Digital Twin Driven Four-Dimensional Path Planning of Collaborative Robots for Assembly Tasks in Industry 5.0
Abstract
1. Introduction
- A DT framework is developed for simulating real-world industrial environments and achieving the path planning optimization of collaborative robots in assembly tasks;
- The DT is optimized for path planning of industrial robotic arms in the conditions of Industry 5.0;
- The integration of assembly information into the robot’s path planning;
- The management of multiple robots in an industrial environment and determination of their operating time and time deficiencies during the performed tasks.
2. Materials and Methods
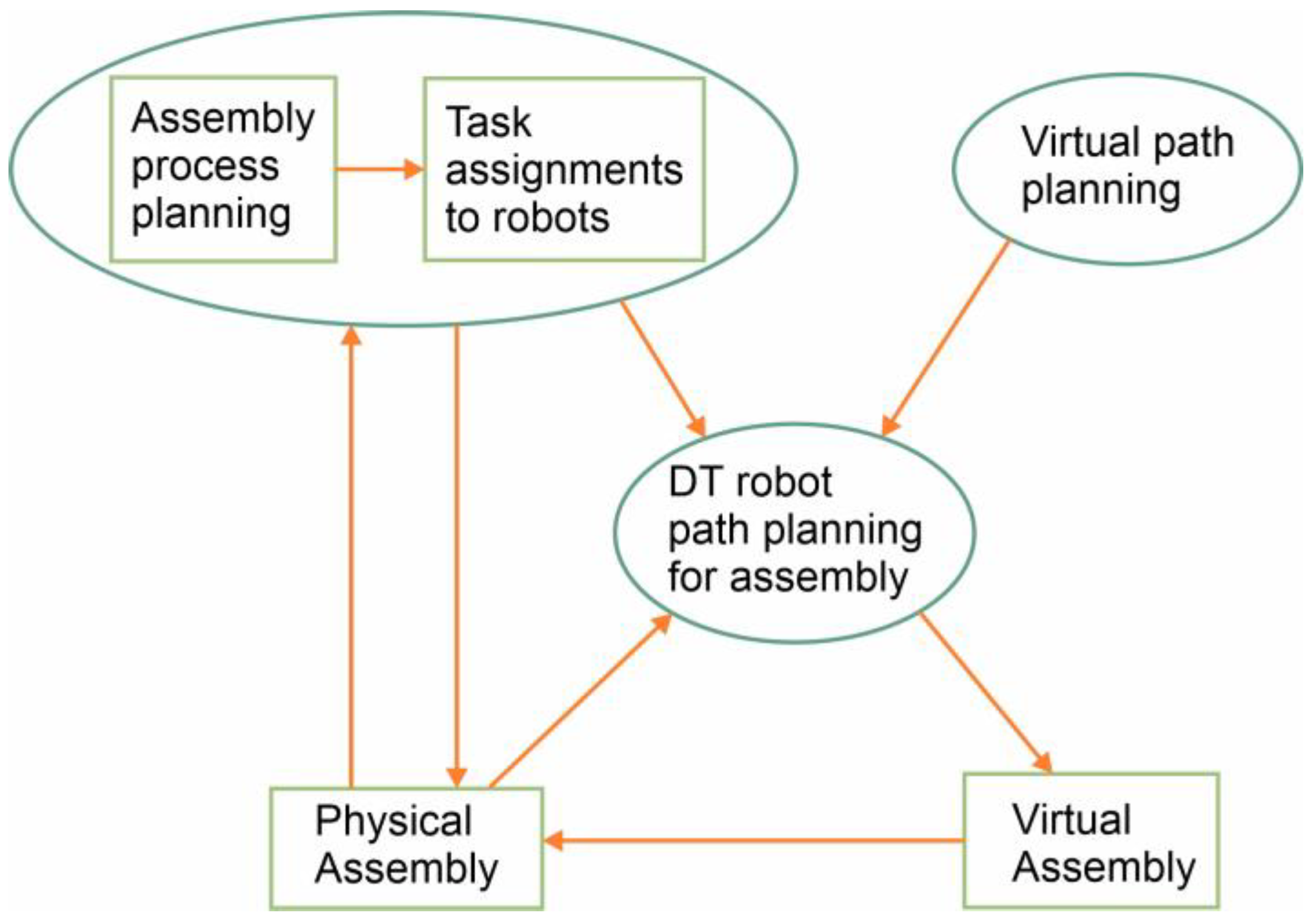
2.1. Digital Twin
2.1.1. Physical Assembly Task Assignment for Every Robot
2.1.2. Virtual Path Planning Process
2.1.3. Digital Twin Platform System
2.1.4. Digital Twin Process Data
2.1.5. Communication and Connectivity
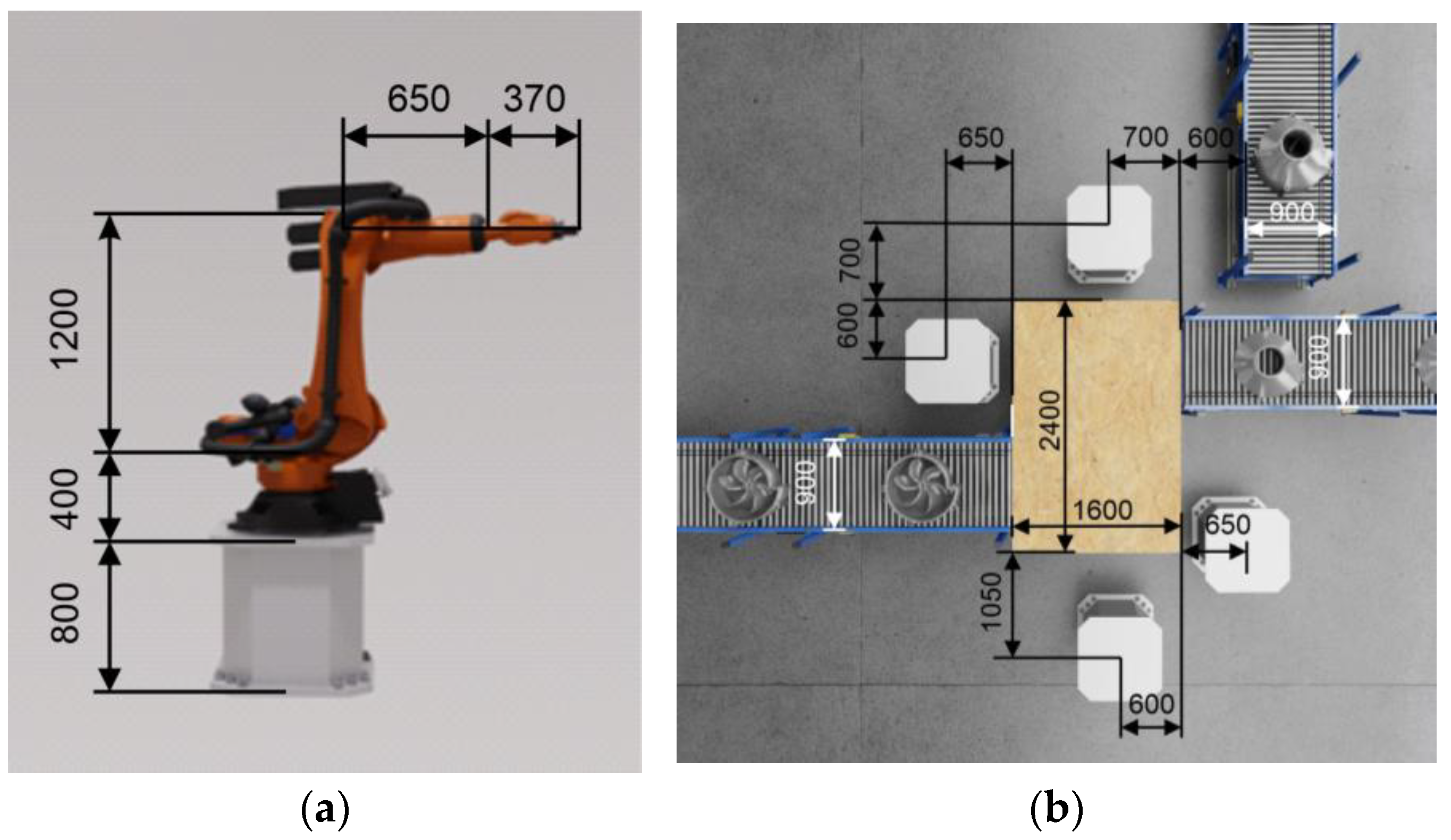
2.2. Modeling of the Environment
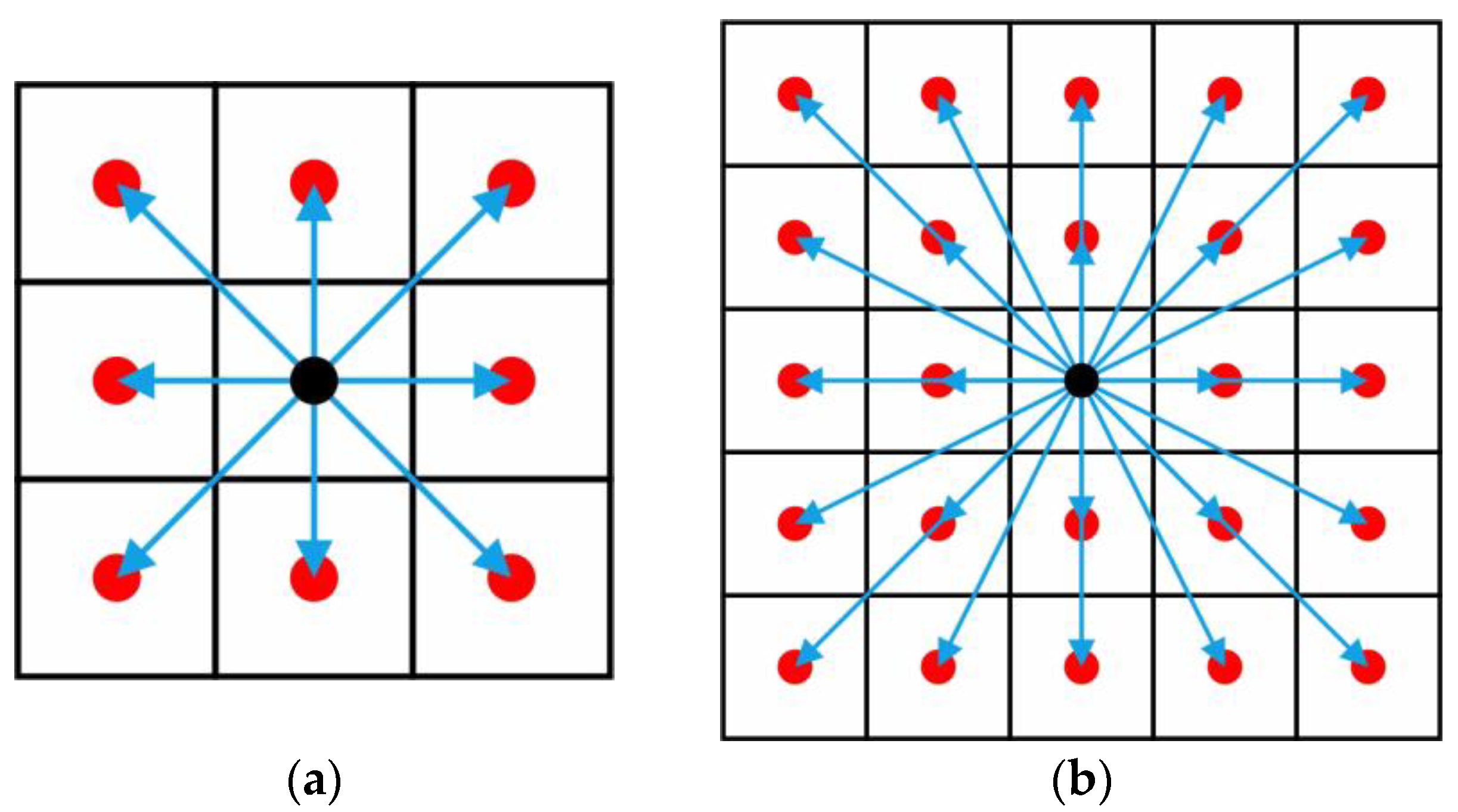
2.3. Artificial Fish Swarm Algorithm
3. Results
4. Discussion
- Enriching the library of digital models of machinery while preserving their interaction and connectivity;
- Investigating the security, stability, and consistency of industrial networks, due to the large volumes of data transmissions between the physical and digital environments;
- The utilization of a DT establishes a direct interdependence between the DT and the execution of industrial processes. The handling of potential failures of the DT as the related communication and data collection infrastructures needs to be investigated;
- Leveraging the contribution of the presented study related to the path planning alongside the integration of a temporal variable to the DT system for optimizing the industrial production scheduling.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Maddikunta, P.K.R.; Pham, Q.V.; B, P.; Deepa, N.; Dev, K.; Gadekallu, T.R.; Ruby, R.; Liyanage, M. Industry 5.0: A Survey on Enabling Technologies and Potential Applications. J. Ind. Inf. Integr. 2022, 26, 100257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Erp, T.; Carvalho, N.G.P.; Gerolamo, M.C.; Gonçalves, R.; Rytter, N.G.M.; Gladysz, B. Industry 5.0: A New Strategy Framework for Sustainability Management and Beyond. