Melanins of Inonotus Obliquus: Bifidogenic and Antioxidant Properties
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Melanin Production
2.3. Phenolic Content and Antioxidant Activity Determination
2.4. Inonotus Obliquus Melanin Assays
2.5. Microorganisms and Culture Media
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
Inonotus Obliquus Melanins Physicochemical Profile
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cui, Y.; Kim, D.S.; Park, K.S. Antioxidant effect of Inonotus obliquus. J. Ethnopharm. 2005, 96, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mashkovsky, M.D. Pharmaceuticals; Novaya Volna: Sochi, Russia, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Shashkina, M.Y.; Shashkin, P.N.; Sergeev, A.V. Chemical and medicobiological properties of chaga (review). Pharm. Chem. J. 2006, 40, 560–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novik, G.I.; Sidorenko, A.V. Bifidobacterium problems and new technologies of medical probiotics. Health Environ. Issues 2006, 4, 119–126. [Google Scholar]
- Kukulyanskaya, T.A.; Kurchenko, V.P.; Babitskaya, V.G. Physical and chemical properties of melanins produced by chaga in natural conditions and during cultivation. Appl. Biochem. Microbiol. 2002, 38, 68–72. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sysoeva, M.A.; Ivanova, G.A.; Gamayurova, V.S.; Ziyatdinova, G.K.; Budnikov, G.K.; Zakharova, L.Y.; Voronin, M.A. Improvement of the antioxidant properties of aqueous extracts and melanin of chaga. I. Treatment of chaga aqueous extracts with aqueous solutions of hyperbranched polymers. Khimiia Rastit. Syria (Chem. Plant Raw Mater.) 2010, 2, 105–108. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Burmasova, M.A.; Sysoeva, M.A. Chemical Composition Biological Activity of the BuOH Fraction from Chaga Melanin. Pharm. Chem. J. 2017, 51, 292–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, G.; Yang, Q.; He, C. Effect of ascorbic acid and cysteine hydrochloride on growth of Bifidobacterium bifidum. Adv. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 5, 678–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorskaya, E.M.; Bondarenko, V.M.; Vorobyev, A.A.; Budanova, E.V. Stimulator of Growth of Lactobacillus, Escherichia Coli, and Bifidobacteria. Patent RU 2062787, 27 June 1996. (In Russian). [Google Scholar]
