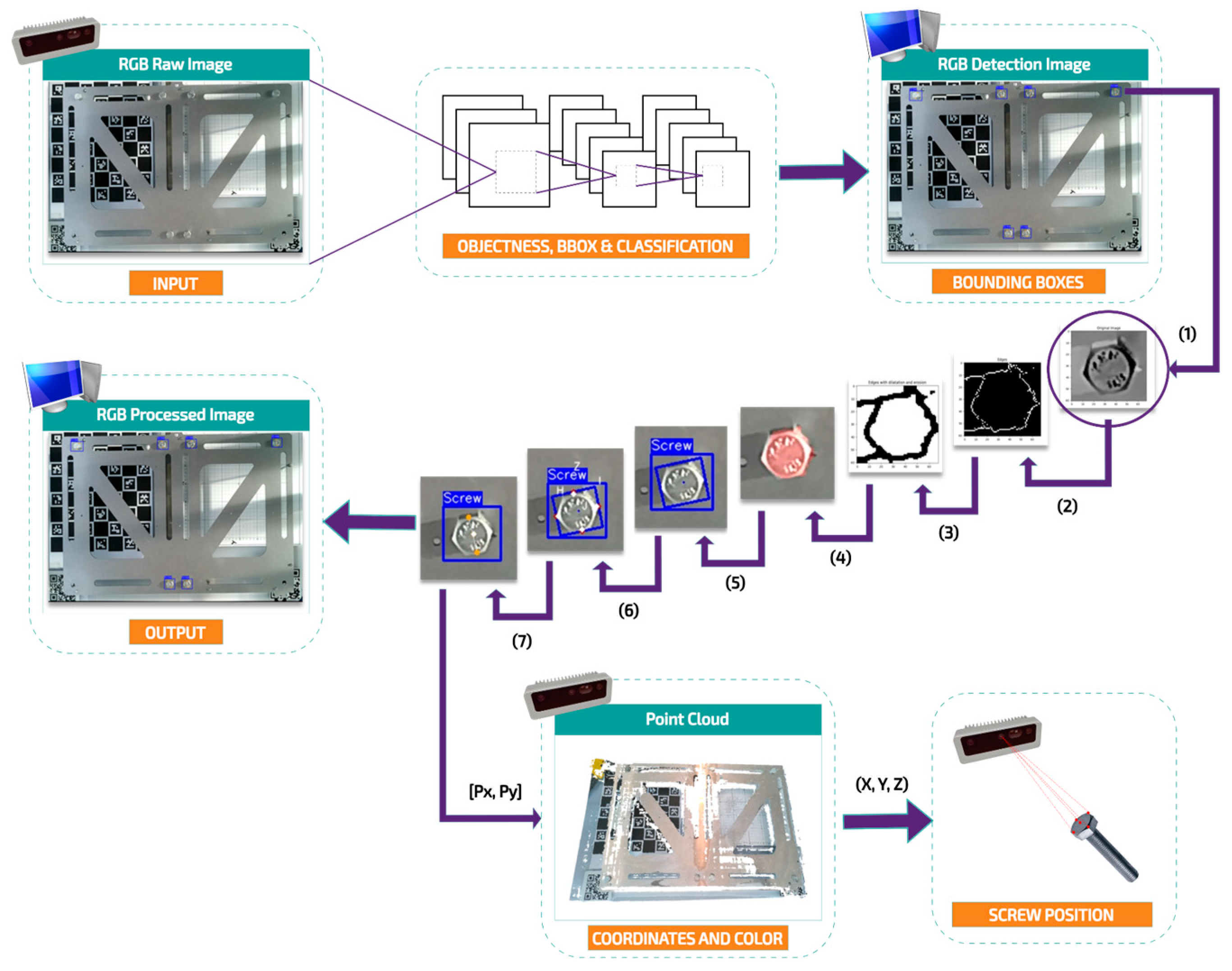
The scene perception module is designed to acquire and transmit key sensor data to the workstation to enable detection, identification, and precise localization of the components to be disassembled. The workstation, acting as the system’s core, communicates bidirectionally with the physical execution module and with the MR interface module. In this context, the workstation module processes the perception data using computer vision algorithms and convolutional neural networks (CNNs), allowing robust semantic segmentation and accurate pose estimation for each identified component. The proposed algorithm consists of different stages in which mechanical components are detected, segmented, and localized in the physical environment. These stages are illustrated in
Figure 3, which shows the complete processing flow from image capture to the three-dimensional localization of the elements of interest—in this case, hex-head screws.
Everything begins with the acquisition of a raw RGB image captured by a camera installed in the work cell. This image serves as the starting point for the perception system, whose role is to extract, classify, and locate relevant elements within the disassembly area. Once the image is captured, the screw detection stage begins. Here, a convolutional neural network based on the YOLO object detection architecture, which is optimized for real-time scenes, analyzes the scene and locates possible screws. The model evaluates the likelihood that an object of interest is present and delineates its outlines with bounding boxes that enclose each screw in the image.
It is important to note that YOLO is used exclusively for rapid object localization, not for detailed shape analysis. For that purpose, the next stage leverages classical computer vision techniques to segment each detected region and compute anchor coordinates and centroids for every screw. As shown in the middle sequence of the figure, the screw’s contours are first extracted (1), then refined through binarization (2), morphological operations (3), and segmentation (4). From this sequence, the algorithm obtains an individualized binary mask for each screw. This aids in calculating the screw’s orientation (5) and detecting its contours (6). This process is done by fitting an ellipse to the largest contour in order to determine its angle of orientation. With these data, the minimum area rectangle that circumscribes the contour is computed, corresponding to the oriented bounding box. Finally, the vertices and centroid of each screw are extracted, and the midpoints of each of its sides are computed (7). The algorithm outputs the raw image overlaid with the bounding boxes and the pixel coordinates of each screw.
In parallel, a three-dimensional (3D) point cloud is obtained from the camera’s depth sensors. This 3D map associates the pixels of the processed image [Px, Py] with a physical coordinate (X, Y, Z). Using the 2D coordinates previously extracted from the image’s bounding boxes, the system transforms these data into real 3D positions.
This perception workflow not only enables reliable, localized detection of components but also lays the foundation for precise and safe human–robot interaction in complex and highly variable disassembly tasks.
3.3. Mixed-Reality Interface and HRI Method
The human–robot interface resides on the HMD and is aimed at facilitating the operator’s decision-making in human–robot collaborative disassembly. In this way, any user, without needing robotics knowledge, can carry out this process easily and intuitively, without introducing potential errors.
The proposed system is based on overlaying digital information elements on the HMD lenses such as virtual buttons, information panels, and dialog windows with which the user can interact in real time. Interaction is carried out in a multimodal manner, combining hand tracking, voice commands, and gaze detection. To achieve this, the capabilities offered by the Mixed Reality Toolkit (MRTK) on the Unity 3D platform are utilized, which allow specific profiles to be configured for each input modality.
On one hand, the hand-tracking profile enables actions like pressing virtual buttons or dragging digital panels with one’s fingers. On the other hand, the voice recognition profile allows voice commands to be assigned to actions without needing to use hand gestures. Finally, the capabilities of the eye-tracking profile are combined with the spatial recognition system to activate controls and contextual information exactly at the user’s point of focus. In this way, digital information is dynamically projected into the user’s environment to guide them intuitively through the process.
Additionally, the system features a digital panel that displays in real time the image provided by the perception module, on which the bounded regions corresponding to the components identified by the detection algorithm are graphically represented. The application receives the image from the broker and creates a 2D texture that is assigned to a Raw Image object in Unity. Furthermore, the application receives the coordinates and the number of detected components to instantiate arrow-shaped red objects over them in the virtual environment.
Leveraging the various tracking mechanisms of the MR application, it is possible to capture signals from the operator and transform them into commands for the cobot. One of the proposed interaction methods is based on projecting a digital pointer onto the user’s right index finger to indicate disassembly components to the application. Likewise, the user can plan the disassembly with a similar mechanism via gaze by configuring a spatial observer through the profiles provided by MRTK. Using the exact position and direction of the user’s gaze, a digital pointer is projected at the intersection of the gaze’s raycast and the spatial mesh. In this way, the user can select the disassembly sequence by focusing on each of the components.
In this way, voice commands are used to store the 3D coordinates of the digital pointer in the virtual workspace and publish them to the broker, or to request information about the activity. This exchange of information between the MR application and the broker is carried out via the Rosbridge WebSocket server provided by the ROS# framework.