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 461, 142271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Wang, B.; Li, X.; Zheng, P.; Mourtzis, D.; Wang, L. Industry 5.0 and Society 5.0—Comparison, Complementation and Co-Evolution. J. Manuf. Syst. 2022, 64, 424–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, J.; Sha, W.; Wang, B.; Zheng, P.; Zhuang, C.; Liu, Q.; Wuest, T.; Mourtzis, D.; Wang, L. Industry 5.0: Prospect and Retrospect. J. Manuf. Syst. 2022, 65, 279–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fosso-Wamba, S.; Guthrie, C. Artificial Intelligence and Industry 4.0 and 5.0: A Bibliometric Study and Research Agenda. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2024, 239, 718–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adel, A.; Alani, N.H.; Jan, T. Factories of the Future in Industry 5.0—Softwarization, Servitization, and Industrialization. Internet Things 2024, 28, 101431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tóth, A.; Nagy, L.; Kennedy, R.; Bohuš, B.; Abonyi, J.; Ruppert, T. The Human-Centric Industry 5.0 Collaboration Architecture. MethodsX 2023, 11, 102260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leirmo, T.L. Digital Twins for Industry 5.0: Unlocking the Human Potential. Procedia CIRP 2024, 130, 761–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valette, E.; Bril El-Haouzi, H.; Demesure, G. Industry 5.0 and Its Technologies: A Systematic Literature Review upon the Human Place into IoT- and CPS-Based Industrial Systems. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2023, 184, 109426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahan, A.S.M.; Kathiravan, S.; Lokesh, M.; Raffik, R. Role of Cobots over Industrial Robots in Industry 5.0: A Review. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Advancements in Electrical, Electronics, Communication, Computing and Automation, ICAECA, Coimbatore, India, 16–17 June 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Hu, G.; Sun, Y.; Soon, J. An Overview of Collaborative Robotic Manipulation in Multi-Robot Systems. Annu. Rev. Control 2020, 49, 113–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia Simões, A.; Lucas Soares, A.; Barros, A.C. Factors Influencing the Intention of Managers to Adopt Collaborative Robots (Cobots) in Manufacturing Organizations. J. Eng. Technol. Manag. 