Abstract
Despite advancements in healthcare facilities for diagnosis and treatment, cancer remains the leading cause of death worldwide. As prevention is always better than cure, efficient strategies are needed in order to deal with the menace of cancer. The use of phytochemicals as adjuvant chemotherapeutic agents in heterogeneous human carcinomas like breast, colon, lung, ovary, and prostate cancers has shown an upward trend during the last decade or so. Flavonoids are well-known products of plant derivatives that are reportedly documented to be therapeutically active phytochemicals against many diseases encompassing malignancies, inflammatory disorders (cardiovascular disease, neurodegenerative disorder), and oxidative stress. The current review focuses on two key flavonols, fisetin and quercetin, known for their potential pharmacological relevance. Also, efforts have been made to bring together most of the concrete studies pertaining to the bioactive potential of fisetin and quercetin, especially in the modulation of a range of cancer signaling pathways. Further emphasis has also been made to highlight the molecular action of quercetin and fisetin so that one could explore cancer initiation pathways and progression, which could be helpful in designing effective treatment strategies.
1. Introduction
The incidence of malignant diseases and the prevalence of cancer mortality is proliferating at an amplified rate across the developed and developing countries [1]. New Globocan 2018 cancer data from 185 countries documented 18.1 million new cancer cases and 9.6 million cancer-related deaths (GALOBOCAN 2018). Although the improvement of diagnostic tools, advanced treatment approaches, and cancer awareness programs have resulted in a remarkable drop in cancer mortality in the United States, cancer prevalence is still growing continuously [1]. This is attributed to smoking habits, alcohol consumption, unhealthy food, stress, and no or insufficient exercise amongst people in the developed and developing world [2]. There are different therapeutic modalities for cancer treatment available, including surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, immunotherapy, and targeted therapy. Tamoxifen in estrogen receptor-positive breast tumor, Herceptin in Her 2+ breast cancer, epithelial growth factor receptor (EGRF) inhibitors (erlotinib, afatinib, osimertinib, and fefitinib) in non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC), K-ras inhibitors (cetuximab) in colon cancer, B-Raf inhibitors (vemurafenib, dabrafenib, and encorafenib) in melanoma, and gleevec for ABL-BCL (translocation of c-ABL gene sequences from chromosome 9 into the BCR gene on chromosome 22) positive leukemia have been used widely in clinical settings [3]. However, cancer cells can evade death by gaining resistance to various treatment modalities, which has diluted the expected outcome of these therapies [4,5,6]. This has necessitated the discovery of alternative treatment strategies to cure cancer patients. Numerous in vitro studies in conjunction with ex vivo studies have exemplified the anti-cancer effects of natural products such as flavonoids [7,8,9,10]. Specifically, fisetin and quercetin, two well-studied flavonoids, have shown remarkable anti-cancer effects in multiple in vitro and in vivo systems. Different events in cancer initiation and progression such as apoptosis, extracellular matrix remodeling, epithelial to mesenchymal transition, cancer-associated inflammation, and oxidative stress can be controlled by fisetin and quercetin [11,12]. In vitro studies showed that fisetin and quercetin could also act against chemotherapeutic resistance in several cancers [13,14]. Numerous cancer-related molecules such as anti-apoptotic and pro-apoptotic proteins, cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs), cyclins, matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), and growth factors have been shown to be modulated by fisetin and quercetin (Figure 1 and Figure 2). Quercetin can also bind to a G protein coupled receptors to activate a G protein and calcium-dependent pathway which leads to tumor cell death [13,14,15]. In addition, these phytochemicals also exhibit synergistic effects where they enhance the anti-tumor activity of many anti-cancer drug molecules (Table 1). The present review highlights the important anti-cancer roles of quercetin and fisetin in various in-vitro/ex-vivo studies.
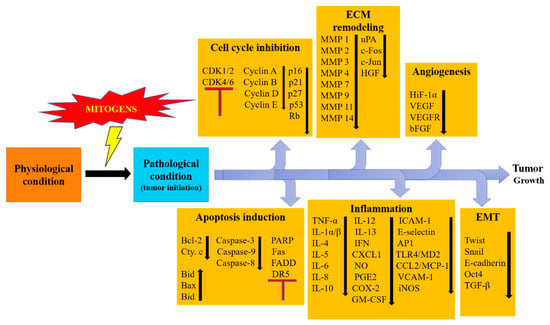
Figure 1.
Showing regulation of different cancer related processes under the effect of flavonoids. All these processes are crucial in carcinogenesis and play key roles for cancer initiation and progression. Flavonoids effectively act at these processes to inhibit cancer growth.

Figure 2.
Figure showing regulation of different cancer associated signaling pathways. Deregulation of these pathways has been determined in human malignancies. Flavonoids control the deregulation of these pathways and cancer proliferation.

Table 1.
Synergistic effects.
2. Chemistry of Fisetin and Quercetin
Structurally, fisetin has two aromatic rings which are linked through a three-carbon oxygenated heterocyclic ring, and is supplemented with four hydroxyl group substitutions and one oxo group [38,39] (Figure 3a). It is usually present in different fruits and vegetables such as strawberries, apples, onions, and cucumbers [40] and in various trees and shrubs belonging to the Fabaceae and Anacardiaceae families, as well as quebracho colorado and pinophyta species [39]. Fisetin has low aqueous solubility and bioavailability. The biological activity of fisetin is due to the presence of hydroxyl groups at the 3, 7, 3’, 4’ positions and oxo group at the 4 position with double bond between C2 and C3. Quercetin belongs to the polyphenolic class and is found in many fruits, red onion, and the roots and leaves of many vegetables. It also has very poor solubility and oral bioavailability. Quercetin has five hydroxyl groups on C6-C3-C6 backbone structure, in particular a 3-OH group on the pyrone ring (Figure 3b) [41].
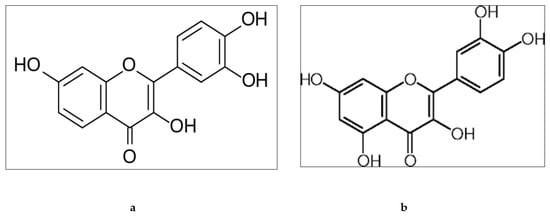
Figure 3.
Chemical structure of fisetin (a) and quercetin (b).
3. Regulation of Cancer-Related Processes
3.1. Activation of Intrinsic Apoptotic Pathway
Various cytotoxic chemotherapy drugs activate apoptotic processes in tumor cells by up-regulating and down-regulating the expression of different pro-apoptotic and anti-apoptotic proteins, respectively [42,43]. Similarly, flavonoids have been demonstrated to activate apoptotic processes in exorbitant cancer cell lines and animal models. Mechanistically, regulation of the release of cytochrome c from mitochondria, caspase-3 and caspase-9 mRNA and protein expression, and B-cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2) and Bcl-2 associated X (Bax) levels, were found to be regulated in the fisetin-treated cancer cell line (oral squamous carcinoma) [44]. Further, Li et al. also documented the apoptotic capacity of fisetin in T24 and EJ human bladder cancer cells, acting through overexpression of Bax, Bcl2 associated agonist of cell death (Bad), and Bcl-2 antagonist/Killer 1 (Bak) and inhibition of Bcl-2 and B-cell lymphoma-extra large (Bcl-xL) [45]. In a similar manner, apoptosis was seen in the U266 myeloma cancer cell line, which was mediated by activation of caspase-3, Bax, Bcl-2-like protein 11 (Bim), Bad, and inhibition of Bcl-2 and myeloid cell leukemia-1 (Mcl-1L) [46]. This phytochemical was also shown to exhibit an anti-tumor effect in the NCI-H460 NSCLC cell line through activation of caspase-9 and caspase-3 and inhibition of Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL, with adjacent effects on DNA fragmentation and depolarization of the mitochondrial membrane [47]. Another study identified that fisetin at 5–80 µM significantly reduced the viability of A431 human epidermoid carcinoma cells by the release of cytochrome c, reducing the anti-apoptotic protein expression of Bcl-2, Bcl-xL, and Mcl-1 along with elevation of pro-apoptotic protein expression (Bax, Bak, and Bad) and caspase cleavage and poly-ADP-ribose polymerase (PARP) protein [48]. The in-vitro and in-vivo administration of fisetin promoted caspase-8 and cytochrome c expression, possibly by impeding the aberrant activation of insulin growth factor receptor 1 and Akt proteins in oxaliplatin/irinotecan-resistant colorectal tumor cells [49]. In uveal melanoma cells, apoptosis was reported to be induced using fisetin by inhibiting the expression of Bcl-2 family proteins and increasing Bax levels, cytochrome c release, and activities of various caspases, whereas it was not cytotoxic to healthy retinal pigment epithelial cells [50]. The in vitro activity of fisetin in the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway has been acknowledged to be effective in the treatment of oral carcinomas. Fisetin enhanced the expression of pro-apoptotic proteins Bak and Bax but reduced anti-apoptotic protein expression (Bcl-2 and Bcl-x), while it also led to activation of caspase-3, caspase-8, caspase-9, and augmented sustained release of cytochrome c and apoptosis-inducing factor expression in HSC3 [51] and SCC-4 oral carcinoma cells [52]. Further, Khan et al. found fisetin (10-60 µM) treatment resulted in activation of apoptosis, poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) cleavage, modulation of Bcl-2 family protein expression (Bak, Bad, Bid, Bcl-xL), inhibition of the phoshoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt signaling pathway, and activation of caspase 3, caspase-9, and-8 enzyme activity in LNCaP prostate cancer cell lines [53]. Similarly, evidence suggests that quercetin can also activate apoptosis through a mitochondrial pathway involving the activation of caspase-3 and caspase-9 and by the release of cytochrome c and cleavage of PARP in acute lymphoblastic leukemia (HPB-ALL and HL-60) and prostate cancer cells (DU-145 and PC-3) [54,55,56]. Moreover, a myriad of studies has shown anti-apoptotic (Bcl-xL and Bcl-2) and pro-apoptotic (Bax) protein modulation by quercetin in human colon, oesophageal adenocarcinoma, and leukemia cells [57,58,59]. In addition, quercetin treatment also resulted in an attenuated Bcl-xL to Bcl-xS ratio and augmented translocation of Bax protein to mitochondrial membrane in LNCaP human prostate cancer cells [60]. In vitro studies with human cancer cell lines HaCaT keratinocytes, established the anti-tumorigenic effect of quercetin through Bax over-expression and release of cytochrome c and translocation of factors inducting apoptosis into the nucleus [61]. Similar effects of quercetin have also been reported in CLL and acute myeloid leukemia cell line HL-60; this phytochemical treatment activated the pro-apoptotic signaling cascade through PARP-1 cleavage and caspase activation, and also initiated autophagy events by the increased expression of light chain 3-II, decreased expression of p62, and formation of acidic vesicular organelles [62].
