Control Strategies for Two-Wheeled Self-Balancing Robotic Systems: A Comprehensive Review
Abstract
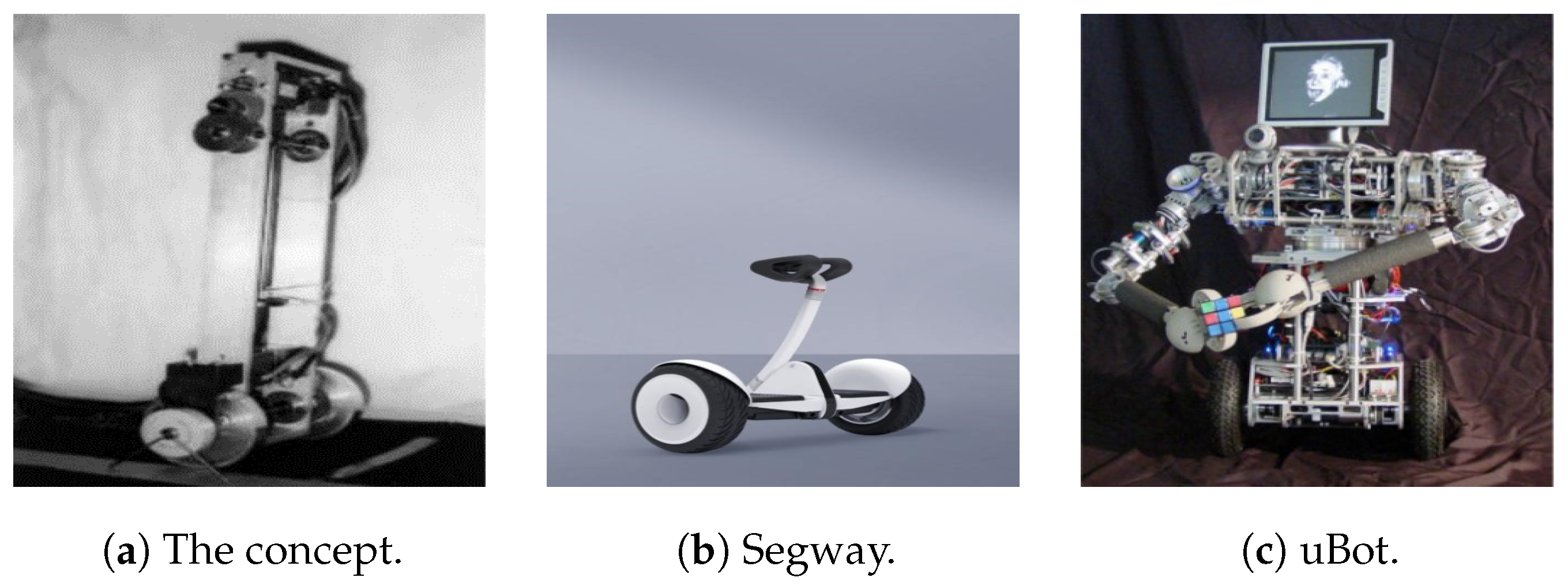
1. Introduction
2. Dynamic Modeling of TWSBRs
2.1. Physics-Based Modeling
2.1.1. Newtonian Mechanics
2.1.2. Lagrangian Mechanics
2.1.3. Kane’s Method
2.2. Linearization and State–Space Representation
2.2.1. Linearization from the Equilibrium Point
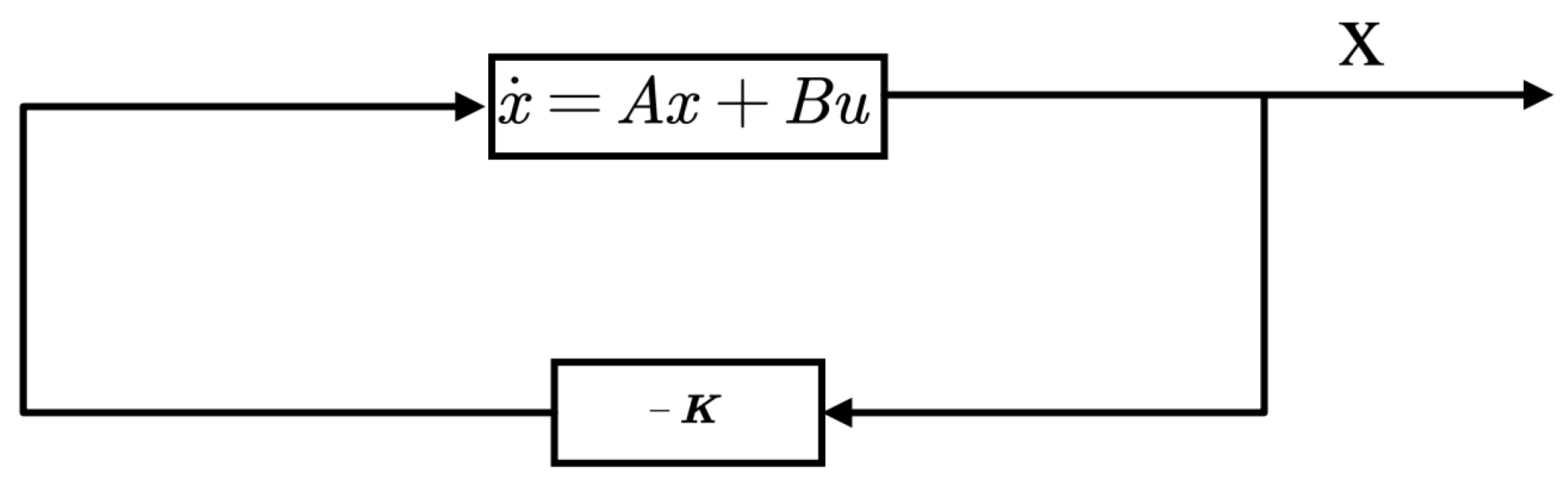
2.2.2. Using State Feedback
2.3. Decoupling Approaches
2.4. Data-Driven Modeling Approaches
2.4.1. Black Box Model
2.4.2. Gray Box Model
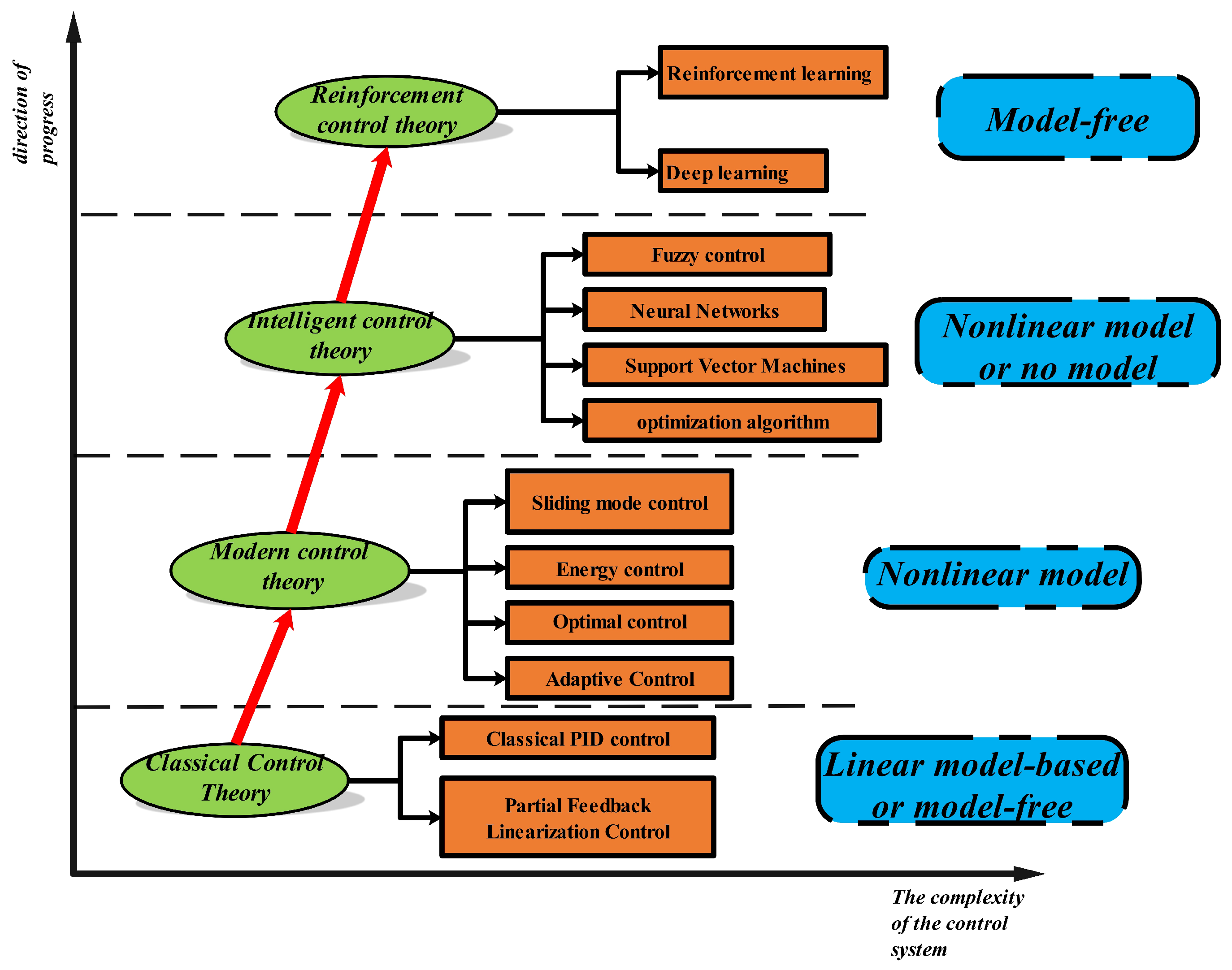
3. Control Methodologies for TWSBRs: An Overview