2020, 57, 101574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galin, R.; Meshcheryakov, R. Automation and Robotics in the Context of Industry 4.0: The Shift to Collaborative Robots. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 537, 032073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, S.; Vasu, V.; Srinadh, K.V.S. Advances and Perspectives in Collaborative Robotics: A Review of Key Technologies and Emerging Trends. Discov. Mech. Eng. 2023, 2, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.V.; Kemény, Z.; Váncza, J.; Wang, L. Human–Robot Collaborative Assembly in Cyber-Physical Production: Classification Framework and Implementation. CIRP Ann. 2017, 66, 5–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, S.; Liu, H.; Wang, X.V. Overview of Human-Robot Collaboration in Manufacturing. In Lecture Notes in Mechanical Engineering; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 15–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, A.A.; Bilberg, A. Collaborative Robots in Assembly: A Practical Approach for Tasks Distribution. Procedia CIRP 2019, 81, 665–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faccio, M.; Granata, I.; Minto, R. Task Allocation Model for Human-Robot Collaboration with Variable Cobot Speed. J. Intell. Manuf. 2024, 35, 793–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weingartshofer, T.; Bischof, B.; Meiringer, M.; Hartl-Nesic, C.; Kugi, A. Optimization-Based Path Planning Framework for Industrial Manufacturing Processes with Complex Continuous Paths. Robot. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 2023, 82, 102516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, S.; Kjellander, J.A.P. Path Planning for Laser Scanning with an Industrial Robot. Rob. Auton. Syst. 2008, 56, 615–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Wang, X.; Xie, Z.; Gao, J.; Li, F.; Gu, X. A Collision-Free Path Planning Approach Based on Rule Guided Lazy-PRM with Repulsion Field for Gantry Welding Robots. Rob. Auton. Syst. 2024, 174, 104633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrahman, M.; Macatulad, E.; Lei, B.; Quintana, M.; Miller, C.; Biljecki, F. What is a Digital Twin anyway? Deriving the definition for the built environment from over 15,000 scientific publications. Build. Environ. 