3.2. Activation of the Extrinsic Apoptotic Pathway
Several studies have illustrated the anti-tumor function of plant-derived products via activation of extrinsic apoptotic pathways [63,64]. Fisetin treatment administered in a time- and dose-dependent manner led to induction of apoptosis in HeLa cervical cancer by activation of caspases (3 and 8) and PARP cleavage [65]. Similarly, in human colon cancer cells (HCT-1160), fisetin-mediated apoptosis was also observed involving DNA condensation, cleavage of PARP, enhanced caspase-8 expression, Fas ligand, death receptor 5, and tumor necrotic factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL-R1) expression [66]. Further, fisetin-promoted apoptotic activation was also seen in DU145, LNCaP, and PC3 human prostate cancer cells [53,67]. Quercetin (>20µM) induced caspase-dependent extrinsic apoptosis by upregulating the expression of caspase-3 and caspase-8, and inducing the cleavage of PARP in a HER2-overexpressing (BT-474) breast cancer cell line [68], consistent with the earlier reports in another leukemia cell line (CEM, K562 and Nalm6) [69].
3.3. Activation of Cell Cycle Arrest through the G0/G1 Check Point
Multiple in vitro studies have also noticed the cell cycle regulatory function of bioactive compounds mediated through CDKs and cyclin proteins [70,71]. Recent studies revealed that fisetin binds with CDK6, which in turn blocks its activity with an inhibitory concentration (IC50) at a concentration of 0.85 μM [72]. For instance, fisetin is identified as a regulator of cell cycle checkpoints, leading to cell arrest through CDK inhibition in HL60 cells and astrocyte cells over the G0/G1, S, and G2/M phases [73,74]. Sabarwal et al. and colleagues analyzed fisetin-induced proliferation inhibition in adenocarcinoma gastric cell line (AGS) and SNU-1 human gastric carcinoma cells, through a remarkable attenuation of G1 phase cyclins and CDKs level, while exhibiting elevated levels of p53 and its S15 phosphorylation [75]. Further, fisetin treatment has also been documented to arrest cell cycle growth in G0/G1 phase by enhancing the p53 and p21 gene expression, while reducing CDK4, CDK2, cyclin D1, and cyclin A in bladder cancer cell lines T24 and EJ [45]. In addition, at 10–60 μM fisetin concentration, prostate cancer cells PC3, LNCaP, and CWR22Ry1 had decreased cellular viability and decreased levels of D1, D2, and E cyclins and their activating partners CDK2, and CDKs 4/ 6, with consequent induction of KIP1/p27 and WAF1/p21 [53]. Fisetin (10–60 µM) treatment also shows a notable accumulation of the tumor cell population in the G1 phase of the cell cycle, accompanied by a concomitant decrease in the S-phase and G2/M-phase cell population [53].
Similar to fisetin, treatment of vascular smooth muscle cells with quercetin induced G1 cell cycle arrest through alleviation of D1/Cdk4 and E/Cdk2 and upregulation of p21 [76]. In addition, quercetin mediated anti-proliferation effects in different human cancer cells including hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cells, ovarian cancer SKOV 3 cells, and malignant mesothelioma (MM) MSTO-211H and H2452 cells [77] through cell cycle inhibition at G0/G1 to G2/M checkpoint [78]. In colon cancer cell lines, such as Caco2 [79] and SW480 [80], quercetin has been reported to inhibit cell cycle in a concentration-dependent (5 to 160 µM) manner. Furthermore, quercetin inhibited the cell cycle in colon cancer stem cells [81]. Quercetin-induced G0/G1-phase arrest occurred when expression of CDK2 and CDK4 was inhibited in HL-60 myeloid leukemia cells [62].
3.4. Activation of Cell Cycle Arrest through G2/M Check Point
Flavonoids can also block the cell cycle division at the G2/M check point [8]. For example, treatment of A431 cells with fisetin resulted in G2/M phase arrest [48]. Poor et al. demonstrated that among 18 tested compounds, diosmetin, fisetin, apigenin, luteolin, and quercetin provoked spectacular G2/M phase arrest in the hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cell line [82].
Similarly, quercetin enhanced the expression of retinoblastoma (Rb) gene in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells HK1 and CNE2 and blocked the cell cycle in the G2/M phase [83]. Moreover, a concentration-dependent anti-tumor effect of quercetin was observed as a result of G2/M phase arrest in an in vitro study using lung carcinoma cell lines H1299 and A549A [84]. In addition, quercetin-mediated upregulation of p21, p27, p53, and Chk2 followed by downregulation of CDK1, cyclin B, pRb phosphorylation, and G2/M phase arrest were also reported in hepatocellular carcinoma [85,86]. Quercetin was also shown to inhibit cell cycle in G2/M phase in breast carcinoma (MCF-7) [87], leukemia (U937 cells) [88], and esophageal adenocarcinoma cell lines (OE33) [89].
3.5. Regulation of Extracellular Matrix Remodeling
The extracellular matrix (ECM) is an integral part of tissue and plays important functions [90]. Multiple studies described ECM remodeling as a key feature in lung, breast, ovarian, cervical, prostate, and colon cancer [91]. In a study, fisetin displayed tumor inhibitory effects by blocking MMP-2 and MMP-9 at mRNA and protein levels in prostate PC-3 cells [92]. Similarly, fisetin can also inhibit MMP-1, MMP-9, MMP-7, MMP-3, and MMP-14 gene expression linked with ECM remodeling in human umbilical vascular endothelial cells (HUVECs) and HT-1080 fibrosarcoma cells [93]. An interesting scientific finding from a recent study manifested that fisetin downregulates expression and reduces urokinase plasminogen activator (uPA) activity in human cervical adenocarcinoma SiHa and CaSki cells, responsible for activation of MMPs [94]. Furthermore, fisetin in a concentration-dependent manner (10–50 μM concentration) significantly inhibited regular serum, growth-enhancing supplement, and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-mediated growth in in vivo (mice) and in vitro (A549 and DU145, HUVECs) system, in addition to its effects on MMP-2 and MMP-9 [95].
A drop in MMP-2 and MMP-9 activity was detected in addition to its effects on other several apoptotic pathways after quercetin treatment in multiple cancer cell lines i.e., human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC), colon cancer (Caco-2 cells), and breast cancer (MCF-7 cells) [96,97,98]. Furthermore, anti-metastatic effects of quercetin were also explored and documented in the chicken chorioallantoic membrane assay using prostate cancer line PC-3 [99]. There also exists strong evidence that quercetin inhibits VEGF-related angiogenesis in several tumorigenic cell lines such as SN38 gastric cancer cells [100], osteosarcoma [101], and retinoblastoma (Rb) [102].
3.6. Regulation of Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition
Epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) is a key process in cancer invasion or progression [103,104,105,106,107,108,109]. Flavonoids have been shown to regulate the ECM remodeling and hence, cell invasion. The anti-metastasis effects of fisetin (5–20 μM) were revealed in melanoma cells, occurring through downregulation of mesenchymal markers (vimentin, N-cadherin, snail, and fibronectin) and upregulation of epithelial markers (desmoglein and E-cadherin) [110]. In in vitro and raft cultures, Pal et al. found that fisetin treatment minimized tumor invasion and tumor cell migration of BRAF V600E mutation-positive melanoma cells and alleviated EMT by decreasing vimentin, Twist1, N-cadherin, Snail1, ZEB1, Slug, and fibronectin expression, and escalating E-cadherin levels [16]. The in vitro findings from another study by Li et al. concluded that fisetin could significantly overpower growth and metastasis in MDA-MB-231 and BT549 triple-negative breast cancer cell lines, thereby blocking the EMT process induced through the phosphatase and tensin homolog/protein kinase B/glycogen synthase kinase 3 (PTEN/Akt/GSK-3β) signaling pathway [111].
Similarly, the recent scientific literature has also documented that quercetin prevented transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β)-induced EMT in PC-3 prostate cancer cells, through inhibition of TGF-β-induced expression of N-cadherin and vimentin along with increased E-cadherin expression. Additionally, quercetin significantly decreased the TGF-β-induced expression of Snail, Twist, and Slug [112]. Quercetin treatment was also illustrated to affect the migration capacity of head and neck cancer-derived sphere cells through decreased production of N-cadherin, twist, and vimentin [113]. Quercetin was also reported to decrease CT26 and MC38 colorectal carcinoma lung metastasis and also regulated the expression of EMT markers (E-cadherin, N-cadherin, Snail, and β-catenin) which in turn inhibited the expression of MMPs [114].
4. Control of Cancer-Associated Signaling Pathways by Fisetin and Quercetin
4.1. Regulation of PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway
The PI3K/Akt pathway has been correlated with many fundamental processes during cancer development [115,116,117,118]. It plays a significant role in apoptosis, survival, and angiogenesis [119,120,121,122]. Therefore, this pathway could be a major target in cancer inhibition. Flavonoids have the potential to interact with this signaling pathway. Promising effects of fisetin on this pathway have been well reviewed by George [123]. Fisetin significantly reduced the viability of human osteosarcoma (U-2 OS) cells in a concentration-dependent manner (20–100 µm) through modulation of PI3K/Akt signaling cascades [124]. Similarly, fisetin inhibited PI3K expression and phosphorylation of Akt [53]. In a detailed study using fisetin, the blocking of Akt by exogenous siRNA in prostate cancer cells (LNCaP) caused an elevated Bad and Bax expression, and decreased expression of Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL, which suggested that these effects are mediated in part through Akt [53]. Further, in Raji cells (human Burkitt’s lymphoma cells), fisetin treatment activated the apoptotic process through inhibiting both PI3K and mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling pathways [125]. Pal et al. presented the inhibitory effect of fisetin treatment on PI3K signaling pathway implicated through Akt phosphorylation of Akt in nude mice implanted with A375 and SKH-1 melanoma cells and SKH-1 hairless mice [16,126].
Moreover, a sustained inhibition of PI3K, Akt and cross-communication between PI3K and extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERKs) was described in quercetin-treated HepG2 hepatocellular carcinoma cells [127]. An elevation in endocannabinoids receptor (CB1-R) expression following quercetin treatment has been noted in colon and breast cancer cell lines, which in turn inhibited survival signaling pathways such as PI3K/Akt/mTOR [128,129]. Cancer stem cells (CSCs) have recently gained major importance as novel targets in targeted cancer therapy and quercetin research is further supported by its inherent capacity to inhibit CSCs through the PI3K/Akt and MAPK/ERK pathways in prostate CSCs [130] and the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathways in breast CSCs [131].
4.2. Regulation of the Nuclear Factor Kappa Light Chain Enhancer of Activated B Cells Signaling Pathway
The nuclear factor kappa light chain enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB) signaling pathway has a remarkable role in pathologic conditions such as cancer [132,133]. Suppression of NF-κB pathway in tumorigenic cells usually leads to tumor regression, which makes the NF-κB pathway a promising therapeutic target [134,135]. The effects of fisetin on this pathway have been investigated by Sung et al. in several cancer cell lines including Daudi human Burkitt lymphoma cells, H1299 human lung adenocarcinoma cells, and A293 human embryonic kidney cells. Fisetin inhibited TNF-induced IκBα degradation, NF-dependent IκBα phosphorylation and ubiquitination, TNF-induced IκBα kinase activation, p65 phosphorylation and its nuclear translocation, NF-κB-dependent anti-apoptotic gene expression (cIAP1/2, survivin, Bcl-2, XIAP, Bcl-xL and TRAF-1), and expression of cyclin D1, c-Myc, COX-2, MMP-9, VEGF, and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1), thereby revealing the numerous effects of fisetin on this pathway [17]. In another study, the treatment of COX-2 overexpressing HT29 human colon cancer cells with fisetin resulted in activation of apoptosis and inhibition of COX-2 and the Wnt/EGFR/NF-kB pathway [136]. In addition, fisetin treatment reversed 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA) mediated cell migration in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells, which caused NF-κB inactivation and downregulation of MMP-9 expression [137]. Another study found fisetin mediated downregulation of Syk, Src, and IκBα through inhibition of nuclear translocation of p65/NF-κB [138].
