Robot-Assisted Glovebox Teleoperation for Nuclear Industry
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Challenge Statement
2.1. Glovebox Challenges
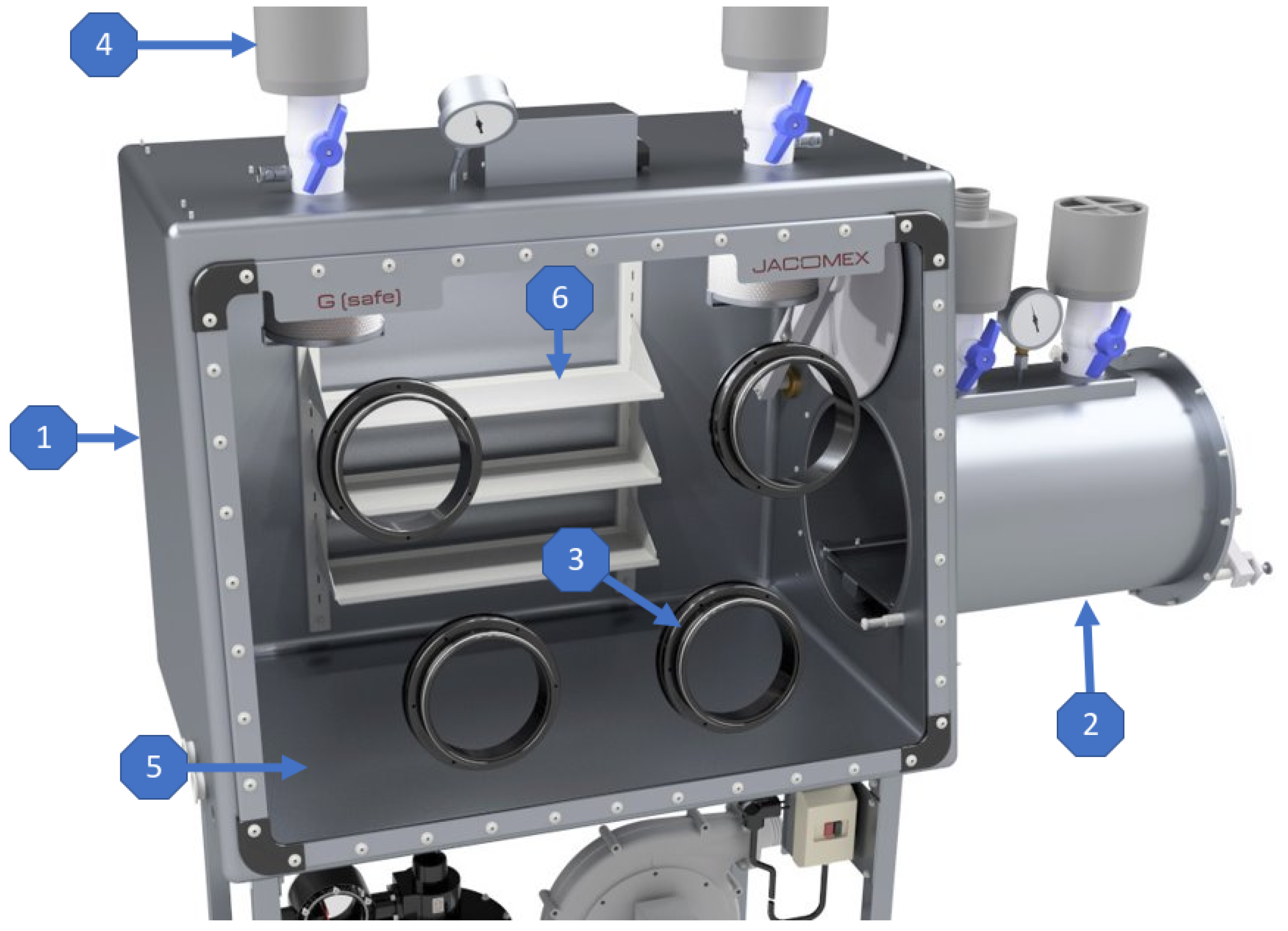
2.1.1. Hull
2.1.2. Windows
2.1.3. Glove Ports
2.1.4. Posting in/out Ports
2.1.5. Environment Monitoring and Maintenance Equipment
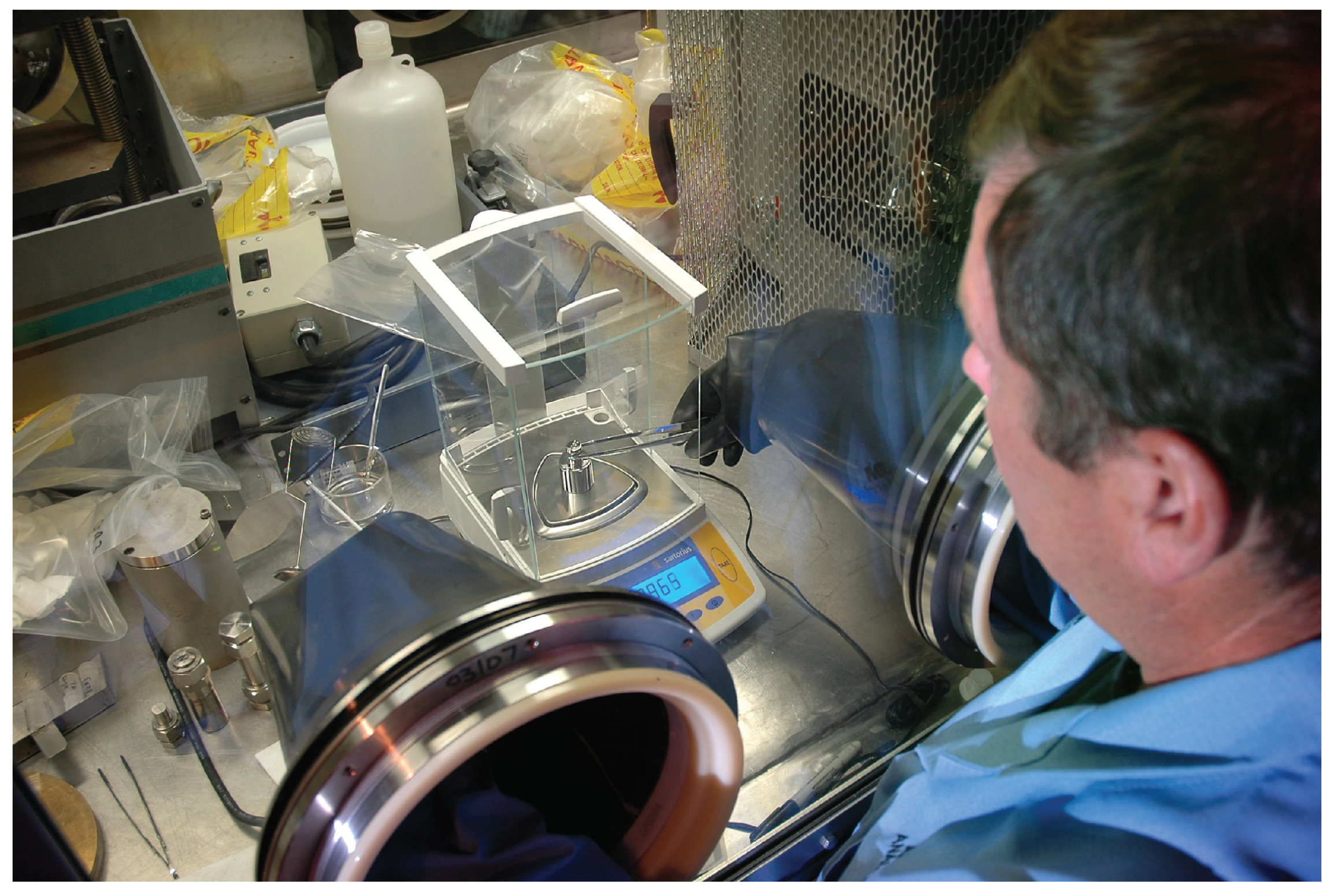