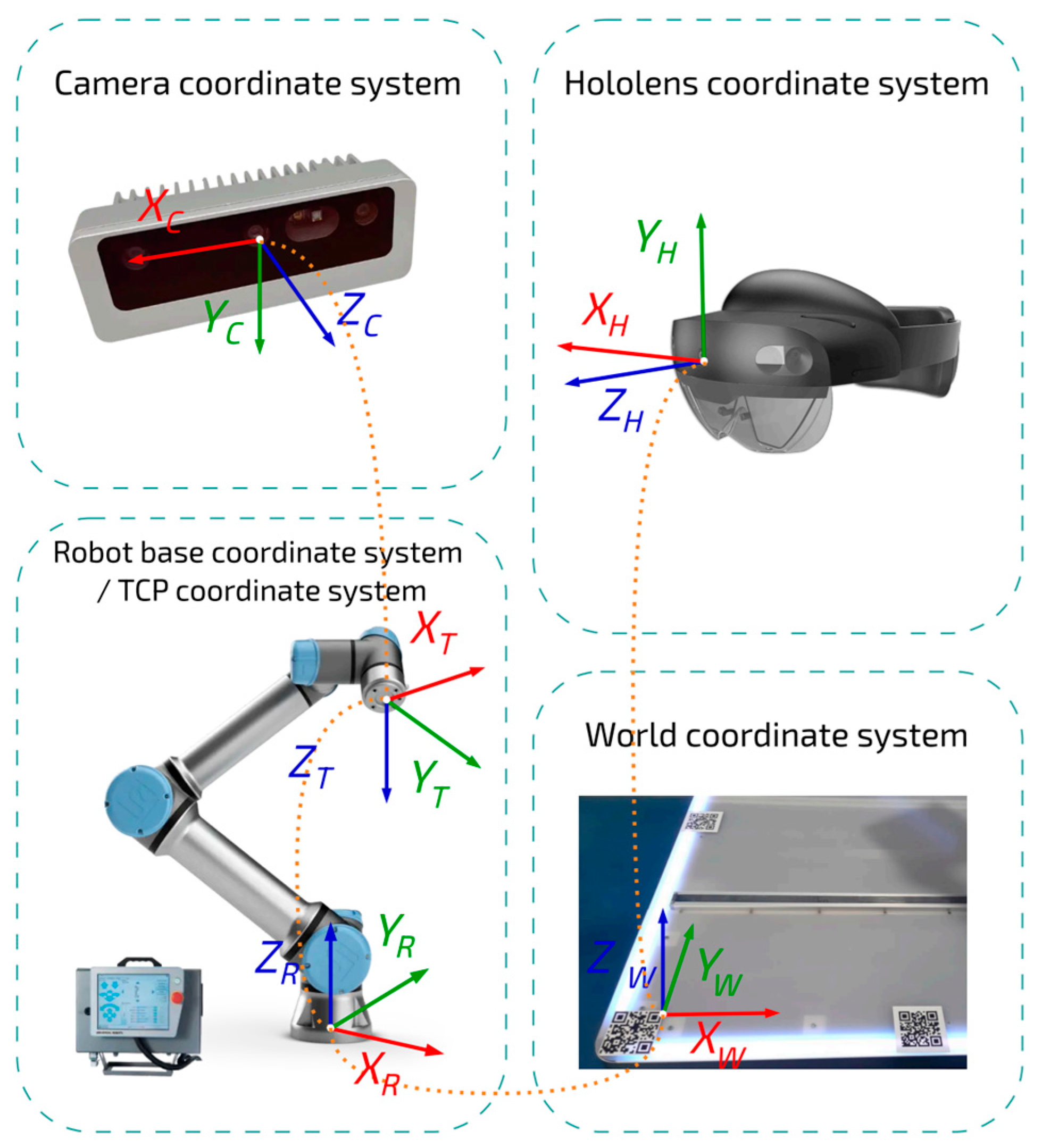
3.4. Synchronisation of Virtual and Physical Environments
The following subsection describes the method used during human–robot collaborative disassembly to identify and disassemble the screws indicated by the user. Transforming the user’s indications into commands for the cobot requires aligning the coordinate reference frames of the devices involved. This alignment is achieved by estimating homogeneous transformation matrices (HTMs) using the hand–eye calibration technique. This procedure links the coordinate system (CS) of the HMD,
HCS = {
Xh, Yh, Zh}, and the camera frame,
CCS = {
Xc, Yc, Zc}, with the global CS,
WCS = {
Xw, Yw, Zw}, thus establishing a spatial correspondence with the assembly, as detailed in Ref. [
11]. Since the camera is mounted on the cobot’s wrist, it is necessary to calculate the HTM that relates the CCS to the robot arm’s base reference frame,
RCS = {
Xr, Yr, Zr}, during disassembly. The HTMs that relate the HCS and CCS to the WCS
and
are defined in Equations (1) and (2).
The calculation of the HCS-to-WCS transformation is performed by measuring coincident points in HCS and WCS via hand–eye calibration. However, this relationship varies according to the initial position of the MR application, due to the indeterminate nature of Unity’s CS. In Ref. [
11], three QR codes are used to determine
by measuring their position on the HCS at the start of the application. In this work, however, an alternative method is proposed to avoid having the HMD detect QR codes each time the MR application starts. This method consists of placing the HMD in the same position every time the application is started, and subsequently loading the coordinates of the QR codes during the digital environment initialization. To achieve this, the MR application is launched when the HMD is turned on, and the coordinates of the QR codes detected in the last session are loaded. In this way, the operator’s task is made easier and the disassembly process is expedited.
The position of a component in the HCS,
, is transformed to the WCS by applying
. In this way, the component’s position in the WCS,
, is obtained as given by Equation (1):
The camera provides the position of the same component in the CCS
. Since the camera is placed on the robotic arm,
is set to locate the CCS with respect to the RCS. Subsequently, to express this position in the WCS, it is combined with the
matrix, which links the RCS to the WCS. This relationship is summarized in Equation (2):
However, the matrix is not constant, as it varies depending on the tool’s position and orientation in the RCS. For this reason, it is necessary to determine the relationship between the CCS and the tool’s coordinate system, TCS = {Xt, Yt, Zt}, via the matrix . In contrast to the , which varies with the cobot’s pose, this is constant, since it maintains a fixed distance and rotation with respect to the TCS.
To estimate
, a set of points of interest visible in the point cloud generated by the camera are identified, and the coordinates of those same points are manually measured in the RCS. Once these correspondences between points expressed in the CCS and in the TCS are established, a least squares method is applied to obtain the optimal transformation matrix that aligns both coordinate systems. Finally, knowing the
via the cobot’s control interface, one can solve Equation (3):
where
is equal to the inverse of
, as shown in Equation (4):
To locate the CCS with respect to the WCS, it is necessary to calculate the matrix
. This matrix is computed by measuring the coordinates of the three aforementioned QR codes in the RCS. Through these measurements, the relationship between the RCS and the WCS is established, allowing the vision system information to be accurately integrated with the global environment via Equation (5):
where
is the inverse of
. Finally, the relationship between a point in the global system
and its position in the CCS
is established, as expressed in Equation (6):
Figure 4 illustrates the sequence of transformations required to convert a point between the different coordinate systems of the setup. The orange dashed lines represent the forward and inverse relationships of each HTM to relate the reference frames involved in the system. In this way, precise and safe interaction in the disassembly operation is ensured.