Youn et. al. confirmed that quercetin inhibited the growth of NSCLC (H460) by suppressing the NF-κB [139]. Another study, investigated the time dependent inactivation of NF-κB pathway with NF-κB binding activity which leads to the reduced survival and proliferation of HepG2 cell [140]. In human cell colon cancer (CACO-2 and SW-620 cell) quercetin also known to block the proliferation via inhibition of NF-κB pathway [141].
4.3. Regulation of JAK/STAT Signaling Pathway
The effects of Janus kinase/signal transducers and activators of transcription (JAK/STAT) signaling on tumor cell survival, proliferation, and invasion have made this pathway a favorite target for drug development and cancer therapy [142]. It was found that fisetin mediated apoptosis by regulation of the JAK/STAT and c-Kit pathways in K562 human chronic myeloid leukemia cells [143].
Additionally, it was suggested that quercetin inhibited the transcriptional activity of STAT3 and reduced the expression of STAT3 targeted genes such MM 2, MMP 9, Mcl-1, and VEGF in melanoma [144]. Furthermore, treatment with quercetin at 10 μM markedly inhibited JAK2 and STAT1 phosphorylation, and nuclear translocation of phosphorylated STAT1 in poly (dA:dT)-treated and interferon gamma-primed keratinocytes [145]. Michaud et al. suggested that quercetin reduced interleukin-6 (IL-6), stimulated JAK1 and STAT3 activation, and subsequently reduced the recruitment of cyclin D1 and MMP 2 genes in glioblastoma [146,147]. Mukherjee et al., described that quercetin also showed anti-tumor effects through downregulating the IL-6/STAT3 signaling pathway in NSCLC A549 cells [148].
4.4. Regulation of p38MAPK Pathway
Deregulation of p38 MAPK has been associated with advanced stages and short survival in cancer patients [149]. In human NCI-H460 NSCLC, fisetin regulated production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reduced the activation of p38 MAPK signaling pathway [150]. Similarly, the fistein treatment in HL-60 human acute promyelocytic leukemia cells caused inhibition of MAPK signaling and modulated DNA binding signaling pathways [73]. Furthermore, fistein treatment was also documented to reduce TPA-induced MCF-7 breast cancer cell invasion through inactivation of p38 MAPK signaling [137].
It was found that quercetin-mediated apoptosis was induced by ROS-dependent ASK1⁄p38 pathway activation [151]. In AGS gastric cancer cells, quercetin inhibited the MAPK cancer associated pathway and TRPM7 channels thereby acting as potential therapeutic agent for gastric carcinoma treatment [152]. Quercetin additionally induced apoptosis in breast cancer cells (MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231) through inhibition of p38 MAPK signaling leading to decrease in twist gene expression [153]. Lim et al. suggested that quercetin inhibited the phosphorylation of Akt, P70S6K, and S6 proteins, while it increased phosphorylation of P38, c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK), ERK1/2, and P90RSK proteins in JAR and JEG3 choriocarcinoma cell lines [154].
4.5. Regulation of ERK Signaling Pathway
The ERK signaling pathway is another major determinant for diverse cellular processes such as proliferation, differentiation, and survival [155]. In addition, various in vitro and ex vivo studies have also determined the anti-tumor effects of flavonoids mediated through ERK1/2 signaling inhibition. Fisetin is one of the flavonoids that has been found to suppress ERK1/2 signaling in human gastric (SGC7901), hepatic (HepG2), colorectal (Caco-2), and pancreatic cancer cells (Suit-2) [156,157]. In human NCI-H460 NSCLC, fisetin induced ROS generation and suppressed ERK through its phosphorylation [150]. Fisetin has also been documented to decrease the survival in CCA cholangiocarcinoma cells through modulating ERK phosphorylation, reduction of phospho-p65 and c-myc oncogene expression [158]. Similarly, a combination of N-acetylcysteine treatment and fisetin inhibited ERK protein phosphorylation in COLO-205 colon carcinoma cells [159]. Another study also found that fisetin had an anti-tumor effect in human glioma GBM8401 cells, via the regulation of ERK 1/2 and ADAM9 expression [160]. Further, quercetin caused HL-60 myeloid leukemia cell death by ERK signaling mediated apoptosis [161]. Quercetin was found to be engaged in inhibiting the ERK pathway, which subsequently suppressed angiogenesis [162,163]. Furthermore, recent data revealed that quercetin decreased prostate CSC survival and invasion through regulating MAPK/ERK signaling pathways [130].
4.6. Regulation of the Akt/mTOR/p70S6K Pathway
A range of studies has described the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway’s involvement in the initiation of angiogenesis. Natural products such as flavonoids may be used to target this cancer-related pathway [115]. Fisetin reduced Akt phosphorylation, p70S6K, mTOR, and mitf proteins in 451Lu human melanoma cells, which in turn inhibited angiogenesis [164]. Furthermore, in addition to melanoma [18], fisetin was found to be effective in leukemia [165] and lymphoma cells through this pathway. Following treatment with fisetin, the viability of 4T1, MCF-7, and MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells was reduced through interfering with the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway [166]. Fisetin was found to be an inhibitor of PI3K/Akt/ mTOR pathways [167] and an inducer of autophagia [168] in prostate cancer cell lines.
Quercetin was also documented to impede tumor proliferation and angiogenesis by targeting the VEGF receptor-2 (VEGF-R2) and Akt/mTOR/P70S6K signaling pathway in a mouse prostate cancer xenograft model [169]. The Akt/AMPK/mTOR pathway was shown to be one of the targets of quercetin in MDA-MB-231 and MDA-MB-435 breast cancer cells [170]. Furthermore, quercetin also induced Akt-mTOR mediated autophagy in breast cancer cells where it reduced the migration and metastasis of cells through MMP-2, MMP-9, and VEGF inhibition [171].
4.7. Regulation of Nrf2 Signaling Pathways
The Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 (Keap1)-nuclear factor E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) pathway is the major signaling cascade for defense and survival against endogenous and exogenous stress [172,173]. It has been found that fisetin increased the protein level and accumulation Nrf2 and down regulated the protein levels of Keap1 [174]. Fisetin also rapidly enhanced the expression of both Nrf2 and activating transcription factor 4 (ATF4) along with distinct mechanism leading to ATF-dependent gene transcription [175]. Treatment of cancer cells with quercetin caused dissociation of the Nrf2-Keap1 complex, and translocation of Nrf2 to the nucleus [176,177]. It has been found that treatment of HepG2 hepatocellular carcinoma cells with quercetin initiated antioxidant response element (ARE) binding activity and NQO1 expression [177]. Additionally, quercetin also prevented degradation of Nrf2 and stabilized it by maintaining the Keap1 protein levels without affecting Keap1-Nrf2 complex [177]. Further, quercetin-mediated overexpression of detoxification enzymes (phase II) was also demonstrated in human HuTu 80 duodenum adenocarcinoma cells and Caco-2 colorectal adenocarcinoma cells [178]. Recently, the anti-tumorigenic effects of quercetin was reported to be mediated by increased Nrf2 expression in MSTO-211H and H2452 malignant mesothelioma cells [179].
5. Regulation of Various Growth Factors
Growth factors are the key mediators for activation of several cancer-related signaling pathways [180]. Growth factors influence cell transformation and activation of growth-promoting pathways in tumor cells [181]. Flavonoid compounds are also able to control the expression of these growth factors. Mechanistically fisetin-induced anti-angiogenesis led to reduced VEGF and epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) expression [76,136]. Several in vivo studies in rats narrated downregulation of bVEGF and basic fibroblast growth factor which direct tumor growth inhibition, and alleviation of tumor proliferation, and angiogenesis [19]. Quercetin attenuated tumor proliferation, invasion, and migration through inhibiting hepatocyte growth factor (HGF)/c-Met signaling in melanoma cells [182]. Quercetin is also reported to reduce the insulin-like growth factors (IGFs) via increasing binding protein-3 (IGFBP-3) proteins and led apoptosis in the prostate cancer cell line PC-3 [183]. The effects of quercetin was promising enough to formulate novel gold nanoparticle conjugates of quercetin that induced apoptosis [184] and inhibited EMT, angiogenesis, and invasiveness through EGFR/PI3K/Akt and EGFR/VEGFR-2-mediated pathways respectively [185].
6. Regulation of Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines
Inflammation has been correlated with 20–40% of cancer cases. The blocking of cytokines is best used as an adjunct therapy together with tumoricidal drugs [186]. Fisetin attenuated aflatoxin B1 (AFB1)-mediated carcinogenesis by neutralizing elevated levels of IL-1α and TNF-α in rat model of hepatocellular carcinoma [187]. Other research groups have demonstrated a fisetin-mediated inhibitory effect against pro-inflammatory cytokines (e.g., TNF-R, IL-6, IL-8, and IL-1β), nitric oxide, and Th2-type cytokines (basophil-induced) in human mast cells [188,189]. The key allergic airway inflammation mediators, including Th2-associated cytokines (IL-13, IL-4, and IL-5), thymic stromal lymphoprotein, eotaxin-1, and transcription factor (GATA-3) in lungs respectively, were known to have reduced expression after fisetin treatment [190]. Moreover, fisetin is also known to reduce the level of inflammatory cytokines (IL-6, TNFα, and IL-1βIL-6) and expression of cell proliferation markers [126]. Fisetin suppressed IL-1β-mediated expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase, nitric oxide, interleukin-6, tumor necrotic factor-α, prostaglandin E2, cyclooxygenase-2 (iNOS, NO, IL-6, TNF-α, PGE2, and COX-2), and significantly decreased the degradation of Sox-9 and aggrecan, and reduced SIRT1 inactivation. In contrast, quercetin supplementation significantly decreased the infiltration of inflammatory cells as well as the levels of TNF-α and IL-1β in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid and plasma of gerbils exposed to benzo[a]pyrene (BaP) or BaP+ β-carotene in A549 adenocarcinoma alveolar basal epithelial cells [191]. Quercetin inhibited TNF-induced interferon-γ-inducible protein 10 and macrophage inflammatory protein 2 gene expression in MODE-K cells [192]. Quercetin attenuated IL-1β-induced expression of ICAM-1 mRNA and protein in a dose-dependent manner in human A549 adenocarcinoma alveolar basal epithelial cells [193].