2.1.6. Glovebox Internals
2.2. Challenges of Robots in Gloveboxes
2.2.1. Mechatronics Challenges
2.2.2. Control and Intelligent Systems Challenges
3. Previous Work
4. The RAIN Solution: Teleoperated Robotic Manipulation
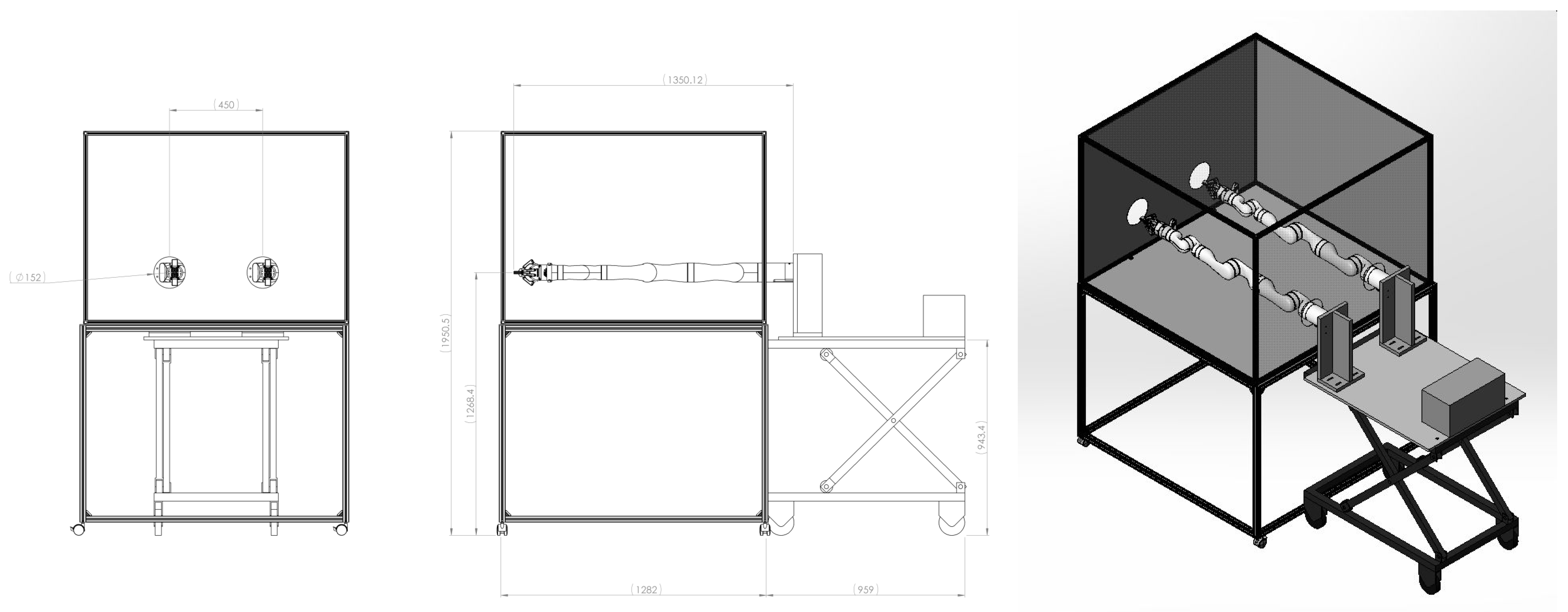
4.1. Hardware
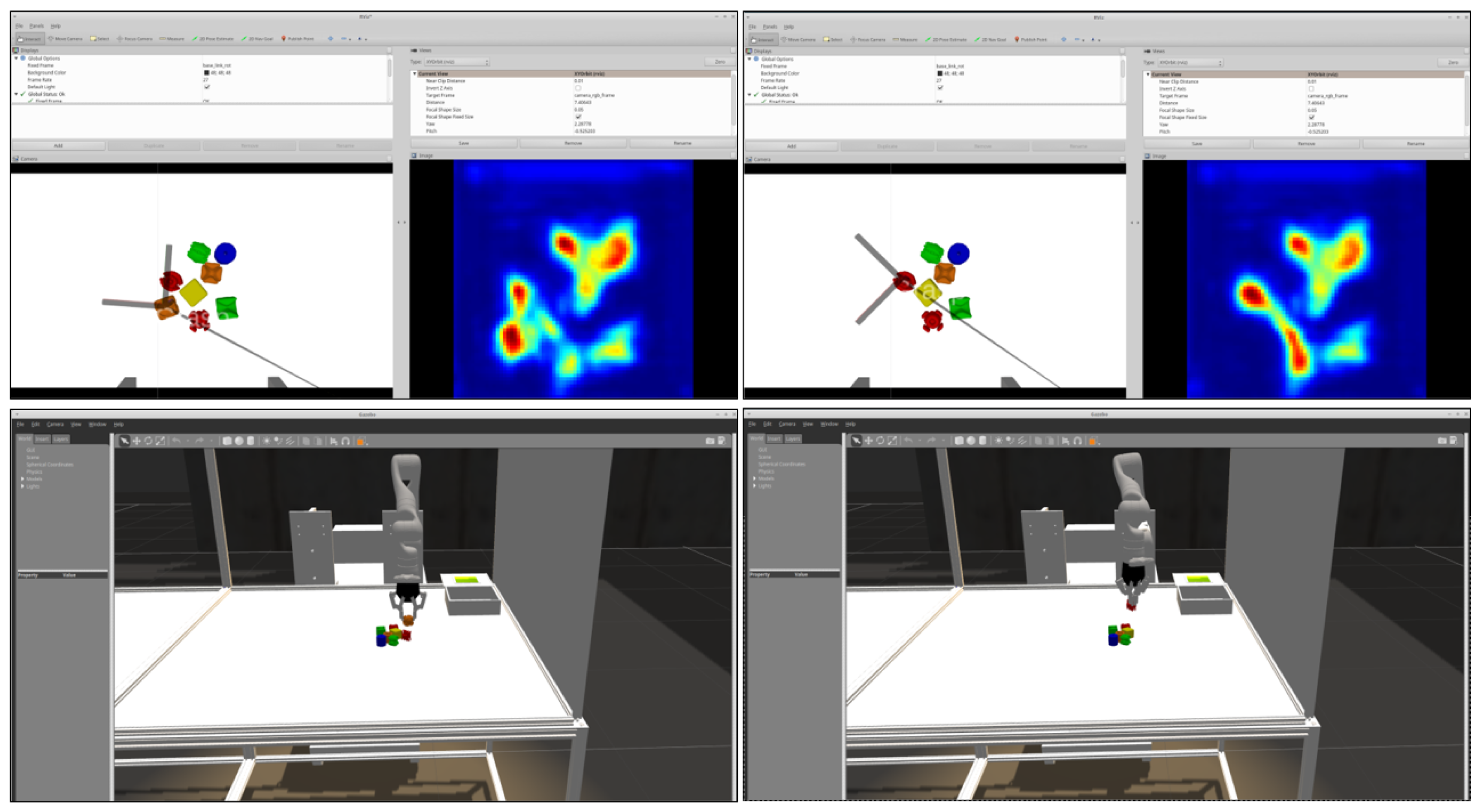
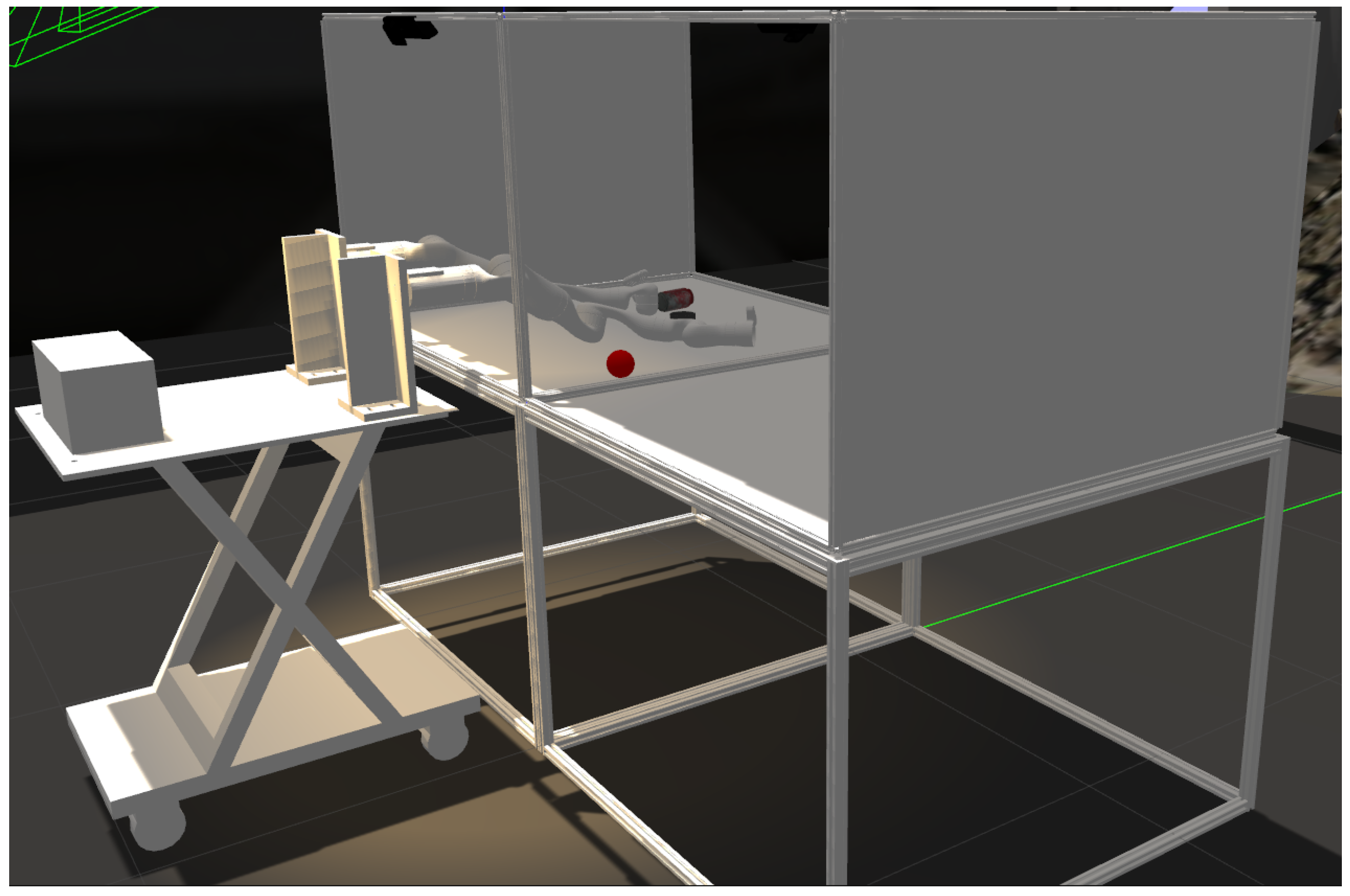
4.2. Simulator