3.5. Communication and Execution Tasks
The management of communication and real-time task execution is critical in the proposed system. The communication model implemented uses a publish–subscribe scheme via topics, where each module is represented as a node that publishes relevant data and subscribes to specific messages, allowing component decoupling and facilitating scalability. In
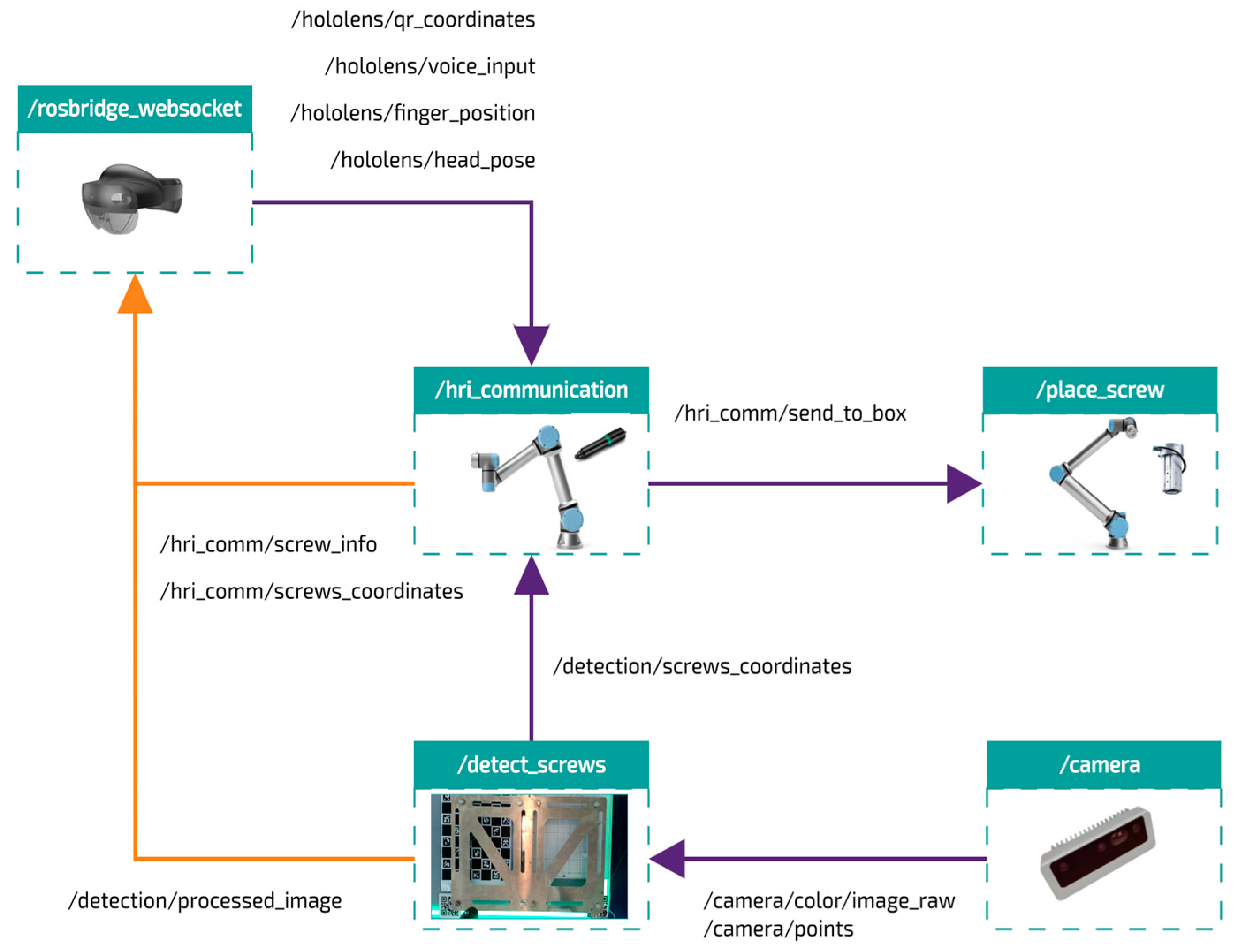
Figure 5, the organization of the nodes that connect the main modules and coordinate the execution of the activity is illustrated according to the publish/subscribe protocol.
The MR interface communicates with the system through the aforementioned Rosbridge WebSocket gateway. This server acts as a system node and transmits the messages between the broker and the HMD. This node publishes, among others, the topic /hololens/qr_coordinates, which allows the HMD to be located in the robot’s base frame; /hololens/voice_input, where the operator’s voice commands are transferred; /hololens/finger_position, which records the index finger’s position; and /hololens/head_pose, which provides the information necessary to adjust the robot’s speed according to the operator’s distance. Additionally, the node subscribes to data from the vision module, which include the detected screws’ locations and the processed image while the robot is idle. This enables the projection of digital arrows onto the visible screws and improves the operator’s interaction in the MR environment.
The architecture also incorporates error handling mechanisms to ensure that communication failures or data losses are promptly detected and managed. Furthermore, periodic status checks between nodes help maintain synchronization and guarantee system integrity during prolonged operations.
On the other hand, the scene perception module captures the image and point cloud and publishes this information on the topics /camera/color/image_raw and /camera/points. The /detect_screws node processes this information and publishes the results of the screw detection and segmentation analysis via /detection/screws_in_image and /detection/processed_image, allowing the central system to have the precise information needed for decision-making about the tasks to be performed.
Finally, the workstation, whose communication node is the main module of the physical environment, integrates machine vision and MR data to coordinate the execution and exchange of information with the collaborative robots. Based on this information, the system plans and sends trajectories to the cobots, ensuring a continuous and reliable flow of instructions in real time.
4. Case Study and System Evaluation
4.1. Experimental Setup
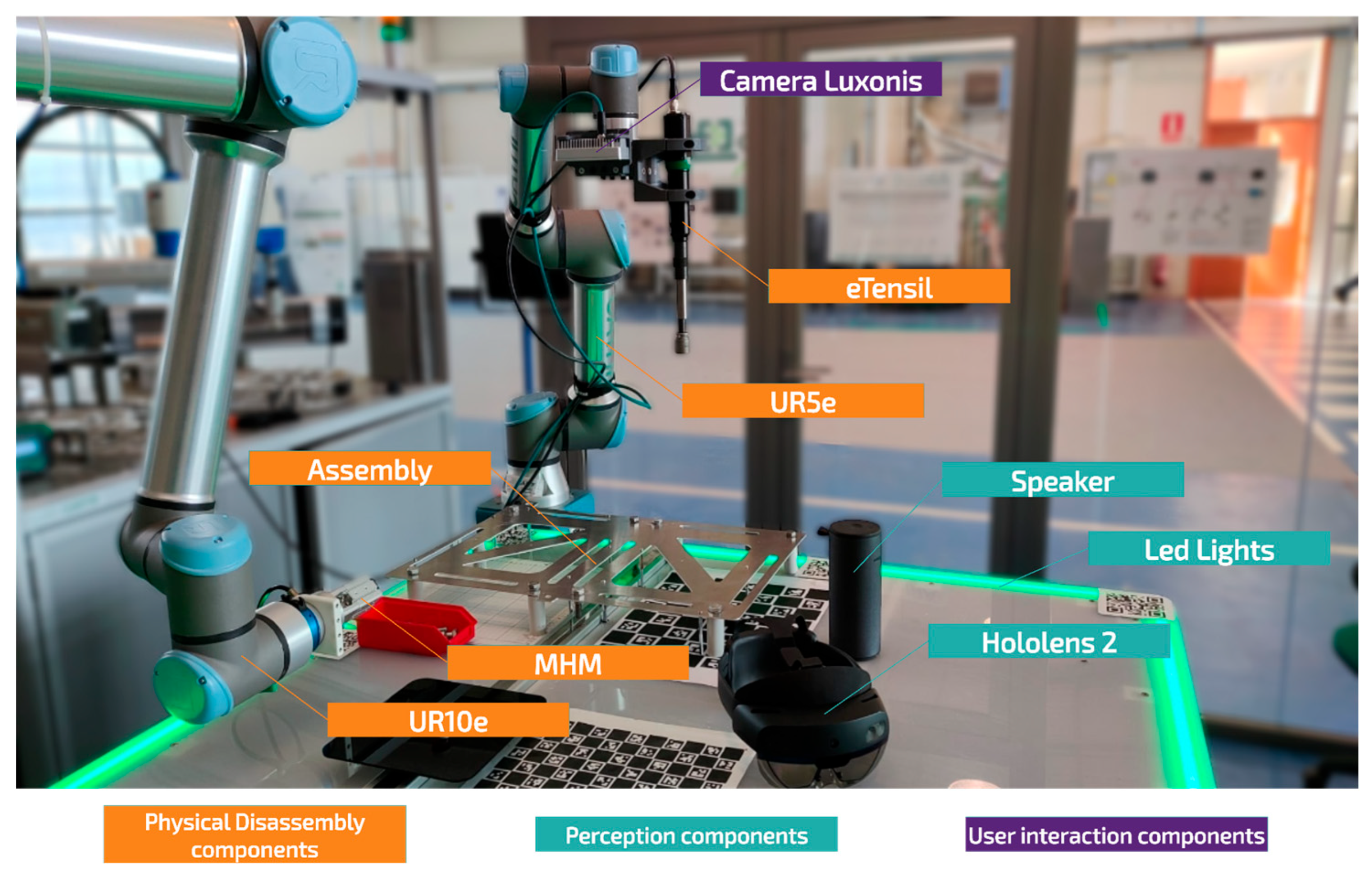
The proposed system was applied to disassemble an aluminum metal part secured with eight M10 hex-head screws. This part is placed on a worktable equipped with LED lights that change color according to the status of the cobot performing the disassembly. The robotic arm chosen for this task is a UR5e of Universal Robots (Odense, Denmark) equipped with eTensil of FIAM (Torino, Italy) screwdriving system, whose design includes a magnetized 17 mm hex socket to retain the screw after unscrewing. As mentioned earlier, releasing the screw requires the use of a second cobot to separate the screw from the magnetized socket and place it in a bin outside the UR5e’s reach. The robotic system selected for this function is a UR10e cobot of Universal Robots equipped with MHM-X7400A magnetic gripper of SMC (Tokyo, Japan).