7. Regulation of Heat Shock Proteins
Heat shock proteins (HSPs) such as HSP70, HSP90, and HSP27 stabilize the functions of overexpressed and mutated cancer genes, and hence, increase the growth and survival of cancers [194]. HSPs are also released from cancer cells and influence malignant properties by receptor-mediated signaling [195]. Researchers reported that quercetin stimulate apoptosis in prostate cancer and B-CPAP human papillary thyroid cancer cells resulting from inhibition of casein kinase II or calcium/calmodulin kinase II, leading to HSP induction and downregulation of HSP70 and HSP90 protein expression [196]. Quercetin found to suppressed the HSP27 and COX-2 and induced G1 phase arrest in U251 glioma cells [197]. Numerous studies have documented the promising role of HSP90 protein in combating cancer, as this supreme protein molecule is reported to be involved in cell survival pathways [20,198,199]. Kim et al. presented and discussed the fisetin-mediated inhibition of cellular proliferation by HSP70 and HSP27 regulation, and Bcl-2-associated athanogene 3, which can stabilize Bcl-2 protein family members, thereby protecting cancer cells from apoptosis in HCT-116 human colon cancer cells [200]. One of the paramount signaling pathway, Notch/AKT/mTOR in tumor aggressiveness, has reported to be downregulated by quercetin plus shHSP27, leading to significant apoptosis in U937 leukemia cells [201].
8. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Fisetin and quercetin are some of the most prevalent plant flavonoids that are reportedly present in many fruits and vegetables such as apples and onions. The bioactive potential of fisetin and quercetin has been established, especially in the modulation of a range of cancer signaling pathways. The anti-cancer, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant roles exhibited by these flavonols have been reportedly found to be associated with their ability of apoptotic activation, cell cycle arrest, regulating ECM remodeling, and inhibiting EMT. Many studies of fisetin and quercetin have been highlighted in this review for their modulatory potential in different cancer related signaling pathways and growth factors such as Akt, JNK, p38MAPK, NF-κB, and VEGF cytokines and chemokines, paving the way to delineate the mechanism of action of these therapeutically active flavonols. Research is in progress to identify the newer plant based therapeutic agents. Easley availability, safe in use and cheaper cost increasing the popularity and acceptability of herbal medicine. As per the World Health Organization, about 60% of the world´s population and about 80% of the population of developing countries rely on herbal medicine. According to an estimate, herbal industry reached at around US$100 billion in shares, with an annual growth rate of about 15%. However, there are also several concerns with use of these phytochemicals as drugs with respect to their pharmacognosy and standardization compared with conventional drugs. There should be an improvement in the technologies used for the categorization (such as HPLC/MS, LC/MS, NMR), storage, and quality control of these compounds. For the last two decades, research has been underway to evaluate the clinical validity of phototherapy. Clinical trials are required to further prove the clinical efficacy of these phytochemicals.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.K. and H.S.T.; Methodology, V.K.G., V.A. and M.K.; Writing—original draft preparation, D.K.; Writing—review and editing, M.B.Y., K.S., S.S.S., Supervision, H.S.T. All author read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to gratefully acknowledge the Department of Histopathology, Post Graduate Institute of Medical Education and Research (PGIMER), Chandigarh, and Maharishi Markandeshwar (Deemed to be University) and Mullana-Ambala, Haryana, for providing the platform to complete this review.
Conflicts of Interest
Authors declare no conflict of interests.
References
- American Cancer Society. Cancer Facts & Figures 2016; American Cancer Society: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2016; Available online: https://www.cancer.org/content/dam/cancer-org/research/cancer-facts-and-statistics/annual-cancer-facts-and-figures/2016/cancer-facts-and-figures-2016.pdf (accessed on 3 August 2018).
- Soto, A.M.; Sonnenschein, C. Environmental causes of cancer: Endocrine disruptors as carcinogens. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2010, 6, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawyers, C. Targeted cancer therapy. Nature 2004, 432, 294–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Housman, G.; Byler, S.; Heerboth, S.; Lapinska, K.; Longacre, M.; Snyder, N.; Sarkar, S. Drug Resistance in Cancer: An Overview. Cancers 2014, 6, 1769–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holohan, C.; Van Schaeybroeck, S.; Longley, D.B.; Johnston, P.G. Cancer drug resistance: An evolving paradigm. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2013, 13, 714–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottesman, M.M. Mechanisms of Cancer Drug Resistance. Annu. Med. 2002, 53, 615–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashyap, D.; Sharma, A.; Tuli, H.S.; Sak, K.; Garg, V.K.; Buttar, H.S.; Setzer, W.N.; Sethi, G. Apigenin: A natural bioactive flavone-type molecule with promising therapeutic function. J. Funct. Foods 2018, 48, 457–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashyap, D.; Sharma, A.; Sak, K.; Tuli, H.S.; Buttar, H.S.; Bishayee, A. Fisetin: A bioactive phytochemical with potential for cancer prevention and pharmacotherapy. Life Sci. 2018, 194, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashyap, D.; Sharma, A.; Tuli, H.S.; Sak, K.; Mukherjee, T.; Bishayee, A. Molecular targets of celastrol in cancer: Recent trends and advancements. Crit. Rev. Oncol. 2018, 128, 70–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashyap, D.; Mondal, R.; Tuli, H.S.; Kumar, G.; Sharma, A.K. Molecular targets of gambogic acid in cancer: recent trends and advancements. Tumour Biol. 2016, 37, 12915–12925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashyap, D.; Tuli, H.S.; Garg, V.K.; Goel, N.; Bishayee, A. Oncogenic and Tumor-Suppressive Roles of MicroRNAs with Special Reference to Apoptosis: Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Potential. Mol. Diagn. Ther. 2018, 22, 179–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, W.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, Y.; Zhu, B.; Chen, Z. Fisetin, a dietary bioflavonoid, reverses acquired Cisplatin-resistance of lung adenocarcinoma cells through MAPK/Survivin/Caspase pathway. Am. J. Transl. 2015, 7, 2045–2052. [Google Scholar]
- Shanmugam, M.K.; Lee, J.H.; Chai, E.Z.P.; Kanchi, M.M.; Kar, S.; Arfuso, F.; Dharmarajan, A.; Kumar, A.P.; Ramar, P.S.; Looi, C.Y.; et al. Cancer prevention and therapy through the modulation of transcription factors by bioactive natural compounds. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2016, 40–41, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmugam, M.K.; Kannaiyan, R.; Sethi, G. Targeting Cell Signaling and Apoptotic Pathways by Dietary Agents: Role in the Prevention and Treatment of Cancer. Nutr. Cancer. 2011, 63, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Ginkel, P.R.; Yan, M.B.; Bhattacharya, S.; Polans, A.S.; Kenealey, J.D. Natural Products Induce a G Protein-Mediated Calcium Pathway Activating p53 in Cancer Cells. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2015, 288, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, H.C.; Baxter, R.D.; Hunt, K.M.; Agarwal, J.; Elmets, C.A.; Athar, M.; Afaq, F. Fisetin, a phytochemical, potentiates sorafenib-induced apoptosis and abrogates tumor growth in athymic nude mice implanted with BRAF-mutated melanoma cells. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 28296–28311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, B.; Pandey, M.K.; Aggarwal, B.B. Fisetin, an Inhibitor of Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 6, Down-Regulates Nuclear Factor- B-Regulated Cell Proliferation, Antiapoptotic and Metastatic Gene Products through the Suppression of TAK-1 and Receptor-Interacting Protein-Regulated I B Kinase Activation. Mol. Pharmacol. 2007, 71, 1703–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, H.C.; Diamond, A.C.; Strickland, L.R.; Kappes, J.C.; Katiyar, S.K.; Elmets, C.A.; Athar, M.; Afaq, F. Fisetin, a dietary flavonoid, augments the anti-invasive and anti-metastatic potential of sorafenib in melanoma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 1227–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, R.; Samadder, T.; Gupta, S.; Surolia, A.; Shaha, C. Anticancer Activity of a Combination of Cisplatin and Fisetin in Embryonal Carcinoma Cells and Xenograft Tumors. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2011, 10, 255–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.-S.; Lien, G.-S.; Shen, S.-C.; Yang, L.-Y.; Chen, Y.-C. HSP90 Inhibitors, Geldanamycin and Radicicol, Enhance Fisetin-Induced Cytotoxicity via Induction of Apoptosis in Human Colonic Cancer Cells. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013, 987612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimaszewska-Wiśniewska, A.; Halas-Wisniewska, M.; Tadrowski, T.; Gagat, M.; Grzanka, D.; Grzanka, A. Paclitaxel and the dietary flavonoid fisetin: A synergistic combination that induces mitotic catastrophe and autophagic cell death in A549 non-small cell lung cancer cells. Cancer Cell Int. 2016, 16, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, B.D.; Kalvala, A.K.; Koneru, M.; Mahesh, J.; Kuncha, M.; Rachamalla, S.S.; Sistla, R. Ameliorative effect of fisetin on cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats via modulation of NF-κB activation and antioxidant defence. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e105070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, J.F.; Oliveira, H.; Pinho, S.; Pimentel, F.; Almeida, L.; Van Zoelen, E.; Santos, C. Cytotoxic and genotoxic activity of fisetin (3, 3’, 4’, 7-tetrahydroxyflavone) in an osteosarcoma in vitro model. Planta Med. 2014, 80, P1L4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touil, Y.S.; Seguin, J.; Scherman, D.; Chabot, G.G. Improved antiangiogenic and antitumour activity of the combination of the natural flavonoid fisetin and cyclophosphamide in Lewis lung carcinoma-bearing mice. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2011, 68, 445–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.T.; Lin, C.L.; Lin, T.Y.; Cheng, C.W.; Yang, S.F.; Lin, C.L.; Wu, C.C.; Hsieh, Y.H.; Tsai, J.P. Synergistic effect of fisetin combined with sorafenib in human cervical cancer HeLa cells through activation of death receptor-5 mediated caspase-8/caspase-3 and the mitochondria-dependent apoptotic pathway. Tumour Biol. 2016, 37, 6987–6996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasemaa, K.; Everaus, H.; Sak, K. Potentiation of luteolin cytotoxicity by flavonols fisetin and quercetin in human chronic lymphocytic leukemia cell lines. Food Funct. 2016, 7, 3815–3824. [Google Scholar]
- Senggunprai, L.; Kukongviriyapan, V.; Prawan, A.; Kukongviriyapan, U. Quercetin and EGCG Exhibit Chemopreventive Effects in Cholangiocarcinoma Cells via Suppression of JAK/STAT Signaling Pathway. Phytother. Res. 2016, 28, 841–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appari, M.; Babu, K.R.; Kaczorowski, A.; Gros, W.; Her, I.; Gross, W.; Herr, I. Sulforaphane, quercetin and catechins complement each other in elimination of advanced pancreatic cancer by miR-let-7 induction and K-ras inhibition. Int. J. Oncol. 2014, 45, 1391–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, N.; Wang, G.; Song, L. Quercetin synergizes with 2-methoxyestradiol inhibiting cell growth and inducing apoptosis in human prostate cancer cells. Oncol. Rep. 2013, 30, 357–363. [Google Scholar]