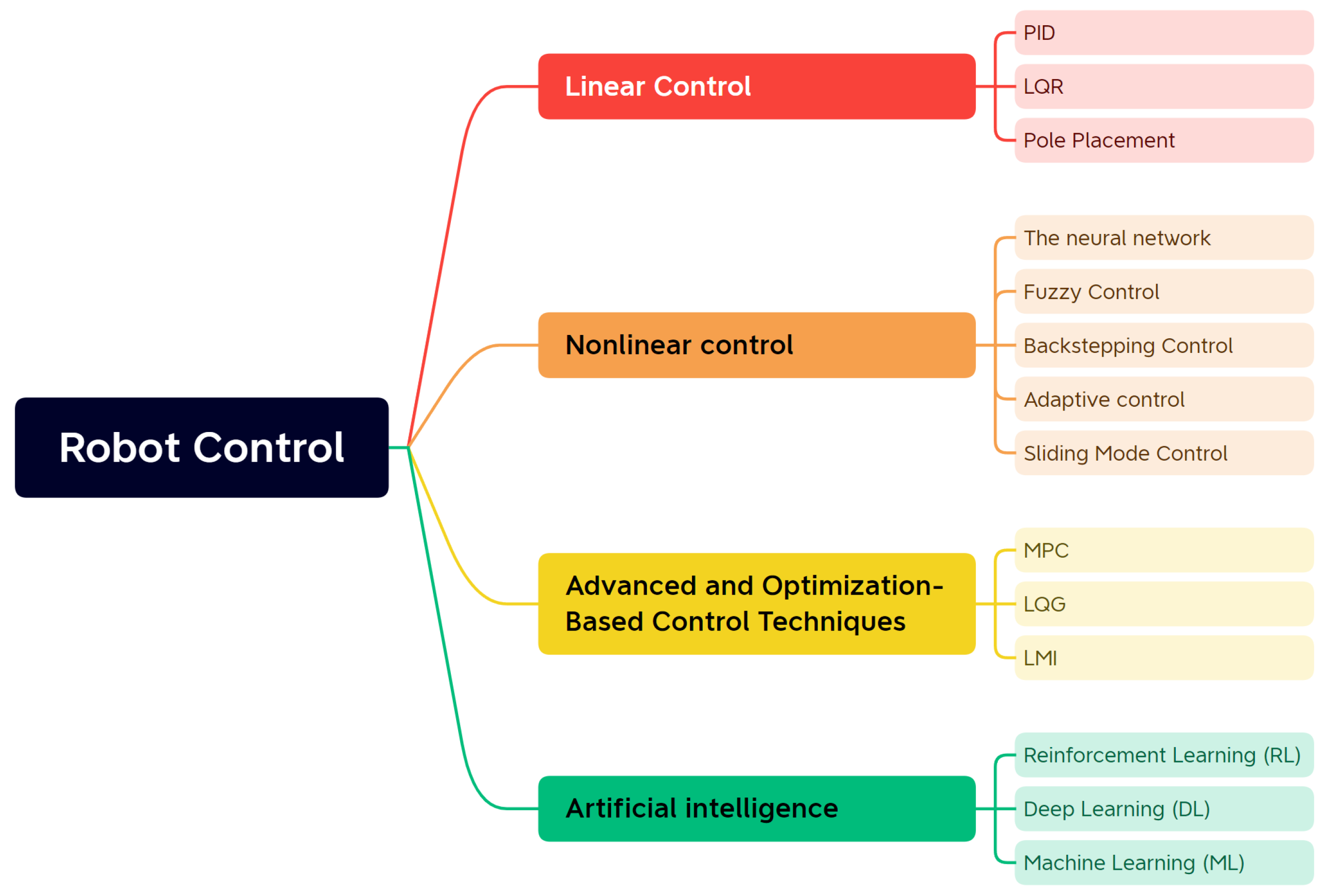
3.1. Linear Control Strategies
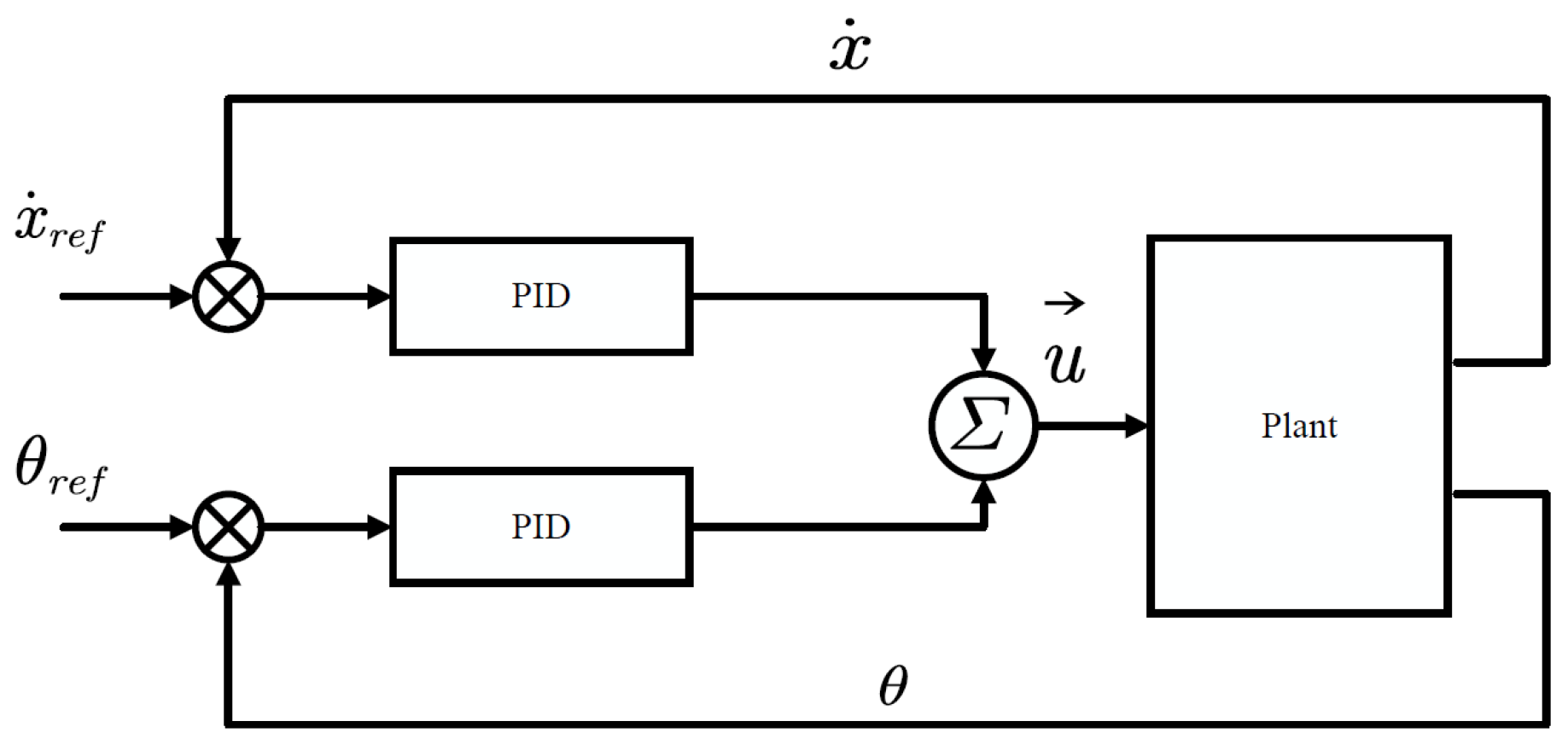
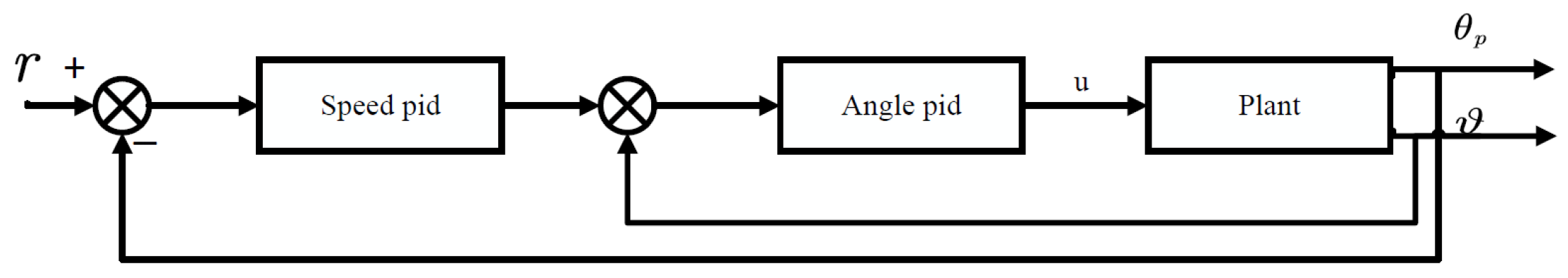
3.1.1. PID Control
3.1.2. LQR Control
3.2. Nonlinear Control Strategies
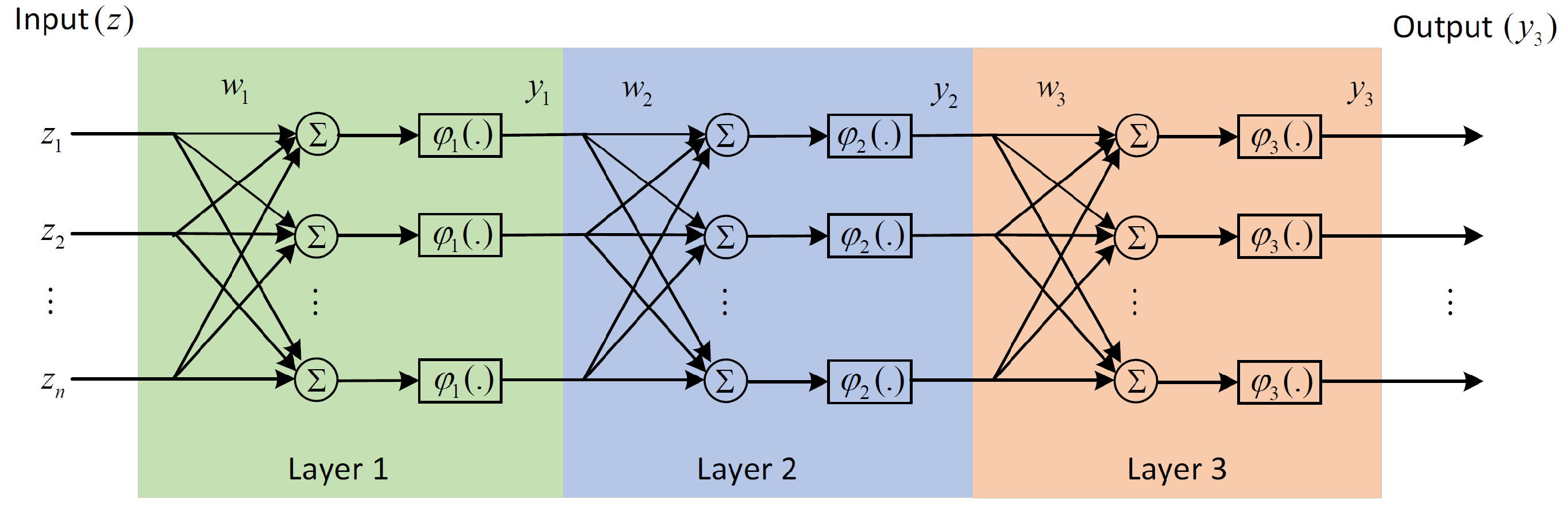
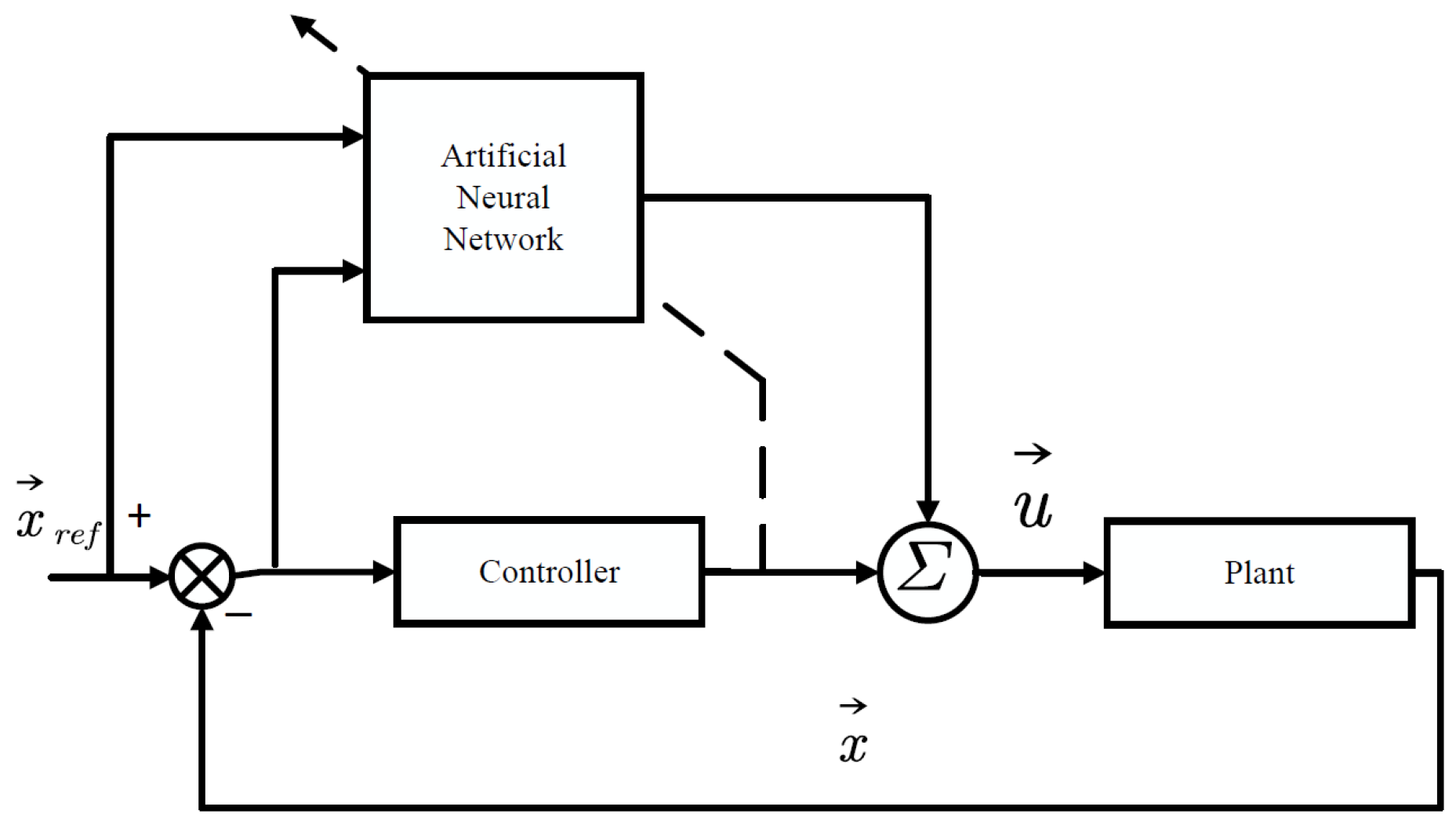
3.2.1. The Neural Network
- Estimating unknown system dynamics or model uncertainties in adaptive or sliding mode control frameworks;
- Learning inverse dynamics or optimal control policies in model-free settings;
- Enhancing trajectory tracking performance and noise robustness in hybrid control strategies.