The workstation consists of a HP Z1 G8 Tower Desktop PC with a 11th Gen Intel® Core™ i7-11700 @ 2.50 GHz processor, an GeForce RTX 3070 GPU of NVIDIA (Santa Clara, CA, USA), and Ubuntu 22.04 LTS as the operating system. This component serves as the brain of the system, enabling real-time communication among the system’s different modules and ensuring smooth, efficient operation. To this end, Vulcanexus ROS2 Humble is used as the communication broker, offering a robust middleware based on Fast DDS, an efficient implementation of the Data Distribution Service (DDS) protocol that ensures fast and reliable information transmission between nodes.
Additionally, the OAK-D-PRO-POE-AF camera of Luxonis (Denver, CO, USA) was selected for simultaneous acquisition of RGB images and point clouds in real time. For its integration into the ecosystem, the DepthAI ROS driver package is used to handle communication with the hardware and synchronize the image and depth streams.
Finally, an Hololens 2 device of Microsoft (Redmond, WA, USA) provides an immersive interface between the operator and the robotic system, enabling multimodal interaction through voice commands, hand gestures, and eye tracking for natural and intuitive communication with the virtual environment and the robot. Through the HL2’s lenses, holograms synchronized with the physical environment display contextual information and interactive virtual models of the elements to be disassembled. The HL2 notifies the user of new events via voice messages, though some are played through a Bluetooth speaker for greater clarity or volume in noisy industrial environments.
Figure 6 shows a photograph of the work cell where each system component is visible: components of the physical disassembly module are highlighted in orange, the perception module’s camera appears in purple, and the HL2 with user interaction elements like the speaker and LED lights are shown in turquoise.
4.2. Demonstration
Initially, the necessary ROS2 nodes were launched to establish communication between the workstation, the cobots, and the depth camera. During this initial phase, parameters configured in a MongoDB database were loaded, defining the operating modes, thresholds, and technical specifications of the detection and segmentation model.
Upon completing initialization, the cobots moved to their home positions, waiting for the operator’s instructions to begin the physical operation. The operator received an audio message with information on the number of screws present in the assembly, and was guided to put on and turn on the HL2.
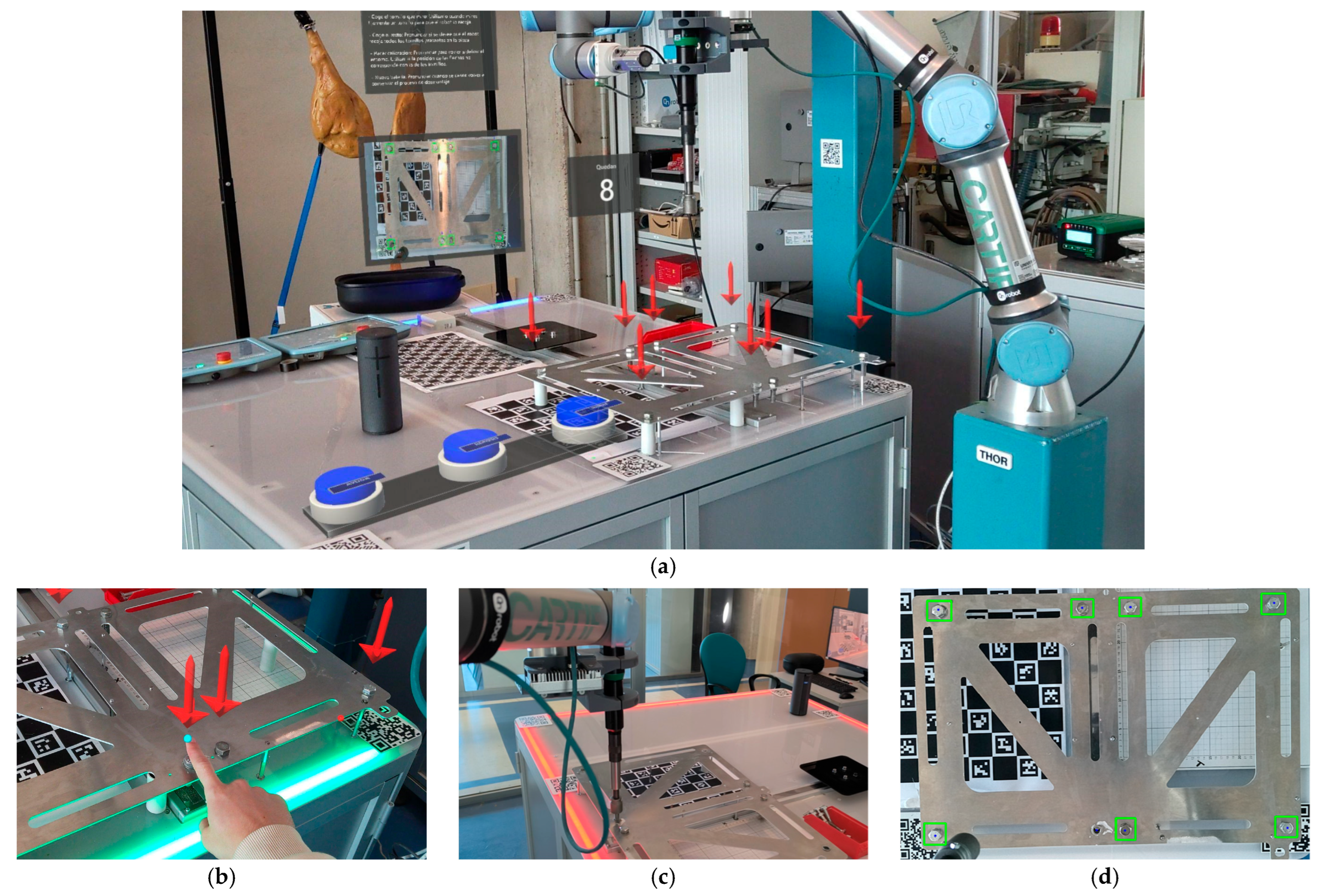
When the MR device was activated, the application ran automatically in Kiosk mode via the Windows Device Portal API. This allowed immediate loading of the reference coordinates linked to the QR codes, which facilitated the precise positioning of the robot in the MR device’s spatial frame. At this point, as shown in
Figure 7a, the operator saw through the MR lenses a digital interface composed of information panels, arrows indicating the locations of the screws detected by the system, and virtual controls for positioning the UR5e cobot at predefined positions.
As mentioned earlier, the HRI is carried out through multimodal commands, integrating voice, touch gestures, and eye tracking. For hand selection, a blue digital pointer was projected onto the user’s index finger; for gaze selection, a pointer was rendered on the collision mesh at the precise ray-cast intersection. By pointing at a screw with their index finger and issuing the voice command in Spanish “Recoge este tornillo” (“Pick up this screw”), the application stored and published to ROS2 the 3D coordinates corresponding to the digital pointer projected in blue onto the operator’s finger, as shown in
Figure 7b. The coordinates obtained in these steps were compared with those previously determined by the vision detection system using Euclidean distance calculations for precise selection of the target screw.
Once the target screw was identified, the UR5e cobot performed the unscrewing operation and returned to its home position, as shown in
Figure 7c. The unscrewing sequence was configured based on the torque and the screw length, parameters that are defined in the system prior to execution to ensure proper force application and complete removal. Additionally, the precise location of the tool center point (TCP), corresponding to the screwdriver socket, was established through a prior calibration phase. This process determined the position and orientation of the tool relative to the robot’s wrist, ensuring accurate alignment with the screw axis during operation.
Subsequently, a specific algorithm visually verified the correct extraction of the screw by capturing and analyzing images with bounding boxes around the detected screws, as illustrated in
Figure 7d. This verification was performed by checking whether a screw was still detected within a square area of 5 cm
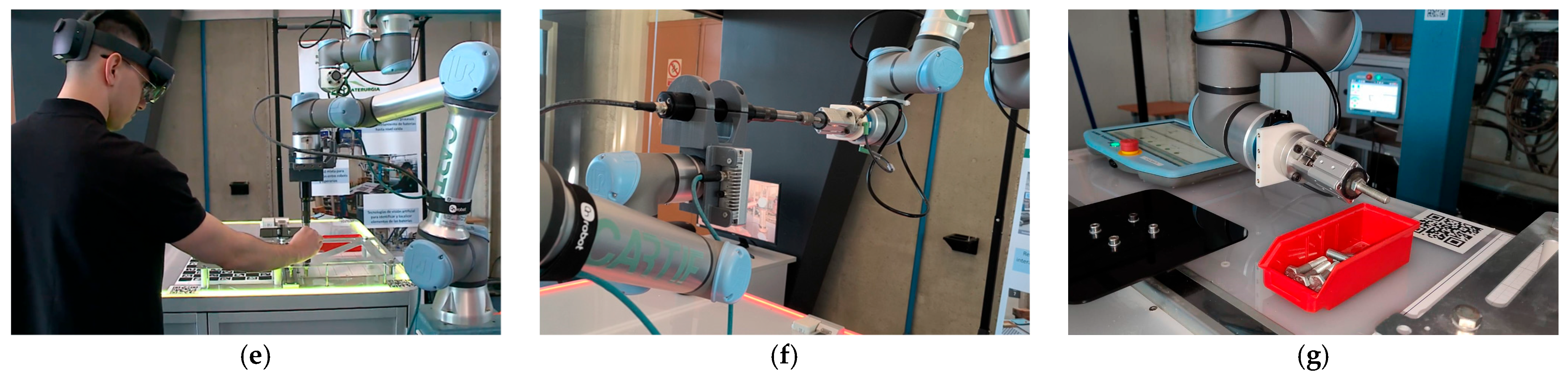
2 centered on the robot’s predefined pickup position. In the event of a failed extraction, the UR5e approached the screw and activated Freedrive mode, which releases the arm’s joints so that the operator can manually adjust the tool’s position over the screw head, as shown in
Figure 7e.