- Nessa, M.U.; Beale, P.; Chan, C.; Yu, J.Q.; Huq, F. Synergism from Combinations of Cisplatin and Oxaliplatin with Quercetin and Thymoquinone in Human Ovarian Tumor Models. Anticancer Res. 2011, 31, 3789–3797. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Guo, Q.; Chen, J.; Chen, Z. Quercetin Enhances Cisplatin Sensitivity of Human Osteosarcoma Cells by Modulating microRNA-217-KRAS Axis Molecules. Cells 2015, 38, 638–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, T.-C.; Wu, J.M. Targeting CWR22Rv1 Prostate Cancer Cell Proliferation and Gene Expression by Combinations of the Phytochemicals EGCG, Genistein and Quercetin. Anticancer. Res. 2009, 29, 4025–4032. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bądziul, D.; Jakubowicz-Gil, J.; Langner, E.; Rzeski, W.; Głowniak, K.; Gawron, A. The effect of quercetin and imperatorin on programmed cell death induction in T98G cells in vitro. Pharmacol. Rep. 2014, 66, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arias, N.; Macarulla, M.T.; Aguirre, L.; Milton, I.; Portillo, M.P. The combination of resveratrol and quercetin enhances the individual effects of these molecules on triacylglycerol metabolism in white adipose tissue. Eur. J. Nutr. 2016, 55, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atashpour, S.; Fouladdel, S.; Movahhed, T.K.; Barzegar, E.; Hossein, M.; Ostad, S.N.; Azizi, E. Quercetin induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in CD133+ cancer stem cells of human colorectal HT29 cancer cell line and enhances anticancer effects of doxorubicin. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2015, 18, 635–643. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Di, L.G.; Pagliuca, M.; Perillo, T.; Zarrella, A.; Verde, A.; De Placido, S.; Buonerba, C. Complete Response and Fatigue Improvement with the Combined Use of Cyclophosphamide and Quercetin in a Patient with Metastatic Bladder Cancer: A Case Report. Medicine 2016, 95, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Meenakshi, K.; Imran, S.; Neeta, S. Curcumin and Quercetin Combined with Cisplatin to Induce Apoptosis in Human Laryngeal Carcinoma Hep-2 Cells through the Mitochondrial Pathway. J. Cancer Mol. 2007, 3, 121–128. [Google Scholar]
- Harborne, J. Progress in the Chemistry of Organic Natural Products. Phytochemistry 1975, 14, 1470–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jash, S.K.; Mondal, S. Bioactive flavonoid fisetin—A molecule of pharmacological interest. J. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2014, 2, 89–128. [Google Scholar]
- Kimira, M.; Arai, Y.; Shimoi, K.; Watanabe, S. Japanese Intake of Flavonoids and Isoflavonoids from Foods. J. Epidemiol. 1998, 8, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marais, J.P.J.; Deavours, B.; Dixon, R.A.; Ferreira, D. The Stereochemistry of Flavonoids; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 1–46. [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann, S.H.; Earnshaw, W.C. Induction of apoptosis by cancer chemotherapy. Exp. Cell Res. 2000, 256, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makin, G.; Hickman, J.A. Apoptosis and cancer chemotherapy. Cell Tissue Res. 2000, 301, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, B.-S.; Choi, N.-E.; Lee, J.H.; Kang, H.-M.; Yu, S.-B.; Kim, H.-J.; Kang, H.-K.; Kim, I.-R. Crosstalk between Fisetin-induced Apoptosis and Autophagy in Human Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. J. Cancer 2019, 10, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Cheng, Y.; Qu, W.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, H.; Tian, B. Fisetin, a dietary flavonoid, induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis through activation of p53 and inhibition of NF-κB pathways in bladder cancer cells. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2011, 108, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, K.Y.; Jeong, S.-J.; Kim, S.-H.; Jung, J.H.; Kim, J.-H.; Koh, W.; Chen, C.-Y.; Kim, S.-H. Activation of reactive oxygen species/AMP activated protein kinase signaling mediates fisetin-induced apoptosis in multiple myeloma U266 cells. Cancer Lett. 2012, 319, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, K.A.; Piao, M.J.; Hewage, S.R.K.M.; Ryu, Y.S.; Oh, M.C.; Kwon, T.K.; Chae, S.; Hyun, J.W. Fisetin induces apoptosis and endoplasmic reticulum stress in human non-small cell lung cancer through inhibition of the MAPK signaling pathway. Tumour Boil. 2016, 37, 9615–9624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, H.C.; Sharma, S.; Elmets, C.A.; Athar, M.; Afaq, F. Fisetin inhibits growth, induces G2/M arrest and apoptosis of human epidermoid carcinoma A431 cells: Role of mitochondrial membrane potential disruption and consequent caspases activation. Exp. Dermatol. 2013, 22, 470–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeng, L.-B.; Velmurugan, B.K.; Chen, M.-C.; Hsu, H.-H.; Ho, T.-J.; Day, C.-H.; Lin, Y.-M.; Padma, V.V.; Tu, C.-C.; Huang, C.-Y. Fisetin mediated apoptotic cell death in parental and Oxaliplatin/irinotecan resistant colorectal cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 7134–7142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Hu, D.-N.; Lin, H.-W.; Yang, W.-E.; Hsieh, Y.-H.; Chien, H.-W.; Yang, S.-F. Fisetin induces apoptosis through mitochondrial apoptosis pathway in human uveal melanoma cells. Environ. Toxicol. 2018, 33, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, Y.-L.; Hung, F.-M.; Lee, C.-H.; Yeh, M.-Y.; Lee, M.-H.; Lu, H.-F.; Chen, Y.-L.; Liu, J.-Y.; Chung, J.-G. Fisetin Induces Apoptosis of HSC3 Human Oral Cancer Cells Through Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Dysfunction of Mitochondria-mediated Signaling Pathways. In Vivo 2017, 31, 1103–1114. [Google Scholar]
- Su, C.-H.; Kuo, C.-L.; Lu, K.-W.; Yu, F.-S.; Ma, Y.-S.; Yang, J.-L.; Chu, Y.-L.; Chueh, F.-S.; Liu, K.-C.; Chung, J.-G.; et al. Fisetin-induced apoptosis of human oral cancer SCC-4 cells through reactive oxygen species production, endoplasmic reticulum stress, caspase-, and mitochondria-dependent signaling pathways. Environ. Toxicol. 2017, 32, 1725–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.; Afaq, F.; Syed, D.N.; Mukhtar, H. Fisetin, a novel dietary flavonoid, causes apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in human prostate cancer LNCaP cells. CARCIN 2008, 29, 1049–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, M.; Palumbo, R.; Tedesco, I.; Mazzarella, G.; Russo, P.; Iacomino, G.; Russo, G.L. Quercetin and anti-CD95(Fas/Apo1) enhance apoptosis in HPB-ALL cell line. FEBS Lett. 1999, 462, 322–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, I.-K.; Lin-Shiau, S.-Y.; Lin, J.-K. Induction of apoptosis by apigenin and related flavonoids through cytochrome c release and activation of caspase-9 and caspase-3 in leukaemia HL-60 cells. Eur. J. Cancer 1999, 35, 1517–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aalinkeel, R.; Bindukumar, B.; Reynolds, J.L.; Sykes, D.E.; Mahajan, S.D.; Chadha, K.C.; Schwartz, S.A. The Dietary Bioflavonoid, Quercetin, Selectively Induces Apoptosis of Prostate Cancer Cells by Down-Regulating the Expression of Heat Shock Protein 90. Prostate 2008, 68, 1773–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mutoh, M.; Takahashi, M.; Fukuda, K.; Komatsu, H.; Enya, T.; Matsushima-Hibiya, Y.; Mutoh, H.; Sugimura, T.; Wakabayashi, K. Suppression by Flavonoids of Cyclooxygenase-2 Promoter-dependent Transcriptional Activity in Colon Cancer Cells: Structure-Activity Relationship. Jpn. J. Cancer 2000, 91, 686–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheong, E. Synthetic and naturally occurring COX-2 inhibitors suppress proliferation in a human oesophageal adenocarcinoma cell line (OE33) by inducing apoptosis and cell cycle arrest. CARCIN 2004, 25, 1945–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Daniel, K.G.; Chen, M.S.; Kuhn, D.J.; Landis-Piwowar, K.R.; Dou, Q.P. Dietary flavonoids as proteasome inhibitors and apoptosis inducers in human leukemia cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2005, 69, 1421–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.-H.; Szczepanski, M.; Lee, Y.J. Role of Bax in quercetin-induced apoptosis in human prostate cancer cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2008, 75, 2345–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.-C.; Lee, W.-R.; Yang, L.-Y.; Tsai, H.-H.; Yang, L.-L.; Chen, Y.-C. Quercetin enhancement of arsenic-induced apoptosis via stimulating ROS-dependent p53 protein ubiquitination in human HaCaT keratinocytes. Exp. Dermatol. 2012, 21, 370–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.-L.; Chow, J.-M.; Chang, J.-H.; Wen, Y.-C.; Lin, Y.-W.; Yang, S.-F.; Lee, W.-J.; Chien, M.-H. Quercetin simultaneously induces G0/G1-phase arrest and caspase-mediated crosstalk between apoptosis and autophagy in human leukemia HL-60 cells. Environ. Toxicol. 2017, 32, 1857–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuli, H.S.; Kashyap, D.; Sharma, A.K. Cordycepin: A Cordyceps Metabolite with Promising Therapeutic Potential. In Fungal Metabolites, Reference Series in Phytochemistry; Springer Nature: Basingstoke, UK, 2015; pp. 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Kashyap, D.; Sharma, A.; Tuli, H.S.; Sak, K.; Punia, S.; Mukherjee, T.K. Kaempferol—A dietary anticancer molecule with multiple mechanisms of action: Recent trends and advancements. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 30, 203–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, T.H.; Yang, S.F.; Tsai, S.J.; Hsieh, S.C.; Huang, Y.C.; Bau, D.T.; Hsieh, Y.H. Fisetin induces apoptosis in human cervical cancer HeLa cells through ERK1/2-mediated activation of caspase-8-/caspase-3-dependent pathway. Arch. Toxicol. 2012, 86, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, D.Y.; Park, J.H.Y.; Park, J.H.Y. Induction of p53 contributes to apoptosis of HCT-116 human colon cancer cells induced by the dietary compound fisetin. Am. J. Physiol. Liver Physiol. 2009, 296, G1060–G1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krol, W.; Szliszka, E.; Helewski, K.J.; Mizgala, E. The dietary flavonol fisetin enhances the apoptosis-inducing potential of TRAIL in prostate cancer cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2011, 39, 771–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, H.-S.; Ku, J.M.; Choi, H.-S.; Choi, Y.K.; Woo, J.-K.; Kim, M.; Kim, I.; Na, C.H.; Hur, H.; Jang, B.-H.; et al. Quercetin induces caspase-dependent extrinsic apoptosis through inhibition of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 signaling in HER2-overexpressing BT-474 breast cancer cells. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 36, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, S.; Somasagara, R.R.; Hegde, M.; Nishana, M.; Tadi, S.K.; Srivastava, M.; Choudhary, B.; Raghavan, S.C. Quercetin, a Natural Flavonoid Interacts with DNA, Arrests Cell Cycle and Causes Tumor Regression by Activating Mitochondrial Pathway of Apoptosis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathew, C.C.; Crosariol, M.; Laro, E.; Li, Z.; Pertell, R.G. Cyclins and cell cycle control in cancer and disease. Gene Cancer 2012, 3, 649–657. [Google Scholar]