3.2.2. Fuzzy Control
- The Mamdani-type fuzzy control, one of the earliest proposed methods, handles input and output fuzzification through fuzzy rules and reasoning. In this method, the IF part corresponds to the fuzzy input set, while the THEN part represents the fuzzy output set. Control output is determined through fuzzy logic and defuzzification processes.
- The Takagi–Sugeno-type fuzzy control, based on the Takagi–Sugeno model, is a widely adopted method that uses fuzzy rules and linear functions to describe system behavior. Unlike the Mamdani type, its output is not a fuzzy set but a linear function, enabling more flexible modeling and control of nonlinear systems.
3.2.3. Backstepping Control
3.2.4. Adaptive Control
3.2.5. Sliding Mode Control
- Terminal Sliding Mode Control (TSMC):Introduces nonlinear sliding manifolds to ensure faster convergence near the equilibrium and achieve finite-time stability [92].
- Integral Sliding Mode Control (ISMC):Incorporates integral action in the sliding surface to guarantee zero steady-state error even under system uncertainties [93].
- High-Order Sliding Mode Control (HOSMC):Like the super-twisting algorithm, this achieves chattering-free control by acting on higher derivatives of the sliding variable [94].
3.3. Advanced and Optimization-Based Control Techniques
3.3.1. Model Predictive Control
3.3.2. Linear Quadratic Gaussian Control
3.3.3. Linear Matrix Inequality-Based Control
3.4. Artificial Intelligence
3.4.1. Reinforcement Learning (RL)
3.4.2. Deep Learning (DL)
3.4.3. Machine Learning (ML)
4. Supporting Techniques for Control Implementation
4.1. Differentiator, Filter, and Observer
4.2. Optimization and Multi-Objective Optimization Algorithms
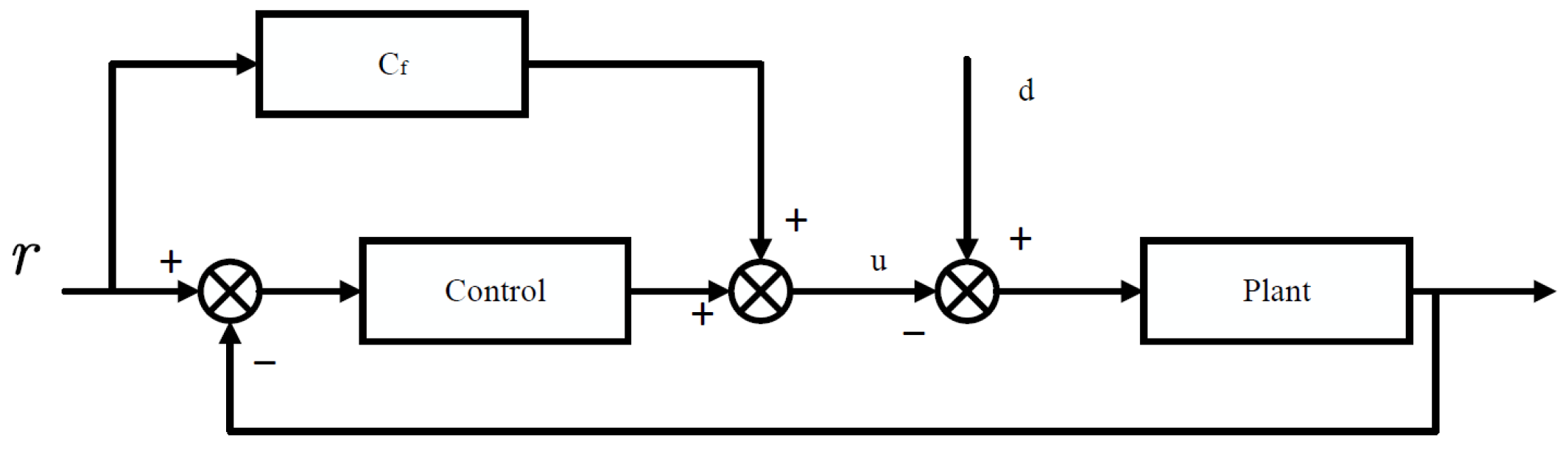
4.3. Feedforward Control Strategies
- Cascaded control structures:In hierarchical or multi-loop frameworks, feedforward components in the inner loop can significantly reduce the control effort required from the outer-loop feedback controller [129].
- Disturbance compensation:When disturbances such as terrain slopes or payload variations can be predicted or measured in advance, feedforward compensation enables preemptive mitigation [6].
5. Comparative Analysis and Discussion
5.1. Advantages and Limitations of Controllers
5.2. Guidelines for Control Method Selection
- System complexity and task objectives: For example, LQR and PID are often sufficient for structured environments and set-point regulation, while MPC and RL may be better suited for dynamic, trajectory-based tasks requiring predictive or adaptive behaviors.
- Computational resources:Methods like PID and SMC are suitable for deployment on low-cost microcontrollers, whereas deep reinforcement learning typically requires high-end computing platforms with GPU acceleration.
- Robustness and adaptability:If robustness to disturbances and model uncertainties is essential, SMC and MPC provide reliable performance, whereas RL and adaptive control can offer flexibility in unstructured environments at the cost of increased complexity.
- Ease of implementation and tuning: Classical methods like PID and SMC are straightforward to implement and tune manually. In contrast, learning-based methods (e.g., RL, DL) may involve intensive training and hyperparameter optimization.