Finally, after the UR5e successfully extracted the screw, it transferred it to the UR10e cobot, which separated the screw from the magnetized socket and stored it in a designated bin for components disassembled during the process, as shown in
Figure 7f,g.
4.3. Evaluation and Results
4.3.1. Object Detection Performance
YOLO convolutional neural networks models were chosen due to their proven efficiency and capability for real-time object detection, a fundamental characteristic for industrial applications. It’s important to note that these models are essentially cutting-edge Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) that process images end-to-end, resulting in high inference speed and competitive performance. The selection was justified by their ability to handle the inherent complexity of screw detection under various conditions.
First, the detection performance of YOLOv8 and YOLOv11 convolutional neural networks models was comparatively evaluated for identifying and localizing screws in battery plates. Those two model versions have been preferred for object detection studies over older versions primarily due to their superior balance of accuracy and speed, coupled with optimized model architectures that lead to better performance and efficiency. As the newest iterations, they represent the cutting edge of YOLO research, offering a more robust and streamlined framework for various vision AI tasks—specifically, object detection.
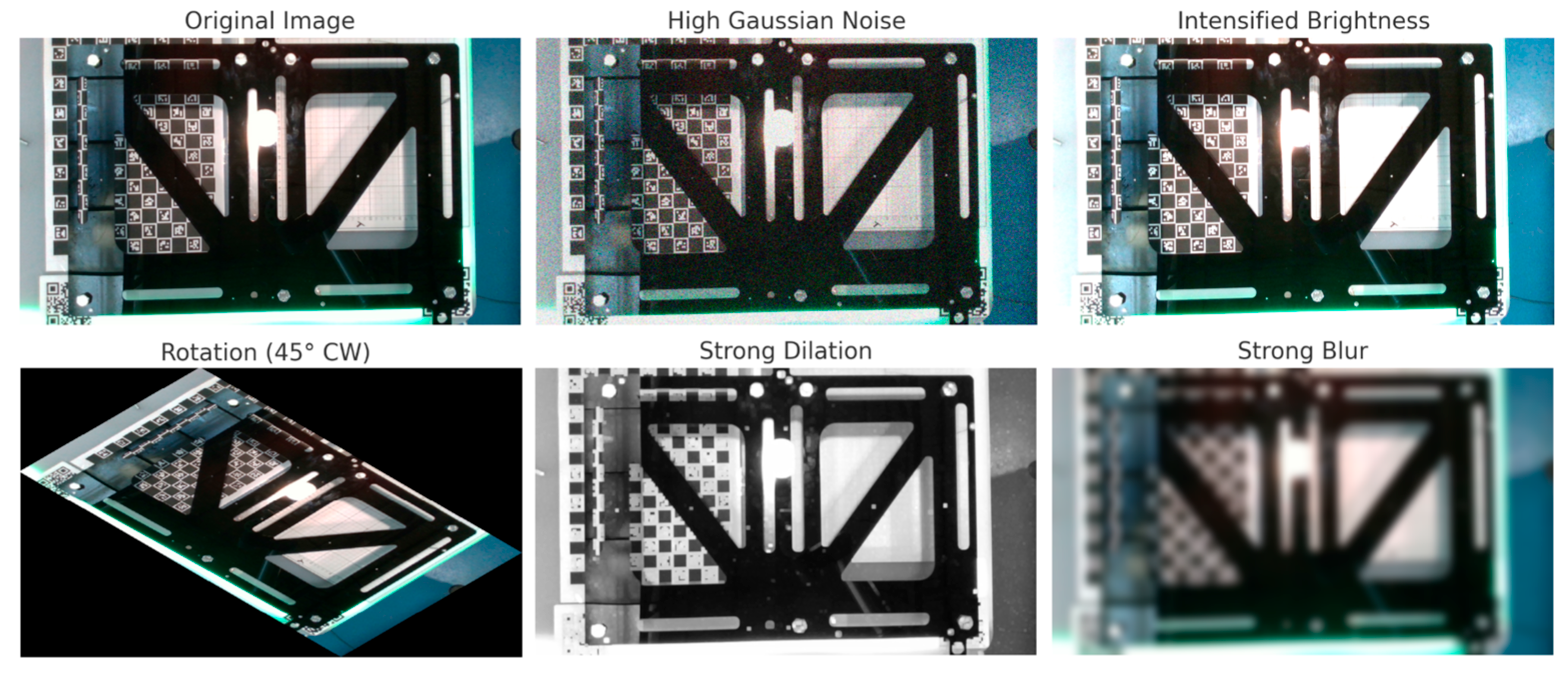
The training of the models involved a manually annotated dataset comprising 492 original images, with a total of 11,868 labeled instances of different screw positions and batteries. This dataset, with images standardized to 640 × 640 pixel resolution, was then substantially expanded via robust data augmentation techniques (rotations, illumination variations, high Gaussian noise) to reach a final training set of 4420 images. This substantial increase in data greatly improved the generalization ability of both models by exposing them to a greater variability of examples.
Figure 8 shows examples of augmentation.
For a detailed understanding of the data utilized and the preprocessing techniques applied, the key characteristics of the annotated dataset, including its size, composition, and image resolution, are summarized in
Table 1. Complementarily, the specific parameters for the data augmentation techniques employed during training, such as rotation, scaling, brightness adjustments, Gaussian noise addition, blur, and dilation, are detailed in
Table 2.
Once the data were prepared, from the dataset, 491 images were kept for testing that represent 10% of the overall dataset (4911), and two data splits for training and validation with the rest, 80%/20% and 70%/30%, were explored to assess the impact of the validation set size on the model’s generalization. Leveraging transfer learning from models pre-trained on large datasets significantly accelerated the process, with standard optimizers and combined loss functions employed to ensure accurate and robust predictions across various conditions. For screw detection, YOLOv8 and YOLOv11 models were trained under carefully selected hyperparameter configurations to maximize performance. Specifically, an initial learning rate of 0.001 was employed and subsequently reduced by a step decay scheduler over the training epochs. The AdamW optimizer, configured with a weight decay of 0.0005, was utilized for its efficiency and effectiveness in mitigating overfitting as much as possible. Training was conducted with a batch size of 32 for computational efficiency and gradient stability across 5000 epochs, with early stopping mechanisms considered based on validation performance. All input images were uniformly resized to a 640 × 640 resolution to serve as input to the neural network.
Standard object detection metrics were used to evaluate the models, including confusion matrices and precision–recall curves.