- Malumbres, M. Cyclin and related kinase in cancer. JBUON 2007, 1, S45–S52. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, H.; Chang, D.; Baratte, B.; Meijer, L.; Schulze-Gahmen, U. Crystal structure of a human cyclin-dependent kinase 6 complex with a flavonol inhibitor, fisetin. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, 737–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adan, A.; Baran, Y. The pleiotropic effects of fisetin and hesperetin on human acute promyelocytic leukemia cells are mediated through apoptosis, cell cycle arrest, and alterations in signaling networks. Cancer Biol. 2015, 36, 8973–8984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Yao, F.; Li, K.; Zhang, L.; Yin, G.; Du, M.; Wu, B. Fisetin regulates astrocyte migration and proliferation in vitro. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2017, 39, 783–790. [Google Scholar]
- Sabarwal, A.; Agarwal, R.; Singh, R.P. Fisetin inhibits cellular proliferation and induces mitochondria-dependent apoptosis in human gastric cancer cells. Mol. Carcinogen. 2017, 56, 499–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcocer, F.; Whitley, D.; Salazar-Gonzalez, J.F.; Jordan, W.D.; Sellers, M.T.; Eckhoff, D.E.; Suzuki, K.; Macrae, C.; Bland, K.I. Quercetin inhibits human vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration. Surgery 2002, 131, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Li, L.; Fang, L.; Xie, H.; Yao, W.; Zhou, X.; Xiong, Z.; Wang, L.; Li, Z.; Luo, F. Quercetin reduces cyclin D1 activity and induces G1 phase arrest in HepG2 cells. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 12, 516–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catanzaro, D.; Ragazzi, E.; Vianello, C.; Caparrotta, L.; Montopoli, M. Effect of Quercetin on Cell Cycle and Cyclin Expression in Ovarian Carcinoma and Osteosarcoma Cell Lines. Prod. Commun. 2015, 10, 1365–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Erk, M.J.; Roepman, P.; van der Lende, T.R.; Stierum, R.H.; Aarts, J.M.; van Bladeren, P.J.; van Ommen, B. Integrated assessment by multiple gene expression analysis of quercetin bioactivity on anticancer-related mechanisms in colon cancer cells in-vitro. Eur. J. Nutr. 2005, 44, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, B.-E.; Wang, M.-X.; Li, R.-Q. Quercetin Inhibit Human SW480 Colon Cancer Growth in Association with Inhibition of Cyclin D 1 and Survivin Expression through Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway. Cancer Investig. 2009, 27, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szaryńska, M.; Olejniczak, A.; Kobiela, J.; Spychalski, P.; Kmieć, Z. Therapeutic strategies against cancer stem cells in human colorectal cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 7653–7668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poór, M.; Zrínyi, Z.; Kőszegi, T. Structure related effects of flavonoid aglycones on cell cycle progression of HepG2 cells: Metabolic activation of fisetin and quercetin by catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT). Biomed. Pharmacother. 2016, 83, 998–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, C.; Tran, E.; Nguyen, T.; Ong, C.; Lee, S.; Lee, J.; Ng, C.; Leong, C.; Huynh, H. Quercetin-induced growth inhibition and cell death in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells are associated with increase in Bad and hypophosphorylated retinoblastoma expressions. Oncol. Rep. 2004, 11, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, P.-C.; Liu, H.-F.; Chao, J.-I. Survivin and p53 Modulate Quercetin-induced Cell Growth Inhibition and Apoptosis in Human Lung Carcinoma Cells. J. Boil. Chem. 2004, 279, 55875–55885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, C.; Liu, X.; Jia, P.; Yan, Z.; Li, X.; Liu, H. Quercetin induces cell-cycle G1 arrest through elevating CDK inhibitors p21 and p27 in human hepatoma cell line (HepG2). Methods Find. Exp. Clin. Pharmacol. 2007, 29, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, J.Y.; Kwon, Y.T.; Rhee, J.G.; Lee, Y.J.; Jeong, J.-H.; Jeong, J. Effects of low dose quercetin: Cancer cell-specific inhibition of cell cycle progression. J. Cell. Biochem. 2009, 106, 73–82. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, J.-A.; Kim, J.-Y.; Lee, J.-Y.; Kang, C.-M.; Kwon, H.-J.; Yoo, Y.-D.; Kim, T.-W.; Lee, Y.-S.; Lee, S.-J. Induction of cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human breast cancer cells by quercetin. Int. J. Oncol. 2001, 19, 837–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, T.-J.; Kim, O.H.; Kim, Y.H.; Lim, J.H.; Kim, S.; Park, J.-W.; Kwon, T.K. Quercetin arrests G2/M phase and induces caspase-dependent cell death in U937 cells. Cancer Lett. 2006, 240, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhao, X.-H.; Wang, Z.-J. Flavones and flavonols exert cytotoxic effects on a human oesophageal adenocarcinoma cell line (OE33) by causing G2/M arrest and inducing apoptosis. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2008, 46, 2042–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnans, C.; Chou, J.; Werb, Z. Remodelling the extracellular matrix in development and disease. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Boil. 2014, 15, 786–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, T.R.; Erler, J.T. Remodeling and homeostasis of the extracellular matrix: implications for fibrotic diseases and cancer. Model. Mech. 2011, 4, 165–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chien, C.S.; Shen, K.H.; Huang, J.S.; Ko, S.C.; Shih, Y.W. Antimetastatic potential of fisetin involves inactivation of the PI3K/Akt and JNK signaling pathways with downregulation of MMP-2/9 expressions in prostate cancer PC-3 cells. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2010, 333, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Jang, Y.-J.; Choi, Y.J.; Jang, J.W.; Kim, J.-H.; Rho, Y.-K.; Kim, I.J.; Kim, H.-J.; Leem, M.J.; Lee, S.-T. Fisetin Inhibits Matrix Metalloproteinases and Reduces Tumor Cell Invasiveness and Endothelial Cell Tube Formation. Nutr. Cancer 2013, 65, 1192–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, R.-H.; Hsieh, S.-C.; Yu, Y.-L.; Huang, M.-H.; Huang, Y.-C.; Hsieh, Y.-H. Fisetin Inhibits Migration and Invasion of Human Cervical Cancer Cells by Down-Regulating Urokinase Plasminogen Activator Expression through Suppressing the p38 MAPK-Dependent NF-κB Signaling Pathway. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e71983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhat, T.A.; Nambiar, D.; Pal, A.; Agarwal, R.; Singh, R.P. Fisetin inhibits various attributes of angiogenesis in-vitro and in-vivo—Implications for angioprevention. Carcinogenesis 2012, 33, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C.-Y.; Lien, C.-H.; Lee, M.-F.; Huang, C.-Y. Quercetin suppresses cellular migration and invasion in human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC). BioMedicine 2016, 6, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, M.; Song, Y.; Zhang, X. Quercetin Suppresses the Migration and Invasion in Human Colon Cancer Caco-2 Cells Through Regulating Toll-like Receptor 4/Nuclear Factor-κB Pathway. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2016, 12, S237–S244. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.-W.; Hou, W.-C.; Shen, S.-C.; Juan, S.-H.; Ko, C.-H.; Wang, L.-M.; Chen, Y.-C. Quercetin inhibition of tumor invasion via suppressing PKC /ERK/AP-1-dependent matrix metalloproteinase-9 activation in breast carcinoma cells. CARCIN 2008, 29, 1807–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijayababu, M.R.; Arunkumar, A.; Kanagaraj, P.; Venkataraman, P.; Krishnamoorthy, G.; Arunakaran, J. Quercetin downregulates matrix metalloproteinases 2 and 9 proteins expression in prostate cancer cells (PC-3). Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2006, 287, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, C.-S.; Hou, Y.-C.; Pai, M.-H.; Lin, M.-T.; Yeh, S.-L. Effects of quercetin combined with anticancer drugs on metastasis-associated factors of gastric cancer cells: in vitro and in vivo studies. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2018, 51, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, H.; Hong, W.; Fan, P.; Qian, D.; Zhu, J.; Bai, B. Quercetin Inhibits Cell Migration and Invasion in Human Osteosarcoma Cells. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 43, 553–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Zhao, X.; Xu, J.; Zhang, H. Quercetin inhibits angiogenesis-mediated human retinoblastoma growth by targeting vascular endothelial growth factor receptor. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 3343–3348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brabletz, T.; Kalluri, R.; Nieto, M.A.; Weinberg, R.A. EMT in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2018, 18, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roche, J. The Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition in Cancer. Cancers 2018, 10, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bal, A.; Joshi, K.; Dos, A.; Kashyap, D.; Singh, G. Significance of Epithelial Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) in Breast Cancer and Implications on Lymph Node Metastasis. Modern Pathol. 2015, 28, 34A. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, X.; Ahn, K.S.; Wang, L.Z.; Kim, C.; Deivasigamni, A.; Arfuso, F.; Um, J.-Y.; Kumar, A.P.; Chang, Y.-C.; Kumar, D.; et al. Ascochlorin Enhances the Sensitivity of Doxorubicin Leading to the Reversal of Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2016, 15, 2966–2976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, J.-H.; Nam, D.; Um, J.-Y.; Jung, S.H.; Sethi, G.; Ahn, K.S. Bergamottin Suppresses Metastasis of Lung Cancer Cells through Abrogation of Diverse Oncogenic Signaling Cascades and Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition. Molecules 2018, 23, 1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, S.H.; Ko, J.H.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, C.; Lee, H.; Nam, D.; Lee, J.; Lee, S.G.; Yang, W.M.; Um, J.Y.; et al. Ginkgolic Acid Inhibits Invasion and Migration and TGF-β-Induced EMT of Lung Cancer Cells Through PI3K/Akt/mTOR Inactivation. J. Cell. Physiol. 2017, 232, 346–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syn, N.; Wang, L.; Sethi, G.; Thiery, J.-P.; Goh, B.-C. Exosome-Mediated Metastasis: From Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition to Escape from Immunosurveillance. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2016, 37, 606–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, H.C.; Sharma, S.; Strickland, L.R.; Katiyar, S.K.; Ballestas, M.E.; Athar, M.; Elmets, C.A.; Afaq, F. Fisetin Inhibits Human Melanoma Cell Invasion through Promotion of Mesenchymal to Epithelial Transition and by Targeting MAPK and NFκB Signaling Pathways. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, 86338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Gong, X.; Jiang, R.; Lin, D.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, A.; Li, H.; Zhang, X.; Wan, J.; Kuang, G.; et al. Fisetin Inhibited Growth and Metastasis of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer by Reversing Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition via PTEN/Akt/GSK3β Signal Pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baruah, M.M.; Khandwekar, A.P.; Sharma, N. Quercetin modulates Wnt signaling components in prostate cancer cell line by inhibiting cell viability, migration, and metastases. Cancer Biol. 2016, 37, 14025–14034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.W.; Hu, F.W.; Yu, C.C.; Wang, H.H.; Feng, H.P.; Lan, C.; Tsai, L.L.; Chang, Y.C. Quercetin in elimination of tumor initiating stem-like and mesenchymal transformation property in head and neck cancer. Head Neck 2013, 35, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kee, J.