6. Challenges and Future Directions
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 2-DOF | Two Degrees of Freedom |
| A2C | Advantage Actor-Critic |
| ABC | Artificial Bee Colony |
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| ANN | Artificial Neural Network |
| ASMC | Adaptive Sliding Mode Control |
| BPNN | Backpropagation Neural Network |
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Network |
| CSA | Clonal Selection Algorithm |
| DE | Differential Evolution |
| DL | Deep Learning |
| DHTSMC | Dual Hierarchical Terminal Sliding Mode Control |
| DQN | Deep Q-Network |
| FLC | Fuzzy Logic Controller |
| FLQG | Fuzzy Linear Quadratic Gaussian |
| FLQR | Fuzzy Linear Quadratic Regulator |
| FNN | Fuzzy Neural Network |
| FOPID | Fractional-Order Proportional-Integral-Derivative |
| FOSMC | Fractional-Order Sliding Mode Control |
| GA | Genetic Algorithm |
| GT2FLC | General Type-2 Fuzzy Logic Controller |
| H∞ | H-Infinity Control |
| H2 | H2 Performance Index |
| HOSMC | High-Order Sliding Mode Control |
| HSMC | Hierarchical Sliding Mode Control |
| HTSMC | Hierarchical Terminal Sliding Mode Control |
| IT2FLC | Interval Type-2 Fuzzy Logic Controller |
| ITAE | Integral of Time-weighted Absolute Error |
| JS | Jellyfish Search |
| JSO | Jellyfish Search Optimization |
| KF | Kalman Filter |
| LMI | Linear Matrix Inequality |
| LQ | Linear Quadratic |
| LQG | Linear Quadratic Gaussian |
| LQR | Linear Quadratic Regulator |
| MDHTSMC | Modified Dual Hierarchical Terminal Sliding Mode Control |
| MPC | Model Predictive Control |
| MRAC | Model Reference Adaptive Control |
| MSE | Mean Squared Error |
| MTWSBR | Modified Two-Wheeled Self-Balancing Robot |
| MWIP | Moving Wheel Inverted Pendulum |
| NGT2FLC | Non-Singleton General Type-2 FLC |
| NLQG | Nonlinear Linear Quadratic Gaussian |
| NM | Nelder–Mead |
| PD | Proportional-Derivative |
| PD-PI | Proportional-Derivative Proportional-Integral |
| PID | Proportional-Integral-Derivative |
| PO | Peak Overshoot |
| PPO | Proximal Policy Optimization |
| PSO | Particle Swarm Optimization |
| Q-learning | Q-Learning Reinforcement Algorithm |
| ResNet-18 | Residual Neural Network with 18 Layers |
| RBFNN | Radial Basis Function Neural Network |
| RMSE | Root Mean Squared Error |
| SDRE | State-Dependent Riccati Equation |
| SE | Sensed Environment |
| SMC | Sliding Mode Control |
| TSMC | Terminal Sliding Mode Control |
| STSMC | Super-Twisting Sliding Mode Control |
| TWIP | Two-Wheeled Inverted Pendulum |
| TWSBR | Two-Wheeled Self-Balancing Robot |
| VGG16 | Visual Geometry Group 16-layer CNN Model |
| VU-IT1FLC | Variable Universe Interval Type-1 Fuzzy Logic Controller |
| VU-IT2FLC | Variable Universe Interval Type-2 Fuzzy Logic Controller |
References
- Nguyen, V.-T.; Duong, D.-N.; Phan, D.-H.; Bui, T.-L.; HoangVan, X.; Tan, P.-X. Adaptive Nonlinear PD Controller of Two-Wheeled Self-Balancing Robot with External Force. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2024, 81, 2337–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadimitriou, K.D.; Murasovs, N.; Giannaccini, M.E.; Aphale, S.S. Genetic Algorithm-based Control of a Two-Wheeled Self-Balancing Robot. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 2025, 111, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; Li, X. Research on Stability Control System of Two-Wheel Heavy-Load Self-Balancing Vehicles in Complex Terrain. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 7682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elias, G.H.S. Optimal Control for Two-Wheeled Self-Balancing Robot Based on Butterfly Optimization Algorithm. Int. J. Eng. Technol. 2024, 13, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio, F.; Valero, F.; Llopis-Albert, C. A Review of Mobile Robots: Concepts, Methods, Theoretical Framework, and Applications. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2019, 16, 1729881419839596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Mohamad Nor, N.; Umar, S.N.H. Modified Dual Hierarchical Terminal Sliding Mode Control Design for Two-Wheeled Self-Balancing Robot. Electronics 2025, 14, 2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Yao, J.-T.; Wang, Y.-B.; Liu, Z.-S.; Xu, Y.-D.; Zhao, Y.-S. Design and motion analysis of reconfigurable wheel-legged mobile robot. Def. Technol. 2022, 18, 1023–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Guo, J.; Liu, L.; Liu, Y.; Leng, J. Bioinspired multimodal soft robot driven by a single dielectric elastomer actuator and two flexible electroadhesive feet. Extrem. Mech. Lett. 2022, 53, 101720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.B.; Chuthong, T.; Do, C.D.; Thor, M.; Billeschou, P.; Larsen, J.C.; Manoonpong, P. iCrawl: An inchworm-inspired crawling robot. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 200655–200668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Tang, Q.; Sun, T.; Dong, R. Research on stability of the four-wheeled robot for emergency obstacle avoidance on the slope. Recent Patents Eng. 2021, 15, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmez, Y.; Koca, G.O.; Akpolat, Z.H. Clonal selection algorithm based control for two-wheeled self-balancing mobile robot. Simul. Model. Pract. Theory 2022, 118, 102552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ünker, F. Proportional control moment gyroscope for two-wheeled self-balancing robot. J. Vib. Control 2021, 28, 2310–2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voth, D. Segway to the Future [autonomous mobile robot]. IEEE Intell. Syst. 2005, 20, 5–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado-Spíndola, A.; Campa, R.; Bugarin, E.; Soto, I. Design and real-time implementation of a nonlinear regulation controller for the RMP-100 Segway TWIP. Mechatronics 2021, 79, 102668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Cui, X.; Zhu, Y.; Tang, S. A new self-reconfigurable modular robotic system ubot: Multi-mode locomotion and self-reconfiguration. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Shanghai, China, 9–13 May 2011; pp. 1020–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Zhu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Piao, S.; Yang, E. Bio-inspired locomotion control for ubot self-reconfigurable modular robot. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Control, Automation and Diagnosis (ICCAD), Rome, Italy, 10–12 May 2023; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamil, O.; Jamil, M.; Ayaz, Y.; Ahmad, K. Modeling, control of a two-wheeled self-balancing robot. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Robotics and Emerging Allied Technologies in Engineering (iCREATE), Islamabad, Pakistan, 22–24 April 2014; pp. 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juang, H.-S.; Lum, K.-Y. Design and control of a two-wheel self-balancing robot using the arduino microcontroller board. In Proceedings of the 2013 10th IEEE International Conference on Control and Automation (ICCA), Hangzhou, China, 12–14 June 2013; pp. 634–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahler, B.; Haase, J. Mathematical model and control strategy of a two-wheeled self-balancing robot. In Proceedings of the IECON 2013-39th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Vienna, Austria, 10–13 November 2013; pp. 4198–4203. [Google Scholar]
- Uddin, N. Lyapunov-based control system design of two-wheeled robot. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Computer, Control, Informatics and Its Applications (IC3INA), Jakarta, Indonesia, 23–26 October 2017; pp. 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, H. Design of a LEGO NXT two-wheeled self-balanced robot based on inverted pendulum model. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2013, 341–342, 737–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junfeng, W.; Wanying, Z. Research on control method of two-wheeled self-balancing robot. In Proceedings of the 2011 Fourth International Conference on Intelligent Computation Technology and Automation, Shenzhen, China, 28–29 March 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karam, E.H.; Habeeb, R.; Mjeed, N.M. A new approach in design of sliding mode controller by optimization state feedback for two wheeled self balancing robot. Int. J. Open Inf. Technol. 2020, 8, 39–44. [Google Scholar]