- Ervolder, T.M. Preliminary activation of freeze-dried biomass and the subsequent development of bifidobacteria in the “Bifidok” product. Dairy Ind. 2002, 12, 41–42. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Novic, G.I.; Shtaida, A.A.; Schweitzer-Day, E. The Culture Media for the Cultivation of Lactobacteria and Bifidobacteria. Patent BY 12140, 30 October 2008. [Google Scholar]
- State Pharmacopoeia of the USSR; Medicina: Moscow, Russia, 1989.
- Sysoeva, A.V.; Kuznetsova, O.Yu.; Gamayurova, V.S.; Sukhanov, P.P.; Khalitov, F.G. Investigation of chaga aqueous extracts. II. Influence of the extraction method on the properties of the studied system. Bull. Technol. Univ. 2003, 2, 172–176. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Sysoeva, M.A.; Sysoeva, E.V.; Gamayurova, V.S.; Sysoeva, A.V. Method of Obtaining Aqueous Extracts of Chaga. Patent RU 2406514, 20 December 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Burmasova, M.A.; Sysoeva, M.A. Content of the butanol extracts of chaga melanin. Khimiia Rastit. Syria (Chem. Plant Raw Mater.) 2012, 1, 149–152. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Nikitina, S.A.; Habibrahmanova, V.R.; Sysoeva, M.A. Development of dietary supplements based on chaga melanin. In Proceedings of the X International Conference of Young Scientists “Food Technologies and Biotechnology”, Kazan, Russian, 15–18 May 2012; pp. 135–138. [Google Scholar]
- Pohloudek-Fabini, R.; Beyrich, T. Organic Analysis; Chemistry: Leningrad, Russia, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Tusevski, O.; Kostovska, A.; Iloska, A.; Trajkovska, L.; Simic, S.G. Phenolic production and antioxidant properties of some Macedonian medicinal plants. Cent. Eur. J. Biol. 2014, 9, 888–900. [Google Scholar]
- GOST R 54037-2010 Foodstuffs. Determination of Water-Soluble Antioxidants Content by Amperometric Method in Vegetables, Fruits, Products of Their Processing, Alcoholic and Soft Drinks 2010; Standartinform: Moscow, Russia, 2011; p. 12. [Google Scholar]