-Y.; Han, Y.-H.; Kim, D.-S.; Mun, J.-G.; Park, J.; Jeong, M.-Y.; Um, J.-Y.; Hong, S.-H. Inhibitory effect of quercetin on colorectal lung metastasis through inducing apoptosis, and suppression of metastatic ability. Phytomedicine 2016, 23, 1680–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.; Afaq, F.; Khusro, F.H.; Mustafa Adhami, V.; Suh, Y.; Mukhtar, H. Dual inhibition of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt and mammalian target of rapamycin signaling in human nonsmall cell lung cancer cells by a dietary flavonoid fisetin. Int. J. Cancer 2012, 130, 1695–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashyap, D.; Mittal, S.; Sak, K.; Singhal, P.; Tuli, H.S. Molecular mechanisms of action of quercetin in cancer: Recent advances. Cancer Biol. 2016, 37, 12927–12939. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, S.S.; Yap, W.N.; Arfuso, F.; Kar, S.; Wang, C.; Cai, W.; Dharmarajan, A.M.; Sethi, G.; Kumar, A.P. Targeting the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in gastric carcinoma: A reality for personalized medicine? World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 12261–12273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Nie, J.; Ma, X.; Wei, Y.; Peng, Y.; Wei, X. Targeting PI3K in cancer: Mechanisms and advances in clinical trials. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fruman, D.A.; Rommel, C. PI3K and cancer: lessons, challenges and opportunities. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2014, 13, 140–156. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fresno Vara, J.Á.; Casado, E.; de Castro, J.; Cejas, P.; Belda-Iniesta, C.; González-Barón, M. P13K/Akt signalling pathway and cancer. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2004, 30, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer, I.A.; Arteaga, C.L. The PI3K/AKT Pathway as a Target for Cancer Treatment. Annu. Rev. Med. 2015, 67, 11–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martini, M.; De Santis, M.C.; Braccini, L.; Gulluni, F.; Hirsch, E. PI3K/AKT signaling pathway and cancer: an updated review. Ann. Med. 2014, 46, 372–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- George, V.C. Promising tumor inhibiting potentials of Fisetin through PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Am. J. Transl. 2016, 8, 1293–1294. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.-M.; Li, W.-Y.; Huang, M.-Y.; Zhang, X.-Q. Fisetin, a dietary flavonoid induces apoptosis via modulating the MAPK and PI3K/Akt signalling pathways in human osteosarcoma (U-2 OS) cells. World J. Pharmacol. 2015, 10, 820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.Y.; Lee, J.Y.; Byun, B.J.; Kim, S.H. Fisetin targets phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase and induces apoptosis of human B lymphoma Raji cells. Toxicol. Rep. 2015, 2, 984–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, H.C.; Athar, M.; Elmets, C.A.; Afaq, F. Fisetin inhibits UVB-induced cutaneous inflammation and activation of PI3K/AKT/NFκB signaling pathways in SKH-1 hairless mice. Photochem. Photobiol. 2015, 91, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granado-Serrano, A.B.; Martín, M.A.; Bravo, L.; Ramos, S.; Goya, L. Quercetin Induces Apoptosis via Caspase Activation, Regulation of Bcl-2, and Inhibition of PI-3-Kinase/Akt and ERK Pathways in a Human Hepatoma Cell Line (HepG2). J. Nutr. 2006, 136, 2715–2721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Refolo, M.G.; D’Alessandro, R.; Malerba, N.; Laezza, C.; Bifulco, M.; Messa, C.; Caruso, M.G.; Notarnicola, M.; Tutino, V. Anti-Proliferative and Pro Apoptotic Effects of Flavonoid Quercetin Are Mediated by CB1 Receptor in Human Colon Cancer Cell Lines. J. Cell. Physiol. 2015, 230, 2973–2980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulati, N.; Laudet, B.; Zohrabian, V.M.; Murali, R.; Jhanwar-Uniyal, M. The antiproliferative effect of Quercetin in cancer cells is mediated via inhibition of the PI3K-Akt/PKB pathway. Anticancer. Res. 2006, 26, 1177–1181. [Google Scholar]
- Erdogan, S.; Turkekul, K.; Dibirdik, I.; Doganlar, O.; Doganlar, Z.B.; Bilir, A.; Oktem, G. Midkine downregulation increases the efficacy of quercetin on prostate cancer stem cell survival and migration through PI3K/AKT and MAPK/ERK pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 107, 793–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhou, N.; Wang, J.; Liu, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, Q.; Gao, L.; Wang, R. Quercetin suppresses breast cancer stem cells (CD44+/CD24–) by inhibiting the PI3K/Akt/mTOR-signaling pathway. Life Sci. 2018, 196, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Y.; Shen, S.; Verma, I.M. NF-κB, an active player in human cancer. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2014, 2, 823–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.H.; Hong, J.T. Role of NF-κB in cancer and inflammatory disease and their therapeutic approches. Cells 2016, 5, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erstad, D.J.; Cusack, J.C., Jr. Targeting the NF-κB pathways in cancer therapy Surgical Oncology. Clin. N. Am. 2013, 22, 705–746. [Google Scholar]
- Godwin, P.; Baird, A.M.; Heavey, S.; Barr, P.; O’Byrne, K.J.; Gately, K. Targeting NF-κB to Overcame resistance to chemotherapy. Front. Oncol. 2013, 3, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, Y.; Afaq, F.; Johnson, J.J.; Mukhtar, H. A plant flavonoid fisetin induces apoptosis in colon cancer cells by inhibition of COX2 and Wnt/EGFR/NF-κB-signaling pathways. Carcinogenesis 2009, 30, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noh, E.-M.; Park, Y.-J.; Kim, J.-M.; Kim, M.-S.; Kim, H.-R.; Song, H.-K.; Hong, O.-Y.; So, H.-S.; Yang, S.-H.; Kim, J.-S.; et al. Fisetin regulates TPA-induced breast cell invasion by suppressing matrix metalloproteinase-9 activation via the PKC/ROS/MAPK pathways. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 764, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Kim, M.-Y.; Kim, J.-H.; Cho, J.Y. Fisetin Suppresses Macrophage-Mediated Inflammatory Responses by Blockade of Src and Syk. Biomol. Ther. 2015, 23, 414–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youn, H.; Jeong, J.C.; Jeong, Y.S.; Kim, E.J.; Um, S.J. Quercetin potentiates the apoptosis by inhibiting nuclear factor-κaB siganling in H460 lung cancer cells. Biol. Pharmacol. Bull. 2013, 36, 944–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granado-Serrano, A.B.; Martín, M.Á.; Bravo, L.; Goya, L.; Ramos, S. Quercetin Modulates NF-κB and AP-1/JNK Pathways to Induce Cell Death in Human Hepatoma Cells. Nutr. Cancer 2010, 62, 390–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.-A.; Zhang, S.; Yin, Q.; Zhang, J. Quercetin induces human colon cancer cells apoptosis by inhibiting the nuclear factor-κB Pathway. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2015, 11, 404–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, P.; Li, W.X. Role of the JAK-STAT Signalling Pathway in Cancer. In eLS; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Adan, A.; Baran, Y. Fisetin and hesperetin induced apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in chronic myeloid leukemia cells accompanied by modulation of cellular signaling. Cancer Biol. 2015, 37, 5781–5795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.-H.; Tse, A.K.-W.; Kwan, H.-Y.; Yu, H.; Cheng, B.C.-Y.; Su, T.; Fong, W.-F.; Yu, Z.-L. Quercetin exerts anti-melanoma activities and inhibits STAT3 signaling. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2014, 87, 424–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.-M.; Kang, J.H.; Yun, M.; Lee, S.-B. Quercetin inhibits the poly(dA:dT)-induced secretion of IL-18 via down-regulation of the expressions of AIM2 and pro-caspase-1 by inhibiting the JAK2/STAT1 pathway in IFN-γ-primed human keratinocytes. Biochem. Biophys. Commun. 2018, 503, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michaud, L.L.; Bousquest, G.N.; Beliveau, R. Quercetin abrogate IL-6/STAT3 signaling and inhibits glioblastoma cell line growth and migration. Exp. Cell Res. 2012, 318, 925–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, D.; Ye, T.; Xiang, Y.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, J.; Lou, B.; Zhang, F.; Chen, B.; Zhou, M. Quercetin inhibits epithelial–mesenchymal transition, decreases invasiveness and metastasis, and reverses IL-6 induced epithelial–mesenchymal transition, expression of MMP by inhibiting STAT3 signaling in pancreatic cancer cells. OncoTargets Ther. 2017, 10, 4719–4729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, A.; Khuda-Bukhsh, A.R. Quercetin Down-regulates IL-6/STAT-3 Signals to Induce Mitochondrial-mediated Apoptosis in a Nonsmall- cell Lung-cancer Cell Line, A549. J. Pharmacopunct. 2015, 18, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCain, J. The MAPK (ERK) Pathway: Investigational Combinations for the Treatment Of BRAF-Mutated Metastatic Melanoma. Pharm. Ther. 2013, 38, 96–108. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, K.A.; Piao, M.J.; Hyun, J.W. Fisetin induces apoptosis in human nonsmall lung cancer cells via a mitochondria-mediated pathway. In-vitro cellular & developmental biology. Animal 2015, 51, 300–309. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.-K.; Hwang, J.-T.; Kwon, D.Y.; Surh, Y.-J.; Park, O.J. Induction of apoptosis by quercetin is mediated through AMPKα1/ASK1/p38 pathway. Cancer Lett. 2010, 292, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.C.; Lee, H.J.; Lim, B.; Ha, K.-T.; Kim, S.Y.; So, I.; Kim, B.J. Quercetin induces apoptosis by inhibiting MAPKs and TRPM7 channels in AGS cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2014, 33, 1657–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranganathan, S.; Halagowder, D.; Sivasithambaram, N.D. Quercetin Suppresses Twist to Induce Apoptosis in MCF-7 Breast Cancer Cells. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0141370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, W.; Yang, C.; Park, S.; Bazer, F.W.; Song, G. Inhibitory Effects of Quercetin on Progression of Human Choriocarcinoma Cells Are Mediated Through PI3K/AKT and MAPK Signal Transduction Cascades. J. Cell. Physiol. 2017, 232, 1428–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambard, J.-C.; Lefloch, R.; Pouysségur, J.; Lenormand, P. ERK implication in cell cycle regulation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2007, 1773, 1299–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Chen, S.; Zhao, Y.; Ye, X. Fisetin inhibits the proliferation of gastric cancer cells and induces apoptosis through suppression of ERK 1/2 activation. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 8442–8446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youns, M.; Hegazy, W.A.H. The Natural Flavonoid Fisetin Inhibits Cellular Proliferation of Hepatic, Colorectal, and Pancreatic Cancer Cells through Modulation of Multiple Signaling Pathways. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0169335. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, N.; Lee, S.H.; Son, J.H.; Lee, J.M.; Kang, M.-J.; Kim, B.H.; Lee, J.-S.; Ryu, J.K.; Kim, Y.