- Mudeng, V.; Hassanah, B.; Priyanto, Y.T.K.; Saputra, O. Design and simulation of two-wheeled balancing mobile robot with pid controller. Int. J. Sustain. Transp. Technol. 2020, 3, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goher, K.M.; Tokhi, M.O. A New Configuration of Two-Wheeled Inverted Pendulum: A Lagrangian-Based Mathematical Approach. In Proceedings of the 4th Annual IEEE Systems Conference, San Diego, CA, USA, 5–8 April 2010; pp. 524–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velagić, J.; Kovač, I.; Panjević, A.; Osmanović, A. Design and control of two-wheeled and self-balancing mobile robot. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Symposium ELMAR, Zadar, Croatia, 13–15 September 2021; pp. 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwendi, C.; Alqarni, M.A.; Anajemba, J.H.; Alfakeeh, A.S.; Zhang, Z.; Bashir, A.K. Robust Navigational Control of a Two-Wheeled Self-Balancing Robot in a Sensed Environment. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 82337–82348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanjavur, K.; Rajagopalan, R. Ease of dynamic modelling of wheeled mobile robots (wmrs) using kane’s approach. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Albuquerque, NM, USA, 25 April 1997; Volume 4, pp. 2926–2931. [Google Scholar]
- Jeyed, H.A.; Ghaffari, A. A Nonlinear Optimal Control Based on the SDRE Technique for the Two-Wheeled Self-Balancing Robot. Aust. J. Mech. Eng. 2022, 20, 722–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bature, A.A.; Buyamin, S.; Ahmad, M.N.; Muhammad, M. A comparison of controllers for balancing two wheeled inverted pendulum robot. Int. J. Mech. Mechatronics Eng. 2014, 14, 62–68. [Google Scholar]
- Rigatos, G.; Busawon, K.; Pomares, J.; Abbaszadeh, M. Nonlinear optimal control for the wheeled inverted pendulum system. Robotica 2020, 38, 29–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, K.; Franch, J.; Agrawal, S.K. Velocity and position control of a wheeled inverted pendulum by partial feedback linearization. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2005, 21, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glushchenko, A.; Lastochkin, K.; Petrov, V. Development of two-wheeled balancing robot optimal control system based on its feedback linearization. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Multi-Conference on Industrial Engineering and Modern Technologies (FarEastCon), Vladivostok, Russia, 1–4 October 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chwa, D. Tracking control of differential-drive wheeled mobile robots using a backstepping-like feedback linearization. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern.-Part Syst. Humans 2010, 40, 1285–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.-C.; Chen, Y.-H.; Wang, Z.-J.; Liu, C.-H.; Lin, P.-C.; Yen, J.-Y. Decoupled multi-loop robust control for a walk-assistance robot employing a two-wheeled inverted pendulum. Machines 2021, 9, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, A.R.; Sup, F.C. A robotic walker based on a two-wheeled inverted pendulum. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 2017, 86, 17–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Teng, M. Modeling and decoupling control for two-wheeled self-balancing robot. In Proceedings of the 2016 Chinese Control and Decision Conference (CCDC), Yinchuan, China, 28–30 May 2016; pp. 5263–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Su, S.-F.; Xia, J.; Wu, Y. Adaptive tracking control of wheeled inverted pendulums with periodic disturbances. IEEE Trans. On Cybern. 2018, 50, 1867–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olfati-Saber, R. Normal forms for underactuated mechanical systems with symmetry. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control. 2002, 47, 305–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olfati-Saber, R. Global configuration stabilization for the vtol aircraft with strong input coupling. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control. 2002, 47, 1949–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, M.; Zhang, X.; Chen, D.; Xu, Z. Hierarchical sliding mode control combined with nonlinear disturbance observer for wheeled inverted pendulum robot trajectory tracking. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 4350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, C.-H.; Hung, Y.-T.; Peng, Y.-F. Design of a decoupling fuzzy control scheme for omnidirectional inverted pendulum real-world control. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 26083–26092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Baig, D.E.Z.; Ali, H.; Ashraf, B.; Khan, S.; Wadood, A.; Kamal, T. Efficient system identification of a two-wheeled robot (twr) using feed-forward neural networks. Electronics 2022, 11, 3584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, N. System identification of two-wheeled robot dynamics using neural networks. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2020, 1577, 012034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozek, P.; Karavaev, Y.L.; Ardentov, A.A.; Yefremov, K.S. Neural network control of a wheeled mobile robot based on optimal trajectories. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2020, 17, 1729881420916077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chouhan, A.S.; Parhi, D.R.; Chhotray, A. Control and balancing of two-wheeled mobile robots using sugeno fuzzy logic in the domain of ai techniques. In Emerging Trends in Engineering, Science and Manufacturing (ETESM-2018); Indira Gandhi Institute of Technology, Sarang: Odisha, India, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, G.-R.; Leu, Y.-K.; Huang, H.-T. Pso-based fuzzy control of a self-balancing two-wheeled robot. In Proceedings of the 2017 Joint 17th World Congress of International Fuzzy Systems Association and 9th International Conference on Soft Computing and Intelligent Systems (IFSA-SCIS), Otsu, Japan, 27–30 June 2017; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moness, M.; Mahmoud, D.; Hussein, A. Real-time mamdani-like fuzzy and fusion-based fuzzy controllers for balancing two-wheeled inverted pendulum. J. Ambient. Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2020, 13, 3577–3593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.-X.; Guo, Z.-Q.; Lee, T.H. Design and implementation of a takagi–sugeno-type fuzzy logic controller on a two-wheeled mobile robot. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2012, 60, 5717–5728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gad, O.M.M.; Saleh, S.Z.M.; Bulbul, M.A.; Khadraoui, S. Design and control of two wheeled self balancing robot (twsbr). In Proceedings of the 2022 Advances in Science and Engineering Technology International Conferences (ASET), Dubai, United Arab Emirates, 21–24 February 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulescu, F.-C.; Szeidert, I.; Filip, I.; Vasar, C. Two-wheeled self-balancing robot. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 15th International Symposium on Applied Computational Intelligence and Informatics (SACI), Timisoara, Romania, 19–21 May 2021; pp. 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikita, T.; Prajwal, K. Pid controller based two wheeled self balancing robot. In Proceedings of the 2021 5th International Conference on Trends in Electronics and Informatics (ICOEI), Tirunelveli, India, 3–5 June 2021; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.; Padhy, P. Design and tuning of pi λ d μ controller for higher order process using pso-nm. In Proceedings of the 2017 Innovations in Power and Advanced Computing Technologies (i-PACT), Vellore, India, 21–22 April 2017; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhao, T.; Guo, B.; Dian, S. Fuzzy fractional-order pid control for two-wheeled self-balancing robots on inclined road surface. Syst. Sci. Control. Eng. 2022, 10, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azar, A.T.; Ammar, H.H.; Barakat, M.H.; Saleh, M.A.; Abdelwahed, M.A. Self-balancing robot modeling and control using two degree of freedom pid controller. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Systems and Informatics 2018; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 64–76. [Google Scholar]