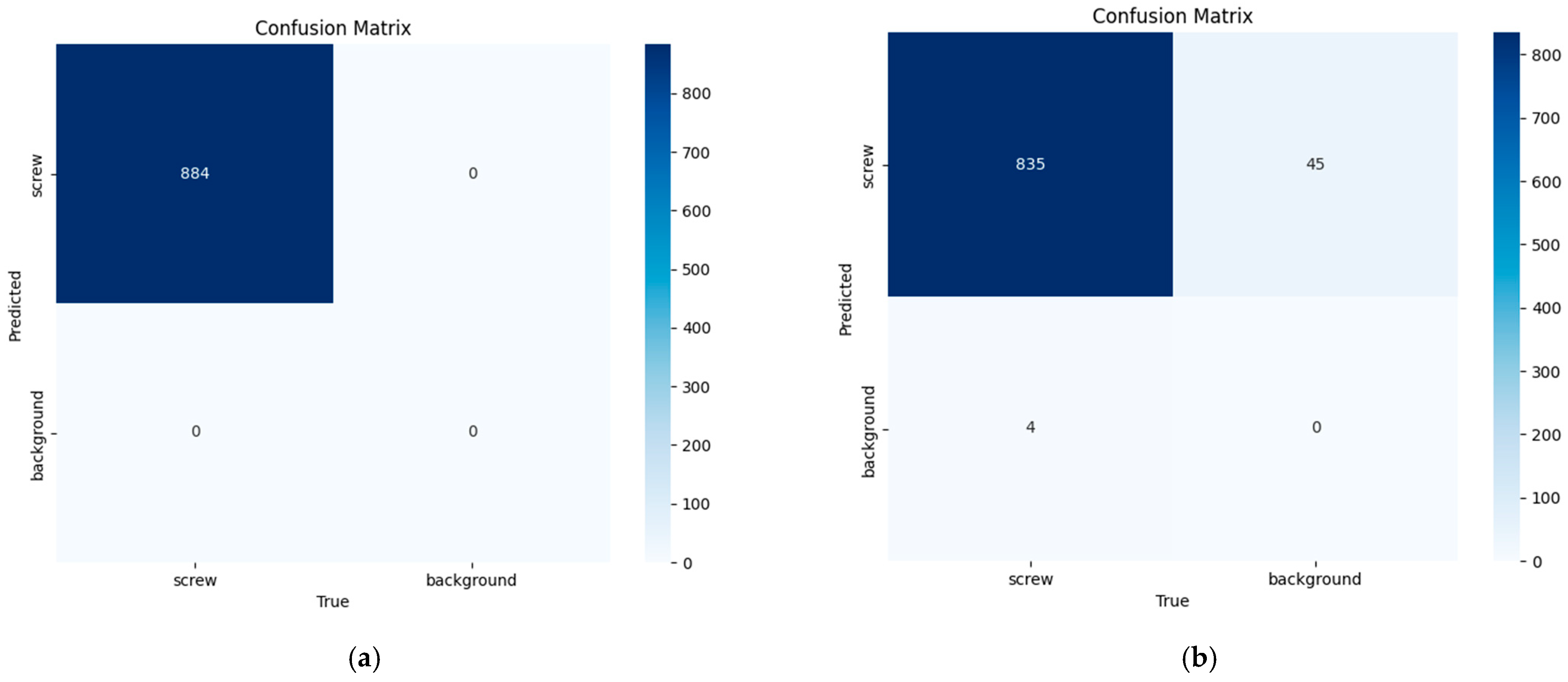
Figure 9 shows the resulting confusion matrices for the YOLOv11 and YOLOv8 models. It can be seen that the YOLOv11 model achieved perfect performance on the “screw” class in the test set: It correctly detected all 884 screws present without mislabeling any element as a screw. This translates to 100% precision and 100% recall. The 100% accuracy in the YOLOv11 model’s confusion matrix is attributed to the high discriminability of screws within the test set, specifically sourced from a highly controlled environment where significant variations in environmental factors such as lighting and screw presentation are inherently unusual. This performance was achieved through a robust training methodology, including extensive data augmentation and regularization, validating the model’s precise and exhaustive detection capabilities within this specific context and its promising applicability in similar, stable industrial settings. In contrast, the YOLOv8 model made some errors: it failed to detect 4 actual screws (false negatives) and confused parts of the background for screws on 45 occasions (false positives). Consequently, although YOLOv8 achieved high performance, its precision and recall were slightly lower (approximately 95% precision and 99.5% recall for the “screw” class), as reflected by the off-diagonal elements in its confusion matrix. These results show that the YOLOv11 version matches or significantly outperforms YOLOv8 in this specific task.
Another important factor for the validity of the system is inference time efficiency, given that the system operates in real time. In the tests, YOLOv11 also achieved slightly lower inference times than YOLOv8. This improvement, though modest, helps the system respond faster to the operator’s commands, which is crucial in an interactive environment. As shown in
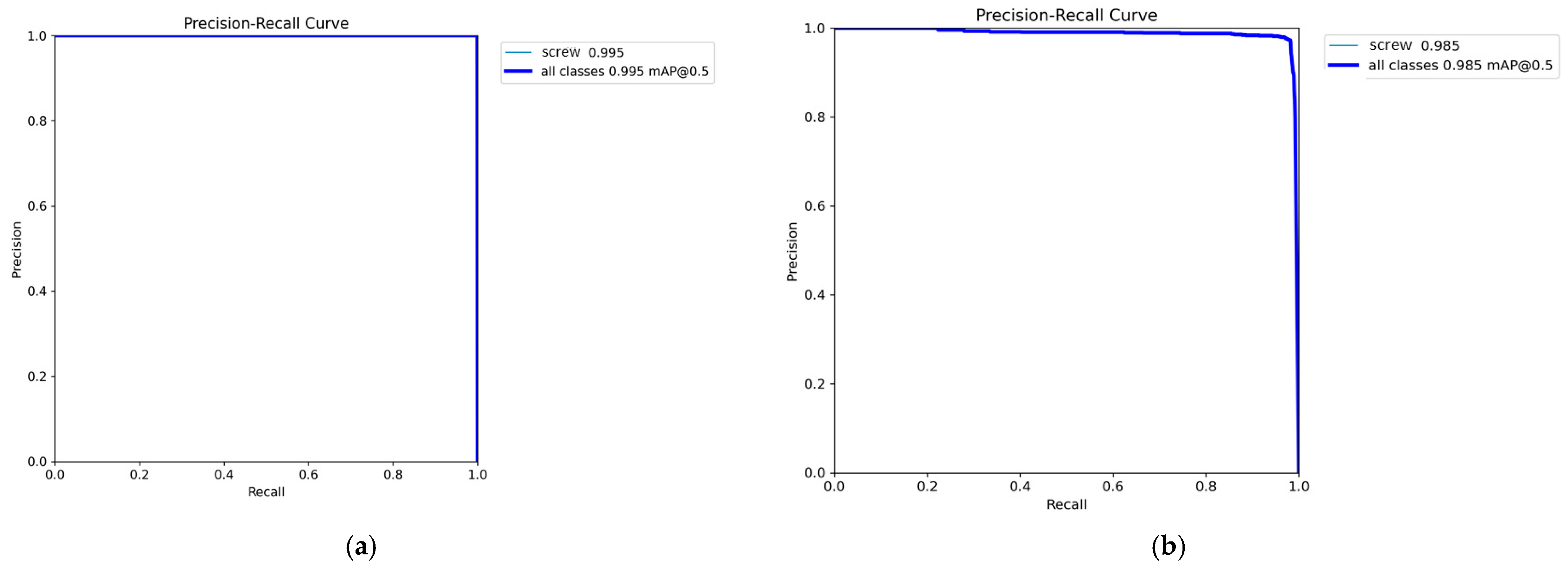
Figure 10, for all these reasons, YOLOv11 was chosen for integration into the proposed system, taking advantage of its higher accuracy and speed. These results, illustrated in the figure, support the strength of the perception module, as the selected model reliably detects disassembly components, providing a solid foundation for the proper functioning of the rest of the system. The graph displays the average precision-recall (PR) result as a thick blue curve, overlaid with a thinner blue curve representing the PR performance for the single class present in the dataset. This overlap occurs because the model was trained and evaluated on only one class.
To ensure the robustness of the comparative results between YOLOv11 and YOLOv8, statistical tests were conducted. This involved training and evaluating both models multiple times to obtain a distribution of their performance metrics (such as mAP). A Wilcoxon signed-rank test was then applied to these paired observations. Using a significance level (α) of 0.05, the resulting p-value allowed us to confirm that the observed performance differences were statistically significant, thus strengthening our conclusions.
The final choice between an 80%/20% or 70%/30% split for the training and validation sets was based on a strategic balance. The 80%/20% split was opted for to maximize the amount of data available for the model to learn, which was considered crucial given the dataset’s size to ensure greater final generalization capability. The 70%/30% split was opted for to obtain a more robust and reliable validation performance estimate, which was considered a priority for fine-tuning hyperparameters and having greater confidence in the early stopping point. Both configurations are valid, but the decision aligned with the primary need to enhance learning within the specific context of the study.