5. Research Areas
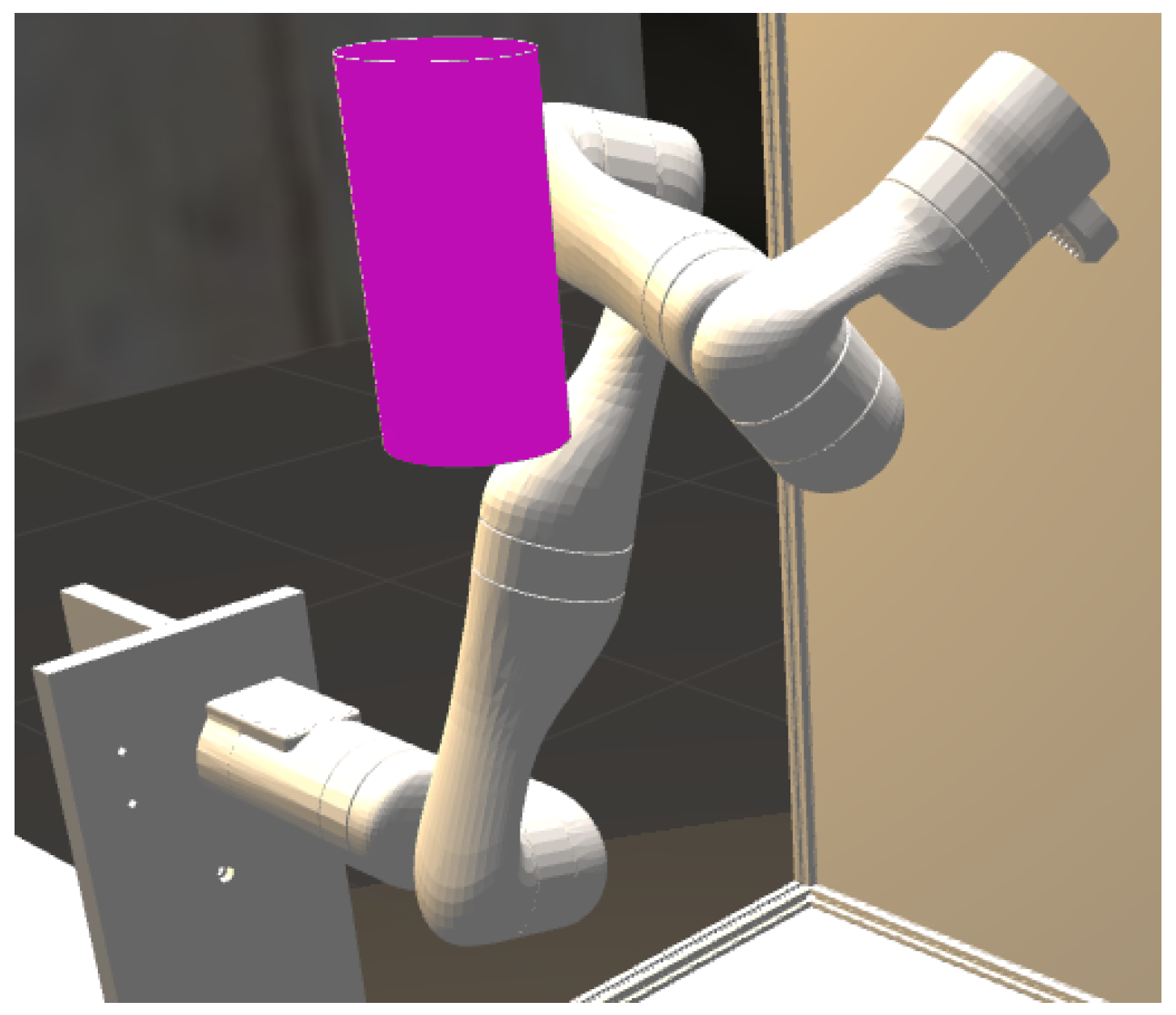
5.1. Autonomous Grasping
5.1.1. Grasp Synthesis
5.1.2. Grasping without Object Model
5.1.3. Grasping in Constrained Environments
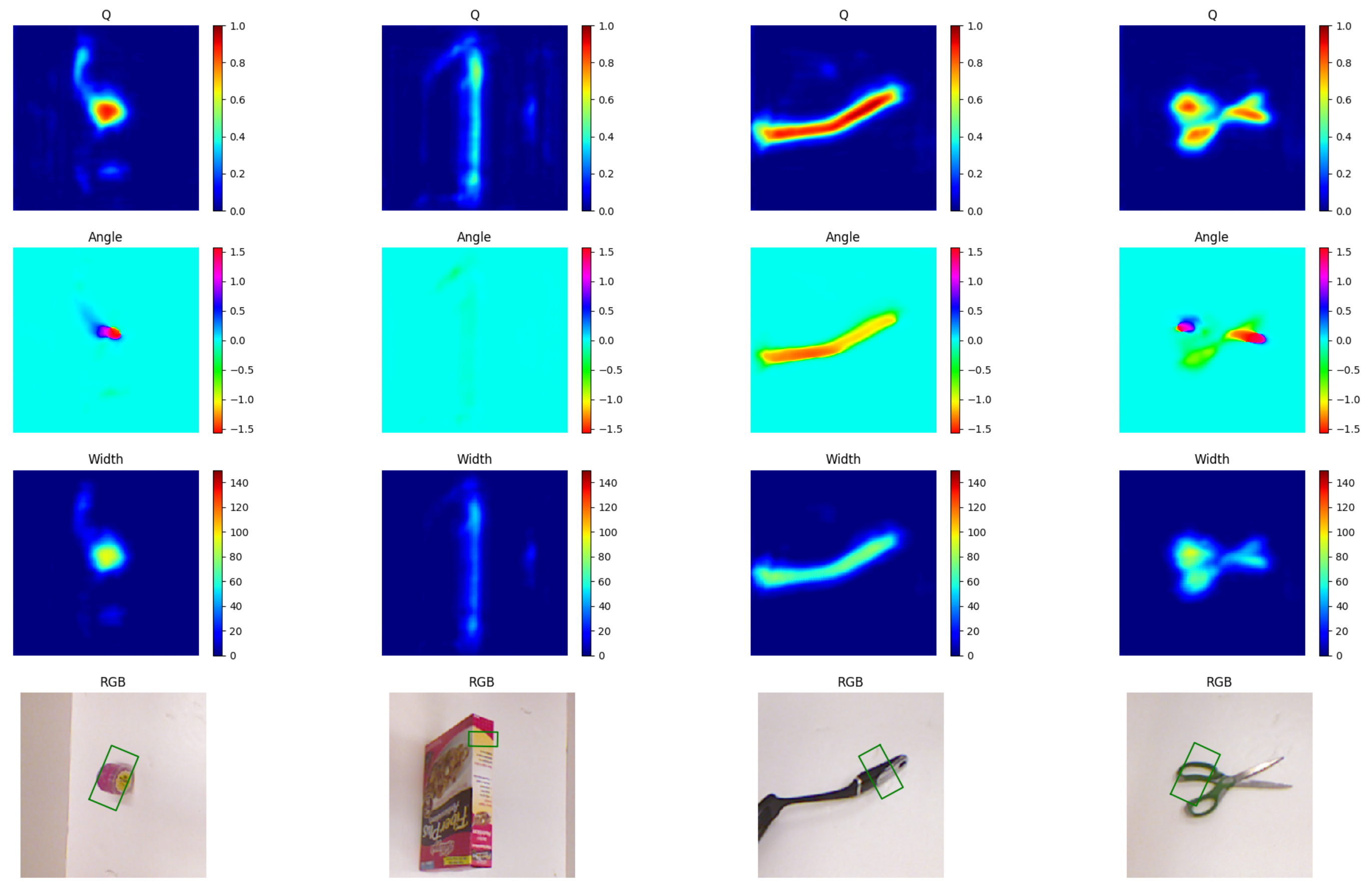
5.2. Grasp Detection Using Deep Learning
5.2.1. Grasp Estimation with Convolutional Neural Networks