2025, 274, 112748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, A.A.; Brem, A. Digital Twins for Collaborative Robots: A Case Study in Human-Robot Interaction. Robot. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 2021, 68, 102092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, Z.; Biglari, R.; Denil, J.; Mertens, J.; Poursoltan, M.; Traoré, M.K. From Modeling and Simulation to Digital Twin: Evolution or Revolution? Simulation 2024, 100, 751–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daraba, D.; Pop, F.; Daraba, C. Digital Twin Used in Real-Time Monitoring of Operations Performed on CNC Technological Equipment. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 10088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreuzer, T.; Papapetrou, P.; Zdravkovic, J. Artificial Intelligence in Digital Twins—A Systematic Literature Review. Data Knowl. Eng. 2024, 151, 102304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sifat, M.M.H.; Choudhury, S.M.; Das, S.K.; Ahamed, M.H.; Muyeen, S.M.; Hasan, M.M.; Ali, M.F.; Tasneem, Z.; Islam, M.M.; Islam, M.R.; et al. Towards Electric Digital Twin Grid: Technology and Framework Review. Energy AI 2023, 11, 100213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L. Digital Twins in Agriculture: A Review of Recent Progress and Open Issues. Electronics 2024, 13, 2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chomiak-Orsa, I.; Hauke, K.; Perechuda, K.; Pondel, M. The Use of Digital Twin in the Sustainable Development of the City on the Example of Managing Parking Resources. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2023, 225, 2183–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebni, M.; Bamakan, S.M.H.; Qu, Q. Digital Twin Based Smart Manufacturing; From Design to Simulation and Optimization Schema. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2023, 221, 1216–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benfer, M.; Peukert, S.; Lanza, G. A Framework for Digital Twins for Production Network Management. Procedia CIRP 2021, 104, 1269–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traini, E.; Antal, G.; Bruno, G.; De Maddis, M.; Lombardi, F.; Panza, L.; Spena, P.R. Hybrid Knowledge Based System Supporting Digital Twins in the Industry 5.0. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2024, 232, 1471–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grieves, M.; Vickers, J. Digital Twin: Mitigating Unpredictable, Undesirable Emergent Behavior in Complex Systems. In Transdisciplinary Perspectives on Complex Systems: New Findings and Approaches; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 85–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.Y.; Kim, D.; Do Noh, S.; Han, H.K.; Kim, N.G.; Kang, Y.S.; Choi, S.H.; Go, D.H.; Song, J.; Lee, D.Y.; et al. Human Digital Twin System for Operator Safety and Work Management. IFIP Adv. Inf. Commun. Technol. 2022, 664, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junnan, Z.; Jiangxin, Y.; Chongxin, Z.; Shuhan, L.; Anwer, N.; Yanlong, C. A Modeling Method of Complex Assembly Based on Digital Twin. Procedia CIRP 2022, 114, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zhou, H.; He, H.; Jiao, G.; Wei, S. A Digital Twin-Based Approach for Quality Control and Optimization of Complex Product Assembly. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Advanced Manufacturing, AIAM 2019, Dublin, Ireland, 17–19 October 2019; pp. 762–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yan, Y.; Hu, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhang, L. A Transfer Reinforcement Learning and Digital-Twin Based Task Allocation Method for Human-Robot Collaboration Assembly. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2025, 144, 110064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Leng, J.; Xie, M.; Yan, H.; Liu, Q. Digital Twin Enabled Optimal Reconfiguration of the Semi-Automatic Electronic Assembly Line with Frequent Changeovers. Robot. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 2022, 77, 102343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zheng, S.; Yu, C.; Wang, Q.; Ke, Y. Digital Thread-Based Modeling of Digital Twin Framework for the Aircraft Assembly System. J. Manuf. Syst. 2022, 65, 406–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Luo, Y.; Peng, Y.; Chen, Y. Industrial Robot Digital Twin System Motion Simulation and Collision Detection. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 1st International Conference on Digital Twins and Parallel Intelligence, DTPI 2021, Beijing, China, 15 July–15 August 2021; pp. 196–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zheng, L.; Fan, W.; Ji, W.; Mao, L.; Wang, L. Knowledge Graph and Function Block Based Digital Twin Modeling for Robotic Machining of Large-Scale Components. Robot. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 2024, 85, 102609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, D.T.; Nam, L.G.; Viet, D.T.; Thang, V.T. A-Star Algorithm for Robot Path Planning Based on Digital Twin. In Lecture Notes in Mechanical Engineering; Springer: Singapore, 2022; pp. 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Yuan, X.; Gu, Q.; Hu, C.; He, D. A Digital Twin System for 6DoF Robot Grasping. In Proceedings of the 35th Chinese Control and Decision Conference, CCDC 2023, Yichang, China, 20–22 May 2023; pp. 3292–3296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chouridis, I.; Mansour, G.; Papageorgiou, V.; Mansour, M.T.; Tsagaris, A. Four-Dimensional Path Planning Methodology for Collaborative Robots Application in Industry 5.0. Robotics 2025, 14, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awouda, A.; Traini, E.; Bruno, G.; Chiabert, P. IoT-Based Framework for Digital Twins in the Industry 5.0 Era. Sensors 2024, 24, 594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attaran, S.; Attaran, M.; Celik, B.G. Digital Twins and Industrial Internet of Things: Uncovering Operational Intelligence in Industry 4.0. Decis. Anal. J. 2024, 10, 100398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saemaldahr, R.; Thapa, B.; Maikoo, K.; Fernandez, E.B. Reference Architectures for the IoT: A Survey. Lect. Notes Data Eng. Commun. Technol. 2021, 72, 635–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Industrial Internet Reference Architecture—Industry IoT Consortium. Available online: https://www.iiconsortium.org/iira/ (accessed on 13 May 2025).
- Guth, J.; Breitenbucher, U.; Falkenthal, M.; Leymann, F.; Reinfurt, L. Comparison of IoT Platform Architectures: A Field Study Based on a Reference Architecture. In Proceedings of the 2016 Cloudification of the Internet of Things, CIoT, Paris, France, 23–25 November 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Reference Architecture for the Internet of Things. Available online: https://wso2.com/whitepapers/a-reference-architecture-for-the-internet-of-things/ (accessed on 13 May 2025).