4.3.2. Experimental Design
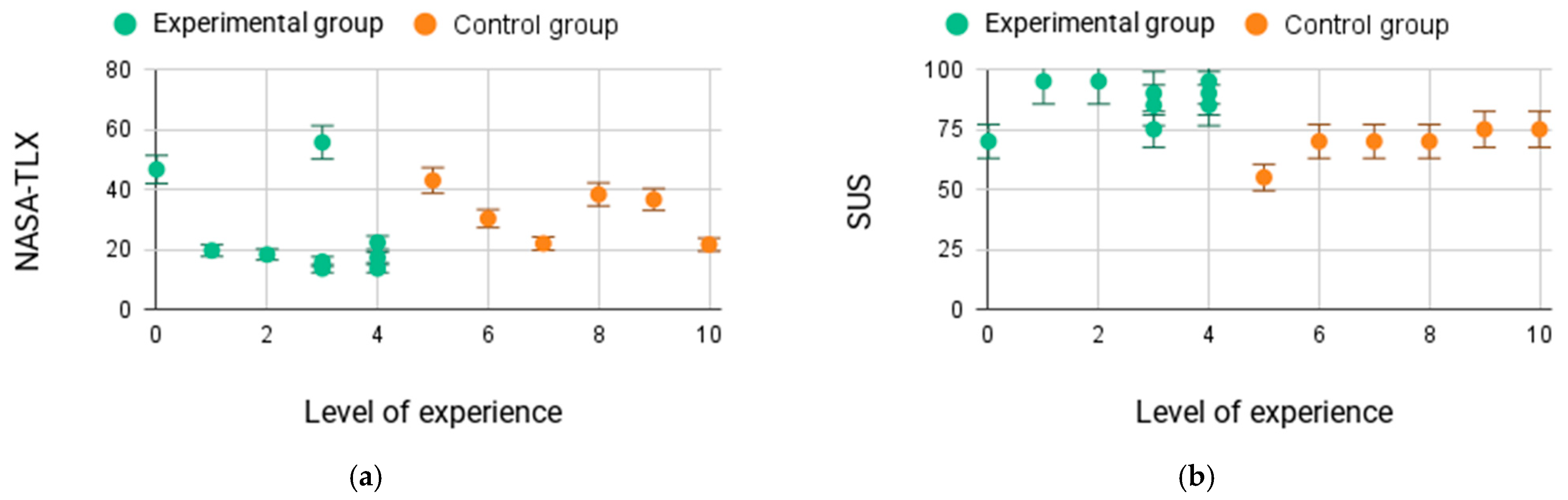
To evaluate the usability and impact of the MR system in an operational setting, an experimental trial was conducted with 15 human participants. The participants had varying levels of experience in robotics and extended reality systems, which were recorded on a scale from 0 to 10, weighted 60% for XR use and 40% for robotics use. From the experimental design phase, two distinct user groups were defined to analyze the effect of expertise on performance: a high-experience group with users whose experience level ranged from 6 to 10 (N = 6), and a low-experience group with users whose experience level ranged from 0 to 5 (N = 9).
In terms of demographics, the participants had an age range between 22 and 50 years, with an average age of 34.7 years. The gender distribution included 10 male and 5 female participants. Regarding their academic and professional background, the cohort was composed of seven engineers, two engineering students, one maintenance technician, one legal professional, two project coordination specialists, one quality assurance specialist, and one logistics support specialist, respectively. This diversity in background was intended to reflect a realistic range of operator profiles in industrial HRI scenarios.
Each participant performed an industrial disassembly task using the proposed system. The task consisted of disassembling a sequence of seven screws using the MR application’s multimodal inputs. Prior to the trial, users completed a brief training phase to become familiar with using the HL2 and the MR interface. In this training, they were instructed on using voice commands and hand gestures to interact with the system, as well as on safety measures and basic operation of the cobots involved. This was done to minimize the learning curve during evaluation, ensuring that the results predominantly reflect the system’s usability rather than the users’ lack of familiarity with the technology.
In the execution phase, each participant carried out the actual disassembly using the metal part described in
Section 4.1, directing the robot’s actions via multimodal commands from the MR interface. A supervisor monitored the trials, recording quantitative performance metrics such as the total task execution time, the number of interventions required, and the number of errors made. Here, an intervention is defined as any assistance or corrective action performed by the supervisor to help the participant (for example, stopping the robot in the face of a potential hazard or assisting with the setup if the user became stuck). An error is understood as an incorrect action by the participant during the task, such as attempting to disassemble a wrong component or causing a failure situation that requires correction.
In the post-evaluation phase, participants answered standardized questionnaires to assess usability using the System Usability Scale (SUS) and cognitive load using the NASA-TLX. The scores from both surveys were kept anonymous and collected for subsequent quantitative analysis. With this experimental design, it was possible to gather both objective information (times, errors, etc.) and subjective information (cognitive load, perceived usability), allowing a comprehensive evaluation of the proposed system’s performance against the traditional method.
4.3.3. Results
During the experimental trials, participants alternated between the available input modalities: hand pointing and gaze tracking. Both methods were effective, but participants generally preferred gaze tracking for being more natural and less physically demanding. The average error rate was 7.5% for gaze selection, compared to 11.2% for finger pointing.
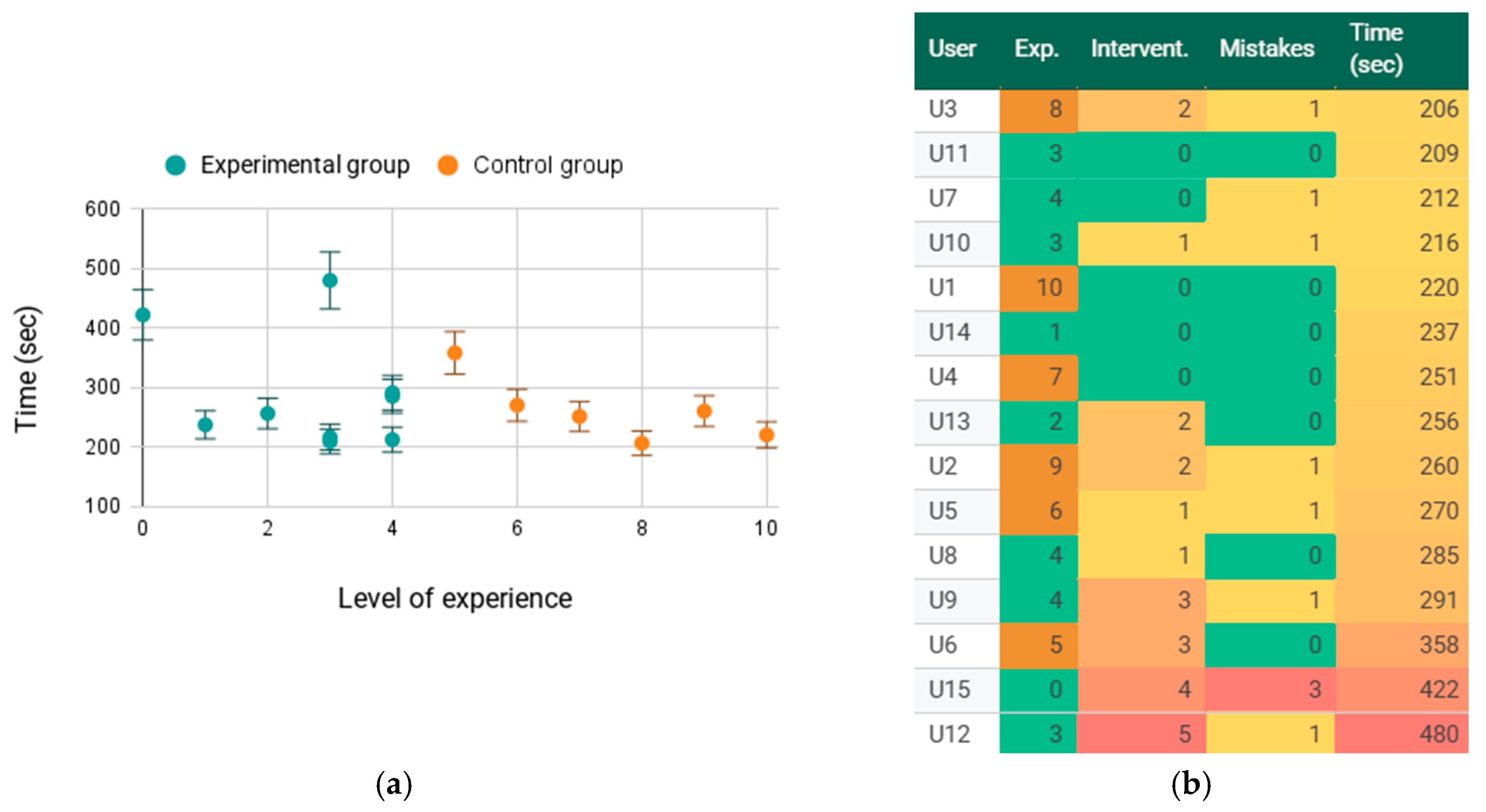
In all cases, participants successfully completed the MR-guided disassembly task. The average execution time was 4 min and 49 s (mean 289 s, SD ≈ 97 s; median 255 s) for the experimental group and 4 min and 1 s (mean 241 s, SD ≈ 27 s; median 251 s) for the control group. The majority of the trials had times clustered between ~3 and 5 min, with only two longer sessions (~7 and 8 min) due to the supervisor’s interventions at different stages of the task. In line with this, the supervisor’s interventions were minimal: in 5 of the 15 trials no external assistance was required, and on 4 other occasions the supervisor intervened voluntarily to highlight some performance aspects of the application. The system did not exhibit critical failures in the tests, and only 9 screws out of 105 were unscrewed in the wrong order, of which 5 were due to errors in executing the commands and 4 were due to detection errors from the HMD when manually indicating screws.