- Peash, S.M.; Das, P.; Ghosh, A.; Islam, N.; Tanjid, A.; Oaishi, H.P.; Paul, B.; Islam, M.M. A smart approach to control a two-wheeled self balancing robot using a pid controller with two degree of freedom. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Mechanical, Industrial and Materials Engineering 2022 (ICMIME2022), Rajshahi, Bangladesh, 20–22 December 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Thwin, L.M.M.; Chan, Y. Application of lqr control for two-wheel self-balancing robot. J. Myanmar Acad. Arts Sci. 2020, 28, 263–272. [Google Scholar]
- Borja, J.; Alvarado, I.; de la Peña, D.M. Low cost two-wheels self-balancing robot for control education powered by stepper motors. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2020, 53, 17518–17523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petcu, R.; Andreescu, G.-D. Two-wheeled inverted-pendulum self-balancing robot with lqr or pid control. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 10th Jubilee International Conference on Computational Cybernetics and Cyber-Medical Systems (ICCC), Reykjavík, Iceland, 6–9 July 2022; pp. 000345–000350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthika, B.; Jisha, V. Nonlinear optimal control of a two wheeled self balancing robot. In Proceedings of the 2020 5th IEEE International Conference on Recent Advances and Innovations in Engineering (ICRAIE), Jaipur, India, 1–3 December 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandarilla, I.; Montoya-Cháirez, J.; Santibáñez, V.; Aguilar-Avelar, C. Moreno-Valenzuela, J. Trajectory tracking control of a self-balancing robot via adaptive neural networks. Eng. Technol. Int. J. 2022, 35, 101259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nghia, V.B.V.; Thien, T.V.; Son, N.N.; Long, M.T. Adaptive neural sliding mode control for two wheel self balancing robot. Int. J. Dyn. Control. 2022, 10, 771–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.-M.; Van-Tiem, N.; Nguyen, T.-T. A neural network combined with sliding mode controller for the two-wheel self-balancing robot. IAES Int. J. Artif. Intell. 2021, 10, 592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maity, A.; Bhargava, S. Design and implementation of a self-balancing two-wheeled robot driven by a feed-forward backpropagation neural network. Int. Res. J. Eng. Technol. 2020, 7, 3876–3881. [Google Scholar]
- Rachmawati, I.D.; Rusimamto, P.W. Perancangan dan implementasi fuzzy logic control untuk pengaturan kestabilan gerak pada two wheels self balancing. J. Tek. Elektro 2020, 9, 717–723. [Google Scholar]
- Mai, T.A.; Anisimov, D.; Dang, T.S.; Dinh, V.N. Development of a microcontroller-based adaptive fuzzy controller for a two-wheeled self-balancing robot. Microsyst. Technol. 2018, 24, 3677–3687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, T.A.; Dang, T.S.; Anisimov, D.; Fedorova, E. Fuzzy-pid controller for two wheels balancing robot based on stm32 microcontroller. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Engineering Technologies and Computer Science (EnT), Moscow, Russia, 26–27 March 2019; pp. 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathoni, K.; Pratama, A.P.; Salim, N.A.; Sulistyawan, V.N. Implementasi kendali keseimbangan gerak two wheels self balancing robot menggunakan fuzzy logic. J. Tek. Elektro 2021, 13, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatti, O.S.; Rizwan, M.; Shiokolas, P.S.; Ali, B. Genetically optimized anfis-based pid controller design for posture-stabilization of self-balancing-robots under depleting battery conditions. J. Control Eng. Appl. Inform. 2019, 21, 22–33. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, B.; Xu, S.; Zhao, G. Variable universe type-ii fuzzy logic control design for the googol’s two-wheeled self-balancing robot. In Proceedings of the 2020 Chinese Automation Congress (CAC), Shanghai, China, 6–8 November 2020; pp. 1500–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Yu, Q.; Dian, S.; Guo, R.; Li, S. Non-singleton general type-2 fuzzy control for a two-wheeled self-balancing robot. Int. Fuzzy Syst. 2019, 21, 1724–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binh, N.T.; Tung, N.A.; Nam, D.P.; Quang, N.H. An adaptive backstepping trajectory tracking control of a tractor trailer wheeled mobile robot. Int. J. Control. Autom. Syst. 2019, 17, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadi, N.H.; Younus, K.K. Path tracking and backstepping control for a wheeled mobile robot (wmr) in a slipping environment. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2020; Volume 671, p. 012005. [Google Scholar]
- Tsai, C.-C.; Ju, S.-Y.; Hsieh, S.-M. Trajectory tracking of a self-balancing two-wheeled robot using backstepping sliding-mode control and fuzzy basis function networks. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Taipei, Taiwan, 18–22 October 2010; pp. 3943–3948. [Google Scholar]
- Thao, N.G.M.; Dat, M.T.; Nghia, D.H.; Phuc, N.H. Nonlinear controllers for two-wheeled self-balancing robot. In Proceedings of the ASEAN Symposium on Automatic Control 2011 (ASAC 2011), Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam, 8–9 November 2011; pp. 8–13. [Google Scholar]
- Ruan, X.; Cai, J. Fuzzy backstepping controllers for two-wheeled self-balancing robot. In Proceedings of the 2009 International Asia Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics, Bangkok, Thailand, 1–2 February 2009; pp. 166–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.-C.; Li, Y.-X.; Tai, F.-C. Backstepping sliding-mode leader-follower consensus formation control of uncertain networked heterogeneous nonholonomic wheeled mobile multirobots. In Proceedings of the 2017 56th Annual Conference of the Society of Instrument and Control Engineers of Japan (SICE), Kanazawa, Japan, 19–22 September 2017; pp. 1407–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, E.; Rehman, A.u.; Khan, O.; Haseeb, M.; Ali, N. Backstepping control design for two-wheeled self balancing robot. In Proceedings of the 2018 1st International Conference on Power, Energy and Smart Grid (ICPESG), Mirpur Azad Kashmir, Pakistan, 9–10 April 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.-X.; He, N.; He, L. Adaptive double fuzzy anti-integral saturation pid control for self-balancing robot with reaction wheel. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 17th International Conference on Control & Automation (ICCA), Naples, Italy, 27–30 June 2022; pp. 56–61. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, B.; Bang, R. A PD Sliding Mode Controller for Two-Wheeled Self-Balancing Robot. J. Sci. Technol.-Tech. Univ. 2011, 83B, 60–66. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, J.; Ding, J.; Tai, Y.; Ma, Z. Control of different-axis two-wheeled self-balancing vehicles. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 158839–158851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Zhao, H.; He, C. Nash game-based adaptive robust control design optimization for the underactuated mechanical system with fuzzy evidence theory. Optim. Control. Appl. Methods 2023, 44, 1251–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Wang, T.; Zhang, K.; Yao, C.; Wang, Z. Adaptive nonlinear control algorithm for a self-balancing robot. IEEE Access 2019, 8, 3751–3760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wang, H.; Huang, Y.; Ping, Z.; Yu, M.; Zheng, X.; Ye, M.; Hu, Y. Robust hierarchical sliding mode control of a two-wheeled self-balancing vehicle using perturbation estimation. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2020, 139, 106584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.-C.; Tsai, C.-C.; Huang, H.-C. Nonlinear adaptive sliding-mode control design for two-wheeled human transportation vehicle. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man and Cybernetics, San Antonio, TX, USA, 11–14 October 2009; pp. 1965–1970. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, H.; Liu, M.; Hu, C.; Zhang, F. Adaptive sliding mode attitude control of two-wheel mobile robot with an integrated learning-based rbfnn approach. Neural Comput. Appl. 2022, 34, 14959–14969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Guo, L.; Xing, B. Cascade sliding mode and rbf network self-adaption controller design for a two-wheeled robot. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Information and Automation (ICIA), Ningbo, China, 1–3 August 2016; pp. 1659–1663. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, M.; Wei, X.; Li, Z. Adaptive sliding-mode control for two-wheeled inverted pendulum vehicle based on zero-dynamics theory. Nonlinear Dyn. 2014, 76, 459–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trentin, J.F.S.; Santos, D.A. Predefined-time global sliding mode control design for a 3d pendulum. Nonlinear Dyn. 2022, 109, 1693–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arani, M.S.; Orimi, H.E.; Xie, W.-F.; Hong, H. Sliding mode control design of a two-wheel inverted pendulum robot: Simulation, design and experiments. In Advances in Motion Sensing and Control for Robotic Applications: Selected Papers from the Symposium on Mechatronics, Robotics, and Control (SMRC’18)-CSME International Congress 2018, Toronto, Canada, 27–30 May 2018; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 93–107. [Google Scholar]