- Khairutdinova, E.I.; Mirgorodskaya, A.B.; Kushnazarova, R.A.; Bekmukhametova, A.M.; Zakharova, L.Y. Aggregation behavior of the corrosion inhibitor N-cetyl-N-methylmorpholinium bromide in mineralized media. Bull. Technol. Univ. 2017, 20, 72–75. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Tepper, E.Z.; Shilnikova, V.K.; Pereverzeva, G.I. Practical Works on Microbiology; Drofa: Moscow, Russia, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Schlegel, G. General Microbiology; Mir: Moscow, Russia, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Sysoeva, M.A.; Habibrahmanova, V.R.; Minkin, B.S.; Gamayurova, V.S.; Petrashen, V.E. Separation of chaga aqueous extracts using ethyl acetate II. Paramegnetic properties of melanin chromogens. Khimiia Rastit. Syria (Chem. Plant Raw Mater.) 2007, 4, 105–109. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Clancy, C.M.R.; Simon, J.D. Ultrastructural organization of eumelanin from Sepia officinalis measured by atomic force microscopy. Biochemistry 2001, 40, 13353–13360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clancy, C.M.R.; Nofsinger, J.B.; Hanks, R.K.; Simon, J.D. A hierarchical self assembly of eumelanin. J. Phys. Chem. 2000, 104, 7871–7873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, G.N.; Miglioranza, L.H.S. Miglioranza Probiotics: The Effects on Human Health and Current Prospects. In Probiotics; Rigobelo, E., Ed.; Intech: London, UK, 2012; Chapter 15; pp. 367–384. [Google Scholar]
- Pereverzeva, E.V.; Shimanets, S.V.; Antipenko, A.A.; Garkun, Y.S.; Rojnova, L.E.; Avad, A.; Pashkevich, S.G.; Kandybo, T.S.; Pereverzev, V.A.; Kulchitsky, V.A. Clinico-physiological features of the neurotropic action of the aquatic extract of the polypore fungus. Bull. Smolensk Med. Acad. Med. Biol. J. 2005, 3, 17–21. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are available from the authors |
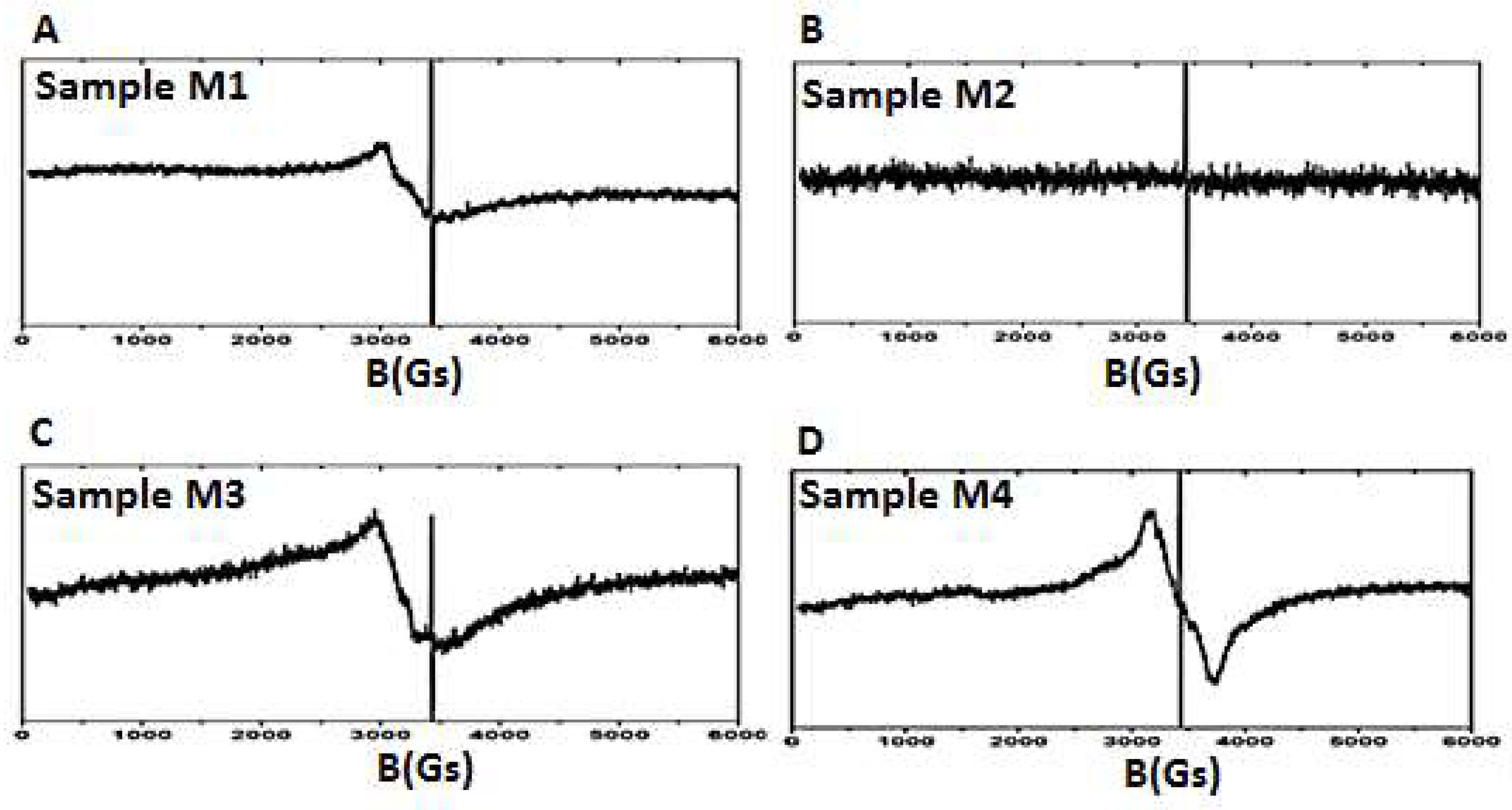
| Object | Pd Index | Size and Quantity of Particles | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Large | Medium | Small | |||||
| Diameter, nm | Intensity, % | Diameter, nm | Intensity, % | Diameter, nm | Intensity, % | ||
| M1 | 1.00 | 356.0 | 71.8 | 64.65 | 16.0 | 22.87 | 10.3 |
| M2 | 0.64 | 396.9 5360 | 80.4 1.4 | 42.64 | 18.2 | - | - |
| M3 | 0.35 | 378.7 5371 | 81.7 1.2 | 96.88 | 17.1 | - | - |
| M4 | 0.85 | 287.1 | 86.7 | - | - | 21.71 2.97 | 5.9 7.4 |