Overall, the system’s performance showed high robustness, maintaining safety and completing the disassembly without interruptions in almost all scenarios. The results suggest greater variability in execution times in the experimental group, where two relatively exceptional cases appear with execution times above 400 s for users U12 and U15. As can be seen in
Figure 11, execution times are adversely affected by the number of interventions and errors made in the application. However, the control group exhibits more uniform dispersion across all experience levels.
An outlier appears in this group with user U6’s trial, which took 358 s. Interventions and errors affected the control group less than the experimental group, yet 80% of users stayed within the 200–300 s range.
It is worth noting that the participants with the lowest performance and highest perceived workload were the legal professional and the maintenance technician. This observation suggests that prior familiarity with technology plays a relevant role in disassembly performance and user experience, whereas no direct relationship was found between execution metrics and participants’ age or gender.
4.3.4. Perceived Usability and Operator Workload
The usability results obtained were very positive. The SUS questionnaire yielded an average score of 79.67 out of 100, with a standard deviation of 12.02 and a median of 75. Most participants rated their experience with the system as highly usable, with individual scores mostly concentrated in the high range between 70 and 95 points. Only one isolated case had a lower score of 55 points, considered an outlier. This indicates that virtually all users found the MR interface intuitive and easy to use.
When analyzing the results by experience level, it was observed that the lower-experience group reported higher average usability, with an average score of 86.7 (SD ≈ 9.0), compared to the high-experience group, which had an average score of 72.0 (SD ≈ 2.7). This suggests that the system was especially intuitive for users with less prior experience.
As for cognitive load, assessed via the NASA-TLX questionnaire, the results indicate a relatively low perceived load, with an overall average score of 27.68 out of 100 (SD ≈ 13.26). Breaking it down by group, the high-experience group exhibited a higher average cognitive load, with an average score of 29.8 (SD ≈ 7.86), while the low-experience group showed a lower average load, with an average score of 24.81 (SD ≈ 15.35). These results suggest that the expert users—possibly due to higher expectations or a more demanding approach to the task—perceived greater effort compared to the less experienced users. Even so, both groups experienced overall moderate to low levels of cognitive load, which confirms the ease of use and the good acceptance of the proposed MR system.
The scatter plots shown in
Figure 12 illustrate the results of the experimental tests performed by the participants after completing the trial. It can be observed that the NASA-TLX results bear a linear relationship with the execution times obtained for each user. By calculating the Pearson correlation coefficient between these two variables, a value of 0.76 was obtained, indicating a strong positive linear correlation. In conclusion, it can be stated that the execution time is directly proportional to the perceived cognitive load: the longer the task duration, the greater the effort reported by the participants. This highlights the importance of minimizing cognitive demands to optimize task performance.
On the other hand, the SUS test results show that the experimental group rated the solution as having higher usability than the control group. As mentioned earlier, this may be due to each participant’s level of rigor and prior knowledge, since the expert users were more critical in their evaluation, whereas the less experienced participants rated the proposed solution’s usefulness and accessibility more positively. This finding emphasizes that familiarity with technology can significantly shape user perceptions of usability.
Additionally, the relationship between perceived cognitive load and the SUS score was examined. In this case, since the relationship was not strictly linear, the Spearman correlation coefficient was used, yielding a value of −0.75. This strong negative correlation suggests that as cognitive load increases, the perceived usability consistently decreases, although not necessarily in a proportional manner. Finally, the relationship between execution time and SUS score was weak, with no conclusive evidence of a significant association, whether linear or monotonic. This indicates that perceived usability was influenced predominantly by cognitive effort rather than by the speed of task completion itself.
5. Discussion
The obtained results demonstrate clear improvements in the operational efficiency and accuracy of the proposed system. All participants were able to complete the disassembly tasks successfully and safely, with execution times of only a few minutes per task. Moreover, a notably low error rate was recorded, with only a minor percentage of out-of-sequence steps across more than one hundred actions, confirming the system’s robustness and precision. Overall, the MR system allowed dynamic and flexible execution of the process, meeting operational requirements without significant interruptions.
User acceptance was also notably high, as reflected in the usability and workload evaluations. The SUS questionnaire yielded an average score of nearly 80/100, indicating that the majority of participants found the MR interface intuitive and user-friendly. Likewise, the perceived cognitive load levels measured with NASA-TLX remained in low to moderate ranges, suggesting that the system does not impose excessive mental effort. Notably, users with less prior experience especially appreciated the solution reporting even higher usability and lower load than the expert users, which indicates a favorable learning curve and high accessibility of the proposed multimodal interface.
Compared to previous studies, our approach offers significant advantages. Unlike traditional remote teleoperation approaches [
18,
19,
20,
21,
22], which typically introduce latency and hinder direct collaboration, the presented system allows the operator to control the robot in real time within the same workspace, improving human–robot synchronization. Recent MR-based disassembly methods [
53,
54] often lack direct robotic control or require extensive task-specific adjustments. Our solution integrates real-time multimodal control and intelligent deep learning-based component detection in a unified platform, providing greater flexibility and overcoming previous limitations, resulting in more natural and efficient human–robot interactions.
Nevertheless, certain limitations and opportunities for improvement have been identified. First, validation was conducted in a controlled environment using a specific disassembly scenario, limiting immediate generalization. Future evaluations across diverse industrial settings and tasks are necessary to confirm broader applicability. In addition, although most users rated the experience positively, some expert users held higher expectations, indicating that additional refinements in the interface or functionalities might be required to satisfy highly specialized operators.
The human–robot interaction mode exhibited distinct behaviors depending on the input modality used. Gaze tracking was generally preferred for its speed and comfort, yet its precision decreased when screws were closely spaced, occasionally leading to misidentification of the target. In contrast, hand pointing provided greater accuracy in such scenarios but involved longer interaction times and was more sensitive to tracking losses, particularly when the index finger was occluded or outside the HL2 camera’s field of view. These observations highlight the need for adaptive interaction strategies that optimize input selection based on task complexity and spatial constraints.
Regarding hardware requirements, the main investment lies in collaborative robots, whereas additional devices like MR headsets and RGB-D cameras have moderate costs and low maintenance needs. Using ROS2 further facilitates system scalability and integration. The MR application could run on various MR or AR devices, but see-through MR headsets are recommended in industry for precise, latency-free workspace visualization.
Lastly, the system relies on vision algorithms that, despite their high accuracy, showed occasional detection errors. Future improvements should focus on enhancing the robustness and reliability of these algorithms to ensure consistent performance across diverse components and industrial conditions.
6. Conclusions and Future Work
In summary, this work presented an MR-based HRI system that enhances disassembly tasks by combining an immersive interface with multimodal commands and deep vision algorithms. It was demonstrated that the solution enables disassemblies to be carried out safely and efficiently, while maintaining high precision in component identification and manipulation. The experimental findings corroborate an enhanced user experience, reflected in high levels of perceived usability and low cognitive load. This set of results distinguishes the proposal as an innovative HRI platform that strengthens direct collaboration between humans and robots in industrial settings, providing greater flexibility compared to traditional approaches and ensuring precision in tasks requiring delicate manipulation.
The differential value of the proposal lies in the unified integration of complementary technologies and approaches. The system combines, for the first time in this domain, real-time robotic control guided by MR with synchronized multimodal inputs (voice, gestures, and gaze), backed by deep learning algorithms for robust part detection. This convergence of capabilities has allowed simultaneous tackling of the challenges of adaptability, safety, and efficiency in disassembly operations. In contrast to previous solutions, our platform offers a more intuitive and adaptive interaction, bridging the gap between the operator and the robot and maximizing operational efficiency without sacrificing safety. In this way, the work contributes to the state of the art with a holistic solution that addresses both the technical aspects of robot control and the user’s experience during the task.
Furthermore, direct comparison with other approaches was not feasible, as current MR-based systems are mostly oriented towards trajectory planning or simple pick-and-place tasks rather than direct robot control in disassembly operations. This limitation in the literature reinforces the significance of the proposed system, for which usability and cognitive load assessments provided a practical means of benchmarking user performance.
As future lines of research, we propose scaling and adapting this system in new industrial environments and scenarios to validate its performance across a variety of use cases. It will be valuable to explore the system’s adaptability to changes in working conditions, different types of products to be dismantled, or even variations in user abilities, seeking to have the solution adjust quickly without the need for complex reprogramming. Additionally, we suggest investigating extended applications beyond disassembly—for example, implementing this MR interface in collaborative assembly processes, in assisted maintenance operations, or in training environments for operators. These extensions would allow for verification that the observed benefits in terms of efficiency, precision, and user acceptance carry over to other domains. Altogether, future work will aim to consolidate and generalize the proposed solution as a versatile tool for human–robot interaction in a wide range of collaborative industrial applications.