5.2.2. Grasp Convolutional Neural Network with Variational Autoencoders
5.3. Assisting the Operator
Augmenting Sensing
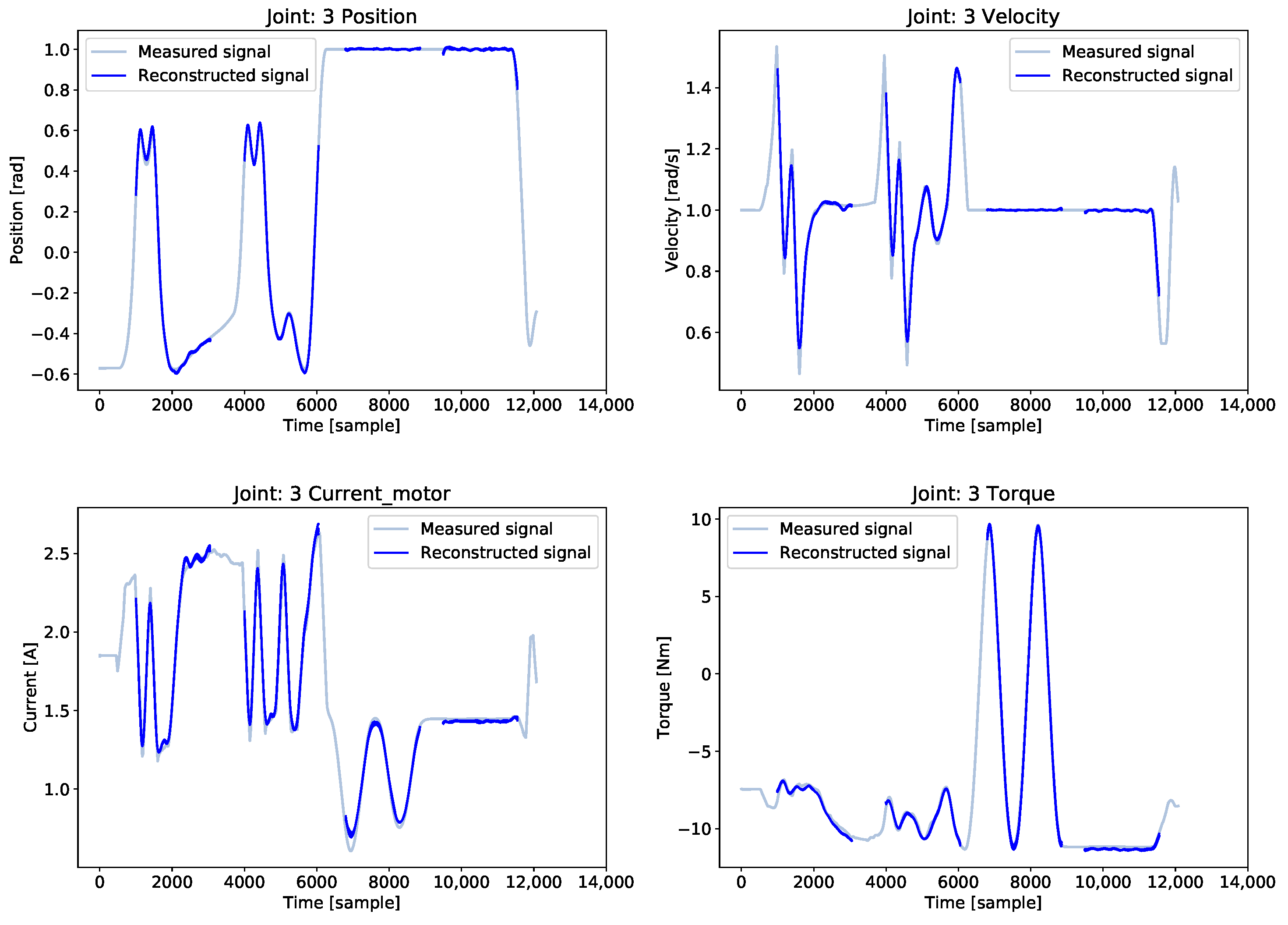
5.4. Condition Monitoring of the Robots
5.5. Operations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bogue, R. Robots in the nuclear industry: A review of technologies and applications. Ind. Robot. 2011, 38, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A.; Alonso Paredes Soto, D.; Veres, S.M.; Rossiter, J. Human robot interaction for future remote manipulations in Industry 4.0. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2020, 53, 10223–10228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RAIN Hub. 2018. Available online: https://rainhub.org.uk/ (accessed on 18 June 2021).