| Object | Conductivity, mS/cm | Zeta Potential | Zeta potential, mV | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| High | Average | Low | ||||||
| Mean, mV | Area, % | Mean, mV | Area, % | Mean, mV | Area, % | |||
| M1 | 0.27 | 138.0 | 0.6 | 18.2 | 9.5 | −16.0 | 89.6 | −14.00 |
| M2 | 0.27 | 131.0 | 2.8 | 43.0 | 2.6 | −27.6 | 87.1 | −17.60 |
| M3 | 0.71 | - | - | - | - | −31.5 | 100.0 | −31.50 |
| M4 | 0.61 | 80.7 | 38.9 | −12.4 | 7.9 | −43.9 | 25.7 | −1.34 |
| Melanin | Total Antioxidant Capacity, (Ascorbic Acid mg-Equivalent)/(g of Melanin) | Antioxidant Activity (Amperiometric Detection), mg/g | Oxidation-Reduction Potential of the Solution, mV | Total FREE Phenolic Substances, mg/cm3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M1 | 0.5555 ± 0.03 | 46.42 ± 2.39 | 4.07 ± 1.67 | 19.23 ± 0.75 |
| M2 | 0.6650 ± 0.06 | 8.78 ± 0.67 | −5.51 ± 2.22 | 22.20 ± 0.40 |
| M3 | 0.2940 ± 0.01 | 21.90 ± 0.54 | −4.16 ± 1.23 | 9.53 ± 0.30 |
| M4 | 0.1113 ± 0.01 | 15.96 ± 2.89 | 323.50 ± 9.09 | 3.01 ± 0.14 |
| Melanin | EPR Spectrum Signals | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wide | Narrow | ||||
| g1 | Int1 | g2 | w2 (Gs) | Int2 | |
| M1 | 2.09 | 3.33 × 107 | 1.999 | 4.1 | 5.55 × 106 |
| M2 | - | - | 1.999 | 3.7 | 1.25 × 106 |
| M3 | 2.12 | 5 × 107 | 1.999 | 5.0 | 3.15 × 105 |
| M4 | 1.99 | 4.62 × 107 | 2.000 | 4.9 | 1.25 × 106 |
| Object | B. bifidum 1 Population Counts, lg CFU*/cm3 | Exponential Growth Rate µ, h−1 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Incubation Period, h | |||||
| 0 | 6 | 12 | 24 | ||
| Control | 5.03 ± 0.04 | 5.20 ± 0.01 | 6.20 ± 0.02 | 8.37 ± 0.07 | 0.46 |
| Ascorbic acid, 10−10 g/cm3 | 5.03 ± 0.03 | 5.27 ± 0.12 | 6.60 ± 0.13 | 8.30 ± 0.11 | 0.45 |
| Ascorbic acid, 10−5 g/cm3 | 5.08 ± 0.11 | 5.28 ± 0.10 | 6.59 ± 0.06 | 8.93 ± 0.03 | 0.55 |
| Object | Concentration g/cm3 | B. bifidum 1 Population Counts, lg CFU/cm3 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Incubation Period, h | ||||
| µ | 0 | 24 | ||
| Control | 0.65 | 4.10 ± 0.27 | 7.20 ± 0.17 | |
| M1 | 10−10 | 0.73 | 4.46 ± 0.09 | 7.66 ± 0.10 |
| M2 | 0.56 | 3.40 ± 0.16 | 6.87 ± 0.09 | |
| M3 | 0.69 | 3.66 ± 0.10 | 8.13 ± 0.10 | |
| M4 | 0.32 | 4.56 ± 0.09 | 7.06 ± 0.09 | |