- Ghahremani, A.; Khalaji, A.K. Simultaneous regulation and velocity tracking control of a two-wheeled self-balancing robot. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Control, Automation and Diagnosis (ICCAD), Rome, Italy, 10–12 May 2023; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Irfan, S.; Mehmood, A.; Razzaq, M.T.; Iqbal, J. Advanced sliding mode control techniques for inverted pendulum: Modelling and simulation. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2018, 21, 753–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.-X.; Guo, Z.-Q.; Lee, T.H. Design and implementation of integral sliding-mode control on an underactuated two-wheeled mobile robot. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2013, 61, 3671–3681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Zhang, M.; Ri, S.; Xiong, C.; Li, Z.; Kang, Y. High-order disturbance-observer-based sliding mode control for mobile wheeled inverted pendulum systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 67, 2030–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yetayew, T.T.; Tesfaye, D.G. Genetic algorithm tuned super twisted sliding mode controller (stsmc) for self-balancing control of a two-wheel electric scooter. In Advances of Science and Technology: 9th EAI International Conference, ICAST 2021, Hybrid Event, Bahir Dar, Ethiopia, 27–29 August 2021; Proceedings, Part I; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 269–287. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, H.; Fang, Q.; Zhong, J.; Shao, Z.P. Time-delayed fractional order adaptive sliding mode control for two-wheel self-balancing vehicles. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2020, 2020, 4529131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, N.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, X. Hierarchical fast terminal sliding mode control for a self-balancing two-wheeled robot on uneven terrains. In Proceedings of the 2017 36th Chinese Control Conference (CCC), Dalian, China, 26–28 July 2017; pp. 4762–4767. [Google Scholar]
- Hazem, Z.B.; Fotuhi, M.J.; Bingül, Z. Development of a fuzzy-lqr and fuzzy-lqg stability control for a double link rotary inverted pendulum. J. Frankl. Inst. 2020, 357, 10529–10556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatoon, S.; Chaturvedi, D.K.; Hasan, N.; Istiyaque, M. Optimal controller design for two wheel mobile robot. In Proceedings of the 2018 3rd International Innovative Applications of Computational Intelligence on Power, Energy and Controls with Their Impact on Humanity (CIPECH), Ghaziabad, India, 1–2 November 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azimi, M.M.; Koofigar, H.R. Model predictive control for a two wheeled self balancing robot. In Proceedings of the 2013 First RSI/ISM International Conference on Robotics and Mechatronics (ICRoM), Tehran, Iran, 13–15 February 2013; pp. 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zad, H.S.; Ulasyar, A.; Zohaib, A.; Hussain, S.S. Optimal controller design for self-balancing two-wheeled robot system. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Frontiers of Information Technology (FIT), Islamabad, Pakistan, 19–21 December 2016; pp. 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, I.K.; Noaman, M.N. Optimal control approach for robot system using lqg technique. J. Eur. Des Syst. Autom. 2022, 55, 671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengupta, I.; Gupta, S.; Deb, D.; Ozana, S. Dynamic stability of an electric monowheel system using lqg-based adaptive control. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 9766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahir, N.M.; Muhammad, M.; Idi, M.; Buyamin, S.; Maijama’a, L.; Yarima, S.I.M. Comparative analysis of observer-based lqr and lmi controllers of an inverted pendulum. Bull. Electr. Eng. Inform. 2020, 9, 2244–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, M.; Tochigi, H.; Njeri, W.; Hayashi, H.; Muguro, J.; Matsushita, K.; Ngetha, H. Robust posture tracking control of stable coaxial two-wheeled agv using the approximate inverse system and LMI. J. Appl. Sci. Eng. Technol. Dev. 2020, 6, 24–42. [Google Scholar]
- He, T.; Chen, X.; Zhu, G.G. A dual-loop robust control scheme with performance separation: Theory and experimental validation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2022, 69, 13483–13493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Rizvi, S.A.A.; Lin, Z. Optimal control of a two-wheeled self-balancing robot by reinforcement learning. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control. 2021, 31, 1885–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinaei, K.; Yazdi, M. Pid controller tuning with deep reinforcement learning policy gradient methods. In Proceedings of the 29th Intermational Conference of Iranian Society of Mechanical Engineers & 8th Conference on Thermal Power Plants, Tehran, Iran, 25–27 May 2021; pp. 25–27. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.-H.G.; Zhou, L.-P. Training end-to-end steering of a self-balancing mobile robot based on rgb-d image and deep convNet. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/ASME International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics (AIM), Boston, MA, USA, 6–9 July 2020; pp. 898–903. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.-H.G.; Zhou, L.-P.; Chao, Y.-H. Self-balancing two-wheeled robot featuring intelligent end-to-end deep visual-steering. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatronics 2020, 26, 2263–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kötz, L.; Almgren, J. Control and Camera-Based State Estimation Using Machine Vision and Machine Learning—A Comparison Study in IMU-Replacing Neural Networks on a Wheeled Inverted Pendulum System. Master’s Thesis, Chalmers University of Technology, Gothenburg, Sweden, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Unluturk, A.; Aydogdu, O. Machine learning based self-balancing and motion control of the underactuated mobile inverted pendulum with variable load. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 104706–104718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna, G.S.; Sumith, D.; Akshay, G. Epersist: A two-wheeled self balancing robot using pid controller and deep reinforcement learning. In Proceedings of the 2022 22nd International Conference on Control, Automation and Systems (ICCAS), Jeju, Republic of Korea, 27 November–1 December 2022; pp. 1488–1492. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, Q.; Wu, J.; Wang, Z. Dynamic balance control of two-wheeled self-balancing pendulum robot based on adaptive machine learning. Int. J. Wavelets Multiresolut. Inf. Process. 2020, 18, 1941002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.-F.; Su, C.-T.; Kao, W.-F.; Lee, B.-K. Vision-based line-following control of a two-wheel self-balancing robot. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Machine Learning and Cybernetics (ICMLC), Chengdu, China, 15–18 July 2018; Volume 1, pp. 319–324. [Google Scholar]