- Worker exposed to Sellafield plutonium had skin removed. BBC News. 2 April 2019. Available online: https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/uk-england-cumbria-47786659 (accessed on 3 July 2021).
- Chen, S.; Demachi, K. A Vision-Based Approach for Ensuring Proper Use of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) in Decommissioning of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 5129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talha, M.; Ghalamzan, E.; Takahashi, C.; Kuo, J.; Ingamells, W.; Stolkin, R. Towards robotic decommissioning of legacy nuclear plant: Results of human-factors experiments with tele-robotic manipulation, and a discussion of challenges and approaches for decommissioning. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Symposium on Safety, Security, and Rescue Robotics (SSRR), Lausanne, Switzerland, 23–27 October 2016; pp. 166–173. [Google Scholar]
- Domning, E.E.; McMahon, T.T.; Sievers, R.H. Robotic and Nuclear Safety for an Automated/Teleoperated Glove Box System; Technical Report; Lawrence Livermore National Lab.: Livermore, CA, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh, A.; Veres, S.M.; Paredes-Soto, D.; Clarke, J.E.; Rossiter, J.A. Intuitive Programming with Remotely Instructed Robots inside Future Gloveboxes. In Proceedings of the Companion of the 2020 ACM/IEEE International Conference on Human-Robot Interaction, Cambridge, UK, 23–26 March 2020; pp. 209–211. [Google Scholar]
- Goiffon, V.; Rolando, S.; Corbière, F.; Rizzolo, S.; Chabane, A.; Girard, S.; Baer, J.; Estribeau, M.; Magnan, P.; Paillet, P.; et al. Radiation Hardening of Digital Color CMOS Camera-on-a-Chip Building Blocks for Multi-MGy Total Ionizing Dose Environments. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2017, 64, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; De Cock, W.; Steyaert, M.; Leroux, P. Design and Assessment of a 6 ps-Resolution Time-to-Digital Converter With 5 MGy Gamma-Dose Tolerance for LIDAR Application. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2012, 59, 1382–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasz, E.; Perez, M. Addressing Nuclear and Hostile Environment Challenges with Intelligent Automation; Technical Report; Lawrence Livermore National Lab.: Livermore, CA, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Akiyama, M. Research and development on decommissioning of nuclear facilities in Japan. Nucl. Eng. Des. 1996, 165, 307–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rollow, T. Type a Accident Investigation of the March 16, 2000 Plutonium-238 Multiple Intake Event at the Plutonium Facility, Los Alamos National Laboratory, New Mexico, United States Department of Energy, Office of Oversight; Office of Oversight Office of Environment, Safety and Health U.S. Department of Energy: Washington, DC, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Hagemeyer, D.; McCormick, Y. DOE 2011 Occupational Radiation Exposure Report, _Prepared for the US Department of Energy, Office of Health, Safety and Security. December 2012; Technical Report; Oak Ridge Institute for Science and Education (ORISE): Oak Ridge, TN, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Wehe, D.K.; Lee, J.; Martin, W.R.; Mann, R.; Hamel, W.; Tulenko, J. Intelligent robotics and remote systems for the nuclear industry. Nucl. Eng. Des. 1989, 113, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harden, T.A.; Lloyd, J.A.; Turner, C.J. Robotics for Nuclear Material Handling at LANL: Capabilities and Needs; Technical Report; Los Alamos National Lab.: Los Alamos, NM, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Pegman, G.; Sands, D. Cost effective robotics in the nuclear industry. Ind. Robot. 2006, 33, 170–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, K.D. Robotic System for Automated Handling of Ceramic Pucks; Technical Report; Lawrence Livermore National Lab.: Livermore, CA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Foster, C. Computer Model and Simulation of a Glove Box Process; Technical Report; Los Alamos National Lab.: Santa Fe, NM, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Turner, C.; Pehl, J. Design of Small Automation Work Cell System Demonstrations; Technical Report; Los Alamos National Lab.: Santa Fe, NM, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Roa, M.A.; Suárez, R. Grasp quality measures: Review and performance. Auton. Robot. 2015, 38, 65–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitamura, A.; Watahiki, M.; Kashiro, K. Remote glovebox size reduction in glovebox dismantling facility. Nucl. Eng. Des. 2011, 241, 999–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharp, A.; Hom, M.W.; Pryor, M. Operator training for preferred manipulator trajectories in a glovebox. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Workshop on Advanced Robotics and its Social Impacts (ARSO), Austin, TX, USA, 8–10 March 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- O’Neil, B.E. Graph-Based World-Model for Robotic Manipulation. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Texas at Austin, Austin, TX, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Önol, A.Ö.; Long, P.; Padır, T. Using contact to increase robot performance for glovebox D&D tasks. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1807.04198. [Google Scholar]
- Long, P.; Padir, T. Evaluating robot manipulability in constrained environments by velocity polytope reduction. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE-RAS 18th International Conference on Humanoid Robots (Humanoids), Beijing, China, 6–9 November 2018; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Quigley, M.; Conley, K.; Gerkey, B.; Faust, J.; Foote, T.; Leibs, J.; Wheeler, R.; Ng, A.Y. ROS: An open-source Robot Operating System. In Proceedings of the ICRA 2009, Kobe, Japan, 12–17 May 2009; Volume 3, p. 5. [Google Scholar]