| M1 | 10−5 | 0.35 | 4.92 ± 0.05 | 6.86 ± 0.10 |
| M2 | 0.60 | 3.40 ± 0.16 | 7.95 ± 0.08 | |
| M3 | 0.54 | 4.53 ± 0.10 | 7.53 ± 0.10 | |
| M4 | 0.50 | 4.40 ± 0.16 | 7.66 ± 0.09 | |
| Object | Concentration, g/cm3 | Oxidation-Reduction Potential in the Medium, mV | Titer, lg CFU/cm3 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 h | 24 h | 0 h | 24 h | ||
| Control | - | −125.28 ± 6.32 | 131.44 ± 6.66 | 5.02 ± 0.10 | 6.35 ± 0.21 |
| M2 | 10−5 | −16.02 ± 3.30 | 114.30 ± 4.63 | 5.24 ± 0.12 | 7.54 ± 0.20 |
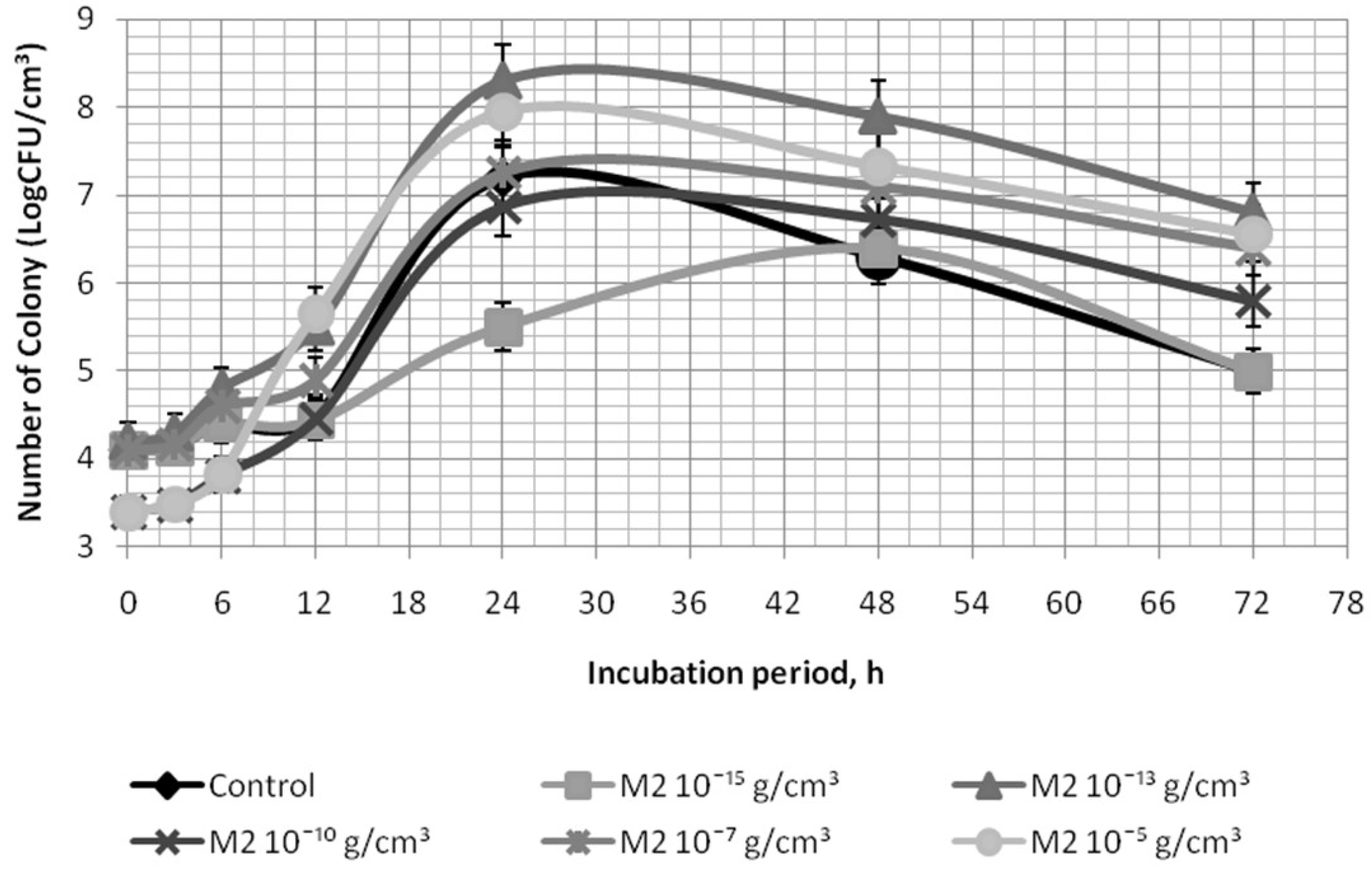
| Object | B. animalis subsp. lactis Population Counts, lg CFU/cm3 | Exponential Growth Rate µ, h−1 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Incubation Period, h | |||||
| 0 | 6 | 12 | 24 | ||
| Control | 6.07 ± 0.27 | 6.13 ± 0.05 | 7.95 ± 0.15 | 8.89 ± 0.04 | 0.70 |
| M2, 10−13 g/cm3 | 6.07 ± 0.27 | 6.14 ± 0.39 | 7.35 ± 0.39 | 8.53 ± 0.25 | 0.29 |
| M2, 10−10 g/cm3 | 6.07 ± 0.27 | 6.43 ± 0.39 | 7.70 ± 0.22 | 9.75 ± 0.14 | 0.51 |
| M2, 10−7 g/cm3 | 6.07 ± 0.27 | 7.91 ± 0.08 | 8.53 ± 0.21 | 9.06 ± 0.40 | 1.49 |
| M2, 10−5 g/cm3 | 6.07 ± 0.27 | 8.11 ± 0.04 | 9.05 ± 0.17 | 9.87 ± 0.09 | 1.61 |
| M2, 10−2 g/cm3 | 6.07 ± 0.27 | 8.26 ± 0.01 | 9.05 ± 0.07 | 9.47 ± 0.26 | 1.86 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Burmasova, M.A.; Utebaeva, A.A.; Sysoeva, E.V.; Sysoeva, M.A. Melanins of Inonotus Obliquus: Bifidogenic and Antioxidant Properties. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 248. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9060248
Burmasova MA, Utebaeva AA, Sysoeva EV, Sysoeva MA. Melanins of Inonotus Obliquus: Bifidogenic and Antioxidant Properties. Biomolecules. 2019; 9(6):248. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9060248
Chicago/Turabian StyleBurmasova, Marina A., Aidana A. Utebaeva, Elena V. Sysoeva, and Maria A. Sysoeva. 2019. "Melanins of Inonotus Obliquus: Bifidogenic and Antioxidant Properties" Biomolecules 9, no. 6: 248. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9060248
APA StyleBurmasova, M. A., Utebaeva, A. A., Sysoeva, E. V., & Sysoeva, M. A. (2019). Melanins of Inonotus Obliquus: Bifidogenic and Antioxidant Properties. Biomolecules, 9(6), 248. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9060248