- Ataç, E.; Yıldız, K.; Ülkü, E.E. Use of pid control during education in reinforcement learning on two wheel balance robot. Gazi Univ. J. Sci. Part C Des. Technol. 2021, 9, 597–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Rashid, S.H.; Hossain, M. Implementation of q learning and deep q network for controlling a self balancing robot model. Robot. Biomimetics 2018, 5, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farias, G.; Garcia, G.; Montenegro, G.; Fabregas, E.; Dormido-Canto, S.; Dormido, S. Reinforcement learning for position control problem of a mobile robot. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 152941–152951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Deng, Y.; Zheng, X.; Zheng, Q.; Liang, B.; Liu, Y. Online reinforcement-learning-based adaptive terminal sliding mode control for disturbed bicycle robots on a curved pavement. Electronics 2022, 11, 3495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srichandan, A.; Dhingra, J.; Hota, M.K. An improved q-learning approach with kalman filter for self-balancing robot using openai. J. Control Autom. Electr. Syst. 2021, 32, 1521–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jmel, I.; Dimassi, H.; Hadj Said, S.; M’Sahli, F. Adaptive observer-based output feedback control for two-wheeled self-balancing robot. Math. Probl. Eng. 2020, 2020, 5162172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jmel, I.; Dimassi, H.; Hadj-Said, S.; M’Sahli, F. Adaptive observer-based sliding mode control for a two-wheeled self-balancing robot under terrain inclination and disturbances. Math. Probl. Eng. 2021, 2021, 8853441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jmel, I.; Dimassi, H.; Hadj-Said, S.; Msahli, F. An adaptive observer for two wheeled self-balancing robot with a varying center of mass. In Proceedings of the 2019 19th International Conference on Sciences and Techniques of Automatic Control and Computer Engineering (STA), Sousse, Tunisia, 24–26 March 2019; pp. 467–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faheem, F.; Anwaar, H.; Zahid, S.; Waseem, H.; Gondal, R.M.; Sarfraz, M. Fractional order controller design for self-balancing two-wheeled robot and performance comparison using different optimization techniques. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Electrical Engineering and Sustainable Technologies (ICEEST), Lahore, Pakistan, 14–15 December 2022; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kien, V.N.; Duy, N.T.; Du, D.H.; Huy, N.P.; Quang, N.H. Robust optimal controller for two-wheel self-balancing vehicles using particle swarm optimization. Int. J. Mech. Eng. Robot. Res. 2023, 12, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jithendra, R.; Mija, S. Pso-super twisting smc for balancing the twip using lego ev3 model. In Proceedings of the 2023 4th International Conference for Emerging Technology (INCET), Belgaum, India, 26–28 May 2023; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohsin, H.H.; Aldair, A.A.; Al-Hussaibi, W.A. Optimal proportional integral derivative controller for two-wheeled self-balanced mobile robots based on particle swarm algorithm. Univ. Thi-Qar J. Eng. Sci. 2022, 12, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Pang, H.; Liu, L.; Zheng, L.; Wang, L.; Liu, M. A RISE-based asymptotic prescribed performance trajectory tracking control of two-wheeled self-balancing mobile robot. Nonlinear Dyn. 2024, 112, 15327–15348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alayasrah, M.M.; Al-Qaisi, A.; Sharkas, M. Dual Loop Control for a Two-Wheeled Balancing Robot. In Proceedings of the 2005 International Conference on Mechatronics, Istanbul, Turkey, 20–23 September 2005; pp. 237–242. [Google Scholar]
- Ruan, X.; Chen, J. On-line NNAC for two-wheeled self-balancing robot based on feedback-error-learning. In Proceedings of the 2010 2nd International Workshop on Intelligent Systems and Applications (ISA), Wuhan, China, 22–23 May 2010; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Li, J.; Zhou, J. Research on two-round self-balancing robot slam based on the gmapping algorithm. Sensors 2023, 23, 2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

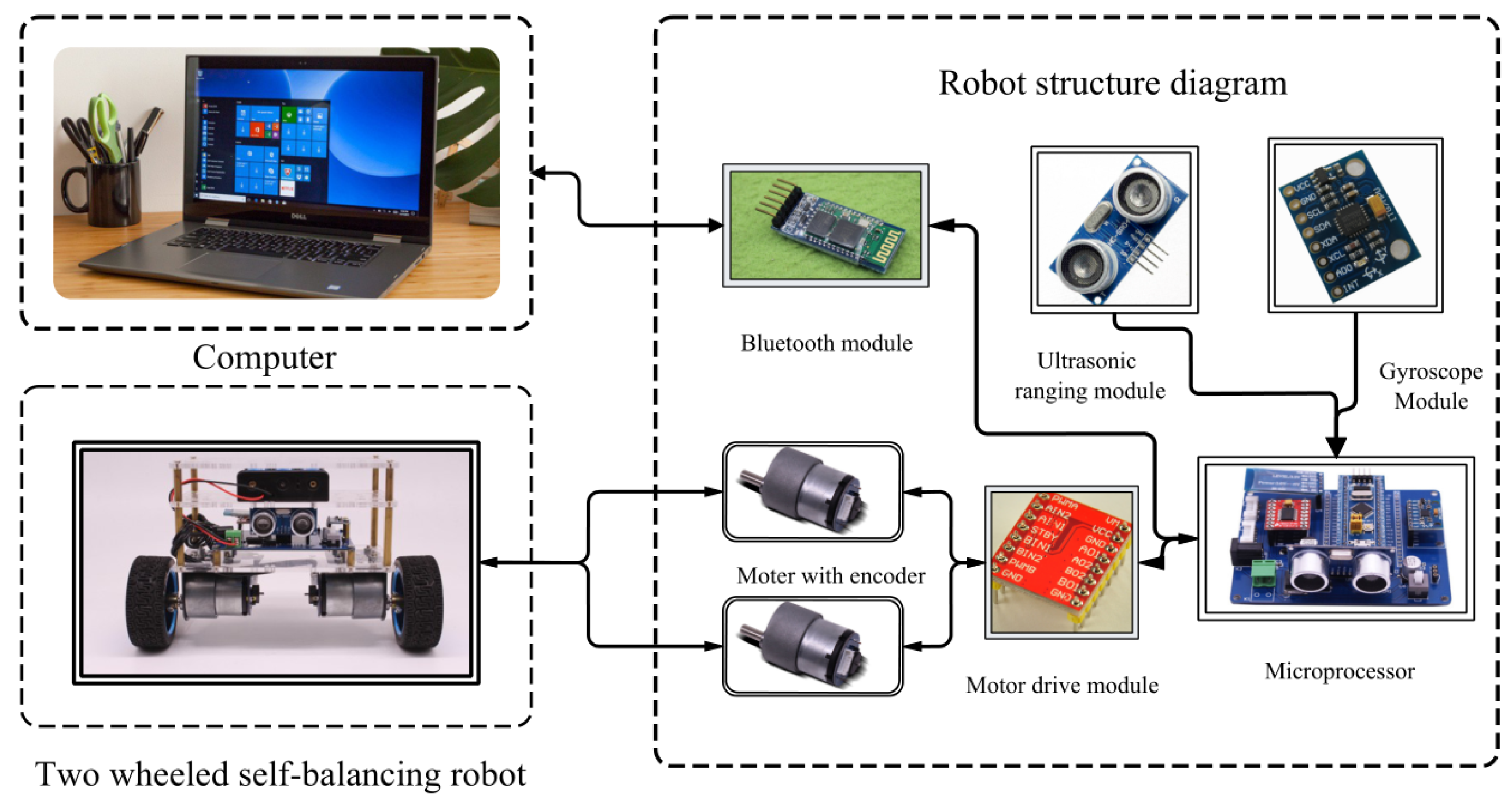
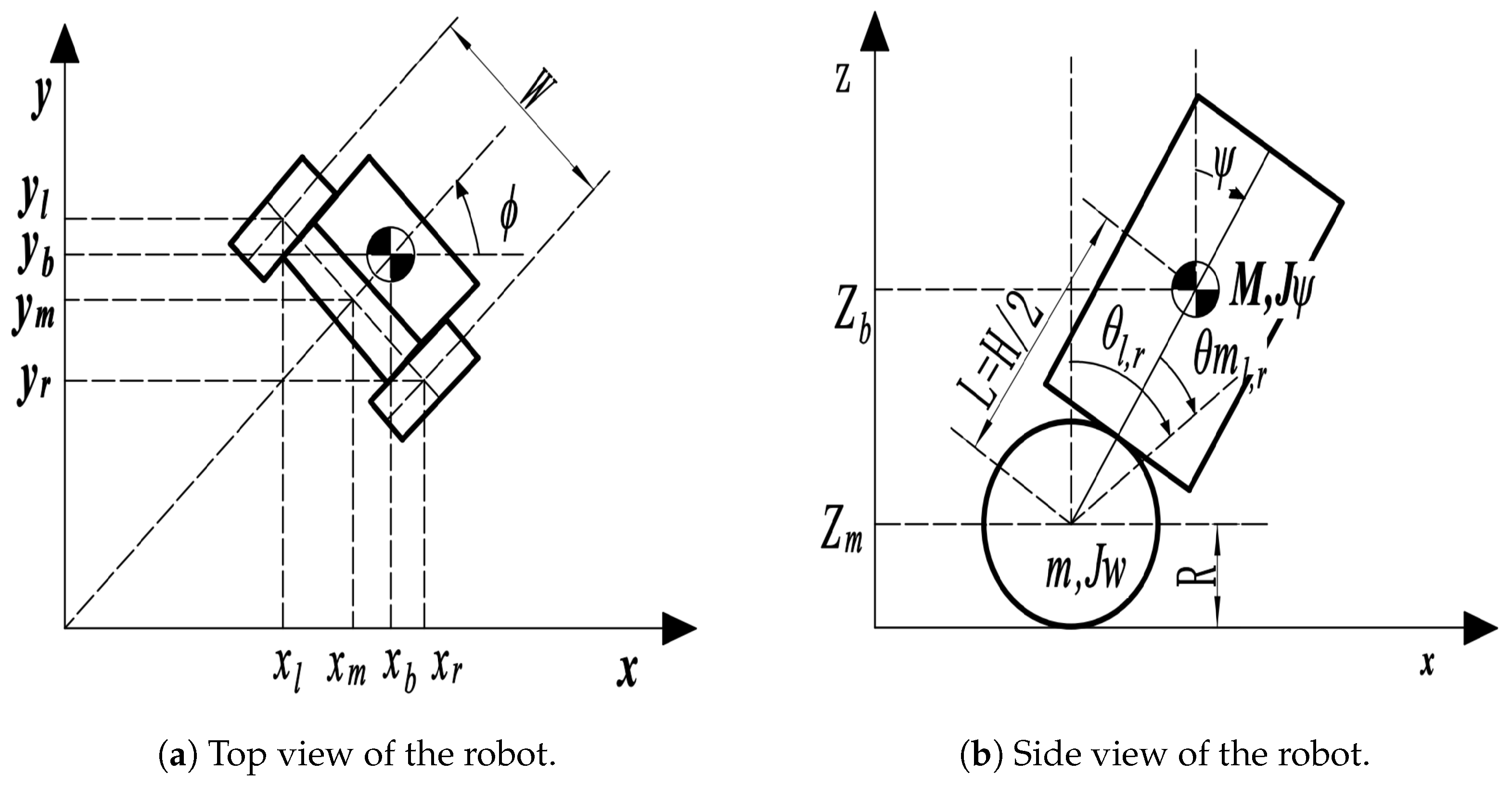
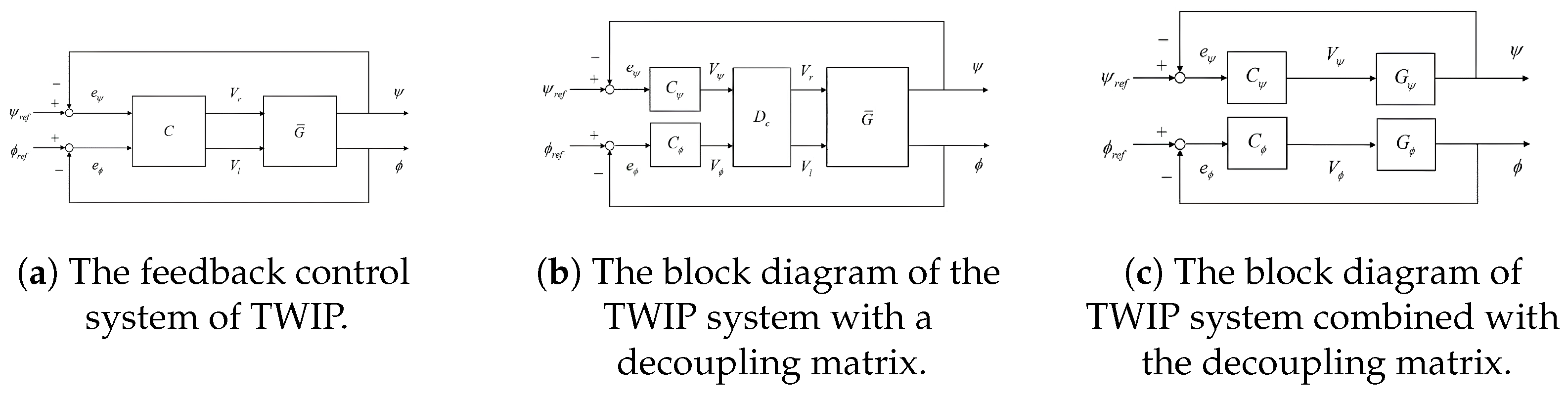
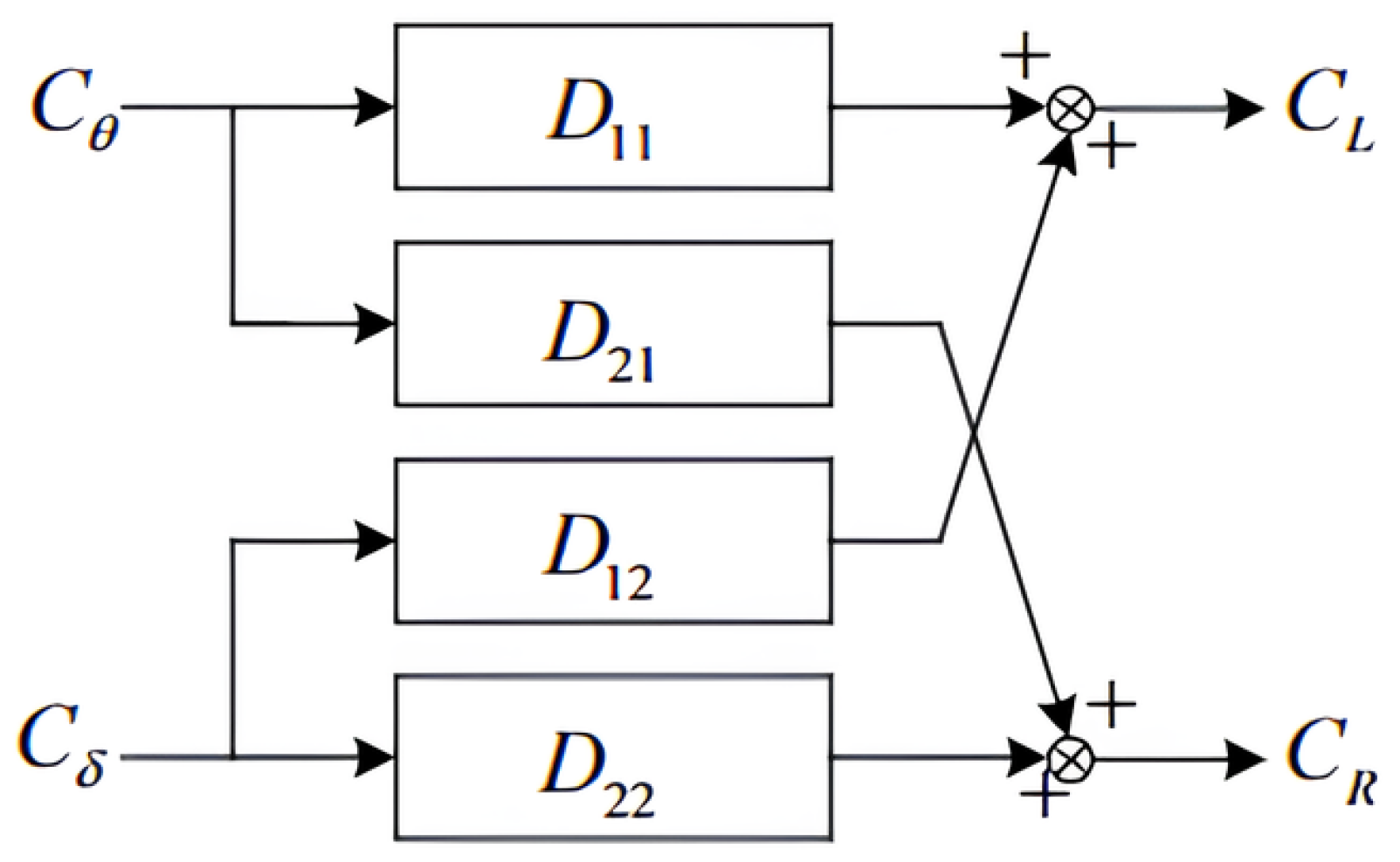
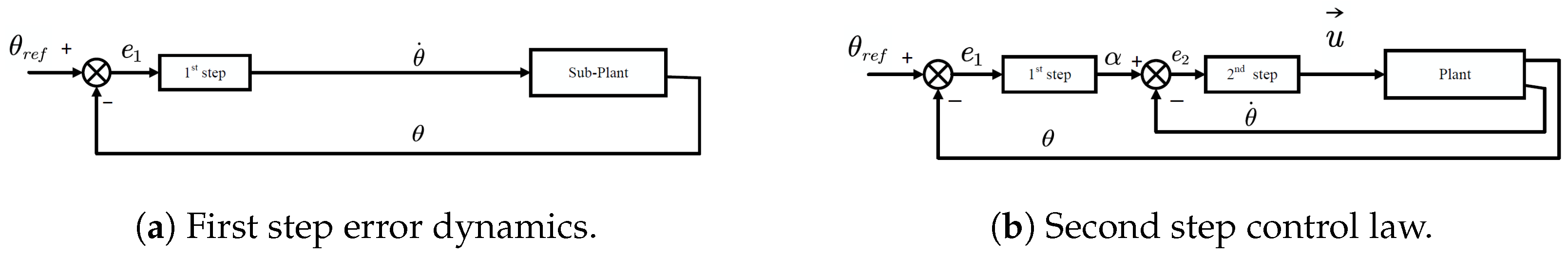
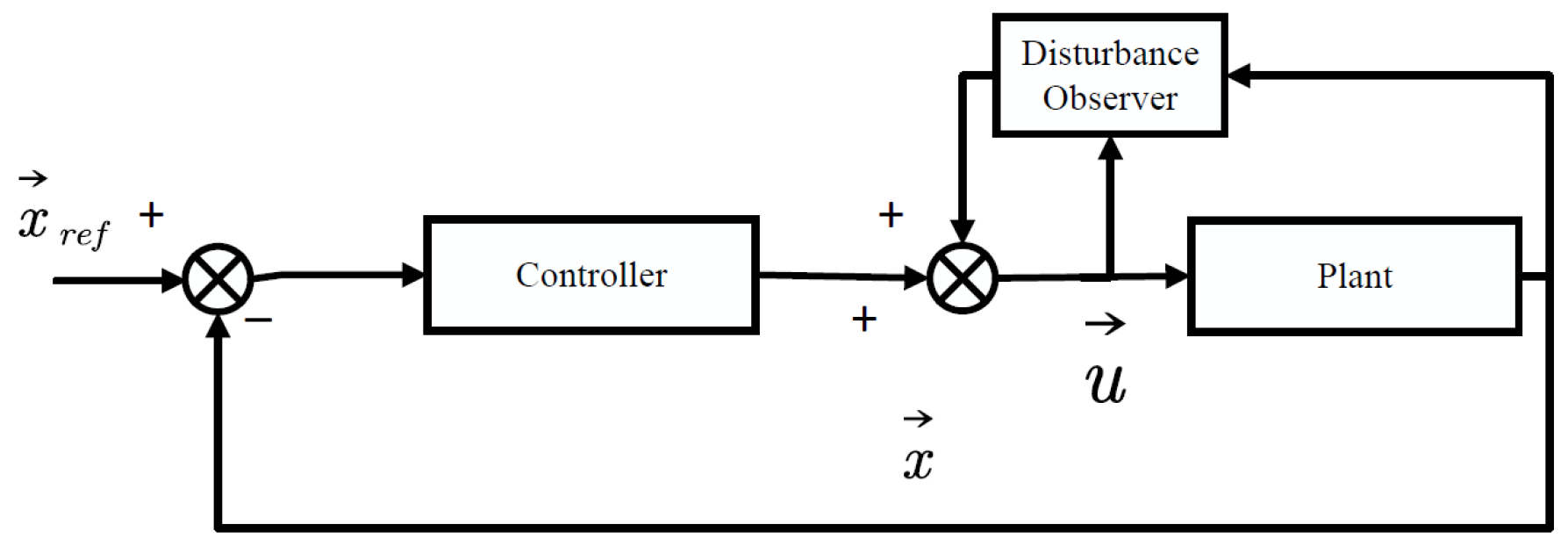
| No. | Authors | Year | Method | Input | Output | Adapt. Param. | Remarks/HW |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Zheng et al. [82] | 2023 | Nash game | No HW; compensates system uncertainty | |||
| 2 | Su et al. [83] | 2019 | Adapt. control | NVIDIA TX2; handles CG shifts | |||
| 3 | Chen et al. [84] | 2020 | HSMC | MCU; PE-based disturbance rejection | |||
| 4 | Lin et al. [85] | 2009 | HSMC | DSP-TMS320; PE technique used | |||
| 5 | Pang et al. [86] | 2022 | MPLM + RBFNN | u | No HW; reduces dithering, improves accuracy | ||
| 6 | Song et al. [87] | 2018 | Cascade SMC + RBF | No HW; RBF for model uncertainties | |||
| 7 | Yue et al. [88] | 2014 | SMC | No HW; online mechanical parameter tuning |
| No. | Authors | Year | Learning Architecture | Hardware | Platform | Remarks | Key Feature |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reinforcement Learning (RL) | |||||||
| 1 | Emrah et al. [116] | 2021 | Q-learning | STM32F4 | No | Training time reduced by 60% | Efficient convergence |
| 2 | Rahman et al. [117] | 2018 | DQN | No | No | Requires hyperparameter tuning | Deep RL implementation |
| 3 | Guo et al. [107] | 2021 | Q-learning | No | No | Feedback RL solving LQR | RL-based optimal control |
| 4 | Farias et al. [118] | 2020 | Q-learning | No | No | Improved with more iterations | Iterative policy refinement |
| 5 | Sinaei et al. [108] | 2021 | A2C, PPO | No | No | Automatic tuning of PID | Model-free PID tuning |
| 6 | Zhu et al. [119] | 2022 | PPO | No | No | Online TSMC tuning via GD | RL-tuned sliding mode |
| 7 | Srichandan et al. [120] | 2021 | Q-learning + KF | No | No | Kalman filter improves estimation | State estimation enhancement |
| Deep Learning (DL) | |||||||
| 8 | Li et al. [109] | 2020 | CNN | No | i7-7700HQ, GTX1050 | RGB-D environment understanding | Visual perception |
| 9 | Li et al. [110] | 2020 | ResNet-18 | Arduino Uno | i7-7700HQ, GTX1050 | Depth image based ConvNet for steering | Image-based control |
| 10 | Kotz et al. [111] | 2023 | VGG16, MobileNetV2 | Raspberry Pi 3 | RTX A2000 | State estimation via vision+RL | Vision-integrated RL |
| Machine Learning (ML) | |||||||
| 11 | Unluturk et al. [112] | 2022 | ANN | STM32F103C8T6 | No | Lean angle improvement up to 55% | ANN-based stabilization |
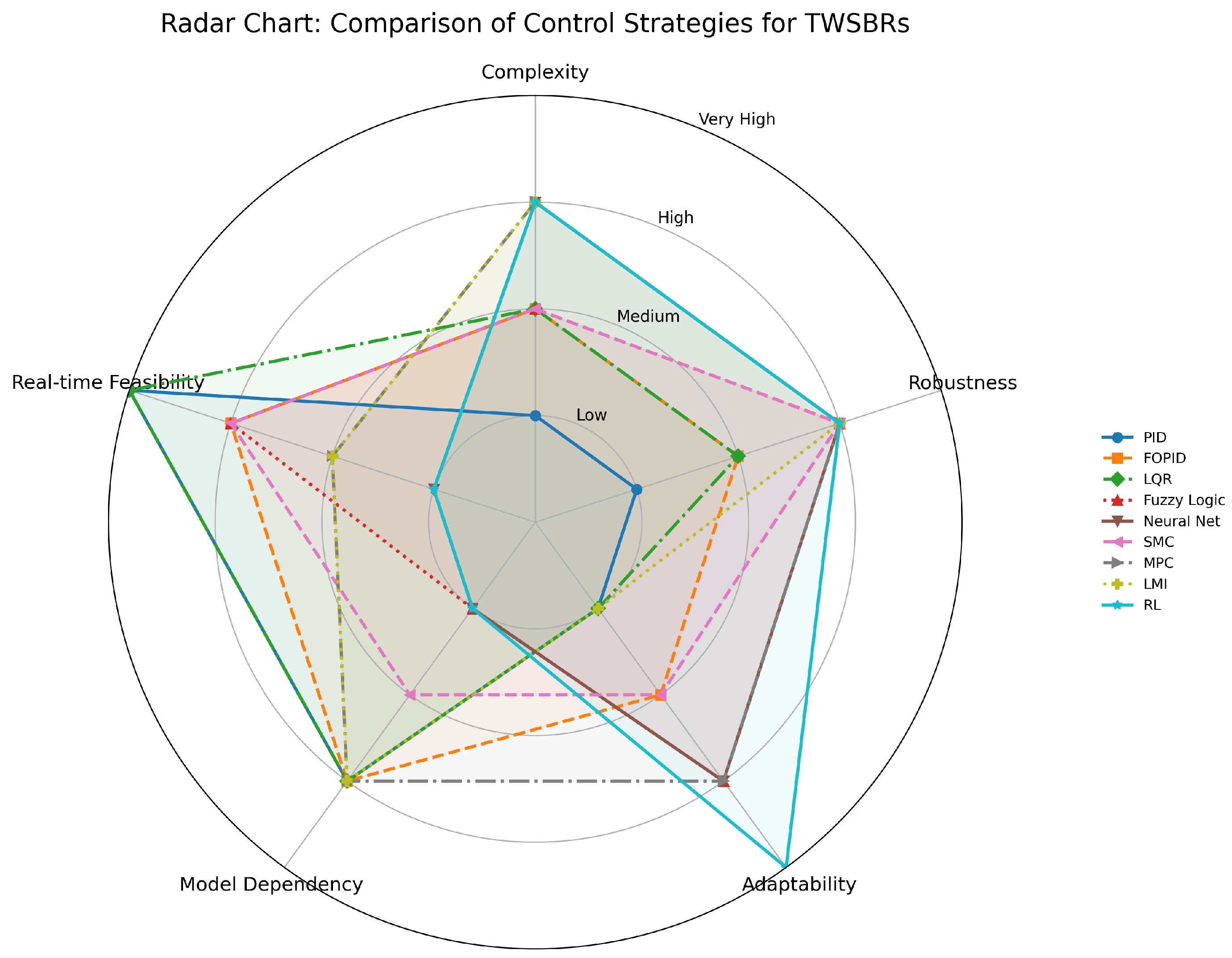
| Control Strategy | Complexity | Robustness | Adaptability | Model Dependency | Real-Time Feasibility | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PID | Low | Low | Low | High | Excellent | Basic balance and low-speed tasks |
| FOPID | Medium | Medium | Medium | High | Good | Improved control with flexibility |
| LQR | Medium | Medium | Low | High | Excellent | Optimal control with known model |
| Fuzzy Logic | Medium | High | High | Low | Good | Uncertain environments |
| Neural Networks | High | High | High | Low | Poor | Learning-based control |
| SMC | Medium | High | Medium | Medium | Good | Robust tracking, disturbance rejection |
| MPC | High | High | High | High | Medium | Constrained optimal control |
| LMI | High | High | Low | High | Medium | Theoretical guarantees |
| Reinforcement Learning | High | High | Very High | Low | Poor | Autonomous adaptive control |
| Application Scenario | PID/LQR | SMC/MPC | Adaptive/Fuzzy | RL/DL |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Structured environment, low cost | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| Dynamic tasks, nonlinear model | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Strong disturbances | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| Limited computational resources | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| High adaptability required | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| Learning-based perception tasks | ✓ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, H.; Mohamad Nor, N. Control Strategies for Two-Wheeled Self-Balancing Robotic Systems: A Comprehensive Review. Robotics 2025, 14, 101. https://doi.org/10.3390/robotics14080101
Zhang H, Mohamad Nor N. Control Strategies for Two-Wheeled Self-Balancing Robotic Systems: A Comprehensive Review. Robotics. 2025; 14(8):101. https://doi.org/10.3390/robotics14080101
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Huaqiang, and Norzalilah Mohamad Nor. 2025. "Control Strategies for Two-Wheeled Self-Balancing Robotic Systems: A Comprehensive Review" Robotics 14, no. 8: 101. https://doi.org/10.3390/robotics14080101
APA StyleZhang, H., & Mohamad Nor, N. (2025). Control Strategies for Two-Wheeled Self-Balancing Robotic Systems: A Comprehensive Review. Robotics, 14(8), 101. https://doi.org/10.3390/robotics14080101