- González, C.; Solanes, J.E.; Muñoz, A.; Gracia, L.; Girbés-Juan, V.; Tornero, J. Advanced teleoperation and control system for industrial robots based on augmented virtuality and haptic feedback. J. Manuf. Syst. 2021, 59, 283–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacinto-Villegas, J.M.; Satler, M.; Filippeschi, A.; Bergamasco, M.; Ragaglia, M.; Argiolas, A.; Niccolini, M.; Avizzano, C.A. A Novel Wearable Haptic Controller for Teleoperating Robotic Platforms. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2017, 2, 2072–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burroughes, G. Glovebox Robotics Simulator; GitHub: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Averta, G.; Angelini, F.; Bonilla, M.; Bianchi, M.; Bicchi, A. Incrementality and hierarchies in the enrollment of multiple synergies for grasp planning. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2018, 3, 2686–2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Xu, J.; Wang, X.; Li, Z. On quality functions for grasp synthesis, fixture planning, and coordinated manipulation. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2004, 1, 146–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahler, J.; Patil, S.; Kehoe, B.; Van Den Berg, J.; Ciocarlie, M.; Abbeel, P.; Goldberg, K. Gp-gpis-opt: Grasp planning with shape uncertainty using gaussian process implicit surfaces and sequential convex programming. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE international conference on robotics and automation (ICRA), Seattle, WA, USA, 26–30 May 2015; pp. 4919–4926. [Google Scholar]
- Romano, J.M.; Hsiao, K.; Niemeyer, G.; Chitta, S.; Kuchenbecker, K.J. Human-inspired robotic grasp control with tactile sensing. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2011, 27, 1067–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, A.T.; Knoop, S.; Christensen, H.I.; Allen, P.K. Automatic grasp planning using shape primitives. In Proceedings of the 2003 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (Cat. No. 03CH37422), Taipei, Taiwan, 14–19 September 2003; Volume 2, pp. 1824–1829. [Google Scholar]
- Bonilla, M.; Farnioli, E.; Piazza, C.; Catalano, M.; Grioli, G.; Garabini, M.; Gabiccini, M.; Bicchi, A. Grasping with soft hands. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE-RAS International Conference on Humanoid Robots, Madrid, Spain, 18–20 November 2014; pp. 581–587. [Google Scholar]
- Berenson, D.; Diankov, R.; Nishiwaki, K.; Kagami, S.; Kuffner, J. Grasp planning in complex scenes. In Proceedings of the 2007 7th IEEE-RAS International Conference on Humanoid Robots, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 29 November–1 December 2007; pp. 42–48. [Google Scholar]
- Diankov, R.; Kanade, T.; Kuffner, J. Integrating grasp planning and visual feedback for reliable manipulation. In Proceedings of the 2009 9th IEEE-RAS International Conference on Humanoid Robots, Paris, France, 7–10 December 2009; pp. 646–652. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, Z.; Zoellner, J.M.; Dillmann, R. Automatic optimal grasp planning based on found contact points. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE/ASME International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics, Xi’an, China, 2–5 July 2008; pp. 1053–1058. [Google Scholar]
- Hertkorn, K. Shared Grasping: A Combination of Telepresence and Grasp Planning; KIT Scientific Publishing: Karlsruhe, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, D.; Liu, Y.H.; Wang, M.Y.; Wang, S. Automatic selection of fixturing surfaces and fixturing points for polyhedral workpieces. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 2001, 17, 833–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Khoury, S.; Li, M.; Billard, A. Bridging the gap: One shot grasp synthesis approach. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Vilamoura-Algarve, Portugal, 7–12 October 2012; pp. 2027–2034. [Google Scholar]
- El-Khoury, S.; Li, M.; Billard, A. On the generation of a variety of grasps. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2013, 61, 1335–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zheng, Y. Computing the best grasp in a discrete point set with wrench-oriented grasp quality measures. Auton. Robot. 2019, 43, 1041–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahler, J.; Liang, J.; Niyaz, S.; Laskey, M.; Doan, R.; Liu, X.; Ojea, J.A.; Goldberg, K. Dex-Net 2.0: Deep Learning to Plan Robust Grasps with Synthetic Point Clouds and Analytic Grasp Metrics. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1703.09312. [Google Scholar]
- Kumra, S.; Kanan, C. Robotic grasp detection using deep convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, San Diego, CA, USA, 29 October–2 November 2007; pp. 769–776. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y.; Sun, Y. Robot grasp planning based on demonstrated grasp strategies. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2015, 34, 26–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baerlocher, P.; Boulic, R. An inverse kinematics architecture enforcing an arbitrary number of strict priority levels. Vis. Comput. 2004, 20, 402–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Zhou, K.; Tong, Y.; Desbrun, M.; Bao, H.; Guo, B. Mesh Puppetry: Cascading Optimization of Mesh Deformation with Inverse Kinematics. ACM Trans. Graph. 2007, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi, V.; Kimmel, A.; Bekris, K.; Kapadia, M. Geometric reachability analysis for grasp planning in cluttered scenes for varying end-effectors. In Proceedings of the 2017 13th IEEE Conference on Automation Science and Engineering (CASE), Xi’an, China, 20–23 August 2017; pp. 764–769. [Google Scholar]
- Altobelli, A.; Tokatli, O.; Burroughes, G.; Skilton, R. Optimal Grasping Pose Synthesis in a Constrained Environment. Robotics 2021, 10, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eppner, C.; Deimel, R.; Alvarez-Ruiz, J.; Maertens, M.; Brock, O. Exploitation of environmental constraints in human and robotic grasping. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2015, 34, 1021–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvietti, G.; Malvezzi, M.; Gioioso, G.; Prattichizzo, D. Modeling compliant grasps exploiting environmental constraints. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Seattle, WA, USA, 26–30 May 2015; pp. 4941–4946. [Google Scholar]