-T. Fisetin Reduces Cell Viability Through Up-Regulation of Phosphorylation of ERK1/2 in Cholangiocarcinoma Cells. Anticancer. Res. 2016, 36, 6109–6116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.S.; Lien, G.S.; Shen, S.C.; Yang, L.Y.; Chen, Y.C. N-acetyl-l-cysteine enhances fisetin-induced cytotoxicity via induction of ROS-independent apoptosis in human colonic cancer cells. Mol. Carcinog. 2014, 53, E119–E129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.M.; Hsieh, Y.H.; Hwang, J.M.; Jan, H.J.; Hsieh, S.C.; Lin, S.H.; Lai, C.Y. Fisetin suppresses ADAM9 expression and inhibits invasion of glioma cancer cells through increased phosphorylation of ERK1/2. Tumor Biol. 2015, 36, 3407–3415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.J.; Hsiao, M.; Chang, J.L.; Yang, S.F.; Tseng, T.H.; Cheng, C.W.; Chow, J.M.; Lin, K.H.; Lin, Y.W.; Liu, C.C.; et al. Quercetin induces mitochondrial-derived apoptosis via reactive oxygen species-mediated ERK activation in HL-60 leukemia cells and xenograft. Arch. Toxicol. 2015, 89, 1103–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Qin, C.; Fan, X.; Li, Y.; Gu, B. Inhibitory effects of quercetin on angiogenesis in larval zebrafish and human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 723, 360–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.-F.; Lin, L.-P.; Li, M.-H.; Zhang, Y.-X.; Tong, Y.-G.; Xiao, D.; Ding, J. Quercetin, a dietary-derived flavonoid, possesses antiangiogenic potential. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2003, 459, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, D.N.; Afaq, F.; Maddodi, N.; Johnson, J.J.; Sarfaraz, S.; Ahmad, A.; Setaluri, V.; Mukhtar, H. Inhibition of human melanoma cell growth by dietary flavonoid fisetin is associated with disruption of Wnt/β-catenin signaling and decreased Mitf levels. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2011, 131, 1291–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ash, D.; Subramanian, M.; Surolia, A.; Shaha, C. Nitric oxide is the key mediator of death induced by fisetin in human acute monocytic leukemia cells. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2015, 5, 481–497. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.; Ma, X.; Li, Q.; Yang, Y.; Xu, X.; Sun, J.; Yu, M.; Cao, K.; Yang, L.; Yang, G.; et al. Anti-cancer effects of fisetin on mammary carcinoma cells via regulation of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway: In vitro and in vivo studies. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 42, 811–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhami, V.M.; Syed, D.N.; Khan, N.; Mukhtar, H. Dietary flavonoid fisetin: A novel dual inhibitor of PI3K/Akt and mTOR for prostate cancer management. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2012, 84, 1277–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, Y.; Afaq, F.; Khan, N.; Johnson, J.J.; Khusro, F.H.; Mukhtar, H. Fisetin induces autophagic cell death through suppression of mTOR signaling pathway in prostate cancer cells. CARCIN 2010, 31, 1424–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratheeshkumar, P.; Budhraja, A.; Son, Y.O.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Ding, S.; Wang, L.; Hitron, A.; Lee, J.C.; Xu, M.; et al. Quercetin Inhibits Angiogenesis Mediated Human Prostate Tumor Growth by Targeting VEGFR- 2 Regulated AKT/mTOR/P70S6K Signaling Pathways. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, A.R.; Castillo-Pichardo, L.; Gerena, Y.; Dharmawardhane, S. Anti-Breast Cancer Potential of Quercetin via the Akt/AMPK/Mammalian Target of Rapamycin (mTOR) Signaling Cascade. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0157251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, L.; Huang, S.; Yin, X.; Zan, Y.; Guo, Y.; Han, L. Quercetin suppresses the mobility of breast cancer by suppressing glycolysis through Akt-mTOR pathway mediated autophagy induction. Life Sci. 2018, 208, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menegon, S.; Columbano, A.; Giordano, S. The Dual Roles of NRF2 in Cancer. Trends Mol. Med. 2016, 22, 578–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghunath, A.; Sundarraj, K.; Arfuso, F.; Sethi, G.; Perumal, E. Dysregulation of Nrf2 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Role in Cancer Progression and Chemoresistance. Cancers 2018, 10, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Zheng, W.; Feng, X.; Yang, F.; Qin, H.; Wu, S.; Hou, D.X.; Chen, J. Nrf2-ARE siganling acts as master pathway for the cellular anti-oxidant activity of fisetin. Molecules 2019, 24, 708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehren, J.L.; Maher, P. Concurrent regulation of the transcription factors Nrf2 and ATF4 mediates the enhancement of glutathione levels by the flavonoid fisetin. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2013, 85, 1816–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinkova-Kostova, A.T.; Holtzclaw, W.D.; Cole, R.N.; Itoh, K.; Wakabayashi, N.; Katoh, Y.; Yamamoto, M.; Talalay, P. Direct evidence that sulfhydryl groups of Keap1 are the sensors regulating induction of phase 2 enzymes that protect against carcinogens and oxidants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 11908–11913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanigawa, S.; Fujii, M.; Hou, D.-X. Action of Nrf2 and Keap1 in ARE-mediated NQO1 expression by quercetin. Radic. Boil. Med. 2007, 42, 1690–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odenthal, J.; Van Heumen, B.W.H.; Roelofs, H.M.J.; Morsche, R.H.M.T.; Marian, B.; Nagengast, F.M.; Peters, W.H.M. The Influence of Curcumin, Quercetin, and Eicosapentaenoic Acid on the Expression of Phase II Detoxification Enzymes in the Intestinal Cell Lines HT-29, Caco-2, HuTu 80, and LT97. Nutr. Cancer 2012, 64, 856–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.-J.; Lee, D.M.; Lee, S.-H. Nrf2 Expression and Apoptosis in Quercetin-treated Malignant Mesothelioma Cells. Mol. Cells 2015, 38, 416–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witsch, E.; Sela, M.; Yarden, Y. Roles for Growth Factors in Cancer Progression. Physiology 2010, 25, 85–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhury, E.; Tiash, S. Growth factor receptors: promising drug targets in cancer. J. Cancer Metastasis 2015, 1, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.-H.; Cheng, C.-Y.; Su, T.; Fu, X.-Q.; Guo, H.; Li, T.; Tse, A.K.-W.; Kwan, H.-Y.; Yu, H.; Yu, Z.-L.; et al. Quercetin inhibits HGF/c-Met signaling and HGF-stimulated melanoma cell migration and invasion. Mol. Cancer 2015, 14, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayababu, M.R.; Arunkumar, A.; Kanagaraj, P.; Arunakaran, J. Effects of quercetin on insulin-like growth factors (IGFs) and their binding protein-3 (IGFBP-3) secretion and induction of apoptosis in human prostate cancer cells. J. Carcinog. 2006, 5, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakrishnan, S.; Mukherjee, S.; Das, S.; Bhat, F.A.; Singh, P.R.; Patra, C.R.; Arunakaran, J. Gold nanoparticles-conjugated quercetin induces apoptosis via inhibition of EGFR/PI3K/Akt-mediated pathway in breast cancer cell lines (MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231). Cell Biochem. 2017, 35, 217–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakrishnan, S.; Bhat, F.A.; Singh, P.R.; Mukherjee, S.; Elumalai, P.; Das, S.; Patra, C.R.; Arunakaran, J. Gold nanoparticle-conjugated quercetin inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition, angiogenesis and invasiveness via EGFR/VEGFR-2-mediated pathway in breast cancer. Cell Prolif. 2016, 49, 678–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakoff-Nahoum, S. Why cancer and inflammation? Yale J. Biol. Med. 2006, 79, 123–130. [Google Scholar]
- Maurya, B.K.; Trigun, S.K. Fisetin Modulates Antioxidant Enzymes and Inflammatory Factors to Inhibit Aflatoxin-B1 Induced Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Rats. Oxid. Med. Cell. Long. 2016, 2016, 1972793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Tu, Y.-C.; Lian, T.-W.; Hung, J.-T.; Yen, J.-H.; Wu, M.-J. Distinctive Antioxidant and Antiinflammatory Effects of Flavonols. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 9798–9804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.-H.; Lee, S.; Son, H.-Y.; Park, S.-B.; Kim, M.-S.; Choi, E.-J.; Singh, T.S.K.; Ha, J.-H.; Lee, M.-G.; Kim, J.-E.; et al. Flavonoids inhibit histamine release and expression of proinflammatory cytokines in mast cells. Arch. Pharmacal 2008, 31, 1303–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.-Y.; Hung, S.-K.; Fu, S.-L. Immunosuppressive Effects of Fisetin in Ovalbumin-Induced Asthma through Inhibition of NF-κB Activity. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 10496–10504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, S.-T.; Chuang, C.-H.; Yeh, C.-L.; Liao, J.-W.; Liu, K.-L.; Tseng, M.-J.; Yeh, S.-L. Quercetin supplementation suppresses the secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines in the lungs of Mongolian gerbils and in A549 cells exposed to benzo[a]pyrene alone or in combination with β-carotene: In vivo and ex vivo studies. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2012, 23, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hölzlwimmer, G.; Quintanilla-Fend, L.; Ruiz, P.A.; Braune, A.; Haller, D. Quercetin Inhibits TNF-Induced NF-κB Transcription Factor Recruitment to Proinflammatory Gene Promoters in Murine Intestinal Epithelial Cells. J. Nutr. 2007, 137, 1208–1215. [Google Scholar]
- Ying, B.; Yang, T.; Song, X.; Hu, X.; Fan, H.; Lu, X.; Chen, L.; Cheng, D.; Wang, T.; Liu, D.; et al. Quercetin inhibits IL-1 β-induced ICAM-1 expression in pulmonary epithelial cell line A549 through the MAPK pathways. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2009, 36, 1825–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuli, H.S. Celastrol Mediated Hsp90 Protein Inhibition in Cancer. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 5, 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Moser, C.; Lang, S.A.; Stoeltzing, O. Heat-shock protein 90 (Hsp90) as a molecular target for therapy of gastrointestinal cancer. Anticancer. Res. 2009, 29, 2031–2042. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Altundağ, E.M.; Kasacı, T.; Yılmaz, A.M.; Karademir, B.; Koçtürk, S.; Taga, Y.; Yalçın, A.S. Quercetin-Induced Cell Death in Human Papillary Thyroid Cancer (B-CPAP) Cells. J. Thyroid. Res. 2016, 2016, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Tang, C.; Li, L.; Li, R.; Fan, Y. Quercetin sensitizes glioblasoma to t-AUCB by dual inhibition of HSP27 and COX-2 in vitro and in vivo. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 35, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahalingam, D.; Swords, R.; Carew, J.S.; Nawrocki, S.T.; Bhalla, K.; Giles, F.J. Targeting HSP90 for cancer therapy. Br. J. Cancer 2009, 100, 1523–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Revathi, B.; Prashanth, K. Potential Hsp90 Inhibitors: A Novel Target for Cancer Therapy. Chemotherapy 2015, 4, 146. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.A.; Lee, S.; Kwon, B.-M.; Han, D.C. Fisetin, a dietary flavonoid, induces apoptosis of cancer cells by inhibiting HSF1 activity through blocking its binding to the hsp70 promoter. CARCIN 2015, 36, 696–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Dong, X.S.; Gao, H.Y.; Jiang, Y.F.; Jin, Y.L.; Chang, Y.Y.; Chen, L.Y.; Wang, J.H. Suppression of HSP27 increases the antitumor effects of quercetin in human leukemia U937 cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 13, 689–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).