- Breivold, H.P. A Survey and Analysis of Reference Architectures for the Internet-of-Things. In Proceedings of the Twelfth International Conference on Software Engineering Advances, Athens, Greece, 8–12 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Mashaly, M. Connecting the Twins: A Review on Digital Twin Technology & Its Networking Requirements. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2021, 184, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Liu, C.; Wang, K.I.K.; Huang, H.; Xu, X. Digital Twin-Driven Smart Manufacturing: Connotation, Reference Model, Applications and Research Issues. Robot. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 2020, 61, 101837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, F.; Qi, Q.; Liu, A.; Kusiak, A. Data-Driven Smart Manufacturing. J. Manuf. Syst. 2018, 48, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chouridis, I.; Mansour, G.; Papageorgiou, V.; Mansour, M.T.; Tsagaris, A. Enhanced Hybrid Artificial Fish Swarm Algorithm for Three-Dimensional Path Planning Applied to Robotic Systems. Robotics 2025, 14, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, D.; Hanwei, Z.; Qingyong, Z.; Ruopu, W. Correlation of Coordinate Transformation Parameters. Geod. Geodyn. 2012, 3, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Wang, S.; Chiel, H.J.; Thomas, P.J.; Tarkhov, D.A.; Malykhina, G.F. Neural Network Modelling Methods for Creating Digital Twins of Real Objects. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1236, 012056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Jiang, P.; Jiang, W. Web-Based Digital Twin Modeling and Remote Control of Cyber-Physical Production Systems. Robot. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 2020, 64, 101956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, K.; Xu, W.; Yao, B.; Zhou, Z.; Pham, D.T. Digital Twin-Based Energy Modeling of Industrial Robots. Commun. Comput. Inf. Sci. 2018, 946, 333–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolescu, A.; Ilie, F.-M.; Tudor-George, A. Forward and inverse kinematics study of industrial robots taking into account constructive and functional parameter’s modeling. Proc. Manuf. Syst. 2015, 10, 157. [Google Scholar]
- Omniverse Platform for OpenUSD | NVIDIA. Available online: https://www.nvidia.com/en-eu/omniverse/ (accessed on 25 May 2025).
- Chouridis, I.; Mansour, G.; Tsagaris, A. Three-Dimensional Path Planning Optimization for Length Reduction of Optimal Path Applied to Robotic Systems. Robotics 2024, 13, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, L.X.; Shao, Z.J.; Qian, J.X. An Optimizing Method Based on Autonomous Animats: Fish-Swarm Algorithm. Syst. Eng.-Theory Pract. 2002, 22, 32–38. [Google Scholar]
- Zainal, N.; Zain, A.M.; Sharif, S. Overview of Artificial Fish Swarm Algorithm and Its Applications in Industrial Problems. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2015, 815, 253–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chouridis, I.; Mansour, G.; Chouridis, A.; Papageorgiou, V.; Mansour, M.T.; Tsagaris, A. Digital Twin Driven Four-Dimensional Path Planning of Collaborative Robots for Assembly Tasks in Industry 5.0. Robotics 2025, 14, 97. https://doi.org/10.3390/robotics14070097
Chouridis I, Mansour G, Chouridis A, Papageorgiou V, Mansour MT, Tsagaris A. Digital Twin Driven Four-Dimensional Path Planning of Collaborative Robots for Assembly Tasks in Industry 5.0. Robotics. 2025; 14(7):97. https://doi.org/10.3390/robotics14070097
Chicago/Turabian StyleChouridis, Ilias, Gabriel Mansour, Asterios Chouridis, Vasileios Papageorgiou, Michel Theodor Mansour, and Apostolos Tsagaris. 2025. "Digital Twin Driven Four-Dimensional Path Planning of Collaborative Robots for Assembly Tasks in Industry 5.0" Robotics 14, no. 7: 97. https://doi.org/10.3390/robotics14070097
APA StyleChouridis, I., Mansour, G., Chouridis, A., Papageorgiou, V., Mansour, M. T., & Tsagaris, A. (2025). Digital Twin Driven Four-Dimensional Path Planning of Collaborative Robots for Assembly Tasks in Industry 5.0. Robotics, 14(7), 97. https://doi.org/10.3390/robotics14070097