- Saut, J.P.; Sahbani, A.; El-Khoury, S.; Perdereau, V. Dexterous manipulation planning using probabilistic roadmaps in continuous grasp subspaces. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, San Diego, CA, USA, 29 October–2 November 2007; pp. 2907–2912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tournassoud, P.; Lozano-Perez, T.; Mazer, E. Regrasping. In Proceedings of the 1987 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Raleigh, NC, USA, 31 March–3 April 1987; Volume 4, pp. 1924–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaguer, B.; Carpin, S. Bimanual regrasping from unimanual machine learning. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Saint Paul, MN, USA, 14–18 May 2012; pp. 3264–3270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Chen, W.; Wang, H.; Wang, J. Manipulator motion planning using flexible obstacle avoidance based on model learning. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2017, 14, 1729881417703930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogar, M.; Srinivasa, S. A framework for push-grasping in clutter. Robot. Sci. Syst. 2011, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaValle, S.M.; Kuffner, J.J., Jr. Randomized kinodynamic planning. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2001, 20, 378–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenz, I.; Lee, H.; Saxena, A. Deep Learning for Detecting Robotic Grasps. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1301.3592. [Google Scholar]
- Depierre, A.; Dellandréa, E.; Chen, L. Jacquard: A Large Scale Dataset for Robotic Grasp Detection. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1803.11469. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, J.; Angelova, A. Real-Time Grasp Detection Using Convolutional Neural Networks. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.3128. [Google Scholar]
- Kumra, S.; Kanan, C. Robotic Grasp Detection using Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1611.08036. [Google Scholar]
- Morrison, D.; Corke, P.; Leitner, J. Closing the Loop for Robotic Grasping: A Real-time, Generative Grasp Synthesis Approach. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.05172. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P.; Welling, M. Auto-Encoding Variational Bayes. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1312.6114. [Google Scholar]
- Sohn, K.; Lee, H.; Yan, X. Learning Structured Output Representation using Deep Conditional Generative Models. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; Cortes, C., Lawrence, N., Lee, D., Sugiyama, M., Garnett, R., Eds.; Curran Associates, Inc.: San Jose, CA, USA, 2015; Volume 28. [Google Scholar]
- Oord, A.v.d.; Vinyals, O.; Kavukcuoglu, K. Neural Discrete Representation Learning. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1711.00937. [Google Scholar]
- Kumra, S.; Joshi, S.; Sahin, F. Antipodal Robotic Grasping using Generative Residual Convolutional Neural Network. arXiv 2020, arXiv:1909.04810. [Google Scholar]
- Morrison, D.; Corke, P.; Leitner, J. EGAD! an Evolved Grasping Analysis Dataset for diversity and reproducibility in robotic manipulation. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.01314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.; Killpack, M.D.; Edsinger, A.; Kemp, C.C. Reaching in clutter with whole-arm tactile sensing. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2013, 32, 458–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, K.; Zheng, J.; Wang, Y.; Hu, J. A Multi-Heuristic A* Algorithm Based on Stagnation Detection for Path Planning of Manipulators in Cluttered Environments. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 135870–135881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, L.; Billard, A.; Slotine, J. Avoidance of Convex and Concave Obstacles with Convergence Ensured Through Contraction. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2019, 4, 1462–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, P.D.H.; Hoffmann, M.; Pattacini, U.; Metta, G. A fast heuristic Cartesian space motion planning algorithm for many-DoF robotic manipulators in dynamic environments. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE-RAS 16th International Conference on Humanoid Robots (Humanoids), Cancun, Mexico, 15–17 November 2016; pp. 884–891. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, J.; Divvala, S.; Girshick, R.; Farhadi, A. You Only Look Once: Unified, Real-Time Object Detection. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 779–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.C.; Papandreou, G.; Kokkinos, I.; Murphy, K.; Yuille, A.L. DeepLab: Semantic Image Segmentation with Deep Convolutional Nets, Atrous Convolution, and Fully Connected CRFs. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1606.00915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rusu, R.B.; Cousins, S. 3D is here: Point Cloud Library (PCL). In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Shanghai, China, 9–13 May 2011; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischler, M.A.; Bolles, R.C. Random sample consensus: A paradigm for model fitting with applications to image analysis and automated cartography. Commun. ACM 1981, 24, 381–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tokatli, O.; Das, P.; Nath, R.; Pangione, L.; Altobelli, A.; Burroughes, G.; Jonasson, E.T.; Turner, M.F.; Skilton, R. Robot-Assisted Glovebox Teleoperation for Nuclear Industry. Robotics 2021, 10, 85. https://doi.org/10.3390/robotics10030085
Tokatli O, Das P, Nath R, Pangione L, Altobelli A, Burroughes G, Jonasson ET, Turner MF, Skilton R. Robot-Assisted Glovebox Teleoperation for Nuclear Industry. Robotics. 2021; 10(3):85. https://doi.org/10.3390/robotics10030085
Chicago/Turabian StyleTokatli, Ozan, Pragna Das, Radhika Nath, Luigi Pangione, Alessandro Altobelli, Guy Burroughes, Emil T. Jonasson, Matthew F. Turner, and Robert Skilton. 2021. "Robot-Assisted Glovebox Teleoperation for Nuclear Industry" Robotics 10, no. 3: 85. https://doi.org/10.3390/robotics10030085
APA StyleTokatli, O., Das, P., Nath, R., Pangione, L., Altobelli, A., Burroughes, G., Jonasson, E. T., Turner, M. F., & Skilton, R. (2021). Robot-Assisted Glovebox Teleoperation for Nuclear Industry. Robotics, 10(3), 85. https://doi.org/10.3390/robotics10030085






